(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
|
|
|
- Jean Mabel Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
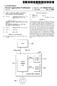
1 (19) United States US 20140O32702A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 Ozawa (43) Pub. Date: (54) CONTENT DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM, CONTROL APPARATUS, AND CONTENT (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G06F 12/0802 ( ) DISTRIBUTION METHOD USPC /213 (75) Inventor: Kazunori Ozawa, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Nec Corporation, Tokyo (JP) (57) ABSTRACT (21) Appl. No.: 14/111,967 A control apparatus calculates an access frequency for a (22) PCT Filed: Apr. 20, 2012 content item stored in each of a plurality of cache servers (86). PCT No.: PCT/UP2O12AO60689 temporarily holding the content item based on a number of accesses to the content item, determines an arrangement of S371 (c)(1), content items to the plurality of cache servers using at least (2), (4) Date: Oct. 15, 2013 one of load status of the plurality of cache servers, topology O O information of the mobile network, location information of a (30) Foreign Application Priority Data terminal requesting a content item, and the access frequency, Apr. 22, 2011 (JP)... loos instructs the plurality of cache servers to hold a content item according to the determined arrangement, and, upon recep Publication Classification tion of a request for a content item from a terminal, instructs a cache server holding the requested content item among the (51) Int. Cl. plurality of cache servers to send the requested content item G06F 2/08 ( ) via a packet forwarding apparatus. 1 OO 15 O MOBENEWORK C C 19 O O SGSN: GGSN APPAR ATUS N STR- SERVER BUTION SysA. - -r 19 2 All- 17 O SERVER iss APPARATUS Efs ssn AUS 1 65 As GGSN,,, E. 102 MOBLE s policy"., 's ERA. sy APPAR-, 's NA ATS ', ', -- SGSN APPAR GGSN sy N - ATS O 19 ON. CACHE SERVER 97. RNC APPAR ATUS
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 4 US 2014/ A1 0 N3] NOO
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 4 US 2014/ A1 NOON NOWOO LNGNOO C3S3B
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 4 US 2014/ A1 G 1,
5 Patent Application Publication Sheet 4 of 4 US 2014/ A1 "{O}}} NOO 0 \, N34 N00
6 CONTENT DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM, CONTROL APPARATUS, AND CONTENT DISTRIBUTION METHOD REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION This application is based upon and claims the ben efit of the priority of Japanese Patent Application No filed on Apr. 22, 2011, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein in its entirety by reference thereto. TECHNICAL FIELD 0002 The present invention relates to a content distribu tion system, control apparatus, and content distribution method, and particularly to a content distribution system, control apparatus for the same, and content distribution method that cache content (content item) Such as videos, images, audio, Software, and applications in a mobile network and distribute the content to terminals such as mobile tele phones, Smartphones, PCS (Personal Computers), and game devices. BACKGROUND As the speed and capacity of mobile networks increase, content distribution that distributes content to mobile terminals via a mobile network is becoming popular. In the near future, it is expected that the speed and capacity of mobile networks will increase even further due to technolo gies such as LTE (Long Term Evolution) and EPC (Evolved Packet Core) Patent Literature (PTL) 1 describes a technology that reduces the access time and prevents network congestion by providing a cache apparatus in a content distribution sys tem. PTL 1: 0005 Japanese Patent Kokai Publication No. JP A SUMMARY The entire disclosure of the above Patent Literature 1 is incorporated herein in its entirety by reference thereto. The following analysis is given by the present inventor It is predicted that the amount of data traffic in a mobile network will increase eight- to tenfold by 2013, com pared to the current amount, and that the majority of the data will be video content. Further, the size of video content has been increasing due to the performance increase of terminals associated with the rapid spread of Smartphones, and high capacity content in high-definition resolution is expected to be distributed in a mobile network in the near future Meanwhile, when distributing content such as images, videos, audio, Software, and applications in a con ventional mobile network, a content distribution server receives content requests from all terminals via a packet for warding apparatus and distributes content to all the terminals via the packet forwarding apparatus In such a configuration, however, the following problem occurs. First, when access from the terminals con centrates on popular content, the traffic reaches and concen trates on the content distribution server in the mobile network and a rapid increase in the networkload causes congestion in the mobile network. Especially when the number of the ter minals increases or the size of content is large, the network is often overcrowded and delay and packet loss occur, causing frozen images and intermittent audio on the terminal side Second, since the distance between the terminals and the content distribution server is long, it takes time for content to reach the terminals, increasing the delay time between a request issued by a terminal and the playback of the content, and deteriorating the end user's QoE (Quality of Experience) Therefore, there is a need in the art to avoid conges tion when content is distributed in a mobile network According to a first aspect of the present invention, there is provided a content distribution system. The content distribution system comprises in a mobile network: a plurality of packet forwarding apparatuses that forward a packet; a plurality of cache servers that temporarily hold a content item and send the contentitem via any one of the plurality of packet forwarding apparatuses; and a control apparatus that controls the plurality of cache servers. The control apparatus com prises: an access measurement unit that calculates an access frequency for a content item stored in each of the plurality of cache servers based on a number of accesses to the content item; a content arrangement determining unit that determines an arrangement of content items to the plurality of cache servers using at least one of load status of the plurality of cache servers, topology information of the mobile network, location information of a terminal requesting a content item, and the access frequency, and that instructs the plurality of cache servers to hold a content item according to the deter mined arrangement; and a cache server selection unit that, upon reception of a request for a content item from a terminal, instructs a cache server holding the requested content item among the plurality of cache servers to send the requested content item. The content arrangement determining unit may determine the arrangement of content items at a predeter mined time interval or when a predetermined condition is met According to a second aspect of the present inven tion, there is provided a control apparatus that controls in a mobile network a plurality of cache servers that temporarily hold a content item. The control apparatus comprises: an access measurement unit that calculates an access frequency for a content item stored in each of the plurality of cache servers based on a number of accesses to the content item; a content arrangement determining unit that determines an arrangement of content items to the plurality of cache servers using at least one of load status of the plurality of cache servers, topology information of the mobile network, location information of a terminal requesting a content item, and the access frequency, and that instructs the plurality of cache servers to hold a content item according to the determined arrangement; and a cache server selection unit that, upon reception of a request for a content item from a terminal, instructs a cache server holding the requested content item among the plurality of cache servers to send the requested content item via a packet forwarding apparatus. The content arrangement determining unit may determine the arrange ment of content items at a predetermined time interval or when a predetermined condition is met According to a third aspect of the present invention, there is provided a content distribution method. The content distribution method comprises: by a control apparatus that controls in a mobile network a plurality of cache servers that temporarily hold a content item, calculating an access fre
7 quency for a content item stored in each of the plurality of cache servers based on a number of accesses to the content item; determining an arrangement of content items to the plurality of cache servers using at least one of load status of the plurality of cache servers, topology information of the mobile network, location information of a terminal request ing a content item, and the access frequency; instructing the plurality of cache servers to hold a content item according to the determined arrangement; and upon reception of a request for a content item from a terminal, instructing a cache server holding the requested content item among the plurality of cache servers to send the requested content item via a packet forwarding apparatus. The control apparatus may determine the arrangement of content items at a predetermined time interval or when a predetermined condition is met The present invention provides the following advan tage, but not restricted thereto. According to a content distri bution system, control apparatus, and content distribution method relating to the present invention, congestion can be avoided when content is distributed in a mobile network. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0016 FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of a content distribution system according to a first exemplary embodiment FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating an example of a control apparatus in the content distribution system accord ing to the first exemplary embodiment FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating an example of a cache server in the content distribution system according to the first exemplary embodiment FIG. 4 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of a content distribution system relating to a second exem plary embodiment. PREFERRED MODES In the present disclosure, there are various possible modes, which include the following, but not restricted thereto. First, a summary of the present invention will be given. Note that drawing reference signs in the Summary are illustrated examples solely for facilitating understanding and are not intended to limit the present invention to illustrated examples With reference to FIGS. 1, 2, and 4, a content dis tribution system of the present invention comprises in a mobile network (150, 250): a plurality of packet forwarding apparatuses (SGSN/GGSN apparatuses 1901 to 190 N in FIG. 1 or S/P-GW apparatuses to 290 N in FIG. 4) that forward a packet; a plurality of cache servers (110 1 to 110 N) that temporarily hold a content item and send the content item via any one of the plurality of packet forwarding appa ratuses (1901 to 190 N to 290 N); and a control apparatus (160) that controls the plurality of cache servers (110 1 to 110 N). The control apparatus (160) comprises: an access measurement unit (184) that calculates an access fre quency for a content item stored in each of the plurality of cache servers (110 1 to 110 N) based on a number of accesses to the content item; a content arrangement determin ing unit (185) that determines an arrangement of content items to the plurality of cache servers (110 1 to 110 N) using at least two of load status of the plurality of cache servers (110 1 to 110 N), topology information of the mobile net work (150, 250), location information of a terminal (mobile terminal 170) requesting a content item, and the access fre quency, and that instructs the plurality of cache servers (110 1 to 110 N) to hold a content item according to the determined arrangement; and a cache server selection unit (187) that, upon reception of a request for a content item from a terminal (170), instructs a cache server holding the requested content item among the plurality of cache servers (110 1 to 110 N) to send the requested content item According to the content distribution system relat ing to the present invention, congestion can be avoided when content is distributed in the mobile network (150,250) Further, in the present invention, the following modes are possible. (Mode 1) A content distribution system may be the content distribution system according to the first aspect. (Mode 2) The content arrangement determining unit may arrange a content item to a cache server with a Smallest X Cij*A*Swhere Ajdenotes an access frequency for a jth content item, Sa size of the jth content item, and Cia cost function for an ith cache server among the plurality of cache SWCS. (Mode 3) The content arrangement determining unit may cal culate the cost function Cibased on load information of the ith cache server among the plurality of cache servers, the topology information of the mobile network, and the location information of the terminal, or on the load information and the topology information. (Mode 4) The content arrangement determining unit may determine an arrangement of content items at a predeter mined time interval or when a predetermined condition is met. (Mode 5) The access measurement unit may collect a number of accesses to a content item stored in each of the plurality of cache servers at a predetermined time interval or when a predetermined condition is met (Mode 6) The plurality of packet forwarding apparatuses may be SGSN apparatuses, GGSN apparatuses, or SGSN/GGSN apparatuses in a mobile network, or S-GW apparatuses, P-GW apparatuses, or S/P-GW apparatuses in a mobile EPC network. (Mode 7) 0030 The content may include at least one of video, still image, Voice, audio, software, application, and data. (Mode 8) A control apparatus may be the control apparatus according to the second aspect.
8 (Mode 9) In the control apparatus, the content arrangement determining unit may arrange a content item to a cache server with a smallest X Cij Aj*Swhere Ajdenotes an access fre quency for ajth content item, Sa size of the jth content item, and Ci a cost function for an ith cache server among the plurality of cache servers. (Mode 10) In the control apparatus, the content arrangement determining unit may calculate the cost function Cibased on load information of the ith cache server among the plurality of cache servers, the topology information of the mobile net work, and the location information of the terminal, or on the load information and the topology information. (Mode 11) A content distribution method may be the content distribution method according to the third aspect. (Mode 12) In the content distribution method, the control appa ratus may arrange a content item to a cache server with a smallestx CiAj*Swhere Ajdenotes an access frequency a jth contentitem, Sa size of the jth content item, and Cia cost function for an ith cache server among the plurality of cache SWCS. (Mode 13) In the content distribution method, the control appa ratus may calculate the cost function Cibased on load infor mation of the ith cache server among the plurality of cache servers, the topology information of the mobile network, and the location information of the terminal, or on the load infor mation and the topology information. First Exemplary Embodiment A configuration and operation of a content distribu tion system according to a first exemplary embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 3. Note that the content mentioned in the exemplary embodiments below is assumed to be video, but the same configuration can be employed when the content is a still image, audio, Voice, Software, application, and data FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example of the content distribution system of the present exemplary embodiment. In the present exemplary embodi ment, a 3G (3rd Generation) mobile network is used as the mobile network 150, and an SGSN/GGSN apparatus is used as the packet forwarding apparatus In FIG. 1, as content 100, a distribution server appa ratus 120 stores a compression-encoded bit stream of content including at least one type of content (video, still images, audio, voice, etc.) or a file storing a compression-encoded bit stream in advance Over the mobile network 150, Nnumber (N2) of the SGSN/GGSN apparatuses 1901 to 190 N are disposed, RNC (Radio Network Controller) apparatuses 1951 to 195 L (L 2) are connected to the SGSN/GGSN apparatus 1901, and RNC apparatuses 1971 to 197 L are connected to the SGSN/GGSN apparatus 190 N. Note that L. number of RNC apparatuses are connected to the SGSN/GGSN appara tus as well, but they are omitted in FIG. 1 to save space. Further, M number (M2) of base station apparatuses are connected to each RNC apparatus. For instance, M number of base station apparatuses to 180 Mare connected to the RNC apparatus Here, one cache server is connected to each SGSN/ GGSN apparatus. For instance, to the SGSN/GGSN appara tus 1901, the cache server is connected Further, N number (N2) of the cache servers to 110 N are connected by a cache server interface to each other. Further, N number of the cache servers to 110 N are connected to the single control apparatus The mobile terminal 170 writes an IP (Internet Pro tocol) address of the distribution server apparatus 120 and issues a delivery connection request message. Then, a base station apparatus in the service area (any one of the base station apparatuses 1811 to 181 M in the case of FIG. 1) receives the connection request message and sends the con nection request message to the RNC apparatus (the RNC apparatus 195 L in the case of FIG. 1) that manages the base station apparatuses. 0044) The RNC apparatus 195 L receives the connection request message from the base station apparatus, stores the connection request message, the IP address of the distribution server apparatus 120, and an IP address of the mobile terminal 170 in the payload of the GTP-U (GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) Tunneling Protocol for User Plane) protocol, and forwards a GTP packet to the SGSN/GGSN apparatus 1901 that manages the RNC apparatuses 1951 to 195 L. Here, the SGSN/GGSN apparatus refers to a configuration in which an SGSN (serving GPRS SupportNode) apparatus and a GGSN (Gateway GPRS Support Node) apparatus are inte grated Next, the SGSN/GGSN apparatus 1901 receives the GTP packet The cache server is connected to the SGSN/ GGSN apparatus 1901 and the cache server 110 N is con nected to the SGSN/GGSN apparatus 190 N To the control apparatus 160, the cache servers to 110 N and a policy apparatus 165 are connected. The control apparatus 160 receives the load status informa tion and the access level information for each piece of the content from each cache server, receives the location infor mation of the mobile terminal 170 from the packet forwarding apparatus, receives the network topology information from the policy apparatus 165, determines the arrangement of the content to the cache servers using at least two of these pieces of information, and issues a content arrangement instruction to each cache server. Further, according to criteria based on the location information of the mobile terminal 170 and the load status information, the control apparatus 160 selects a cache server meeting the criteria in response to a content request from the mobile terminal 170, and instructs the selected cache server to distribute the content to the mobile terminal 170 via the packet forwarding apparatus Next, the configuration of the control apparatus 160 will be described with reference to FIG. 2. FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example of the control apparatus 160. With reference to FIG. 2, the control apparatus 160 comprises a control signal transmitting/receiving unit 161, the access measurement unit 184, the content arrange ment determining unit 185, the cache server selection unit 187, a content map creation/storage unit 167, and a content acquirement instruction unit 168.
9 0049. The control signal transmitting/receiving unit 161 receives the access frequency information of each piece of the content and the load information of each cache server from each of the cache servers to 110 N, outputs the former to the access measurement unit 184, and outputs the latter to the content arrangement determining unit 185 and the cache server selection unit 187. Further, the control signal transmit ting/receiving unit 161 receives information Such as the cost of each link from the policy apparatus 165 as the network topology information, and outputs it to the content arrange ment determining unit 185. Furthermore, the control signal transmitting/receiving unit 161 receives the location informa tion of the mobile terminal 170 from the packet forwarding apparatus 1901, and outputs it to the content arrangement determining unit 185 and the cache server selection unit The access measurement unit 184 collects the num ber of accesses to each piece of the content from each cache server at each predetermined time interval or whenever a predetermined condition is met, add them up for each piece of the content, aggregates the access frequency to all the cache servers for each piece of the content, and outputs the results to the content arrangement determining unit 185. Here, for instance, the predetermined condition may be when the num ber of accesses to particular content exceeds a predetermined threshold value, or any other condition may be used The content arrangement determining unit 185 receives the load information of the cache servers, the net work topology information, and the location information of the mobile terminal 170 from the control signal transmitting/ receiving unit 161, receives the access frequency of each piece of the content from the access measurement unit 184, calculates Mathematical Formula 1 for each of the plurality of pieces of the content, and determines a cache server that should hold the content. Since the total storage capacity of all the cache servers is limited, it is not realistic to determine a cache server that should hold each piece of the content. There fore, the arrangement of content may be determined within a predetermined and restricted range of content. For instance, a method that restricts the content to the one having access levels, collected by the access measurement unit 185, in the top P can be employed From Math. 1, the content arrangement determining unit 185 selects a cache serveri with the smallest Di. Here, Di in Math. 1 denotes an evaluation function for an ith cache server, Cia cost function foranith cache server, Ajthe access frequency for anjith piece of the content; and Sthe size of the jthpiece of the content. Further, X, represents the sum regard ing j. Here, the cost function Ci is calculated according to criteria predetermined from the network topology informa tion, the load information of the ith cache server, and the location information of the mobile terminal Three types of information (the network topology information, the load information, and the location informa tion) are used in Math. 1, but two types may be used as well. When two types are used, criteria consisting of the network information and the load information of the cache servers may be employed for the calculation of the cost function Cij Further, the content arrangement determining unit 185 may perform the calculation of the content arrangement by Math. 1 and instructs a cache server to cache the target content at a predetermined time interval or whenever a pre determined condition is met. Here, for instance, the predeter mined condition may be when the access frequency collected by the access measurement unit 184 changes compared to the access frequency in the past and the degree of the change exceeds a predetermined threshold value, or any other condi tion may be used. Further, the content arrangement determin ing unit 185 may use a mathematical formula other than Math The cache server selection unit 187 receives the location information of the mobile terminal 170, the load information of each cache server, and the information of the content requested by the mobile terminal 170 (for instance the URL (Uniform Resource Locator) of the content, etc.) from the control signal transmitting/receiving unit 161 and receives a content map from the content map creation/storage unit 167. Here, the content map is a map that indicates which content each cache server caches. The cache server selection unit 187 first selects a cache server group that caches the content requested by the mobile terminal 170, and selects a cache server with a load not greater than a predetermined threshold value and closest to the mobile terminal 170 using the load information and the location information. The cache server selection unit 187 instructs the selected cache server to distribute the content requested by the mobile terminal 170 to the packet forwarding apparatus Next, the content map creation/storage unit 167 receives a content list from each of the cache servers to 110 N via the control signal transmitting/receiving unit 161 at a predetermined time interval, creates the content map that shows which content is temporarily stored in which cache server, and stores it The content acquirement instruction unit 168 reads the content map from the content map creation/storage unit 167 and determines whether or not the content acquirement instruction unit 168 itself temporarily stores the content requested by the mobile terminal 170. If it does, the content acquirement instruction unit 168 does not send any notifica tion to the other cache servers. On the other hand, if it does not, after determining which cache server among the cache servers other than this cache server stores the content from the content map, the content acquirement instruction unit 168 outputs a content acquirement notification to the cache server via the control signal transmitting/receiving unit 161. The content acquirement notification includes the following two notifications, i.e., a notification of the IP address of the cache server that stores the requested content and a notification that instructs to acquire the content. Further, when the requested content is not stored by any cache server, the IP address of the distribution server apparatus 120 is notified, instead of the IP address of the cache server Next, as a configuration example of the cache server, the configuration of the cache server connected to the SGSN/GGSN apparatus 1901 will be described with refer ence to FIG. 3. Note that, since the other cache servers to 110 N are configured identically to the cache server 110 1, the explanation will be omitted FIG.3 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example of the cache server With reference to FIG.3, the cache server comprises a control signal transmit ting/receiving unit 111, an analysis unit 115, a content tem porary storage unit 113, a content list creation unit 116, a content acquirement unit 112, an access counting unit 130, and a load status detection unit The control signal transmitting/receiving unit 111 receives the connection request message and the reception IP
10 address of the mobile terminal 170 from the mobile terminal 170, the GTP packet that stores the URL of the requested content, and the location information of the mobile terminal 170 from the SGSN/GGSN apparatus 1901, and outputs these pieces of the information to the analysis unit The analysis unit 115 reads the content of the con nection request message stored in the payload of the GTP packet, extracts information Such as the reception IP address of the mobile terminal 170 and the URL of the requested content, and sends these pieces of information to the control apparatus 160 via the control signal transmitting/receiving unit 111. Further, the analysis unit 115 sends the location information of the mobile terminal 170 to the control appa ratus According to a content arrangement decision instruction sent from the control apparatus 160 and received via the control signal transmitting/receiving unit 111, the content acquirement unit 112 reads the content instructed to be placed from another cache server or the distribution server apparatus 120, and stores the content in the content temporary storage unit The content temporary storage unit 113 temporarily stores the content acquired from another cache server or the distribution server apparatus The content list creation unit 116 creates a content list of all the content stored in the content temporary storage unit 113 at a predetermined time interval or when a predeter mined condition is met, and sends the content list to the control apparatus 160 via the control signal transmitting/ receiving unit 111 at a predetermined time interval The access counting unit 130 counts the number of the connection requests from the mobile terminal 170 within a predetermined time range for each piece of the content stored by the cache server in the content temporary storage unit 113, calculates the number of accesses for each piece of the content, and sends the results to the control apparatus 160 via the control signal transmitting/receiving unit The load status detection unit 135 measures a load status Q of the cache server at a predetermined time interval or when a predetermined condition is met, and sends the measured load status Q to the control apparatus 160 via the control signal transmitting/receiving unit 111. Here, for instance, the predetermined condition may be when the con trol apparatus 160 requests the cache server to transmit the load status or any other condition may be used For instance, the load status detection unit 135 may calculate the load status Q according to Mathematical For mula In Math. 2, Q denotes an index indicating the load status of the cache server; S the size of a jth piece of the content temporarily stored in the cache server; and Aj the number of requests for the jth piece of the content. Note that the load condition status? detection unit 135 may use any other criteria In FIG. 1, one SGSN/GGSN apparatus is connected to one cache server, but a single cache server may be con nected to a plurality of SGSN/GGSN apparatuses, or one SGSN/GGSN apparatus may be connected to a plurality of cache servers The distribution server apparatus 120 may be con nected to the cache servers to 110 N. (0071. Further, in FIG. 1, the SGSN/GGSN apparatus that integrates an SGSN apparatus with a GGSN apparatus is used, but a configuration in which the SGSN apparatus and the GGSN apparatus are separated may be employed. In this configuration, at least one cache server may be connected to the SGSN apparatus or the GGSN apparatus. (0072 Further, the mobile terminal 170 may be a mobile telephone, Smartphone, or PC with a data communication card, as long as it can communicate with a mobile 3G net work. Second Exemplary Embodiment A configuration and operation of a content distribu tion system according to a second exemplary embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 4. FIG. 4 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example of the content distribution system of the present exemplary embodiment. In FIG. 4, since components designated with the same numbers as in FIG. 1 operate identically to those in FIG. 1, the expla nation will be omitted. (0074. With reference to FIG.4, an LTE (Long Term Evo lution)/epc (Evolved Packet Core) network, which is a 3.9" generation mobile network, is used as the mobile network 250 in the present exemplary embodiment, instead of the 3G mobile packet network. In the LTE, only enodeb apparatuses are used, instead of the functions of the base station apparatus and the RNC apparatus. (0075) Further, in the EPC, an S/P-GW (Serving/Packet Data Network Gateway) apparatus is connected to the eno deb apparatus. Here, the S/P-GW apparatus means a configu ration in which an S-GW apparatus and a P-GW apparatus are integrated. With reference to FIG.4, M number of enodeb apparatuses are connected to a single S/P-GW apparatus. For instance, enodebapparatuses to 260 Mare connected to an S/P-GW apparatus Here, one cache server is connected to each S/P-GW apparatus. For instance, the cache server is connected to the S/P-GW apparatus The mobile terminal 170 writes the IP address of the distribution server apparatus 120 and issues a delivery con nection request message. Then, an enodeb apparatus in the service area of the mobile terminal 170 (any one of the eno deb apparatuses to 261 M in the case of FIG. 4) receives the connection request message. One of the enodeb apparatuses to 261 M Stores the connection request message, the IP address of the distribution server apparatus 120, and the IP address of the mobile terminal 170 in the payload of the GTP protocol, and forwards a GTP packet to an S/P-GW apparatus The cache server has the same configuration as the one shown in FIG.3. In the present exemplary embodi ment, however, the control signal transmitting/receiving unit 111 is connected to the S/P-GW apparatus Therefore, the control signal transmitting/receiving unit 111 receives the connection request message from the mobile terminal 170, the GTP packet storing the IP address, etc., and the location information of the mobile terminal 170 from the S/P-GW apparatus Further, each of the other cache servers to 110 N performs the exchange described above with the connected S/P-GW apparatus Further, in the present exemplary embodiment, the distribution server apparatus 120 is connected to the S/P-GW apparatuses to 290 N.
11 0080. In FIG. 4, one cache server is connected to one single S/P-GW apparatus, but a cache server may be con nected to a plurality of S/P-GW apparatuses, or one S/P-GW apparatus may be connected to a plurality of cache servers Further, the distribution server apparatus 120 may be connected to the cache servers to 110 N In FIG. 4, the S/P-GW apparatus that integrates an S-GW apparatus with a P-GW apparatus is used, but a con figuration in which the S-GW apparatus and the P-GW appa ratus are separated may be employed. In this configuration, at least one cache server may be connected to the S-GW appa ratus or the P-GW apparatus. I0083. Further, the mobile terminal 170 may be a mobile telephone, Smartphone, or PC with a data communication card, as long as it can communicate with a 3.9G mobile network According to the content distribution systems relat ing to the first and the second exemplary embodiments, the following effects can be obtained. First, by having the control apparatus determine the arrangement of content in the cache servers using at least two evaluation criteria out of the load status information, the access level information, the location information of the terminal, and the network topology infor mation and instruct a cache server to cache the placed content, the traffic of the mobile network can be dispersed, and the concentration of the network load and congestion in the mobile network can be avoided even when accesses concen trate on popular content. At this time, even with increases in the number of terminals and the size of the content, delay or packet loss will not occur, and the terminals will not experi ence any frozen image and intermittent audio Second, by having the control apparatus select a cache server that meets predetermined criteria based on the location information of the terminal, and having this cache server distribute the content to the terminal, the time it takes for the content to reach the terminal can be reduced and the delay time between the request issuance by the terminal and the content playback can be greatly shortened since the dis tance of content delivery can be shortened compared to the conventional method in which content is delivered from a distribution server, greatly improving the end user's QoE (Quality of Experience) Third, the terminals do not need to be modified in order to achieve the first and the second effects Further, the disclosure of Patent Literature listed above is incorporated herein in its entirety by reference thereto. It should be noted that other objects, features and aspects of the present invention will become apparent in the entire disclosure and that modifications may be done without departing the gist and scope of the present invention as dis closed herein and claimed as appended herewith. Also it should be noted that any combination of the disclosed and/or claimed elements, matters and/or items may fall under the modifications aforementioned. REFERENCE SIGNS LIST : content to 110 N: cache server : control signal transmitting/receiving unit 0091) 112: content acquirement unit : content temporary storage unit : analysis unit 0094) 116: content list creation unit : distribution server apparatus : access counting unit : load status detection unit : mobile network ( : control apparatus : control signal transmitting/receiving unit : policy apparatus : content map creation/storage unit 0103) 168: content acquirement instruction unit : mobile terminal to 180 M, 1811 to 181 M, 1821 to 182 M, 1831 to 183 M: base station apparatus : access measurement unit : content arrangement determining unit 0108) 187: cache server selection unit 0109) 1901 to 190 N: SGSN/GGSN apparatus to 195 L, 1971 to 197 L: RNC apparatus : mobile network to 260 M, 2611 to 261 M, to 262 M: enodeb apparatus to 290 N: S/P-GW apparatus 1. A content distribution system, comprising in a mobile network: a plurality of packet forwarding apparatuses that forward a packet; a plurality of cache servers that temporarily hold a content item and send the content item via any one of the plu rality of packet forwarding apparatuses; and a control apparatus that controls the plurality of cache servers, the control apparatus comprises: an access measurement unit that calculates an access fre quency for a content item stored in each of the plurality of cache servers based on a number of accesses to the content item; a content arrangement determining unit that determines an arrangement of content items to the plurality of cache servers using at least one of load status of the plurality of cache servers, topology information of the mobile net work, location information of a terminal requesting a contentitem, and the access frequency, and that instructs the plurality of cache servers to hold a content item according to the determined arrangement; and a cache server selection unit that, upon reception of a request for a content item from a terminal, instructs a cache server holding the requested content item among the plurality of cache servers to send the requested con tent item, the content arrangement determining unit determines the arrangement of content items at a predetermined time interval or when a predetermined condition is met. 2. The content distribution system according to claim 1, the content arrangement determining unit arranges a con tent item to a cache server with a smallest X Cij*A*S where A denotes an access frequency for a jth content item, S a size of the jth content item, and Cilja cost function for an ith cache server among the plurality of cache servers. 3. The content distribution system according to claim 2, the content arrangement determining unit calculates the cost function Cij based on load information of the ith cache server among the plurality of cache servers, the topology information of the mobile network, and the
12 location information of the terminal, or on the load infor mation and the topology information. 4. (canceled) 5. The content distribution system according to claim 1, the access measurement unit collects a number of accesses to a content item stored in each of the plurality of cache servers at a predetermined time interval or when a pre determined condition is met. 6. The content distribution system according to claim 1, the plurality of packet forwarding apparatuses are SGSN apparatuses, GGSN apparatuses, or SGSN/GGSN appa ratuses in a mobile network, or S-GW apparatuses, P-GW apparatuses, or S/P-GW apparatuses in a mobile EPC network. 7. The content distribution system according to claim 1, the content item include at least one of video, still image, Voice, audio, Software, application, and data. 8. A control apparatus that controls in a mobile network a plurality of cache servers that temporarily hold a content item, the control apparatus comprising: an access measurement unit that calculates an access fre quency for a content item stored in each of the plurality of cache servers based on a number of accesses to the content item; a content arrangement determining unit that determines an arrangement of content items to the plurality of cache servers using at least one of load status of the plurality of cache servers, topology information of the mobile net work, location information of a terminal requesting a contentitem, and the access frequency, and that instructs the plurality of cache servers to hold a content item according to the determined arrangement; and a cache server selection unit that, upon reception of a request for a content item from a terminal, instructs a cache server holding the requested content item among the plurality of cache servers to send the requested con tent item via a packet forwarding apparatus, the content arrangement determining unit determines the arrangement of content items at a predetermined time interval or when a predetermined condition is met. 9. The control apparatus according to claim 8, the content arrangement determining unit arranges a con tent item to a cache server with a smallest X,Cij*A*S where Adenotes an access frequency for a jth content item, S a size of the jth content item, and Cilja cost function for an ith cache server among the plurality of cache servers. 10. The control apparatus according to claim 9, the content arrangement determining unit calculates the cost function Cij based on load information of the ith cache server among the plurality of cache servers, the topology information of the mobile network, and the location information of the terminal, or on the load infor mation and the topology information. 11. A content distribution method, comprising: by a control apparatus that controls in a mobile network a plurality of cache servers that temporarily hold a content item, calculating an access frequency for a content item stored in each of the plurality of cache servers based on a number of accesses to the content item; determining an arrangement of content items to the plural ity of cache servers using at least one of load status of the plurality of cache servers, topology information of the mobile network, location information of a terminal requesting a content item, and the access frequency; instructing the plurality of cache servers to hold a content item according to the determined arrangement; and upon reception of a request for a content item from a terminal, instructing a cache server holding the requested content item among the plurality of cache servers to send the requested content item via a packet forwarding apparatus, the control apparatus determines the arrangement of con tent items at a predetermined time interval or when a predetermined condition is met. 12. The content distribution method according to claim 11, the control apparatus arranges a content item to a cache server with a smallest X Cij*Aj*Swhere Ajdenotes an access frequency a jth content item, Sa size of the jth content item, and Cilja cost function for an ith cache server among the plurality of cache servers. 13. The content distribution method according to claim 12, the control apparatus calculates the cost function Cibased on load information of the ith cache server among the plurality of cache servers, the topology information of the mobile network, and the location information of the terminal, or on the load information and the topology information.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013
 (19) United States US 2013 O148568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0148568 A1 IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION DEVICE, (52) U.S. Cl. TETHERING
(19) United States US 2013 O148568A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0148568 A1 IIMOR (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION DEVICE, (52) U.S. Cl. TETHERING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
ED 302C A t 302B (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. streaming media server
 (19) United States US 201401 15115A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0115115 A1 Kuang (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PLAYING Publication Classification STREAMING
(19) United States US 201401 15115A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0115115 A1 Kuang (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PLAYING Publication Classification STREAMING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 US 20170069991A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0069991 A1 HOmb0 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) ELECTRONIC APPARATUS H05K L/4 (2006.01) (71) Applicant:
US 20170069991A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0069991 A1 HOmb0 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) ELECTRONIC APPARATUS H05K L/4 (2006.01) (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020040308A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0040308A1 Hasegawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2002 (54) METHOD OF VALIDATING ENTRANCE TO (30) Foreign
(19) United States US 20020040308A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0040308A1 Hasegawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2002 (54) METHOD OF VALIDATING ENTRANCE TO (30) Foreign
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Kitazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 29, 2004
 US 20040O82364A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0082364 A1 Kitazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 29, 2004 (54) BASE STATION, RADIO COMMUNICATION (30) Foreign
US 20040O82364A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0082364 A1 Kitazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 29, 2004 (54) BASE STATION, RADIO COMMUNICATION (30) Foreign
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140355048A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0355048A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF MOBILE Publication Classification
US 20140355048A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0355048A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152762 A1 Asano et al. US 2006O152762A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) IMAGE FORMING APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152762 A1 Asano et al. US 2006O152762A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) IMAGE FORMING APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 201600.48535A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0048535 A1 Shaw (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) INFORMATION SEARCHING METHOD (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant:
US 201600.48535A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0048535 A1 Shaw (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) INFORMATION SEARCHING METHOD (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013
 US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198313 A1 Kitamura et al. US 2006O198313A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198313 A1 Kitamura et al. US 2006O198313A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR
$26) 6, 2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun.
 (19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
US 20150358424A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0358424 A1 BRAUN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2015 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING (52) U.S. Cl. DATABASE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0128245A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0128245 A1 Inagaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) DISTANCE MEASUREMENT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010.0128245A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0128245 A1 Inagaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) DISTANCE MEASUREMENT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
Gammalcode. Frame 1, Frame 2. drive signal. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Timing code.
 (19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Niwa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008
 (19) United States US 20080000981A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000981 A1 Niwa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) BARCODE PRINT DATA CREATION (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20080000981A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000981 A1 Niwa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) BARCODE PRINT DATA CREATION (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0140065 A1 FISHER et al. US 201701 40065A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) AUTOMATED ASSISTANCE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0140065 A1 FISHER et al. US 201701 40065A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) AUTOMATED ASSISTANCE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2
 US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(FSN JSO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.253,522 B2
 US009,22B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9.3,522 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2016 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING DATA FLOW (56) References Cited OF MIRRORLINK SYSTEM (71) Applicant:
US009,22B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9.3,522 B2 Lee (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2016 (54) METHOD FOR CONTROLLING DATA FLOW (56) References Cited OF MIRRORLINK SYSTEM (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080117477A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0117477 A1 Fujise (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2008 (54) FACSIMILE APPARATUS AND CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 20080117477A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0117477 A1 Fujise (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2008 (54) FACSIMILE APPARATUS AND CONTROL METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009009 1775A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0091775 A1 Yoshida (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 9, 2009 (54) IMAGE FORMING SYSTEM UTILIZING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2009009 1775A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0091775 A1 Yoshida (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 9, 2009 (54) IMAGE FORMING SYSTEM UTILIZING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0185389A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0185389 A1 Nakamura (43) Pub. Date: Jul.18, 2013 (54) IN-VEHICLE GATEWAY APPARATUS, COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2013 0185389A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0185389 A1 Nakamura (43) Pub. Date: Jul.18, 2013 (54) IN-VEHICLE GATEWAY APPARATUS, COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0240763 A1 Urakawa et al. US 20140240763A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) FUNCTION EXECUTION DEVICE Applicants:Yutaka
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0240763 A1 Urakawa et al. US 20140240763A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) FUNCTION EXECUTION DEVICE Applicants:Yutaka
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9426741B2 (12) United States Patent Wu et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 9.426,741 B2 Aug. 23, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) () (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING
USOO9426741B2 (12) United States Patent Wu et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 9.426,741 B2 Aug. 23, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) () (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9442667B2 (12) United States Patent Drosch (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.442,667 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (30) (51) (52) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR
USOO9442667B2 (12) United States Patent Drosch (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.442,667 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (30) (51) (52) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
SCSI routing table (90) and a SCSI to Fibre Channel routing table (92). The system receives a cross bus transfer of data
 US00604.1381A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,041,381 Hoese (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2000 54 FIBRE CHANNEL TO SCSI ADDRESSING OTHER PUBLICATIONS METHOD AND SYSTEM Hoese, Geoffrey B.,
US00604.1381A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,041,381 Hoese (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2000 54 FIBRE CHANNEL TO SCSI ADDRESSING OTHER PUBLICATIONS METHOD AND SYSTEM Hoese, Geoffrey B.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
Printer. Data input/ Printout unit. processor) Control unit. (Raster image RIP. Display unit. Image
 (19) United States US 20070057978A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0057978A1 Hagiwara (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2007 (54) PRINTER AND PRINTING METHOD (75) Inventor: Takahiro
(19) United States US 20070057978A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0057978A1 Hagiwara (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2007 (54) PRINTER AND PRINTING METHOD (75) Inventor: Takahiro
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O104164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0104164 A1 YASUDA (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) CAMERA BODY (71) Applicant: PANASONIC CORPORATION, Osaka
(19) United States US 2015O104164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0104164 A1 YASUDA (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) CAMERA BODY (71) Applicant: PANASONIC CORPORATION, Osaka
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 20060285691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0285691 A1 Chin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 21, 2006 (54) NATIONAL SECURITY ALERTING IN COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO8836702B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,702 B2 Yoon et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) RAY TRACING CORE AND METHOD FOR (58) Field of Classification Search PROCESSING
(12) United States Patent USOO8836702B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,702 B2 Yoon et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) RAY TRACING CORE AND METHOD FOR (58) Field of Classification Search PROCESSING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0025825 A1 UKKOLA et al. US 2014.0025825A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND APPARATUS IN A WEB SERVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0025825 A1 UKKOLA et al. US 2014.0025825A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) METHOD AND APPARATUS IN A WEB SERVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Frequency. Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 (19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,399,323 B1
 US0093.99323B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2016 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL PRINTING USPC... 425/470; 264/401, 497, 212, 308 STRUCTURE See application
US0093.99323B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2016 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL PRINTING USPC... 425/470; 264/401, 497, 212, 308 STRUCTURE See application
(12) United States Patent
 US007 124333B2 (12) United States Patent Fukushima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,124.333 B2 Oct. 17, 2006 (54) RETRANSMISSION PACKET STRUCTURE HAVING MULTIPLE SEQUENCE NUMBERS (75)
US007 124333B2 (12) United States Patent Fukushima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,124.333 B2 Oct. 17, 2006 (54) RETRANSMISSION PACKET STRUCTURE HAVING MULTIPLE SEQUENCE NUMBERS (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2. Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100091772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/009 1772 A1 CederVallet al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2010 (54) PROVIDING IPTV MULTICASTS (76) Inventors: Mats
(19) United States US 20100091772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/009 1772 A1 CederVallet al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2010 (54) PROVIDING IPTV MULTICASTS (76) Inventors: Mats
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. (52) U.S. Cl. OBAN REQUEST WDEO SEGMENT AJ)O RANGE.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282773 A1 Hurst US 20140282773A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) CHUNKING OF MULTIPLE TRACKAUDIO
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282773 A1 Hurst US 20140282773A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) CHUNKING OF MULTIPLE TRACKAUDIO
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150277823A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0277823 A1 NAKAYAMA (43) Pub. Date: (54) PRINTERAPPARATUS, PRINTING METHOD, AND NON-TRANSTORY COMPUTER READABLE
(19) United States US 20150277823A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0277823 A1 NAKAYAMA (43) Pub. Date: (54) PRINTERAPPARATUS, PRINTING METHOD, AND NON-TRANSTORY COMPUTER READABLE
( 12 ) United States Patent
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Daddis, Jr. et al. ( 54 ) ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONING UNIT TESTING ( 71 ) Applicant : Carrier Corporation, Farmington, CT ( US ) HAO WALA NAMAN UTAMA UNATAKA MA NA MALO MATTER
( 12 ) United States Patent Daddis, Jr. et al. ( 54 ) ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONING UNIT TESTING ( 71 ) Applicant : Carrier Corporation, Farmington, CT ( US ) HAO WALA NAMAN UTAMA UNATAKA MA NA MALO MATTER
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,385,897 B1
 US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1
 USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0031621 A1 Liu US 2014003 1621A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 30, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) CUTTINGAPPARATUS WITH IMAGE CAPTURE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0031621 A1 Liu US 2014003 1621A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 30, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) CUTTINGAPPARATUS WITH IMAGE CAPTURE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2
 US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000
 USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8462728B2 (12) United States Patent Stojanovski et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,728 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD AND WIRELESS SYSTEM FOR ACHIEVING LOCALANCHORING OFA MOBILE NODE
USOO8462728B2 (12) United States Patent Stojanovski et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8.462,728 B2 Jun. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD AND WIRELESS SYSTEM FOR ACHIEVING LOCALANCHORING OFA MOBILE NODE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
US 2006O164425A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0164425A1 Parke (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2006 (54) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification UPDATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0335343A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0335343 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN (52)
(19) United States US 2013 0335343A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0335343 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN (52)
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2. Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008
 United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O141898A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/014 1898A1 Riphin (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CELL PHONE CHARGING SYSTEM Publication Classification
US 2016O141898A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/014 1898A1 Riphin (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CELL PHONE CHARGING SYSTEM Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0083276 A1 Barsness et al. US 20090083276A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) INSERTING DATA INTO AN IN-MEMORY DISTRIBUTED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0083276 A1 Barsness et al. US 20090083276A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 26, 2009 (54) INSERTING DATA INTO AN IN-MEMORY DISTRIBUTED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. ? 200
 (19) United States US 20070288373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0288373 A1 Wilkes (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) TRANSACTION ALERT MESSAGES ASSOCATED WITH FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS
(19) United States US 20070288373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0288373 A1 Wilkes (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) TRANSACTION ALERT MESSAGES ASSOCATED WITH FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS
(12) United States Patent
 USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
USOO97296.58B2 (12) United States Patent Trahan et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 2017 (54) SYSTEM FOR MANAGING WEB-BASED CONTENT DATA AND APPLICATIONS (76) Inventors: Chris Trahan,
