OCARINA ("Optimizations to Compel Adoption of RINA") Michael Welzl RINA Workshop Research Day i2cat Barcelona
|
|
|
- Aubrey Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OCARINA ("Optimizations to Compel Adoption of RINA") Michael Welzl RINA Workshop Research Day i2cat Barcelona
2 Project overview 5-year project funded by Norwegian research council, started 1 October 2016; 1 postdoc + 3 Ph.D. students Focused on performance. Assumptions: 1. RINA needs to show fantastic performance, 2. RINA can show fantastic performance! 3 main WPs: cong. control, routing, Internet deployment RINA forces us to think differently about network algorithms such as routing and congestion control E.g., Internet-like "end-to-end" congestion control could be implemented in a RINA network, but that would be a very strange configuration 2
3 Two major mistakes of Internet CC. 1. First produce congestion, then react to it CC. is not only about controlling a problem after it happens: CC. is about determining the right sending rate at any time Congestion is also not binary, and loss and delay are bad signals Solution: create a meaningful "load" signal that does not embed a very specific algorithm (give some freedom to designers) 2. Clueless about underlying infrastructure, by design Inevitable result of Internet layering: "IP over everything" (good idea), "TCP optimized to blindly run over IP" (bad idea) "Cross-layer" solutions show: we could do better; but they can never be standardized because they don't fit the Internet model... and PEPs pragmatically improve things but "shouldn't exist" Solution: use per-dif loops, work with back-pressure 3
4 Addressing problem #1: Fixing ECN Why is it broken? Cost incurred in the network is additive per hop (see NUM theory), but can't re-mark a marked packet Note: cost not additive when packets are dropped Originally not a major problem because ECN signal should be rare; but poor signal Better "load" signal in DCTCP-style usage: instantaneous queue marking, count marks / RTT Even better "load" signal when marking before a queue even grows (virtual Q) Better signal quality, more problems with multiple links 4
5 Problems of using ECN as load It is not additive; it s a product: (p r : end-to-end marking probability) (p l : link marking probability) Modern controllers such as DCTCP converge at high marking probabilities. The theory (e.g. Network Utility Maximization (NUM)) needs an additive signal; a product value deviates much in high marking probabilities ( > 0.04)! 5
6 Our Solution Extending the KKT theorem to include functions as multipliers, and then use as multiplier. With a lot of math and stability analysis of course Results: (assuming a logarithmic utility) Numerical Simulation results results deviation (previous theory) our method x (1) : avg. rate of a five-hop flow x (2) : avg. rate of a one-hop flow Advantages: 1. New signal is a pretty general solution; just conveys "load", and could (relatively) easily be extended to multi-bit 2. New signal is probably good input to load-based routing too 3. RED as an already-deployed solution can be used; only small changes at senders and receivers 6
7 How it works
8 Applications Obtaining utility function when the marking probability is high, e.g. DCTCP: Deflating marking probability Playing with the base of log And the potential of dealing with virtual ("phantom") queues!
9 Addressing problem #2: Per-DIF loops PRISTINE background A sequence of DIFs doing TCP CC. is much like a sequence of split-tcp PEPs can be beneficial [1] Examples on the next slides However, controls using recursive queue based feedback can have stability issues (+ delay from multiple queues) [2] Envision to address this with logistic growth based control [3] + new "fixed" ECN More on the next slides 1. Peyman Teymoori, Michael Welzl, Stein Gjessing, Eduard Grasa, Roberto Riggio, Kewin Rausch, Domenico Siracusa: "Congestion Control in the Recursive InterNetworking Architecture (RINA)", IEEE ICC 2016, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, May David Hayes, Peyman Teymoori, Michael Welzl: "Feedback in Recursive Congestion Control", 13th European Workshop on Performance Engineering (EPEW 2016), Chios, Greece, 5-7 October Peyman Teymoori, David Hayes, Michael Welzl, Stein Gjessing: "Even Lower Latency, Even Better Fairness: Logistic Growth Congestion Control in Datacenters", IEEE LCN 2016, Dubai, UAE, Nov 2016.
10 Horizontal: Consecutive DIFs Topology: Results:
11 Vertical: Stacked DIFs Topology: Results: 1 sender, 1 receiver: Sender sends flow 1 (large) at 0, and flow 2 (small) at time 10.
12 Logistic Growth: Population Dynamics Proven to be globally asymptotically stable K = carrying capacity N t = 0 r = growth rate N N t is maximized N t = Time
13 LGC in a chain Multiple Loops Foodchain model: various stability analyses exist... x1=x1+x1 r (C1 x1 q1) x2=x2+x2 r (C2 x2 q2) x3=x3+x3 r (C3 x3 q3) C1 = min (x2, L1,1, L1,2) C2 = min (x3, L2) q 1 reflects the congestion measure at both routers 1 and C 1 C 2 C 3 L 1,2 L 1,1 L 2 L 3 router 1 router 2 router
14 What about Machine Learning? Remy (offline learning), PCC + Vivace (online learning) derive "optimal" TCP behavior ML! Like in a self-driving car! Self-driving! 14
15 Limitations of e2e CC There are many... e.g. consider the "vertical stacking" case: Remy etc. can't help here either More "modern" example: especially with 5G, PHY link capacity can change a lot, and quickly TCP cannot quickly react to it: TCP can't be sure a signal is from the bottleneck IETF failure; recent example: "throughput guidance" Only safe to reduce the rate (and only if signal trustworthy) Survey of such ideas that failed in the IETF: draft-dawkins-panrg-what-not-to-do RINA is an opportunity to apply ML to better-scoped problems! 15
16 Deployment We can consider RINA-under-IP, RINA overlay, and RINA-IP gateways... But we can also consider "switching over"! Once a host discovers that the whole path to the other end is RINA-enabled, switch Today, often, paths are short (Google, FB,... are not far away from you) TCP/IP are only rendez-vous protocols Some recent IETF standards could help A little ironic J 16
17 Transport Services (IETF TAPS WG) Makes apps independent of protocol and network interface Finished surveying and condensing services provided by: TCP, MPTCP, UDP, UDP-Lite, SCTP, LEDBAT Now working on Proposed Standard API + implementation guidance, with Apple among others; implementations: Apple, NEAT (open source) API properties: callback-based, message-oriented Hides protocols, but supports all features of all protocols above + plan: QUIC Some example protocol properties (some also: protocol & path selection): Reliability, Ordering, Per-Message Reliability, 0-RTT Session Establishment, RTX and ICMP notification, Checksum coverage control, Capacity profile (normal, low latency, CBR, scavenger), Interface type, Multiplexing (multistreaming), Relative Niceness within group Various security parameters 17
18 Interface diagram (taken from: Brian Trammell, IETF 101) 18
19 Provisioning Domains (PvDs) (INTAREA WG) Router Advertisement (RA) option from first-hop router conveys FQDN that host can use to retrieve extra info about network access characteristics via HTTP over TLS query Applications then select (via local IP address) which PvD to use, and can learn config. params for transport layer and above Example from NEAT project (Gorry Fairhurst, Tom Jones (University of Aberdeen) André Venne, Eric Bruneau (Cisco) ) 19
20 Conclusion Congestion control RINA "forces" us to do it in a fundamentally different, and (probably) inherently better way better throughput, less latency This will enable load-based routing chance for much higher throughput... and there are interesting deployment opportunities 20
21 Thank you! Questions? 21
The Transport Layer is Dead Long Live the Transport Layer! Michael Welzl University of Oslo / University of Rome Tor Vergata
 The Transport Layer is Dead Long Live the Transport Layer! Michael Welzl University of Oslo / University of Rome Tor Vergata 15. 01. 2018 1 Michael Welzl University of Oslo / University of Rome Tor Vergata
The Transport Layer is Dead Long Live the Transport Layer! Michael Welzl University of Oslo / University of Rome Tor Vergata 15. 01. 2018 1 Michael Welzl University of Oslo / University of Rome Tor Vergata
Transport Services Internet Transport's Last Chance? Michael Welzl
 Transport Services Internet Transport's Last Chance? Michael Welzl IMDEA Networks 31. October 2014 Outline Problem Solution 2 Problem 3 What s the problem? The Internet works! I work, too! Could be faster
Transport Services Internet Transport's Last Chance? Michael Welzl IMDEA Networks 31. October 2014 Outline Problem Solution 2 Problem 3 What s the problem? The Internet works! I work, too! Could be faster
The Transport Layer is Dead Long Live the Transport Layer! Michael Welzl Net Group, University of Rome Tor Vergata
 The Transport Layer is Dead Long Live the Transport Layer! Michael Welzl Net Group, University of Rome Tor Vergata 30. 09. 2017 1 Outline 1. The problem 2. The solution 1. IETF Transport Services (TAPS)
The Transport Layer is Dead Long Live the Transport Layer! Michael Welzl Net Group, University of Rome Tor Vergata 30. 09. 2017 1 Outline 1. The problem 2. The solution 1. IETF Transport Services (TAPS)
Data Center TCP (DCTCP)
 Data Center Packet Transport Data Center TCP (DCTCP) Mohammad Alizadeh, Albert Greenberg, David A. Maltz, Jitendra Padhye Parveen Patel, Balaji Prabhakar, Sudipta Sengupta, Murari Sridharan Cloud computing
Data Center Packet Transport Data Center TCP (DCTCP) Mohammad Alizadeh, Albert Greenberg, David A. Maltz, Jitendra Padhye Parveen Patel, Balaji Prabhakar, Sudipta Sengupta, Murari Sridharan Cloud computing
CSE 461 Midterm Winter 2018
 CSE 461 Midterm Winter 2018 Your Name: UW Net ID: General Information This is a closed book/laptop examination. You have 50 minutes to answer as many questions as possible. The number in parentheses at
CSE 461 Midterm Winter 2018 Your Name: UW Net ID: General Information This is a closed book/laptop examination. You have 50 minutes to answer as many questions as possible. The number in parentheses at
Better transport Michael Welzl
 Better transport Michael Welzl KIT, Karlsruhe 15. May 2014 Context 15 years of almost only transport layer research Because it s so bad and I d like to fix it 1. Gradual, deployable (reasonable) Strong
Better transport Michael Welzl KIT, Karlsruhe 15. May 2014 Context 15 years of almost only transport layer research Because it s so bad and I d like to fix it 1. Gradual, deployable (reasonable) Strong
Schahin Rajab TCP or QUIC Which protocol is most promising for the future of the internet?
 Schahin Rajab sr2@kth.se 2016 04 20 TCP or QUIC Which protocol is most promising for the future of the internet? Table of contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Background 4 2.1 TCP 4 2.2 UDP 4 2.3 QUIC 4 2.4 HTTP
Schahin Rajab sr2@kth.se 2016 04 20 TCP or QUIC Which protocol is most promising for the future of the internet? Table of contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Background 4 2.1 TCP 4 2.2 UDP 4 2.3 QUIC 4 2.4 HTTP
INF3190 A critical look at the Internet / alternative network architectures. Michael Welzl
 INF390 A critical look at the Internet / alternative network architectures Michael Welzl What s the problem? The Internet works! I work, too! Could be faster Could be safer Could be more reliable (Internet):
INF390 A critical look at the Internet / alternative network architectures Michael Welzl What s the problem? The Internet works! I work, too! Could be faster Could be safer Could be more reliable (Internet):
Data Center TCP (DCTCP)
 Data Center TCP (DCTCP) Mohammad Alizadeh, Albert Greenberg, David A. Maltz, Jitendra Padhye Parveen Patel, Balaji Prabhakar, Sudipta Sengupta, Murari Sridharan Microsoft Research Stanford University 1
Data Center TCP (DCTCP) Mohammad Alizadeh, Albert Greenberg, David A. Maltz, Jitendra Padhye Parveen Patel, Balaji Prabhakar, Sudipta Sengupta, Murari Sridharan Microsoft Research Stanford University 1
PCC: Performance-oriented Congestion Control
 PCC: Performance-oriented Congestion Control Michael Schapira Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Compira Labs (co-founder and chief scientist) Performance-oriented Congestion Control PCC: Re-architecting
PCC: Performance-oriented Congestion Control Michael Schapira Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Compira Labs (co-founder and chief scientist) Performance-oriented Congestion Control PCC: Re-architecting
Congestion Metacontrol to achieve a Deadline Aware Less than Best Effort service
 Congestion Metacontrol to achieve a Deadline Aware Less than Best Effort service David Hayes together with David Ros, Andreas Petlund, Iffat Ahmed, Lars Erik Storbukås, and Hugo Wallenburg ICCRG 13 November
Congestion Metacontrol to achieve a Deadline Aware Less than Best Effort service David Hayes together with David Ros, Andreas Petlund, Iffat Ahmed, Lars Erik Storbukås, and Hugo Wallenburg ICCRG 13 November
RMCAT - Shared Bottleneck Detection and Coupled Congestion Control vs. QoS for WebRTC Michael Welzl
 RMCAT - Shared Bottleneck Detection and Coupled Congestion Control vs. QoS for WebRTC Michael Welzl CAIA, Swinburne University, Melbourne 4. December 2014 Contributors Main people behind this work: Shared
RMCAT - Shared Bottleneck Detection and Coupled Congestion Control vs. QoS for WebRTC Michael Welzl CAIA, Swinburne University, Melbourne 4. December 2014 Contributors Main people behind this work: Shared
Square Pegs in a Round Pipe: Wire-Compatible Unordered Delivery In TCP and TLS
 Square Pegs in a Round Pipe: Wire-Compatible Unordered Delivery In TCP and TLS Jana Iyengar*, Bryan Ford + Syed Obaid Amin* +, Michael F. Nowlan +, Nabin Tiwari* *Franklin & Marshall College + Yale University
Square Pegs in a Round Pipe: Wire-Compatible Unordered Delivery In TCP and TLS Jana Iyengar*, Bryan Ford + Syed Obaid Amin* +, Michael F. Nowlan +, Nabin Tiwari* *Franklin & Marshall College + Yale University
The Impact of Transport Header Encryption on Operation and Evolution of the Internet. draft-fairhurst-tsvwg-transport-encrypt-04
 The Impact of Transport Header Encryption on Operation and Evolution of the Internet draft-fairhurst-tsvwg-transport-encrypt-04 Gorry Fairhurst, Colin Perkins Transport Transports discover and adapt to
The Impact of Transport Header Encryption on Operation and Evolution of the Internet draft-fairhurst-tsvwg-transport-encrypt-04 Gorry Fairhurst, Colin Perkins Transport Transports discover and adapt to
draft-johansson-rmcat-scream-cc
 SCReAM Self-Clocked Rate Adaptation for Multimedia draft-johansson-rmcat-scream-cc Ingemar Johansson Zaheduzzaman Sarker Ericsson Research Main features Self-clocked framework similar to TCP Functional
SCReAM Self-Clocked Rate Adaptation for Multimedia draft-johansson-rmcat-scream-cc Ingemar Johansson Zaheduzzaman Sarker Ericsson Research Main features Self-clocked framework similar to TCP Functional
Data Center TCP(DCTCP)
 Data Center TCP(DCTCP) Mohammad Alizadeh * +, Albert Greenberg *, David A. Maltz *, Jitendra Padhye *, Parveen Patel *, Balaji Prabhakar +, Sudipta Sengupta *, Murari Sridharan * * + Microsoft Research
Data Center TCP(DCTCP) Mohammad Alizadeh * +, Albert Greenberg *, David A. Maltz *, Jitendra Padhye *, Parveen Patel *, Balaji Prabhakar +, Sudipta Sengupta *, Murari Sridharan * * + Microsoft Research
A New Internet? RIPE76 - Marseille May Jordi Palet
 A New Internet? RIPE76 - Marseille May 2018 Jordi Palet (jordi.palet@theipv6company.com) -1 (a quick) Introduction to HTTP/2, QUIC and DOH and more RIPE76 - Marseille May 2018 Jordi Palet (jordi.palet@theipv6company.com)
A New Internet? RIPE76 - Marseille May 2018 Jordi Palet (jordi.palet@theipv6company.com) -1 (a quick) Introduction to HTTP/2, QUIC and DOH and more RIPE76 - Marseille May 2018 Jordi Palet (jordi.palet@theipv6company.com)
6. Correspondence relationship between Educational goals and Course goals
 1. Course Title (Course Code) Fundamentals of Information Networks (2201) 2. Instructor Teruaki YOKOYAMA 3. Term Fall 2 4. Outline and Objectives In this course the students study the technologies for
1. Course Title (Course Code) Fundamentals of Information Networks (2201) 2. Instructor Teruaki YOKOYAMA 3. Term Fall 2 4. Outline and Objectives In this course the students study the technologies for
Congestion Control In the Network
 Congestion Control In the Network Brighten Godfrey cs598pbg September 9 2010 Slides courtesy Ion Stoica with adaptation by Brighten Today Fair queueing XCP Announcements Problem: no isolation between flows
Congestion Control In the Network Brighten Godfrey cs598pbg September 9 2010 Slides courtesy Ion Stoica with adaptation by Brighten Today Fair queueing XCP Announcements Problem: no isolation between flows
TAPS-related topics from the NEAT project. Naeem Khademi (NEAT project) TAPS WG - IETF 97 Seoul- South Korea 16 November 2016
 TAPS-related topics from the NEAT project Naeem Khademi (NEAT project) TAPS WG - IETF 97 Seoul- South Korea 16 November 2016 Introduction on NEAT NEAT project has been ongoing since March 2015 NEAT library
TAPS-related topics from the NEAT project Naeem Khademi (NEAT project) TAPS WG - IETF 97 Seoul- South Korea 16 November 2016 Introduction on NEAT NEAT project has been ongoing since March 2015 NEAT library
ADVANCED TOPICS FOR CONGESTION CONTROL
 ADVANCED TOPICS FOR CONGESTION CONTROL Congestion Control The Internet only functions because TCP s congestion control does an effective job of matching traffic demand to available capacity. TCP s Window
ADVANCED TOPICS FOR CONGESTION CONTROL Congestion Control The Internet only functions because TCP s congestion control does an effective job of matching traffic demand to available capacity. TCP s Window
Wireless TCP Performance Issues
 Wireless TCP Performance Issues Issues, transport layer protocols Set up and maintain end-to-end connections Reliable end-to-end delivery of data Flow control Congestion control Udp? Assume TCP for the
Wireless TCP Performance Issues Issues, transport layer protocols Set up and maintain end-to-end connections Reliable end-to-end delivery of data Flow control Congestion control Udp? Assume TCP for the
CS 556 Advanced Computer Networks Spring Solutions to Midterm Test March 10, YOUR NAME: Abraham MATTA
 CS 556 Advanced Computer Networks Spring 2011 Solutions to Midterm Test March 10, 2011 YOUR NAME: Abraham MATTA This test is closed books. You are only allowed to have one sheet of notes (8.5 11 ). Please
CS 556 Advanced Computer Networks Spring 2011 Solutions to Midterm Test March 10, 2011 YOUR NAME: Abraham MATTA This test is closed books. You are only allowed to have one sheet of notes (8.5 11 ). Please
MPTCP and BBR performance over Internet satellite paths. Nicolas KUHN
 MPTCP and BBR performance over Internet satellite paths Nicolas KUHN nicolas.kuhn@cnes.fr Myth #1: SATCOM systems are quite specific Indeed: Limited frequency resource (regulation, etc.) Dish alignment
MPTCP and BBR performance over Internet satellite paths Nicolas KUHN nicolas.kuhn@cnes.fr Myth #1: SATCOM systems are quite specific Indeed: Limited frequency resource (regulation, etc.) Dish alignment
Congestion Control for High Bandwidth-delay Product Networks
 Congestion Control for High Bandwidth-delay Product Networks Dina Katabi, Mark Handley, Charlie Rohrs Presented by Chi-Yao Hong Adapted from slides by Dina Katabi CS598pbg Sep. 10, 2009 Trends in the Future
Congestion Control for High Bandwidth-delay Product Networks Dina Katabi, Mark Handley, Charlie Rohrs Presented by Chi-Yao Hong Adapted from slides by Dina Katabi CS598pbg Sep. 10, 2009 Trends in the Future
Our pre-taps work on transport services Michael Welzl
 Our pre-taps work on transport services Michael Welzl TAPS, 92 nd IETF meeting 23. March 2015 Outline / disclaimer Overview of results documented in MSc. thesis + paper [Stefan Jörer: A Protocol-Independent
Our pre-taps work on transport services Michael Welzl TAPS, 92 nd IETF meeting 23. March 2015 Outline / disclaimer Overview of results documented in MSc. thesis + paper [Stefan Jörer: A Protocol-Independent
Attaining the Promise and Avoiding the Pitfalls of TCP in the Datacenter. Glenn Judd Morgan Stanley
 Attaining the Promise and Avoiding the Pitfalls of TCP in the Datacenter Glenn Judd Morgan Stanley 1 Introduction Datacenter computing pervasive Beyond the Internet services domain BigData, Grid Computing,
Attaining the Promise and Avoiding the Pitfalls of TCP in the Datacenter Glenn Judd Morgan Stanley 1 Introduction Datacenter computing pervasive Beyond the Internet services domain BigData, Grid Computing,
TCP so far Computer Networking Outline. How Was TCP Able to Evolve
 TCP so far 15-441 15-441 Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 14: TCP Performance & Future Peter Steenkiste Fall 2016 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f16 Reliable byte stream protocol Connection establishments
TCP so far 15-441 15-441 Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 14: TCP Performance & Future Peter Steenkiste Fall 2016 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f16 Reliable byte stream protocol Connection establishments
Next Steps Spring 2011 Lecture #18. Multi-hop Networks. Network Reliability. Have: digital point-to-point. Want: many interconnected points
 Next Steps Have: digital point-to-point We ve worked on link signaling, reliability, sharing Want: many interconnected points 6.02 Spring 2011 Lecture #18 multi-hop networks: design criteria network topologies
Next Steps Have: digital point-to-point We ve worked on link signaling, reliability, sharing Want: many interconnected points 6.02 Spring 2011 Lecture #18 multi-hop networks: design criteria network topologies
Flow-start: Faster and Less Overshoot with Paced Chirping
 Flow-start: Faster and Less Overshoot with Paced Chirping Joakim Misund, Simula and Uni Oslo Bob Briscoe, Independent IRTF ICCRG, Jul 2018 The Slow-Start
Flow-start: Faster and Less Overshoot with Paced Chirping Joakim Misund, Simula and Uni Oslo Bob Briscoe, Independent IRTF ICCRG, Jul 2018 The Slow-Start
Performance-oriented Congestion Control
 Performance-oriented Congestion Control Mo Dong, Qingxi Li, Doron Zarchy*, P. Brighten Godfrey and Michael Schapira* University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign *Hebrew University of Jerusalem Qingxi Li
Performance-oriented Congestion Control Mo Dong, Qingxi Li, Doron Zarchy*, P. Brighten Godfrey and Michael Schapira* University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign *Hebrew University of Jerusalem Qingxi Li
Moving Beyond Sockets
 Moving Beyond Sockets Architecture and Observations Tommy Pauly (tpauly@apple.com) TAPS IETF 97, November 2016, Seoul 1 Context TAPS is about providing easier ways to use various transport protocols, and
Moving Beyond Sockets Architecture and Observations Tommy Pauly (tpauly@apple.com) TAPS IETF 97, November 2016, Seoul 1 Context TAPS is about providing easier ways to use various transport protocols, and
Networking and Internetworking 1
 Networking and Internetworking 1 Today l Networks and distributed systems l Internet architecture xkcd Networking issues for distributed systems Early networks were designed to meet relatively simple requirements
Networking and Internetworking 1 Today l Networks and distributed systems l Internet architecture xkcd Networking issues for distributed systems Early networks were designed to meet relatively simple requirements
The Impact of Transport Header Encryption on Operation and Evolution of the Internet
 The Impact of Transport Header Encryption on Operation and Evolution of the Internet draft-fairhurst-tsvwg-transport-encrypt-04 Gorry Fairhurst University of Aberdeen Colin Perkins University of Glasgow
The Impact of Transport Header Encryption on Operation and Evolution of the Internet draft-fairhurst-tsvwg-transport-encrypt-04 Gorry Fairhurst University of Aberdeen Colin Perkins University of Glasgow
Discussion: Messaging
 Discussion: Messaging Michael Welzl TAPS @ IETF 98 Chicago, 28.3.2017 1 From draft-gjessing-taps-minset-04 Transport features that require app knowledge + allow fall-back to TCP Sending Reliably transfer
Discussion: Messaging Michael Welzl TAPS @ IETF 98 Chicago, 28.3.2017 1 From draft-gjessing-taps-minset-04 Transport features that require app knowledge + allow fall-back to TCP Sending Reliably transfer
Lecture 15: Datacenter TCP"
 Lecture 15: Datacenter TCP" CSE 222A: Computer Communication Networks Alex C. Snoeren Thanks: Mohammad Alizadeh Lecture 15 Overview" Datacenter workload discussion DC-TCP Overview 2 Datacenter Review"
Lecture 15: Datacenter TCP" CSE 222A: Computer Communication Networks Alex C. Snoeren Thanks: Mohammad Alizadeh Lecture 15 Overview" Datacenter workload discussion DC-TCP Overview 2 Datacenter Review"
LEDBAT++: Low priority TCP Congestion Control in Windows
 LEDBAT++: Low priority TCP Congestion Control in Windows Praveen Balasubramanian pravb@microsoft.com Background Software updates, telemetry, or error reporting Should not interfere with Skype call, interactive
LEDBAT++: Low priority TCP Congestion Control in Windows Praveen Balasubramanian pravb@microsoft.com Background Software updates, telemetry, or error reporting Should not interfere with Skype call, interactive
Reducing Latency in Internet Access Links with Mechanisms in Endpoints and within the Network
 Reducing Latency in Internet Access Links with Mechanisms in Endpoints and within the Network Naeem Khademi Networks and Distributed Systems Group Department of Informatics University of Oslo PhD Defense
Reducing Latency in Internet Access Links with Mechanisms in Endpoints and within the Network Naeem Khademi Networks and Distributed Systems Group Department of Informatics University of Oslo PhD Defense
Expires: August 30, 2018
 TAPS Working Group Internet-Draft Intended status: Informational Expires: August 30, 2018 T. Pauly, Ed. Apple Inc. B. Trammell, Ed. ETH Zurich A. Brunstrom Karlstad University G. Fairhurst University of
TAPS Working Group Internet-Draft Intended status: Informational Expires: August 30, 2018 T. Pauly, Ed. Apple Inc. B. Trammell, Ed. ETH Zurich A. Brunstrom Karlstad University G. Fairhurst University of
Congestion Control. Brighten Godfrey CS 538 January Based in part on slides by Ion Stoica
 Congestion Control Brighten Godfrey CS 538 January 31 2018 Based in part on slides by Ion Stoica Announcements A starting point: the sliding window protocol TCP flow control Make sure receiving end can
Congestion Control Brighten Godfrey CS 538 January 31 2018 Based in part on slides by Ion Stoica Announcements A starting point: the sliding window protocol TCP flow control Make sure receiving end can
A New Internet? Introduction to HTTP/2, QUIC and DOH
 A New Internet? Introduction to HTTP/2, QUIC and DOH and more LACNIC 29 - Panamá May 2018 Jordi Palet (jordi.palet@theipv6company.com) -1 Internet is Changing More and more, Internet traffic is moving
A New Internet? Introduction to HTTP/2, QUIC and DOH and more LACNIC 29 - Panamá May 2018 Jordi Palet (jordi.palet@theipv6company.com) -1 Internet is Changing More and more, Internet traffic is moving
Packet Scheduling in Data Centers. Lecture 17, Computer Networks (198:552)
 Packet Scheduling in Data Centers Lecture 17, Computer Networks (198:552) Datacenter transport Goal: Complete flows quickly / meet deadlines Short flows (e.g., query, coordination) Large flows (e.g., data
Packet Scheduling in Data Centers Lecture 17, Computer Networks (198:552) Datacenter transport Goal: Complete flows quickly / meet deadlines Short flows (e.g., query, coordination) Large flows (e.g., data
A Path Layer for the Internet
 A Path Layer for the Internet Enabling Network Operations on Encrypted Traffic Mirja Kühlewind, Tobias Bühler, Brian Trammell, ETH Zürich Stephan Neuhaus, Roman Müntener, Zürich Univ. of Applied Sciences
A Path Layer for the Internet Enabling Network Operations on Encrypted Traffic Mirja Kühlewind, Tobias Bühler, Brian Trammell, ETH Zürich Stephan Neuhaus, Roman Müntener, Zürich Univ. of Applied Sciences
Transport Protocols for Data Center Communication. Evisa Tsolakou Supervisor: Prof. Jörg Ott Advisor: Lect. Pasi Sarolahti
 Transport Protocols for Data Center Communication Evisa Tsolakou Supervisor: Prof. Jörg Ott Advisor: Lect. Pasi Sarolahti Contents Motivation and Objectives Methodology Data Centers and Data Center Networks
Transport Protocols for Data Center Communication Evisa Tsolakou Supervisor: Prof. Jörg Ott Advisor: Lect. Pasi Sarolahti Contents Motivation and Objectives Methodology Data Centers and Data Center Networks
CS268: Beyond TCP Congestion Control
 TCP Problems CS68: Beyond TCP Congestion Control Ion Stoica February 9, 004 When TCP congestion control was originally designed in 1988: - Key applications: FTP, E-mail - Maximum link bandwidth: 10Mb/s
TCP Problems CS68: Beyond TCP Congestion Control Ion Stoica February 9, 004 When TCP congestion control was originally designed in 1988: - Key applications: FTP, E-mail - Maximum link bandwidth: 10Mb/s
RINA essentials. Eduard Grasa, FP7 PRISTINE. Evolution and Revolution in the Internet Software Defined Networks and new network architectures
 Evolution and Revolution in the Internet Software Defined Networks and new network architectures RINA essentials Eduard Grasa, FP7 PRISTINE Pisa, October 2015 #ict-pristine 1 WHY RINA? 2 The TCP/IP model
Evolution and Revolution in the Internet Software Defined Networks and new network architectures RINA essentials Eduard Grasa, FP7 PRISTINE Pisa, October 2015 #ict-pristine 1 WHY RINA? 2 The TCP/IP model
CS244 Advanced Topics in Computer Networks Midterm Exam Monday, May 2, 2016 OPEN BOOK, OPEN NOTES, INTERNET OFF
 CS244 Advanced Topics in Computer Networks Midterm Exam Monday, May 2, 2016 OPEN BOOK, OPEN NOTES, INTERNET OFF Your Name: Answers SUNet ID: root @stanford.edu In accordance with both the letter and the
CS244 Advanced Topics in Computer Networks Midterm Exam Monday, May 2, 2016 OPEN BOOK, OPEN NOTES, INTERNET OFF Your Name: Answers SUNet ID: root @stanford.edu In accordance with both the letter and the
Chapter 3 outline. 3.5 Connection-oriented transport: TCP. 3.6 Principles of congestion control 3.7 TCP congestion control
 Chapter 3 outline 3.1 Transport-layer services 3.2 Multiplexing and demultiplexing 3.3 Connectionless transport: UDP 3.4 Principles of reliable data transfer 3.5 Connection-oriented transport: TCP segment
Chapter 3 outline 3.1 Transport-layer services 3.2 Multiplexing and demultiplexing 3.3 Connectionless transport: UDP 3.4 Principles of reliable data transfer 3.5 Connection-oriented transport: TCP segment
WebRTC: IETF Standards Update September Colin Perkins
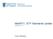 WebRTC: IETF Standards Update September 2016 Colin Perkins WebRTC Goals Server SIP+SDP Server Service SIP+SDP SIP+SDP Alice RTP Bob Alice API RTP API Bob The SIP framework is overly complex and rigid hinders
WebRTC: IETF Standards Update September 2016 Colin Perkins WebRTC Goals Server SIP+SDP Server Service SIP+SDP SIP+SDP Alice RTP Bob Alice API RTP API Bob The SIP framework is overly complex and rigid hinders
One More Bit Is Enough
 One More Bit Is Enough Yong Xia, RPI Lakshmi Subramanian, UCB Ion Stoica, UCB Shiv Kalyanaraman, RPI SIGCOMM 05, Philadelphia, PA 08 / 23 / 2005 Motivation #1: TCP doesn t work well in high b/w or delay
One More Bit Is Enough Yong Xia, RPI Lakshmi Subramanian, UCB Ion Stoica, UCB Shiv Kalyanaraman, RPI SIGCOMM 05, Philadelphia, PA 08 / 23 / 2005 Motivation #1: TCP doesn t work well in high b/w or delay
cs/ee 143 Communication Networks
 cs/ee 143 Communication Networks Chapter 4 Internetworking Text: Walrand & Parekh, 2010 Steven Low CMS, EE, Caltech Warning These notes are not self-contained, probably not understandable, unless you also
cs/ee 143 Communication Networks Chapter 4 Internetworking Text: Walrand & Parekh, 2010 Steven Low CMS, EE, Caltech Warning These notes are not self-contained, probably not understandable, unless you also
Lecture 10: Internetworking"
 Lecture 10: Internetworking" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 2 due NOW! Lecture 10 Overview" Spanning Tree Internet Protocol Service model Packet format 2 Spanning Tree Algorithm" Each bridge
Lecture 10: Internetworking" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 2 due NOW! Lecture 10 Overview" Spanning Tree Internet Protocol Service model Packet format 2 Spanning Tree Algorithm" Each bridge
Transparent Flow Mapping for NEAT
 Transparent Flow Mapping for Felix Weinrank, Michael Tüxen Münster University of Applied Sciences Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Stegerwaldstrasse 39 D-48565 Steinfurt Germany
Transparent Flow Mapping for Felix Weinrank, Michael Tüxen Münster University of Applied Sciences Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Stegerwaldstrasse 39 D-48565 Steinfurt Germany
Congestion Control for High Bandwidth-delay Product Networks. Dina Katabi, Mark Handley, Charlie Rohrs
 Congestion Control for High Bandwidth-delay Product Networks Dina Katabi, Mark Handley, Charlie Rohrs Outline Introduction What s wrong with TCP? Idea of Efficiency vs. Fairness XCP, what is it? Is it
Congestion Control for High Bandwidth-delay Product Networks Dina Katabi, Mark Handley, Charlie Rohrs Outline Introduction What s wrong with TCP? Idea of Efficiency vs. Fairness XCP, what is it? Is it
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP. JY Le Boudec 2014
 1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2014 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2014 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
QUIC. Internet-Scale Deployment on Linux. Ian Swett Google. TSVArea, IETF 102, Montreal
 QUIC Internet-Scale Deployment on Linux TSVArea, IETF 102, Montreal Ian Swett Google 1 A QUIC History - SIGCOMM 2017 Protocol for HTTPS transport, deployed at Google starting 2014 Between Google services
QUIC Internet-Scale Deployment on Linux TSVArea, IETF 102, Montreal Ian Swett Google 1 A QUIC History - SIGCOMM 2017 Protocol for HTTPS transport, deployed at Google starting 2014 Between Google services
IP Routing. Bharat S. Chaudhari International Institute of Information Technology Pune, India
 IP Routing Bharat S. Chaudhari International Institute of Information Technology Pune, India June 21, 2005 Network Devices: Ø The networking and internetworking devices are divided in the following categories:
IP Routing Bharat S. Chaudhari International Institute of Information Technology Pune, India June 21, 2005 Network Devices: Ø The networking and internetworking devices are divided in the following categories:
Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan. Transport Layer. By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri
 Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan Transport Layer By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri TCP/IP protocol suite 2 Transport Layer The transport layer is responsible for process-to-process
Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan Transport Layer By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri TCP/IP protocol suite 2 Transport Layer The transport layer is responsible for process-to-process
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP. JY Le Boudec 2014
 1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2014 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2014 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
Random Early Detection (RED) gateways. Sally Floyd CS 268: Computer Networks
 Random Early Detection (RED) gateways Sally Floyd CS 268: Computer Networks floyd@eelblgov March 20, 1995 1 The Environment Feedback-based transport protocols (eg, TCP) Problems with current Drop-Tail
Random Early Detection (RED) gateways Sally Floyd CS 268: Computer Networks floyd@eelblgov March 20, 1995 1 The Environment Feedback-based transport protocols (eg, TCP) Problems with current Drop-Tail
CSE 123A Computer Networks
 CSE 123A Computer Networks Winter 2005 Lecture 14 Congestion Control Some images courtesy David Wetherall Animations by Nick McKeown and Guido Appenzeller The bad news and the good news The bad news: new
CSE 123A Computer Networks Winter 2005 Lecture 14 Congestion Control Some images courtesy David Wetherall Animations by Nick McKeown and Guido Appenzeller The bad news and the good news The bad news: new
The Internetworking Problem. Internetworking. A Translation-based Solution
 Cloud Cloud Cloud 1 The Internetworking Problem Internetworking Two nodes communicating across a network of networks How to transport packets through this heterogeneous mass? A B The Internetworking Problem
Cloud Cloud Cloud 1 The Internetworking Problem Internetworking Two nodes communicating across a network of networks How to transport packets through this heterogeneous mass? A B The Internetworking Problem
Cloud e Datacenter Networking
 Cloud e Datacenter Networking Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica e delle Tecnologie dell Informazione DIETI Laurea Magistrale in Ingegneria Informatica Prof.
Cloud e Datacenter Networking Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica e delle Tecnologie dell Informazione DIETI Laurea Magistrale in Ingegneria Informatica Prof.
ECE 333: Introduction to Communication Networks Fall 2001
 ECE 333: Introduction to Communication Networks Fall 2001 Lecture 28: Transport Layer III Congestion control (TCP) 1 In the last lecture we introduced the topics of flow control and congestion control.
ECE 333: Introduction to Communication Networks Fall 2001 Lecture 28: Transport Layer III Congestion control (TCP) 1 In the last lecture we introduced the topics of flow control and congestion control.
TCP EX MACHINA: COMPUTER-GENERATED CONGESTION CONTROL KEITH WINSTEIN AND HARI BALAKRISHNAN. Presented by: Angela Jiang
 TCP EX MACHINA: COMPUTER-GENERATED CONGESTION CONTROL KEITH WINSTEIN AND HARI BALAKRISHNAN Presented by: Angela Jiang Network congestion Cause: Sources trying to send data faster than the network can process
TCP EX MACHINA: COMPUTER-GENERATED CONGESTION CONTROL KEITH WINSTEIN AND HARI BALAKRISHNAN Presented by: Angela Jiang Network congestion Cause: Sources trying to send data faster than the network can process
Computer Networks. Course Reference Model. Topic. Congestion What s the hold up? Nature of Congestion. Nature of Congestion 1/5/2015.
 Course Reference Model Computer Networks 7 Application Provides functions needed by users Zhang, Xinyu Fall 204 4 Transport Provides end-to-end delivery 3 Network Sends packets over multiple links School
Course Reference Model Computer Networks 7 Application Provides functions needed by users Zhang, Xinyu Fall 204 4 Transport Provides end-to-end delivery 3 Network Sends packets over multiple links School
Introduction to Internetworking
 Introduction to Internetworking Introductory terms Communications Network Facility that provides data transfer services An internet Collection of communications networks interconnected by bridges and/or
Introduction to Internetworking Introductory terms Communications Network Facility that provides data transfer services An internet Collection of communications networks interconnected by bridges and/or
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: TCP
 CSC 4900 Computer Networks: TCP Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Chapter 3 outline 3.1 Transport-layer services 3.2 Multiplexing and demultiplexing 3.3 Connectionless transport: UDP 3.4 Principles of reliable
CSC 4900 Computer Networks: TCP Professor Henry Carter Fall 2017 Chapter 3 outline 3.1 Transport-layer services 3.2 Multiplexing and demultiplexing 3.3 Connectionless transport: UDP 3.4 Principles of reliable
ConEx Concepts and Uses
 ConEx Concepts and Uses draft-moncaster-conex-concepts-uses-02 Toby Moncaster John Leslie (JLC) Bob Briscoe (BT) Rich Woundy (Comcast) Draft status draft-moncaster-conex-concepts-uses-02 Individual draft
ConEx Concepts and Uses draft-moncaster-conex-concepts-uses-02 Toby Moncaster John Leslie (JLC) Bob Briscoe (BT) Rich Woundy (Comcast) Draft status draft-moncaster-conex-concepts-uses-02 Individual draft
Performance-oriented Congestion Control
 Performance-oriented Congestion Control Mo Dong, Qingxi Li, Doron Zarchy*, P. Brighten Godfrey and Michael Schapira* University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign *Hebrew University of Jerusalem Mo Dong Qingxi
Performance-oriented Congestion Control Mo Dong, Qingxi Li, Doron Zarchy*, P. Brighten Godfrey and Michael Schapira* University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign *Hebrew University of Jerusalem Mo Dong Qingxi
An Abstract Application Layer Interface to Transport Services draft-trammell-taps-interface-01
 An Abstract Application Layer Interface to Transport Services draft-trammell-taps-interface-01 Brian Trammell TAPS IETF 101 Montreal Tue 17 July 2018 1 Interface Design Principles ( 3) (a review) We set
An Abstract Application Layer Interface to Transport Services draft-trammell-taps-interface-01 Brian Trammell TAPS IETF 101 Montreal Tue 17 July 2018 1 Interface Design Principles ( 3) (a review) We set
The Impact of Transport Header Encryption on Operation and Evolution of the Internet
 The Impact of Transport Header Encryption on Operation and Evolution of the Internet draft-fairhurst-tsvwg-transport-encrypt Gorry Fairhurst University of Aberdeen (MAMI) Colin Perkins University of Glasgow
The Impact of Transport Header Encryption on Operation and Evolution of the Internet draft-fairhurst-tsvwg-transport-encrypt Gorry Fairhurst University of Aberdeen (MAMI) Colin Perkins University of Glasgow
Developing Multipath TCP. Damon Wischik, Mark Handley, Costin Raiciu
 Developing Multipath TCP Damon Wischik, Mark Handley, Costin Raiciu 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 2 * * 1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000
Developing Multipath TCP Damon Wischik, Mark Handley, Costin Raiciu 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 2 * * 1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000
Chapter III: Transport Layer
 Chapter III: Transport Layer UG3 Computer Communications & Networks (COMN) Mahesh Marina mahesh@ed.ac.uk Slides thanks to Myungjin Lee and copyright of Kurose and Ross Principles of congestion control
Chapter III: Transport Layer UG3 Computer Communications & Networks (COMN) Mahesh Marina mahesh@ed.ac.uk Slides thanks to Myungjin Lee and copyright of Kurose and Ross Principles of congestion control
Congestion Control. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Congestion Control Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/25 Congestion Control how do you send as fast as possible, without overwhelming the network? challenges the fastest
Congestion Control Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/25 Congestion Control how do you send as fast as possible, without overwhelming the network? challenges the fastest
SPDY - A Web Protocol. Mike Belshe Velocity, Dec 2009
 SPDY - A Web Protocol Mike Belshe Velocity, Dec 2009 What is SPDY? Concept SPDY is an application layer protocol for transporting content over the web with reduced latency. Basic Features 1. Multiplexed
SPDY - A Web Protocol Mike Belshe Velocity, Dec 2009 What is SPDY? Concept SPDY is an application layer protocol for transporting content over the web with reduced latency. Basic Features 1. Multiplexed
EE 610 Part 2: Encapsulation and network utilities
 EE 610 Part 2: Encapsulation and network utilities Objective: After this experiment, the students should be able to: i. Understand the format of standard frames and packet headers. Overview: The Open Systems
EE 610 Part 2: Encapsulation and network utilities Objective: After this experiment, the students should be able to: i. Understand the format of standard frames and packet headers. Overview: The Open Systems
CS519: Computer Networks. Lecture 5, Part 4: Mar 29, 2004 Transport: TCP congestion control
 : Computer Networks Lecture 5, Part 4: Mar 29, 2004 Transport: TCP congestion control TCP performance We ve seen how TCP the protocol works Sequencing, receive window, connection setup and teardown And
: Computer Networks Lecture 5, Part 4: Mar 29, 2004 Transport: TCP congestion control TCP performance We ve seen how TCP the protocol works Sequencing, receive window, connection setup and teardown And
An experimental study of the learnability of congestion control
 An experimental study of the learnability of congestion control Anirudh Sivaraman, Keith Winstein, Pratiksha Thaker, Hari Balakrishnan MIT CSAIL http://web.mit.edu/remy/learnability August 31, 2014 1 /
An experimental study of the learnability of congestion control Anirudh Sivaraman, Keith Winstein, Pratiksha Thaker, Hari Balakrishnan MIT CSAIL http://web.mit.edu/remy/learnability August 31, 2014 1 /
Network Layer (1) Networked Systems 3 Lecture 8
 Network Layer (1) Networked Systems 3 Lecture 8 Role of the Network Layer Application Application The network layer is the first end-to-end layer in the OSI reference model Presentation Session Transport
Network Layer (1) Networked Systems 3 Lecture 8 Role of the Network Layer Application Application The network layer is the first end-to-end layer in the OSI reference model Presentation Session Transport
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP. JY Le Boudec 2015
 1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2015 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2015 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
This tutorial will help you in understanding IPv4 and its associated terminologies along with appropriate references and examples.
 About the Tutorial Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version in the development of the Internet Protocol (IP) and the first version of the protocol to be widely deployed. IPv4 is described
About the Tutorial Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version in the development of the Internet Protocol (IP) and the first version of the protocol to be widely deployed. IPv4 is described
Data Communications and Networks Spring Syllabus and Reading Assignments
 Data Communications and Networks Spring 2018 Syllabus and Assignments Revision Date: January 24, 2018 Course : This course teaches the design and implementation techniques essential for engineering robust
Data Communications and Networks Spring 2018 Syllabus and Assignments Revision Date: January 24, 2018 Course : This course teaches the design and implementation techniques essential for engineering robust
DIBS: Just-in-time congestion mitigation for Data Centers
 DIBS: Just-in-time congestion mitigation for Data Centers Kyriakos Zarifis, Rui Miao, Matt Calder, Ethan Katz-Bassett, Minlan Yu, Jitendra Padhye University of Southern California Microsoft Research Summary
DIBS: Just-in-time congestion mitigation for Data Centers Kyriakos Zarifis, Rui Miao, Matt Calder, Ethan Katz-Bassett, Minlan Yu, Jitendra Padhye University of Southern California Microsoft Research Summary
An Approach to Flexible QoS Routing with Active Networks
 U Innsbruck Informatik - 1 An Approach to Flexible QoS Routing with Active Networks Michael Welzl Alfred Cihal Max Mühlhäuser Leopold Franzens University Innsbruck Johannes Kepler University Linz TU Darmstadt
U Innsbruck Informatik - 1 An Approach to Flexible QoS Routing with Active Networks Michael Welzl Alfred Cihal Max Mühlhäuser Leopold Franzens University Innsbruck Johannes Kepler University Linz TU Darmstadt
Discovering Provisioning Domain Names and Data
 Discovering Provisioning Domain Names and Data draft-bruneau-intarea-provisioning-domains-01 B. Bruneau, P. Pfister, D. Schinazi, T. Pauly, E. Vyncke Hosts and networks are multi-homed Just a few examples
Discovering Provisioning Domain Names and Data draft-bruneau-intarea-provisioning-domains-01 B. Bruneau, P. Pfister, D. Schinazi, T. Pauly, E. Vyncke Hosts and networks are multi-homed Just a few examples
Wireless Network Security Spring 2013
 Wireless Network Security 14-814 Spring 2013 Patrick Tague Class #10 MAC Layer Misbehavior MAC Misbehavior Agenda Analysis of the 802.11 MAC protocol Selfish / greedy 802.11 MAC misbehavior Malicious 802.11
Wireless Network Security 14-814 Spring 2013 Patrick Tague Class #10 MAC Layer Misbehavior MAC Misbehavior Agenda Analysis of the 802.11 MAC protocol Selfish / greedy 802.11 MAC misbehavior Malicious 802.11
Congestion Control in the Recursive InterNetworking Architecture (RINA)
 Congestion Control in the Recursive InterNetworking Architecture (RINA) Peyman Teymoori, Michael Welzl, Stein Gjessing, Eduard Grasa, Roberto Riggio, Kewin Rausch, Domenico Siracusa Department of Informatics,
Congestion Control in the Recursive InterNetworking Architecture (RINA) Peyman Teymoori, Michael Welzl, Stein Gjessing, Eduard Grasa, Roberto Riggio, Kewin Rausch, Domenico Siracusa Department of Informatics,
Bandwidth Allocation & TCP
 Bandwidth Allocation & TCP The Transport Layer Focus Application Presentation How do we share bandwidth? Session Topics Transport Network Congestion control & fairness Data Link TCP Additive Increase/Multiplicative
Bandwidth Allocation & TCP The Transport Layer Focus Application Presentation How do we share bandwidth? Session Topics Transport Network Congestion control & fairness Data Link TCP Additive Increase/Multiplicative
OpenADN: A Case for Open Application Delivery Networking
 OpenADN: A Case for Open Application Delivery Networking Subharthi Paul, Raj Jain, Jianli Pan Washington University in Saint Louis {Pauls, jain, jp10}@cse.wustl.edu International Conference on Computer
OpenADN: A Case for Open Application Delivery Networking Subharthi Paul, Raj Jain, Jianli Pan Washington University in Saint Louis {Pauls, jain, jp10}@cse.wustl.edu International Conference on Computer
IPv6 at Google. Lorenzo Colitti
 IPv6 at Google Lorenzo Colitti lorenzo@google.com Why IPv6? IPv4 address space predictions (G. Huston) Why IPv6? Cost Buying addresses will be expensive Carrier-grade NAT may be expensive Lots of session
IPv6 at Google Lorenzo Colitti lorenzo@google.com Why IPv6? IPv4 address space predictions (G. Huston) Why IPv6? Cost Buying addresses will be expensive Carrier-grade NAT may be expensive Lots of session
Computer Networking. Queue Management and Quality of Service (QOS)
 Computer Networking Queue Management and Quality of Service (QOS) Outline Previously:TCP flow control Congestion sources and collapse Congestion control basics - Routers 2 Internet Pipes? How should you
Computer Networking Queue Management and Quality of Service (QOS) Outline Previously:TCP flow control Congestion sources and collapse Congestion control basics - Routers 2 Internet Pipes? How should you
CS644 Advanced Networks
 What we know so far CS644 Advanced Networks Lecture 6 Beyond TCP Congestion Control Andreas Terzis TCP Congestion control based on AIMD window adjustment [Jac88] Saved Internet from congestion collapse
What we know so far CS644 Advanced Networks Lecture 6 Beyond TCP Congestion Control Andreas Terzis TCP Congestion control based on AIMD window adjustment [Jac88] Saved Internet from congestion collapse
XCP: explicit Control Protocol
 XCP: explicit Control Protocol Dina Katabi MIT Lab for Computer Science dk@mit.edu www.ana.lcs.mit.edu/dina Sharing the Internet Infrastructure Is fundamental Much research in Congestion Control, QoS,
XCP: explicit Control Protocol Dina Katabi MIT Lab for Computer Science dk@mit.edu www.ana.lcs.mit.edu/dina Sharing the Internet Infrastructure Is fundamental Much research in Congestion Control, QoS,
Need For Protocol Architecture
 Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture
 Recursive InterNetwork Architecture Abraham Matta Computer Science Boston U. Short presentation at the November 1 st, 2010 CS Seminar on Faculty Projects 1 What s wrong with Ad-Hoc Wireless Network Laptop
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture Abraham Matta Computer Science Boston U. Short presentation at the November 1 st, 2010 CS Seminar on Faculty Projects 1 What s wrong with Ad-Hoc Wireless Network Laptop
MPTCP Application Considerations. draft-scharf-mptcp-api-00.txt. Michael Scharf Alan Ford
 MPTCP Application Considerations draft-scharf-mptcp-api-00.txt Michael Scharf Alan Ford November 9, 2009 Scope From MPTCP Charter: e. An extended
MPTCP Application Considerations draft-scharf-mptcp-api-00.txt Michael Scharf Alan Ford November 9, 2009 Scope From MPTCP Charter: e. An extended
Just enough TCP/IP. Protocol Overview. Connection Types in TCP/IP. Control Mechanisms. Borrowed from my ITS475/575 class the ITL
 Just enough TCP/IP Borrowed from my ITS475/575 class the ITL 1 Protocol Overview E-Mail HTTP (WWW) Remote Login File Transfer TCP UDP RTP RTCP SCTP IP ICMP ARP RARP (Auxiliary Services) Ethernet, X.25,
Just enough TCP/IP Borrowed from my ITS475/575 class the ITL 1 Protocol Overview E-Mail HTTP (WWW) Remote Login File Transfer TCP UDP RTP RTCP SCTP IP ICMP ARP RARP (Auxiliary Services) Ethernet, X.25,
Need For Protocol Architecture
 Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
Chapter 2 CS420/520 Axel Krings Page 1 Need For Protocol Architecture E.g. File transfer Source must activate communications path or inform network of destination Source must check destination is prepared
CPSC 441 COMPUTER COMMUNICATIONS MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION
 CPSC 441 COMPUTER COMMUNICATIONS MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Professor: Carey Williamson March 2, 2012 This is a CLOSED BOOK exam. Textbooks, notes, laptops,
CPSC 441 COMPUTER COMMUNICATIONS MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTION Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Professor: Carey Williamson March 2, 2012 This is a CLOSED BOOK exam. Textbooks, notes, laptops,
