CHAPTER 12 ASDA ANALYSIS EXAMPLES REPLICATION-MPLUS 5.21 GENERAL NOTES ABOUT ANALYSIS EXAMPLES REPLICATION
|
|
|
- Cecil Miller
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 12 ASDA ANALYSIS EXAMPLES REPLICATION-MPLUS 5.21 GENERAL NOTES ABOUT ANALYSIS EXAMPLES REPLICATION These examples are intended to provide guidance on how to use the commands/procedures for analysis of complex sample survey data and assume all data management and other preliminary work is done. The relevant syntax for the procedure of interest is shown first along with the associated output for that procedure(s). In some examples, there may be more than one block of syntax and in this case all syntax is first presented followed by the output produced. In some software packages certain procedures or options are not available but we have made every attempt to demonstrate how to match the output produced by Stata 10+ in the textbook. Check the ASDA website for updates to the various software tools we cover. NOTES ABOUT ANALYSIS OF LONGITUDINAL DATA IN MPLUS 5.21 The analysis replication examples were all run using Mplus Mplus is an advanced modeling tool and offers the ability to correctly account for complex sample survey data for all analytic techniques. Mplus can perform analysis of longitudinal data using a two-level approach and incorporate level specific weights. In Mplus, the number of levels is assumed to be one more than is used to refer to a model. For example, a two-level model in Mplus is actually performing a three-level analysis. This is due to the way Mplus handles levels in the syntax and setup of the analysis. The example from Chapter 12 of ASDA uses 4 time points (2000, 2002, 2004, 2006) nested within individuals nested within SECUs, using HRS data from 2000, 2002, 2004 and The levels, therefore, are time points (level 1) within individuals (level 2) within SECUs (level 3). Through use of "TYPE=TWOLEVEL" along with two variables on the "CLUSTER" statement we properly account for the multi-level approach as well as the complex sample design. In addition, use of the "WITHIN" weight (level 1 weight) with the "BWEIGHT" (level 2 weight) allows the analyst to use weights for levels 1 (within) and 2 (between). Furthermore, the weights can be scaled as needed. In this example, use of the WTSCALE= ECLUSTER (sum to effective sample size) and BWTSCALE = SAMPLE (product of the within weights and the between weights sum to sample size) options are demonstrated to scale the level weights as needed. This approach is comparable to the Stata gllamm command and provides nearly exact results (slightly different due to variable division/rounding). Some of the fine points of this approach are use of a unique cluster variable with a different value for each person in the data set, setting any missing data on the weights to zero, dividing the total assets variable expressed in $1000 by 100 to accomodate the Mplus output limits (multiply by 100 to convert to scale presented in ASDA), use of TYPE=COMPLEX TWOLEVEL RANDOM and ESTIMATOR=MLR on the ANALYSIS command, and the declaration of within/between weights. On the MODEL statement, use of the %WITHIN% and %BETWEEN% commands are used to specify the level specific models. Data preparation in advance of Mplus included extraction of the variables of interest and output to a delimited text file. For additional help and detail, see the Mplus User s Guide.
2 Mplus VERSION 5 MUTHEN & MUTHEN INPUT INSTRUCTIONS Title: ANALYSIS EXAMPLE 12.0 LONGITUDINAL DATA EXAMPLE HRS DATA Data: FILE IS "F:\brahms\applied_analysis_book\Mplus\testmplus_v3.txt"; Variable: NAMES ARE yrssince00 totassets000 newsecu hhidpn baseweight l1weight ; Missing are. ; weight = l1weight ; wtscale= ecluster ; bweight = baseweight ; bwtscale = sample ; usevar = yrssince00 n_tasset ; between= ; within = yrssince00 ; cluster = newsecu hhidpn ; Define: n_tasset = totassets000/100 ; Analysis: type is twolevel random complex ; estimator=mlr ; Model: %within% n_tasset on yrssince00 ; %between% n_tasset ; Variable name contains more than 8 characters. Only the first 8 characters will be printed in the output. Variable: YRSSINCE00
3 Variable name contains more than 8 characters. Only the first 8 characters will be printed in the output. Variable: TOTASSETS000 Variable name contains more than 8 characters. Only the first 8 characters will be printed in the output. Variable: BASEWEIGHT Data set contains cases with missing on all variables except x-variables. These cases were not included in the analysis. Number of cases with missing on all variables except x-variables: WARNING(S) FOUND IN THE INPUT INSTRUCTIONS ANALYSIS EXAMPLE 12.0 LONGITUDINAL DATA EXAMPLE HRS DATA SUMMARY OF ANALYSIS Number of groups 1 Number of observations 6840 Number of dependent variables 1 Number of independent variables 1 Number of continuous latent variables 0 Observed dependent variables Continuous N_TASSET Observed independent variables YRSSINCE Variables with special functions Cluster variable NEWSECU HHIDPN Weight variable (effective cluster-size scaling) L1WEIGHT Between weight variable (sample-size scaling) BASEWEIG Within variables YRSSINCE
4 Estimator Information matrix MLR OBSERVED Maximum number of iterations 1000 Convergence criterion 0.100D-05 Maximum number of EM iterations 500 Convergence criteria for the EM algorithm Loglikelihood change Relative loglikelihood change Derivative Minimum variance 0.100D D D D-03 Maximum number of steepest descent iterations 20 Maximum number of iterations for H Convergence criterion for H1 Optimization algorithm 0.100D-03 EMA Input data file(s) F:\brahms\applied_analysis_book\Mplus\testmplus_v3.txt Input data format FREE SUMMARY OF DATA Number of missing data patterns 1 COVARIANCE COVERAGE OF DATA Minimum covariance coverage value PROPORTION OF DATA PRESENT Covariance Coverage N_TASSET YRSSINCE N_TASSET YRSSINCE THE MODEL ESTIMATION TERMINATED NORMALLY
5 TESTS OF MODEL FIT Chi-Square Test of Model Fit Value 0.002* Degrees of Freedom 0 P-Value Scaling Correction Factor for MLR * The chi-square value for MLM, MLMV, MLR, ULSMV, WLSM and WLSMV cannot be used for chi-square difference tests. MLM, MLR and WLSM chi-square difference testing is described in the Mplus Technical Appendices at See chi-square difference testing in the index of the Mplus User's Guide. Chi-Square Test of Model Fit for the Baseline Model Value Degrees of Freedom 1 P-Value CFI/TLI CFI TLI Loglikelihood H0 Value H0 Scaling Correction Factor for MLR H1 Value H1 Scaling Correction Factor for MLR
6 Information Criteria Number of Free Parameters 4 Akaike (AIC) Bayesian (BIC) Sample-Size Adjusted BIC (n* = (n + 2) / 24) RMSEA (Root Mean Square Error Of Approximation) Estimate SRMR (Standardized Root Mean Square Residual) Value for Within Value for Between MODEL RESULTS Two-Tailed Estimate S.E. Est./S.E. P-Value Within Level N_TASSET ON YRSSINCE Residual Variances N_TASSET Between Level Means N_TASSET Variances N_TASSET QUALITY OF NUMERICAL RESULTS Condition Number for the Information Matrix 0.449E-01 (ratio of smallest to largest eigenvalue)
MPLUS Analysis Examples Replication Chapter 13
 MPLUS Analysis Examples Replication Chapter 13 Mplus includes all input code and output in the *.out file. This document contains all code and selected output from the weighted multilevel models presented
MPLUS Analysis Examples Replication Chapter 13 Mplus includes all input code and output in the *.out file. This document contains all code and selected output from the weighted multilevel models presented
Binary IFA-IRT Models in Mplus version 7.11
 Binary IFA-IRT Models in Mplus version 7.11 Example data: 635 older adults (age 80-100) self-reporting on 7 items assessing the Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADL) as follows: 1. Housework (cleaning
Binary IFA-IRT Models in Mplus version 7.11 Example data: 635 older adults (age 80-100) self-reporting on 7 items assessing the Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADL) as follows: 1. Housework (cleaning
MPLUS Analysis Examples Replication Chapter 10
 MPLUS Analysis Examples Replication Chapter 10 Mplus includes all input code and output in the *.out file. This document contains selected output from each analysis for Chapter 10. All data preparation
MPLUS Analysis Examples Replication Chapter 10 Mplus includes all input code and output in the *.out file. This document contains selected output from each analysis for Chapter 10. All data preparation
CHAPTER 18 OUTPUT, SAVEDATA, AND PLOT COMMANDS
 OUTPUT, SAVEDATA, And PLOT Commands CHAPTER 18 OUTPUT, SAVEDATA, AND PLOT COMMANDS THE OUTPUT COMMAND OUTPUT: In this chapter, the OUTPUT, SAVEDATA, and PLOT commands are discussed. The OUTPUT command
OUTPUT, SAVEDATA, And PLOT Commands CHAPTER 18 OUTPUT, SAVEDATA, AND PLOT COMMANDS THE OUTPUT COMMAND OUTPUT: In this chapter, the OUTPUT, SAVEDATA, and PLOT commands are discussed. The OUTPUT command
Mplus Short Courses Topic 8. Multilevel Modeling With Latent Variables Using Mplus: Longitudinal Analysis
 Mplus Short Courses Topic 8 Multilevel Modeling With Latent Variables Using Mplus: Longitudinal Analysis Linda K. Muthén Bengt Muthén Copyright 2011 Muthén & Muthén www.statmodel.com 02/11/2011 1 Table
Mplus Short Courses Topic 8 Multilevel Modeling With Latent Variables Using Mplus: Longitudinal Analysis Linda K. Muthén Bengt Muthén Copyright 2011 Muthén & Muthén www.statmodel.com 02/11/2011 1 Table
Mplus Short Courses Topic 8. Multilevel Modeling With Latent Variables Using Mplus: Longitudinal Analysis
 Mplus Short Courses Topic 8 Multilevel Modeling With Latent Variables Using Mplus: Longitudinal Analysis Linda K. Muthén Bengt Muthén Copyright 2009 Muthén & Muthén www.statmodel.com 3/11/2009 1 Table
Mplus Short Courses Topic 8 Multilevel Modeling With Latent Variables Using Mplus: Longitudinal Analysis Linda K. Muthén Bengt Muthén Copyright 2009 Muthén & Muthén www.statmodel.com 3/11/2009 1 Table
lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling
 lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling Yves Rosseel Department of Data Analysis Belgium Modern Modeling Methods Conference May 22, 2012 University of Connecticut Yves Rosseel lavaan: an
lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling Yves Rosseel Department of Data Analysis Belgium Modern Modeling Methods Conference May 22, 2012 University of Connecticut Yves Rosseel lavaan: an
Scaling of Sampling Weights For Two Level Models in Mplus 4.2. September 2, 2008
 Scaling of Sampling Weights For Two Level Models in Mplus 4.2 September 2, 2008 1 1 Introduction In survey analysis the data usually is not obtained at random. Units are typically sampled with unequal
Scaling of Sampling Weights For Two Level Models in Mplus 4.2 September 2, 2008 1 1 Introduction In survey analysis the data usually is not obtained at random. Units are typically sampled with unequal
Estimation of a hierarchical Exploratory Structural Equation Model (ESEM) using ESEMwithin-CFA
 Estimation of a hierarchical Exploratory Structural Equation Model (ESEM) using ESEMwithin-CFA Alexandre J.S. Morin, Substantive Methodological Synergy Research Laboratory, Department of Psychology, Concordia
Estimation of a hierarchical Exploratory Structural Equation Model (ESEM) using ESEMwithin-CFA Alexandre J.S. Morin, Substantive Methodological Synergy Research Laboratory, Department of Psychology, Concordia
**************************************************************************************************************** * Single Wave Analyses.
 ASDA2 ANALYSIS EXAMPLE REPLICATION SPSS C11 * Syntax for Analysis Example Replication C11 * Use data sets previously prepared in SAS, refer to SAS Analysis Example Replication for C11 for details. ****************************************************************************************************************
ASDA2 ANALYSIS EXAMPLE REPLICATION SPSS C11 * Syntax for Analysis Example Replication C11 * Use data sets previously prepared in SAS, refer to SAS Analysis Example Replication for C11 for details. ****************************************************************************************************************
CHAPTER 7 ASDA ANALYSIS EXAMPLES REPLICATION-SPSS/PASW V18 COMPLEX SAMPLES
 CHAPTER 7 ASDA ANALYSIS EXAMPLES REPLICATION-SPSS/PASW V18 COMPLEX SAMPLES GENERAL NOTES ABOUT ANALYSIS EXAMPLES REPLICATION These examples are intended to provide guidance on how to use the commands/procedures
CHAPTER 7 ASDA ANALYSIS EXAMPLES REPLICATION-SPSS/PASW V18 COMPLEX SAMPLES GENERAL NOTES ABOUT ANALYSIS EXAMPLES REPLICATION These examples are intended to provide guidance on how to use the commands/procedures
WebSEM: Structural Equation Modeling Online
 WebSEM: Structural Equation Modeling Online Zhiyong Zhang and Ke-Hai Yuan August 27, 2012 118 Haggar Hall, Department of Psychology, University of Notre Dame 1 Thanks The development of the path diagram
WebSEM: Structural Equation Modeling Online Zhiyong Zhang and Ke-Hai Yuan August 27, 2012 118 Haggar Hall, Department of Psychology, University of Notre Dame 1 Thanks The development of the path diagram
SEM 1: Confirmatory Factor Analysis
 SEM 1: Confirmatory Factor Analysis Week 2 - Fitting CFA models Sacha Epskamp 10-04-2017 General factor analysis framework: in which: y i = Λη i + ε i y N(0, Σ) η N(0, Ψ) ε N(0, Θ), y i is a p-length vector
SEM 1: Confirmatory Factor Analysis Week 2 - Fitting CFA models Sacha Epskamp 10-04-2017 General factor analysis framework: in which: y i = Λη i + ε i y N(0, Σ) η N(0, Ψ) ε N(0, Θ), y i is a p-length vector
CHAPTER 13 EXAMPLES: SPECIAL FEATURES
 Examples: Special Features CHAPTER 13 EXAMPLES: SPECIAL FEATURES In this chapter, special features not illustrated in the previous example chapters are discussed. A cross-reference to the original example
Examples: Special Features CHAPTER 13 EXAMPLES: SPECIAL FEATURES In this chapter, special features not illustrated in the previous example chapters are discussed. A cross-reference to the original example
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 Introduction CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Mplus is a statistical modeling program that provides researchers with a flexible tool to analyze their data. Mplus offers researchers a wide choice of models, estimators,
Introduction CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Mplus is a statistical modeling program that provides researchers with a flexible tool to analyze their data. Mplus offers researchers a wide choice of models, estimators,
Repeated Measures Part 4: Blood Flow data
 Repeated Measures Part 4: Blood Flow data /* bloodflow.sas */ options linesize=79 pagesize=100 noovp formdlim='_'; title 'Two within-subjecs factors: Blood flow data (NWK p. 1181)'; proc format; value
Repeated Measures Part 4: Blood Flow data /* bloodflow.sas */ options linesize=79 pagesize=100 noovp formdlim='_'; title 'Two within-subjecs factors: Blood flow data (NWK p. 1181)'; proc format; value
Last updated January 4, 2012
 Last updated January 4, 2012 This document provides a description of Mplus code for implementing mixture factor analysis with four latent class components with and without covariates described in the following
Last updated January 4, 2012 This document provides a description of Mplus code for implementing mixture factor analysis with four latent class components with and without covariates described in the following
CHAPTER 16 ANALYSIS COMMAND
 ANALYSIS Command CHAPTER 16 ANALYSIS COMMAND THE ANALYSIS COMMAND ANALYSIS: In this chapter, the ANALYSIS command is discussed. The ANALYSIS command is used to describe the technical details of the analysis
ANALYSIS Command CHAPTER 16 ANALYSIS COMMAND THE ANALYSIS COMMAND ANALYSIS: In this chapter, the ANALYSIS command is discussed. The ANALYSIS command is used to describe the technical details of the analysis
Conditional and Unconditional Regression with No Measurement Error
 Conditional and with No Measurement Error /* reg2ways.sas */ %include 'readsenic.sas'; title2 ''; proc reg; title3 'Conditional Regression'; model infrisk = stay census; proc calis cov; /* Analyze the
Conditional and with No Measurement Error /* reg2ways.sas */ %include 'readsenic.sas'; title2 ''; proc reg; title3 'Conditional Regression'; model infrisk = stay census; proc calis cov; /* Analyze the
Annotated multitree output
 Annotated multitree output A simplified version of the two high-threshold (2HT) model, applied to two experimental conditions, is used as an example to illustrate the output provided by multitree (version
Annotated multitree output A simplified version of the two high-threshold (2HT) model, applied to two experimental conditions, is used as an example to illustrate the output provided by multitree (version
Performance of Latent Growth Curve Models with Binary Variables
 Performance of Latent Growth Curve Models with Binary Variables Jason T. Newsom & Nicholas A. Smith Department of Psychology Portland State University 1 Goal Examine estimation of latent growth curve models
Performance of Latent Growth Curve Models with Binary Variables Jason T. Newsom & Nicholas A. Smith Department of Psychology Portland State University 1 Goal Examine estimation of latent growth curve models
CHAPTER 11 EXAMPLES: MISSING DATA MODELING AND BAYESIAN ANALYSIS
 Examples: Missing Data Modeling And Bayesian Analysis CHAPTER 11 EXAMPLES: MISSING DATA MODELING AND BAYESIAN ANALYSIS Mplus provides estimation of models with missing data using both frequentist and Bayesian
Examples: Missing Data Modeling And Bayesian Analysis CHAPTER 11 EXAMPLES: MISSING DATA MODELING AND BAYESIAN ANALYSIS Mplus provides estimation of models with missing data using both frequentist and Bayesian
Part I. Hierarchical clustering. Hierarchical Clustering. Hierarchical clustering. Produces a set of nested clusters organized as a
 Week 9 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Part I December 2, 2012 Hierarchical Clustering 1 / 1 Produces a set of nested clusters organized as a Hierarchical hierarchical clustering
Week 9 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Part I December 2, 2012 Hierarchical Clustering 1 / 1 Produces a set of nested clusters organized as a Hierarchical hierarchical clustering
lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling and more Version (BETA)
 lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling and more Version 0.4-9 (BETA) Yves Rosseel Department of Data Analysis Ghent University (Belgium) June 14, 2011 Abstract The lavaan package is developed
lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling and more Version 0.4-9 (BETA) Yves Rosseel Department of Data Analysis Ghent University (Belgium) June 14, 2011 Abstract The lavaan package is developed
Comparison of computational methods for high dimensional item factor analysis
 Comparison of computational methods for high dimensional item factor analysis Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén November 14, 2012 Abstract In this article we conduct a simulation study to compare several
Comparison of computational methods for high dimensional item factor analysis Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén November 14, 2012 Abstract In this article we conduct a simulation study to compare several
A Beginner's Guide to. Randall E. Schumacker. The University of Alabama. Richard G. Lomax. The Ohio State University. Routledge
 A Beginner's Guide to Randall E. Schumacker The University of Alabama Richard G. Lomax The Ohio State University Routledge Taylor & Francis Group New York London About the Authors Preface xv xvii 1 Introduction
A Beginner's Guide to Randall E. Schumacker The University of Alabama Richard G. Lomax The Ohio State University Routledge Taylor & Francis Group New York London About the Authors Preface xv xvii 1 Introduction
PSY 9556B (Feb 5) Latent Growth Modeling
 PSY 9556B (Feb 5) Latent Growth Modeling Fixed and random word confusion Simplest LGM knowing how to calculate dfs How many time points needed? Power, sample size Nonlinear growth quadratic Nonlinear growth
PSY 9556B (Feb 5) Latent Growth Modeling Fixed and random word confusion Simplest LGM knowing how to calculate dfs How many time points needed? Power, sample size Nonlinear growth quadratic Nonlinear growth
The Mplus modelling framework
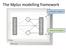 The Mplus modelling framework Continuous variables Categorical variables 1 Mplus syntax structure TITLE: a title for the analysis (not part of the syntax) DATA: (required) information about the data set
The Mplus modelling framework Continuous variables Categorical variables 1 Mplus syntax structure TITLE: a title for the analysis (not part of the syntax) DATA: (required) information about the data set
Introduction to SAS proc calis
 Introduction to SAS proc calis /* path1.sas */ %include 'SenicRead.sas'; title2 ''; /************************************************************************ * * * Cases are hospitals * * * * stay Average
Introduction to SAS proc calis /* path1.sas */ %include 'SenicRead.sas'; title2 ''; /************************************************************************ * * * Cases are hospitals * * * * stay Average
Confirmatory Factor Analysis on the Twin Data: Try One
 Confirmatory Factor Analysis on the Twin Data: Try One /************ twinfac2.sas ********************/ TITLE2 'Confirmatory Factor Analysis'; %include 'twinread.sas'; proc calis corr; /* Analyze the correlation
Confirmatory Factor Analysis on the Twin Data: Try One /************ twinfac2.sas ********************/ TITLE2 'Confirmatory Factor Analysis'; %include 'twinread.sas'; proc calis corr; /* Analyze the correlation
I How does the formulation (5) serve the purpose of the composite parameterization
 Supplemental Material to Identifying Alzheimer s Disease-Related Brain Regions from Multi-Modality Neuroimaging Data using Sparse Composite Linear Discrimination Analysis I How does the formulation (5)
Supplemental Material to Identifying Alzheimer s Disease-Related Brain Regions from Multi-Modality Neuroimaging Data using Sparse Composite Linear Discrimination Analysis I How does the formulation (5)
The lavaan tutorial. Yves Rosseel Department of Data Analysis Ghent University (Belgium) December 18, 2017
 The lavaan tutorial Yves Rosseel Department of Data Analysis Ghent University (Belgium) December 18, 2017 Abstract If you are new to lavaan, this is the place to start. In this tutorial, we introduce the
The lavaan tutorial Yves Rosseel Department of Data Analysis Ghent University (Belgium) December 18, 2017 Abstract If you are new to lavaan, this is the place to start. In this tutorial, we introduce the
Stat 500 lab notes c Philip M. Dixon, Week 10: Autocorrelated errors
 Week 10: Autocorrelated errors This week, I have done one possible analysis and provided lots of output for you to consider. Case study: predicting body fat Body fat is an important health measure, but
Week 10: Autocorrelated errors This week, I have done one possible analysis and provided lots of output for you to consider. Case study: predicting body fat Body fat is an important health measure, but
SEM 1: Confirmatory Factor Analysis
 SEM 1: Confirmatory Factor Analysis Week 3 - Measurement invariance and ordinal data Sacha Epskamp 17-04-2018 General factor analysis framework: in which: y i = Λη i + ε i y N(0, Σ) η N(0, Ψ) ε N(0, Θ),
SEM 1: Confirmatory Factor Analysis Week 3 - Measurement invariance and ordinal data Sacha Epskamp 17-04-2018 General factor analysis framework: in which: y i = Λη i + ε i y N(0, Σ) η N(0, Ψ) ε N(0, Θ),
SEM 1: Confirmatory Factor Analysis
 SEM 1: Confirmatory Factor Analysis Week 3 - Measurement invariance and ordinal data Sacha Epskamp 18-04-2017 General factor analysis framework: in which: y i = Λη i + ε i y N(0, Σ) η N(0, Ψ) ε N(0, Θ),
SEM 1: Confirmatory Factor Analysis Week 3 - Measurement invariance and ordinal data Sacha Epskamp 18-04-2017 General factor analysis framework: in which: y i = Λη i + ε i y N(0, Σ) η N(0, Ψ) ε N(0, Θ),
Multiple Imputation with Mplus
 Multiple Imputation with Mplus Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén Version 2 September 29, 2010 1 1 Introduction Conducting multiple imputation (MI) can sometimes be quite intricate. In this note we provide
Multiple Imputation with Mplus Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén Version 2 September 29, 2010 1 1 Introduction Conducting multiple imputation (MI) can sometimes be quite intricate. In this note we provide
Lecture 13: Model selection and regularization
 Lecture 13: Model selection and regularization Reading: Sections 6.1-6.2.1 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis October 23, 2017 1 / 17 What do we know so far In linear regression, adding predictors always
Lecture 13: Model selection and regularization Reading: Sections 6.1-6.2.1 STATS 202: Data mining and analysis October 23, 2017 1 / 17 What do we know so far In linear regression, adding predictors always
Introduction to Factor Analysis for Marketing
 Introduction to Factor Analysis for Marketing SKIM/Sawtooth Software Conference 2016, Rome Chris Chapman, Google. April 2016. Special thanks to Josh Lewandowski at Google for helpful feedback (errors are
Introduction to Factor Analysis for Marketing SKIM/Sawtooth Software Conference 2016, Rome Chris Chapman, Google. April 2016. Special thanks to Josh Lewandowski at Google for helpful feedback (errors are
Linear Model Selection and Regularization. especially usefull in high dimensions p>>100.
 Linear Model Selection and Regularization especially usefull in high dimensions p>>100. 1 Why Linear Model Regularization? Linear models are simple, BUT consider p>>n, we have more features than data records
Linear Model Selection and Regularization especially usefull in high dimensions p>>100. 1 Why Linear Model Regularization? Linear models are simple, BUT consider p>>n, we have more features than data records
Package FMsmsnReg. March 30, 2016
 Package FMsmsnReg March 30, 2016 Type Package Title Regression Models with Finite Mixtures of Skew Heavy-Tailed Errors Version 1.0 Date 2016-03-29 Author Luis Benites Sanchez and Rocio Paola Maehara and
Package FMsmsnReg March 30, 2016 Type Package Title Regression Models with Finite Mixtures of Skew Heavy-Tailed Errors Version 1.0 Date 2016-03-29 Author Luis Benites Sanchez and Rocio Paola Maehara and
Conducting a Path Analysis With SPSS/AMOS
 Conducting a Path Analysis With SPSS/AMOS Download the PATH-INGRAM.sav data file from my SPSS data page and then bring it into SPSS. The data are those from the research that led to this publication: Ingram,
Conducting a Path Analysis With SPSS/AMOS Download the PATH-INGRAM.sav data file from my SPSS data page and then bring it into SPSS. The data are those from the research that led to this publication: Ingram,
Page 1 of 8. Language Development Study
 Page 1 of 8 Language Development Study /* cread3.sas Read Castilla's language development data */ options nodate linesize=79 noovp formdlim=' '; title "Castilla's Language development Study"; proc format;
Page 1 of 8 Language Development Study /* cread3.sas Read Castilla's language development data */ options nodate linesize=79 noovp formdlim=' '; title "Castilla's Language development Study"; proc format;
Introduction to Mplus
 Introduction to Mplus May 12, 2010 SPONSORED BY: Research Data Centre Population and Life Course Studies PLCS Interdisciplinary Development Initiative Piotr Wilk piotr.wilk@schulich.uwo.ca OVERVIEW Mplus
Introduction to Mplus May 12, 2010 SPONSORED BY: Research Data Centre Population and Life Course Studies PLCS Interdisciplinary Development Initiative Piotr Wilk piotr.wilk@schulich.uwo.ca OVERVIEW Mplus
STA431 Handout 9 Double Measurement Regression on the BMI Data
 STA431 Handout 9 Double Measurement Regression on the BMI Data /********************** bmi5.sas **************************/ options linesize=79 pagesize = 500 noovp formdlim='-'; title 'BMI and Health:
STA431 Handout 9 Double Measurement Regression on the BMI Data /********************** bmi5.sas **************************/ options linesize=79 pagesize = 500 noovp formdlim='-'; title 'BMI and Health:
Supplementary Material. 4) Mplus input code to estimate the latent transition analysis model
 WORKING CONDITIONS AMONG HIGH-SKILLED WORKERS S1 Supplementary Material 1) Representativeness of the analytic sample 2) Cross-sectional latent class analyses 3) Mplus input code to estimate the latent
WORKING CONDITIONS AMONG HIGH-SKILLED WORKERS S1 Supplementary Material 1) Representativeness of the analytic sample 2) Cross-sectional latent class analyses 3) Mplus input code to estimate the latent
Estimation of Item Response Models
 Estimation of Item Response Models Lecture #5 ICPSR Item Response Theory Workshop Lecture #5: 1of 39 The Big Picture of Estimation ESTIMATOR = Maximum Likelihood; Mplus Any questions? answers Lecture #5:
Estimation of Item Response Models Lecture #5 ICPSR Item Response Theory Workshop Lecture #5: 1of 39 The Big Picture of Estimation ESTIMATOR = Maximum Likelihood; Mplus Any questions? answers Lecture #5:
NOTE: Any use of trade, product or firm names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government.
 U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) MMA(1) NOTE: Any use of trade, product or firm names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. NAME MMA, A Computer Code for
U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) MMA(1) NOTE: Any use of trade, product or firm names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. NAME MMA, A Computer Code for
Sistemática Teórica. Hernán Dopazo. Biomedical Genomics and Evolution Lab. Lesson 03 Statistical Model Selection
 Sistemática Teórica Hernán Dopazo Biomedical Genomics and Evolution Lab Lesson 03 Statistical Model Selection Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales Universidad de Buenos Aires Argentina 2013 Statistical
Sistemática Teórica Hernán Dopazo Biomedical Genomics and Evolution Lab Lesson 03 Statistical Model Selection Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales Universidad de Buenos Aires Argentina 2013 Statistical
Generalized Additive Models
 :p Texts in Statistical Science Generalized Additive Models An Introduction with R Simon N. Wood Contents Preface XV 1 Linear Models 1 1.1 A simple linear model 2 Simple least squares estimation 3 1.1.1
:p Texts in Statistical Science Generalized Additive Models An Introduction with R Simon N. Wood Contents Preface XV 1 Linear Models 1 1.1 A simple linear model 2 Simple least squares estimation 3 1.1.1
Multiple Group CFA in AMOS (And Modification Indices and Nested Models)
 Multiple Group CFA in AMOS (And Modification Indices and Nested Models) For this lab we will use the Self-Esteem data. An Excel file of the data is available at _www.biostat.umn.edu/~melanie/ph5482/data/index.html
Multiple Group CFA in AMOS (And Modification Indices and Nested Models) For this lab we will use the Self-Esteem data. An Excel file of the data is available at _www.biostat.umn.edu/~melanie/ph5482/data/index.html
A Course in Machine Learning
 A Course in Machine Learning Hal Daumé III 13 UNSUPERVISED LEARNING If you have access to labeled training data, you know what to do. This is the supervised setting, in which you have a teacher telling
A Course in Machine Learning Hal Daumé III 13 UNSUPERVISED LEARNING If you have access to labeled training data, you know what to do. This is the supervised setting, in which you have a teacher telling
NAG Library Routine Document G13DPF.1
 NAG Library Routine Document Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised terms and other implementation-dependent
NAG Library Routine Document Note: before using this routine, please read the Users Note for your implementation to check the interpretation of bold italicised terms and other implementation-dependent
Using Mplus Monte Carlo Simulations In Practice: A Note On Non-Normal Missing Data In Latent Variable Models
 Using Mplus Monte Carlo Simulations In Practice: A Note On Non-Normal Missing Data In Latent Variable Models Bengt Muth en University of California, Los Angeles Tihomir Asparouhov Muth en & Muth en Mplus
Using Mplus Monte Carlo Simulations In Practice: A Note On Non-Normal Missing Data In Latent Variable Models Bengt Muth en University of California, Los Angeles Tihomir Asparouhov Muth en & Muth en Mplus
CHAPTER 7 EXAMPLES: MIXTURE MODELING WITH CROSS- SECTIONAL DATA
 Examples: Mixture Modeling With Cross-Sectional Data CHAPTER 7 EXAMPLES: MIXTURE MODELING WITH CROSS- SECTIONAL DATA Mixture modeling refers to modeling with categorical latent variables that represent
Examples: Mixture Modeling With Cross-Sectional Data CHAPTER 7 EXAMPLES: MIXTURE MODELING WITH CROSS- SECTIONAL DATA Mixture modeling refers to modeling with categorical latent variables that represent
We know intuitively that some measurements are more reliable than others.
 1 Some measurements are more equal than others. We know intuitively that some measurements are more reliable than others. Measurements that are more reliable should have greater weight or influence in
1 Some measurements are more equal than others. We know intuitively that some measurements are more reliable than others. Measurements that are more reliable should have greater weight or influence in
Path Analysis using lm and lavaan
 Path Analysis using lm and lavaan Grant B. Morgan Baylor University September 10, 2014 First of all, this post is going to mirror a page on the Institute for Digital Research and Education (IDRE) site
Path Analysis using lm and lavaan Grant B. Morgan Baylor University September 10, 2014 First of all, this post is going to mirror a page on the Institute for Digital Research and Education (IDRE) site
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Growth Rate Models: Emphasizing Growth Rate Analysis through Growth Curve Modeling
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Growth Rate Models: Emphasizing Growth Rate Analysis through Growth Curve Modeling Zhiyong Zhang a, John J. McArdle b, and John R. Nesselroade c a University of Notre Dame; b University
RESEARCH ARTICLE Growth Rate Models: Emphasizing Growth Rate Analysis through Growth Curve Modeling Zhiyong Zhang a, John J. McArdle b, and John R. Nesselroade c a University of Notre Dame; b University
Cost Functions in Machine Learning
 Cost Functions in Machine Learning Kevin Swingler Motivation Given some data that reflects measurements from the environment We want to build a model that reflects certain statistics about that data Something
Cost Functions in Machine Learning Kevin Swingler Motivation Given some data that reflects measurements from the environment We want to build a model that reflects certain statistics about that data Something
Latent Variable Modeling Using Mplus: Day 1
 Latent Variable Modeling Using Mplus: Day 1 Bengt Muthén & Linda Muthén Mplus www.statmodel.com October, 2012 Bengt Muthén & Linda Muthén Mplus Modeling 1/ 186 Table of Contents I 1 1. Mplus Background
Latent Variable Modeling Using Mplus: Day 1 Bengt Muthén & Linda Muthén Mplus www.statmodel.com October, 2012 Bengt Muthén & Linda Muthén Mplus Modeling 1/ 186 Table of Contents I 1 1. Mplus Background
Paper SDA-11. Logistic regression will be used for estimation of net error for the 2010 Census as outlined in Griffin (2005).
 Paper SDA-11 Developing a Model for Person Estimation in Puerto Rico for the 2010 Census Coverage Measurement Program Colt S. Viehdorfer, U.S. Census Bureau, Washington, DC This report is released to inform
Paper SDA-11 Developing a Model for Person Estimation in Puerto Rico for the 2010 Census Coverage Measurement Program Colt S. Viehdorfer, U.S. Census Bureau, Washington, DC This report is released to inform
Adaptive Filtering using Steepest Descent and LMS Algorithm
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 4 October 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Adaptive Filtering using Steepest Descent and LMS Algorithm Akash Sawant Mukesh
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 4 October 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Adaptive Filtering using Steepest Descent and LMS Algorithm Akash Sawant Mukesh
MODELING FORCED-CHOICE DATA USING MPLUS 1
 MODELING FORCED-CHOICE DATA USING MPLUS 1 Fitting a Thurstonian IRT model to forced-choice data using Mplus Anna Brown University of Cambridge Alberto Maydeu-Olivares University of Barcelona Author Note
MODELING FORCED-CHOICE DATA USING MPLUS 1 Fitting a Thurstonian IRT model to forced-choice data using Mplus Anna Brown University of Cambridge Alberto Maydeu-Olivares University of Barcelona Author Note
Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics
 SPSS Complex Samples 15.0 Specifications Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics When you conduct sample surveys, use a statistics package dedicated to producing correct estimates for complex sample
SPSS Complex Samples 15.0 Specifications Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics When you conduct sample surveys, use a statistics package dedicated to producing correct estimates for complex sample
Appendices for Auxiliary Variables in Mixture Modeling: 3-Step Approaches Using Mplus. Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén
 Appendices for Auxiliary Variables in Mixture Modeling: 3-Step Approaches Using Mplus Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén 1 1 Appendix A: Step 3 of the 3-step method done manually versus all steps done
Appendices for Auxiliary Variables in Mixture Modeling: 3-Step Approaches Using Mplus Tihomir Asparouhov and Bengt Muthén 1 1 Appendix A: Step 3 of the 3-step method done manually versus all steps done
Performing Cluster Bootstrapped Regressions in R
 Performing Cluster Bootstrapped Regressions in R Francis L. Huang / October 6, 2016 Supplementary material for: Using Cluster Bootstrapping to Analyze Nested Data with a Few Clusters in Educational and
Performing Cluster Bootstrapped Regressions in R Francis L. Huang / October 6, 2016 Supplementary material for: Using Cluster Bootstrapping to Analyze Nested Data with a Few Clusters in Educational and
Week 5: Multiple Linear Regression II
 Week 5: Multiple Linear Regression II Marcelo Coca Perraillon University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus Health Services Research Methods I HSMP 7607 2017 c 2017 PERRAILLON ARR 1 Outline Adjusted R
Week 5: Multiple Linear Regression II Marcelo Coca Perraillon University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus Health Services Research Methods I HSMP 7607 2017 c 2017 PERRAILLON ARR 1 Outline Adjusted R
7. Collinearity and Model Selection
 Sociology 740 John Fox Lecture Notes 7. Collinearity and Model Selection Copyright 2014 by John Fox Collinearity and Model Selection 1 1. Introduction I When there is a perfect linear relationship among
Sociology 740 John Fox Lecture Notes 7. Collinearity and Model Selection Copyright 2014 by John Fox Collinearity and Model Selection 1 1. Introduction I When there is a perfect linear relationship among
NCSS Statistical Software
 Chapter 327 Geometric Regression Introduction Geometric regression is a special case of negative binomial regression in which the dispersion parameter is set to one. It is similar to regular multiple regression
Chapter 327 Geometric Regression Introduction Geometric regression is a special case of negative binomial regression in which the dispersion parameter is set to one. It is similar to regular multiple regression
22s:152 Applied Linear Regression
 22s:152 Applied Linear Regression Chapter 22: Model Selection In model selection, the idea is to find the smallest set of variables which provides an adequate description of the data. We will consider
22s:152 Applied Linear Regression Chapter 22: Model Selection In model selection, the idea is to find the smallest set of variables which provides an adequate description of the data. We will consider
Reddit Recommendation System Daniel Poon, Yu Wu, David (Qifan) Zhang CS229, Stanford University December 11 th, 2011
 Reddit Recommendation System Daniel Poon, Yu Wu, David (Qifan) Zhang CS229, Stanford University December 11 th, 2011 1. Introduction Reddit is one of the most popular online social news websites with millions
Reddit Recommendation System Daniel Poon, Yu Wu, David (Qifan) Zhang CS229, Stanford University December 11 th, 2011 1. Introduction Reddit is one of the most popular online social news websites with millions
6. Linear Discriminant Functions
 6. Linear Discriminant Functions Linear Discriminant Functions Assumption: we know the proper forms for the discriminant functions, and use the samples to estimate the values of parameters of the classifier
6. Linear Discriminant Functions Linear Discriminant Functions Assumption: we know the proper forms for the discriminant functions, and use the samples to estimate the values of parameters of the classifier
ABSTRACT ESTIMATING UNKNOWN KNOTS IN PIECEWISE LINEAR- LINEAR LATENT GROWTH MIXTURE MODELS. Nidhi Kohli, Doctor of Philosophy, 2011
 ABSTRACT Title of Document: ESTIMATING UNKNOWN KNOTS IN PIECEWISE LINEAR- LINEAR LATENT GROWTH MIXTURE MODELS Nidhi Kohli, Doctor of Philosophy, 2011 Directed By: Dr. Gregory R. Hancock, and Dr. Jeffrey
ABSTRACT Title of Document: ESTIMATING UNKNOWN KNOTS IN PIECEWISE LINEAR- LINEAR LATENT GROWTH MIXTURE MODELS Nidhi Kohli, Doctor of Philosophy, 2011 Directed By: Dr. Gregory R. Hancock, and Dr. Jeffrey
Chapter 15 Mixed Models. Chapter Table of Contents. Introduction Split Plot Experiment Clustered Data References...
 Chapter 15 Mixed Models Chapter Table of Contents Introduction...309 Split Plot Experiment...311 Clustered Data...320 References...326 308 Chapter 15. Mixed Models Chapter 15 Mixed Models Introduction
Chapter 15 Mixed Models Chapter Table of Contents Introduction...309 Split Plot Experiment...311 Clustered Data...320 References...326 308 Chapter 15. Mixed Models Chapter 15 Mixed Models Introduction
Introduction to SAS proc calis
 Introduction to SAS proc calis /* path1.sas */ %include 'SenicRead.sas'; title2 'Path Analysis Example for 3 Observed Variables'; /************************************************************************
Introduction to SAS proc calis /* path1.sas */ %include 'SenicRead.sas'; title2 'Path Analysis Example for 3 Observed Variables'; /************************************************************************
Package GWRM. R topics documented: July 31, Type Package
 Type Package Package GWRM July 31, 2017 Title Generalized Waring Regression Model for Count Data Version 2.1.0.3 Date 2017-07-18 Maintainer Antonio Jose Saez-Castillo Depends R (>= 3.0.0)
Type Package Package GWRM July 31, 2017 Title Generalized Waring Regression Model for Count Data Version 2.1.0.3 Date 2017-07-18 Maintainer Antonio Jose Saez-Castillo Depends R (>= 3.0.0)
CSE 258 Lecture 5. Web Mining and Recommender Systems. Dimensionality Reduction
 CSE 258 Lecture 5 Web Mining and Recommender Systems Dimensionality Reduction This week How can we build low dimensional representations of high dimensional data? e.g. how might we (compactly!) represent
CSE 258 Lecture 5 Web Mining and Recommender Systems Dimensionality Reduction This week How can we build low dimensional representations of high dimensional data? e.g. how might we (compactly!) represent
D-Optimal Designs. Chapter 888. Introduction. D-Optimal Design Overview
 Chapter 888 Introduction This procedure generates D-optimal designs for multi-factor experiments with both quantitative and qualitative factors. The factors can have a mixed number of levels. For example,
Chapter 888 Introduction This procedure generates D-optimal designs for multi-factor experiments with both quantitative and qualitative factors. The factors can have a mixed number of levels. For example,
Adjusting for Unequal Selection Probability in Multilevel Models: A Comparison of Software Packages
 Adusting for Unequal Selection Probability in Multilevel Models: A Comparison of Software Packages Kim Chantala Chirayath Suchindran Carolina Population Center, UNC at Chapel Hill Carolina Population Center,
Adusting for Unequal Selection Probability in Multilevel Models: A Comparison of Software Packages Kim Chantala Chirayath Suchindran Carolina Population Center, UNC at Chapel Hill Carolina Population Center,
Information Criteria Methods in SAS for Multiple Linear Regression Models
 Paper SA5 Information Criteria Methods in SAS for Multiple Linear Regression Models Dennis J. Beal, Science Applications International Corporation, Oak Ridge, TN ABSTRACT SAS 9.1 calculates Akaike s Information
Paper SA5 Information Criteria Methods in SAS for Multiple Linear Regression Models Dennis J. Beal, Science Applications International Corporation, Oak Ridge, TN ABSTRACT SAS 9.1 calculates Akaike s Information
Expectation Maximization (EM) and Gaussian Mixture Models
 Expectation Maximization (EM) and Gaussian Mixture Models Reference: The Elements of Statistical Learning, by T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, J. Friedman, Springer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Unsupervised Learning Motivation
Expectation Maximization (EM) and Gaussian Mixture Models Reference: The Elements of Statistical Learning, by T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani, J. Friedman, Springer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Unsupervised Learning Motivation
Package SeleMix. R topics documented: November 22, 2016
 Package SeleMix November 22, 2016 Type Package Title Selective Editing via Mixture Models Version 1.0.1 Date 2016-11-22 Author Ugo Guarnera, Teresa Buglielli Maintainer Teresa Buglielli
Package SeleMix November 22, 2016 Type Package Title Selective Editing via Mixture Models Version 1.0.1 Date 2016-11-22 Author Ugo Guarnera, Teresa Buglielli Maintainer Teresa Buglielli
Analysis of Incomplete Multivariate Data
 Analysis of Incomplete Multivariate Data J. L. Schafer Department of Statistics The Pennsylvania State University USA CHAPMAN & HALL/CRC A CR.C Press Company Boca Raton London New York Washington, D.C.
Analysis of Incomplete Multivariate Data J. L. Schafer Department of Statistics The Pennsylvania State University USA CHAPMAN & HALL/CRC A CR.C Press Company Boca Raton London New York Washington, D.C.
ALTERNATIVE METHODS FOR CLUSTERING
 ALTERNATIVE METHODS FOR CLUSTERING K-Means Algorithm Termination conditions Several possibilities, e.g., A fixed number of iterations Objects partition unchanged Centroid positions don t change Convergence
ALTERNATIVE METHODS FOR CLUSTERING K-Means Algorithm Termination conditions Several possibilities, e.g., A fixed number of iterations Objects partition unchanged Centroid positions don t change Convergence
CDAA No. 4 - Part Two - Multiple Regression - Initial Data Screening
 CDAA No. 4 - Part Two - Multiple Regression - Initial Data Screening Variables Entered/Removed b Variables Entered GPA in other high school, test, Math test, GPA, High school math GPA a Variables Removed
CDAA No. 4 - Part Two - Multiple Regression - Initial Data Screening Variables Entered/Removed b Variables Entered GPA in other high school, test, Math test, GPA, High school math GPA a Variables Removed
[/TTEST [PERCENT={5}] [{T }] [{DF } [{PROB }] [{COUNTS }] [{MEANS }]] {n} {NOT} {NODF} {NOPROB}] {NOCOUNTS} {NOMEANS}
![[/TTEST [PERCENT={5}] [{T }] [{DF } [{PROB }] [{COUNTS }] [{MEANS }]] {n} {NOT} {NODF} {NOPROB}] {NOCOUNTS} {NOMEANS} [/TTEST [PERCENT={5}] [{T }] [{DF } [{PROB }] [{COUNTS }] [{MEANS }]] {n} {NOT} {NODF} {NOPROB}] {NOCOUNTS} {NOMEANS}](/thumbs/81/84586501.jpg) MVA MVA [VARIABLES=] {varlist} {ALL } [/CATEGORICAL=varlist] [/MAXCAT={25 ** }] {n } [/ID=varname] Description: [/NOUNIVARIATE] [/TTEST [PERCENT={5}] [{T }] [{DF } [{PROB }] [{COUNTS }] [{MEANS }]] {n}
MVA MVA [VARIABLES=] {varlist} {ALL } [/CATEGORICAL=varlist] [/MAXCAT={25 ** }] {n } [/ID=varname] Description: [/NOUNIVARIATE] [/TTEST [PERCENT={5}] [{T }] [{DF } [{PROB }] [{COUNTS }] [{MEANS }]] {n}
Clustering Lecture 5: Mixture Model
 Clustering Lecture 5: Mixture Model Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1 Outline Basics Motivation, definition, evaluation Methods Partitional Hierarchical Density-based Mixture model Spectral methods Advanced topics
Clustering Lecture 5: Mixture Model Jing Gao SUNY Buffalo 1 Outline Basics Motivation, definition, evaluation Methods Partitional Hierarchical Density-based Mixture model Spectral methods Advanced topics
Machine Learning. Topic 5: Linear Discriminants. Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013
 Machine Learning Topic 5: Linear Discriminants Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013 Thanks to Mark Cartwright for his extensive contributions to these slides Thanks to Alpaydin, Bishop, and Duda/Hart/Stork
Machine Learning Topic 5: Linear Discriminants Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013 Thanks to Mark Cartwright for his extensive contributions to these slides Thanks to Alpaydin, Bishop, and Duda/Hart/Stork
Package freeknotsplines
 Version 1.0.1 Date 2018-05-17 Package freeknotsplines June 10, 2018 Title Algorithms for Implementing Free-Knot Splines Author , Philip Smith , Pierre Lecuyer
Version 1.0.1 Date 2018-05-17 Package freeknotsplines June 10, 2018 Title Algorithms for Implementing Free-Knot Splines Author , Philip Smith , Pierre Lecuyer
Clustering. CS294 Practical Machine Learning Junming Yin 10/09/06
 Clustering CS294 Practical Machine Learning Junming Yin 10/09/06 Outline Introduction Unsupervised learning What is clustering? Application Dissimilarity (similarity) of objects Clustering algorithm K-means,
Clustering CS294 Practical Machine Learning Junming Yin 10/09/06 Outline Introduction Unsupervised learning What is clustering? Application Dissimilarity (similarity) of objects Clustering algorithm K-means,
CSE 255 Lecture 5. Data Mining and Predictive Analytics. Dimensionality Reduction
 CSE 255 Lecture 5 Data Mining and Predictive Analytics Dimensionality Reduction Course outline Week 4: I ll cover homework 1, and get started on Recommender Systems Week 5: I ll cover homework 2 (at the
CSE 255 Lecture 5 Data Mining and Predictive Analytics Dimensionality Reduction Course outline Week 4: I ll cover homework 1, and get started on Recommender Systems Week 5: I ll cover homework 2 (at the
SGN (4 cr) Chapter 11
 SGN-41006 (4 cr) Chapter 11 Clustering Jussi Tohka & Jari Niemi Department of Signal Processing Tampere University of Technology February 25, 2014 J. Tohka & J. Niemi (TUT-SGN) SGN-41006 (4 cr) Chapter
SGN-41006 (4 cr) Chapter 11 Clustering Jussi Tohka & Jari Niemi Department of Signal Processing Tampere University of Technology February 25, 2014 J. Tohka & J. Niemi (TUT-SGN) SGN-41006 (4 cr) Chapter
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701
 Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Clustering and EM Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Clustering K-means Mixture of Gaussians Expectation Maximization Variational Methods 2 Clustering 3 K-
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Clustering and EM Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Clustering K-means Mixture of Gaussians Expectation Maximization Variational Methods 2 Clustering 3 K-
Package RPMM. September 14, 2014
 Package RPMM September 14, 2014 Type Package Title Recursively Partitioned Mixture Model Version 1.20 Date 2014-09-13 Author E. Andres Houseman, Sc.D. and Devin C. Koestler, Ph.D. Maintainer E. Andres
Package RPMM September 14, 2014 Type Package Title Recursively Partitioned Mixture Model Version 1.20 Date 2014-09-13 Author E. Andres Houseman, Sc.D. and Devin C. Koestler, Ph.D. Maintainer E. Andres
Data Analytics for. Transmission Expansion Planning. Andrés Ramos. January Estadística II. Transmission Expansion Planning GITI/GITT
 Data Analytics for Andrés Ramos January 2018 1 1 Introduction 2 Definition Determine which lines and transformers and when to build optimizing total investment and operation costs 3 Challenges for TEP
Data Analytics for Andrés Ramos January 2018 1 1 Introduction 2 Definition Determine which lines and transformers and when to build optimizing total investment and operation costs 3 Challenges for TEP
Package ssmn. R topics documented: August 9, Type Package. Title Skew Scale Mixtures of Normal Distributions. Version 1.1.
 Package ssmn August 9, 2016 Type Package Title Skew Scale Mixtures of Normal Distributions Version 1.1 Date 2016-08-08 Author Luis Benites Sanchez and Clecio da Silva Ferreira Maintainer Luis Benites Sanchez
Package ssmn August 9, 2016 Type Package Title Skew Scale Mixtures of Normal Distributions Version 1.1 Date 2016-08-08 Author Luis Benites Sanchez and Clecio da Silva Ferreira Maintainer Luis Benites Sanchez
Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics
 PASW Complex Samples 17.0 Specifications Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics When you conduct sample surveys, use a statistics package dedicated to producing correct estimates for complex sample
PASW Complex Samples 17.0 Specifications Correctly Compute Complex Samples Statistics When you conduct sample surveys, use a statistics package dedicated to producing correct estimates for complex sample
Gaussian Mixture Models method and applications
 Gaussian Mixture Models method and applications Jesús Zambrano PostDoctoral Researcher School of Business, Society and Engineering www.mdh.se FUDIPO project. Machine Learning course. Oct.-Dec. 2017 Outline
Gaussian Mixture Models method and applications Jesús Zambrano PostDoctoral Researcher School of Business, Society and Engineering www.mdh.se FUDIPO project. Machine Learning course. Oct.-Dec. 2017 Outline
The EMCLUS Procedure. The EMCLUS Procedure
 The EMCLUS Procedure Overview Procedure Syntax PROC EMCLUS Statement VAR Statement INITCLUS Statement Output from PROC EMCLUS EXAMPLES-SECTION Example 1: Syntax for PROC FASTCLUS Example 2: Use of the
The EMCLUS Procedure Overview Procedure Syntax PROC EMCLUS Statement VAR Statement INITCLUS Statement Output from PROC EMCLUS EXAMPLES-SECTION Example 1: Syntax for PROC FASTCLUS Example 2: Use of the
22s:152 Applied Linear Regression
 22s:152 Applied Linear Regression Chapter 22: Model Selection In model selection, the idea is to find the smallest set of variables which provides an adequate description of the data. We will consider
22s:152 Applied Linear Regression Chapter 22: Model Selection In model selection, the idea is to find the smallest set of variables which provides an adequate description of the data. We will consider
SOCY7706: Longitudinal Data Analysis Instructor: Natasha Sarkisian. Panel Data Analysis: Fixed Effects Models
 SOCY776: Longitudinal Data Analysis Instructor: Natasha Sarkisian Panel Data Analysis: Fixed Effects Models Fixed effects models are similar to the first difference model we considered for two wave data
SOCY776: Longitudinal Data Analysis Instructor: Natasha Sarkisian Panel Data Analysis: Fixed Effects Models Fixed effects models are similar to the first difference model we considered for two wave data
