IEEE 1901 HD-PLC (High Definition Power Line Communication) Abstract
|
|
|
- Patricia Fleming
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IEEE 1901 HD-PLC (High Definition Power Line Communication) Abstract The growing penetration of the internet throughout the society has also brought advantages to SOHOs and home networks. As networks develop, the demand for more multimedia content has grown along with the demand for faster network equipment. It is also widely known that HD- PLC systems that do not require new cables to be installed are convenient for network use with portables, where reliability and speed are main factors in power line communication. The PLC adaptor and PLC module will enable ubiquitous home networking and include high-speed data transmission technology using home power lines. This report shows that the HD-PLC system ensures advantages through the link everywhere concept that features 1) No wiring needed (all power plugs perform as information plugs), 2) Easy connection (just plug-in and connect to network) 3) Achieving AV transmission (with high communication throughput and realizing QoS) 1. Introduction At Panasonic Communications we provide users with the PLC adaptor and the PLC module which incorporates into their equipment so as to create ubiquitous home networks using highspeed data transmission technology via home power lines. In this paper we introduce the features of these devices, with a focus on the HD-PLC products, Physical Layer and Media Access Control Layer technology, which do not require additional wiring (all power outlets become data connections), allow easy connectivity (network connections are established merely by inserting the power plug), and provide AV transmission (fast communication throughput and QoS).
2 1.1. Overview of the IEEE 1901 HD-PLC IP The HD-PLC IP system from Panasonic System Networks is composed of the MAC, PHY and associated blocks required to implement a complete HD-PLC solution. The MAC and the Modem are conformant to the Wavelet MAC/PHY of IEEE 1901 and co-existence specification (ISP) The HD-PLC IP system consists of MAC software, MAC hardware and PHY hardware. The upper software portion of the HD-PLC MAC is implemented in ANSI C. The lower software portion of the HD-PLC MAC is implemented in assembly and executes on microcode engines. The hardware portion of the HD-PLC MAC and the PHY are implemented as synthesizable cores in Hardware description language. The IP system may be integrated into a single chip solution along with an application processor sub-system, or may be synthesized on a separate chip as a peripheral to the application processor sub-system. Figure 1 shows a structural example of a separate chip. This chip is separated into a microcomputer processing section, a PHY processing section, and a MAC processing section. The LSI is connected to a PLC analog front-end, an Ethernet PHY, SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) and Flash ROM (Flash Read Only Memory) as peripheral devices. IEEE 1901 HD-PLC LSI GPIO UART CPU PLC_PHY AFE OSC CLK Power Line PLC_MAC Flash Interface SDRAM Controller Ethernet MAC Flash SDRAM Ethernet PHY Ethernet Fig. 1 LSI block Diagram
3 1.2. Examples of the HD-PLC LSI, Adaptor and Module Table 1 lists the sample specifications of a PLC adaptor, and Figure 2 shows an external view of the PLC adaptor PLC-HP240EA, the PLC module board DRT-J520 and the PLC LSI KHN The size of the module board is at roughly around 70 mm x 30 mm. The KHN13200 includes a fully integrated AFE with A/D, D/A converter and PGA (Programmable Gain Amp.). Table 1 Specifications of the PLC Adaptor (PLC-HP240EA) Standard IEEE 1901 HD-PLC Frequency Band 2 MHz ~ 28 MHz Modulation Wavelet OFDM (32 PAM to 2 PAM) Transmission PHY Rate 240 Mbps(theoretical maximum transmission rate) Access Method CSMA/CA, DVTP(Dynamic Virtual Token Passing) Security AES 128-bit Encryption by Auto Setting Error Correction Reed-Solomon and Convolutional/Viterbi or LDPC-CC Power consumption 2.3W Fig. 2 Adaptor PLC-HP240EA Module DRT-J520 LSI KHN13200 (by I-O DATA) (by MITSUMI ELECTRIC) (by Kawasaki Microelectronics) 2. HD-PLC Physical Layer Technology 2.1. Overview of the Physical (PHY) Layer The HD-PLC PHY uses Wavelet OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) technology to provide highly efficient transmission and can coexist with existing systems (shortwave broadcasts and ham radio). Highly efficient transmission is possible with Wavelet OFDM through appropriate modulation of the sub-carrier and having no GI (Guard Interval). Moreover, deep notches over -35 dbc (flexible notches) can be created at the desired bandwidth by not using arbitrary sub-carriers. In the HD-PLC, PHY speed of up to approximately 240 Mbps is achieved at a bandwidth of 26 MHz. In addition, high-quality, highly reliable communications are achieved even in poor quality home power transmission routes through the use of strong error correction coding and a diversity mode.
4 2.2. Time-Waveform in the Wavelet OFDM In the FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) OFDM, a conventional technology, it was necessary to have a GI which was used to maintain orthogonality and a redundant signal for waveform rectification which was required to create a low side-lobe level in each sub-carrier. In Wavelet OFDM, the GI and the redundant signal for waveform rectification are absent; instead, a filter with a long impulse response is used. As a result, the time-waveform of each sub-carrier is transmitted in superposition while orthogonality is maintained, as shown in Figure 3. In the same fashion, orthogonality is maintained in each sub-carrier as well. In this fashion, the Wavelet OFDM represents a method appropriate for highly efficient transmission. Amplitude 4.00E E E E E E E E E Normalized time Fig. 3 Time-waveform of the sub-carrier 2.3. Wavelet OFDM Spectrum Figure 4 shows the Wavelet OFDM spectrum. In the Wavelet OFDM, bandwidth is limited by a filter which has a long impulse response, as shown in Figure 3. As a result, a low side-lobe over -35 dbc can be readily achieved. Consequently, even if there is narrowband interference from existing systems, the effect is only present in some sub-carriers, and ICI (Inter-Carrier Interference) level can be suppressed. Amplitude [db] Normalized frequency [Hz] Fig. 4 Wavelet OFDM spectrum A notch with attenuation over 35 db can be easily created by not using sub-carriers present in an arbitrary frequency bandwidth, as shown in Figure 5 (in Figure 5, notches are formed in the North America amateur radio bandwidth). In this manner, Wavelet OFDM, which can easily coexist with existing systems, is a good format for PLC.
5 Fig. 5 HD-PLC spectrum 3. HD-PLC Media Access Control 3.1. Overview of Media Access Control (MAC) HD-PLC MAC is an architecture that particularly emphasizes on AV transmission, and provides a function to maintain QoS (Quality of Service), a function to estimate transmission channels, and a function to improve transmission efficiency Quality of Service (QoS) Architecture The HD-PLC QoS control function has a role in determining and controlling the schedule for channel access. Using Beacon frames, the controller notifies other stations of the medium access schedule up to the next Beacon frame. During each beacon interval there are three distinct blocks of time as shown in Fig 6. The first is the beacon extent, which is a fixed time period in which the HD-PLC Master terminal is required to send a Beacon frame. The second is the contention free period (CFP), which is used for transmission by HD-PLC terminals that require reserved bandwidth on a scheduled basis. The third is the contention period (CP), which provides a best effort service; this service might include preference settings for the transmitted frames. The HD-PLC MAC supports 16 levels of priority for each data frame transmitted. 8 of these priority levels are user specifiable. TDMA channel access is realized during a CFP period, but it is an optional service. Beacon CFP CP Fig. 6 Scheduling
6 3.3. CSMA/CA The fundamental media access protocol of the HD-PLC is a procedure called carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA). During the CP, three media access mechanisms work to reduce the collisions: 1) CSMA/CA access, 2) priority control CSMA/CA, and 3) Dynamic Virtual Token Passing (DVTP) access. For the easy realization of the Quality of Service (QoS), priority control CSMA/CA mechanism is provided on the basis of the CSMA architecture. The priority control CSMA/CA has an additional two state following CIFS (Contention Inter-Frame Space) in the contention period, the gap state and the CONTENTION state (as shown in Figure 7) and completely separate the transmission opportunity between Higher User Priority and other priorities. By using the GAP state, the higher User Priority data can contend without other lower User Priority data because the other lower User Priority data just wait until the end of the GAP state and does not participate in the contention with the Back off mechanism. Fig. 7 Media State of priority control CSMA/CA 3.4. Dynamic Virtual Token Passing (DVTP) DVTP (Dynamic Virtual Token Passing) is a distinctive media access mechanism based on the carrier sense and virtual token technique in which frame transmission arbitration is autonomously carried out by using slots, where the period after a data frame is divided into fixed-length time units (equivalent to the carrier detection time: 54 µs), and through this system collision avoidance on the network can be accomplished. When DVTP mechanism is available in a CP, IFS based priority control CSMA/CA is not available during the CP. Virtual Token slot TX Data of # (1)Terminal #2 has a transmission right. Virtual Token slot (2)Terminal #4 has a transmission right. Fig. 8 Media access control by DTVP
7 3.5. Frame concatenation As speed in the physical layer (PHY) increases, the time available for the payload in the frame decreases, and the gap, which requires a certain amount of time, between the header and frame becomes a huge overhead and hence it cannot be ignored. Thus, in HD-PLC MAC, overhead is reduced and transmission efficiency is improved by creating a frame with several Ethernet packets which allows creating one container block. A container block can consist of a maximum of 60 segment blocks, as shown in Figure 9. Each segment block can consist of up to 31 aggregated MSDU (MAC Service Data Unit). Preamble Header Container Block Segment Block Segment Block Segment Block Control Payload Fig. 9 Frame structure Moreover, when an error occur, the efficiency is improved though selective repeat process. Figure 10 shows frames with eight segments. In the first frame, when an error occurs in segment blocks 2, 4, and 5, that information is sent from the reception side to the transmission side in the response frame. The response frame includes an NAK/ACK (Negative Acknowledgement / Acknowledgement) in all segment blocks. In the next frame, the data for 2, 4, and 5, where the errors occurred, are repeated, and the data from 9 onward is sent. Header Header Fig. 10 Selective repeat ARQ (Auto Repeat request)
8 4. Channel Estimation Transmission environment is a particular problem for home power line communications as shown in Figure 11. When the electrical equipment is plugged in or when the operation is started or stopped, the power supply circuit outputs various levels of noise. Fig. 11 transmission environment of in-home power line The goal of the Channel Estimation (CE) procedure is to assess the channel status upon data transmission. The CE is designed to achieve the maximum throughput by effectively using power line communication media. As shown in Fig.12 HD-PLC adopts variable bit loading on each carrier for a Discrete Multi-tone (DMT) technology. It is possible to use the media effectively by estimating the channel status before and after transmission and providing information such as the best modulation parameter to a transmit terminal. CNR bits f f Fig. 12 Example of DMT determined by CE
9 5. ISP (Inter System Protocol) Overview ISP allows power line resources to be shared among non-interoperable systems by TDM (Time Domain Multiplex). Coexistence signaling is carried out by the use of periodically repeating ISP windows that are used to convey information on coexisting system presence, resource requirements and resynchronization request. Each PLC system category is allocated a particular ISP window in a round robin fashion. ISP allows TDM to be implemented between coexisting in-home systems and an access system. The overall ISP TDM structure is shown in Figure 13. There are four such structures in every 24 AC_CYCLE.TDM resources are allocated according to the Table 2. Here HD-PLC is called IH-W. Fig. 13 General TDMA structure Table 2 Resource allocation Index ISP Field TDM Slot number ACC IH-W IH-O IH-G BW IH-G - IH-G IH-G IH-G IH-G IH-G IH-G IH-G IH-G 2 - IH-W IH-W IH-W IH-W IH-W IH-W IH-W IH-W IH-W IH-O - - IH-O IH-O IH-O IH-O IH-O IH-O IH-O IH-O 4 - IH-W - IH-G - IH-W IH-W IH-G IH-W IH-W IH-G IH-G IH-G 5 - IH-W IH-O - - IH-W IH-W IH-O IH-O IH-O IH-W IH-W IH-O IH-O IH-G - IH-G IH-O IH-O IH-O IH-O IH-G IH-G IH-G 7 - IH-W IH-O IH-G - IH-W IH-W IH-O IH-O IH-O IH-G IH-G IH-G 8 ACC FB ACC ACC ACC ACC ACC ACC ACC ACC 9 ACC - - IH-G PB IH-G IH-G IH-G IH-G ACC ACC IH-G IH-G 10 ACC - - IH-G FB IH-G IH-G IH-G ACC ACC ACC ACC IH-G 11 ACC IH-W - - PB IH-W IH-W IH-W IH-W ACC ACC IH-W IH-W 12 ACC IH-W - - FB IH-W IH-W IH-W ACC ACC ACC ACC IH-W 13 ACC - IH-O - PB IH-O IH-O IH-O IH-O ACC ACC IH-O IH-O 14 ACC - IH-O - FB IH-O IH-O IH-O ACC ACC ACC ACC IH-O 15 ACC IH-W - IH-G PB IH-W IH-W IH-G IH-W ACC ACC IH-G IH-G 16 ACC IH-W - IH-G FB IH-W IH-W IH-G ACC ACC ACC ACC IH-G 17 ACC IH-W IH-O - PB IH-W IH-W IH-O IH-O ACC ACC IH-W IH-O 18 ACC IH-W IH-O - FB IH-W IH-W IH-O ACC ACC ACC ACC IH-O 19 ACC - IH-O IH-G PB IH-G IH-O IH-O IH-O ACC ACC IH-G IH-G 20 ACC - IH-O IH-G FB IH-G IH-O IH-O ACC ACC ACC ACC IH-G 21 ACC IH-W IH-O IH-G PB IH-W IH-W IH-O IH-O ACC ACC IH-G IH-G 22 ACC IH-W IH-O IH-G FB IH-W IH-W IH-O ACC ACC ACC ACC IH-G
10 6. Dynamic Notching and Dynamic power control The dynamic notching provides reduction of interference between HD-PLC and short wave radio broadcast as shown in figure 14. The HD-PLC with dynamic notching modem will periodically sense the ingress and identify the presence of short wave radio broadcast signal. Dynamic notching works at least in the frequency allocations as defined by the ITU-R Radio Regulations or each region for radio broadcast services. Moreover, when the HD-PLC doesn t need maximum transmission power to get good performance, the transmission power is reduced dynamically. Fig. 14 Dynamic Notching 7. Conclusion As described above, the HD-PLC technology is used in the PHY layer, thus achieving efficiency in high-frequency use and dynamic notches. Using QoS technology, high-speed transmission of various applications such as AV transmission and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) are achieved in the MAC layer, thus allowing superiority in a stable, highly secure ubiquitous link
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 4 Wireless LAN Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Contents What is a Wireless LAN? Applications and Requirements Transmission
Next-Generation Power Line Communications and Standardization
 Next-Generation Power Line Communications and Standardization Hisao Koga 200812IEEE P1901HD-PLCHigh Definition Power Line Communication PLCPower Line Communication PHYPHYsical layer32 PAMPulse Amplitude
Next-Generation Power Line Communications and Standardization Hisao Koga 200812IEEE P1901HD-PLCHigh Definition Power Line Communication PLCPower Line Communication PHYPHYsical layer32 PAMPulse Amplitude
original standard a transmission at 5 GHz bit rate 54 Mbit/s b support for 5.5 and 11 Mbit/s e QoS
 IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
CS 716: Introduction to communication networks. - 8 th class; 17 th Aug Instructor: Sridhar Iyer IIT Bombay
 CS 716: Introduction to communication networks - 8 th class; 17 th Aug 2011 Instructor: Sridhar Iyer IIT Bombay Key points to consider for MAC Types/Modes of communication: Although the medium is shared,
CS 716: Introduction to communication networks - 8 th class; 17 th Aug 2011 Instructor: Sridhar Iyer IIT Bombay Key points to consider for MAC Types/Modes of communication: Although the medium is shared,
An Efficient MAC Scheme with Modified RTS/CTS of IEEE P1901
 An Efficient MAC Scheme with Modified RTS/CTS of IEEE P1901 Jae Yong Park 1, Choong Seon Hong 2, Sungwon Lee 3 Department of Computer Engineering, Kyung Hee University, 1 Seocheon, Giheung, Yongin, Gyeonggi,
An Efficient MAC Scheme with Modified RTS/CTS of IEEE P1901 Jae Yong Park 1, Choong Seon Hong 2, Sungwon Lee 3 Department of Computer Engineering, Kyung Hee University, 1 Seocheon, Giheung, Yongin, Gyeonggi,
04/11/2011. Wireless LANs. CSE 3213 Fall November Overview
 Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
Wireless LANs CSE 3213 Fall 2011 4 November 2011 Overview 2 1 Infrastructure Wireless LAN 3 Applications of Wireless LANs Key application areas: LAN extension cross-building interconnect nomadic access
ETSI Project BRAN Hiperlan Type 2 for IEEE 1394 Applications System Overview
 ETSI Project BRAN Hiperlan Type 2 for IEEE 1394 Applications System Overview Source : Jamshid Khun Jush (Ericsson) (THOMSON multimedia) 1 HIPERLAN/2 Standard A new standard developed by the ETSI Project
ETSI Project BRAN Hiperlan Type 2 for IEEE 1394 Applications System Overview Source : Jamshid Khun Jush (Ericsson) (THOMSON multimedia) 1 HIPERLAN/2 Standard A new standard developed by the ETSI Project
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview. Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University
 Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University Medium Access Control Topology 3 Simplex and Duplex 4 FDMA TDMA CDMA DSSS FHSS Multiple Access Methods Notice: CDMA and spread spectrum
Lecture 4: Wireless MAC Overview Hung-Yu Wei National Taiwan University Medium Access Control Topology 3 Simplex and Duplex 4 FDMA TDMA CDMA DSSS FHSS Multiple Access Methods Notice: CDMA and spread spectrum
Overview of WiMAX (Chapter 2) ENE 490 MON 13:30-16:30 Asst. Prof. Suwat Pattaramalai
 (Chapter 2) ENE 490 MON 13:30-16:30 Asst. Prof. Suwat Pattaramalai Background on IEEE 802.16 and WiMAX (Table 2.1 and Table 2.2) Salient Features of WiMAX OFDM-based physical layer: good resistance to
(Chapter 2) ENE 490 MON 13:30-16:30 Asst. Prof. Suwat Pattaramalai Background on IEEE 802.16 and WiMAX (Table 2.1 and Table 2.2) Salient Features of WiMAX OFDM-based physical layer: good resistance to
Physical Layer. Medium Access Links and Protocols. Point-to-Point protocols. Modems: Signaling. Modems Signaling. Srinidhi Varadarajan
 P Physical Layer Srinidhi Varadarajan Medium Access Links and Protocols Three types of links : point-to-point (single wire, e.g. PPP, SLIP) broadcast (shared wire or medium; e.g, Ethernet, Wavelan, etc.)
P Physical Layer Srinidhi Varadarajan Medium Access Links and Protocols Three types of links : point-to-point (single wire, e.g. PPP, SLIP) broadcast (shared wire or medium; e.g, Ethernet, Wavelan, etc.)
Strengthening Unlicensed Band Wireless Backhaul
 be in charge Strengthening Unlicensed Band Wireless Backhaul Use TDD/TDMA Based Channel Access Mechanism WHITE PAPER Strengthening Unlicensed Band Wireless Backhaul: Use TDD/TDMA Based Channel Access Mechanism
be in charge Strengthening Unlicensed Band Wireless Backhaul Use TDD/TDMA Based Channel Access Mechanism WHITE PAPER Strengthening Unlicensed Band Wireless Backhaul: Use TDD/TDMA Based Channel Access Mechanism
An Overview of the upcoming HomePlug AV Standard
 An Overview of the upcoming HomePlug AV Standard Kaywan H. Afkhamie, Srinivas Katar, Larry Yonge R&D Department Intellon Corporation Ocala, FL, USA {kaywan.afkhamie, srinivas.katar, larry.yonge}@intellon.com
An Overview of the upcoming HomePlug AV Standard Kaywan H. Afkhamie, Srinivas Katar, Larry Yonge R&D Department Intellon Corporation Ocala, FL, USA {kaywan.afkhamie, srinivas.katar, larry.yonge}@intellon.com
Initial PHY Layer System Proposal for Sub 11 GHz BWA
 Initial PHY Layer System Proposal for Sub 11 GHz BWA Document Number: 802.16.3p-00/40 Date Submitted: 2000-11-08 Source: Anader Benyamin-Seeyar Voice: (514) 822-2014 Harris Corporation Inc. Fax: (514)
Initial PHY Layer System Proposal for Sub 11 GHz BWA Document Number: 802.16.3p-00/40 Date Submitted: 2000-11-08 Source: Anader Benyamin-Seeyar Voice: (514) 822-2014 Harris Corporation Inc. Fax: (514)
WNC-0300USB. 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL
 WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
WNC-0300USB 11g Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL Contents 1. Introduction...3 1.1 Product Feature...3 1.2 System Requirement...3 2. Getting Start...3 2.1 LED Indicators...3 2.2 Install the 54Mbps Wireless
Dual core architecture with custom N-PLC optimized DSP and Data Link Layer 32bit controller
 SM2400 N-PLC Transceiver MultiStandard Narrowband Power Line Communication Modem Communication technology by: Semitech Semiconductor Product Overview The SM2400 is the ultimate Narrowband Power Line Communication
SM2400 N-PLC Transceiver MultiStandard Narrowband Power Line Communication Modem Communication technology by: Semitech Semiconductor Product Overview The SM2400 is the ultimate Narrowband Power Line Communication
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 13 Wireless LANs
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 13 Wireless LANs Wireless LAN Topology Infrastructure LAN Connect to stations on wired LAN and in other cells May do automatic handoff Ad hoc LAN No hub Peer-to-peer
Delivering Voice over IEEE WLAN Networks
 Delivering Voice over IEEE 802.11 WLAN Networks Al Petrick, Jim Zyren, Juan Figueroa Harris Semiconductor Palm Bay Florida Abstract The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard was developed primarily for packet
Delivering Voice over IEEE 802.11 WLAN Networks Al Petrick, Jim Zyren, Juan Figueroa Harris Semiconductor Palm Bay Florida Abstract The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard was developed primarily for packet
Multiple Access Protocols
 Multiple Access Protocols Computer Networks Lecture 2 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 Multiple Access to a Shared Channel The medium (or its sub-channel) may be shared by multiple stations (dynamic allocation) just
Multiple Access Protocols Computer Networks Lecture 2 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 Multiple Access to a Shared Channel The medium (or its sub-channel) may be shared by multiple stations (dynamic allocation) just
PowerLine AV Wi-Fi AC1200 Starter Kit
 Product Highlights High-speed Data Streaming Powerline AV2 1000 allows for Gigabit speeds over home electrical wiring, making it suitable for highbandwidth activities like HD media streaming Easy Setup
Product Highlights High-speed Data Streaming Powerline AV2 1000 allows for Gigabit speeds over home electrical wiring, making it suitable for highbandwidth activities like HD media streaming Easy Setup
ECE442 Communications Lecture 3. Wireless Local Area Networks
 ECE442 Communications Lecture 3. Wireless Local Area Networks Husheng Li Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring, 2014 Wireless Local Networks 1 A WLAN links two or more devices using
ECE442 Communications Lecture 3. Wireless Local Area Networks Husheng Li Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Spring, 2014 Wireless Local Networks 1 A WLAN links two or more devices using
Lecture 16: QoS and "
 Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Lecture 16: QoS and 802.11" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren HW 4 due now! Lecture 16 Overview" Network-wide QoS IntServ DifServ 802.11 Wireless CSMA/CA Hidden Terminals RTS/CTS CSE 123 Lecture
Topics. Link Layer Services (more) Link Layer Services LECTURE 5 MULTIPLE ACCESS AND LOCAL AREA NETWORKS. flow control: error detection:
 1 Topics 2 LECTURE 5 MULTIPLE ACCESS AND LOCAL AREA NETWORKS Multiple access: CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA, token passing, channelization LAN: characteristics, i basic principles i Protocol architecture Topologies
1 Topics 2 LECTURE 5 MULTIPLE ACCESS AND LOCAL AREA NETWORKS Multiple access: CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA, token passing, channelization LAN: characteristics, i basic principles i Protocol architecture Topologies
Link Layer and LANs 안상현서울시립대학교컴퓨터 통계학과.
 Link Layer and LANs 안상현서울시립대학교컴퓨터 통계학과 ahn@venus.uos.ac.kr Data Link Layer Goals: understand principles behind data link layer services: error detection, correction sharing a broadcast channel: multiple
Link Layer and LANs 안상현서울시립대학교컴퓨터 통계학과 ahn@venus.uos.ac.kr Data Link Layer Goals: understand principles behind data link layer services: error detection, correction sharing a broadcast channel: multiple
EL2745 Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks
 EL2745 Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks www.kth.se/student/program-kurser/kurshemsidor/kurshemsidor/control/el2745 Lecture 5 Stockholm, February 2, 2012 Carlo Fischione Royal Institute of Technology
EL2745 Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks www.kth.se/student/program-kurser/kurshemsidor/kurshemsidor/control/el2745 Lecture 5 Stockholm, February 2, 2012 Carlo Fischione Royal Institute of Technology
The following CompTIA Network+ domain objectives and examples are covered in this module:
 Module 1 / Topologies and Infrastructure Topologies and Infrastructure The following CompTIA Network+ domain objectives and examples are covered in this module: CompTIA Network+ Certification Domain Areas
Module 1 / Topologies and Infrastructure Topologies and Infrastructure The following CompTIA Network+ domain objectives and examples are covered in this module: CompTIA Network+ Certification Domain Areas
Links Reading: Chapter 2. Goals of Todayʼs Lecture. Message, Segment, Packet, and Frame
 Links Reading: Chapter 2 CS 375: Computer Networks Thomas Bressoud 1 Goals of Todayʼs Lecture Link-layer services Encoding, framing, and error detection Error correction and flow control Sharing a shared
Links Reading: Chapter 2 CS 375: Computer Networks Thomas Bressoud 1 Goals of Todayʼs Lecture Link-layer services Encoding, framing, and error detection Error correction and flow control Sharing a shared
Multiple Access in Cellular and Systems
 Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Multiple Access in Cellular and 802.11 Systems 1 GSM The total bandwidth is divided into many narrowband channels. (200 khz in GSM) Users are given time slots in a narrowband channel (8 users) A channel
Announcements : Wireless Networks Lecture 11: * Outline. Power Management. Page 1
 Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 11: 802.11* Please mail survey team information» Can include topic preferences now if you have them Submit project designs through blackboard Homework 2
Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 11: 802.11* Please mail survey team information» Can include topic preferences now if you have them Submit project designs through blackboard Homework 2
Mohamed Khedr.
 Mohamed Khedr http://webmail.aast.edu/~khedr Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Week 13 Week 14 Week 15 Overview Packet Switching IP addressing
Mohamed Khedr http://webmail.aast.edu/~khedr Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Week 13 Week 14 Week 15 Overview Packet Switching IP addressing
Topics for Today. More on Ethernet. Wireless LANs Readings. Topology and Wiring Switched Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet. 4.3 to 4.
 Topics for Today More on Ethernet Topology and Wiring Switched Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet Wireless LANs Readings 4.3 to 4.4 1 Original Ethernet Wiring Heavy coaxial cable, called thicknet,
Topics for Today More on Ethernet Topology and Wiring Switched Ethernet Fast Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet Wireless LANs Readings 4.3 to 4.4 1 Original Ethernet Wiring Heavy coaxial cable, called thicknet,
COP - Systems COPS POE. Powerline AV with PoE. Installation Manual
 COP - Systems Installation Manual Powerline AV with PoE COPS- 928- POE Ethernet Cable Model Number: COPS-928-POE HomePlug AV PowerStreaming Device with Power over Ethernet Powerline Network Room 1 Room
COP - Systems Installation Manual Powerline AV with PoE COPS- 928- POE Ethernet Cable Model Number: COPS-928-POE HomePlug AV PowerStreaming Device with Power over Ethernet Powerline Network Room 1 Room
3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE
 3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE 802.11 WCOM, WLAN, 1 References [1] J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, 2nd Ed., Pearson, 2003. [2] Martin Sauter, "From GSM to LTE", chapter 6, Wiley, 2011. [3] wiki to
3.1. Introduction to WLAN IEEE 802.11 WCOM, WLAN, 1 References [1] J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, 2nd Ed., Pearson, 2003. [2] Martin Sauter, "From GSM to LTE", chapter 6, Wiley, 2011. [3] wiki to
Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) PW Chapter Medium Access. Chapter 8 Overview
 Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) PW0-105 Chapter 8 802.11 Medium Access Chapter 8 Overview CSMA/CA vs. CSMA/CD Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) Point Coordination Function (PCF) Hybrid
Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA) PW0-105 Chapter 8 802.11 Medium Access Chapter 8 Overview CSMA/CA vs. CSMA/CD Distributed Coordination Function (DCF) Point Coordination Function (PCF) Hybrid
Overview of Broadband Cable Access Technologies
 Overview of Broadband Cable Access Technologies Shaohua Zhao, PhD Communications Technologies Group, ASTRI 26 Oct 2012 1 Outline Introduction Technologies EPoC MoCA HINOC ASTRI s Project Development: HINOC
Overview of Broadband Cable Access Technologies Shaohua Zhao, PhD Communications Technologies Group, ASTRI 26 Oct 2012 1 Outline Introduction Technologies EPoC MoCA HINOC ASTRI s Project Development: HINOC
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks. Medium Access Control and IEEE
 http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/teaching/pwsn-2011/wsn_course.shtml Lecture 7 Stockholm, November 8, 2011 Medium Access Control and IEEE 802.15.4 Royal Institute of Technology - KTH Stockholm, Sweden e-mail:
http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/teaching/pwsn-2011/wsn_course.shtml Lecture 7 Stockholm, November 8, 2011 Medium Access Control and IEEE 802.15.4 Royal Institute of Technology - KTH Stockholm, Sweden e-mail:
CHAPTER 7 MAC LAYER PROTOCOLS. Dr. Bhargavi Goswami Associate Professor & Head Department of Computer Science Garden City College
 CHAPTER 7 MAC LAYER PROTOCOLS Dr. Bhargavi Goswami Associate Professor & Head Department of Computer Science Garden City College MEDIUM ACCESS CONTROL - MAC PROTOCOLS When the two stations transmit data
CHAPTER 7 MAC LAYER PROTOCOLS Dr. Bhargavi Goswami Associate Professor & Head Department of Computer Science Garden City College MEDIUM ACCESS CONTROL - MAC PROTOCOLS When the two stations transmit data
CCM 4300 Lecture 5 Computer Networks, Wireless and Mobile Communications. Dr Shahedur Rahman. Room: T115
 CCM 4300 Lecture 5 Computer Networks, Wireless and Mobile Communications Dr Shahedur Rahman s.rahman@mdx.ac.uk Room: T115 1 Recap of Last Session Described the physical layer Analogue and Digital signal
CCM 4300 Lecture 5 Computer Networks, Wireless and Mobile Communications Dr Shahedur Rahman s.rahman@mdx.ac.uk Room: T115 1 Recap of Last Session Described the physical layer Analogue and Digital signal
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Multiple Access Links and Protocols
 Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types of links : point-to-point PPP for dial-up access point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host broadcast (shared wire or medium) old-fashioned Ethernet
Data Link Layer: Multi Access Protocols
 Digital Communication in the Modern World Data Link Layer: Multi Access Protocols http://www.cs.huji.ac.il/~com1 com1@cs.huji.ac.il Some of the slides have been borrowed from: Computer Networking: A Top
Digital Communication in the Modern World Data Link Layer: Multi Access Protocols http://www.cs.huji.ac.il/~com1 com1@cs.huji.ac.il Some of the slides have been borrowed from: Computer Networking: A Top
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks. Csci 4211 David H.C. Du
 Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Csci 4211 David H.C. Du Wireless LAN IEEE 802.11 a, b, g IEEE 802.15 Buletooth Hidden Terminal Effect Hidden Terminal Problem Hidden terminals A, C cannot hear each
Chapter 6 Wireless and Mobile Networks Csci 4211 David H.C. Du Wireless LAN IEEE 802.11 a, b, g IEEE 802.15 Buletooth Hidden Terminal Effect Hidden Terminal Problem Hidden terminals A, C cannot hear each
Wireless LAN -Architecture
 Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Wireless LAN -Architecture IEEE has defined the specifications for a wireless LAN, called IEEE 802.11, which covers the physical and data link layers. Basic Service Set (BSS) Access Point (AP) Distribution
Chapter 6 The Link Layer and LANs
 Chapter 6 The Link Layer and LANs A note on the use of these Powerpoint slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the
Chapter 6 The Link Layer and LANs A note on the use of these Powerpoint slides: We re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They re in PowerPoint form so you see the
BiPAC BiPAC User Manual
 BiPAC 2071 HomePlug AV 200 Ethernet Adapter BiPAC 2072 HomePlug AV 200 Ethernet Bridge with AC-Pass Through User Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1...1 Introduction...1 Specifications...2 Features...3
BiPAC 2071 HomePlug AV 200 Ethernet Adapter BiPAC 2072 HomePlug AV 200 Ethernet Bridge with AC-Pass Through User Manual Table of Contents Chapter 1...1 Introduction...1 Specifications...2 Features...3
Media Access Control. Networked Systems (H) Lecture 5
 Media Access Control Networked Systems (H) Lecture 5 Lecture Outline Controlling access to the channel Link contention Media access control protocols Contention-based protocols CSMA/CD Token ring Slotted
Media Access Control Networked Systems (H) Lecture 5 Lecture Outline Controlling access to the channel Link contention Media access control protocols Contention-based protocols CSMA/CD Token ring Slotted
MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1
 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS AND WIFI 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS LINKS, PROTOCOLS Two types of links : point-to-point broadcast (shared wire or medium) POINT-TO-POINT PPP for dial-up
MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS AND WIFI 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS PROTOCOLS 2. 1 MULTIPLE ACCESS LINKS, PROTOCOLS Two types of links : point-to-point broadcast (shared wire or medium) POINT-TO-POINT PPP for dial-up
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560. Wireless Technologies. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth. Bluetooth 7/3/2014.
 Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Advanced Mobile Computing and Networking - CS 560 Assessment CA 40% - Assignment 20% - 2 Tests 10% each Exam 60% Wireless Technologies, Infrared Data Association (),, and Institute of Electrical and Electronic
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Define a high rate wireless personal area network (HR WPAN) List the different HR WPAN standards
Abstract of the Book
 Book Keywords IEEE 802.16, IEEE 802.16m, mobile WiMAX, 4G, IMT-Advanced, 3GPP LTE, 3GPP LTE-Advanced, Broadband Wireless, Wireless Communications, Cellular Systems, Network Architecture Abstract of the
Book Keywords IEEE 802.16, IEEE 802.16m, mobile WiMAX, 4G, IMT-Advanced, 3GPP LTE, 3GPP LTE-Advanced, Broadband Wireless, Wireless Communications, Cellular Systems, Network Architecture Abstract of the
CABLE NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO CABLE NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES AND PROTOCOLS
 CABLE NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO CABLE NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES AND PROTOCOLS Peter R. Egli 1/15 Contents 1. Cable network architecture 2. Relevant cable network standards 3. DOCSIS 2/15 1. Cable Network architecture
CABLE NETWORKS INTRODUCTION TO CABLE NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES AND PROTOCOLS Peter R. Egli 1/15 Contents 1. Cable network architecture 2. Relevant cable network standards 3. DOCSIS 2/15 1. Cable Network architecture
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371
 Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Wireless Communication and Networking CMPT 371 Wireless Systems: AM, FM Radio TV Broadcast Satellite Broadcast 2-way Radios Cordless Phones Satellite Links Mobile Telephony Systems Wireless Local Loop
Analysis of IEEE e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs
 Analysis of IEEE 802.11e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs Stefan Mangold, Sunghyun Choi, Guido R. Hiertz, Ole Klein IEEE Wireless Communications, December 2003 Presented by Daeseon Park, Student No.2005-30231
Analysis of IEEE 802.11e for QoS Support in Wireless LANs Stefan Mangold, Sunghyun Choi, Guido R. Hiertz, Ole Klein IEEE Wireless Communications, December 2003 Presented by Daeseon Park, Student No.2005-30231
An Efficient Scheduling Scheme for High Speed IEEE WLANs
 An Efficient Scheduling Scheme for High Speed IEEE 802.11 WLANs Juki Wirawan Tantra, Chuan Heng Foh, and Bu Sung Lee Centre of Muldia and Network Technology School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological
An Efficient Scheduling Scheme for High Speed IEEE 802.11 WLANs Juki Wirawan Tantra, Chuan Heng Foh, and Bu Sung Lee Centre of Muldia and Network Technology School of Computer Engineering Nanyang Technological
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks
 Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks https://www.kth.se/social/course/el2745/ Lecture 5 January 31, 2013 Carlo Fischione Associate Professor of Sensor Networks e-mail: carlofi@kth.se http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/
Principles of Wireless Sensor Networks https://www.kth.se/social/course/el2745/ Lecture 5 January 31, 2013 Carlo Fischione Associate Professor of Sensor Networks e-mail: carlofi@kth.se http://www.ee.kth.se/~carlofi/
IEEE MAC Sublayer (Based on IEEE )
 IEEE 802.11 MAC Sublayer (Based on IEEE 802.11-1999) Wireless Networking Sunghyun Choi, Associate Professor Multimedia & Wireless Networking Lab. (MWNL) School of Electrical Engineering Seoul National
IEEE 802.11 MAC Sublayer (Based on IEEE 802.11-1999) Wireless Networking Sunghyun Choi, Associate Professor Multimedia & Wireless Networking Lab. (MWNL) School of Electrical Engineering Seoul National
Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit. Manual
 Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit Manual Dear Customer, Thanks for choosing Hamlet. Please carefully follow the instructions for its use and maintenance and, once this item has run its life span, we kindly
Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit Manual Dear Customer, Thanks for choosing Hamlet. Please carefully follow the instructions for its use and maintenance and, once this item has run its life span, we kindly
CS 43: Computer Networks. 27: Media Access Contd. December 3, 2018
 CS 43: Computer Networks 27: Media Access Contd. December 3, 2018 Last Class The link layer provides lots of functionality: addressing, framing, media access, error checking could be used independently
CS 43: Computer Networks 27: Media Access Contd. December 3, 2018 Last Class The link layer provides lots of functionality: addressing, framing, media access, error checking could be used independently
The Link Layer and LANs. Chapter 6: Link layer and LANs
 The Link Layer and LANs EECS3214 2018-03-14 4-1 Chapter 6: Link layer and LANs our goals: understand principles behind link layer services: error detection, correction sharing a broadcast channel: multiple
The Link Layer and LANs EECS3214 2018-03-14 4-1 Chapter 6: Link layer and LANs our goals: understand principles behind link layer services: error detection, correction sharing a broadcast channel: multiple
200M Powerline Wireless N Extender
 200M Powerline Wireless Extender High Speed Wireless Extension via Home s Powerline With HomePlug AV technology, the PLAET Powerline Wireless Extender efficiently share up to 200/300Mbps high speed In-house
200M Powerline Wireless Extender High Speed Wireless Extension via Home s Powerline With HomePlug AV technology, the PLAET Powerline Wireless Extender efficiently share up to 200/300Mbps high speed In-house
Wireless LANs. The Protocol Stack The Physical Layer The MAC Sublayer Protocol The Frame Structure Services 802.
 Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Wireless LANs The 802.11 Protocol Stack The 802.11 Physical Layer The 802.11 MAC Sublayer Protocol The 802.11 Frame Structure Services 56 802.11 The 802.11 Working Group The IEEE 802.11 was formed in July
Configure n on the WLC
 Configure 802.11n on the WLC Document ID: 108184 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions 802.11n An Overview How Does 802.11n Provide Greater Throughput
Configure 802.11n on the WLC Document ID: 108184 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions 802.11n An Overview How Does 802.11n Provide Greater Throughput
Lecture 6 Datalink Framing, Switching. From Signals to Packets
 Lecture 6 Datalink Framing, Switching David Andersen Department of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 15-441 Networking, Spring 2005 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~srini/15-441/s05/ 1 From Signals to
Lecture 6 Datalink Framing, Switching David Andersen Department of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 15-441 Networking, Spring 2005 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~srini/15-441/s05/ 1 From Signals to
Modems, DSL, and Multiplexing. CS158a Chris Pollett Feb 19, 2007.
 Modems, DSL, and Multiplexing CS158a Chris Pollett Feb 19, 2007. Outline Finish up Modems DSL Multiplexing The fastest modems Last day, we say the combinations and phases used to code symbols on a 2400
Modems, DSL, and Multiplexing CS158a Chris Pollett Feb 19, 2007. Outline Finish up Modems DSL Multiplexing The fastest modems Last day, we say the combinations and phases used to code symbols on a 2400
COS 140: Foundations of Computer Science
 COS 140: Foundations of Computer Science ALOHA Network Protocol Family Fall 2017 Homework 2 Introduction 3 Network Protocols.......................................................... 3 Problem.................................................................
COS 140: Foundations of Computer Science ALOHA Network Protocol Family Fall 2017 Homework 2 Introduction 3 Network Protocols.......................................................... 3 Problem.................................................................
Embedded networks combining Power Line and Wireless communications
 Embedded networks combining Power Line and Wireless communications WSPL2008, Thessaloniki, 2&3/10 / 2008 Fabienne Nouvel, Patrice Maziero IETR, UMR CNRS 6164,INSA of Rennes e.mail : fabienne.nouvel@insa-rennes.fr
Embedded networks combining Power Line and Wireless communications WSPL2008, Thessaloniki, 2&3/10 / 2008 Fabienne Nouvel, Patrice Maziero IETR, UMR CNRS 6164,INSA of Rennes e.mail : fabienne.nouvel@insa-rennes.fr
EnGenius EAP-9550 Indoor Access Point
 Product Name: Manufacturer: - Model Number: NET-EL-EAP9550 Please Note the has been discontinued, for alternative wireless equipment please check out Ubiquiti UniFi UAP LR EnGenius EAP9550 Indoor Access
Product Name: Manufacturer: - Model Number: NET-EL-EAP9550 Please Note the has been discontinued, for alternative wireless equipment please check out Ubiquiti UniFi UAP LR EnGenius EAP9550 Indoor Access
Lecture 6. Data Link Layer (cont d) Data Link Layer 1-1
 Lecture 6 Data Link Layer (cont d) Data Link Layer 1-1 Agenda Continue the Data Link Layer Multiple Access Links and Protocols Addressing Data Link Layer 1-2 Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types
Lecture 6 Data Link Layer (cont d) Data Link Layer 1-1 Agenda Continue the Data Link Layer Multiple Access Links and Protocols Addressing Data Link Layer 1-2 Multiple Access Links and Protocols Two types
Chapter 5: Link layer
 Chapter 5: Link layer our goals: v understand principles behind link layer services: error detection, correction sharing a broadcast channel: multiple access link layer addressing local area networks:
Chapter 5: Link layer our goals: v understand principles behind link layer services: error detection, correction sharing a broadcast channel: multiple access link layer addressing local area networks:
Links. CS125 - mylinks 1 1/22/14
 Links 1 Goals of Today s Lecture Link-layer services Encoding, framing, and error detection Error correction and flow control Sharing a shared media Channel partitioning Taking turns Random access Shared
Links 1 Goals of Today s Lecture Link-layer services Encoding, framing, and error detection Error correction and flow control Sharing a shared media Channel partitioning Taking turns Random access Shared
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017
 ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 5.4: Multiple Access Protocols Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527
ECE 4450:427/527 - Computer Networks Spring 2017 Dr. Nghi Tran Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Lecture 5.4: Multiple Access Protocols Dr. Nghi Tran (ECE-University of Akron) ECE 4450:427/527
4G Mobile Communications
 4G Mobile Communications Welcome to 4G The term 4G is used broadly to include several types of broadband wireless access communication systems, not only cellular telephone systems. One of the terms to
4G Mobile Communications Welcome to 4G The term 4G is used broadly to include several types of broadband wireless access communication systems, not only cellular telephone systems. One of the terms to
1/29/2008. From Signals to Packets. Lecture 6 Datalink Framing, Switching. Datalink Functions. Datalink Lectures. Character and Bit Stuffing.
 /9/008 From Signals to Packets Lecture Datalink Framing, Switching Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Mellon University Analog Signal Digital
/9/008 From Signals to Packets Lecture Datalink Framing, Switching Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Mellon University Analog Signal Digital
ISO/IEC INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 16504 First edition 2011-11-15 Information technology Telecommunications and information exchange between systems MAC and PHY for operation in TV white space Technologies
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 16504 First edition 2011-11-15 Information technology Telecommunications and information exchange between systems MAC and PHY for operation in TV white space Technologies
Mobile WiMAX in the Evolving Wireless Broadband Landscape
 Mobile WiMAX in the Evolving Wireless Broadband Landscape TECHNOLOGY BACKGROUNDER Introduction Even with the surprising variety of wireless broadband technologies available today, Mobile WiMAX (IEEE 802.16e)
Mobile WiMAX in the Evolving Wireless Broadband Landscape TECHNOLOGY BACKGROUNDER Introduction Even with the surprising variety of wireless broadband technologies available today, Mobile WiMAX (IEEE 802.16e)
ZigBee/ David Sanchez Sanchez.
 ZigBee/802.15.4 David Sanchez Sanchez david.sanchezs@upf.edu Lecture Overview 1. Introduction and motivation to ZigBee 2. ZigBee/802.15.4 specification 1. Definitions 2. MAC communication modes 3. Network
ZigBee/802.15.4 David Sanchez Sanchez david.sanchezs@upf.edu Lecture Overview 1. Introduction and motivation to ZigBee 2. ZigBee/802.15.4 specification 1. Definitions 2. MAC communication modes 3. Network
WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK
 1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
1 WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORK Dr. H. K. Verma Distinguished Professor (EEE) Sharda University, Greater Noida (Formerly: Deputy Director and Professor of Instrumentation Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee)
CHAPTER TWO LITERATURE REVIEW
 CHAPTER TWO LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction. This chapter provides in detail about the multiple access technologies and the OCDMA system. It starts with a discussion on various existing multiple-access
CHAPTER TWO LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction. This chapter provides in detail about the multiple access technologies and the OCDMA system. It starts with a discussion on various existing multiple-access
Networks 15.2 Multiplexing Technologies Access Networks 15.5 Common Peripheral Interfaces
 Chapter 15 Computer and Multimedia Networks 15.11 Basics of Computer and Multimedia Networks 15.2 Multiplexing Technologies 15.3 LAN and WAN 15.4 Access Networks 15.5 Common Peripheral Interfaces 15.6
Chapter 15 Computer and Multimedia Networks 15.11 Basics of Computer and Multimedia Networks 15.2 Multiplexing Technologies 15.3 LAN and WAN 15.4 Access Networks 15.5 Common Peripheral Interfaces 15.6
Lecture 4. Data Transmission Modes and Switching. Data Transmission & Switching 1-1
 Lecture 4 Data Transmission Modes and Switching Data Transmission & Switching 1-1 Agenda Introduction to Data Transmission Modes Parallel and Serial Transmission Transmission Media Guided and unguided
Lecture 4 Data Transmission Modes and Switching Data Transmission & Switching 1-1 Agenda Introduction to Data Transmission Modes Parallel and Serial Transmission Transmission Media Guided and unguided
Power Line Communication standards for in-vehicle networks
 Power Line Communication standards for in-vehicle networks Philippe Tanguy, Fabienne Nouvel, Patrice Maziéro To cite this version: Philippe Tanguy, Fabienne Nouvel, Patrice Maziéro. Power Line Communication
Power Line Communication standards for in-vehicle networks Philippe Tanguy, Fabienne Nouvel, Patrice Maziéro To cite this version: Philippe Tanguy, Fabienne Nouvel, Patrice Maziéro. Power Line Communication
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing. Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
 CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part II WiFi vs 802.11 IEEE 802.11 Features Hidden Node
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) Part II WiFi vs 802.11 IEEE 802.11 Features Hidden Node
Research on Hybrid Network Technologies of Power Line Carrier and Wireless MAC Layer Hao ZHANG 1, Jun-yu LIU 2, Yi-ying ZHANG 3 and Kun LIANG 3,*
 2017 International Conference on Computer, Electronics and Communication Engineering (CECE 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-476-9 Research on Hybrid Network Technologies of Power Line Carrier and Wireless MAC Layer
2017 International Conference on Computer, Electronics and Communication Engineering (CECE 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-476-9 Research on Hybrid Network Technologies of Power Line Carrier and Wireless MAC Layer
CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer
 CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer LOCAL CISCO ACADEMY ELSYS TU INSTRUCTOR: STELA STEFANOVA 1 Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission; Objectives Describe how the
CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer LOCAL CISCO ACADEMY ELSYS TU INSTRUCTOR: STELA STEFANOVA 1 Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission; Objectives Describe how the
Data Transmission and Home Networks. Gralla: part 2
 Data Transmission and Home Networks Gralla: part 2 A Home Network Home network Firewall Hub/ Switch 192.168.1.1/ 137.42.12.12 ADSL Modem Internet Operator's services 192.168.1.140 192.168.1.100 External
Data Transmission and Home Networks Gralla: part 2 A Home Network Home network Firewall Hub/ Switch 192.168.1.1/ 137.42.12.12 ADSL Modem Internet Operator's services 192.168.1.140 192.168.1.100 External
MAC Sublayer(1) Principal service of the Medium Access Control Sublayer: Allocating a single broadcast channel (mostly a LAN) among competing users
 MAC Sublayer(1) Principal service of the Medium Access Control Sublayer: Allocating a single broadcast channel (mostly a LAN) among competing users Static Channel Allocation: Frequency Division Multiplexing
MAC Sublayer(1) Principal service of the Medium Access Control Sublayer: Allocating a single broadcast channel (mostly a LAN) among competing users Static Channel Allocation: Frequency Division Multiplexing
Medium Access Control. IEEE , Token Rings. CSMA/CD in WLANs? Ethernet MAC Algorithm. MACA Solution for Hidden Terminal Problem
 Medium Access Control IEEE 802.11, Token Rings Wireless channel is a shared medium Need access control mechanism to avoid interference Why not CSMA/CD? 9/15/06 CS/ECE 438 - UIUC, Fall 2006 1 9/15/06 CS/ECE
Medium Access Control IEEE 802.11, Token Rings Wireless channel is a shared medium Need access control mechanism to avoid interference Why not CSMA/CD? 9/15/06 CS/ECE 438 - UIUC, Fall 2006 1 9/15/06 CS/ECE
Medium Access Control in Wireless Sensor Networks
 Medium Access Control in Wireless Sensor Networks Davide Quaglia, Damiano Carra LIVELLO DATALINK 2 1 Goals Reliable and efficient communication between two nodes on the same physical medium Cable (Wired)
Medium Access Control in Wireless Sensor Networks Davide Quaglia, Damiano Carra LIVELLO DATALINK 2 1 Goals Reliable and efficient communication between two nodes on the same physical medium Cable (Wired)
A Simulation Study of the PLC-MAC Performance using Network Simulator-2
 A Simulation Study of the PLC-MAC Performance using Network Simulator-2 Min-Soo Kim, Dong-Min Son*, Young-Bae Ko and Young-Hyun Kim** Graduate School of Information & Communication, Ajou University, Korea
A Simulation Study of the PLC-MAC Performance using Network Simulator-2 Min-Soo Kim, Dong-Min Son*, Young-Bae Ko and Young-Hyun Kim** Graduate School of Information & Communication, Ajou University, Korea
LANCOM Techpaper IEEE n Overview
 Advantages of 802.11n The new wireless LAN standard IEEE 802.11n ratified as WLAN Enhancements for Higher Throughput in september 2009 features a number of technical developments that promise up to six-times
Advantages of 802.11n The new wireless LAN standard IEEE 802.11n ratified as WLAN Enhancements for Higher Throughput in september 2009 features a number of technical developments that promise up to six-times
Local Area Networks (LANs) SMU CSE 5344 /
 Local Area Networks (LANs) SMU CSE 5344 / 7344 1 LAN/MAN Technology Factors Topology Transmission Medium Medium Access Control Techniques SMU CSE 5344 / 7344 2 Topologies Topology: the shape of a communication
Local Area Networks (LANs) SMU CSE 5344 / 7344 1 LAN/MAN Technology Factors Topology Transmission Medium Medium Access Control Techniques SMU CSE 5344 / 7344 2 Topologies Topology: the shape of a communication
Wireless 150N ADSL2+ Modem Router For ADSL (Annex A), 150 Mbps Wireless n, QoS, with 4-Port 10/100 Mbps LAN Switch Part No.
 Wireless 150N ADSL2+ Modem Router For ADSL (Annex A), 150 Mbps Wireless 802.11n, QoS, with 4-Port 10/100 Mbps LAN Switch Part No.: 525299 The INTELLINET NETWORK SOLUTIONS Wireless 150N ADSL2+ Modem Router
Wireless 150N ADSL2+ Modem Router For ADSL (Annex A), 150 Mbps Wireless 802.11n, QoS, with 4-Port 10/100 Mbps LAN Switch Part No.: 525299 The INTELLINET NETWORK SOLUTIONS Wireless 150N ADSL2+ Modem Router
Medium Access Control in Wireless IoT. Davide Quaglia, Damiano Carra
 Medium Access Control in Wireless IoT Davide Quaglia, Damiano Carra LIVELLO DATALINK 2 Goals Reliable and efficient communication between two nodes on the same physical medium Cable (Wired) Wireless Assumptions
Medium Access Control in Wireless IoT Davide Quaglia, Damiano Carra LIVELLO DATALINK 2 Goals Reliable and efficient communication between two nodes on the same physical medium Cable (Wired) Wireless Assumptions
COS 140: Foundations of Computer Science
 COS 140: Foundations of C S Network Protocol Family Fall 2017 Copyright c 2002 2017 UMaine School of Computing and Information S 1 / 25 Homework Homework Slides, book Chapter 24 on line Homework: All exercises
COS 140: Foundations of C S Network Protocol Family Fall 2017 Copyright c 2002 2017 UMaine School of Computing and Information S 1 / 25 Homework Homework Slides, book Chapter 24 on line Homework: All exercises
Data Link Layer: Collisions
 Data Link Layer: Collisions 1 Multiple Access Data Link layer divided into two sublayers. The upper sublayer is responsible for datalink control, The lower sublayer is responsible for resolving access
Data Link Layer: Collisions 1 Multiple Access Data Link layer divided into two sublayers. The upper sublayer is responsible for datalink control, The lower sublayer is responsible for resolving access
ECB N Multi-Function Client Bridge
 ECB9300 is a multi-functioned 11n product with 7 major multi-functions, is designed to operate in every working environment for enterprises. ECB9300 is a Wireless Network device that delivers up to 3x
ECB9300 is a multi-functioned 11n product with 7 major multi-functions, is designed to operate in every working environment for enterprises. ECB9300 is a Wireless Network device that delivers up to 3x
MOVING BEYOND THE STANDARD: CREATING ADDITIONAL BANDWIDTH THROUGH EXTENDING DOCSIS 2.0. Jack Moran, Distinguished Member of the Technical Staff
 MOVING BEYOND THE STANDARD: CREATING ADDITIONAL BANDWIDTH THROUGH EXTENDING DOCSIS 2.0 Jack Moran, Distinguished Member of the Technical Staff Motorola Broadband Communications Sector Abstract Advanced
MOVING BEYOND THE STANDARD: CREATING ADDITIONAL BANDWIDTH THROUGH EXTENDING DOCSIS 2.0 Jack Moran, Distinguished Member of the Technical Staff Motorola Broadband Communications Sector Abstract Advanced
WiMedia Ultra-wideband: Efficiency Considerations of the Effects of Protocol Overhead on Data Throughput. January All Rights Reserved.
 WiMedia Ultra-wideband: Efficiency Considerations of the Effects of Protocol Overhead on Data Throughput January 2009. All Rights Reserved. Contributed by WiMedia member company Abstract Today s wireless
WiMedia Ultra-wideband: Efficiency Considerations of the Effects of Protocol Overhead on Data Throughput January 2009. All Rights Reserved. Contributed by WiMedia member company Abstract Today s wireless
Wireless LANs. ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications
 Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
Wireless LANs ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Aim: Aim and Contents Understand how IEEE 802.11 wireless LANs work Understand what influences the performance of wireless LANs Contents: IEEE
Wireless Router at Home
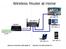 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
