(12) United States Patent
|
|
|
- Kristian George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
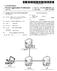
1 USOO B2 (12) United States Patent Cho et al. (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR PROVIDING DIGITAL SIGNATURE (71) Applicant: ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS RESEARCH INSTITUTE, Daejeon (KR) (72) Inventors: Young-Seob Cho, Daejeon (KR): Soo-Hyung Kim, Daejeon (KR): Jong-Hyouk Noh, Daejeon (KR); Sang-Rae Cho, Daejeon (KR): Jin-Man Cho, Daejeon (KR): Dae-Seon Choi, Daejeon (KR); Seung-Hyun Kim, Daejeon (KR); Seok-Hyun Kim, Daejeon (KR): Seung-Hun Jin, Daejeon (KR) (73) Assignee: ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS RESEARCH INSTITUTE, Daejeon (KR) (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 68 days. (21) Appl. No.: 14/617,187 (22) Filed: Feb. 9, 2015 (65) Prior Publication Data US 2015/ A1 Aug. 13, 2015 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Feb. 10, 2014 (KR) OO14991 (51) Int. Cl. H04L 29/06 ( ) H04L 9/32 ( ) H04L 9/08 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H04L 9/3247 ( ); H04L 9/0861 ( ); H04L 9/3263 ( ); H04L 2209/805 ( ) (10) Patent No.: US 9,509,516 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 2016 (58) Field of Classification Search CPC. H04L 9/3247; H04L 9/0861; H04L 9/3263; H04L 9/0822; H04L 63/0442; H04L 2009/805; HO4L 2463/062: HO4L 2463/041 IPC... HO4L 9/3247 See application file for complete search history. (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 7,028, 180 B1 * 4/2006 Aull... GO6F 21,335 T13,156 7,194,620 B1* 3/2007 Hayes... HO4L ,280 (Continued) FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS KR A 11/2003 KR A 10, 2011 (Continued) Primary Examiner Krisna Lim (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Rabin & Berdo, P.C. (57) ABSTRACT Disclosed are an apparatus and method for providing a digital signature. The apparatus includes a certificate unit, an input unit receives a selection input for a certificate related to signature content received from a signature-requesting terminal, and a control unit for determining whether the certificate unit is capable of performing a digital signature function corresponding to a selected certificate. If the cer tificate unit is capable of performing the digital signature function, the certificate unit creates a digital signature based on a private key corresponding to the selected certificate when the control unit commands the certificate unit to create a digital signature. Further, if the certificate unit is not capable of performing the digital signature function, the control unit creates a digital signature based on a private key corresponding to a certificate selected from the certificate unit. The control unit transmits the digital signature to the signature-requesting terminal. 20 Claims, 11 Drawing Sheets 100 s MOBILE TERMINAL 200 SIGNATURE-REQUESTING TERMINAL RECEIVE INPUT CONCERNTNG -S104 CONFIRMATION OF SIGNATURE CONTENT CHECK CERTIEA6NuNT S105 RECEIVENPUT CONCERNING SELECTION--S107 OF CERTIFICATE S101-- CREATESIGNATURE CONTENT SIGNATURE CONTENTS103) RECEIVE PASSWORD -S109 ERTIFICAT S111 UNIT CAPASLE OF DIGITAL SIGNATURES113) PERFORMINGDIGITAL SIGNATURE YES UNCTION NC) CREATE DIGITAL Sid S115 DIGITALSIGNATURES117)
2 US 9,509,516 B2 Page 2 (56) 7,240,366 8,291,231 8, /O /02O / / , References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 7/ , , , , , , , 2010 T/2010 Buch... HO4L 29, ,225 Ueno et al. Moore... HO4L 9, O,277 Brown... HO4L 63, Dillaway... HO4L , 176 Lee et al. Kim... HO4L 63, , 176 Grebovich... HO4L 9,321 T13,156 Gerdes, Jr.... HO4L 9, , /O A1* 12, fO A1 2014/OOO6788 A1* 6, , / A1* 9, , A1* 12/2014 Mouille... G06F 21, , 176 Park et al. Ignatchenko... HO4L 63, , 175 Li... HO4L ,246 Agarwal... HO4L 9, , 176 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS KR A KR A KR A KR A WO WO A1 * cited by examiner 12/2011 T /2013 8, , 2009
3 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet 1 of 11 US 9,509,516 B2 3OO - Y - 100
4 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet 2 of 11 US 9,509,516 B2 DISPLAY UNIT CONTROL UNIT SHORT-RANGE COMMUNICATION UNIT EXTERNAL COMMUNICATION UNIT 120 CERTIFICATE UNIT FIG. 2
5 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet 3 of 11 US 9,509,516 B2 1OO 2OO MOBILE TERMINAL SIGNATURE-REQUESTING TERMINAL RECEIVE INPUT CONCERNING CONFIRMATION OF SIGNATURE CONTENT SIGNATURE CONTENT(S103) CREATE SIGNATURE CONTENT CHECK CERTIFICATION UNIT RECEIVE INPUT CONCERNING SELECTION OF CERTIFICATE RECEIVE PASSWORD CERTIFICATE UNIT CAPABLE OF PERFORMING DIGITAL SIGNATURE FUNCTION? DIGITAL SIGNATURE(S113) NO CREATE DIGITAL SIGNATURE DIGITAL SIGNATURE(S117) FIG. 3
6 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet 4 of 11 US 9,509,516 B2 200 APPLY FOR SMART MEMBERSHIP DIGITAL SIGNATURE MESSAGE IS SENDING FIG. 4
7 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet S of 11 US 9,509,516 B2 Touch Sign REQUESTING COMPANY COMPANY NAME SIGNATURE PURPOSE APPLY FOR MEMBERSHIP WITH CARD SIGNATURE CONTENT PERSONAL INFORMATION, AGREEMENT, ETC. VIEW THE ORIGINAL TEXT CONFIRM CANCEL FIG. 5
8 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet 6 of 11 US 9,509,516 B2 Touch Sign SELECT CERTIFICATE FINANCE/HONG CARD GIL-DONG/ SD STOCK/ HONG GIL-DONG/ SELECT YOUR CERTIFICATE TO BE USED CERTIFICATE OF 'HONG GIL-DONG IS USED PLEASE ENTER YOUR CERTIFICATE PASSWORD CONFIRM CANCEL FIG. 6
9 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet 7 of 11 US 9,509,516 B2 Touch Sign DIGITAL SIGNATURE CREATION CERTIFICATE CARD PLEASE TOUCH 'HONG GIL-DONG'S CERTIFICATE CARD FIG. 7
10 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet 8 of 11 US 9,509,516 B SIGNATURE MOBILE TERMINAL SERVER REQUESTING TERMINAL S2O1 RECEIVE TERMINAL INFORMATION RECEIVE INPUT CONCERNING CONFIRMATION OF SIGNATURE CONTENT SESSION INFORMATION (S205) REQUEST SIGNATURE CONTENT(S2O6 ) SIGNATURE CONTENT(S207) CREATE SIGNATURE S2O3 CONTENT SIGNATURE CONTENT AND TERMINAL INFORMATION(S204) CHECK CERTIFICATE UNIT RECEIVE CERTIFICATE SELECTION INPUT RECEIVE PASSWORD CERTIFICATE UNIT CAPABLE OF PERFORMING DIGITAL SIGNATURE FUNCTION? S217 DIGITAL SIGNATURE(S219) NO CREATE DIGITAL SIGNATURE DIGITAL SIGNATURE(S223) DIGITAL SIGNATURE(S225) FIG. 8
11 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet 9 of 11 US 9,509,516 B2 SMART PAD DESCRIPTION MOBILE PHONE NUMBER 010- * * *- : * * DIGITAL SIGNATURE REQUEST FIG. 9
12 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet 10 of 11 US 9,509,516 B2 TOUCH SIGN WAITING FOR TOUCH SIGN 3 O :::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::: C A N C E L SECONDS WAITING FOR TOUCH SIGN FIG 10
13 U.S. Patent Nov. 29, 2016 Sheet 11 of 11 US 9,509,516 B2 Touch Sign PLEASE CHECK NUMBERS DISPLAYED ON SMART PAD, AND THEN ENTER THE REMAINING NUMBERS ANTI-PHISHING SECURITY CODE 3 A X 9 FIG. 11
14 1. APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR PROVIDING DIGITAL SIGNATURE CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION This application claims the benefit of Korean Patent Application No filed Feb. 10, 2014, which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety into this application. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Technical Field The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for providing a digital signature. 2. Description of the Related Art When engaging in electronic commerce (e-commerce), digital (electronic) signature technology for electronically providing a personal signet using a certificate has been widely used in various fields Such as online banking and the cyber trading of stocks. A digital signature provides security and convenience in a large number of e-commerce activities by functioning as a user's signet for e-commerce, thus contributing to rapid activation of online e-commerce Ser vices. Further, certificates have become essential in real life to such an extent that most adults who engage in economic activities in a domestic area are assigned certificates and use the certificates. Such digital signature technology has been used in Such a way that a user accesses a server for providing an online service, creates a digital signature on a personal computer (PC) or a Smart terminal, and transfers signature content to the server through the PC or smart terminal. That is, existing digital signature technology is chiefly used in a situation in which a user is connected online to a service provider. However, recently, with the rapid popularization of smart terminals such as Smartphones or Smart pads, which provide an Internet access function and on which various applica tions can be freely installed and used by users, e-commerce services have been activated even in an offline environment in which a user and a service provider perform trading in a face-to-face manner. Therefore, an apparatus and method capable of providing a digital signature that may be intuitively and conveniently used by a user in an offline face-to-face trading environment are currently required. In connection with this, Korean Patent Application Pub lication No discloses a technology related to Cash Remittance Method Based on Digital Codes Using Hash Function and Electronic Signature'. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Accordingly, the present invention has been made keep ing in mind the above problems occurring in the prior art, and an object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus and method that are capable of providing a digital signature in an offline environment. An apparatus for providing a digital signature according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a certificate unit; an input unit for receiving a selection input for a certificate related to signature content received from a signature-requesting terminal; and a control unit for deter mining whether the certificate unit is capable of performing a digital signature function corresponding to a selected certificate, wherein, if it is determined that the certificate US 9,509,516 B unit is capable of performing the digital signature function, the certificate unit creates a digital signature based on a private key corresponding to the selected certificate when the control unit commands the certificate unit to create a digital signature, wherein, if it is determined that the cer tificate unit is not capable of performing the digital signature function, the control unit creates a digital signature based on a private key corresponding to a certificate selected from the certificate unit, and wherein the control unit transmits the digital signature to the signature-requesting terminal. The apparatus may further include a short-range commu nication unit, wherein when a touch with the signature requesting terminal is made, the control unit receives the signature content from the signature-requesting terminal through the short-range communication unit. When the certificate unit is located outside of the appa ratus, the short-range communication unit may receive the digital signature from the certificate unit when the certificate unit is touched. The short-range communication unit may be a Near-Field Communication (NFC) module. The apparatus may further include an external communi cation unit for receiving the signature content from the signature-requesting terminal through a server. The external communication unit may transmit the digital signature to the signature-requesting terminal. The signature content may be encrypted using an encryp tion key by the signature-requesting terminal and the encryption key may be generated based on a security code by the signature-requesting terminal; and the control unit may generate an encryption key based on the security code, and decrypt the signature content using the encryption key. The external communication unit may receive a partially hidden security code, together with the signature content, through the server, and the control unit may be configured to, when the input received through the input unit matches a hidden field of the security code, generate an encryption key based on the security code. The external communication unit may receive session information corresponding to the signature content received by the server, transmit a user identifier to the server in response to the session information, and receive signature content transmitted from the server when the user identifier matches a user identifier transmitted from the signature requesting terminal to the server. The user identifier may be user information that has been shared with the signature-requesting terminal in advance. Further, a method for providing a digital signature accord ing to an embodiment of the present invention includes receiving, by an input unit, a selection input for a certificate related to signature content received from a signature requesting terminal; determining, by a control unit, whether the certificate unit is capable of performing a digital signa ture function corresponding to a selected certificate; if it is determined that the certificate unit is capable of performing the digital signature function, creating, by the certificate unit, a digital signature based on a private key corresponding to the selected certificate when the control unit commands the certificate unit to create a digital signature; if it is determined that the certificate unit is not capable of per forming the digital signature function, creating, by the control unit, a digital signature based on a private key corresponding to a certificate selected from the certificate unit; and transmitting, by the control unit, the digital signa ture to the signature-requesting terminal. The method may further include, when a touch with the signature-requesting terminal is made, receiving the signa
15 3 ture content from the signature-requesting terminal through a short-range communication unit. The method may further include, when the certificate unit is located outside, receiving, by the short-range communi cation unit, the digital signature from the certificate unit when the certificate unit is touched. The short-range com munication unit may be a Near-Field Communication (NFC) module. The method may further include receiving, by an external communication unit, the signature content from the signa ture-requesting terminal through a server. The method may further include transmitting, by the external communication unit, the digital signature to the signature-requesting terminal. The signature content may be encrypted using an encryp tion key by the signature-requesting terminal, and the encryption key may be generated based on a security code by the signature-requesting terminal; and the method may further include generating, by the control unit, the encryp tion key based on the security code, and decrypting, by the control unit, the signature content using the encryption key. The method may further include receiving, by the external communication unit, a partially hidden security code, together with the signature content, through the server; and generating, by the control unit, an encryption key based on the security code when the input received through the input unit matches a hidden field of the security code. Receiving, by the external communication unit, the sig nature content from the signature-requesting terminal through the server may include receiving, by the external communication unit, session information corresponding to the signature content received by the server; transmitting, by the external communication unit, a user identifier to the server in response to the session information; and receiving, by the external communication unit, signature content trans mitted from the server when the user identifier matches a user identifier transmitted from the signature-requesting terminal to the server. The user identifier may be user information that has been shared with the signature-requesting terminal in advance. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The above and other objects, features and advantages of the present invention will be more clearly understood from the following detailed description taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, in which: FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a system for providing a digital signature according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing an apparatus for providing a digital signature according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing a method for providing a digital signature according to a first embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an example in which a signature-requesting terminal transmits signature content to a mobile terminal according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 5 is a diagram showing an example in which the mobile terminal receives an input concerning the confirma tion of signature content according to an embodiment of the present invention; US 9,509,516 B FIG. 6 is a diagram showing an example in which the mobile terminal receives an input concerning the selection of a certificate according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 7 is a diagram showing a state in which a certificate card for digital signature touches the mobile terminal according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing a method for providing a digital signature according to a second embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 9 is a diagram showing an example in which the signature-requesting terminal receives mobile terminal information according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 10 is a diagram showing a screen on which a security code to be transmitted to the mobile terminal is created according to an embodiment of the present invention; and FIG. 11 is a diagram showing an example in which the mobile terminal receives an input corresponding to a hidden field of a security card according to an embodiment of the present invention. DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Embodiments of the present invention are described with reference to the accompanying drawings in order to describe the present invention in detail so that those having ordinary knowledge in the technical field to which the present inven tion pertains can easily practice the present invention. How ever, the present invention may be implemented in various forms and is not limited by the following embodiments. In the drawings, the illustration of components that are not directly related to the present invention will be omitted for clear description of the present invention. Further, the same reference numerals are used to designate the same or similar elements throughout the drawings. Throughout the entire specification and claims, it should be understood that a representation indicating that a certain part includes a component means that other components, not described, may be further included, without excluding a possibility that one or more other components will be added, unless a description to the contrary is specifically pointed out in context. Further, throughout the entire specification, it should be understood that a representation indicating that a first com ponent is connected to a second component may include the case where the first component is electrically connected to the second component with some other component inter posed therebetween, as well as the case where the first component is directly connected to the second component. Hereinafter, an apparatus and method for providing a digital signature according to embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the attached drawings. In the following description, individual communication units of a mobile terminal transmit and receive data and information, but the present invention is not limited to such a structure. That is, a control unit may transmit and receive data and information through each communication unit. First, a digital signature provision system according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 1. FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a digital signature provision system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
16 5 The digital signature provision system according to the embodiment of the present invention includes a mobile terminal 100, a signature-requesting terminal 200, and a Server 300. The mobile terminal 100 of the present invention may include a mobile phone, a Smartphone, a notebook computer (laptop computer), a digital broadcasting terminal, a Per sonal Digital Assistant (PDA), a Portable Multimedia Player (PMP), a navigation terminal, etc. However, those skilled in the art will appreciate that the configuration according to the embodiment described in the present specification may also be applied to fixed terminals, such as a digital TV or a desktop computer, with the exception of cases that may be applied only to the mobile terminal 100. The signature-requesting terminal 200 according to the embodiment of the present invention transmits signature content to the mobile terminal 100, and receives a digital signature from the mobile terminal 100. Further, the signa ture-requesting terminal 200 transmits the signature content and terminal information to the server 300. The server 300 receives the signature content and the terminal information from the signature-requesting terminal 200. Further, the server 300 receives a digital signature from the mobile terminal 100, and transmits the digital signature to the signature-requesting terminal 200. Below, individual components of a digital signature pro vision apparatus will be described in detail with reference to FIG 2. FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a digital signature provision apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. In the present specification, the digital signature provision apparatus may be a mobile terminal 100. Therefore, a description will be made on the assumption that the digital signature provision apparatus is the mobile terminal 100. The mobile terminal 100 according to the embodiment of the present invention includes a control unit 110, a certificate unit 120, an external communication unit 130, a short-range communication unit 140, an input unit 150, and a display unit 160. However, since the components shown in FIG. 1 are not always essential, the mobile terminal 100 may be implemented using more components or fewer components than those of FIG. 1. The control unit 110 controls the overall operation of the mobile terminal 100. The control unit 110 may create a digital signature based on a private key. The certificate unit 120 includes one or more certificates. Further, the certificate unit 120 may create digital signatures based on private keys corresponding to the certificates. In FIG. 2, the mobile terminal 100 includes the certificate unit 120, but the present invention may also be applied to a case where a separate certificate unit 120 is located outside of the mobile terminal 100. The certificate unit 120 according to the embodiment of the present invention may include an Integrated Circuit (IC) card-type certificate card that enables non-contact short range wireless communication and a certificate Secure Ele ment (SE) that can be embedded in a smart phone. A certificate SE may be a Universal Integrated Circuit Card (UICC) managed by a mobile communication company, or a Secure Digital (SD) card that can be inserted into and used in an SD slot. Further, the certificate unit 120 may have a digital signature function for creating digital signatures corresponding to respective certificates. Furthermore, the certificate unit 120 may store private keys corresponding to the certificates. Also, when the certificate unit 120 does not US 9,509,516 B have a digital signature function, private keys corresponding to certificates may be stored in the certificate unit 120. The external communication unit 130 receives signature content from the server 300. Further, the external commu nication unit 130 transmits a digital signature to the server 3OO. The external communication unit 130 may transmit and receive wireless signals to and from at least one of a base station, an external terminal, and the server over a mobile communication network. The wireless signals may include a Voice call signal, a video call signal, or various types of data based on the sending/receiving of text/multimedia messages. The external communication unit 130 may include a communication module that uses Wireless Local Area Net work (WLAN)(Wi-Fi), Wireless broadband (Wilbro), World Interoperability for Microwave Access (Wimax), or High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA). The short-range communication unit 140 denotes a mod ule for short-range communication. Here, Bluetooth, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), infrared communication (IrDA: infrared Data Association), Ultra Wideband (UWB), ZigBee, Near-Field Communication (NFC), or the like may be used as short-range communication technology. The short-range communication unit 140 according to an embodiment of the present invention may be an NFC module. The short-range communication unit 140 may receive signature content from the signature-requesting ter minal 200. Further, the short-range communication unit 140 may transmit a digital signature to the signature-requesting terminal 200. The input unit 150 generates input data allowing a user to control the operation of the mobile terminal 100. The input unit 150 may be implemented using a keypad dome Switch, a touch pad (resistive/capacitive type), a jog wheel, a jog switch, or the like. The display unit 160 displays (outputs) information pro cessed by the mobile terminal 100. For example, when the mobile terminal 100 is in a call mode, the display unit 160 displays a User Interface (UI) or a Graphical User Interface (GUI) related to a call. When the mobile terminal 100 is in a video call mode or a capturing mode, captured and/or received images are displayed or, alternatively, a related UI or GUI is displayed. The display unit 160 may include at least one of a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), a Thin Film Transistor LCD (TFT LCD), an Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED), a flexible display, and a three-dimensional (3D) display. Among the displays, some displays may be implemented in a transparent or light-transmissive type so that the outside of the display may be viewed through the display. This may be referred to as a transparent display, and a representative example of the transparent display includes a Transparent OLED (TOLED) or the like. The rear structure of the display unit 160 may also be implemented in a light-transmissive structure. By means of this structure, the user may view an object located behind a terminal body through an area occupied by the display unit 160 of a terminal body. When the display unit 160 and a sensor for sensing a touch action (hereinafter referred to as a touch sensor) form a mutual layered structure (hereinafter referred to as a touch screen), the display unit 160 may also be used as an input device as well as an output device. The touch sensor may have the form of for example, a touch film, a touch sheet, a touch pad, etc. The touch sensor may be configured to convert a change in pressure applied to a specific region of the display unit 160 or a change in capacitance or the like occurring in a
17 7 specific region of the display unit 160 into an electrical input signal. The touch sensor may be configured to detect even pressure applied upon making a touch, as well as a touched location and area. When a touch input to the touch sensor is present, a signal(s) corresponding to the touch input is sent to a touch controller. The touch controller processes the signal(s) and transmits data corresponding thereto to the control unit 110. In this way, the control unit 110 may recognize which region of the display unit 160 has been touched. Below, a method for providing a digital signature accord ing to a first embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. 3 to 7. FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing a digital signature provision method according to a first embodiment of the present invention. The signature-requesting terminal 200 creates signature content at step S101. The signature-requesting terminal 200 transmits the sig nature content to the short-range communication unit 140 of the mobile terminal 100 at step S103. The transmission of the signature content may be performed by a physical touch between the signature-requesting terminal 200 and the mobile terminal 100. When the signature-requesting termi nal 200 touches the mobile terminal 100, the mobile terminal 100 receives the signature content from the signature-re questing terminal 200 through an NFC module. FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an example in which the signature-requesting terminal transmits signature content to the mobile terminal according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 4, upon transmitting signature content to the mobile terminal 100, the signature-requesting terminal 200 may display the content of a signature request on a screen. The signature content according to an embodiment of the present invention may include information about a company requesting a digital signature, or the purpose of a signature. The input unit of the mobile terminal 100 receives an input concerning the confirmation of signature content at step S104. FIG. 5 is a diagram showing an example in which the mobile terminal receives an input concerning the confirma tion of signature content according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 5, a user confirms signature content displayed on the display unit 160 and then makes an input concerning the confirmation of signature content through the input unit 150. The control unit 110 checks the certificate unit 120 at step S105. By means of this procedure, the type of certificate unit 120 may be checked by the control unit 110. Further, when the certificate unit 120 is a UICC or SD card, it is embedded in the mobile terminal 100, so that the control unit 110 may check the certificate unit without requiring a separate user input. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, when the certificate unit 120 is located outside of the mobile terminal 100, the control unit 110 connects the mobile terminal 100 to the certificate unit 120 by checking the certificate unit 120. The input unit 150 receives an input concerning the selection of a certificate from among a plurality of certifi cates stored in the certificate unit 120 at step S107. The input unit 150 may also receive a selection input for a certificate related to the signature content. US 9,509,516 B FIG. 6 is a diagram showing an example in which the mobile terminal receives an input concerning the selection of a certificate according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 6, the certificate unit 120 may store one or more certificates. The display unit 160 displays one or more certificates stored in the certificate unit 120. The user selects one from among the displayed certificates and makes an input concerning the selection of the certificate. The input of the user concerning the selection of the certificate is received through the input unit 150. The input unit 150 receives a password for the selected certificate as the input concerning the selection of the certificate at step S109. Thereafter, the control unit 110 determines whether the certificate unit 120 is capable of performing a digital sig nature function corresponding to the selected certificate at step S111. If it is determined that the certificate unit 120 is capable of performing the digital signature function corre sponding to the selected certificate, the control unit 110 commands the certificate unit 120 to create a digital signa ture. The certificate unit 120 creates a digital signature based on a private key corresponding to the selected certificate in compliance with the command of the control unit 110. The short-range communication unit 140 transmits the digital signature created in accordance with the selected certificate by the certificate unit 120 to the signature-request ing terminal 200 at step S113. If it is determined that the certificate unit 120 is not capable of performing the digital signature function corre sponding to the selected certificate, the control unit 110 creates a digital signature based on a private key correspond ing to the certificate selected from the certificate unit 120 at step S115. In this case, the control unit 110 may inquire whether a private key corresponding to the certificate selected from the certificate unit 120 is stored. The short-range communication unit 140 transmits the digital signature created by the control unit 110 to the signature-requesting terminal 200 at step S117. FIG. 7 is a diagram showing a state in which a certificate card for a digital signature touches a mobile terminal accord ing to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 7, in order for the mobile terminal 100 to acquire a digital signature from a certificate card located outside of the mobile terminal 100, the certificate card must touch the mobile terminal 100. Here, the mobile terminal 100 receives signature content or a private key from the certificate card through the short-range communication unit 140 or the NFC module. In this case, the certificate card may also include a short-range communication unit. In this regard, the certificate card may include an NFC module or an NFC antenna. While the control unit 110 creates a digital signature based on the private key of the certificate card, a touch between the certificate card and the mobile terminal 100 may need to be maintained in some cases. The short-range communication unit 140 transmits the digital signature created by the certificate unit 120 to the signature-requesting terminal 200 at step S117. Further, the short-range communication unit 140 may also transmit the digital signature created by the control unit 110 to the signature-requesting terminal 200. Below, a digital signature provision method according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. 8 to 11. FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing a digital signature provision method according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
18 The digital signature provision method according to the second embodiment of the present invention is identical to that of the first embodiment, except the following compo nents which will be described. In particular, FIG. 8 illustrates a method by which the mobile terminal 100 provides a digital signature when the mobile terminal 100 does not include an NFC module. The signature-requesting terminal 200 receives terminal information at step S201. The terminal information accord ing to an embodiment of the present invention may include the phone number of the mobile terminal 100. Further, the terminal information according to the embodiment of the present invention may also include the identification (ID) code of the mobile terminal 100, or the ID of the user of the mobile terminal 100 stored in the server 300. Furthermore, the terminal information may include information about the user of the mobile terminal 100. FIG. 9 is a diagram showing an example in which a signature-requesting terminal receives mobile terminal information according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 9, the signature-requesting terminal 200 may receive the phone number of the mobile terminal 100 through the display unit 160 or the input unit 150. The signature-requesting terminal 200 creates signature content at step S203. Here, the signature-requesting terminal 200 may create a security code. FIG. 10 is a diagram showing a screen on which a security code to be transmitted to the mobile terminal is created according to an embodiment of the present invention. The security code is composed of values of any character string that is randomly generated to prevent the server 300 from perceiving the signature content. For example, when a security code is implemented as an 8-digit code, the mobile terminal 100 that received the security code displays 8-digit information on the screen. However, the signature-request ing terminal 200 may process any 4 digits as hidden values by indicating the hidden values by asterisks (*) and transfer resulting 8-digit information to the server 300. That is, the signature-requesting terminal 200 transmits a partially hid den security code to the server 300. The signature-requesting terminal 200 generates an encryption key, required to encrypt the signature content, using a hash function. In this case, the signature-requesting terminal 200 may perform the encryption of signature content, the generation of an encryp tion key, or the creation of a security code using a separate application or program. The signature-requesting terminal 200 generates an encryption key based on the security code. For example, the signature-requesting terminal 200 may generate an encryp tion key using a security code (SHA256). The signature-requesting terminal 200 may encrypt the signature content using the encryption key and transfer the encrypted signature content to the server 300. Via the above processing, the signature content may be prevented from being leaked to the user of the server 300. The signature-requesting terminal 200 transmits the sig nature content and terminal information to the server 300 at step S204. The signature-requesting terminal 200 may trans mit the signature content to the server 300 over a network. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, the signature-requesting terminal 200 may transmit a secu rity code, together with the signature content. The security code at this time may be partially hidden. Further, the signature content at this time may be encrypted by the signature-requesting terminal 200. US 9,509,516 B The server 300 transmits session information to the exter nal communication unit 130 of the mobile terminal 100 at step S205. The server 300 may transmit the session infor mation to the external communication unit 130 of the mobile terminal 100 based on the received terminal information. The session information according to an embodiment of the present invention may include notification information indi cating that the server 300 has received the signature content. That is, the server 300 transmits the session information to the external communication unit 130 in response to the received signature content. In this case, the transmission of the session information by the server may be performed using a push method. The mobile terminal 100 that receives the session information may also execute an application related to the creation or transmission of a digital signature. Therefore, according to the embodiment of the present invention, the user of the mobile terminal 100 does not need to manually execute the application. Thereafter, the external communication unit 130 of the mobile terminal 100 requests signature content from the server 300. In this case, the external communication unit 130 of the mobile terminal 100 may request a security code, together with signature content, from the server 300. Fur ther, the external communication unit 130 of the mobile terminal 100 may transmit a user identifier to the server 300. The server 300 checks the user identifier and transmits the signature content to the external communication unit 130 of the mobile terminal 100 at step S207. Here, the server 300 may transmit a security code, together with the signature content, to the external communication unit 130 of the mobile terminal 100. The security code at this time may be partially hidden. The user identifier according to an embodi ment of the present invention may be information about the user of the mobile terminal 100 that has been shared in advance between the server 300 and the mobile terminal 100. Therefore, even if a terminal, the session information of which is intercepted by a malicious application, requests the transmission of signature content, the server 300 does not transmit signature content to a terminal which did not transmit a user identifier. That is, the server 300 according to the embodiment of the present invention transmits sig nature content only to the mobile terminal 100 of an autho rized user, that is, the mobile terminal 100, with which the server 300 has shared a user identifier in advance. Further, the signature content transmitted from the server 300 may be encrypted by the signature-requesting terminal 200. The server 300 determines whether the received user identifier is that of the user who has been previously registered in the server 300. If the user is the previously registered user, the server 300 checks whether the phone number of the mobile terminal 100 included in the terminal information transmitted from the signature-requesting ter minal 200 matches the phone number of the mobile terminal 100 that transmitted the corresponding user identifier, and thus it may be determined whether the user of the mobile terminal 100 that transmitted the user identifier is an autho rized user. The input unit 150 of the mobile terminal 100 receives an input concerning the confirmation of the signature content at step S209. The user confirms the signature content displayed on the display unit 160 and makes an input concerning the confir mation of the signature content through the input unit 150. In accordance with the embodiment of the present inven tion, before receiving an input concerning the confirmation
19 11 of the signature content, the input unit 150 of the mobile terminal 100 may receive an input corresponding to a hidden field of a security code. The display unit 160 displays a partially hidden security code received from the server 300 on the screen. Thereafter, the input unit 150 receives characters or numerals corre sponding to the hidden field of the security code. When an input corresponding to the hidden field of the security code received through the input unit 150 matches the content of the hidden field of the security code, the control unit 110 generates an encryption key. The control unit 110 decrypts the signature content using the generated encryption key. FIG. 11 is a diagram showing an example in which the mobile terminal receives an input corresponding to a hidden field of a security code according to an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 11, the control unit 110 requests the user to input characters or numerals corresponding to a hidden field of a security code. Such a request may be output via the display unit 160. A description will be made below on the assumption that the signature-requesting terminal 200 creates an 8-digit security code of 3A That is, the signature-request ing terminal 200 transmits a security code, part of which is hidden by asterisks (*), that is, a code of 3A**X9**, to the Server 300. The server 300 forwards the partially hidden security code to the mobile terminal 100. Thereafter, the input unit 150 receives characters or numerals corresponding to the hidden field of the security code. When input values corresponding to the hidden field of the security code received through the input unit 150 are sequentially 5, 2, 1, and 3, the control unit 110 generates an encryption key. The control unit 110 decrypts the signature content using the generated encryption key. A procedure after step S209 will be described below. The user confirms the signature content displayed on the display unit 160, and makes an input concerning the confirmation of the signature content through the input unit 150. The control unit 110 checks the certificate unit 120 at step S211. The control unit 110 may determine the type of certificate unit 120 through this procedure. When the certificate unit 120 is a UICC or SD card, it is embedded in the mobile terminal 100, and thus the control unit 110 may check the certification unit 120 without a separate user input. In accordance with an embodiment of the present inven tion, when the certificate unit 120 is located outside of the mobile terminal 100, the control unit 110 connects the mobile terminal 100 to the certificate unit 120 by checking the certificate unit 120. The input unit 150 receives an input concerning the selection of a certificate from among certificates Stored in the certificate unit 120 at step S213. The input unit 150 may also receive a selection input for a certificate related to the signature content. The certificate unit 120 may store one or more certificates. The display unit 160 displays the one or more certificates stored in the certificate unit 120. The user selects any one from among displayed certifi cates and makes an input concerning the selection of the certificate. The input concerning the selection of the certifi cate by the user is received by the input unit 150. The input unit 150 receives a password for the selected certificate as the input concerning the selection of the certificate at step S215. US 9,509,516 B Thereafter, the control unit 110 determines whether the certificate unit 120 is capable of performing a digital sig nature function corresponding to the selected certificate at step S217. If it is determined that the certificate unit 120 is capable of performing the digital signature function corre sponding to the selected certificate, the control unit 110 commands the certificate unit 120 to create a digital signa ture. The certificate unit 120 creates a digital signature based on a private key in compliance with the command from the control unit 110. The external communication unit 130 transmits the digital signature created by the certificate unit 120 to the server 300 at step S219. In contrast, if it is determined that when the certificate unit 120 is not capable of performing the digital signature function corresponding to the selected certificate, the control unit 110 creates a digital signature based on a private key corresponding to the certificate selected from the certificate unit 120 at step S221. In this case, the control unit 110 may inquire whether a private key corresponding to the certificate selected from the certificate unit 120 is stored. The external communication unit 130 transmits the digital signature created by the control unit 110 to the server 300 at step S223. The server 300 transmits the received digital signature to the signature-requesting terminal 200 at step S225. In accordance with an embodiment of the present inven tion, when a mobile terminal includes a short-range com munication unit, a digital signature may be transmitted to a signature-requesting terminal through the short-range com munication unit. Further, in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, when a mobile terminal does not include a short-range communication unit, a digital signature may be transmitted to a signature-requesting terminal over an exter nal communication network. Furthermore, in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, only an authorized user may receive signature content using a security code. As described above, although preferred embodiments of the present invention have been described in detail, the Scope of the present invention is not limited thereto, and those skilled in the art will appreciate that various modifi cations and changes based on the basic concept of the present invention are possible without departing from the Scope and spirit of the invention as disclosed in the accom panying claims. What is claimed is: 1. An apparatus for providing a digital signature, com prising: a certificate unit configured to store one or more certifi cates and to generate digital signatures based on private keys corresponding to the one or more certificates; a display unit configured to display certificate information based on signature content received from a signature requesting terminal; an input unit for receiving a selection input for a certifi cate related to the displayed certificate information; and a control unit for determining whether the certificate unit is capable of performing a digital signature generation function corresponding to a selected certificate, wherein, the control unit is configured to command the certificate unit to create the digital signature based on a private key corresponding to the selected certificate based on determining that the certificate unit is capable of performing the digital signature generation function,
20 13 wherein, the control unit is configured to create the digital signature based on a private key corresponding to the selected certificate based on determining that the cer tificate unit is not capable of performing the digital signature generation function, and wherein the control unit is configured to transmit the digital signature to the signature-requesting terminal. 2. The apparatus of claim 1, further comprising a short range communication unit, wherein when a touch with the signature-requesting ter minal is made, the control unit receives the signature content from the signature-requesting terminal through the short-range communication unit. 3. The apparatus of claim 2, wherein when the certificate unit is located outside of the apparatus, the short-range communication unit receives the digital signature from the certificate unit when the certificate unit is touched. 4. The apparatus of claim 3, wherein the short-range communication unit is a Near-Field Communication (NFC) module. 5. The apparatus of claim 1, further comprising an exter nal communication unit for receiving the signature content from the signature-requesting terminal through a server. 6. The apparatus of claim 5, wherein the external com munication unit transmits the digital signature to the signa ture-requesting terminal. 7. The apparatus of claim 6, wherein: the signature content is encrypted using an encryption key by the signature-requesting terminal, and the encryp tion key is generated based on a security code by the signature-requesting terminal, and the control unit generates an encryption key based on the Security code, and decrypts the signature content using the encryption key. 8. The apparatus of claim 7, wherein: the external communication unit receives a partially hid den security code, together with the signature content, through the server, and the control unit is configured to, when the input received through the input unit matches a hidden field of the Security code, generate an encryption key based on the security code. 9. The apparatus of claim 5, wherein the external com munication unit receives session information corresponding to the signature content received by the server, transmits a user identifier to the server in response to the session information, and receives signature content transmitted from the server when the user identifier matches a user identifier transmitted from the signature-requesting terminal to the SeVer. 10. The apparatus of claim 9, wherein the user identifier is user information that has been shared with the signature requesting terminal in advance. 11. A method for providing a digital signature, compris ing: displaying, by a display unit, certificate information based on signature content received from a signature-request ing terminal; receiving, by an input unit, a selection input for a certifi cate related to the displayed certificate information: determining, by a control unit, whether the certificate unit is capable of performing a digital signature generation function corresponding to a selected certificate; US 9,509,516 B commanding, by the control unit, the certificate unit to create the digital signature based on a private key corresponding to the selected certificate based on deter mining that the certificate unit is capable of performing the digital signature generation function; creating, by the control unit, the digital signature based on the private key corresponding to the selected certificate based on determining that the certificate unit is not capable of performing the digital signature generation function; and transmitting, by the control unit, the digital signature to the signature-requesting terminal. 12. The method of claim 11, further comprising, when a touch with the signature-requesting terminal is made, receiv ing the signature content from the signature-requesting terminal through a short-range communication unit. 13. The method of claim 12, further comprising, when the certificate unit is located outside, receiving, by the short range communication unit, the digital signature from the certificate unit when the certificate unit is touched. 14. The method of claim 13, wherein the short-range communication unit is a Near-Field Communication (NFC) module. 15. The method of claim 11, further comprising receiving, by an external communication unit, the signature content from the signature-requesting terminal through a server. 16. The method of claim 15, further comprising transmit ting, by the external communication unit, the digital signa ture to the signature-requesting terminal. 17. The method of claim 16, wherein: the signature content is encrypted using an encryption key by the signature-requesting terminal, and the encryp tion key is generated based on a security code by the signature-requesting terminal, and the method further comprises generating, by the control unit, the encryption key based on the security code, and decrypting, by the control unit, the signature content using the encryption key. 18. The method of claim 17, further comprising: receiving, by the external communication unit, a partially hidden security code, together with the signature con tent, through the server; and generating, by the control unit, an encryption key based on the security code when the input received through the input unit matches a hidden field of the security code. 19. The method of claim 15, wherein receiving, by the external communication unit, the signature content from the signature-requesting terminal through the server comprises: receiving, by the external communication unit, session information corresponding to the signature content received by the server: transmitting, by the external communication unit, a user identifier to the server in response to the session information; and receiving, by the external communication unit, signature content transmitted from the server when the user identifier matches a user identifier transmitted from the signature-requesting terminal to the server. 20. The method of claim 19, wherein the user identifier is user information that has been shared with the signature requesting terminal in advance.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9577942B2 (12) United States Patent Lee et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,577.942 B2 *Feb. 21, 2017 (54) COMMUNICATION TERMINAL APPARATUS AND METHOD OF PERFORMING COMMUNICATION BY USING
USOO9577942B2 (12) United States Patent Lee et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,577.942 B2 *Feb. 21, 2017 (54) COMMUNICATION TERMINAL APPARATUS AND METHOD OF PERFORMING COMMUNICATION BY USING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2
 US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0186073 A1 Bryan et al. US 201701 86.073A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SHOPPING CART DISPLAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0186073 A1 Bryan et al. US 201701 86.073A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SHOPPING CART DISPLAY
/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].
![/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. / client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].](/thumbs/90/103929709.jpg) US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
(12) United States Patent
 US0085223.05B2 (12) United States Patent Cho et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (30) (51) (52) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR UPDATING USER IDENTIFIERS (IDS) Inventors: Yeong-Sub Cho, Daejeon (KR):
US0085223.05B2 (12) United States Patent Cho et al. (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (30) (51) (52) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR UPDATING USER IDENTIFIERS (IDS) Inventors: Yeong-Sub Cho, Daejeon (KR):
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,325,795 B2
 US009325795B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kim et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2016 (54) METHOD OF AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING (58) Field of Classification Search (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) ()
US009325795B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kim et al. () Date of Patent: Apr. 26, 2016 (54) METHOD OF AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING (58) Field of Classification Search (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) ()
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
ED 302C A t 302B (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009.01430 12A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143012 A1 JEON (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) BLUETOOTH-ENABLED MOBILE Publication Classification TERMINAL
US 2009.01430 12A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0143012 A1 JEON (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 4, 2009 (54) BLUETOOTH-ENABLED MOBILE Publication Classification TERMINAL
(FSN JSO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Frequency. Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 (19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
(12) United States Patent
 USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2. Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008
 United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9426741B2 (12) United States Patent Wu et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 9.426,741 B2 Aug. 23, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) () (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING
USOO9426741B2 (12) United States Patent Wu et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 9.426,741 B2 Aug. 23, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) () (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0019726A1 Park et al. US 2006OO19726A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LOCKINGAPPARATUS OF SWING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0019726A1 Park et al. US 2006OO19726A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LOCKINGAPPARATUS OF SWING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,237,112 B1
 USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 (57) USPC /412. Initiate wireless Connection. Discover.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
wo W /1997 * cited by examiner
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Cunningham et al.
 US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.253,522 B2
 US009,22B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9.3,522 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2016 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING DATA FLOW (56) References Cited OF MIRRORLINK SYSTEM (71) Applicant:
US009,22B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9.3,522 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2016 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING DATA FLOW (56) References Cited OF MIRRORLINK SYSTEM (71) Applicant:
1a " " " ), Gigi Nii
 USOO8295862B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,295,862 B2 Suresh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM TO ENABLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 455/466 COMMUNICATION THROUGHSMS (58)
USOO8295862B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,295,862 B2 Suresh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM TO ENABLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 455/466 COMMUNICATION THROUGHSMS (58)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2
 US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
W15. Keung Wong, Hong Kong (HK) (21) Appl. No.: 09/875,350. (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong, Hong Kong (HK); Hoi (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9442667B2 (12) United States Patent Drosch (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.442,667 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (30) (51) (52) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR
USOO9442667B2 (12) United States Patent Drosch (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.442,667 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (30) (51) (52) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
336w 330 FPGA / 330 MW} Compgnenf _/14 / 38 US 7,774,801 B1. Aug. 10, 2010 (56) (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: (12) United States Patent Fitkin
 US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9660456B2 (12) United States Patent Dwelley et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) SWITCHING OF CONDUCTOR PAIR IN POWER
USOO9660456B2 (12) United States Patent Dwelley et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 23, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) SWITCHING OF CONDUCTOR PAIR IN POWER
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1. Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
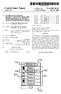 USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
Note: Text based on automatic Optical Character Recognition processes. SAMSUNG GALAXY NOTE
 Note: Text based on automatic Optical Character Recognition processes. SAMSUNG GALAXY NOTE PRIORITY This application is a Continuation of U.S. application Ser. No. 14/540,447, which was filed in the U.S.
Note: Text based on automatic Optical Character Recognition processes. SAMSUNG GALAXY NOTE PRIORITY This application is a Continuation of U.S. application Ser. No. 14/540,447, which was filed in the U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0240763 A1 Urakawa et al. US 20140240763A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) FUNCTION EXECUTION DEVICE Applicants:Yutaka
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0240763 A1 Urakawa et al. US 20140240763A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) FUNCTION EXECUTION DEVICE Applicants:Yutaka
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,548,906 B1. Pelican (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 1, 2013
 United States Patent USOO8548906B1 (12) () Patent No.: Pelican (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 1, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 6,272.472 B1* 8/2001 Danneels et al.... 705/27 AUTOMATC SAVINGS UPON EVENT
United States Patent USOO8548906B1 (12) () Patent No.: Pelican (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 1, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 6,272.472 B1* 8/2001 Danneels et al.... 705/27 AUTOMATC SAVINGS UPON EVENT
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1
 USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013
 US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7366822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,366,822 B2 KWalk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE (56) References Cited CAPABLE OF READING AND WRITING
(12) United States Patent USOO7366822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,366,822 B2 KWalk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE (56) References Cited CAPABLE OF READING AND WRITING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(12) United States Patent
 US0088.12887B2 (12) United States Patent Liu et al. (54) ELECTRONIC DISPLAY DEVICE AUTOMATICALLY TURNS ON OR OFF ACCORDING TO WHETHER AUSERN FRONT OF THE DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Xu Liu, Shanghai (CN);
US0088.12887B2 (12) United States Patent Liu et al. (54) ELECTRONIC DISPLAY DEVICE AUTOMATICALLY TURNS ON OR OFF ACCORDING TO WHETHER AUSERN FRONT OF THE DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Xu Liu, Shanghai (CN);
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2. McDOWell et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2006
 United States Patent US007039435B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,039.435 B2 McDOWell et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2006 (54) PROXIMITY REGULATION SYSTEM FOR 6, 195,562 B1* 2/2001 Pirhonen et al.... 455,553.1
United States Patent US007039435B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,039.435 B2 McDOWell et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2006 (54) PROXIMITY REGULATION SYSTEM FOR 6, 195,562 B1* 2/2001 Pirhonen et al.... 455,553.1
Is more than one finger placed on touchpad surface?
 USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. streaming media server
 (19) United States US 201401 15115A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0115115 A1 Kuang (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PLAYING Publication Classification STREAMING
(19) United States US 201401 15115A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0115115 A1 Kuang (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PLAYING Publication Classification STREAMING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,385,897 B1
 US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140355048A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0355048A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF MOBILE Publication Classification
US 20140355048A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0355048A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2. Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060200568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0200568 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification CONVERTING SMS MESSAGE
(19) United States US 20060200568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0200568 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification CONVERTING SMS MESSAGE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 201601 17448A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0117448 A1 VANDE CRAEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM FORMANAGING ACCESS TO (52) U.S. Cl. MEDICAL DATA
(19) United States US 201601 17448A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0117448 A1 VANDE CRAEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM FORMANAGING ACCESS TO (52) U.S. Cl. MEDICAL DATA
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,711,263 B1
 USOO6711263B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nordenstam et al. () Date of Patent: Mar. 23, 2004 (54) SECURE DISTRIBUTION AND PROTECTION 5,517,567 5/1996 Epstein... 380/247 OF ENCRYPTION KEY
USOO6711263B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nordenstam et al. () Date of Patent: Mar. 23, 2004 (54) SECURE DISTRIBUTION AND PROTECTION 5,517,567 5/1996 Epstein... 380/247 OF ENCRYPTION KEY
(12) United States Patent
 US007548755B2 (12) United States Patent Kim () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 16, 2009 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR CONVERTING SMS MESSAGE INTO MMS COMPLIANT IMAGE FILE IN MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
US007548755B2 (12) United States Patent Kim () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 16, 2009 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR CONVERTING SMS MESSAGE INTO MMS COMPLIANT IMAGE FILE IN MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2
 US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1
 USOO6199163B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1 Dumas et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 9 (54) HARD DISK PASSWORD LOCK 5,231,662 * 7/1993 van Rumpt et al.... 380/9 5,283,828
USOO6199163B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1 Dumas et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 9 (54) HARD DISK PASSWORD LOCK 5,231,662 * 7/1993 van Rumpt et al.... 380/9 5,283,828
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004
 (19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9729447B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,729.447 B2 *Aug. 8, 2017 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52)
USOO9729447B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,729.447 B2 *Aug. 8, 2017 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004.0029581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0029581 A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE PHONE BEING SEPARATED INTO (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004.0029581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0029581 A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE PHONE BEING SEPARATED INTO (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
231 age sins N3 : as a. (12) United States Patent US 8,194,335 B2. Jun. 5, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 USOO8194,335B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,194,335 B2 Jun. 5, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) OPTICAL LENS ON WAFER LEVEL AND RELATED
USOO8194,335B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,194,335 B2 Jun. 5, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) OPTICAL LENS ON WAFER LEVEL AND RELATED
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150382196A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0382 196A1 Hillier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) PERSONAL AREA NETWORKSYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150382196A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0382 196A1 Hillier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 31, 2015 (54) PERSONAL AREA NETWORKSYSTEMAND (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/00994.67 A1 KANG US 2015.0099.467A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 9, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) METHOD OF AND DEVICE FOR BROADCASTING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/00994.67 A1 KANG US 2015.0099.467A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 9, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) METHOD OF AND DEVICE FOR BROADCASTING
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 HUI (43) Pub. Date: Mar.
 US 20150067353A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0067353 A1 HUI (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2015 (54) STORAGE MANAGEMENT DEVICE AND (52) US. Cl. STORAGE MANAGEMENT
US 20150067353A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0067353 A1 HUI (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2015 (54) STORAGE MANAGEMENT DEVICE AND (52) US. Cl. STORAGE MANAGEMENT
(12) United States Patent
 US0085319B2 (12) United States Patent Jiang et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Sep., 2013 (54) MESSAGE PROCESSING METHOD AND SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Xiyuan Jiang, Shanghai (CN); Shukun Wang, Beijing
US0085319B2 (12) United States Patent Jiang et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Sep., 2013 (54) MESSAGE PROCESSING METHOD AND SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Xiyuan Jiang, Shanghai (CN); Shukun Wang, Beijing
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0072119A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/00721 19 A1 PARK (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 21, 2013 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. CONNECTING WITH
(19) United States US 2013 0072119A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/00721 19 A1 PARK (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 21, 2013 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. CONNECTING WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(12) United States Patent
 US00795391 OB2 (12) United States Patent Kakish (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) ALL-IN-ONE PERSONAL COMPUTER WITH EXTERNAL VIDEO INPUT (75) Inventor: Musa Ibrahim Kakish, Anaheim,
US00795391 OB2 (12) United States Patent Kakish (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) ALL-IN-ONE PERSONAL COMPUTER WITH EXTERNAL VIDEO INPUT (75) Inventor: Musa Ibrahim Kakish, Anaheim,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
HLR/HLR-T. (12) United States Patent US 8,331,990 B2. Dec. 11, (45) Date of Patent: AUCIAUC-T. (10) Patent No.:
 USOO8331990B2 (12) United States Patent LarssOn (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2012 (54) METHOD FORACTIVATING SIM CARDS (75) Inventor: Thomas Larsson, Alvsjo (SE) (73) Assignee: Giesecke
USOO8331990B2 (12) United States Patent LarssOn (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 11, 2012 (54) METHOD FORACTIVATING SIM CARDS (75) Inventor: Thomas Larsson, Alvsjo (SE) (73) Assignee: Giesecke
