United States Patent (19) Finkelstein et al.
|
|
|
- Bruno West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
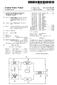
1 United States Patent (19) Finkelstein et al. USOO540602A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Apr. 25, ). METHOD FOR KEY MANAGEMENT OF POINT TO-POINT COMMUNICATIONS 75 Inventors: Louis D. Finkelstein, Wheeling; Daniel P. Brown, Elmhurst; Larry C. Puhl, Sleepy Hollow, all of Ill. 73 Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Schaumburg, Ill. 21 Appl. No.: 127,718 (22 Filed: Sep. 27, ) Int. Cl.... H04L 9/00 52 U.S.C /21: 380/28; 380/49 58) Field of Search /21, 28, 29, 30, 380/49, 48 56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 5,124,117 6/1992 Tatebayashi et al /21 5,239,294 8/1993 Flanders et al.. 5,301,247 4/1994 Rasmussen et al /21 Primary Examiner-David C. Cain Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Anthony G. Sitko 57 ABSTRACT A method of secure key distribution in a communica tion system having a plurality of subscriber units and an infrastructure communication centerisprovided. A first subscriber unit sends a request to the infrastructure communication center for a secure communication link with a second subscriber unit. This request includes an encrypted session encryption key which was encrypted with a first subscriber registration The infrastruc ture communication center decrypts the encrypted ses sion encryption key with the first subscriber registration Subsequently, the infrastructure communication center re-encrypts the session encryption key with a second subscriber registration This re-encrypted session encryption key is sent to the second subscriber unit. In an alternative method, the first subscriber unit and the infrastructure communication center a priori know a session Therefore, the infrastructure com munication center only needs to encrypt and send the session encryption key to the second subscriber unit, in response to a request by the first subscriber unit. 22 Claims, 2 Drawing Sheets 200 REQUEST A SECRE COUNICATION LINK DECRYPT. AN ENCRYPTE) WITH A FIRST SUBSCRIBER RE-ENCRYPT SESSION ENCRYPTION KEY WITH A SECOND SUBSCRIBER DELETE DECRYPTED. SEND ENRYPTED TO SECONO SUBSCRIBER UNIT DECRYPT ENCRYPTED WITH THE SECOND SUBSCRIBER COUNICATE A TESSAGE ENCRYPTED BY SESSION KEY FROT A FIRST SUBSCRIBER UNIT TO THE SECONO SUBSCRIBER UNIT ENABE ENCRYPTE) CONFERENCE COUNICATIONLINK
2 U.S. Patent Apr. 25, 1995
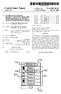
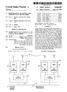
3 U.S. Patent Apr. 25, 1995 Sheet 2 of 2 AV REQUEST A SECURE 202 COUNICATION LINK DECRYPT. AN ENCRYPTED WITH A FIRST SUBSCRIBER RE-ENCRYPT SESSION ENCRYPTION KEY WITH A SECOND SUBSCRIBER DELETE DECRYPTED 208 SEND ENCRYPTED 210 TO SECOND SUBSCRIBER UNIT DECRYPT ENCRYPTED WITH THE SECOND SUBSCRIBER COMUNICATE A WESSAGE ENCRYPTED BY SESSION KEY FRO A FIRST SUBSCRIBER UNIT TO THE SECONO SUBSCRIBER UNIT ENABLE ENCRYPTED CONFERENCE 216 COMUNICATIONLINK C END D-218 AW 6.3 CBEGINDY-300 REQUEST A SECURE 302 COMUNICATION LINK WHERE SESSION KEY IS A PRIORI KNOWN ENCRYPT SESSION ENCRYPTIONKEY WITH A 306 SECOND SUBSCRIBER DELETE DECRYPTED 308 SEND ENCRYPTED 310 TO SECONO SUBSCRIBER UNIT DECRYPT ENCRYPTED WITH THE SECOND 312 SUBSCRIBER COMUNICATE A WESSAGE ENCRYPTED BY SESSION KEY FRO A FIRST 314 SUBSCRIBER UNIT TO THE SECOND SUBSCRIBER UNIT ENABLE ENCRYPTE) CONFERENCE 316 COUNICATION LINK C END D-318
4 1. METHOD FOR KEY MANAGEMENT OF PONT-TO-POINT COMMUNICATIONS RELATED INVENTIONS. The present invention is related to the following invention which is assigned to the assignee of the pres ent invention. Method and Apparatus for Efficient Real-Time Authentication and Encryption in a Con munication System by Brown et al. having U.S. Ser. No. 08/084,644, and filed on Jun. 28, FIELD OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to communication sys tems and, more particularly, to encryption key manage ment of point-to-point communications. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Many communications systems currently use encryp tion to enhance security of the systems. These commu nication systems include cellular radio telephone com munication system, personal communication systems, paging systems, as well as wireline and wireless data networks. By way of example a cellular communication system will be described below; however, it will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that the encryp tion techniques described can be readily extended to other communication systems without departing from the scope and spirit of the present invention. Turning now to cellular communication systems, these systems typically include subscriber units (such as mobile or portable units) which communicate with a fixed net work communication unit via radio frequency (RF) communication links. A typical cellular communication system includes at least one base station (i.e., communi cation unit) and a switching center (i.e., an infrastruc ture communication center). Present cellular communi cation systems are designed to encrypt communications on an RF link between a subscriber unit and a base station unit through the use of an encryption key known to both units so that others who intercept the RF link communication link will be unable to listen to the com munication (e.g., unable to eavesdrop on a voice con versation). One such RF link encryption technique is described in the United States Digital Cellular (USDC) standard (known as IS-54 and IS-55) and published by the Elec tronic Industries Association (EIA), 2001 Eye Street, N.W., Washington, D.C The USDC system encryption technique utilizes a series of specialized messages which must be passed between the subscriber unit and a base site communication unit before a session encryption key is known to both units. This encryption key is based upon shared secret data (SSD)in USDC system. For an authentication process an SSDA key is used. Similarly, for a voice privacy function an SSDB key is used. For the voice privacy function, the initial transmitted subscriber message contains an authentica tion response, but no other data is encrypted. The com mand to begin an encryption process is sent from the service provider (i.e., base site communication unit) to the subscriber after the subscriber has been assigned a traffic channel. Further, current system architecture design is focused on bringing encryption to data as well as voice. Data consists of either synchronous or packet data. Ideally, an encryption key should be provided for each data communication session. In a synchronous data environment, a session key is an encryption key which is used for the duration of a single (e.g., circuit switched) data communication (i.e., call'). Similarly in a data packet environment, a session key is an encryp tion key which is used from the time that the communi cation unit registers with a serving system until the next time that the communication unit re-registers. In addi tion, in a previously-cited related invention entitled "Method and Apparatus for Efficient Real-Time Au thentication and Encryption in a Communication Sys tem by Brown et al. having U.S. Ser. No. 08/084,644, and filed on Jun. 28, 1993, another encryption key is proposed for USDC system which is termed an SSDC key and which is used for data packet encryption. In these communication systems, packetized data also needs to be encrypted. Packetized data adds an addi tional problem to the typical encryption process. This is because packets of data may arrive at different times at a subscriber unit of a communication unit (i.e., packet messages are connectionless'). These packets need to be reassembled and decrypted in the same order in which they were encrypted. In addition, an encryption key can only be negotiated when a subscriber performs a registration. Therefore, a need exists for an encryption technique which can alleviate these problems associated with packetized data. However, these previously known encryption tech niques do not address all of the possible eavesdropping vulnerabilities inherent in a communication channel. Eavesdropping may still occur at other points in the communication channel between the subscriber unit and an endpoint target communication device such as through wiretapping of a land-line phone. Such a com munication between a subscriber unit and an endpoint target communication device is termed a "point-to point' communication. The communication may travel along several different physical communication links before being ultimately coupled via a communication link between the subscriber and target devices. For example in the cellular environment, a user of a sub scriber unit may place a voice call to a target communi cation device located at a place of business. In order for that call to be completed, a communication channel must be set up on an RF link to a base site communica tion unit. In addition, the communication channel must be extended through the public switched telephone network (PSTN) to the place of business. This place of business may have a private telephone network con nected to the PSTN. As a result, the communication channel may also need to be extended through the pri vate network to ultimately connect with the target communication device. Currently, encryption tech niques are only being applied to individual components of the entire communication channel (e.g., the RF link in USDC system may be encrypted). However, this leaves other components such as the PSTN or private network vulnerable to eavesdropping through wiretap ping. Therefore, a need also exists for an encryption technique which can alleviate these problems associated with eavesdropping at other points of the communica tion channel. SUMMARY OF THE ENVENTION These needs and others are substantially met through provision of a method of secure key distribution in a communication system having a plurality of subscriber units and an infrastructure communication center. A first subscriber unit sends a request to the infrastructure
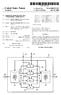
5 3 communication center for a secure communication link with a second subscriber unit. This request includes an encrypted session encryption key which was encrypted with a first subscriber registration The infrastruc ture communication center decrypts the encrypted ses sion encryption key with the first subscriber registration Subsequently, the infrastructure communication center re-encrypts the session encryption key with a second subscriber registration This re-encrypted session encryption key is sent to the second subscriber unit. In an alternative method, the first subscriber unit and the infrastructure communication center a priori know a session Therefore, the infrastructure com munication center only needs to encrypt and send the session encryption key to the second subscriber unit, in response to a request by the first subscriber unit. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a preferred em bodiment communication system having a first and a second subscriber unit as well as an infrastructure con necting the subscriber units in accordance with the present invention. FIG. 2 is a flow chart of a preferred embodiment encryption method used by the first and the second subscriber unit over the infrastructure as shown in FIG. 1 in accordance with the present invention. FIG. 3 is a flow chart of an alternative preferred embodiment encryption method used by the first and the second subscriber unit over the infrastructure as shown in FIG. 1 in accordance with the present inven tion. DETALED DESCRIPTION FIG. 1 generally depicts a first 100 and a second 102 subscriber communication unit (e.g., a radiotelephone) as well as an infrastructure such as an infrastructure communication center or switch 104 and first 106 and second 108 cellular radio base sites. In the following example the subscriber units 100 and 102 are serviced by the same infrastructure switch 104. The first subscriber unit 100 forms a communication channel with the first base site 106 by an RF link 110. Similarly, the second subscriber unit 102 forms a communication channel to the second base site 108 by an RF link 112. In addition, the first base site 106 and the second base site 108 form communication channels to the infrastructure switch 104 by wirelines 114 and 116, respectively. However, it will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that multiple switches (e.g., a cellular switch, a local PSTN switch, and/or a long distance carrier switch) could be used to connect the two subscriber units. In addition, the two subscriber units may be a part of two different cellular systems or one connected to a wirefine and one a part of a cellular system. Further, the sub scriber units could be communicating data rather than voice over a communication channel such as through an Advanced Radio Data Information Service (i.e., ARD IS (R) a joint venture between Motorola, Inc, and IBM) or a personal communication system (PCS) which is connected to the PSTN through a Mobile Network Integration (MNI) protocol without departing from the scope and spirit of the present invention. Referring now to FIG. 2, a flow chart of a preferred embodiment "point-to-point' encryption scheme used by the first 100 and the second 102 subscriber unit over the infrastructure 104,106, and 108 is shown. One of the most important elements of this preferred embodiment 4. encryption scheme is the encryption key management in a "point-to-point' communication system. As is de scribed in USDC system, each subscriber unit estab lishes a series of RF link encryption keys (e.g., SSD4 5 and SSDB keys) upon registration with a cellular infra structure network. These encryption keys, which are known to the subscriber unit and the cellular infrastruc ture network, are also known as registration keys. In addition as proposed by Brown et al., another encryp 10 tion key, termed an SSDc key, may be generated by each subscriber unit for use in data encryption. This SSDC may also generate a session encryption key (SEK) which is valid for use during only one synchro nous data communication session or one packet data 15 registration session. The session encryption key (SEK) may be used to encrypt a "point-to-point' communica tion between the first 100 and the second 102 subscriber units such that the communication may even be en crypted as it passes through the infrastructure switch The overall security of a communication channel between the first 100 and the second 102 subscriber units depends upon the secure passing of a session key to both subscriber units. Flowchart elements 200 through outline a preferred embodiment technique for se curely passing these session encryption keys. A first subscriber unit 100 makes 202 a request to the infra structure communication center 104 for a secure com munication link with a second subscriber unit 102 via 30 the RF link 110, first base site 106 and wireline 114. This request preferably includes a session encryption key (SEK) which has been encrypted with a first subscriber registration key (SSD1C). The infrastructure communi cation center 104 decrypts 204 the encrypted session 35 encryption key (SEK) with the first subscriber registra tion key (SSD1C). Subsequently, the infrastructure communication center re-encrypts 206 the session en cryption key (SEK) with a second subscriber registra tion key (SSD2C). At this point the infrastructure com munication center 104 no longer needs the decrypted session encryption key and may optionally delete 208 the session key from an infrastructure memory device which temporarily stored the session This deleting of the decrypted session key may enhance the overall 45 security of the communication system by eliminating the possibility that someone could get unauthorized access to the session keys by tapping into the infrastruc ture communication center 104 storage memory. The infrastructure communication center 104 then sends the encrypted session encryption key (SEK) to the second subscriber unit 102 via wireline 116, second base site 108 and RF link 112. The second subscriber unit 102 decrypts 212 the encrypted session encryption key (SEK) with the second subscriber registration key 55 (SSD2C). Finally, a message encrypted by the session encryption key (SEK) is communicated 214 between the first subscriber unit 100 and the second subscriber unit 102 transparently (i.e., without the decryption by the infrastructure) through the infrastructure communi cation center 104. This message may be decrypted by either subscriber unit 100 or 102 with the session en cryption key (SEK). This method of session key (SEK) management also works for broadcast messaging systems wherein the 65 encrypted session key (SEK) may be sent in step 210 to a plurality of second subscriber units 102 such that broadcast messages may be encrypted by the session key (SEK).
6 5 In addition, an encrypted conference communication link may be enabled 216 by the infrastructure communi cation center 104 through one of two methods. This type of conference communication link is also known as a fractional-duplex mode of encrypted speech for con ference applications. The first subscriber unit 100 would broadcast the session key (SEK) to the other parties in the conference call. Then once the session key (SEK) is established, a conversation can proceed whereby each talker can speak individually to all of the others. A smooth conversation flow requires that either an agree ment exist between all participants concerning the order of the talkers (which is common on amateur radio nets), or that an automatic speech detector select the "talker' and route the "talker's' encrypted speech to the other subscriber units. Automatic speech detection and direc tional routing are common in speakerphone devices for conversations between two endpoints; however, through sophisticated automatic routers at infrastruc ture communication centers 104 it is possible to handle three or more endpoints at a time. One method for enabling automatic routing by the infrastructure com munication center 104 involves decrypting subsequent communications from all of the subscriber units in the conference communication link with the decrypted session encryption key (SEK) which was previously stored in the memory of the infrastructure communica tion center 104. Another method for enabling automatic routing by the infrastructure communication center 104 involves participating subscriber units 100 and 102 pro viding communication activity information to the infra structure communication center 104. Referring now to FIG. 3, a flow chart of an alterna tive preferred embodiment "point-to-point' encryption scheme used by the first 100 and the second 102 sub scriber unit over the infrastructure 104, 106, and 108 is shown. Flowchart elements 300 through 318 outline the alternative preferred embodiment technique for se curely passing these session encryption keys. In this alternative preferred embodiment, the first subscriber unit 100 and the infrastructure communication center 104 a priori know (i.e., have previously determined) the value of the session key (SEK) through the subscriber unit registration process or some other way. Therefore, the first subscriber unit 100 makes 302 a request, with out including the session encryption key (SEK), to the infrastructure communication center 104 for a secure communication link with a second subscriber unit 102 via the RF link 110, first base site 106 and wireline 114. Subsequently, the infrastructure communication center encrypts 306 the session encryption key (SEK) with a second subscriber registration key (SSD2C). At this point the infrastructure communication center 104 no longer needs the decrypted session encryption key and may optionally delete 308 the session key from an infra structure memory device which temporarily stored the session The infrastructure communication center 104 then sends 310 the encrypted session encryption key (SEK) to the second subscriber unit 102 via wireline 116, second base site 108 and RF link 112. The second subscriber unit 102 decrypts 312 the encrypted session encryption key (SEK) with the second subscriber regis tration key (SSD2C). Finally, a message encrypted by the session encryption key (SEK) is communicated 314 between the first subscriber unit 100 and the second subscriber unit 102 transparently (i.e., without the de cryption by the infrastructure) through the infrastruc ture communication center 104. This message may be 5 O decrypted by either subscriber unit 100 or 102 with the session encryption key (SEK). It will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that an encrypted conference communication link may be enabled 316 for this alterna tive preferred embodiment encryption scheme in a man ner similar to the one previously described in reference to the preferred embodiment encryption scheme shown in FIG. 2. Although the invention has been described and illus trated with a certain degree of particularity, it is under stood that the present disclosure of embodiments has been made by way of example only and that numerous changes in the arrangement and combination of parts as well as steps may be resorted to by those skilled in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as claimed. For example, the communication channel could alternatively be an electronic data bus, wireline, optical fiber link, satellite link, or any other type of communication channel. What is claimed is: 1. A method of secure key distribution in a communi cation system having a plurality of subscriber units and an infrastructure communication center, comprising: nication link with a second subscriber unit, the request including an encrypted session encryption key, the session encryption key being encrypted with a first subscriber registration key; (b) decrypting, by the infrastructure communication center, the encrypted session encryption key with the first subscriber registration key; (c) re-encrypting, by the infrastructure communica tion center, the session encryption key with a sec ond subscriber registration key; and (d) sending the encrypted session encryption key to the second subscriber unit. 2. The method of claim 1 further comprising the step of communicating a message encrypted by the session encryption key from the first subscriber unit to the second subscriber unit transparently through the infra structure communication center. 3. The method of claim 1 further comprising the step of decrypting, by the second subscriber unit, the en crypted session encryption key with the second sub scriber registration 4. The method of claim 1 wherein the sending step 5. The method of claim 1 further comprising the step of deleting, by the infrastructure communication center, the decrypted session encryption key from a memory device. 6. The method of claim 1 further comprising the step link, by the infrastructure communication center, 7. The method of claim 1 further comprising the step link, by participating subscriber units, through provid ing communication activity information to the infra structure communication center. 8. A method of secure key distribution in a communi cation system having a plurality of subscriber units and an infrastructure communication center, comprising:
7 7 nication link with a second subscriber unit, the request including an encrypted session encryption key, the session encryption key being encrypted with a first subscriber registration key; - (b) decrypting, by the infrastructure communication center, the encrypted session encryption key with the first subscriber registration key; (c) re-encrypting, by the infrastructure communica tion center, the session encryption key with a sec ond subscriber registration key; (d) deleting, by the infrastructure communication center, the decrypted session encryption key from a memory device; (e) sending the encrypted session encryption key to the second subscriber unit; (f) decrypting, by the second subscriber unit, the encrypted session encryption key with the second subscriber registration key; and (g) communicating a message encrypted by the ses sion encryption key from the first subscriber unit to the second subscriber unit transparently through the infrastructure communication center. 9. The method of claim 8 wherein the sending step 10. The method of claim 8 further comprising the step link, by the infrastructure communication center, 11. The method of claim 8 further comprising the step link, by participating subscriber units, through provid ing communication activity information to the infra structure communication center. 12. A method of secure key distribution in a commu nication system having a plurality of subscriber units and an infrastructure communication center, compris 1ng: nication link with a second subscriber unit, the first subscriber unit and the infrastructure communica tion center a priori knowing a session key; (b) encrypting, by the infrastructure communication center, the session encryption key with a second subscriber registration key; and (c) sending tire encrypted session encryption key to the second subscriber unit. 13. The method of claim 12 further comprising the step of communicating a message encrypted by the session encryption key from the first subscriber unit to the second subscriber unit transparently through the infrastructure communication center. 14. The method of claim 12 further comprising the step of decrypting, by the second subscriber unit, the encrypted session encryption key with the second sub scriber registration 15. The method of claim 12 wherein the sending step 16. The method of claim 12 further comprising the step of deleting, by the infrastructure communication center, the decrypted session encryption key from a memory device. 17. The method of claim 12 further comprising the tion link, by the infrastructure communication center, 18. The method of claim 12 further comprising the tion link, by participating subscriber units, through providing communication activity information to the infrastructure communication center. 19. A method of secure key distribution in a commu nication system having a plurality of subscriber units and an infrastructure communication center, compris 1ng: nication link with a second subscriber unit, the first subscriber unit and the infrastructure communica tion center a priori knowing a session key; (b) encrypting, by the infrastructure communication center, the session encryption key with a second subscriber registration key; (c) deleting, by the infrastructure communication center, the decrypted session encryption key from a memory device; (d) sending the encrypted session encryption key to the second subscriber unit; (e) decrypting, by the second subscriber unit, the encrypted session encryption key with the second subscriber registration key; and (f) communicating a message encrypted by the ses sion encryption key from the first subscriber unit to the second subscriber unit transparently through the infrastructure communication center. 20. The method of claim 19 wherein the sending step 21. The method of claim 19 further comprising the tion link, by the infrastructure communication center, 22. The method of claim 19 further comprising the tion link, by participating subscriber units, through providing communication activity information to the infrastructure communication center. k ck k 2k k 65
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1. Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011
 US007991882B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1 Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011 (54) COMMUNICATIONS NETWORK WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS FLOW CONTROL (75) Inventor: Robert
US007991882B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,991,882 B1 Parkhill (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 2, 2011 (54) COMMUNICATIONS NETWORK WITH OTHER PUBLICATIONS FLOW CONTROL (75) Inventor: Robert
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2
 US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000
 USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent
 US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B1
 US007844295B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,844.295 B1 Ngan (45) Date of Patent: Nov.30, 2010 (54) USING AWIRELESS INTERCOM TO 2004/0009.751 A1 1/2004 Michaelis et al.... 455,434 TALK-AROUNDA
US007844295B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,844.295 B1 Ngan (45) Date of Patent: Nov.30, 2010 (54) USING AWIRELESS INTERCOM TO 2004/0009.751 A1 1/2004 Michaelis et al.... 455,434 TALK-AROUNDA
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O191242A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191242 A1 Sommer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FAILURE DETERMINATION IN AN OPTICAL COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75)
(19) United States US 2002O191242A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0191242 A1 Sommer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FAILURE DETERMINATION IN AN OPTICAL COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) United States Patent Cunningham et al.
 US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
US007765264B2 (12) United States Patent Cunningham et al. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) SELECTION OF MODE ACCORDING TO MESSAGE CHARACTERISTICS (75) Inventors: Ivy F. Cunningham,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,856,601 B1. Bell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005
 USOO68566O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bell et al. () Date of Patent: Feb., 2005 (54) SHARED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (56) References Cited RESOURCES FOR COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES U.S.
USOO68566O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bell et al. () Date of Patent: Feb., 2005 (54) SHARED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (56) References Cited RESOURCES FOR COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0186073 A1 Bryan et al. US 201701 86.073A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SHOPPING CART DISPLAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0186073 A1 Bryan et al. US 201701 86.073A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SHOPPING CART DISPLAY
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 O'Kelly 54. SYSTEM FOR AND ED S I75 Inventor: Cathal P. O'Kelly, Maidenhead, United Kingdom 73 Assignee: Northern Telecom Limited, Montreal, Canada 21 22 Appl. No.: 539,30 Filed:
United States Patent 19 O'Kelly 54. SYSTEM FOR AND ED S I75 Inventor: Cathal P. O'Kelly, Maidenhead, United Kingdom 73 Assignee: Northern Telecom Limited, Montreal, Canada 21 22 Appl. No.: 539,30 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
US 6,587,555 B1. Jul. 1, Cripe et al. (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73) (Us) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56)
 (12) United States Patent Cripe et al. US006587555B1 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,587,555 B1 Jul. 1, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) VIRTUAL PBX Inventors: Daniel E.
(12) United States Patent Cripe et al. US006587555B1 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,587,555 B1 Jul. 1, 2003 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) VIRTUAL PBX Inventors: Daniel E.
/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].
![/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. / client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].](/thumbs/90/103929709.jpg) US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,117,152 B1 Mukherji et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006
 United States Patent US007 117152B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,117,152 B1 Mukherji et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH 6,449,588 B1* 9/2002 Bowman-Amuah... TO3/21
United States Patent US007 117152B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,117,152 B1 Mukherji et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH 6,449,588 B1* 9/2002 Bowman-Amuah... TO3/21
(SA INFORMATION) (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. (19) United States ESP/AH REQUEST SA KEY MANAGEMENT FACILITY
 (19) United States US 2008O137863A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0137863 A1 THOMAS (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR USING A KEY MANAGEMENT FACILITY TO NEGOTATE A
(19) United States US 2008O137863A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0137863 A1 THOMAS (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR USING A KEY MANAGEMENT FACILITY TO NEGOTATE A
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,269,252 B1
 USOO62692B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hutchings et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 31, 2001 (54) PROGRAMMABLE BRIDGING APPARATUS 5,564,076 10/1996 Auvray... 455/76 TO CONNECT MULTIPLE NETWORKS
USOO62692B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hutchings et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 31, 2001 (54) PROGRAMMABLE BRIDGING APPARATUS 5,564,076 10/1996 Auvray... 455/76 TO CONNECT MULTIPLE NETWORKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,377,725 B1
 USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462728B2 (12) United States Patent Stojanovski et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,728 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD AND WIRELESS SYSTEM FOR ACHIEVING LOCALANCHORING OFA MOBILE NODE
USOO8462728B2 (12) United States Patent Stojanovski et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,728 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD AND WIRELESS SYSTEM FOR ACHIEVING LOCALANCHORING OFA MOBILE NODE
United States Patent (19) Haines
 United States Patent (19) Haines 11 45 Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,697,107 Sep. 29, 1987 54) (75) (73) 21 22) (51) 52) (58) (56) FOUR-STATE I/O CONTROL CIRCUIT Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed:
United States Patent (19) Haines 11 45 Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,697,107 Sep. 29, 1987 54) (75) (73) 21 22) (51) 52) (58) (56) FOUR-STATE I/O CONTROL CIRCUIT Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed:
W15. Keung Wong, Hong Kong (HK) (21) Appl. No.: 09/875,350. (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong, Hong Kong (HK); Hoi (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O132582A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0132582 A1 Mooney (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE EXTENSION USING WIRELESS PICONET (76) Inventor: Philip D.
(19) United States US 2002O132582A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0132582 A1 Mooney (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE EXTENSION USING WIRELESS PICONET (76) Inventor: Philip D.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0009.525A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0009525A1 Evslin (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIRELESS PHONE WITH INTERFACE TO DIFFERENT NETWORKS (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2005.0009.525A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0009525A1 Evslin (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIRELESS PHONE WITH INTERFACE TO DIFFERENT NETWORKS (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OO63464A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0063464 A1 Akram et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) HIGH-SPEED DATA AND POWER SOURCE Publication Classification
US 2004OO63464A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0063464 A1 Akram et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) HIGH-SPEED DATA AND POWER SOURCE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,526,272 B1
 USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1
 USOO6199163B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1 Dumas et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 9 (54) HARD DISK PASSWORD LOCK 5,231,662 * 7/1993 van Rumpt et al.... 380/9 5,283,828
USOO6199163B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1 Dumas et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 9 (54) HARD DISK PASSWORD LOCK 5,231,662 * 7/1993 van Rumpt et al.... 380/9 5,283,828
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Cannon et al. USOO6549792B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Apr., 2003 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) JP ACCELEROMETER INFLUENCED COMMUNICATION DEVICE Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Cannon et al. USOO6549792B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Apr., 2003 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) JP ACCELEROMETER INFLUENCED COMMUNICATION DEVICE Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,832,425 B2 Tomasso (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2014
 USOO8832425B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Tomasso (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2014 (54) WIDE AREA NETWORK ACCESS 2010/0017599 A1* 1/2010 Sellars et al...... 713/156 MANAGEMENT COMPUTER
USOO8832425B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Tomasso (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2014 (54) WIDE AREA NETWORK ACCESS 2010/0017599 A1* 1/2010 Sellars et al...... 713/156 MANAGEMENT COMPUTER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0064.075 A1 Chatterjee US 20170064.075A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) CONTINUOUS CALL RECORDING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0064.075 A1 Chatterjee US 20170064.075A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) CONTINUOUS CALL RECORDING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0325960 A1 Agarwal et al. US 2013 0325960A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) CLIENTSIDE SHARING OF
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0325960 A1 Agarwal et al. US 2013 0325960A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) CLIENTSIDE SHARING OF
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
(12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
336w 330 FPGA / 330 MW} Compgnenf _/14 / 38 US 7,774,801 B1. Aug. 10, 2010 (56) (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: (12) United States Patent Fitkin
 US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
231 age sins N3 : as a. (12) United States Patent US 8,194,335 B2. Jun. 5, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 USOO8194,335B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,194,335 B2 Jun. 5, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) OPTICAL LENS ON WAFER LEVEL AND RELATED
USOO8194,335B2 (12) United States Patent Hsueh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,194,335 B2 Jun. 5, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) OPTICAL LENS ON WAFER LEVEL AND RELATED
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1. Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. and the callee. APPCAON SERVER.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0226362 A1 Kim et al. US 2010O226362A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) INTELLIGENT CALL MAPPING AND ROUTING FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0226362 A1 Kim et al. US 2010O226362A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) INTELLIGENT CALL MAPPING AND ROUTING FOR
III III IIII. United States Patent (19) 5,546,397. Mahany. Aug. 13, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Mahany (54) HIGH RELIABILITY ACCESS POINT FOR WIRELESS LOCAL AREANETWORK (75) Inventor: Ronald L. Mahany, Cedar Rapids, Iowa 73) Assignee: Norand Corporation, Cedar Rapids, Iowa
United States Patent (19) Mahany (54) HIGH RELIABILITY ACCESS POINT FOR WIRELESS LOCAL AREANETWORK (75) Inventor: Ronald L. Mahany, Cedar Rapids, Iowa 73) Assignee: Norand Corporation, Cedar Rapids, Iowa
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
FL (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Kwan (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2005
 US 2005O177868A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0177868A1 Kwan (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROTECTING Related U.S. Application Data AGAINST
US 2005O177868A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0177868A1 Kwan (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROTECTING Related U.S. Application Data AGAINST
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060O881 67A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0088167 A1 Bade et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR BACKUP AND RESTORE OF A CONTEXT
(19) United States US 20060O881 67A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0088167 A1 Bade et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR BACKUP AND RESTORE OF A CONTEXT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1
 USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,941,156 B2
 USOO6941156B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Mooney (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC HANDOFF FOR WIRELESS 5,774.805 A * 6/1998 Zicker... 455/426.1 PICONET MULTIMODE CELL PHONE
USOO6941156B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Mooney (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC HANDOFF FOR WIRELESS 5,774.805 A * 6/1998 Zicker... 455/426.1 PICONET MULTIMODE CELL PHONE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120327.933A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0327933 A1 Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADJACENCY DISCOVERY THROUGH (52) U.S. Cl.... 370/390 MULTICAST
US 20120327.933A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0327933 A1 Retana et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADJACENCY DISCOVERY THROUGH (52) U.S. Cl.... 370/390 MULTICAST
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,614,769 B1
 USOO6614769B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Erlick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATIONS UNIT FOR SEAMLESS 6,400,946 B1 6/2002 Vazvan et al.... 455/432 (NYSEYENEYORKS
USOO6614769B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Erlick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATIONS UNIT FOR SEAMLESS 6,400,946 B1 6/2002 Vazvan et al.... 455/432 (NYSEYENEYORKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
260k] 2801K].éGND MROUT I.12
![260k] 2801K].éGND MROUT I.12 260k] 2801K].éGND MROUT I.12](/thumbs/94/118236695.jpg) United States Patent [19] Nesheiwat et al. US00589 2777A [11] Patent Number: 5,892,777 [45] Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 [54] APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR OBSERVING THE MODE OF A MEMORY DEVICE [75] Inventors:
United States Patent [19] Nesheiwat et al. US00589 2777A [11] Patent Number: 5,892,777 [45] Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 [54] APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR OBSERVING THE MODE OF A MEMORY DEVICE [75] Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Pinard et al.
 United States Patent (19) Pinard et al. US005454032A 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 1995 54 METHOD OF ESTABLISHING COMMUNICATION LINK TO ONE OF MULTIPLE DEVICES ASSOCIATED WITH SINGLETELEPHONE
United States Patent (19) Pinard et al. US005454032A 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 1995 54 METHOD OF ESTABLISHING COMMUNICATION LINK TO ONE OF MULTIPLE DEVICES ASSOCIATED WITH SINGLETELEPHONE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
Query Request. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Listening Module. Expiration Module. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010463 A1 Christenson et al. US 2011 0010463A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) PROPOGATION OF DNS SERVER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010463 A1 Christenson et al. US 2011 0010463A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) PROPOGATION OF DNS SERVER
(12) United States Patent
 US008271592B2 (12) United States Patent Maltempo (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 18, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) METHODS, SYSTEMS, AND COMPUTER PROGRAM PRODUCTS FOR
US008271592B2 (12) United States Patent Maltempo (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 18, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) METHODS, SYSTEMS, AND COMPUTER PROGRAM PRODUCTS FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Jones et al.
 United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,931,133 B2
 USOO6931.133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,931,133 B2 Andrews et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 16, 2005 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM OF SECURELY 5,825,880 A * 10/1998 Sudia et al.... 713/18O
USOO6931.133B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,931,133 B2 Andrews et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 16, 2005 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM OF SECURELY 5,825,880 A * 10/1998 Sudia et al.... 713/18O
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,158,627 B1
 US007 158627 B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Lu (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR INHIBITING (56) References Cited SOFTSWITCH OVERLOAD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
US007 158627 B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Lu (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR INHIBITING (56) References Cited SOFTSWITCH OVERLOAD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013
 US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013
 (19) United States US 2013 O148568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0148568 A1 IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION DEVICE, (52) U.S. Cl. TETHERING
(19) United States US 2013 O148568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0148568 A1 IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION DEVICE, (52) U.S. Cl. TETHERING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent 2 Number: LOe: 5,616,900 Seewoster (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 1997
 IIII US005616900A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent 2 Number: LOe: 5,616,900 Seewoster (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 1997 54 ATM KEYPAD OPERATING DEVICE 4,234,932 11/1980 Gorgens... 364/900 4,453,074
IIII US005616900A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent 2 Number: LOe: 5,616,900 Seewoster (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 1997 54 ATM KEYPAD OPERATING DEVICE 4,234,932 11/1980 Gorgens... 364/900 4,453,074
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7941.543B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941.543 B2 Moussallam et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MIGRATING 2002/0169781 A1* 11/2002 Poole et al....
USOO7941.543B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941.543 B2 Moussallam et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MIGRATING 2002/0169781 A1* 11/2002 Poole et al....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
/ - 11 r e 100/ 108a 112. : fit. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States. 118a
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0071360A1 Crapp et al. US 2005.0071360A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR INTELLIGENT SCRIPT SWAPPING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0071360A1 Crapp et al. US 2005.0071360A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR INTELLIGENT SCRIPT SWAPPING
US A. United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,285, Frank et al. 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 8, 1994
 O III US0052854.96A United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,285,496 9 Frank et al. 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 8, 1994 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING ASECURE PAGNG SYSTEM 5,103,459 4/1992
O III US0052854.96A United States Patent (19) (11) Patent Number: 5,285,496 9 Frank et al. 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 8, 1994 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR PROVIDING ASECURE PAGNG SYSTEM 5,103,459 4/1992
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
SCSI routing table (90) and a SCSI to Fibre Channel routing table (92). The system receives a cross bus transfer of data
 US00604.1381A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,041,381 Hoese (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2000 54 FIBRE CHANNEL TO SCSI ADDRESSING OTHER PUBLICATIONS METHOD AND SYSTEM Hoese, Geoffrey B.,
US00604.1381A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,041,381 Hoese (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2000 54 FIBRE CHANNEL TO SCSI ADDRESSING OTHER PUBLICATIONS METHOD AND SYSTEM Hoese, Geoffrey B.,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007809394B1 () Patent No.: Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 20 (54) TRANSMIT POWER CONTROL INA (56) References Cited WIRELESS SYSTEM U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent US007809394B1 () Patent No.: Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 20 (54) TRANSMIT POWER CONTROL INA (56) References Cited WIRELESS SYSTEM U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO93 13456B2 (12) United States Patent Stephens et al. (10) Patent No.: US 9,313.456 B2 (45) Date of Patent: *Apr. 12, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) VIDEO COMMUNICATION
USOO93 13456B2 (12) United States Patent Stephens et al. (10) Patent No.: US 9,313.456 B2 (45) Date of Patent: *Apr. 12, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) VIDEO COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O324O76A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0324076 A1 Zerr et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PAIRING A Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O324O76A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0324076 A1 Zerr et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PAIRING A Publication Classification
The method includes: (1) Sending, by a client, a request to
 USOO5956490A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,956,490 Buchholz et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 21, 1999 54 METHOD, CLIENT DEVICE, SERVER AND 5,742,773 4/1998 Blomfield-Brown et al... 395/200.58
USOO5956490A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,956,490 Buchholz et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 21, 1999 54 METHOD, CLIENT DEVICE, SERVER AND 5,742,773 4/1998 Blomfield-Brown et al... 395/200.58
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sallberg USOO6519252B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 11, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR CONNECTING A CALL TO A MOBILE SUBSCRIBER CONNECTED TO THE INTERNET (75)
(12) United States Patent Sallberg USOO6519252B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 11, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR CONNECTING A CALL TO A MOBILE SUBSCRIBER CONNECTED TO THE INTERNET (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,763,102 B1
 USOO6763102B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 2004 (54) METHOD FOR HANDLING INCOMING 5,220,596 A * 6/1993 Patel... 379/93.24 CALLS DIRECTED TO AVIRTUAL
USOO6763102B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 13, 2004 (54) METHOD FOR HANDLING INCOMING 5,220,596 A * 6/1993 Patel... 379/93.24 CALLS DIRECTED TO AVIRTUAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090 154708A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0154708 A1 Kolar Sunder et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYMMETRIC KEY DISTRIBUTION FRAMEWORK FOR THE INTERNET
(19) United States US 20090 154708A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0154708 A1 Kolar Sunder et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYMMETRIC KEY DISTRIBUTION FRAMEWORK FOR THE INTERNET
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Al-Sahli (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 2010
 US 2010O332389A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0332389 A1 Al-Sahli (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 2010 (54) SIM CHIP BANK SYSTEMAND METHOD Publication Classification
US 2010O332389A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0332389 A1 Al-Sahli (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 2010 (54) SIM CHIP BANK SYSTEMAND METHOD Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2
 US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,408,074 B1
 USOO6408074B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: LOughran (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) HARDWARE ARCHITECTURE FOR A 4.914,697 A * 4/1990 Dabbish et al.... 380/28 CONFIGURABLE CIPHER DEVICE
USOO6408074B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: LOughran (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) HARDWARE ARCHITECTURE FOR A 4.914,697 A * 4/1990 Dabbish et al.... 380/28 CONFIGURABLE CIPHER DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
R. LOCAL. (12) United States Patent US 7,729,366 B2. Jun. 1, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: (51) Mok et al. (54) (75)
 US007729366B2 (12) United States Patent Mok et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 20 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) () () (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD, APPARATUS AND SYSTEM FOR NETWORK MOBILITY
US007729366B2 (12) United States Patent Mok et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Jun. 1, 20 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) () () (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD, APPARATUS AND SYSTEM FOR NETWORK MOBILITY
