n HW7 due in about ten days n HW8 will be optional n No CLASS or office hours on Tuesday n I will catch up on grading next week!
|
|
|
- Bathsheba Poppy McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Announcements SMT Solvers, Symbolic Execution n HW7 due in about ten days n HW8 will be optional n No CLASS or office hours on Tuesday n I will catch up on grading next week! n Presentations n Some of you haven t sent me their selections n Please do! n Quiz 6 Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 2 Outline n (for HW7) n Symbolic Execution n Overview and applications n Challenges n Tools and techniques n is a language for specifying input to SMT solvers (e.g., Z3) n declare an integer constant x n (assert (> x 0)) add x>0 to known facts n checks if there exist an assignment that makes all known facts true; returns (sat) or (unsat) n (get-model) print this assignment Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 3 n Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 4 (declare-const a Int) (declare-fun f (Int Bool) Int) (assert (> a 10)) (assert (< (f a true) 100)) Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 5 n Your homework is to write a Tiny Dafny n Given an IMP program { P c { Q generate verification conditions in n Verify conditions with Z3 n Yet another programming language, OCaml! n Some pitfalls n Function calls: (f arg1 arg2) NOT f(arg1,arg2)! n == is reference equality. Use (String.equal s1 s2) 6 1
2 n Suppose we need to verify { P c { Q n Generate wp(c,q) n Program verifies when P => wp(c,q) is valid n A logical formula is valid when true for all inputs n Encoding n Duality of satisfiability and validity: F is valid iff!f is unsatisfiable n Ask: is!(p => wp(c,q)) satisfiable n If (unsat) program is correct n If (sat) our program is incorrect, we ll get model 7 Example requires: x == 1 x == -2 ensures: y == 0 { y = x + 4; if (x > 0) { y = x*x - 1; else { y = y + x; wp(,{y=0) =?? (x=1 or x=-2) => ((x>0 and x*x-1 = 0) or (x<=0 and x+4+x=0)) code: (assert (and (or (= x 1) (= x -2)) (not (or (and (<= x 0) (= (+ (+ x 4) x) 0)) (and (> x 0) (= (- (* x x) 1) 0)) )))) Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 8 Example requires: x == 1 x == -5 ensures: y == 0 { y = x + 4; if (x > 0) { y = x*x - 1; else { y = y + x; vc(,{y=0) = wp(,{y=0) =?? (x=1 or x=-5) => ((x>0 and x*x-1 = 0) or (x<=0 and x+4+x=0)) code: (assert (and (or (= x 1) (= x -5)) (not (or (and (<= x 0) (= (+ (+ x 4) x) 0)) (and (> x 0) (= (- (* x x) 1) 0)) )))) (get-model) Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 9 Another Example Is this formula valid? (x>0 and x+5 > 5) or (x<=0 and (x=0 => x + x + 5 = 5)) code: (assert (not (and (> x 0) (> (+ x 5) 5)))) (assert (not (and (<= x 0) (or (not (= x 0)) (= (+ (+ x x) 5) 5))))) Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova (example from MIT 2015 Program Analysis OCW) 10 SMT Solvers n SAT Solvers are at the heard of SMT Solvers n In practice, optimizations on SMT expressions is crucial n Simple identities (x+0=x, x*0=0) n E.g., (simplify (> (+ x 5) 5)) yields (not (<= x 0)) n Theory of arrays: n E.g., (simplify (select (store a 42 x) 42)) n Cache solver queries n Remove useless variables Outline n (for HW7) n Symbolic Execution n Overview and applications n Challenges n Tools and techniques n Reading: A Survey of Symbolic Execution Techniques by Baldoni et al. Oct 2017 Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 11 Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 12 2
3 Classical References n Robert S. Boyer, Bernard Elspas, and Karl N. Levitt, Select: A Formal System for Testing and Debugging Programs by Symbolic Execution, ICRS 1975 n James C. King, Symbolic Execution and Program Testing, CACM, 19(7): , 1976 n William E. Howden, Symbolic Testing and the Dissect Symbolic Evaluation System IEEE TSE, 3(4): , Resurgence and Applications n More powerful computers lead to much more powerful reasoning tools (e.g., Z3) n Systems that started a resurgence n DART by Godefroid and Sen, PLDI 2005 n EXE by Cadar, Ganesh, Pawlowski, Dill and Engler, CCS 2006 Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 14 Symbolic Execution Example 1 void foobar (int a, int b) { int x = 1, y = 0; if (a!= 0) { y = 3+x; if (b == 0) x = 2*(a+b); { x-y!= 0 Symbolic variables: e.g., a: α, b: β State σ: map from variables to expressions (either symbolic or concrete) Evaluation of program statements Path condition (for path p): a logical formula F s.t. if F is true, execution takes path p Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova (example due to Baldoni et al.) 15 T Example 1 σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà0 π = α!=0 4. y=3+x; σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà4 π = α!=0 5. if (b == 0) σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà4 π = α!=0 β=0 6. x=2*(a+b); T σ = { aàα,bàβ π = true 2. x=1; y=0; σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà0 π = true 3. if (a!= 0) σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà2*(α+β),yà4 π = α!=0 β=0 8. assert { x-y!= 0 NOT OK: 2*(α+β)-4 = 0 α!=0 β=0 F σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà0 π = α=0 8. assert { x-y!= 0 OK. σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà0 π = α!=0 β!=0 8. assert { x-y!= 0 OK. F 16 n Why? Motivation for Symbolic Execution n One symbolic execution path covers many actual inputs n Exactly the set of inputs that satisfy the path condition n Thus, we cover a lot more of the program input space than testing Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 17 VC Generation Works Too void foobar (int a, int b) { int x = 1, y = 0; if (a!= 0) { y = 3+x; if (b == 0) x = 2*(a+b); { x-y!= 0 Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 18 3
4 VC generation vs. Symbolic Execution? n VC generation = Backward reasoning n HW7 Challenges to Symbolic Execution? n State space explosion (Path explosion) n n conditionals generate 2 n paths n Symbolic execution = Forward reasoning n HW8 (one option): Add a symbolic execution engine as another interpreter of IMP programs Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 19 n Memory: how to handle pointers and arrays? n Constraint solving: are SMT solvers good enough to solve complex constraints? n Edge of program, i.e., libraries and binary code: how do we handle them, with no benefit of high-level static analysis? Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 20 n We can think of program execution as a DAG n Nodes n i represent states n Edges (n i,n j ) represent state transitions n We need strategies/heuristics for graph exploration n At each step, how do we chose which paths to explore and which paths to drop n There are many strategies and heuristics! n DFS n BFS n Advantages n Simplicity n Drawbacks n Generally, unguided by other knowledge n DFS can get stuck in one part of program n BFS considered the better one Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 21 Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 22 n Heuristic try to steer towards paths more likely to fail assertions n Run symbolic execution engine for a limited period of time n One big idea: randomness n At each step choose paths at random n Consensus: randomness works very well! n Any new heuristic must compare with random n A drawback: reproducibility Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 23 Run Different Searches at the Same Time n Advantages? n May achieves better coverage as it explores different strategies n Strategies target certain kinds of bugs better than others n Drawbacks? n As good as best search strategy but wastes time running other search strategies too Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 24 4
5 Libraries and Binary Code n Edges of the program n Libraries, binary code n One way n Pull in library code (libc, glibc) n Hard. Symbolic execution easily gets stuck n Another way n Summaries (stubs) for library code n Also hard. A lot of work and often unsound n Conclolic execution gets around these Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 25 Concolic Execution n Another big idea, due to Sen et al., FSE 2005 n Mixes concrete and symbolic execution n One variation: dynamic symbolic execution n Instrument program to do symbolic execution n Select some inputs n Run path from start to finish, maintaining concrete state and symbolic state n When finished, generate a new path condition by negating last path condition n Solve path condition and if satisfiable, generate input and run 26 Concolic Execution, Example σ = { aàα,bàβ π = true 2. x=1; y=0; σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà0 π = true 3. if (a!= 0) σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà0 π = α!=0 4. y=3+x; σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà4 π = α!=0 5. if (b == 0) σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà4 π = α!=0 β=0 6. x=2*(a+b); Suppose we chose inputs a=1, b=1. Concrete σ = { aà1,bà1,xà1,yà0 at 3 and 4 Concrete σ = { aà1,bà1,xà1,yà4 at 5 and 8 σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà1,yà4 π = α!=0 β!=0 8. assert { x-y!= 0 OK. σ = { aàα,bàβ,xà2*(α+β),yà4 π = α!=0 β=0 8. assert { x-y!= 0 NOT OK! 2*(α+β)-4 α!=0 β=0 = 0 is satisfiable 1. Now negate β!=0 2. Ask solver for new inputs, e.g., a=1, b=0 3. Run program again 27 Concolic Execution n Why this works? n Search is guided by a concrete path, therefore there are shadow concrete values for most symbolic variables n Thus, SMT formula becomes easier to solve Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 28 Recent Success n SAGE n Microsoft, concolic execution n Finds bugs in file parsers n Microsoft continuously runs SAGE! n Mayhem n Combines BFS and advanced search techniques n Runs on binary code n Automatically generates exploits when bug found n KLEE n Symbolically executes LLVM bitcode 29 Spring 18 CSCI 4450/6450, A Milanova 30 5
CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers. Fall Symbolic Execution
 CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fall 2015 Symbolic Execution Introduction Static analysis is great Lots of interesting ideas and tools Commercial companies sell, use static analysis It all looks good
CMSC 430 Introduction to Compilers Fall 2015 Symbolic Execution Introduction Static analysis is great Lots of interesting ideas and tools Commercial companies sell, use static analysis It all looks good
CYSE 411/AIT681 Secure Software Engineering Topic #17: Symbolic Execution
 CYSE 411/AIT681 Secure Software Engineering Topic #17: Symbolic Execution Instructor: Dr. Kun Sun Software has bugs To find them, we use testing and code reviews But some bugs are still missed Rare features
CYSE 411/AIT681 Secure Software Engineering Topic #17: Symbolic Execution Instructor: Dr. Kun Sun Software has bugs To find them, we use testing and code reviews But some bugs are still missed Rare features
Software has bugs. Static analysis 4/9/18. CYSE 411/AIT681 Secure Software Engineering. To find them, we use testing and code reviews
 CYSE 411/AIT681 Secure Software Engineering Topic #17: Symbolic Execution Instructor: Dr. Kun Sun Software has bugs To find them, we use testing and code reviews But some bugs are still missed Rare features
CYSE 411/AIT681 Secure Software Engineering Topic #17: Symbolic Execution Instructor: Dr. Kun Sun Software has bugs To find them, we use testing and code reviews But some bugs are still missed Rare features
CMSC 631 Program Analysis and Understanding. Spring Symbolic Execution
 CMSC 631 Program Analysis and Understanding Spring 2013 Symbolic Execution Introduction Static analysis is great Lots of interesting ideas and tools Commercial companies sell, use static analysis It all
CMSC 631 Program Analysis and Understanding Spring 2013 Symbolic Execution Introduction Static analysis is great Lots of interesting ideas and tools Commercial companies sell, use static analysis It all
Symbolic Execution. Wei Le April
 Symbolic Execution Wei Le 2016 April Agenda What is symbolic execution? Applications History Interal Design: The three challenges Path explosion Modeling statements and environments Constraint solving
Symbolic Execution Wei Le 2016 April Agenda What is symbolic execution? Applications History Interal Design: The three challenges Path explosion Modeling statements and environments Constraint solving
Symbolic Execution. Michael Hicks. for finding bugs. CMSC 631, Fall 2017
 Symbolic Execution for finding bugs Michael Hicks CMSC 631, Fall 2017 Software has bugs To find them, we use testing and code reviews But some bugs are still missed Rare features Rare circumstances Nondeterminism
Symbolic Execution for finding bugs Michael Hicks CMSC 631, Fall 2017 Software has bugs To find them, we use testing and code reviews But some bugs are still missed Rare features Rare circumstances Nondeterminism
Symbolic and Concolic Execution of Programs
 Symbolic and Concolic Execution of Programs Information Security, CS 526 Omar Chowdhury 10/7/2015 Information Security, CS 526 1 Reading for this lecture Symbolic execution and program testing - James
Symbolic and Concolic Execution of Programs Information Security, CS 526 Omar Chowdhury 10/7/2015 Information Security, CS 526 1 Reading for this lecture Symbolic execution and program testing - James
Symbolic Execution for Bug Detection and Automated Exploit Generation
 Symbolic Execution for Bug Detection and Automated Exploit Generation Daniele Cono D Elia Credits: Emilio Coppa SEASON Lab season-lab.github.io May 27, 2016 1 / 29 Daniele Cono D Elia Symbolic Execution
Symbolic Execution for Bug Detection and Automated Exploit Generation Daniele Cono D Elia Credits: Emilio Coppa SEASON Lab season-lab.github.io May 27, 2016 1 / 29 Daniele Cono D Elia Symbolic Execution
Introduction to Symbolic Execution
 Introduction to Symbolic Execution Classic Symbolic Execution 1 Problem 1: Infinite execution path Problem 2: Unsolvable formulas 2 Problem 3: symbolic modeling External function calls and system calls
Introduction to Symbolic Execution Classic Symbolic Execution 1 Problem 1: Infinite execution path Problem 2: Unsolvable formulas 2 Problem 3: symbolic modeling External function calls and system calls
Symbolic Memory with Pointers
 Symbolic Memory with Pointers Marek Trtík 1, and Jan Strejček 2 1 VERIMAG, Grenoble, France Marek.Trtik@imag.fr 2 Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic strejcek@fi.muni.cz Abstract.
Symbolic Memory with Pointers Marek Trtík 1, and Jan Strejček 2 1 VERIMAG, Grenoble, France Marek.Trtik@imag.fr 2 Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic strejcek@fi.muni.cz Abstract.
Automatic Software Verification
 Automatic Software Verification Instructor: Mooly Sagiv TA: Oded Padon Slides from Eran Yahav and the Noun Project, Wikipedia Course Requirements Summarize one lecture 10% one lecture notes 45% homework
Automatic Software Verification Instructor: Mooly Sagiv TA: Oded Padon Slides from Eran Yahav and the Noun Project, Wikipedia Course Requirements Summarize one lecture 10% one lecture notes 45% homework
Symbolic Execu.on. Suman Jana
 Symbolic Execu.on Suman Jana Acknowledgement: Baishakhi Ray (Uva), Omar Chowdhury (Purdue), Saswat Anand (GA Tech), Rupak Majumdar (UCLA), Koushik Sen (UCB) What is the goal? Tes.ng Tes%ng approaches are
Symbolic Execu.on Suman Jana Acknowledgement: Baishakhi Ray (Uva), Omar Chowdhury (Purdue), Saswat Anand (GA Tech), Rupak Majumdar (UCLA), Koushik Sen (UCB) What is the goal? Tes.ng Tes%ng approaches are
Testing, Fuzzing, & Symbolic Execution
 Testing, Fuzzing, & Symbolic Execution Software Testing The most common way of measuring & ensuring correctness Input 2 Software Testing The most common way of measuring & ensuring correctness Input Observed
Testing, Fuzzing, & Symbolic Execution Software Testing The most common way of measuring & ensuring correctness Input 2 Software Testing The most common way of measuring & ensuring correctness Input Observed
Symbolic Execution, Dynamic Analysis
 Symbolic Execution, Dynamic Analysis http://d3s.mff.cuni.cz Pavel Parízek CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE faculty of mathematics and physics Symbolic execution Pavel Parízek Symbolic Execution, Dynamic Analysis
Symbolic Execution, Dynamic Analysis http://d3s.mff.cuni.cz Pavel Parízek CHARLES UNIVERSITY IN PRAGUE faculty of mathematics and physics Symbolic execution Pavel Parízek Symbolic Execution, Dynamic Analysis
Testing & Symbolic Execution
 Testing & Symbolic Execution Software Testing The most common way of measuring & ensuring correctness Input 2 Software Testing The most common way of measuring & ensuring correctness Input Observed Behavior
Testing & Symbolic Execution Software Testing The most common way of measuring & ensuring correctness Input 2 Software Testing The most common way of measuring & ensuring correctness Input Observed Behavior
Symbolic Execution. Joe Hendrix Galois, Inc SMT Summer School galois
 Symbolic Execution Joe Hendrix Galois, Inc SMT Summer School 2015 Galois, Inc We solve hard research problems for clients. Symbolic Execution is a technique for mapping code into logic. is widely used
Symbolic Execution Joe Hendrix Galois, Inc SMT Summer School 2015 Galois, Inc We solve hard research problems for clients. Symbolic Execution is a technique for mapping code into logic. is widely used
Automated Software Analysis Techniques For High Reliability: A Concolic Testing Approach. Moonzoo Kim
 Automated Software Analysis Techniques For High Reliability: A Concolic Testing Approach Moonzoo Kim Contents Automated Software Analysis Techniques Background Concolic testing process Example of concolic
Automated Software Analysis Techniques For High Reliability: A Concolic Testing Approach Moonzoo Kim Contents Automated Software Analysis Techniques Background Concolic testing process Example of concolic
DART: Directed Automated Random Testing
 DART: Directed Automated Random Testing Patrice Godefroid Nils Klarlund Koushik Sen Bell Labs Bell Labs UIUC Presented by Wei Fang January 22, 2015 PLDI 2005 Page 1 June 2005 Motivation Software testing:
DART: Directed Automated Random Testing Patrice Godefroid Nils Klarlund Koushik Sen Bell Labs Bell Labs UIUC Presented by Wei Fang January 22, 2015 PLDI 2005 Page 1 June 2005 Motivation Software testing:
Abstractions and small languages in synthesis CS294: Program Synthesis for Everyone
 Abstractions and small languages in synthesis CS294: Program Synthesis for Everyone Ras Bodik Emina Torlak Division of Computer Science University of California, Berkeley Today Today: we describe why high-level
Abstractions and small languages in synthesis CS294: Program Synthesis for Everyone Ras Bodik Emina Torlak Division of Computer Science University of California, Berkeley Today Today: we describe why high-level
DART: Directed Automated Random Testing. CUTE: Concolic Unit Testing Engine. Slide Source: Koushik Sen from Berkeley
 DAR: Directed Automated Random esting CUE: Concolic Unit esting Engine Slide Source: Koushik Sen from Berkeley Verification and esting We would like to prove programs correct Verification and esting We
DAR: Directed Automated Random esting CUE: Concolic Unit esting Engine Slide Source: Koushik Sen from Berkeley Verification and esting We would like to prove programs correct Verification and esting We
Static Analysis and Bugfinding
 Static Analysis and Bugfinding Alex Kantchelian 09/12/2011 Last week we talked about runtime checking methods: tools for detecting vulnerabilities being exploited in deployment. So far, these tools have
Static Analysis and Bugfinding Alex Kantchelian 09/12/2011 Last week we talked about runtime checking methods: tools for detecting vulnerabilities being exploited in deployment. So far, these tools have
Tackling the Path Explosion Problem in Symbolic Execution-driven Test Generation for Programs
 2010 19th IEEE Asian Test Symposium Tackling the Path Explosion Problem in Symbolic Execution-driven Test Generation for Programs Saparya Krishnamoorthy, Michael S. Hsiao and Loganathan Lingappan Department
2010 19th IEEE Asian Test Symposium Tackling the Path Explosion Problem in Symbolic Execution-driven Test Generation for Programs Saparya Krishnamoorthy, Michael S. Hsiao and Loganathan Lingappan Department
Improving Program Testing and Understanding via Symbolic Execution
 Improving Program Testing and Understanding via Symbolic Execution Kin-Keung Ma PhD Dissertation Defense December 9 th, 2011 Motivation } Every year, billions of dollars are lost due to software system
Improving Program Testing and Understanding via Symbolic Execution Kin-Keung Ma PhD Dissertation Defense December 9 th, 2011 Motivation } Every year, billions of dollars are lost due to software system
References: Thomas A. Henzinger (1996): The theory of hybrid automata In: Annual IEEE Symposium on Logic in Computer Science
 Hybrid Systems Modeling In today's fast evolving technologies where the line between analog and digital systems is getting blurred, systems consist of a mix of continuous and discrete components. A discrete
Hybrid Systems Modeling In today's fast evolving technologies where the line between analog and digital systems is getting blurred, systems consist of a mix of continuous and discrete components. A discrete
Lecture Notes on Real-world SMT
 15-414: Bug Catching: Automated Program Verification Lecture Notes on Real-world SMT Matt Fredrikson Ruben Martins Carnegie Mellon University Lecture 15 1 Introduction In the previous lecture we studied
15-414: Bug Catching: Automated Program Verification Lecture Notes on Real-world SMT Matt Fredrikson Ruben Martins Carnegie Mellon University Lecture 15 1 Introduction In the previous lecture we studied
Complete Instantiation of Quantified Formulas in Satisfiability Modulo Theories. ACSys Seminar
 Complete Instantiation of Quantified Formulas in Satisfiability Modulo Theories Yeting Ge Leonardo de Moura ACSys Seminar 2008.12 Motivation SMT solvers have been successful Quantified smt formulas are
Complete Instantiation of Quantified Formulas in Satisfiability Modulo Theories Yeting Ge Leonardo de Moura ACSys Seminar 2008.12 Motivation SMT solvers have been successful Quantified smt formulas are
HAMPI A Solver for String Theories
 HAMPI A Solver for String Theories Vijay Ganesh MIT (With Adam Kiezun, Philip Guo, Pieter Hooimeijer and Mike Ernst) Dagstuhl, 2010 Motivation for String Theories String-manipulating programs ü String
HAMPI A Solver for String Theories Vijay Ganesh MIT (With Adam Kiezun, Philip Guo, Pieter Hooimeijer and Mike Ernst) Dagstuhl, 2010 Motivation for String Theories String-manipulating programs ü String
PLDI 2016 Tutorial Automata-Based String Analysis
 PLDI 2016 Tutorial Automata-Based String Analysis Tevfik Bultan, Abdulbaki Aydin, Lucas Bang Verification Laboratory http://vlab.cs.ucsb.edu Department of Computer Science Common Usages of Strings } Input
PLDI 2016 Tutorial Automata-Based String Analysis Tevfik Bultan, Abdulbaki Aydin, Lucas Bang Verification Laboratory http://vlab.cs.ucsb.edu Department of Computer Science Common Usages of Strings } Input
In Our Last Exciting Episode
 In Our Last Exciting Episode #1 Lessons From Model Checking To find bugs, we need specifications What are some good specifications? To convert a program into a model, we need predicates/invariants and
In Our Last Exciting Episode #1 Lessons From Model Checking To find bugs, we need specifications What are some good specifications? To convert a program into a model, we need predicates/invariants and
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics
 Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics Meeting 10, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 Announcements Homework 3 due tonight Homework 2 is graded 13 (mean), 14 (median), out of 21 total, but Graduate class: final project
Introduction to Axiomatic Semantics Meeting 10, CSCI 5535, Spring 2009 Announcements Homework 3 due tonight Homework 2 is graded 13 (mean), 14 (median), out of 21 total, but Graduate class: final project
KLEE: Effective Testing of Systems Programs Cristian Cadar
 KLEE: Effective Testing of Systems Programs Cristian Cadar Joint work with Daniel Dunbar and Dawson Engler April 16th, 2009 Writing Systems Code Is Hard Code complexity Tricky control flow Complex dependencies
KLEE: Effective Testing of Systems Programs Cristian Cadar Joint work with Daniel Dunbar and Dawson Engler April 16th, 2009 Writing Systems Code Is Hard Code complexity Tricky control flow Complex dependencies
Dynamic Software Model Checking
 Dynamic Software Model Checking Patrice Godefroid Microsoft Research Page 1 September 2014 Ed Clarke: A man, An idea LASER 2011 summer school (Elba island, Italy) Page 2 September 2014 Ed Clarke: A man,
Dynamic Software Model Checking Patrice Godefroid Microsoft Research Page 1 September 2014 Ed Clarke: A man, An idea LASER 2011 summer school (Elba island, Italy) Page 2 September 2014 Ed Clarke: A man,
Research on Fuzz Testing Framework based on Concolic Execution
 017 International Conference on Computer Science and Application Engineering (CSAE 017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-505-6 Research on uzz Testing ramework based on Concolic Execution Xiong Xie and Yuhang Chen *
017 International Conference on Computer Science and Application Engineering (CSAE 017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-505-6 Research on uzz Testing ramework based on Concolic Execution Xiong Xie and Yuhang Chen *
Overview AEG Conclusion CS 6V Automatic Exploit Generation (AEG) Matthew Stephen. Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas
 CS 6V81.005 Automatic Exploit Generation (AEG) Matthew Stephen Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas February 20 th, 2012 Outline 1 Overview Introduction Considerations 2 AEG Challenges
CS 6V81.005 Automatic Exploit Generation (AEG) Matthew Stephen Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas February 20 th, 2012 Outline 1 Overview Introduction Considerations 2 AEG Challenges
Symbolic Computation via Program Transformation
 Symbolic Computation via Program Transformation Henrich Lauko, Petr Ročkai and Jiří Barnat Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic Symbolic Computation Motivation verify programs with inputs from the environment
Symbolic Computation via Program Transformation Henrich Lauko, Petr Ročkai and Jiří Barnat Masaryk University Brno, Czech Republic Symbolic Computation Motivation verify programs with inputs from the environment
CUTE: A Concolic Unit Testing Engine for C
 CUTE: A Concolic Unit Testing Engine for C Koushik Sen Darko Marinov Gul Agha University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Goal Automated Scalable Unit Testing of real-world C Programs Generate test inputs
CUTE: A Concolic Unit Testing Engine for C Koushik Sen Darko Marinov Gul Agha University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Goal Automated Scalable Unit Testing of real-world C Programs Generate test inputs
A CutEr Tool. Kostis Sagonas
 A CutEr Tool Kostis Sagonas Overview Testing demo: unit, property-based, and concolic testing in Erlang Concolic execution for Erlang demo Support for type specifications short demo CutEr: A Concolic Unit
A CutEr Tool Kostis Sagonas Overview Testing demo: unit, property-based, and concolic testing in Erlang Concolic execution for Erlang demo Support for type specifications short demo CutEr: A Concolic Unit
Abstract Interpretation
 Abstract Interpretation Ranjit Jhala, UC San Diego April 22, 2013 Fundamental Challenge of Program Analysis How to infer (loop) invariants? Fundamental Challenge of Program Analysis Key issue for any analysis
Abstract Interpretation Ranjit Jhala, UC San Diego April 22, 2013 Fundamental Challenge of Program Analysis How to infer (loop) invariants? Fundamental Challenge of Program Analysis Key issue for any analysis
Test Automation. 20 December 2017
 Test Automation 20 December 2017 The problem of test automation Testing has repetitive components, so automation is justified The problem is cost-benefit evaluation of automation [Kaner] Time for: test
Test Automation 20 December 2017 The problem of test automation Testing has repetitive components, so automation is justified The problem is cost-benefit evaluation of automation [Kaner] Time for: test
n n Try tutorial on front page to get started! n spring13/ n Stack Overflow!
 Announcements n Rainbow grades: HW1-6, Quiz1-5, Exam1 n Still grading: HW7, Quiz6, Exam2 Intro to Haskell n HW8 due today n HW9, Haskell, out tonight, due Nov. 16 th n Individual assignment n Start early!
Announcements n Rainbow grades: HW1-6, Quiz1-5, Exam1 n Still grading: HW7, Quiz6, Exam2 Intro to Haskell n HW8 due today n HW9, Haskell, out tonight, due Nov. 16 th n Individual assignment n Start early!
Program Analysis and Constraint Programming
 Program Analysis and Constraint Programming Joxan Jaffar National University of Singapore CPAIOR MasterClass, 18-19 May 2015 1 / 41 Program Testing, Verification, Analysis (TVA)... VS... Satifiability/Optimization
Program Analysis and Constraint Programming Joxan Jaffar National University of Singapore CPAIOR MasterClass, 18-19 May 2015 1 / 41 Program Testing, Verification, Analysis (TVA)... VS... Satifiability/Optimization
Automated Software Testing
 Automated Software Testing for the 21 st Century Patrice Godefroid Microsoft Research Page 1 June 2015 Outline Two parts: 1. Some recent advances on automated software testing Technical developments Applications
Automated Software Testing for the 21 st Century Patrice Godefroid Microsoft Research Page 1 June 2015 Outline Two parts: 1. Some recent advances on automated software testing Technical developments Applications
Dynamic Symbolic Execution using Eclipse CDT
 Dynamic Symbolic Execution using Eclipse CDT Andreas Ibing Chair for IT Security TU München Boltzmannstrasse 3, 85748 Garching, Germany Email: andreas.ibing@tum.de Abstract Finding software bugs before
Dynamic Symbolic Execution using Eclipse CDT Andreas Ibing Chair for IT Security TU München Boltzmannstrasse 3, 85748 Garching, Germany Email: andreas.ibing@tum.de Abstract Finding software bugs before
Computer Science II CSci 1200 Sections 1-4,6 Week 6, Friday Class October 5, 2001 Linked Lists, Part 2
 Computer Science II CSci 1200 Sections 1-4,6 Week 6, Friday Class October 5, 2001 Linked Lists, Part 2 Announcements Tests will be returned next Friday. We will discuss test content, test preparations,
Computer Science II CSci 1200 Sections 1-4,6 Week 6, Friday Class October 5, 2001 Linked Lists, Part 2 Announcements Tests will be returned next Friday. We will discuss test content, test preparations,
Ranking Functions for Loops with Disjunctive Exit-Conditions
 Ranking Functions for Loops with Disjunctive Exit-Conditions Rody Kersten 1 Marko van Eekelen 1,2 1 Institute for Computing and Information Sciences (icis), Radboud University Nijmegen 2 School for Computer
Ranking Functions for Loops with Disjunctive Exit-Conditions Rody Kersten 1 Marko van Eekelen 1,2 1 Institute for Computing and Information Sciences (icis), Radboud University Nijmegen 2 School for Computer
Meeting14:Denotations
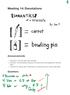 Meeting14:Denotations Announcements Homework 3 due next week Friday at 6:00pm Reminder: 5-minute feedback discussion with Sean is part of the assignment ("interview light") Talk (with me, with the class
Meeting14:Denotations Announcements Homework 3 due next week Friday at 6:00pm Reminder: 5-minute feedback discussion with Sean is part of the assignment ("interview light") Talk (with me, with the class
ECE 587 Hardware/Software Co-Design Lecture 11 Verification I
 ECE 587 Hardware/Software Co-Design Spring 2018 1/23 ECE 587 Hardware/Software Co-Design Lecture 11 Verification I Professor Jia Wang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Illinois Institute
ECE 587 Hardware/Software Co-Design Spring 2018 1/23 ECE 587 Hardware/Software Co-Design Lecture 11 Verification I Professor Jia Wang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Illinois Institute
Announcements. Testing. Announcements. Announcements
 Announcements Testing HW0, HW1, and HW2 are graded Grades and feedback in Submitty Email us at csci2600@cs.lists.rpi.edu Use Submitty discussion board! HW0, HW1, and HW2, Quiz 1 and 2 Grades in Submitty
Announcements Testing HW0, HW1, and HW2 are graded Grades and feedback in Submitty Email us at csci2600@cs.lists.rpi.edu Use Submitty discussion board! HW0, HW1, and HW2, Quiz 1 and 2 Grades in Submitty
Software Testing CS 408. Lecture 6: Dynamic Symbolic Execution and Concolic Testing 1/30/18
 Software Testing CS 408 Lecture 6: Dynamic Symbolic Execution and Concolic Testing 1/30/18 Relevant Papers CUTE: A Concolic Unit Testing Engine for C Koushik Sen, Darko Marinov, Gul Agha Department of
Software Testing CS 408 Lecture 6: Dynamic Symbolic Execution and Concolic Testing 1/30/18 Relevant Papers CUTE: A Concolic Unit Testing Engine for C Koushik Sen, Darko Marinov, Gul Agha Department of
Alive: Provably Correct InstCombine Optimizations
 Alive: Provably Correct InstCombine Optimizations David Menendez Santosh Nagarakatte Rutgers University John Regehr University of Utah Nuno Lopes Microsoft Research Can We Trust Compilers? Any large software
Alive: Provably Correct InstCombine Optimizations David Menendez Santosh Nagarakatte Rutgers University John Regehr University of Utah Nuno Lopes Microsoft Research Can We Trust Compilers? Any large software
Symbolic Execution for Software Testing: Three Decades Later
 doi:10.1145/2408776.2408795 The challenges and great promise of modern symbolic execution techniques, and the tools to help implement them. By Cristian Cadar and Koushik Sen Symbolic Execution for Software
doi:10.1145/2408776.2408795 The challenges and great promise of modern symbolic execution techniques, and the tools to help implement them. By Cristian Cadar and Koushik Sen Symbolic Execution for Software
Principles of Program Analysis. Lecture 1 Harry Xu Spring 2013
 Principles of Program Analysis Lecture 1 Harry Xu Spring 2013 An Imperfect World Software has bugs The northeast blackout of 2003, affected 10 million people in Ontario and 45 million in eight U.S. states
Principles of Program Analysis Lecture 1 Harry Xu Spring 2013 An Imperfect World Software has bugs The northeast blackout of 2003, affected 10 million people in Ontario and 45 million in eight U.S. states
Program Testing via Symbolic Execution
 Program Testing via Symbolic Execution Daniel Dunbar Program Testing via Symbolic Execution p. 1/26 Introduction Motivation Manual testing is difficult Program Testing via Symbolic Execution p. 2/26 Introduction
Program Testing via Symbolic Execution Daniel Dunbar Program Testing via Symbolic Execution p. 1/26 Introduction Motivation Manual testing is difficult Program Testing via Symbolic Execution p. 2/26 Introduction
Scalable Test Generation by Interleaving Concrete and Symbolic Execution
 Scalable Test Generation by Interleaving Concrete and Symbolic Execution Xiaoke Qin and Prabhat Mishra Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville
Scalable Test Generation by Interleaving Concrete and Symbolic Execution Xiaoke Qin and Prabhat Mishra Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville
QUIZ. What are 3 differences between C and C++ const variables?
 QUIZ What are 3 differences between C and C++ const variables? Solution QUIZ Source: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17349387/scope-of-macros-in-c Solution The C/C++ preprocessor substitutes mechanically,
QUIZ What are 3 differences between C and C++ const variables? Solution QUIZ Source: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17349387/scope-of-macros-in-c Solution The C/C++ preprocessor substitutes mechanically,
Microsoft SAGE and LLVM KLEE. Julian Cohen Manual and Automatic Program Analysis
 Microsoft SAGE and LLVM KLEE Julian Cohen HockeyInJune@isis.poly.edu Manual and Automatic Program Analysis KLEE KLEE [OSDI 2008, Best Paper Award] Based on symbolic execution and constraint solving techniques
Microsoft SAGE and LLVM KLEE Julian Cohen HockeyInJune@isis.poly.edu Manual and Automatic Program Analysis KLEE KLEE [OSDI 2008, Best Paper Award] Based on symbolic execution and constraint solving techniques
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. OCaml Imperative Programming
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Imperative Programming CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 So Far, Only Functional Programming We haven t given you any way so far to change something in memory
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages OCaml Imperative Programming CMSC330 Spring 2018 1 So Far, Only Functional Programming We haven t given you any way so far to change something in memory
Verifying C & C++ with ESBMC
 Verifying C & C++ with ESBMC Denis A Nicole dan@ecs.soton.ac.uk CyberSecuritySoton.org [w] @CybSecSoton [fb & tw] ESBMC ESBMC, the Efficient SMT-Based Context-Bounded Model Checker was originally developed
Verifying C & C++ with ESBMC Denis A Nicole dan@ecs.soton.ac.uk CyberSecuritySoton.org [w] @CybSecSoton [fb & tw] ESBMC ESBMC, the Efficient SMT-Based Context-Bounded Model Checker was originally developed
Software security, secure programming
 Software security, secure programming Fuzzing and Dynamic Analysis Master on Cybersecurity Master MoSiG Academic Year 2017-2018 Outline Fuzzing (or how to cheaply produce useful program inputs) A concrete
Software security, secure programming Fuzzing and Dynamic Analysis Master on Cybersecurity Master MoSiG Academic Year 2017-2018 Outline Fuzzing (or how to cheaply produce useful program inputs) A concrete
CS 565: Programming Languages. Spring 2008 Tu, Th: 16:30-17:45 Room LWSN 1106
 CS 565: Programming Languages Spring 2008 Tu, Th: 16:30-17:45 Room LWSN 1106 Administrivia Who am I? Course web page http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/peugster/cs565spring08/ Office hours By appointment Main
CS 565: Programming Languages Spring 2008 Tu, Th: 16:30-17:45 Room LWSN 1106 Administrivia Who am I? Course web page http://www.cs.purdue.edu/homes/peugster/cs565spring08/ Office hours By appointment Main
Application of Propositional Logic II - How to Test/Verify my C program? Moonzoo Kim
 Application of Propositional Logic II - How to Test/Verify my C program? Moonzoo Kim 2 Solving Various Problems using SAT Solver Sudoku Puzzle Encoding 1 Encoding 2 Verify/Testing C Programs Encoding 3
Application of Propositional Logic II - How to Test/Verify my C program? Moonzoo Kim 2 Solving Various Problems using SAT Solver Sudoku Puzzle Encoding 1 Encoding 2 Verify/Testing C Programs Encoding 3
Cuts from Proofs: A Complete and Practical Technique for Solving Linear Inequalities over Integers
 Cuts from Proofs: A Complete and Practical Technique for Solving Linear Inequalities over Integers Isil Dillig, Thomas Dillig, and Alex Aiken Computer Science Department Stanford University Linear Arithmetic
Cuts from Proofs: A Complete and Practical Technique for Solving Linear Inequalities over Integers Isil Dillig, Thomas Dillig, and Alex Aiken Computer Science Department Stanford University Linear Arithmetic
Meeting13:Denotations
 Meeting13:Denotations Announcements Homework 3 due next week Friday at 6:00pm Homework2Comments Time: 29.2 hours avg Difficulty: 5.4 avg Issues Length? (Part 2 out Wed instead of Mon) Misunderstanding
Meeting13:Denotations Announcements Homework 3 due next week Friday at 6:00pm Homework2Comments Time: 29.2 hours avg Difficulty: 5.4 avg Issues Length? (Part 2 out Wed instead of Mon) Misunderstanding
More on Verification and Model Checking
 More on Verification and Model Checking Wednesday Oct 07, 2015 Philipp Rümmer Uppsala University Philipp.Ruemmer@it.uu.se 1/60 Course fair! 2/60 Exam st October 21, 8:00 13:00 If you want to participate,
More on Verification and Model Checking Wednesday Oct 07, 2015 Philipp Rümmer Uppsala University Philipp.Ruemmer@it.uu.se 1/60 Course fair! 2/60 Exam st October 21, 8:00 13:00 If you want to participate,
Announcements. Lab 1 this week! Homework posted Wednesday (late)
 C++ Basics Announcements Lab 1 this week! Homework posted Wednesday (late) Avoid errors To remove your program of bugs, you should try to test your program on a wide range of inputs Typically it is useful
C++ Basics Announcements Lab 1 this week! Homework posted Wednesday (late) Avoid errors To remove your program of bugs, you should try to test your program on a wide range of inputs Typically it is useful
Processor. Lecture #2 Number Rep & Intro to C classic components of all computers Control Datapath Memory Input Output
 CS61C L2 Number Representation & Introduction to C (1) insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #2 Number Rep & Intro to C Scott Beamer Instructor 2007-06-26 Review Continued rapid
CS61C L2 Number Representation & Introduction to C (1) insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #2 Number Rep & Intro to C Scott Beamer Instructor 2007-06-26 Review Continued rapid
Efficient Symbolic Execution for Software Testing
 Efficient Symbolic Execution for Software Testing Johannes Kinder Royal Holloway, University of London Joint work with: Stefan Bucur, George Candea, Volodymyr Kuznetsov @ EPFL Symbolic Execution Automatically
Efficient Symbolic Execution for Software Testing Johannes Kinder Royal Holloway, University of London Joint work with: Stefan Bucur, George Candea, Volodymyr Kuznetsov @ EPFL Symbolic Execution Automatically
Satisfiability Modulo Bit-precise Theories for Program Exploration
 Satisfiability Modulo Bit-precise Theories for Program Exploration Nikolaj Bjørner, Leonardo de Moura, Nikolai Tillmann Microsoft Research, One Microsoft Way, Redmond, WA, 98074, USA {nbjorner, leonardo,
Satisfiability Modulo Bit-precise Theories for Program Exploration Nikolaj Bjørner, Leonardo de Moura, Nikolai Tillmann Microsoft Research, One Microsoft Way, Redmond, WA, 98074, USA {nbjorner, leonardo,
CS 6371: Advanced Programming Languages
 CS 6371: Advanced Programming Languages Dr. Kevin Hamlen Spring 2017 Fill out, sign, and return prereq forms: Course number: CS 6371 Section: 1 Prerequisites: CS 5343: Algorithm Analysis & Data Structures
CS 6371: Advanced Programming Languages Dr. Kevin Hamlen Spring 2017 Fill out, sign, and return prereq forms: Course number: CS 6371 Section: 1 Prerequisites: CS 5343: Algorithm Analysis & Data Structures
Minimum Satisfying Assignments for SMT. Işıl Dillig, Tom Dillig Ken McMillan Alex Aiken College of William & Mary Microsoft Research Stanford U.
 Minimum Satisfying Assignments for SMT Işıl Dillig, Tom Dillig Ken McMillan Alex Aiken College of William & Mary Microsoft Research Stanford U. 1 / 20 Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMT) Today, SMT solvers
Minimum Satisfying Assignments for SMT Işıl Dillig, Tom Dillig Ken McMillan Alex Aiken College of William & Mary Microsoft Research Stanford U. 1 / 20 Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMT) Today, SMT solvers
Formally Certified Satisfiability Solving
 SAT/SMT Proof Checking Verifying SAT Solver Code Future Work Computer Science, The University of Iowa, USA April 23, 2012 Seoul National University SAT/SMT Proof Checking Verifying SAT Solver Code Future
SAT/SMT Proof Checking Verifying SAT Solver Code Future Work Computer Science, The University of Iowa, USA April 23, 2012 Seoul National University SAT/SMT Proof Checking Verifying SAT Solver Code Future
Applications of Logic in Software Engineering. CS402, Spring 2016 Shin Yoo
 Applications of Logic in Software Engineering CS402, Spring 2016 Shin Yoo Acknowledgements I borrow slides from: Moonzoo Kim Theo C. Ruys (http://spinroot.com/spin/doc/ SpinTutorial.pdf) CBMC & Daniel
Applications of Logic in Software Engineering CS402, Spring 2016 Shin Yoo Acknowledgements I borrow slides from: Moonzoo Kim Theo C. Ruys (http://spinroot.com/spin/doc/ SpinTutorial.pdf) CBMC & Daniel
SMT-Based Bounded Model Checking for Embedded ANSI-C Software. Lucas Cordeiro, Bernd Fischer, Joao Marques-Silva
 SMT-Based Bounded Model Checking for Embedded ANSI-C Software Lucas Cordeiro, Bernd Fischer, Joao Marques-Silva b.fischer@ecs.soton.ac.uk Bounded Model Checking (BMC) Basic Idea: check negation of given
SMT-Based Bounded Model Checking for Embedded ANSI-C Software Lucas Cordeiro, Bernd Fischer, Joao Marques-Silva b.fischer@ecs.soton.ac.uk Bounded Model Checking (BMC) Basic Idea: check negation of given
logistics: ROP assignment
 bug-finding 1 logistics: ROP assignment 2 2013 memory safety landscape 3 2013 memory safety landscape 4 different design points memory safety most extreme disallow out of bounds usually even making out-of-bounds
bug-finding 1 logistics: ROP assignment 2 2013 memory safety landscape 3 2013 memory safety landscape 4 different design points memory safety most extreme disallow out of bounds usually even making out-of-bounds
Ufo: A Framework for Abstraction- and Interpolation-Based Software Verification
 Ufo: A Framework for Abstraction- and Interpolation-Based Software Verification Aws Albarghouthi 1, Yi Li 1, Arie Gurfinkel 2, and Marsha Chechik 1 1 Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto,
Ufo: A Framework for Abstraction- and Interpolation-Based Software Verification Aws Albarghouthi 1, Yi Li 1, Arie Gurfinkel 2, and Marsha Chechik 1 1 Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto,
Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data
 Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data CSCI 2400: Computer Architecture ECE 3217: Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: David Ferry Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides
Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data CSCI 2400: Computer Architecture ECE 3217: Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: David Ferry Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides
Dynamic Path Reduction for Software Model Checking
 Dynamic Path Reduction for Software Model Checking Zijiang Yang 1, Bashar Al-Rawi 2, Karem Sakallah 2, Xiaowan Huang 3, Scott Smolka 3, and Radu Grosu 3 1 Western Michigan University, Kalamazoo, MI, USA
Dynamic Path Reduction for Software Model Checking Zijiang Yang 1, Bashar Al-Rawi 2, Karem Sakallah 2, Xiaowan Huang 3, Scott Smolka 3, and Radu Grosu 3 1 Western Michigan University, Kalamazoo, MI, USA
Generating Small Countermodels. Andrew Reynolds Intel August 30, 2012
 Generating Small Countermodels using SMT Andrew Reynolds Intel August 30, 2012 Acknowledgements Intel Corporation AmitGoel, Sava Krstic University of Iowa Cesare Tinelli, Francois Bobot New York University
Generating Small Countermodels using SMT Andrew Reynolds Intel August 30, 2012 Acknowledgements Intel Corporation AmitGoel, Sava Krstic University of Iowa Cesare Tinelli, Francois Bobot New York University
Decision Procedures. An Algorithmic Point of View. Bit-Vectors. D. Kroening O. Strichman. Version 1.0, ETH/Technion
 Decision Procedures An Algorithmic Point of View Bit-Vectors D. Kroening O. Strichman ETH/Technion Version 1.0, 2007 Part VI Bit-Vectors Outline 1 Introduction to Bit-Vector Logic 2 Syntax 3 Semantics
Decision Procedures An Algorithmic Point of View Bit-Vectors D. Kroening O. Strichman ETH/Technion Version 1.0, 2007 Part VI Bit-Vectors Outline 1 Introduction to Bit-Vector Logic 2 Syntax 3 Semantics
Notes on Non-Chronologic Backtracking, Implication Graphs, and Learning
 Notes on Non-Chronologic Backtracking, Implication Graphs, and Learning Alan J. Hu for CpSc 5 Univ. of British Columbia 00 February 9 These are supplementary notes on these aspects of a modern DPLL-style
Notes on Non-Chronologic Backtracking, Implication Graphs, and Learning Alan J. Hu for CpSc 5 Univ. of British Columbia 00 February 9 These are supplementary notes on these aspects of a modern DPLL-style
Testing, code coverage and static analysis. COSC345 Software Engineering
 Testing, code coverage and static analysis COSC345 Software Engineering Outline Various testing processes ad hoc / formal / automatic Unit tests and test driven development Code coverage metrics Integration
Testing, code coverage and static analysis COSC345 Software Engineering Outline Various testing processes ad hoc / formal / automatic Unit tests and test driven development Code coverage metrics Integration
Where we are going (today)
 Where we are going (today) Q: How do we arrange bits in the memory of the computer? (why do we care? we want the computer to store many individual numbers) A: bytes and words 10110000 00001110 01000010
Where we are going (today) Q: How do we arrange bits in the memory of the computer? (why do we care? we want the computer to store many individual numbers) A: bytes and words 10110000 00001110 01000010
Outline. Logistics. Logistics. Principles of Software (CSCI 2600) Spring Logistics csci2600/
 Outline Principles of Software (CSCI 600) Spring 018 http://www.cs.rpi.edu/academics/courses/spring18/csci600/ Konstantin Kuzmin, kuzmik@cs.rpi.edu Office hours: Monday and Thursday 4:00 pm - 5:30 pm Mailing
Outline Principles of Software (CSCI 600) Spring 018 http://www.cs.rpi.edu/academics/courses/spring18/csci600/ Konstantin Kuzmin, kuzmik@cs.rpi.edu Office hours: Monday and Thursday 4:00 pm - 5:30 pm Mailing
EECS 219C: Computer-Aided Verification Boolean Satisfiability Solving. Sanjit A. Seshia EECS, UC Berkeley
 EECS 219C: Computer-Aided Verification Boolean Satisfiability Solving Sanjit A. Seshia EECS, UC Berkeley Project Proposals Due Friday, February 13 on bcourses Will discuss project topics on Monday Instructions
EECS 219C: Computer-Aided Verification Boolean Satisfiability Solving Sanjit A. Seshia EECS, UC Berkeley Project Proposals Due Friday, February 13 on bcourses Will discuss project topics on Monday Instructions
JPF SE: A Symbolic Execution Extension to Java PathFinder
 JPF SE: A Symbolic Execution Extension to Java PathFinder Saswat Anand 1,CorinaS.Păsăreanu 2, and Willem Visser 2 1 College of Computing, Georgia Institute of Technology saswat@cc.gatech.edu 2 QSS and
JPF SE: A Symbolic Execution Extension to Java PathFinder Saswat Anand 1,CorinaS.Păsăreanu 2, and Willem Visser 2 1 College of Computing, Georgia Institute of Technology saswat@cc.gatech.edu 2 QSS and
IC-Cut: A Compositional Search Strategy for Dynamic Test Generation
 IC-Cut: A Compositional Search Strategy for Dynamic Test Generation Maria Christakis 1 and Patrice Godefroid 2 1 Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich, Switzerland maria.christakis@inf.ethz.ch 2 Microsoft
IC-Cut: A Compositional Search Strategy for Dynamic Test Generation Maria Christakis 1 and Patrice Godefroid 2 1 Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich, Switzerland maria.christakis@inf.ethz.ch 2 Microsoft
Satisfiability Modulo Theories: ABsolver
 Satisfiability Modulo Theories: ABsolver Michael Tautschnig Joint work with: Andreas Bauer Martin Leucker Christian Schallhart Michael Tautschnig 1 Outline 1. Introduction Michael Tautschnig 2 Outline
Satisfiability Modulo Theories: ABsolver Michael Tautschnig Joint work with: Andreas Bauer Martin Leucker Christian Schallhart Michael Tautschnig 1 Outline 1. Introduction Michael Tautschnig 2 Outline
Bug Finding with Under-approximating Static Analyses. Daniel Kroening, Matt Lewis, Georg Weissenbacher
 Bug Finding with Under-approximating Static Analyses Daniel Kroening, Matt Lewis, Georg Weissenbacher Overview Over- vs. underapproximating static analysis Path-based symbolic simulation Path merging Acceleration
Bug Finding with Under-approximating Static Analyses Daniel Kroening, Matt Lewis, Georg Weissenbacher Overview Over- vs. underapproximating static analysis Path-based symbolic simulation Path merging Acceleration
Scope and Introduction to Functional Languages. Review and Finish Scoping. Announcements. Assignment 3 due Thu at 11:55pm. Website has SML resources
 Scope and Introduction to Functional Languages Prof. Evan Chang Meeting 7, CSCI 3155, Fall 2009 Announcements Assignment 3 due Thu at 11:55pm Submit in pairs Website has SML resources Text: Harper, Programming
Scope and Introduction to Functional Languages Prof. Evan Chang Meeting 7, CSCI 3155, Fall 2009 Announcements Assignment 3 due Thu at 11:55pm Submit in pairs Website has SML resources Text: Harper, Programming
Dynamic Symbolic Database Application Testing
 Dynamic Symbolic Database Application Testing Chengkai Li, Christoph Csallner University of Texas at Arlington June 7, 2010 DBTest 2010 Chengkai Li, Christoph Csallner Dynamic Symbolic Database Application
Dynamic Symbolic Database Application Testing Chengkai Li, Christoph Csallner University of Texas at Arlington June 7, 2010 DBTest 2010 Chengkai Li, Christoph Csallner Dynamic Symbolic Database Application
SOFTWARE testing techniques have not progressed significantly
 EDIC RESEARCH PROPOSAL 1 Scalable Automated Testing Using Symbolic Execution Stefan Bucur DSLAB, I&C, EPFL Abstract Current software testing processes involve significant human intervention, which is both
EDIC RESEARCH PROPOSAL 1 Scalable Automated Testing Using Symbolic Execution Stefan Bucur DSLAB, I&C, EPFL Abstract Current software testing processes involve significant human intervention, which is both
CSE413: Programming Languages and Implementation Racket structs Implementing languages with interpreters Implementing closures
 CSE413: Programming Languages and Implementation Racket structs Implementing languages with interpreters Implementing closures Dan Grossman Fall 2014 Hi! I m not Hal J I love this stuff and have taught
CSE413: Programming Languages and Implementation Racket structs Implementing languages with interpreters Implementing closures Dan Grossman Fall 2014 Hi! I m not Hal J I love this stuff and have taught
CSE 413 Languages & Implementation. Hal Perkins Winter 2019 Structs, Implementing Languages (credits: Dan Grossman, CSE 341)
 CSE 413 Languages & Implementation Hal Perkins Winter 2019 Structs, Implementing Languages (credits: Dan Grossman, CSE 341) 1 Goals Representing programs as data Racket structs as a better way to represent
CSE 413 Languages & Implementation Hal Perkins Winter 2019 Structs, Implementing Languages (credits: Dan Grossman, CSE 341) 1 Goals Representing programs as data Racket structs as a better way to represent
Model Counting with Applications to CodeHunt
 Model Counting with Applications to CodeHunt Willem Visser Stellenbosch University South Africa CodeHunt is built on Model Counting SAT or UNSAT? And Some solutions # SAT solutions? Can we use this for
Model Counting with Applications to CodeHunt Willem Visser Stellenbosch University South Africa CodeHunt is built on Model Counting SAT or UNSAT? And Some solutions # SAT solutions? Can we use this for
MLSA: a static bugs analysis tool based on LLVM IR
 International Journal of Networked and Distributed Computing, Vol. 4, No. 3 (July 2016), 137-144 MLSA: a static bugs analysis tool based on LLVM IR Hongliang Liang 1, Lei Wang 1, Dongyang Wu 1, Jiuyun
International Journal of Networked and Distributed Computing, Vol. 4, No. 3 (July 2016), 137-144 MLSA: a static bugs analysis tool based on LLVM IR Hongliang Liang 1, Lei Wang 1, Dongyang Wu 1, Jiuyun
Type Checking and Type Equality
 Type Checking and Type Equality Type systems are the biggest point of variation across programming languages. Even languages that look similar are often greatly different when it comes to their type systems.
Type Checking and Type Equality Type systems are the biggest point of variation across programming languages. Even languages that look similar are often greatly different when it comes to their type systems.
An Introduction to Satisfiability Modulo Theories
 An Introduction to Satisfiability Modulo Theories Philipp Rümmer Uppsala University Philipp.Ruemmer@it.uu.se February 13, 2019 1/28 Outline From theory... From DPLL to DPLL(T) Slides courtesy of Alberto
An Introduction to Satisfiability Modulo Theories Philipp Rümmer Uppsala University Philipp.Ruemmer@it.uu.se February 13, 2019 1/28 Outline From theory... From DPLL to DPLL(T) Slides courtesy of Alberto
Testing, Debugging, and Verification
 Testing, Debugging, and Verification Formal Specification, Part II Srinivas Pinisetty 23 November 2017 Introduction Today: Introduction to Dafny: An imperative language with integrated support for formal
Testing, Debugging, and Verification Formal Specification, Part II Srinivas Pinisetty 23 November 2017 Introduction Today: Introduction to Dafny: An imperative language with integrated support for formal
4.1 Review - the DPLL procedure
 Applied Logic Lecture 4: Efficient SAT solving CS 4860 Spring 2009 Thursday, January 29, 2009 The main purpose of these notes is to help me organize the material that I used to teach today s lecture. They
Applied Logic Lecture 4: Efficient SAT solving CS 4860 Spring 2009 Thursday, January 29, 2009 The main purpose of these notes is to help me organize the material that I used to teach today s lecture. They
OpenMath and SMT-LIB
 James, Matthew England, Roberto Sebastiani & Patrick Trentin 1 Universities of Bath/Coventry/Trento/Trento J.H.@bath.ac.uk 17 July 2017 1 Thanks to EU H2020-FETOPEN-2016-2017-CSA project SC 2 (712689)
James, Matthew England, Roberto Sebastiani & Patrick Trentin 1 Universities of Bath/Coventry/Trento/Trento J.H.@bath.ac.uk 17 July 2017 1 Thanks to EU H2020-FETOPEN-2016-2017-CSA project SC 2 (712689)
