TEPZZ 74_475A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 29/12 ( )
|
|
|
- Doreen Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) TEPZZ 74_47A_T (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 14/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/12 (06.01) (21) Application number: (22) Date of filing: (84) Designated Contracting States: AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR Designated Extension States: BA ME () Priority: KR KR KR KR KR (71) Applicant: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd Gyeonggi-do (KR) (72) Inventors: Lee, Jong-Hyo Gyeonggi-do (KR) Lee, Ji-Hye Gyeonggi-do (KR) Han, Se-Hee Gyeonggi-do (KR) Kang, Jae-Eun Gyeonggi-do (KR) Yang, Chil-Youl Gyeonggi-do (KR) Lee, Myoung-Hwan Gyeonggi-do (KR) Lee, Chun-Ho Gyeonggi-do (KR) Lee, Tae-Young Gyeonggi-do (KR) (74) Representative: Gover, Richard Paul et al HGF Limited Saviour House 9 St Saviourgate York YO1 8NQ (GB) (4) Method and apparatus for allocating an internet protocol address to a client device (7) A method and apparatus are provided for a client device to be allocated an Internet Protocol (IP) address by a Group Owner (GO) device, for direct communication between the client device and the GO device. The method includes transmitting, by the client device, an Association Request message to the GO device, receiving an Association Response message from the GO device, in response to the Association Request message, and receiving, by the client device, an IP address of the client device allocated by the GO device, during an authentication process between the client device and the GO device. EP A1 Printed by Jouve, 7001 PARIS (FR)
2 Description 1. Field of the Invention [0001] The present invention relates generally to a method and apparatus for setting up an Internet Protocol (IP) address in a wireless communication system. 2. Description of the Related Art [0002] The use of a high-speed data services in wireless communication systems is ever-increasing, and a device using a high-speed data service may perform communication by using an Internet Protocol (IP) address. However, a new scheme for setting up an IP address for a device is required SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION [0003] An aim of certain embodiments of the present invention is to provide a method and apparatus for exchanging information for a main communication connection using Out-Of-Band (OOB) communication (for example, Near Field Communication (NFC)) and setting up an IP address according to a role of each device for a high-speed main communication connection in a wireless communication system. [0004] Another aspect of the present invention is to provide a method and apparatus for setting up an IP address using NFC. [000] Another aspect of the present invention is to provide a method and apparatus in which an IP address is allocated in a procedure for exchanging an association request message and an association response message according to the Wi-Fi Direct standard in a wireless communication system. [0006] In accordance with a first aspect of the present invention there is provided a method of allocating an Internet Protocol, IP, address to a client device, for direct communication between the client device and a Group Owner, GO, device, the method comprising: transmitting, by the client device, an Association Request message to the GO device; receiving, by the client device, an Association Response message from the GO device, in response to the Association Request message; and receiving, by the client device, the IP address of the client device allocated by the GO device, during an authentication process between the client device and the GO device. [0007] In accordance with a second aspect of the present invention there is provided a method of allocating an Internet Protocol, IP, address to a client device for direct communication between the client device and a Group Owner, GO, device, the method comprising: receiving, by the GO device, an Association Request message from the client device; transmitting, the GO device, an Association Response message to the client device, in response to the Association Request message; and transmitting, by the GO device, the IP address of the client device to the client device during an authentication process between the GO device and the client device. [0008] In accordance with a third aspect of the present invention there is provided a client device for receiving an allocation an Internet Protocol, IP, address for the client device for direct communication between the client device and a Group Owner, GO, device, the GO device comprising: a transmitter configured to transmit an Association Request message to the GO device; and a receiver configured to receive an Association Response message from the GO device, in response to the Association Request message and to receive the IP address of the client device from the GO device during an authentication process between the GO device and the client device. [0009] In accordance with a fourth aspect of the present invention there is provided a Group Owner, GO, device for allocating an Internet Protocol, IP, address to a client device for direct communication between the client device and the GO device, the GO device comprising: a receiver configured to receive an Association Request message from the client device; and a transmitter configured to transmit an Association Response message to the client device, in response to the Association Request message, and to transmit the IP address of the client device to the client device during an authentication process between the GO device and the client device. [00] In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a method is provided for setting up an IP address between devices in a wireless communication system. The method includes transmitting, by a first device to a second device, an IP address pair proposed by the first device including a first IP address for the first device and a first IP address for the second counterpart device; receiving, by the first device from the second device, an IP pair proposed by the second device including a second IP address for the first device and a second IP address for the second device; determining one of the first device and the second device as a Group Owner (GO) device; determining the one of the first device and the second device not determined as the GO device as a client device; and determining a set IP address of the first device and a set IP address of the second device using the IP address pair proposed by the GO device. [0011] The method may further comprise performing Near Field Communication (NFC) tagging to establish an initial association between the first device and the second device. 2
3 [0012] The method may further comprise discarding the IP address pair proposed by the client device. [0013] The IP address pair proposed by the first device may be transmitted through a Handover Request message and the IP address pair proposed by the second device may be transmitted through a Handover Select message. [0014] The Handover Request message and the Handover Select message may further comprise information for determining the first device and the second device as the client device or the GO device. [001] In accordance with another embodiment of the present invention, a method is provided for a client device to be allocated an IP address by a GO device, for direct communication between the client device and the GO device. The method includes transmitting, by the client device, an IP address allocation request to the GO device through an Association Request message; and receiving, by the client device, an IP address allocated to the client device by the GO device, through an Association Response message. [0016] The Association Request message may include a Client Address item for requesting the IP address of the client device, a Group Owner Address item for requesting an IP address of the GO device, and a Subnet Mask item for requesting information for identification of a subnet used by the client device and the GO device. [0017] The Association Response message may include the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, and information for identification of a subnet used by the client device and the GO device. [0018] The Association Request message may further include a Router Address item including a gateway address. [0019] In accordance with another embodiment of the present invention, a method is provided for a client device to be allocated an IP address by a GO device for direct communication between the client device and the GO device. The method includes transmitting, by the client device, an Association Request message to the GO device; receiving an Association Response message from the GO device, in response to the Association Request message; and receiving, by the client device, the IP address of the client device allocated by the GO device, during an authentication process between the client device and the GO device. [00] The client device may receive the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, and a subnet value used by the GO device through an IP Allocation Key Data Encryption (KDE). [0021] The IP Allocation KDE may be included in a first Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network (LAN) (EAPOL)-Key frame. [0022] The method may further comprise transmitting an IP address request to the GO device in the authentication process between the client device and the GO device. [0023] The client device may transmit the IP address request to the GO device through an IP Address Request Key Data Encapsulation (KDE). [0024] The IP Address Request KDE may be included in a second Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network (LAN) (EAPOL)-Key frame. [002] Receiving the IP address of the client device may comprise: receiving a first random number from the GO device; generating a Pairwise Transient Key (PTK) and a second random number using the first random number and a Pairwise Master Key (PMK); transmitting the second random number and a Message Integrity Check (MIC) key to the GO device; and receiving, from the GO device, the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, a Robust Security Network Information Element (RSN IE), an MIC, and a Group Temporal Key (GTK). [0026] In accordance with another embodiment of the present invention, a method is provided for allocating an IP address to a client device by a GO device for direct communication between the client device and the GO device. The method includes receiving, by the GO device, an Association Request message from the client device; transmitting an Association Response message to the client device, in response to the Association Request message; and transmitting, by the GO device, the IP address of the client device to the client device, during an authentication process between the GO device and the client device. [0027] The GO device may transmit the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, and a subnet value used by the GO device through an IP Allocation Key Data Encapsulation (KDE). [0028] The IP Allocation KDE may be included in an Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network (LAN) (EAPOL) -Key frame. [0029] The method may further comprise receiving an IP address allocation request from the client device in the authentication process between the client device and the GO device. [00] The GO device may receive the IP address allocation request from the client device through an IP Address Request Key Data Encapsulation (KDE). [0031] The IP Address Request KDE may be included in an Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network (LAN) (EAPOL)-Key frame. [0032] Transmitting the IP address of the client device may comprise: transmitting a first random number to the client device; receiving a second random number and a first Message Integrity Check (MIC) from the client device; generating a Pairwise Transient Key (PTK) using the first random number and a Pairwise Master Key (PMK); performing verification with the first MIC; allocating the IP address to be used by the client device; and transmitting the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, a Robust Security Network Information Element (RSN IE), a second MIC, and 3
4 a Group Terminal Key (GTK) to the client device. [0033] In accordance with another embodiment of the present invention, a device is provided for setting up Internet Protocol (IP) addresses with another device in a wireless communication system. The device includes a transmitter configured to transmit, to the another device, an IP address pair proposed by the device including a first IP address for the device and a first IP address for the another; a receiver configured to receive an IP pair proposed by the another device including a second IP address for the device and a second IP address for the another device; and a controller configured to determine one of the device and the another device as a Group Owner (GO) device, determine the one of the device and the another device not determined as the GO device as a client device, and determine a set IP address of the device and a set IP address of the another device using the IP address pair proposed by the GO device. The transmitter and the receiver are configured to perform Near Field Communication (NFC) tagging to establish an initial association between the device and the another device. [0034] The controller may be configured to discard the IP address proposed by the client device. [003] The IP address pair proposed by the device may be transmitted through a Handover Request message and the IP address pair proposed by the another device may be received through a Handover Select message. [0036] The Handover Request message and the Handover Select message may further comprise information for determining the device and the another device as the client device or the GO device. [0037] In accordance with another embodiment of the present invention, a device is provided to be allocated an IP address by a counterpart device for direct communication between the device and the counterpart device. The device includes a controller configured to determine the counterpart device and the device as a Group Owner (GO) device and a client device, respectively; a transmitter configured to transmit an IP address allocation request to the GO device through an Association Request message; and a receiver configured to receive the IP address of the client device allocated by the GO device through an Association Response message, in response to the Association Request message. [0038] The Association Request message may comprise a Client Address item for requesting the IP address of the client device, a Group Owner Address item for requesting an IP address of the GO device, and a Subnet Mask item for requesting information for identification of a subnet used by the client device and the GO device. [0039] The Association Response message may comprise the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, and information for identification of a subnet used by the client device and the GO device. [00] The Association Request message may further comprise a Router Address including a gateway address. [0041] In accordance with another embodiment of the present invention, a client device is provided to be allocated an IP address by a GO device for direct communication between the client device and the GO device. The client device includes a transmitter configured to transmit an Association Request message to the GO device; and a receiver configured to receive an Association Response message from the GO device, in response to the Association Request message, and to receive an IP address of the client device allocated by the GO device during an authentication process between the client device and the GO device. [0042] The receiver may be configured to receive the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, and a subnet value used by the GO device through an IP Allocation Key Data Encryption (KDE). [0043] The IP Allocation KDE may be included in a first Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network (LAN) (EAPOL)-Key frame. [0044] The client device may further comprise: a transmitter configured to transmit an IP address request to the GO device during the authentication process between the client device and the GO device. [004] The transmitter may be configured to transmit the IP address request to the GO device through an IP Address Request Key Data Encapsulation (KDE). [0046] The IP Address Request KDE may be included in a second Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network (LAN) (EAPOL)-Key frame. [0047] The receiver may be configured to receive a first random number, the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, a Robust Security Network Information Element (RSN IE), a Message Integrity Check (MIC), and a Group Temporal Key (GTK) from the GO device, wherein the client device further comprises a controller configured to generate a Pairwise Transient Key (PTK) and a second random number using the first random number and a Pairwise Master Key (PMK), and wherein the transmitter is configured to transmit the second random number and a MIC key to the GO device. [0048] In accordance with another embodiment of the present invention, a GO device is provided for allocating an IP address to a client device for direct communication between the client device and the GO device. The GO device includes a receiver configured to receive an Association Request message from the client device; and a transmitter configured to transmit an Association Response message to the client device, in response to the Association Request message, and to transmit the IP address of the client device to the client device during an authentication process between the GO device and the client device. [0049] The transmitter may be configured to transmit the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, and a subnet value used by the GO device through an IP Allocation Key Data Encapsulation (KDE). 4
5 1 [000] The IP Allocation KDE may be included in a first Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network (LAN) (EAPOL)-Key frame. [001] The receiver may be configured to receive an IP address allocation request from the client device during the authentication process between the client device and the GO device. [002] The receiver may be configured to receive the IP address allocation request from the client device through an IP Address Request Key Data Encapsulation (KDE). [003] The IP Address Request KDE may be included in a second Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network (LAN) (EAPOL)-Key frame. [004] The transmitter may be configured to transmit a first random number, the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, a Robust Security Network Information Element (RSN IE), a first Message Integrity Code (MIC), and a Group Terminal Key (GTK) to the client device, wherein the GO device further comprises a controller configured to generate a Pairwise Transient Key (PTK) using the first random number and a Pairwise Master Key (PMK), to perform verification with a second MIC, and allocate the IP address to be used by the client device, and wherein the receiver is configured to receive a second random number and the second MIC from the client device. [00] Another aspect of the invention provides a computer program comprising instructions arranged, when executed, to implement a method in accordance with any one of the above-described aspects. A further aspect provides machinereadable storage storing such a program. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS [006] The above and other aspects, features, and advantages of certain embodiments of the present invention will be more apparent from the following detailed description taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, in which: FIG. 1 is a signal flow diagram illustrating a method for setting up an IP address in an NFC system according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 2 is a flowchart illustrating a method for setting up an IP address through NFC Data Exchange Format (NDEF) message exchange in a wireless communication system according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 3 is a signal flow diagram illustrating a method of allocating an IP address according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 4 is a flowchart illustrating a method of requesting an IP address by a client device according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. is a flowchart illustrating a method of transmitting an association response message by a GO device according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 6 is a signal flow diagram illustrating a method for allocating an IP address in a 4-way handshake step according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 7 illustrates a format of an Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network (LAN) (EAPOL) Key message exchanged in a 4-way handshake step according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 8 illustrates a basic format for defining Key Data Encapsulation (KDE) per organization or company in a 4-way handshake step according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 9 illustrates an IP Address Allocation KDE inserted into a "Data" field according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. is a signal flow diagram illustrating a method for allocating an IP address in a 4-way handshake step according to an embodiment of the present invention; FIG. 11 illustrates an IP Address Request KDE inserted into a "Data" field according to an embodiment of the present invention; and FIG. 12 illustrates an IP Address Allocation KDE inserted into a "Data" field according to an embodiment of the present invention. 0 [007] Throughout the drawings, like reference numerals will be understood to refer to like parts, components, and structures. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS OF THE INVENTION [008] Various embodiments of the present invention will now be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. In the following description, specific details such as detailed configuration and components are merely provided to assist the overall understanding of these embodiments of the present invention. Therefore, it should be apparent to those skilled in the art that various changes and modifications of the embodiments described herein can be made without departing from the scope of the present invention as defined by the appended claims. In addition, descriptions of well-
6 known functions and constructions are omitted for clarity and conciseness. [009] The terms and words used in the following description and claims are not limited to their dictionary meanings, but, are merely used to provide a clear and consistent understanding of the present invention. Accordingly, it should be apparent to those skilled in the art that the following description of the embodiments of the present invention is provided for illustration purpose only and not for the purpose of limiting the invention as defined by the appended claims and their equivalents. [0060] Throughout the description and claims of this specification, the words "comprise" and "contain" and variations of the words, for example "comprising" and "comprises", means "including but not limited to", and is not intended to (and does not) exclude other components, integers or steps. [0061] Throughout the description and claims of this specification, the singular encompasses the plural unless the context otherwise requires. In particular, where the indefinite article is used, the specification is to be understood as contemplating plurality as well as singularity, unless the context requires otherwise. [0062] Features, integers or characteristics described in conjunction with a particular aspect, embodiment or example of the invention are to be understood to be applicable to any other aspect, embodiment or example described herein unless incompatible therewith. [0063] It will be also be appreciated that, throughout the description and claims of this specification, language in the general form of "X for Y" (where Y is some action, activity or step and X is some means for carrying out that action, activity or step) encompasses means X adapted or arranged specifically, but not exclusively, to do Y. [0064] In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a method is provided, which exchanges information for a communication connection using OOB communication (e.g., NFC) for a high-speed main communication connection (In-Band), and sets up an IP address for a network service according to a role of each device, thereby providing a prompt network service to a user. A first device acts as a Group Owner (GO) and a second device acts as a client. [006] In accordance with another embodiment of the present invention, a method is provided, which delivers role decision information and IP setup information proposed by each of two devices to act as counterpart devices through OOB message exchange and selects an IP address according to a role determined from the exchanged information. [0066] In accordance with another embodiment of the present invention, a method is provided for a GO device to perform an IP setup operation in place of a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, wherein each device transmits role decision information and an IP address through an OOB message. [0067] FIG. 1 is a signal flow diagram illustrating a method for setting up an IP address in an NFC system according to an embodiment of the present invention. [0068] Referring to FIG. 1, a first device and a second device perform NFC tagging in step 1 In step 3, the first device transmits, to the second device, an OOB message including role decision information, e.g., a GO intent value in Wi-Fi Direct, an IP address proposed by the first device, and an IP address usable by the second device. [0069] In step, the second device transmits, to the first device, an OOB message including role decision information, e.g., a GO intent value in Wi-Fi Direct, an IP address proposed by the second device, and an IP address usable by the first device. [0070] Herein, the two IP addresses proposed by the first device and the two IP addresses proposed by the second device are defined as IP pairs. The first device and the second device use the IP pair provided by the counterpart device or the IP pair provided by itself, according to their respective roles, as determined by exchanging role decision information. [0071] That is, if main communication is connected using OOB for Wi-Fi Peer to Peer (P2P), the first device and the second device transmit and receive GO intent values, which are information for determining their roles, and pairs of IP addresses proposed through OOB messages. Herein, the GO intent value may have the same meaning as role decision information. [0072] For example, in FIG. 1, the IP pair proposed by the first device indicates that an IP address of the first device is and an IP address of the second device is The IP pair proposed by the second device indicates that the IP address of the first device is and the IP address of the second device is [0073] In step 7, the role of the first device is determined as a P2P GO and the role of the second device is determined as a P2P client after exchanging of the OOB messages including the IP pairs. Accordingly, the IP pair proposed by the first device is used as the IP addresses of the two devices, and the IP pair proposed by the second device is ignored in step 9. That is, the IP address of the first device is determined as and the IP address of the second device is determined as Using the determined IP addresses, the first device and the second device communicate with each other in step 111. [0074] However, if the role of the first device is determined as the P2P client and the role of the second device is determined as the P2P GO, then the IP pair proposed by the second device is used. That is, the IP address of the first device would be determined as and the IP address of the second device would be determined as
7 [007] In role determination, the GO intent values of a first device and a second device are compared with each other, and the device having a larger GO intent value may be determined to operate as a GO device. If the GO intent values of the two devices are equal to each other, then the device to first send an Association Request message has a higher priority, and thus, may operate as a GO device. By performing existing P2P GO negotiation, the roles of the devices may be determined. [0076] Attribute formats of IP address setup and an Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) are shown in Table 1. 1 Attribute P2P IP Allocation Field Size (Bytes) Table 1 Description Attribute ID 1 Attribute ID Length 2 Length P2P Device Address 6 Terminal MAC Address P2P Group Owner IP Address P2P Client IP Address 4 4 Group Owner IP Address Propose (A Handover Request message includes an IP address of the first device, and a Handover Select message includes an IP address of the second device) Client IP Address Propose (A Handover Request message includes an IP address of the second device, and a Handover Select message includes an IP address of the first device) [0077] The attribute formats of IP address setup and the ARP define information associated with IP addresses included in a Handover Request message and a Handover Select message according to whether the role of the device is a GO device or a client device, as shown in Table 1. [0078] If the first device is a GO device, "P2P GO IP Address" and "P2P Client IP Address" fields proposed by the first device in a Handover Request message are utilized, and "P2P GO IP Address and P2P Client IP Address" fields proposed by the second device in a Handover Select message are discarded. [0079] FIG. 2 is a flowchart illustrating a method for setting up an IP address in an NFC Data Exchange Format (NDEF) scheme for a high-speed link setup in a wireless communication system according to an embodiment of the present invention. [0080] Referring to FIG. 2, a first device and a second device perform NFC tagging in steps 1 and 21. Thereafter, the first device and the second device exchange NDEF messages in steps 3 and 23. Each NDEF message may include an IP pair and role determination information. In steps and 2, the first device and the second device may determine their roles based on the exchanged information. [0081] For example, if the first device is not a P2P GO device in step, i.e., the first device is a P2P client device, the first device uses the IP pair provided by the second device in step 7 and exchanges data with the second device in step 211. However, if the first device is a P2P GO device in step, the first device uses the IP pair provided by the first device in step 9 and exchanges data with the second device in step 211. [0082] Similarly, the second device exchanges data with the first device in step 261, using an IP pair in steps 27 and 29, according to its determined role in step 2. [0083] FIG. 3 is a signal flow diagram illustrating a method for allocating an IP address according to an embodiment of the present invention. [0084] Referring to FIG. 3, in a Probe Request/Response step 1, a first device 3 and a second device 321 discover each other. In a GO negotiation step 3, the first device 3 and the second device 321 perform a process to determine their respective roles. In a Wi-Fi Simple Configuration (WSC) step, the first device 3 and the second device 321 perform a process to request and respond to their association. [008] In step 7, the first device 3 transmits an Association Request Message to the second device 321, and in step 9, the second device 321 transmits an Association Response message to the first device 3. In step 311, the first device 3 and the second device 321 perform a 4-way handshake. [0086] Each of steps 1 to 311 complies with the Wi-Fi Direct standard. [0087] As illustrated in FIG. 3, an IP address is allocated to each device in an Association Request and Association Response message exchange procedure corresponding to Wi-Fi Direct. [0088] The Association Request message is sent from a client device to a GO device, as an association request to the GO device through a GO negotiation procedure. The Association Request message includes a P2P Information Element (IE), which includes items newly proposed in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. 7
8 [0089] The Association Response message is a message sent to the client device from the GO device, in response to the Association Request message through the GO negotiation procedure. The association response message includes a P2P Information Element(IE), which includes items newly proposed in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. [0090] The client device is allocated an IP address through an Association Response message. [0091] For example, the client device inserts items, such as "Group Owner Address", "Client Address", "Subnet Mask", and "Router Address", into a P2P IE included in the Association Request message transmitted to the GO device. [0092] The "GO Address" item includes an IP address of the GO device with which the client desires association. The "Client Address" item includes an IP address allocated to the client device by the GO device. The "Subnet Mask" item includes information for subnet identification to be used by the GO device and the client device. The "Router Address" item includes a gateway address. [0093] The client device may manage the "Group Owner Address" item, the "Client Address" item, the "Subnet Mask" item, and the "Router Address" item as a higher-layer item called "P2P IP Allocation" for management of information items of the P2P IE. If the client device uses the "P2P IP Allocation" item, the Association Request message may use the "P2P IP Allocation" item, without lower-layer items. [0094] The GO device may determine whether the Association Request message received from the client device includes the "Group Owner Address" item, the "Client Address" item, the "Subnet Mask" item, and the "Router Address" item or includes the P2P IP allocation item, and if so, the GO device records values in the respective items to transmit an Association Response message including IP address information to the client device. [009] However, if a value of each item is null in the Association Request message received by the GO device or the client device has not inserted the item into the P2P IE, then the GO device may allocate an IP address through a general DHCP procedure or may not allocate an IP address to the client device. If the GO device receives the Association Request message that does not include the items, the client device has no support for being allocated an IP address in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, and thus, the client device is allocated an IP address through the general DHCP procedure. [0096] Like the Association Request message, the Association Response message may also manage the "Group Owner Address" item, the "Client Address" item, the "Subnet Mask" item, and the "Router Address" item as a higherlayer item, i.e., a "P2P IP Allocation" item. [0097] In a modification of FIG. 3, the GO device and the client device may determine whether an IP address is set prior to the WSC step. In this case, without inserting the "Group Owner Address" item, the "Client Address" item, the "Subnet Mask" item, and the "Router Address" item into the Association Request message, IP address allocation may be determined in advance, for example, Probe Request/Response, GO negotiation, or WSC. That is, prior to an Association Request and a Response message exchange, the GO device may recognize whether or not the client device may be allocated with an IP address. Thus, if the client device can support being allocated an IP address, the GO device may directly include an allocated IP address in the Association Response message in step 9, even if the client device transmits an Association Request message having null values in the "Group Owner Address" item, the "Client Address" item, the "Subnet Mask" item, and the "Router Address" item in step 7. If the client device cannot support being allocated an IP address, the IP address is allocated through the general DHCP procedure. [0098] FIG. 4 is a flowchart illustrating a method for transmitting an Association Request message by a client device according to an embodiment of the present invention. [0099] Referring to FIG. 4, the client device determines whether it can support being allocated an IP address in step 1. If the client device has support for being allocated an IP address, the client device configures a P2P IE indicating it is to be allocated with an IP address, and generates an Association Request message including the P2P IE in step 3. The configuration of the P2P IE has already been described above in relation to FIG. 3, and thus, will not be described in detail again. In step, the client device may transmit the generated Association Request message to the GO device. [00] However, if the client device cannot support being allocated an IP address in step 1, the client device may generate a general Association Request message in step 7 and transmit the general Association Request message to the GO device in step. [01] FIG. is a flowchart illustrating a method for transmitting an Association Response message by a GO device according to an embodiment of the present invention. [02] Referring to FIG., the GO device receives an Association Request message from the client device in step 01. In step 03, the GO device may analyze the received Association Request message, i.e., the "P2P IP Allocation" item or the "Group Owner Address" item, the "Client Address" item, the "Subnet Mask" item, and the "Router Address" item in a P2P IE included in the received Association Request message, to determine if the for the received Association Request message includes IP address allocation request. If IP address allocation-related items are included in the P2P IE, the GO device may generate an Association Response message including input values for the items in step 0. In step 07, the GO device may transmit the generated Association Response message to the client device. 8
9 [03] However, if there is no IP address allocation-related item, as a result of the analysis of the Association Request message in step 03, the GO device generates a general association response message in step 09 and transmits the generated association response message to the client device in step 07. [04] As illustrated in FIG., an IP address is allocated according to a DHCP procedure in an L3 layer of the Wi-Fi Direct standard is performed in an L2 layer, thus providing a method in which an IP address is quickly allocated between devices. Hereinafter, a third embodiment and a fourth embodiment of the present invention propose a method in which an IP address is allocated in consideration of security in the 4-way handshake step of FIG. 3 as a link setup method in the wireless communication system. [0] FIG. 6 is a signal flow diagram illustrating a method for allocating an IP address in a 4-way handshake step according to an embodiment of the present invention. [06] Referring to FIG. 6, a GO device (or an authenticator) 621 may transmit an EAPOL-Key message including an ANonce to the client device (or a supplicant) 6 in step 601. The ANonce is a random number the GO device 621 may generate in a 4-way handshake step. [07] In step 603, the client device 6 may generate an SNonce and then generate a Pairwise Temporal Key (PTK) using the received ANonce. Additionally or alternatively the client device 6 may generate a Pairwise Master Key (PMK). The PMK is a key that the user inputs or that is generated/set through a WSC step. The SNonce is a random number the client device generates in the 4-way handshake step. [08] The client device 6 may generates an EAPOL-Key message including at least one of an SNonce, a Robust Security Network (RSN) IE (e.g., a P2P IE included in a Re-Association Request frame or an Association Request frame), and a Message Integrity Code (MIC), and transmits the generated EAPOL-Key message to the GO device 621 in step 60. [09] The GO device 621 may generate at least one of the PTK using the SNonce, the ANonce, and the PMK, performs verification using the MIC, and allocate an IP address to the client device 6 in step 607. Verification using the MIC determines whether key values are identical to each other. [01] In step 609, the GO device 621 may transmit, to the client device 6, an EAPOL-Key message including at least one ANonce, an RSN IE (an IE included in a Beacon or Probe Response message), an MIC, a Group Terminal Key (GTK), and the IP address allocated to the client device 6 in step 609. [0111] In step 611, the client device 6 may receive at least one of the allocated PTK, GTK, and IP address from the GO device 621, and then may transmits an EAPOL-Key message for confirmation (or ACKnowledgement (ACK)) to the GO device 621 in step 611. [0112] The IP address allocated by the GO device to the client device in step 609 is included in a "Key Data" field of the EAPOL-Key message, and the "Key Data" field complies with a format as will be described below with reference to FIG. 8. [0113] FIG. 7 illustrates a format of an EAPOL Key message exchanged in a 4-way handshake step according to an embodiment of the present invention. [0114] Referring to FIG. 7, in the 4-way handshake step, a client device transmits an item for requesting an IP address through the "Key Data" field having a format of the EAPOL-Key message to a GO device. The GO device transmits the IP address of the client device and the IP address of the GO device through the "Key Data" field having the format of the EAPOL-Key message. [011] FIG. 8 illustrates a basic format for defining Key Data Encapsulation (KDE) per organization or company in the 4-way handshake step according to an embodiment of the present invention. Using KDE a KDE message or packet may be sent. [0116] Referring to FIG. 8, an Organization Unique Identifier (OUI) may be, for example, 0 6F 9A, for Wi-Fi Alliance as defined by the IEEE Standard. A "Data Type" field has a value that identifies KDE for inserting key data exchanged in the 4-way handshake step, and is managed by an OUI organization. For example, "3" is set to distinguish IP Address Allocation KDE and IP Address Request KDE, and this value may be changed into another value or another value may be set. A "Data" field may include, for example, "IP Address Allocation KDE", as illustrated in FIG. 9. [0117] FIG. 9 illustrates an IP Address Allocation KDE, as an example of "Data", according to an embodiment of the present invention. [0118] Referring to FIG. 9, IP Address Allocation KDE is included in the "Data" field as illustrated in FIG. 8, and includes a "Client IP Address" item, a "Group Owner Address" item, and a "Subnet Mask" field. For example, as illustrated in 609 step of FIG. 6, the GO device may record a value for each field provided in IP Address Allocation KDE and transmit the IP address of the client device and the IP address of the GO device to the client device. [0119] FIG. is a signal flow diagram illustrating a method for allocating an IP address in a 4-way handshake step according to an embodiment of the present invention. Specifically, in FIG., after a client device (or supplicant) sends an IP address request to a GO device (or authenticator) 21, the client device is allocated an IP address from the GO device 21. [01] Referring to FIG., the GO device 21 transmits an EAPOL-Key message including an ANonce to the client device in step 01. 9
10 [0121] In step 03, the client device generates an SNonce and then generates a PTK using the received ANonce. The PMK is a key that is input by the user or generated/set by WSC. [0122] In step 0, the client device generates an EAPOL-Key message including information for requesting an SNonce, an RSN IE, an MIC, and an IP address, and transmits the generated EAPOL-Key message to the GO device 21. [0123] In step 07, the GO device 21 generates a PTK using the SNonce included in the received EAPOL-Key message, the ANonce used in step 01, and the PMK, performs verification through the MIC, and allocates an IP address to be used by the client device. [0124] In step 09, the GO device 21 transmits, to the client device, an EAPOL-Key message including an ANonce, an RSN IE, an MIC, a GTK, and the IP address allocated to the client device. [012] In step 11, the client device receives the PTK and the GTK, sets the IP address allocated by the GO device 21, and then transmits an EAPOL-Key message for confirmation to the GO device 21. [0126] The IP address request information transmitted from the client device to the GO device 21 in step 0 is included in the "Key Data" field of the EAPOL-Key message as illustrated in FIG. 7, and the "Key Data" field complies with the format as illustrated in FIG. 8. Thus, in FIG. 8, "OUI" may be, for example, 0 6F 9A, for Wi-Fi Alliance, and may be an IP Address Request KDE of "Data Type". [0127] FIG. 11 illustrates an IP Address Request KDE, as an example of "Data", according to an embodiment of the present invention. [0128] Referring to FIG. 11, a "Requested IP Address" field is used for a client device to send an IP address request to a GO device, and the client device may also request an IP address the client device used before. If a value for the field is "1", IP allocation from the GO device is requested. [0129] An "IP Address Lease Time" field indicates a time for which the client device will use the IP address. If the value for this field is "0", the IP address is to be used for a time designated by the GO device; and if the value of this field is a maximum value, an infinite lease of the IP address is requested. [01] The IP address allocated to the P2P client device in step 09 of FIG. is included in the "Key Data" field as illustrated in FIG. 7 and complies with the format as illustrated in FIG. 8. "OUI" may be, for example, 0 6F 9A, for Wi- Fi Alliance, and an example of "Data Type" may be an IP Address Allocation KDE. [0131] FIG. 12 illustrates an IP Address Allocation KDE inserted into a "Data" field according to an embodiment of the present invention. [0132] Referring to FIG. 12, an IP address allocated to the client device by the GO device is included in a "Client IP Address" field, and the IP address may be an IP address the client device requested, but the GO device may allocate another address depending on circumstances. A "Subnet Mask" field includes information for subnet identification, and a "Group Owner Address" field includes an IP address of a GO device. An "IP Address Lease Time" field indicates a time for which an IP address is valid, and if a value for this field is a maximum value, then it indicates an infinite lease time. [0133] As is apparent from the forgoing description, if an IP address cannot be set in a wireless communication system, role decision and IP address allocation are simultaneously performed, providing high-speed IP address setup. [0134] It will be appreciated that embodiments of the present invention can be realized in the form of hardware, software or a combination of hardware and software. Any such software may be stored in the form of volatile or non-volatile storage, for example a storage device like a ROM, whether erasable or rewritable or not, or in the form of memory, for example RAM, memory chips, device or integrated circuits or on an optically or magnetically readable medium, for example a CD, DVD, magnetic disk or magnetic tape or the like. It will be appreciated that the storage devices and storage media are embodiments of machine-readable storage that are suitable for storing a program or programs comprising instructions that, when executed, implement embodiments of the present invention. [013] Accordingly, embodiments provide a program comprising code for implementing apparatus or a method as claimed in any one of the claims of this specification and a machine-readable storage storing such a program. Still further, such programs may be conveyed electronically via any medium, for example a communication signal carried over a wired or wireless connection and embodiments suitably encompass the same. [0136] While the present invention has been particularly illustrated and described with reference to certain embodiments thereof, various modifications or changes can be made without departing from the scope of the present invention as defined by the appended claims. Claims 1. A method of allocating an Internet Protocol, IP, address to a client device, for direct communication between the client device and a Group Owner, GO, device, the method comprising: transmitting, by the client device, an Association Request message to the GO device;
11 receiving, by the client device, an Association Response message from the GO device, in response to the Association Request message; and receiving, by the client device, the IP address of the client device allocated by the GO device, during an authentication process between the client device and the GO device. 2. The method of claim 1, wherein the client device receives the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, and a subnet value used by the GO device through an IP Allocation Key Data Encryption, KDE. 3. The method of claim 2, wherein the IP Allocation KDE is included in a first Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network, LAN, EAPOL-Key frame. 4. The method of any one of the preceding claims, further comprising transmitting an IP address request to the GO device in the authentication process between the client device and the GO device. 1. The method of claim 4, wherein the client device transmits the IP address request to the GO device through an IP Address Request KDE. 6. The method of claim, wherein the IP Address Request KDE is included in a second EAPOL-Key frame. 7. The method of any one of the preceding claims, wherein receiving the IP address of the client device comprises: 2 receiving by the client device a first random number from the GO device; generating a Pairwise Transient Key, PTK, and a second random number using the first random number and a Pairwise Master Key, PMK; transmitting by the client device the second random number and a Message Integrity Check, MIC, key to the GO device; and receiving, from the GO device, the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, a Robust Security Network Information Element, RSN IE, an MIC, and a Group Temporal Key, GTK. 8. A method of allocating an Internet Protocol, IP, address to a client device for direct communication between the client device and a Group Owner, GO, device, the method comprising: 3 receiving, by the GO device, an Association Request message from the client device; transmitting, by the GO device, an Association Response message to the client device, in response to the Association Request message; and transmitting, by the GO device, the IP address of the client device to the client device during an authentication process between the GO device and the client device. 9. The method of claim 8 wherein the GO device transmits the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, and a subnet value used by the GO device through an IP Allocation Key Data Encapsulation, KDE.. The method of claim 9, wherein the IP Allocation KDE is included in a first Extensible Authentication Protocol over Local Area Network, LAN, EAPOL-Key frame The method of any one of claims 8 to, further comprising receiving an IP address allocation request from the client device during the authentication process between the client device and the GO device The method of claim 11, wherein the GO device receives the IP Address Request from the client device through an IP Address Request KDE. 13. The method of claim 12, wherein the IP Address Request KDE is included in a second EAPOL-Key frame. 14. The method of any one of claims 9 to 13, wherein transmitting the IP address of the client device comprises: transmitting from the GO device a first random number, the IP address of the client device, an IP address of the GO device, a Robust Security Network Information Element, RSN IE, a first Message Integrity Code, MIC, and a Group Terminal Key, GTK, to the client device, generating by the GO device a Pairwise Transient Key, PTK, using the first random number and a Pairwise 11
TEPZZ 6Z8446A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 9/08 ( ) H04L 9/32 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 6Z8446A_T (11) EP 2 608 446 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 9/08 (2006.01) H04L 9/32 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 6Z8446A_T (11) EP 2 608 446 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 9/08 (2006.01) H04L 9/32 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (11) EP 2 493 239 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/35 (21) Application number: 10829523.9 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (11) EP 2 493 239 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/35 (21) Application number: 10829523.9 (22) Date
(51) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 94Z96B_T (11) EP 2 9 96 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.04.17 Bulletin 17/17 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 94Z96B_T (11) EP 2 9 96 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.04.17 Bulletin 17/17 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (06.01) (21) Application
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/34
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 490 138 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/34 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214420.9 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 490 138 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/34 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1214420.9 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ Z7999A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B05B 15/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z7999A_T (11) EP 3 7 999 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.08.17 Bulletin 17/34 (1) Int Cl.: B0B 1/04 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1617686.1 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ Z7999A_T (11) EP 3 7 999 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.08.17 Bulletin 17/34 (1) Int Cl.: B0B 1/04 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1617686.1 (22) Date of filing:
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (11) EP 2 482 24 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/31 (21) Application number: 818282. (22) Date of
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (11) EP 2 482 24 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/31 (21) Application number: 818282. (22) Date of
TEPZZ Z47A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 30/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ _Z47A_T (11) EP 3 131 047 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G06Q /00 (12.01) (21) Application number: 160297.4 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ _ _Z47A_T (11) EP 3 131 047 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G06Q /00 (12.01) (21) Application number: 160297.4 (22) Date of
(51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/24 ( ) WU, Qin
 (19) TEPZZ Z 68A_T (11) EP 3 3 68 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 09.08.17 Bulletin 17/32 (21) Application number: 182297.9 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z 68A_T (11) EP 3 3 68 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 09.08.17 Bulletin 17/32 (21) Application number: 182297.9 (22)
TEPZZ 8_8997A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8_8997A_T (11) EP 2 818 997 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.12.2014 Bulletin 2015/01 (21) Application number: 13174439.3 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8_8997A_T (11) EP 2 818 997 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.12.2014 Bulletin 2015/01 (21) Application number: 13174439.3 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01)
TEPZZ 98 _55A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 98 _A_T (11) EP 2 983 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 1180049.7 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /06 (06.01) G08G 7/00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 98 _A_T (11) EP 2 983 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 1180049.7 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /06 (06.01) G08G 7/00 (06.01)
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/37
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP007312A2* (11) EP 1 7 312 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.09.0 Bulletin 0/37 (1) Int Cl.
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP007312A2* (11) EP 1 7 312 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.09.0 Bulletin 0/37 (1) Int Cl.
(51) Int Cl.: G06F 21/00 ( ) G11B 20/00 ( ) G06Q 10/00 ( )
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 724 699 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/47 (21) Application
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 724 699 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/47 (21) Application
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/56 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 760 963 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.03.07 Bulletin 07/ (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/6 (06.01) (21) Application number: 06018260.7 (22) Date of filing: 31.08.06
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 760 963 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.03.07 Bulletin 07/ (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/6 (06.01) (21) Application number: 06018260.7 (22) Date of filing: 31.08.06
TEPZZ _968ZZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06K 7/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _968ZZA_T (11) EP 3 196 800 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1719738.8 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ _968ZZA_T (11) EP 3 196 800 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1719738.8 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 78779ZB_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 78779ZB_T (11) EP 2 787 790 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 12878644.9 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 78779ZB_T (11) EP 2 787 790 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.07.17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 12878644.9 (22)
TEPZZ 6 8A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 6 8A_T (11) EP 3 121 638 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.01.17 Bulletin 17/04 (21) Application number: 1380032.1 (1) Int Cl.: G02B 27/01 (06.01) G06F 11/16 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 6 8A_T (11) EP 3 121 638 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.01.17 Bulletin 17/04 (21) Application number: 1380032.1 (1) Int Cl.: G02B 27/01 (06.01) G06F 11/16 (06.01)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06T 15/60 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 234 069 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.09.2010 Bulletin 2010/39 (51) Int Cl.: G06T 15/60 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09364002.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 234 069 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.09.2010 Bulletin 2010/39 (51) Int Cl.: G06T 15/60 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 09364002.7 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 8864Z9A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B60W 30/14 ( ) B60W 50/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 8864Z9A_T (11) EP 2 886 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.06. Bulletin /26 (1) Int Cl.: B60W /14 (06.01) B60W 0/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 106043.7
(19) TEPZZ 8864Z9A_T (11) EP 2 886 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 24.06. Bulletin /26 (1) Int Cl.: B60W /14 (06.01) B60W 0/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 106043.7
TEPZZ Z5_748A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z_748A_T (11) EP 3 01 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.08.16 Bulletin 16/31 (21) Application number: 118.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/14 (06.01) H04W 48/18 (09.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z_748A_T (11) EP 3 01 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.08.16 Bulletin 16/31 (21) Application number: 118.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/14 (06.01) H04W 48/18 (09.01)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/45
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 521 319 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.11.2012 Bulletin 2012/45 (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/40 (2006.01) H04L 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11164445.6
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 521 319 A1 (43) Date of publication: 07.11.2012 Bulletin 2012/45 (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/40 (2006.01) H04L 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11164445.6
TEPZZ 57 7 ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2013/13
 (19) TEPZZ 57 7 ZA_T (11) EP 2 573 720 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/13 (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 10/00 (2012.01) (21) Application number: 11182591.5 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 57 7 ZA_T (11) EP 2 573 720 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 27.03.2013 Bulletin 2013/13 (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 10/00 (2012.01) (21) Application number: 11182591.5 (22)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 447 858 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.05.2012 Bulletin 2012/18 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11004965.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 447 858 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.05.2012 Bulletin 2012/18 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11004965.7 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ 85 9Z_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8 9Z_A_T (11) EP 2 83 901 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.04.1 Bulletin 1/14 (21) Application number: 141861.1 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 21/00 (06.01) G01C 2/00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8 9Z_A_T (11) EP 2 83 901 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.04.1 Bulletin 1/14 (21) Application number: 141861.1 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 21/00 (06.01) G01C 2/00 (06.01)
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00182883A1* (11) EP 1 82 883 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 18(3) EPC (43) Date
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00182883A1* (11) EP 1 82 883 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 18(3) EPC (43) Date
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK
 SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK FIELD OF THE DISCLOSURE (01) The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for routing communications in a computer network.
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR ROUTING COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMPUTER NETWORK FIELD OF THE DISCLOSURE (01) The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for routing communications in a computer network.
TEPZZ 8Z9Z A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04L 12/26 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 8Z9Z A_T (11) EP 2 809 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.14 Bulletin 14/49 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/26 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1417000.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 8Z9Z A_T (11) EP 2 809 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.12.14 Bulletin 14/49 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/26 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1417000.4 (22) Date
TEPZZ _4748 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _4748 A_T (11) EP 3 147 483 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 161896.0 (1) Int Cl.: F02C 9/28 (06.01) F02C 9/46 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ _4748 A_T (11) EP 3 147 483 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 161896.0 (1) Int Cl.: F02C 9/28 (06.01) F02C 9/46 (06.01)
TEPZZ _7655_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _76_A_T (11) EP 3 176 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/23 (21) Application number: 1619703.0 (1) Int Cl.: G01J 1/42 (2006.01) G01J 1/02
(19) TEPZZ _76_A_T (11) EP 3 176 1 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.06.2017 Bulletin 2017/23 (21) Application number: 1619703.0 (1) Int Cl.: G01J 1/42 (2006.01) G01J 1/02
TEPZZ 99894ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 99894ZA_T (11) EP 2 998 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.03.16 Bulletin 16/12 (21) Application number: 18973.3 (1) Int Cl.: G07C 9/00 (06.01) B62H /00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 99894ZA_T (11) EP 2 998 9 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.03.16 Bulletin 16/12 (21) Application number: 18973.3 (1) Int Cl.: G07C 9/00 (06.01) B62H /00 (06.01)
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2000/33
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP002842A2* (11) EP 1 028 42 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.08.00 Bulletin 00/33 (1) Int
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP002842A2* (11) EP 1 028 42 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.08.00 Bulletin 00/33 (1) Int
TEPZZ _Z_56ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 17/30 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z_6ZA_T (11) EP 3 1 60 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.12.16 Bulletin 16/49 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 16176.9 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ _Z_6ZA_T (11) EP 3 1 60 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.12.16 Bulletin 16/49 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 17/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 16176.9 (22) Date of filing:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 096 724 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.09.2009 Bulletin 2009/36 (21) Application number: 09153153.3 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 35/04 (2006.01) H01R 24/00 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 096 724 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.09.2009 Bulletin 2009/36 (21) Application number: 09153153.3 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 35/04 (2006.01) H01R 24/00 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
TEPZZ _9 7A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2017/29
 (19) TEPZZ _9 7A_T (11) EP 3 193 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.07.2017 Bulletin 2017/29 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 1/32 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1714829.0 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ _9 7A_T (11) EP 3 193 237 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 19.07.2017 Bulletin 2017/29 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 1/32 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1714829.0 (22) Date
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/32
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 93 663 A1 (43) Date of publication: 06.08.08 Bulletin 08/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 21/00 (06.01) G06F 3/023 (06.01) (21) Application number: 07124.4 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 93 663 A1 (43) Date of publication: 06.08.08 Bulletin 08/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 21/00 (06.01) G06F 3/023 (06.01) (21) Application number: 07124.4 (22) Date
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
Note: Text based on automatic Optical Character Recognition processes. SAMSUNG GALAXY NOTE
 Note: Text based on automatic Optical Character Recognition processes. SAMSUNG GALAXY NOTE PRIORITY This application is a Continuation of U.S. application Ser. No. 14/540,447, which was filed in the U.S.
Note: Text based on automatic Optical Character Recognition processes. SAMSUNG GALAXY NOTE PRIORITY This application is a Continuation of U.S. application Ser. No. 14/540,447, which was filed in the U.S.
TEPZZ_5 695B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ_ 69B_T (11) EP 1 33 69 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 07.08.13 Bulletin 13/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 9/44 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ_ 69B_T (11) EP 1 33 69 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 07.08.13 Bulletin 13/32 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 9/44 (06.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ 5976 A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G08G 5/00 ( ) H04M 1/725 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 976 A T (11) EP 2 97 633 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.0.13 Bulletin 13/22 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /00 (06.01) H04M 1/72 (06.01) (21) Application number: 12193473.1
(19) TEPZZ 976 A T (11) EP 2 97 633 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.0.13 Bulletin 13/22 (1) Int Cl.: G08G /00 (06.01) H04M 1/72 (06.01) (21) Application number: 12193473.1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
TEPZZ Z 7 76A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z 7 76A_T (11) EP 3 037 376 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.16 Bulletin 16/26 (21) Application number: 88.9 (1) Int Cl.: B66C 13/46 (06.01) B66C /06 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z 7 76A_T (11) EP 3 037 376 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.16 Bulletin 16/26 (21) Application number: 88.9 (1) Int Cl.: B66C 13/46 (06.01) B66C /06 (06.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION
 Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series September 06, 2016 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION Dimitri Kanevsky Tara Sainath Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series September 06, 2016 SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION Dimitri Kanevsky Tara Sainath Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application
 From the SelectedWorks of Marc A Sherman February, 2006 Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application Marc A Sherman Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marc_sherman/2/ UNITED
From the SelectedWorks of Marc A Sherman February, 2006 Virtual Private Radio via Virtual Private Network - patent application Marc A Sherman Available at: https://works.bepress.com/marc_sherman/2/ UNITED
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
... (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. icopying unit d:
 (19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013
 US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
ALTERNATIVE CHARGE CONTROL SYSTEM FOR MERCHANDISE DISPLAY SECURITY SYSTEM
 Technical Disclosure Commons InVue Defensive Publications Defensive Publications Series August 11, 2017 ALTERNATIVE CHARGE CONTROL SYSTEM FOR MERCHANDISE DISPLAY SECURITY SYSTEM InVue Security Products
Technical Disclosure Commons InVue Defensive Publications Defensive Publications Series August 11, 2017 ALTERNATIVE CHARGE CONTROL SYSTEM FOR MERCHANDISE DISPLAY SECURITY SYSTEM InVue Security Products
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR FACILITATING SECURE TRANSACTIONS
 FCOOK.001PR PATENT SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR FACILITATING SECURE TRANSACTIONS BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS [0001] Embodiments of various inventive features will now be described with reference to the
FCOOK.001PR PATENT SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR FACILITATING SECURE TRANSACTIONS BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS [0001] Embodiments of various inventive features will now be described with reference to the
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
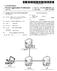 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/40
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 976 218 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01..2008 Bulletin 2008/40 (21) Application number: 07374.8 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (2006.01) H02J 13/00 (2006.01) G06F
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 976 218 A1 (43) Date of publication: 01..2008 Bulletin 2008/40 (21) Application number: 07374.8 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (2006.01) H02J 13/00 (2006.01) G06F
(51) Int Cl.: H04Q 1/14 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 468ZZ8B_T (11) EP 2 468 008 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21..1 Bulletin 1/43 (21) Application number: 748022.0 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 468ZZ8B_T (11) EP 2 468 008 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21..1 Bulletin 1/43 (21) Application number: 748022.0 (22) Date
WO 2017/ Al. 15 June 2017 ( )
 (12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (10) International Publication Number (43) International
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (10) International Publication Number (43) International
Appeal Decision. Appeal No USA ALCATEL-LUCENT USA LTD. Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo, Japan
 Appeal Decision Appeal No. 2014-5131 USA Appellant ALCATEL-LUCENT USA LTD. Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney OKABE, Yuzuru Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney YOSHIZAWA, Hiroshi The case of appeal against the examiner's
Appeal Decision Appeal No. 2014-5131 USA Appellant ALCATEL-LUCENT USA LTD. Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney OKABE, Yuzuru Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney YOSHIZAWA, Hiroshi The case of appeal against the examiner's
(51) Int Cl.: H04N 5/232 ( ) H04N 7/18 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 879 7_B_T (11) EP 2 879 371 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21.12.16 Bulletin 16/1 (1) Int Cl.: H04N /232 (06.01) H04N 7/18
(19) TEPZZ 879 7_B_T (11) EP 2 879 371 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21.12.16 Bulletin 16/1 (1) Int Cl.: H04N /232 (06.01) H04N 7/18
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction
 ( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
( 9 of 13 ) United States Patent Application 20150128094 Kind Code A1 Baldwin; Christopher ; et al. May 7, 2015 Gesture-Based Controls Via Bone Conduction Abstract Concepts and technologies are disclosed
TEPZZ 7Z_ 96A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 7Z_ 96A_T (11) EP 2 701 396 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.02.14 Bulletin 14/09 (21) Application number: 11864123.2
(19) TEPZZ 7Z_ 96A_T (11) EP 2 701 396 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.02.14 Bulletin 14/09 (21) Application number: 11864123.2
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/42
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 242 292 A1 (43) Date of publication: 20..20 Bulletin 20/42 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 8/18 (2009.01) G06Q 30/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 0918121. (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 242 292 A1 (43) Date of publication: 20..20 Bulletin 20/42 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 8/18 (2009.01) G06Q 30/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 0918121. (22) Date
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2
 US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,237,112 B1
 USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
WPA-GPG: Wireless authentication using GPG Key
 Università degli Studi di Bologna DEIS WPA-GPG: Wireless authentication using GPG Key Gabriele Monti December 9, 2009 DEIS Technical Report no. DEIS-LIA-007-09 LIA Series no. 97 WPA-GPG: Wireless authentication
Università degli Studi di Bologna DEIS WPA-GPG: Wireless authentication using GPG Key Gabriele Monti December 9, 2009 DEIS Technical Report no. DEIS-LIA-007-09 LIA Series no. 97 WPA-GPG: Wireless authentication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Frequency. Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 (19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
Lionbridge ondemand for Adobe Experience Manager
 Lionbridge ondemand for Adobe Experience Manager Version 1.1.0 Configuration Guide October 24, 2017 Copyright Copyright 2017 Lionbridge Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Published in the USA. March,
Lionbridge ondemand for Adobe Experience Manager Version 1.1.0 Configuration Guide October 24, 2017 Copyright Copyright 2017 Lionbridge Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Published in the USA. March,
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/18
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP002866A2* (11) EP 1 28 66 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.0.0 Bulletin 0/18 (1) Int Cl.
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP002866A2* (11) EP 1 28 66 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.0.0 Bulletin 0/18 (1) Int Cl.
Publication number: A2
 Patentamt JEuropaisches European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 061 324 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 82301435.2 Int. CI.3: G 06 F 13/00 Date of filing:
Patentamt JEuropaisches European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets Publication number: 0 061 324 A2 EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION Application number: 82301435.2 Int. CI.3: G 06 F 13/00 Date of filing:
TEPZZ 858 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2015/15
 (19) TEPZZ 88 A_T (11) EP 2 88 323 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.04. Bulletin / (21) Application number: 13637.8 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (06.01) G06Q /00 (12.01) G06F
(19) TEPZZ 88 A_T (11) EP 2 88 323 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.04. Bulletin / (21) Application number: 13637.8 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 29/06 (06.01) G06Q /00 (12.01) G06F
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2008/14
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 90 47 A2 (43) Date of publication: 02.04.2008 Bulletin 2008/14 (1) Int Cl.: B2J 9/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07018221.7 (22) Date of filing: 17.09.2007
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 90 47 A2 (43) Date of publication: 02.04.2008 Bulletin 2008/14 (1) Int Cl.: B2J 9/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 07018221.7 (22) Date of filing: 17.09.2007
/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].
![/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. / client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].](/thumbs/90/103929709.jpg) US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
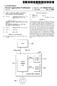 (19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/152.465 Filing Date 8 September 1998 Inventor Richard M. Farnsworth NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed
Serial Number 09/152.465 Filing Date 8 September 1998 Inventor Richard M. Farnsworth NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
TEPZZ 8 44ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06Q 10/08 ( ) G06K 17/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 8 44ZA_T (11) EP 2 811 4 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.12.14 Bulletin 14/0 (1) Int Cl.: G06Q /08 (12.01) G06K 17/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1417090.
(19) TEPZZ 8 44ZA_T (11) EP 2 811 4 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.12.14 Bulletin 14/0 (1) Int Cl.: G06Q /08 (12.01) G06K 17/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1417090.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
System and method for encoding and decoding data files
 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 7,246,177 Anton, et al. July 17, 2007 System and method for encoding and decoding data files Abstract Distributed compression of a data file can comprise a master server
( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 7,246,177 Anton, et al. July 17, 2007 System and method for encoding and decoding data files Abstract Distributed compression of a data file can comprise a master server
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 28 277 A2 (43) Date of publication: 28.11.12 Bulletin 12/48 (21) Application number: 1216844.2 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/24 (06.01) H04L 12/26 (06.01) H04W 24/06
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 28 277 A2 (43) Date of publication: 28.11.12 Bulletin 12/48 (21) Application number: 1216844.2 (1) Int Cl.: H04L 12/24 (06.01) H04L 12/26 (06.01) H04W 24/06
A SYSTEM FOR ENABLING SHORT-TERM FINANCING
 A SYSTEM FOR ENABLING SHORT-TERM FINANCING 5 The present invention relates generally to a system and method for enabling short-term financing, and finds particular, although not exclusive, utility in invoice
A SYSTEM FOR ENABLING SHORT-TERM FINANCING 5 The present invention relates generally to a system and method for enabling short-term financing, and finds particular, although not exclusive, utility in invoice
Is more than one finger placed on touchpad surface?
 USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,526,272 B1
 USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
USOO6526272B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bansal et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 2003 (54) REDUCING CALLING COSTS FOR 6,167,250 A * 12/2000 Rahman et al... 455/408 WIRELESS PHONES USING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140355048A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0355048A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF MOBILE Publication Classification
US 20140355048A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0355048A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
TMCH Report March February 2017
 TMCH Report March 2013 - February 2017 Contents Contents 2 1 Trademark Clearinghouse global reporting 3 1.1 Number of jurisdictions for which a trademark record has been submitted for 3 2 Trademark Clearinghouse
TMCH Report March 2013 - February 2017 Contents Contents 2 1 Trademark Clearinghouse global reporting 3 1.1 Number of jurisdictions for which a trademark record has been submitted for 3 2 Trademark Clearinghouse
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 2009.0245268A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0245268 A1 Pugliese, IV (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) VIDEO ROUTER AND METHOD OF Related U.S. Application
US 2009.0245268A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0245268 A1 Pugliese, IV (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) VIDEO ROUTER AND METHOD OF Related U.S. Application
Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security
 Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security Wireless Security Key factors contributing to higher security risk of wireless networks compared to wired networks include: o Channel Wireless networking typically
Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security Wireless Security Key factors contributing to higher security risk of wireless networks compared to wired networks include: o Channel Wireless networking typically
wo W /1997 * cited by examiner
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
EPO INPADOC 44 years. Dr. Günther Vacek, EPO Patent Information Fair 2016, Tokyo. November 2016
 EPO INPADOC 44 years Dr. Günther Vacek, EPO Patent Information Fair 2016, Tokyo November 2016 Content The INPADOC period Integration into the EPO establishment of principal directorate patent information
EPO INPADOC 44 years Dr. Günther Vacek, EPO Patent Information Fair 2016, Tokyo November 2016 Content The INPADOC period Integration into the EPO establishment of principal directorate patent information
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007 O123021A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0123021 A1 Su et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) CIRCUIT UNDER PAD STRUCTURE AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2007 O123021A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0123021 A1 Su et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) CIRCUIT UNDER PAD STRUCTURE AND (30) Foreign Application
Chapter 17. Wireless Network Security
 Chapter 17 Wireless Network Security IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802 committee for LAN standards IEEE 802.11 formed in 1990 s, to develop a protocol & transmission specifications for wireless LANs (WLANs) Demand
Chapter 17 Wireless Network Security IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802 committee for LAN standards IEEE 802.11 formed in 1990 s, to develop a protocol & transmission specifications for wireless LANs (WLANs) Demand
