(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
|
|
|
- Thomas Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
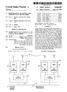
1 (19) United States US 20160O87900A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1 KOLMANC (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) A COMMUNICATION NODE FOR A H04L 2/40 ( ) PACKET-SWITCHED DATANETWORKAND H04B 7/30 ( ) A METHOD FOR OPERATION THEREOF (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H04L 47/21 ( ); H04L 12/ (71) Applicant: CETITEC GMBH, Pforzheim (DE) ( ); H04B 17/30 ( ); H04L 67/1051 ( ); H04L I/0042 ( ): (72) Inventor: Bojan KOLMANIC, Pforzheim (DE) H04L 7/0012 ( ) (21) Appl. No.: 14/891,637 (22) PCT Filed: Dec. 10, 2014 (86). PCT No.: S371 (c)(1), (2) Date: PCT/EP2014/ Nov. 16, 2015 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Dec. 20, 2013 (DE) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. H04L 2/89 ( ) H04L 700 ( ) H04L 29/08 ( ) H04L I/00 ( ) (57) ABSTRACT A communication node for a packet-switched data network is proposed, which comprises an integrated circuit having a system of electronic components for sending and/or receiving audio and/or video data, particularly of an audio and/or video data stream. A media access control component for imple menting a media access control and a physical interface with transmitting and receiving means, by way of which the com munication node is connectable to a communication line of the data network, are provided as components of the system. The media access control component is connected via an internal first interface to the physical interface for exchanging data. The system comprises a real-time clock synchronization unit for synchronizing time information with other commu nication nodes of the data network as well as a queue man agement unit. The real time clock synchronization unit and the queue management unit are fully arranged in the physical interface. System on Chip Eternet VAC Eest PY Traffic Shaping EAV8 Bridge Ay's Nodie AWE Niccie.
2 Patent Application Publication Mar. 24, 2016 Sheet 1 of 4 US 2016/ A1 EAVE Bridge 8-2 re. 16 EAV8 Node EAV Nocie Fig. 1
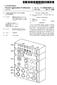
3 Patent Application Publication Mar. 24, 2016 Sheet 2 of 4 US 2016/ A EEE 722 Transport IEEE AS IEEE Qat EEE 802. Ethe et Oriye Fig. 2
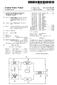
4 Patent Application Publication Mar. 24, 2016 Sheet 3 of 4 US 2016/ A1 Setia Audio interface For example 2S Eternet rai Shaping Y EEE f EAV8 Bridge - I - EAVB Node EAVB Node Fig. 3
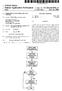
5 Patent Application Publication Mar. 24, 2016 Sheet 4 of 4 US 2016/ A1 1O System on Chip Eternet VAC 27 m s Ethernet 4. res EAVB Bridge 16 ocs SAVS Node SAVS Noce. Fig. 4
6 US 2016/ A1 Mar. 24, 2016 A COMMUNICATION NODE FORA PACKET-SWITCHED DATANETWORKAND A METHOD FOR OPERATION THEREOF The invention relates to a communication node for a packet-switched data network, which comprises an integrated circuit with a system of electronic components for sending and/or receiving audio and/or video data, particularly of an audio and/or video data stream. The invention further relates to a method for operating Such a communication node An integrated circuit with a system of electronic components is known as a system on a chip (SoC). In Such a system, all or a large part of the functions of the system are disposed on a single chip, i.e. an integrated circuit. A system refers here to a combination of various elements, such as logic circuits, clocking and the like, which together provide a spe cific functionality. Such integrated circuits are used for example in embedded systems. A possible field of application of SoCs is for example sending and/or receiving audio and/or Video data (so-called streaming). 0003) A number of IEEE standards for synchro nized and prioritized streaming of audio and video data across networks are combined under the term audio video bridge' (AVB). AVB includes amongst others the standards IEEE 802.1AS (Timing and Synchronisation for Time-Sensitive Applications (gptp)) and IEEE 802.1Qav (Forwarding and queuing for time-sensitive streams). The standard IEEE 1722 (Transport Protocol for Time-Sensitive Applications (Audio Video Transport Protocol, AVTP) is also used in the AVB context. AVB allows using a packet-switched data network, such as for example Ethernet based networks, for duplex transmission of numerous audio and video channels. In the process, time synchronization between communication nodes connected to the data network is carried out by way of time information. By using existing standard Layer-2 MACs (Media Access Controller) and bridges, AVB allows for back ward compatibility between communication nodes using AVB and communication nodes that do not use AVB, whereby these nodes can communicate via customary frame works designed according to the IEEE 802 standard Allowing a communication node to use AVB requires making various modifications to the hardware and software of the communication node. For example, the IEEE 802.1AS standard asks for a more precise timestamp of incoming and outgoing data packets. Timestamping is typi cally carried out within a media access control component (e.g. an Ethernet MAC) of the integrated circuit (SoC) modi fied to that end. This ensures that the sending time of the data packet is as close as possible to the timestamping time. For this reason, this functionality is carried out, as a rule, in hardware (hardware assisted time stamping). In contrast, gen erating synchronization messages as well as messages regarding propagation delays are provided as Software in the media access control component As a rule, a queue management unit described in IEE 802.1Qav is implemented on a FIFO (first in-first out) basis. Hereby, data packets are output according to specific criteria to a communications line of a data network, to which the communication node is connected. However, this requires a certain amount of processing power, in order to be able to fulfill the real-time requirements of AVB The problem underlying the present invention is to provide a communication node for a packet-switched data network, which is adapted for unrestricted use of AVB and at the same time reduces the processing load of the media access control component while fulfilling all real-time requirements. In doing so, the communication node must be backward com patible and be able to communicate with other communica tion nodes that do not support AVB. Another problem under lying the invention is to provide a method for operating Such a communication node This problem is solved by a communication node according to the features of claim 1 and by a method accord ing to the features of claim 13. Advantageous embodiments are set out in the dependent claims In order to solve this problem, a communication node for a packet-switched data network is proposed, which comprises an integrated circuit having a system of electronic components for sending and/or receiving audio and/or video data. The packet-switched data network is particularly Eth ernet or based on Ethernet The integrated circuit particularly comprises a sys tem of electronic components for sending and/or receiving an audio and/or video data stream. Such an integrated circuit with a system of electronic components is provided for example in the form of a SoC. The provided components of the system are at least a media access control component for implementing a media access control and a physical interface with transmitting and receiving means, by way of which the communication node is connectable to a communication line of the data network. The media access control component is for example an Ethernet MAC. The physical interface is for example designed in the form of an Ethernet PHY. This refers to a special integrated circuit or a functional group of an integrated circuit that is responsible for encoding and decod ing data between a purely digital system and a modulated analog system The media access control component is connected via an internal first interface to the physical interface for exchanging data. The system additionally comprises a real time clock synchronization unit for synchronizing time infor mation with other communication nodes of the data network as well as a queue management unit. According to the inven tion, the real time clock synchronization unit and the queue management unit are fully arranged in the physical interface In the proposed communication node, the integrated circuit is relieved of all real-time requirements caused by AVB. Instead, the AVB functionality is arranged in the physi cal interface. This allows for backward compatibility and for a more cost-efficient implementation of an AVB communica tion node, since the design of an AVB-compliant integrated circuit is considerably more complex than equipping the physical interface, which is, as a rule, disposed separately in the communication node, with the necessary components and functionalities. By exchanging a conventional physical inter face with the interface according to the invention, a commu nication node can be made AVB compatible Since the physical interface processes all the tasks related to AVB in real time, the interrupt load on the integrated circuit caused by AVB is considerably reduced. Another advantage is that the internal first interface provided between the physical interface and the media access control compo nent is exclusively available for transmission of data packets (with payload). This means that the bandwidth that is made available by the internal first interface is increased compared to conventional communication nodes, in which AVB tasks are carried out by the media access control component According to an advantageous embodiment, the media access control component does not have any real time
7 US 2016/ A1 Mar. 24, 2016 clock synchronization and queue management functionality. That way, interrupt requests sent to the integrated circuit because of AVB can be avoided. In addition, the communi cation node's backward compatibility is improved According to another advantageous embodiment, the real time clock synchronization unit in the physical inter face is based on the standard IEEE 802.1AS and implements all of its functionalities According to another advantageous embodiment, a first part of the functionality of the real time clock synchro nization unit is carried out, as hardware, in the physical inter face, which is able to, particularly autonomously, implement time synchronization with other communication nodes of the data network. The functionality of the real-time clock syn chronization unit, implemented as hardware, pertains particu larly to providing incoming and outgoing data packets with time stamps in accordance with AVB requirements. Autono mous time synchronization means that no communication is carried out between the physical interface and the media access control components for implementing the provided hardware functionality In another advantageous embodiment, a second part of the functionality of the real time clock synchronization unit is carried out, as Software, in the physical interface, with the aim of implementing a measurement of propagation delays and/or the transmission of information for time synchroniza tion and/or choosing one of the communication nodes of the data network as a master node. This information is used for time synchronization by the communication nodes connected to the data network According to another advantageous embodiment, the real-time clock synchronization unit in the physical inter face comprises at least one register, in which a single or several pieces of time information determined by the real time clock synchronization unit are stored during operation of the communication node, wherein the at least one register is readable via the first interface by the media access control component and/or by another component of the system. For example, one register stores the local time of the communi cation node, which is synchronized with a master time (the so-called grandmaster clock) The first interface, through which data is exchanged within the communication node between the media access control component and the physical interface, is advanta geously the Media Independent Interface (MII) According to another advantageous embodiment, the real-time clock synchronization unit is configurable as master node or as slave node, by storing a predetermined piece of information in a predetermined register during operation of the communication node, the information being readable by the media access control component and/or by another component of the system via the first interface. This allows for time synchronization between the nodes of the packet-switched data network without requiring communica tion with the media access control component or another component of the system According to another embodiment, the physical interface can comprise a device for encoding and/or decoding audio data, particularly according to the IEEE 1722 Transport specification. This device (codec) makes it possible to stream and decode audio data from another communication node, so that the corresponding data can be processed either by a component of the integrated circuit or by another external audio component, without further processing. For example, Such a component can be a sound card within the integrated circuit of the communication node or another external audio terminal (for example an MP3 player) According to another embodiment, the device for encoding and/or decoding audio data can be coupled via a second interface with the system or with an external audio component for directly exchanging data. Particularly, the sec ond interface can be a serial audio interface. Such as for example IS According to another embodiment, the queue man agement unit can be configured to execute the leaky bucket algorithm. Particularly, when the optional second interface is provided, the data received via the second interface from the first interface is processed by the queue management unit according to the used algorithm. By providing the second interface for transmitting audio data, the bandwidth can be further increased via the first interface. Since, according to the invention, managing the queue is no longer carried out in the integrated circuit (SoC) but in the physical interface, the processing load of the integrated circuit, particularly of the media access control component is considerably reduced. The saved processing power can thus be allocated to other tasks by the integrated circuit In order to solve the problem, a method for operat ing a communication node for a packet-switched data net work is furthermore proposed, wherein the communication node is adapted according to the above description. In the method according to the invention, only the real time clock synchronization unit arranged in the physical interface carries out a particularly autonomous time synchronization process with other communication nodes of the data network as well as a measurement of propagation delays and/or the transmis sion of information for time synchronization and/or choosing one of the communication nodes of the data network as a master node The method according to the invention has the same advantages as those described above with respect to the com munication node of the invention The term only means that the media access con trol component or the integrated circuit, respectively a com ponent of the integrated circuit, are not involved in the imple mentation of the mentioned functions and tasks. Particularly, the mentioned tasks are carried without any communication between the physical interface and the integrated circuit According to another embodiment of the proposed method, the queue management unit outputs data packets, which are received from the first and second interface of the system, or optionally of the external audio component, according to specific criteria to the communication line of the data network for transmission According to another embodiment of the method according to the invention, the real-time clock synchroniza tion unit stores one or several pieces of time information in a register or a respective register, in order to provide the one or several pieces of information, for processing, to the media access control component and/or to the one other component of the system, by a read access to the register(s), via the first interface In another embodiment of the method according to the invention, the real-time synchronization unit writes a predetermined piece of information into a predetermined reg ister, wherein the predetermined piece of information indi cates whether the communication node is configured as a master node or as a slave node, wherein the predetermined
8 US 2016/ A1 Mar. 24, 2016 register is readable, by a read access, by the media access control component and/or another component of the system, via the first interface In the following, the invention is described in more detail based on exemplary embodiments with reference to the drawings. In the drawings: 0030 FIG. 1 shows a schematic representation of a packet-switched data network with several communication nodes, wherein one of the communication nodes is designed in the conventional manner for implementing AVB FIG. 2 shows a schematic representation of an AVB Software stack; 0032 FIG. 3 shows a schematic representation of a packet-switched data network with a communication node designed according to a first embodiment of the invention; and 0033 FIG. 4 shows a schematic representation of a packet-switched data network with a communication node designed according to a second embodiment of the invention FIG. 1 shows a schematic representation of a packet-switched data network with several communication nodes 16. In the exemplary embodiment, the data network is Ethernet-based. The communication nodes 16, also known as Ethernet AVB or EAVB nodes, are connected to an Ethernet AVB bridge ( EAVB bridge') via lines 12. In this example, three communication nodes 16 are shown. In practice, this number can vary and can particularly be greater. The lines 12 represent wired or wire-less communication channels. In this example, the communication nodes 16 of the packet-switched data network are designed to implement AVB. To simplify matters, the components that are required to this end are only represented for one of the communication nodes 16. Commu nication nodes 16 that are not designed to implement AVB can also be connected to the EAVB bridge The communication node 16 comprises an inte grated circuit 2 in the form of an SoC (system on a chip) and a physical interface 6 in the form of an Ethernet PHY. The integrated circuit 2 and the physical interface 6 are connected for exchanging data within the communication node 16 by way of an internal first interface 8 in the form of an MII (media independent interface) The integrated circuit 2 comprises electronic com ponents on a common chip. Such as for example digital com ponents, analog components, mixed-signal components and functions for sending and receiving data (RF (radio fre quency) functions). In the field of mobile terminals or con Sumer electronics, the integrated circuit 2 is typically an embedded system It should be noted that in the present description, a SoC is merely an example for an integrated circuit. In the field of desktop computers, a CPU is similarly connected to an Ethernet over PCI The integrated circuit 2 of the communication node 16 comprises a media access control component 4 (Ethernet MAC). In the media access control component 4, there is provided a device 21 implemented as hardware for imple menting AVB, which serves to provide data packets received from the communication node 16 or to be sent by the com munication node 16 to one of the other schematically shown communication nodes 16 with a respective timestamp. This functionality is referred to as PTP-only timestamping. The other functionalities of IEEE 802.1AS (gptp) are imple mented in Software, which is also executed on the media access control component 4. They are for example function alities for implementing a measurement of propagation delays and/or a transmission of information for time synchro nization and/or choosing one of the communication nodes of the data network as a master node In addition, there is provided, in the media access control component 4, a queue management unit 20 (traffic shaping), which delays or rejects data packets to be sent from the communication node 16 to one of the other communica tion nodes 16 based on specific criteria, in order to meet given requirement profiles. A frequently used algorithm is the leaky bucket algorithm The media access control component 4 is generally a component that carries out the MAC (medium access con troller) Sub-layer of layer 2. The media access component 4 is typically designed as a part of the integrated circuit 2 and connected, by way of an internal system bus (not shown), with other components of the integrated circuit for exchanging data. In the case of a CPU, the media access control compo nent 4 is frequently formed on an expansion card (e.g. a PCI card) The media access control component 4 is connected to the physical interface 6 via the first internal interface 8 (MII). The physical interface 6 is also often referred to as a PHYceiver, which is a component that operates on the physi cal layer. For instance, the interface implements 1000Base-T. 100Base-T, etc The first internal interface 8 is a standardized inter face, which is connected to the physical interface 6 for con nection with the media access control component 4. In prac tice, various variants are used, such as for example RGMII (Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface) and SGMII (Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface) When the present description refers to Ethernet, it is the physical layer that is referred to. The transmission can be carried out via a coaxial cable, a twisted pair cable or an optical fiber cable. The speeds can vary between 10 Mb/s and 100 Gb/s. The Ethernet protocol stack operates in a similar fashion as other physical layers and is defined in the OSI layer model (ISO/IEC ). 0044) The EAVB Bridge 14 connects a plurality of com munication nodes 16. The EAVB bridge 14 operates in a similar fashion as known Ethernet switches. In addition, the EAVB bridge 14 supports additional AVB features, such as for example PTP queue processing (traffic shaping) and stream reservation Each of the communication nodes 16 can act as an AVB talker or AVB listener within the data network. As described, the integrated circuit 2 and the physical interface 6 are designed as an embedded system An AVB communication node 16 as described in FIG. 1 additionally comprises an AVB software stack, which is schematically shown in FIG. 2. The reference number 23 refers to an application. In the context of AVB, the application 23 is a streaming application, either as talker or as listener. The reference number 33 indicates an Ethernet driver accord ing to the IEEE 802 standard. The driver 33 constitutes a driver of the media access control component 4. It typically writes Ethernet data packets from the TCP/IP stack 31 into a memory of the media access control component 4 and vice versa. In the case of an AVB protocol, the driver 33 is directly addressed, since all AVB protocols are executed on layer The reference number 25 ( IEE 1722 Transport') refers to a component, which is disposed in the integrated circuit 2, typically outside of the media access control group
9 US 2016/ A1 Mar. 24, , and which is responsible for integrating the transport layer implemented according to IEEE 1722 into the provided sys tem architecture. For example, the component can be an ALSA Sound driver that Supports playback and recording on the Linux operating system The reference number 27 ( IEEE 802.1AS) refers to a software component that is responsible for implementing a measurement of propagation delays, for transmitting infor mation for time synchronization and for choosing a commu nication node of the data network as a master node. This Software component is typically disposed in the integrated circuit 2 and outside of the media access control component The reference number 29 ( IEEE 802.1Qat ) refers to a stream registration protocol that utilizes three different signaling protocols, MMRP, MVRP and MSRP to establish stream reservations in the data network having an EAVB bridge. The software component 29, which does not have any real-time requirements, is typically disposed in the integrated circuit 2 and outside of the media access control component 4. MSRP (Multiple Stream Registration Protocol) is a signaling protocol that allows end nodes to reserve resources of the data network, thus providing quality of service (QoS) when trans mitting and receiving data streams across the entire data network The reference number 31 ( TCP/IO) refers to a set of TCP/IP protocols, which can be for example IP, ARP, ICMP, UDP, TCP, IGMP protocols. The TCP/IP stack is usu ally reserved for the operating system. Like the driver 33, it is disposed, from the standpoint of the OSI layer model, above the media access control component 4 in the integrated circuit By using the variants described in the following exemplary embodiments according to FIGS. 3 and 4, the integrated circuit 2 (SoC) can be freed of all real-time require ments introduced by AVB. As opposed to the other commu nication nodes 16, the reference number 10 refers to a com munication node designed according to the invention (EAVB node). To this end, according to the invention, the real-time clock synchronization unit 21 together with the associated software-controlled functionality (reference number 27 in FIG. 2) and the queue management unit 20 are completely disposed in the physical interface 6. This makes it possible to integrate AVB in the communication node without having to modify the integrated circuit 2. Thereby, backward compat ibility with non-avb-conform communication nodes can be implemented. One advantage thereof is that there are less interrupt requests sent by AVB to the integrated circuit 2. During the execution of AVB applications, the integrated circuit 2 is also considerably less burdened since PTP time synchronization and queue management is handled by the physical interface 6. The same also applies to the handling of data packets in accordance with the IEEE 1722 standard, provided the corresponding functionality is also optionally provided in the physical interface It goes without saying that the corresponding AVB software functionalities can be removed from the software stack of the integrated circuit 2 shown in FIG. 2. This applies particularly to the software components labeled with the ref erence numbers 25, 27 and 29 in FIG.2. It is also clear that the hardware components labeled with the reference numbers 20 and 21 in FIG. 1 are also no longer included in the integrated circuit 2. In accordance with the invention, the integrated circuit 2 shown in FIG. 2 does not support any AVB feature, i.e. neither queue management nor timestamping of data packets. As described, these functionalities are directly implemented in the physical interface The real-time clock synchronization unit 18 designed according to the invention and located inside the physical interface 6 is responsible for time synchronization with the other communication nodes 16. The other commu nication nodes 16 may be designed according to the invention or in the conventional manner. Synchronization takes place in accordance with the IEEE AS standard in the following manner: one of the communication nodes 10, 16, serving as a grandmaster node, sends information that comprises a syn chronized time to all other communication nodes 10, 16 of the data network. Each of these (AVB) communication nodes must correct the time received from the grandmaster node by taking into account a propagation time taken by the data packet received from the grandmaster node to arrive at the communication node. Determining this propagation time requires a forwarding delay and a transmission time. The forwarding delay is the time required by the EAVB bridge 14 for processing the data packet in question. The EAVB bridges 14 can determine this time (also called residence time) them selves The real-time clock synchronization unit 18 is responsible for determining the propagation delay. A corre sponding result is stored in a register (not shown) of the physical interface 6. The integrated circuit 10 or one of its components can read this time for further processing through a read access to the register of the physical interface 6 via the first interface 8. For example MDIO, i.e. a specific interface referred to as PHY Management Interface, can be used as part of the MII to this end. Integrating the timestamp in a PTP message is carried out directly by the real-time clock syn chronization unit 18. The real-time clock synchronization unit 18 additionally has a register for a local time, which is synchronized with the grandmaster clock With a predetermined piece of information stored in another register of the physical interface 6, the real-time clock synchronization unit 18 can be configured as a master or as a slave All PTP messages are transmitted to the media access control component 4. This is necessary for example to execute algorithms that are not real-time sensitive If, as shown in the exemplary embodiments accord ing to FIGS. 3 and 4, the device 35 for encoding and/or decoding audio and/or video data according to IEEE 1722 is provided, the communication node 10 has a second internal interface 37 available for transmitting serial audio data. For example, the interface can be IS. An advantage of this approach is that, in this case, encoding and decoding audio data can be carried out directly in the physical interface 6 and the integrated circuit 2 is relieved of the corresponding pro cessing load. In addition, since transmission of the audio data is carried out via the second interface 37, which, in the case of the integrated circuit 2, is connected to a soundcard contained therein, the first interface 8 provides a high bandwidth for transmitting a payload The first interface 8 (MII) provided in a communi cation node 10 according to the invention includes all current and possible variants as well as future developments, such as for example Reduced Media Independent Interface, Gigabit Media Independent Interface, Reduced Gigabit Media Inde pendent Interface, Serial Gigabit Media Independent Inter face, 10 Gigabit Media Independent Interface. XAUI, GBIC, SFP, SFF, XFP and XFI.
10 US 2016/ A1 Mar. 24, The exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 4 differs from the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 3 in that the physical interface 6 is also integrated in the integrated circuit 2. There are no functional differences Queue management of data packets according to IEEE 1722, i.e. of audio and/or video data to be transmitted by the device 35 for encoding and/or decoding, as well as data packets received by the media access control component 4 via the first interface 8, is carried out by the queue management unit 20, in order to fulfill specific requirements profiles for the data stream. The queue management unit 20 also has one or several registers for configuring the queue flow. The queue management unit 20 is preferably implemented in hardware. LIST OF REFERENCE NUMBERS integrated circuit (system on a chip (SoC)) 0062) 4 media access control component (Ethernet MAC) physical interface (Ethernet PHY.) first interface (MII Media Independent Inter face) communication node (EAVB node) Ethernet line EAVB-bridge (Ethernet AVB bridge) other communication nodes (EAVB node) real-time clock synchronization unit queue management unit (traffic shaping) real-time synchronization unit with limited func tionality Application IEEE IEEE 802.1AS IEEE 802.1Qat TCP/IP IEEE 802 Ethernet driver device for encoding and/or decoding audio and/ or video data (codec) 1. A communication node for a packet-switched data net work, which comprises an integrated circuit with a system of electronic components for sending and/or receiving audio and/or video data, particularly of an audio and/or video data stream, wherein at least a media access control component for implementing a media access control and a physical interface with transmitting and receiving means, by way of which the communication node is connectable to a communication line of the data network, are provided as components of the sys tem, wherein the media access control component is con nected via an internal first interface to the physical interface for exchanging data, and wherein the system comprises a real-time clock synchronization unit for synchronizing time information with other communication nodes of the data net work as well as a queue management unit, characterized in that the real time clock synchronization unit and the queue management unit are fully arranged in the physical inter face. 2. The communication node according to claim 1, charac terized in that the media access control component does not have any functionality of the real time clock synchronization unit and of the queue management unit. 3. The communication node according to claim 1, charac terized in that the real time clock synchronization unit is based on the standard AS and has implemented all of its functionalities. 4. Communication node according to claim 3, character ized in that a first part of the functionality of the real time clock synchronization unit is carried out as hardware, by which time synchronization with other communication nodes of the data network is, particularly autonomously, operable. 5. The communication node according to claim 3, charac terized in that a second part of the functionality of the real time clock synchronization unit is carried out as Software for implementing a measurement of propagation delays and/or the transmission of information for time synchronization and/ or choosing one of the communication nodes of the data network as a master node. 6. The communication node according to claim 1, charac terized in that the real-time clock synchronization unit com prises at least one register, in which a single or several pieces of time information determined by the real-time clock syn chronization unit are stored during operation of the commu nication node, wherein the at least one register is readable via the first interface by the media access control component and/or by another component of the system. 7. The communication node according to claim 1, charac terized in that, the first interface is the Media Independent Interface (MII). 8. The communication node according to claim 1, charac terized in that the real-time clock synchronization unit is configurable as master node or as slave node by storing a predetermined piece of information in a predetermined reg ister during operation of the communication node, the infor mation being readable by the media access control compo nent and/or by another component of the system via the first interface. 9. The communication node according to claim 1, charac terized in that the physical interface comprises a device for encoding and/or decoding audio data, particularly according to the specification IEEE 1722 Transport. 10. The communication node according to claim 9, char acterized in that the device for encoding and/or decoding audio data is coupled via a second interface with the system or with an external audio component for directly exchanging data. 11. The communication node according to claim 10, char acterized in that the second interface is a serial audio inter face, particularly IS. 12. The communication node according to claim 1, char acterized in that the queue management unit is configured to execute the leaky bucket algorithm. 13. A method for operating a communication node for a packet-switched data network, wherein the communication node is adapted according to claim 1, in which only the real time clock synchronization unit arranged in the physical interface carries out a particularly autono mous time synchronization process with other commu nication nodes of the data network as well as a measure ment of propagation delays and/or transmission of information for time synchronization and/or choosing one of the communication nodes of the data network as a master node. 14. The method according to claim 13, wherein the queue management unit outputs data packets, which are received from the first and second interface by the system, or option ally by the external audio component, according to specific criteria, to the communication line of the data network for transmission.
11 US 2016/ A1 Mar. 24, The method according to claim 13, wherein the real time clock synchronization unit stores one or several pieces of time information in a register or a respective register, in order to provide the one or several pieces of information, for pro cessing, to the media access control component and/or to the one other component of the system, by a read access to the register(s), via the first interface. 16. The method according to claim 13, wherein the real time synchronization unit writes a predetermined piece of information into a predetermined register, wherein the prede termined piece of information indicates whether the commu nication node is configured as a master node or as a slave node, wherein the predetermined register is readable, by a read access, by the media access control component and/or another component of the system, via the first interface. k k k k k
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000
 USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,377,725 B1
 USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O191242A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191242 A1 Sommer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FAILURE DETERMINATION IN AN OPTICAL COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75)
(19) United States US 2002O191242A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191242 A1 Sommer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FAILURE DETERMINATION IN AN OPTICAL COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0331698 A1 DETZE et al. US 20150331 698A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FOR LOADING AN APPLICATION CONSISTING OF
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0331698 A1 DETZE et al. US 20150331 698A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FOR LOADING AN APPLICATION CONSISTING OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
W15. Keung Wong, Hong Kong (HK) (21) Appl. No.: 09/875,350. (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong, Hong Kong (HK); Hoi (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0049262A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0049262 A1 Lehtonen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) HANDS-FREE FUNCTION (76) Inventor: Arto Lehtonen, Tampere
(19) United States US 2001.0049262A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0049262 A1 Lehtonen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) HANDS-FREE FUNCTION (76) Inventor: Arto Lehtonen, Tampere
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060098613A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0098613 A1 Kish et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMPROVED DATA THROUGHPUT IN COMMUNICATIONS
(19) United States US 20060098613A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0098613 A1 Kish et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMPROVED DATA THROUGHPUT IN COMMUNICATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004.0156360A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0156360A1 Sexton et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 12, 2004 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PRIORITIZING DATA TRANSFERRED
(19) United States US 2004.0156360A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0156360A1 Sexton et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 12, 2004 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PRIORITIZING DATA TRANSFERRED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090292854A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0292854 A1 KHOO (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 26, 2009 (54) USE OF BOND OPTION TO ALTERNATE BETWEEN PC CONFIGURATION
(19) United States US 20090292854A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0292854 A1 KHOO (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 26, 2009 (54) USE OF BOND OPTION TO ALTERNATE BETWEEN PC CONFIGURATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
III III IIII. United States Patent (19) 5,546,397. Mahany. Aug. 13, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Mahany (54) HIGH RELIABILITY ACCESS POINT FOR WIRELESS LOCAL AREANETWORK (75) Inventor: Ronald L. Mahany, Cedar Rapids, Iowa 73) Assignee: Norand Corporation, Cedar Rapids, Iowa
United States Patent (19) Mahany (54) HIGH RELIABILITY ACCESS POINT FOR WIRELESS LOCAL AREANETWORK (75) Inventor: Ronald L. Mahany, Cedar Rapids, Iowa 73) Assignee: Norand Corporation, Cedar Rapids, Iowa
Wireless devices supports in a simple environment
 USOO8868690B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,868,690 B2 Tsao (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 21, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SUPPORT (52) U.S. Cl. (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63)
USOO8868690B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,868,690 B2 Tsao (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 21, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SUPPORT (52) U.S. Cl. (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63)
Gammalcode. Frame 1, Frame 2. drive signal. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Timing code.
 (19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
Storing metadata about each media item 10
 US 2007 O1987.46A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/019874.6 A1 Myllyla et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, COMPUTER Related U.S. Application Data PROGRAMS
US 2007 O1987.46A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/019874.6 A1 Myllyla et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, COMPUTER Related U.S. Application Data PROGRAMS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1. Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011
 US007991882B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1 Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011 (54) COMMUNICATIONS NETWORK WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS FLOW CONTROL (75) Inventor: Robert
US007991882B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1 Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011 (54) COMMUNICATIONS NETWORK WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS FLOW CONTROL (75) Inventor: Robert
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070276982A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0276982 A1 Denning (43) Pub. Date: (54) THIRD SWITCH FOR VXS/VMEBUS (57) COMPLIANT COMPUTING SYSTEM (76) Inventor:
US 20070276982A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0276982 A1 Denning (43) Pub. Date: (54) THIRD SWITCH FOR VXS/VMEBUS (57) COMPLIANT COMPUTING SYSTEM (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. streaming media server
 (19) United States US 201401 15115A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0115115 A1 Kuang (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PLAYING Publication Classification STREAMING
(19) United States US 201401 15115A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0115115 A1 Kuang (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PLAYING Publication Classification STREAMING
FL (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,856,601 B1. Bell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005
 USOO68566O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bell et al. () Date of Patent: Feb., 2005 (54) SHARED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (56) References Cited RESOURCES FOR COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES U.S.
USOO68566O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bell et al. () Date of Patent: Feb., 2005 (54) SHARED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (56) References Cited RESOURCES FOR COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 US0085319B2 (12) United States Patent Jiang et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Sep., 2013 (54) MESSAGE PROCESSING METHOD AND SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Xiyuan Jiang, Shanghai (CN); Shukun Wang, Beijing
US0085319B2 (12) United States Patent Jiang et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Sep., 2013 (54) MESSAGE PROCESSING METHOD AND SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Xiyuan Jiang, Shanghai (CN); Shukun Wang, Beijing
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,117,152 B1 Mukherji et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006
 United States Patent US007 117152B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,117,152 B1 Mukherji et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH 6,449,588 B1* 9/2002 Bowman-Amuah... TO3/21
United States Patent US007 117152B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,117,152 B1 Mukherji et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH 6,449,588 B1* 9/2002 Bowman-Amuah... TO3/21
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0165014 A1 Nainar et al. US 2016O165O14A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) INTER-DOMAIN SERVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0165014 A1 Nainar et al. US 2016O165O14A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) INTER-DOMAIN SERVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
... (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. icopying unit d:
 (19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,325,795 B2
 US009325795B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kim et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2016 (54) METHOD OF AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING (58) Field of Classification Search (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) ()
US009325795B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kim et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2016 (54) METHOD OF AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING (58) Field of Classification Search (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) ()
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Guan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2016
 (19) United States US 2016.0323427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0323427 A1 Guan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2016 (54) A DUAL-MACHINE HOT STANDBY G06F 9/455 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 2016.0323427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0323427 A1 Guan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2016 (54) A DUAL-MACHINE HOT STANDBY G06F 9/455 (2006.01)
(2GEUs) (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. (19) United States. Giampapa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul.
 (19) United States US 2008O177867A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0177867 A1 Giampapa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2008 (54) CONFIGURATION OF A MEMORY CONTROLLER IN A PARALLEL
(19) United States US 2008O177867A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0177867 A1 Giampapa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 24, 2008 (54) CONFIGURATION OF A MEMORY CONTROLLER IN A PARALLEL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Frequency. Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 (19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080180 107A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0180107 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CABLE TESTER FOR STAGE LIGHTING ENVIRONMENT (75) Inventors: Robin
(19) United States US 20080180 107A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0180107 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CABLE TESTER FOR STAGE LIGHTING ENVIRONMENT (75) Inventors: Robin
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
AUTONOMOUSAGENT TO /310
 (19) United States US 2006O143709A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0143709 A1 Brooks et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NETWORK INTRUSION PREVENTION (75) Inventors: Randall S. Brooks,
(19) United States US 2006O143709A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0143709 A1 Brooks et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) NETWORK INTRUSION PREVENTION (75) Inventors: Randall S. Brooks,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160372114A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0372114A1 Klose et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ANNOUNCEMENT SIGNALING ON BOARD H04W 68/00 (2006.01) AN AIRCRAFT
(19) United States US 20160372114A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0372114A1 Klose et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ANNOUNCEMENT SIGNALING ON BOARD H04W 68/00 (2006.01) AN AIRCRAFT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 (57) USPC /412. Initiate wireless Connection. Discover.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/ A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr.
 US 20140108499A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/0108499 A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) NOTIFICATION SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR (52) US. Cl. SENDING
US 20140108499A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/0108499 A1 Midtun (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 17, 2014 (54) NOTIFICATION SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR (52) US. Cl. SENDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0093144A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0093144 A1 GOODERMUTH et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR COMMUNICATING DATA IN A TRAIN HAVING
(19) United States US 2011 0093144A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0093144 A1 GOODERMUTH et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR COMMUNICATING DATA IN A TRAIN HAVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O232386A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0232386 A1 Dong (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR ALLOWING A UICC TO MANAGE THE POPCONTEXT PARAMETHERS (76)
(19) United States US 2010O232386A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0232386 A1 Dong (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD FOR ALLOWING A UICC TO MANAGE THE POPCONTEXT PARAMETHERS (76)
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 Kurabayashi (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 US 20140237108A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0237108 A1 Kurabayashi (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2014 (54) CLOUD PROCESS MANAGEMENT (52) US. Cl. CPC..... H04L
US 20140237108A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0237108 A1 Kurabayashi (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2014 (54) CLOUD PROCESS MANAGEMENT (52) US. Cl. CPC..... H04L
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004.00399.96A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0039996 A1 Flam (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2004 (54) BIDIRECTIONAL NETWORK LANGUAGE SUPPORT (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2004.00399.96A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0039996 A1 Flam (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2004 (54) BIDIRECTIONAL NETWORK LANGUAGE SUPPORT (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090328030A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0328030 A1 Fries (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTALLING AMANAGEMENT AGENT (52) U.S. Cl.... T17/174 WITH AVIRTUAL
(19) United States US 20090328030A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0328030 A1 Fries (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTALLING AMANAGEMENT AGENT (52) U.S. Cl.... T17/174 WITH AVIRTUAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150277823A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0277823 A1 NAKAYAMA (43) Pub. Date: (54) PRINTERAPPARATUS, PRINTING METHOD, AND NON-TRANSTORY COMPUTER READABLE
(19) United States US 20150277823A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0277823 A1 NAKAYAMA (43) Pub. Date: (54) PRINTERAPPARATUS, PRINTING METHOD, AND NON-TRANSTORY COMPUTER READABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,751,708 Eng et al. 45) Date of Patent: May 12, 1998
 US005751708A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,751,708 Eng et al. 45) Date of Patent: May 12, 1998 54 ACCESS METHOD FOR BROADBAND AND 5,276,703 1/1994 Budin et al.... 370/347 NARROWBAND NETWORKS
US005751708A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,751,708 Eng et al. 45) Date of Patent: May 12, 1998 54 ACCESS METHOD FOR BROADBAND AND 5,276,703 1/1994 Budin et al.... 370/347 NARROWBAND NETWORKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0025825 A1 UKKOLA et al. US 2014.0025825A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND APPARATUS IN A WEB SERVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0025825 A1 UKKOLA et al. US 2014.0025825A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND APPARATUS IN A WEB SERVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. senior. A/ Media Source 145. CD Formot Media 161.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0162939 A1 Bennett et al. US 20070162939A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 12, 2007 (54) PARALLEL TELEVISION BASED VIDEO (76) (21) (22)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0162939 A1 Bennett et al. US 20070162939A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 12, 2007 (54) PARALLEL TELEVISION BASED VIDEO (76) (21) (22)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7844220B2 (12) United States Patent Wang (54) HEADSET, PORTABLE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, AND HEADSET CALLING METHOD (75) Inventor: Weizhong Wang, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: NEC Corporation (JP) (*) Notice:
USOO7844220B2 (12) United States Patent Wang (54) HEADSET, PORTABLE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, AND HEADSET CALLING METHOD (75) Inventor: Weizhong Wang, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: NEC Corporation (JP) (*) Notice:
(MASTER) (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States 05: INTERNAL BUS B #1 PROCESSOR
 (19) United States US 20120057518A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0057518 A1 HERRALA et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) BLUETOOTH NETWORKING (75) Inventors: Sami HERRALA, Oulu (FI);
(19) United States US 20120057518A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0057518 A1 HERRALA et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) BLUETOOTH NETWORKING (75) Inventors: Sami HERRALA, Oulu (FI);
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US00713 0584B2 () Patent No.: US 7,130,584 B2 Hirvonen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR IDENTIFYING 2002fO151327 A1*, 2002 Levitt... 455,556 AND PARING
(12) United States Patent US00713 0584B2 () Patent No.: US 7,130,584 B2 Hirvonen (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR IDENTIFYING 2002fO151327 A1*, 2002 Levitt... 455,556 AND PARING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,256,507 B1
 USOO6256507B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,256,507 B1 Lemieux (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK OTHER PUBLICATIONS SYNCHRONIZATION FOR DATASERVICES PCT
USOO6256507B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,256,507 B1 Lemieux (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 2001 (54) TELECOMMUNICATIONS NETWORK OTHER PUBLICATIONS SYNCHRONIZATION FOR DATASERVICES PCT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
US 20140O82324A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0082324 A1 Elhamias et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2014 (54) METHOD AND STORAGE DEVICE FOR (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0314065 A1 Song et al. US 2014031.4065A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 23, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (60) METHOD AND DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0314065 A1 Song et al. US 2014031.4065A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 23, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (60) METHOD AND DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009.01430 12A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143012 A1 JEON (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) BLUETOOTH-ENABLED MOBILE Publication Classification TERMINAL
US 2009.01430 12A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143012 A1 JEON (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) BLUETOOTH-ENABLED MOBILE Publication Classification TERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. Hall (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013
 (19) United States US 2013 0347009 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0347009 A1 Hall (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) API REDIRECTION FOR LIMITED (52) U.S. Cl. CAPABILITY
(19) United States US 2013 0347009 A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0347009 A1 Hall (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 26, 2013 (54) API REDIRECTION FOR LIMITED (52) U.S. Cl. CAPABILITY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100091772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/009 1772 A1 CederVallet al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2010 (54) PROVIDING IPTV MULTICASTS (76) Inventors: Mats
(19) United States US 20100091772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/009 1772 A1 CederVallet al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2010 (54) PROVIDING IPTV MULTICASTS (76) Inventors: Mats
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160374O14A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0374014 A1 ANYURU (43) Pub. Date: (54) SIM SELECTION (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant: TELEFONAKTIEBOLAGET LM
(19) United States US 20160374O14A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0374014 A1 ANYURU (43) Pub. Date: (54) SIM SELECTION (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant: TELEFONAKTIEBOLAGET LM
Feb. 5, 1997 JP Japan... so limiting the amount of time wasted in standby during
 USOO6O16490A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,016,490 Watanabe et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2000 54) DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM 5,893,912 4/1999 Freund et al.... 707/103 5,893.913
USOO6O16490A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,016,490 Watanabe et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2000 54) DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM 5,893,912 4/1999 Freund et al.... 707/103 5,893.913
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0083276 A1 Barsness et al. US 20090083276A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) INSERTING DATA INTO AN IN-MEMORY DISTRIBUTED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0083276 A1 Barsness et al. US 20090083276A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) INSERTING DATA INTO AN IN-MEMORY DISTRIBUTED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198313 A1 Kitamura et al. US 2006O198313A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198313 A1 Kitamura et al. US 2006O198313A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1
 USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2
 US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
with ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub. No.: US 2018 / A1 19 United States ( 54 ) INFERRING A NETWORK TOPOLOGY ( 52 ) U. S. CI.
 W OLTORIA DI UN AR WAT OLUNTATION US 20180115465A1 19 United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub. No.: US 2018 / 0115465 A1 FRAENKEL et al. ( 43 ) Pub. Date : Apr. 26, 2018 ( 54 ) INFERRING
W OLTORIA DI UN AR WAT OLUNTATION US 20180115465A1 19 United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub. No.: US 2018 / 0115465 A1 FRAENKEL et al. ( 43 ) Pub. Date : Apr. 26, 2018 ( 54 ) INFERRING
- NETWORK / SES A REMOTE
 (19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
