1-Port and 2-Port HWIC data/voice, 4-Port T1/E1 HWIC, and 8-Port T1/E1 Network Module
|
|
|
- Willa Moore
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1-Port and 2-Port HWIC data/voice, 4-Port T1/E1 HWIC, and 8-Port T1/E1 Network Module Last Updated: August 18, 2011, This document describes the following Cisco products: Cisco 1-Port and 2-Port Channelized T1/E1 and ISDN PRI High-Speed WAN Interface Cards (HWICs) 1-port part number: HWIC-1CE1T1-PRI 2-port part number: HWIC-2CE1T1-PRI Provides channelized T1 or E1 connections or ISDN PRI connections Supported on Cisco 2821, Cisco 2851, Cisco 3800, Cisco 2900, and Cisco 3900 series routers Cisco 4-Port T1/E1 HWIC Part number: HWIC-4T1/E1 Provides clear channel T1 or E1 connections Supported on Cisco 2821, Cisco 2851, Cisco 3800, Cisco 2900, and Cisco 3900 series routers Cisco 8-Port Channelized T1/E1 and ISDN PRI High-Speed WAN Network Module Part number: NM-8CE1T1-PRI Provides channelized T1 or E1 connections or ISDN PRI connection Supported on Cisco 3800, Cisco 2900, and Cisco 3900 series routers Americas Headquarters: Cisco Systems, Inc., 170 West Tasman Drive, San Jose, CA USA
2 Finding Feature Information Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the Feature Information for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Modules section on page 29. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to An account on Cisco.com is not required. Contents Restrictions for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module, page 2 Information About T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module, page 3 Configuring the T1/E1 HWICs with Voice Support, page 16 Configuration Examples for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module, page 19 Additional References, page 25 Command Reference, page 26 Feature Information for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Modules, page 29 Restrictions for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Cisco 2811 does not support the HWIC-4T1/E1 module. Voice feature is supported on the 1-Port and 2-Port T1/E1 HWICs. For more information, see Feature Information for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Modules section on page 29. Voice feature is not supported on the 4-Port HWIC and network module. Wetting current is not supported on the HWICs or the network module. V54 loop up/down code recognition is not supported on the HWICs or the network module. The 1-port and 2-port HWICs support up to 32 channels per port (up to 64 channels total on the 2-port HWIC). The 4-port clear channel HWIC supports 1 channel per port or 4 channels total for the HWIC. The 8-port network module is supported only on Cisco 3800 series routers (the Cisco 3825 and Cisco 3845 routers). The 8-port network module supports a maximum of 128 channels. Bit error rate tester (BERT) runs on the entire controller and not on specific channel groups. Because of this, only a limited number of patterns are supported. See the Configuring the T1/E1 HWICs or Network Module section on page 8 for more details. 2
3 Information About T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Information About T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module To configure the T1/E1 HWICs and network module, you should understand the following: Interface Numbering on Cisco 2800 and Cisco 3800 Series Routers, page 3 Independent Clocking Mode, page 4 Interface Numbering on Cisco 2800 and Cisco 3800 Series Routers Table 1 summarizes the interface numbering on Cisco 2811, 2821, and 2851 routers and on Cisco 3800 series routers. Table 2 gives the port numbering for the T1/E1 HWICs and network module. Table 1 Interface Numbering on Cisco 2800 and Cisco 3800 Series Routers Router HWIC Interfaces Network Module Interfaces 2811, 2821, and /HWIC slot/port 1 No support for the 8-port T1/E1 network module /HWIC slot/port 1 Network module slot/port /HWIC slot/port 1 Network module slot/port 3 1. Interface numbering for HWIC interfaces on all routers begins with 0. Then, each router has four HWIC slots that are numbered from 0 to The 3825 router has two network module slots, numbered 1 to The 3845 router has four network module slots, numbered 1 to 4. For illustrations of HWIC slots in the Cisco 2811, 2821, and 2851 routers, see Overview of Cisco 2800 Series Routers. For illustrations of HWIC and network module slots in the Cisco 3825 and 3845 routers, see Overview of Cisco 3800 Series Routers. Table 2 Port Numbering on T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Interface Port Numbering 1-port T1/E1 HWIC 0 2-port T1/E1 HWIC 0 to 1 4-port T1/E1 HWIC 0 to 3 8-port T1/E1 network module 0 to 7 Some examples are as follows: Port 0 of an HWIC in HWIC slot 0: 0/0/0 Port 1 of a 2- or 4-port HWIC in HWIC slot 1: 0/1/1 Port 3 of the 4-port HWIC in HWIC slot 2: 0/2/3 Port 6 of the 8-port network module in network module slot 2: 2/6 3
4 Information About T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Independent Clocking Mode To enable independent clocking mode, use the clock source line independent command to specify that the port can operate on an independent clocking domain. Prior to the addition of the independent keyword, port 0 was the default primary clock source and port 1/2/3 was loop-timed. With independent clocking enabled, this dependency no longer exists, so the independent keyword means that the specific port is independent from the HWIC controller clocking domain. When independent clocking is configured, the port will only support data applications and not voice applications. However, other ports under the same controller that do not have independent clocking enabled (that is, clock still participated) are able to support voice applications on HWIC-1CE1T1-PRI and HWIC-2CE1T1-PRI. 4
5 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Configuring Card Type, page 5 Changing Card Type, page 6 Configuring the T1/E1 HWICs or Network Module, page 8 Configuring the T1/E1 HWICs with Voice Support, page 16 Configuring Card Type To configure the T1/E1 HWICs and network module for T1 or E1 operation, perform the following tasks. Prerequisites The T1/E1 HWICs or network module will not be operational until a card type is configured. SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. card type {t1 e1} slot subslot DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Router> enable configure terminal Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Enters global configuration mode. Step 3 Router# configure terminal card type {t1 e1} slot subslot Router(config)# card type t1 0 2 Specifies T1 or E1 connectivity. slot refers to the network module slot on the 2800 series and 3800 series platform. subslot refers to the HWIC slot on the platform. See the Interface Numbering on Cisco 2800 and Cisco 3800 Series Routers section on page 3. 5
6 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Changing Card Type To change a card type from T1 to E1, or from E1 to T1, perform the following tasks: SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. no card type {t1 e1} slot subslot 4. card type {t1 e1} slot subslot 5. write 6. reload 7. boot DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Router> enable configure terminal Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Enters global configuration mode. Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Router# configure terminal no card type {t1 e1} slot subslot Router(config)# no card type t1 0 2 card type {t1 e1} slot subslot Router(config)# card type e1 0 2 write Optional. Removes the previously configured card type for the HWIC or network module. Specifies T1 or E1 connectivity for the HWIC or network module. Rebuilds the router configuration. Router(config)# write 6
7 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Step 6 Step 7 Command or Action reload Router(config)# reload boot Router(rommon)# boot Purpose Reloads router so that changes can take affect. After this command executes, the router will go to ROM monitor (rommon) mode. Boots the router for the configuration with the newly selected card type. 7
8 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Configuring the T1/E1 HWICs or Network Module SUMMARY STEPS To configure the T1/E1 HWICs or network module, perform the following tasks: 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. network-clock-participate [slot slot-number wic wic-slot] 4. controller {t1 e1} slot/subslot/port 5. framing {sf esf} or framing {crc4 no-crc4} 6. linecode {ami b8zs} or linecode {ami hdb3} 7. fdl {att ansi both} 8. clock source {line internal} 9. line-termination {75-ohm 120-ohm} 10. loopback {diagnostic local {payload line} remote {iboc esf {payload line}}} 11. cablelength long db-loss-value or cablelength short length 12. channel group channel-group-number {timeslots range [speed kbps] unframed} or tdm-group tdm-group-no timeslots timeslot-range 13. ds0-group ds0-group-number timeslots timeslot-list type {e&m-delay-dial e&m-fgd e&m-immediate-start e&m-wink-start ext-sig fgd-eana fxo-ground-start fxo-loop-start fxs-ground-start fxs-loop-start} 14. pri-group timeslots timeslot-range [nfas_d service][voice-dsp] 15. national reserve N sa4 sa5 sa6 sa7 sa8 16. crc-threshold value 17. yellow {generation detection} 18. bert pattern pattern interval time 8
9 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Router> enable configure terminal Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Enters global configuration mode. Router# configure terminal Step 3 network-clock-participate [slot slot-number wic wic-slot] Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Step 7 Router(config)# network-clock-participate wic 0 controller {t1 e1} slot/subslot/port Router(config)# controller t1 1/0 framing {sf esf} or framing {crc4 no-crc4} Router(config-controller)# framing esf linecode {ami b8zs} or linecode {ami hdb3} Router(config-controller)# linecode b8zs fdl {att ansi both} Router(config-controller)# fdl both TDM group configuration only. Allows the ports on a specified network module or interface card to use the network clock for timing. Enters controller configuration mode. For interface numbering conventions on the Cisco 2800 and 3800 series routers, see the Interface Numbering on Cisco 2800 and Cisco 3800 Series Routers section on page 3. In T1 configurations, specifies super frame (sf) or extended super frame (esf) as the frame type for data lines. Default is esf. In E1 configurations, specifies cyclic. redundancy check 4 (crc4) or no-crc4 as the frame type for data lines. Default is crc4. In T1 configurations, specifies alternate mark inversion (AMI) or b8zs as the linecode. Default is b8zs. In E1 configurations, specifies AMI or high-density bipolar 3 (hdb3) as the linecode. Default is hdb3. Note When using linecode AMI, the user is advised to select 56 kbps as the speed or make sure that the channel groups created do not contain all the timeslots. See Step 12. This is to avoid exceeding the 15 zeroes threshold specified by standards. T1 only. Sets the facility data link (fdl) exchange standard for T1 interfaces using esf framing. Can select the ATT standard (ATT TR54016), the ANSI standard (ANSI T1.403), or both standards. Default is ansi. To disable fdl, enter the command no fdl. 9
10 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Step 8 Step 9 Command or Action clock source {line [independent] internal} Router(config-controller)# clock source line line-termination {75-ohm 120-ohm} Router(config-controller)# line-termination 75-ohm Step 10 loopback {diagnostic local {payload line} remote {iboc esf {payload line}}} Router(config-controller)# loopback remote esf line Purpose line specifies that the clocking on this controller is derived from an external source, generally the telephone central office. line independent configures the port to be independent in the TDM docmain, which is when network-clock-participate is configured on the card. internal specifies that the clock is generated by internal controller circuitry. Default is line. E1 only. Sets the line termination on an E1 controller. 75-ohm specifies the 75 ohm unbalanced termination. 120-ohm specifies the 120 ohm balanced termination. Default is 120-ohm. Note On the 4-port HWIC and 8-port network module, line impedance will be set to the same value for each port in a two-port slice automatically. That is, on the 4-port HWIC, ports 0 and 1 will be set to the same value, and ports 2 and 3 will be set to the same value. On the 8-port network module, ports 0 and 1 will be set to the same value, as will ports 2 and 3, ports 4 and 5, and ports 6 and 7. In these cases, a message will be displayed. The example shows the message displayed when the line termination on port 0 is changed: Router(config)# controller e1 0/1/0 Router(config-controller)#line-termination 75-ohm Changing the line termination for ports 0 and 1 to 75 Sets the loopback method for testing the interface. Options are: diagnostic loops transmit signal back to receive local puts the interface into local loopback mode at the payload or line level remote puts the interface into remote loopback mode through an inband bit oriented code (iboc) or, for T1 only, remote esf, which uses fdl codes to set payload or line levels. 10
11 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Step 11 Command or Action cablelength long db-loss-value or cablelength short length Router(config-controller)# cablelength short 133 Purpose T1 only. cablelength long attenuates the pulse from the transmitter using pulse equalization and line build-out. This command applies to cables longer than 660 feet. Loss values are: 0db -7.5db -15db -22.5db Default attenuation is 0db. cablelength short sets transmission attenuation for cable lengths of 660 feet or less. Cable lengths can be specified as follows: 110 for cable lengths from 0 to 110 feet 220 for cable lengths from 110 to 220 feet 330 for cable lengths from 220 to 330 feet 440 for cable lengths from 330 to 440 feet 550 for cable lengths from 440 to 550 feet 660 for cable lengths from 550 to 660 feet There is no default cable length. 11
12 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Step 12 Command or Action channel group channel-group-number {timeslots range [speed kbps] unframed} or tdm-group tdm-group-no timeslots timeslot-range Router(config-controller)# channel group 1 timeslots 1-4 Purpose Note This step does not apply to the clear channel 4-port T1/E1 HWIC. Configures the serial WAN on a T1 or E1 interface by specifying channels and their timeslots. For T1, values are as follows: channel-group-number is from 0 to 23 timeslots range is from 1 to 24 Default value of speed in T1 is 64 kbps. Configuration of speed is optional. For E1, values are as follows: channel-group-number is from 0 to 30 timeslots range is from 1 to 31 Default value of speed in E1 is 64 kbps. Configuration of speed is optional. unframed (E1 only) specifies that all 32 timeslots are to be used for data, and that none are to be used for framing signals. or Configures specified timeslots on T1 or E1 interfaces to create clear channel groups for time division multiplexing. For the tdm-group configuration to work, it is necessary to configure network-clock-participate for the interface in global configuration mode. 12
13 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Step 13 Command or Action ds0-group ds0-group-number timeslots timeslot-list type {e&m-delay-dial e&m-fgd e&m-immediate-start e&m-wink-start ext-sig fgd-eana fxo-ground-start fxo-loop-start fxs-ground-start fxs-loop-start} Router(config-controller)# ds0-group 12 timeslots 1-3 type fxs-loop-start Purpose (Voice only) Defines the T1 channels for use by compressed voice calls and the signaling method the router uses to connect to the PBX or central office. Set up DS0 groups after you have specified codec complexity in the voice-card configuration. For T1, values are as follow: dso-group-number is from 0 to 23 timeslot-list argument is a single number, numbers separated by commas, or a pair of numbers separated by a hyphen to indicate a range of time slots. The signaling method selection for the type keyword depends on the connection that you are making: The E&M interface allows connection for PBX trunk lines (tie lines) and telephone equipment. The Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) interface allows connection of basic telephone equipment and PBX. The Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) interface is for connecting the Central Office (CO) to a standard PBX interface where permitted by local regulations; it is often used for off-premises extensions (OPXs). For E1, values are as follow: dso-group-number is from 0 to 30 timeslot-list argument is a single number, numbers separated by commas, or a pair of numbers separated by a hyphen to indicate a range of time slots. The signaling method selection for the type keyword depends on the connection that you are making: The E&M, FXS, and FXO are similar to T1. R2 signalling. The ds0-group command automatically creates a logical voice port that is numbered as follows: slot/port:ds0-group-number. Although only one voice port is created, applicable calls are routed to any channel in the group. 13
14 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Command or Action Step 14 pri-group timeslots timeslot-range [nfas_d service][voice-dsp] Router(config-controller)# pri-group timeslots 1-5 Purpose Specifies that the controller should be set up as ISDN PRI interface. Note For T1, The network-clock-participate wic/slot <> should be configured, otherwise pri-group configuration is rejected. timeslots range from 1 to 24 23rd channel is the D channel For E1, Note timeslots range from 1 to 31 15th channel is the D channel Default is with no voice-dsp option. Current Service is only for voice mgcp. So, when Service is selected, there is no voice-dsp required or needed. For 1-Port and 2-Port HWIC voice support, user must select voice-dsp. Note The option keyword or voice-dsp is only available to the 1-Port and 2-Port HWIC on ISR-G2 (Cisco 2911, Cisco 2921, Cisco 2951, Cisco 3925, Cisco 3925E, Cisco 3945, and Cisco 3945E). Step 15 Step 16 national reserve N sa4 sa5 sa6 sa7 sa8 Router(config-controller)# national reserve crc-threshold value Router(config-controller)# crc-threshold 500 If a controller is configured as PRI, individual channel groups cannot be configured on that controller. The controller command must be entered before this command can be used. E1 only. Sets the 6 required national bits in E1 in the G.751 frame. Default is T1 only. Defines a severely errored second by specifying the number of crc errors that must occur in one second to reach the severely errored state. Default is
15 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Step 17 Step 18 Command or Action yellow {generation detection} Router(config-controller)# no yellow detection bert pattern pattern interval time Router(config-controller)# bert 2^11 interval 1440 Purpose Enables generation and detection of yellow alarms. Default condition is that generation and detection of yellow alarms are enabled. Use the no form of the command to disable yellow alarm detection. Optional. Activates the Bit Error Rate Tester (bert) with the chosen test pattern for a specified duration. Configure bert patterns on T1/E1 HWICs or network module as follows: When the linecode is AMI, use patterns 2^11, 2^15, or 2^20-QRSS. When the linecode is b8zs or hdb3, use patterns 2^11, 2^15, 2^20-QRSS, or 2^20-O.153. Note If any other bert pattern is chosen, an error message will appear that lists the supported patterns for the configured linecode. A complete listing of bert patterns is in the Cisco IOS Master Commands List, Release interval time is from 1 to 14,400 minutes. 15
16 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Configuring the T1/E1 HWICs with Voice Support Digital voice for 1-Port and 2-Port HWICs are only supported on Cisco c2911 Cisco c3945e ISR-G2 platforms. In this example, one voice pri-group (a pri-group with voice-dsp option) is configured under t1 controller with one ds0-group under another t1 controller from the same HWIC-2CE1T1-PRI for voice support. Note Do not configure a data pri-group with a voice pri-group on the same HWIC. informers# sh run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1763 bytes Last configuration change at 17:16:17 UTC Thu Jul version 15.1 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption hostname informers boot-start-marker boot-end-marker card type t1 0 0 card type e1 0 2 no aaa new-model no network-clock-participate slot 4 no network-clock-participate wic 0 network-clock-participate wic 2 no ipv6 cef ip source-route ip cef multilink bundle-name authenticated isdn switch-type primary-ni voice-card 0 voice-card 4 16
17 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module license udi pid C3900-SPE250/K9 sn FOC13391AMK hw-module pvdm 0/0 redundancy controller T1 0/0/0 cablelength long 0db controller T1 0/0/1 cablelength long 0db controller E1 0/2/0 pri-group timeslots 1-24 voice-dsp controller E1 0/2/1 ds0-group 0 timeslots 1-24 type fxs-loop-start interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address duplex auto speed auto interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto interface GigabitEthernet0/2 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto interface GigabitEthernet0/3 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto interface Serial0/2/0:15 no ip address encapsulation hdlc isdn switch-type primary-ni isdn incoming-voice voice no cdp enable ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server no ip http secure-server ip route ip route nls resp-timeout 1 17
18 How to Configure T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module cpd cr-id 1 control-plane voice-port 0/2/0:15 voice-port 0/2/1:0 voice-port 0/1/0 voice-port 0/1/1 gatekeeper shutdown line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 login transport input all exception data-corruption buffer truncate scheduler allocate end informers# 18
19 Configuration Examples for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Configuration Examples for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module This section shows configuration examples for the 4-port HWIC in both T1 and E1 configurations. 4-Port T1 HWIC, page 19 4-Port E1 HWIC:, page 22 4-Port T1 HWIC In this example, the 4-port HWIC is set to card type T1 and is configured with default settings. Channel groups are defined on ports 0, 1, and 2. router# show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 1454 bytes Last configuration change at 09:49:03 UTC Tue Sep version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption service internal hostname router boot-start-marker boot-end-marker card type t1 0 2 no aaa new-model resource policy no network-clock-participate wic 2 ip cef voice-card 0 no dspfarm controller T1 0/2/0 framing esf linecode b8zs cablelength long 0db channel-group 1 timeslots 5 controller T1 0/2/1 framing esf linecode b8zs cablelength long 0db channel-group 2 timeslots 10 controller T1 0/2/2 19
20 Configuration Examples for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module framing esf linecode b8zs cablelength long 0db channel-group 3 timeslots 15 controller T1 0/2/3 framing esf linecode b8zs cablelength long 0db interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address duplex auto speed auto media-type rj45 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address duplex auto speed auto media-type rj45 interface Serial0/2/0:1 no ip address interface Serial0/2/1:2 no ip address interface Serial0/2/2:3 no ip address ip default-gateway ip route GigabitEthernet0/0 ip http server no ip http secure-server control-plane line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 login scheduler allocate end router# 20
21 Configuration Examples for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module The show controllers t1 command gives the following output: router# show controllers t1 T1 0/2/0 is up. Applique type is Channelized T1 Cablelength is long gain36 0db No alarms detected. alarm-trigger is not set Soaking time: 3, Clearance time: 10 AIS State:Clear LOS State:Clear LOF State:Clear Version info FPGA Rev: , FPGA Type: PRK4 Framing is ESF, Line Code is B8ZS, Clock Source is Line. CRC Threshold is 320. Reported from firmware is 320. Data in current interval (889 seconds elapsed): 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs Total Data (last 24 hours) 1 Line Code Violations, 2 Path Code Violations, 0 Slip Secs, 1 Fr Loss Secs, 1 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins, 1 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 1 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs T1 0/2/1 is up. Applique type is Channelized T1 Cablelength is long gain36 0db No alarms detected. alarm-trigger is not set Soaking time: 3, Clearance time: 10 AIS State:Clear LOS State:Clear LOF State:Clear Version info FPGA Rev: , FPGA Type: PRK4 Framing is ESF, Line Code is B8ZS, Clock Source is Line. CRC Threshold is 320. Reported from firmware is 320. Data in current interval (892 seconds elapsed): 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs Total Data (last 24 hours) 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations, 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins, 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs T1 0/2/2 is up. Applique type is Channelized T1 Cablelength is long gain36 0db No alarms detected. alarm-trigger is not set Soaking time: 3, Clearance time: 10 AIS State:Clear LOS State:Clear LOF State:Clear Version info FPGA Rev: , FPGA Type: PRK4 Framing is ESF, Line Code is B8ZS, Clock Source is Line. CRC Threshold is 320. Reported from firmware is 320. Data in current interval (893 seconds elapsed): 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs Total Data (last 24 hours) 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations, 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins, 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs T1 0/2/3 is up. Applique type is Channelized T1 Cablelength is long gain36 0db No alarms detected. alarm-trigger is not set Soaking time: 3, Clearance time: 10 AIS State:Clear LOS State:Clear LOF State:Clear 21
22 Configuration Examples for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Version info FPGA Rev: , FPGA Type: PRK4 Framing is ESF, Line Code is B8ZS, Clock Source is Line. CRC Threshold is 320. Reported from firmware is 320. Data in current interval (896 seconds elapsed): 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs Total Data (last 24 hours) 0 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations, 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 0 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins, 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs router# 4-Port E1 HWIC: In this example, the 4-port HWIC is set to card type E1, and is configured with default settings. A channel group is defined on port 0. The show running-config command gives the following output: router# show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 1192 bytes Last configuration change at 01:18:52 UTC Wed Sep version 12.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption service internal hostname router boot-start-marker boot-end-marker card type e1 0 2 no aaa new-model resource policy no network-clock-participate wic 2 ip cef voice-card 0 no dspfarm controller E1 0/2/0 channel-group 1 timeslots 5 national reserve controller E1 0/2/1 controller E1 0/2/2 controller E1 0/2/3 22
23 Configuration Examples for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address duplex auto speed auto media-type rj45 interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address duplex auto speed auto media-type rj45 interface Serial0/2/0:1 no ip address ip default-gateway ip route GigabitEthernet0/0 ip http server no ip http secure-server control-plane line con 0 exec-timeout 0 0 stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 login scheduler allocate end router# 23
24 Configuration Examples for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module The show controllers e1 command gives the following output: router# show controllers e1 E1 0/2/0 is up. Applique type is Channelized E1 - balanced No alarms detected. alarm-trigger is not set Version info FPGA Rev: , FPGA Type: PRK4 Framing is CRC4, Line Code is HDB3, Clock Source is Line. CRC Threshold is 320. Reported from firmware is 320. International Bit: 0, National Bits: Data in current interval (621 seconds elapsed): 5 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 2 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs E1 0/2/1 is up. Applique type is Channelized E1 - balanced No alarms detected. alarm-trigger is not set Version info FPGA Rev: , FPGA Type: PRK4 Framing is CRC4, Line Code is HDB3, Clock Source is Line. CRC Threshold is 320. Reported from firmware is 320. Data in current interval (630 seconds elapsed): 5 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 1 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs E1 0/2/2 is up. Applique type is Channelized E1 - balanced No alarms detected. alarm-trigger is not set Version info FPGA Rev: , FPGA Type: PRK4 Framing is CRC4, Line Code is HDB3, Clock Source is Line. CRC Threshold is 320. Reported from firmware is 320. Data in current interval (648 seconds elapsed): 4 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 1 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs E1 0/2/3 is up. Applique type is Channelized E1 - balanced No alarms detected. alarm-trigger is not set Version info FPGA Rev: , FPGA Type: PRK4 Framing is CRC4, Line Code is HDB3, Clock Source is Line. CRC Threshold is 320. Reported from firmware is 320. Data in current interval (660 seconds elapsed): 56 Line Code Violations, 0 Path Code Violations 0 Slip Secs, 0 Fr Loss Secs, 1 Line Err Secs, 0 Degraded Mins 0 Errored Secs, 0 Bursty Err Secs, 0 Severely Err Secs, 0 Unavail Secs router# 24
25 Additional References Additional References Related Documents Related Topic Cisco IOS commands Hardware installation of network modules Document Title Cisco IOS Master Commands List, All Releases Cisco Network Modules Hardware Installation Guide Standards Standard No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards have not been modified by this feature. Title MIBs MIB No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature, and support for existing MIBs have not been modified by this feature. MIBs Link To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: RFCs RFC No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs have not been modified by this feature. Title 25
26 Command Reference Technical Assistance Description The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. Link Command Reference This section documents only commands that are modified. controller 26
27 controller controller To configure a T1, E1, or J1 controller and enter controller configuration mode, use the controller command in global configuration mode. Cisco 2600 and 3600 Series Routers controller {t1 e1 j1} slot/port Cisco 7200 Series and Cisco 7500 Series Routers controller {t1 e1} slot/port Cisco AS5300 Access Servers controller {t1 e1} number Cisco AS5800 Access Servers controller t1 dial-shelf/slot/t3-port:t1-num Cisco 2800 and 3800 Series Routers controller {t1 e1} slot/subslot/port Syntax Description t1 e1 j1 slot/port T1 controller. E1 controller. J1 controller. Backplane slot number and port number on the interface. Refer to your hardware installation manual for the specific values and slot numbers. slot/subslot/port Backplane slot number, subslot number, and port number on the interface. Refer to your hardware installation guide for the specific values, and slot and subslot numbers. number Network processor module (NPM) number, in the range 0 through 2. dial-shelf Dial shelf chassis in the Cisco AS5800 access server that contains the interface card. /t3-port T3 port number. The only valid value is 0. :t1-num T1 timeslot in the T3 line. The value can be from 1 to 28. Defaults No T1, E1, or J1 controller is configured. Command Modes Global configuration 27
28 controller Command History Release Modification 10.0 This command was introduced The e1 keyword was added. 12.0(3)T Support was added for dial shelves on Cisco AS5800 access servers. 12.2(7)XO The j1 keyword was added for the Cisco 2600 and Cisco 3600 series. 12.2(33)SRA This command was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA. 12.4(11)XW The subslot argument was added for the Cisco 2800 and Cisco 3800 series. Usage Guidelines T1 or E1 Fractional Data Lines This command is used in configurations where the router or access server is intended to communicate with a T1 or E1 fractional data line. Additional parameters for the T1 or E1 line must be configured for the controller before the T1 or E1 circuits can be configured by means of the interface global configuration command. To view the status of the controllers use the show controllers command. Examples Cisco 7500 Series Router As a T1 Controller The following example configures the MIP in slot 4, port 0 of a Cisco 7500 series router as a T1 controller: Router(config)# controller t1 4/0 Router(config-controller)# Cisco AS5800 Access Server with Dial Shelf The following example configures the T1 controller in shelf 1, slot 0, port 0: Router(config)# controller t1 1/0/0:1 Router(config-controller)# Cisco 3660 As a J1 Controller The following example configures the Cisco IOS interface card in slot 3, port 0 of a Cisco 3660 as a J1 controller: Router(config)# controller j1 3/0 Router(config-controller)# Related Commands Command bert abort interface serial show controllers content-engine show controllers j1 show controllers t1 Description Resets the T1 or E1 controller. Specifies a serial interface created on a channelized E1 or channelized T1 controller (for ISDN PRI, CAS, or robbed-bit signaling). Displays information about the E1 links supported by the NPM (Cisco 4000) or MIP (Cisco 7500 series). Displays information about the J1 link. Displays the total number of calls and call durations on a T1 controller. 28
29 Feature Information for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Modules Feature Information for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Modules Table 3 lists the features in this module and provides links to specific configuration information. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and software image support. Cisco Feature Navigator enables you to determine which software images support a specific software release, feature set, or platform. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to An account on Cisco.com is not required. Note Table 3 lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature. 29
30 Feature Information for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Modules Table 3 Feature Information for T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module Feature Name Releases Feature Information T1/E1 HWICs and 8-Port T1/E1 Network Module Voice Support on 1-Port and 2-Port HWICs 12.4(11)XW5 12.4(20)T 15.0(1)M3, 15.1(1)T1, 15.1(2)T T1/E1 HWICs are available as follows: Channelized 1-port T1/E1 HWIC Channelized 2-port T1/E1 HWIC Clear channel 4-port T1/E1 HWIC The T1/E1 network module is available as an 8-port channelized T1/E1 network module. T1/E1 HWICs are supported on Cisco 2811, Cisco 2821, Cisco 2851, Cisco 3800, Cisco 2900, and Cisco 3900 series routers. The T1/E1 network module is supported on Cisco 3800, Cisco 2900, and on Cisco 3900 series routers. The following sections provide information about this feature: Information About T1/E1 HWICs and Network Module, page 3 The following commands were introduced or modified: controller. Introduces digital voice support (ds0-group and pri-group) on HWIC-1CE1T1-PRI and HWIC- 2CE1T1-PRI. This feature is introduced to the 1-Port and 2-Port HWIC on the following ISR-G2 platforms. Cisco 2911, Cisco 2921, Cisco 2951, Cisco 3925, Cisco 3925E, Cisco 3945, and Cisco 3945E. Digital voice for 1-Port and 2-Port HWICS is only supported on motherboard (MB) HWIC slots. The CUCM releases CUCM 7.1(5) and CUCM 8.0(2) are the minimum releases supported for voice on HWIC-1CE1T1-PRI and HWIC-2CE1T1-PRI. This release information only applies to MGCP configurations because H.323 and SIP configurations have no CUCM release dependency. The following sections provide information about this feature: Configuring the T1/E1 HWICs or Network Module, page 8 Configuring the T1/E1 HWICs with Voice Support, page 16 30
1-, 2-, and 4-Port T1/E1 HWICs and 8-Port T1/E1 Network Module
 1-, 2-, and 4-Pt T1/E1 HWICs and 8-Pt T1/E1 Netwk Module First Published: November 22, 2007 Last Updated: July 11, 2008 This document describes the following Cisco products: Cisco 1-Pt and 2-Pt Channelized
1-, 2-, and 4-Pt T1/E1 HWICs and 8-Pt T1/E1 Netwk Module First Published: November 22, 2007 Last Updated: July 11, 2008 This document describes the following Cisco products: Cisco 1-Pt and 2-Pt Channelized
Configuring Voice and Data Support on 1-Port, 2-Port, and 4-Port VWIC3
 Configuring Voice and Data Support on 1-Port, 2-Port, and 4-Port VWIC3 Last Updated: February 3, 2011, This module describes how to configure voice and data support on the next generation of voice/wan
Configuring Voice and Data Support on 1-Port, 2-Port, and 4-Port VWIC3 Last Updated: February 3, 2011, This module describes how to configure voice and data support on the next generation of voice/wan
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
 This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
 Effective Cisco IOS-XE Release 3.14.0S, the Cisco ASR-920-24SZ-IM, ASR-920-24SZ-M, ASR-920-24TZ-M Aggregation Services Router supports the following types of interface modules (IMs): 8x1G Cu IM (A900-IMA8T)
Effective Cisco IOS-XE Release 3.14.0S, the Cisco ASR-920-24SZ-IM, ASR-920-24SZ-M, ASR-920-24TZ-M Aggregation Services Router supports the following types of interface modules (IMs): 8x1G Cu IM (A900-IMA8T)
1-Port DSU/CSU T1 WIC for the Cisco 1700, Cisco 2600, Cisco 3600, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers
 1-Port DSU/CSU T1 WIC for the Cisco 1700, Cisco 2600, Cisco 3600, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers Feature History Release Modification 11.2 This feature was introduced on the Cisco 1600 series and Cisco
1-Port DSU/CSU T1 WIC for the Cisco 1700, Cisco 2600, Cisco 3600, and Cisco 3700 Series Routers Feature History Release Modification 11.2 This feature was introduced on the Cisco 1600 series and Cisco
Configuring the Cisco 3825 Mobile Wireless Edge Router in a RAN-O Solution with the Command-Line Interface
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring the Cisco 3825 Mobile Wireless Edge Router in a RAN-O Solution with the Command-Line Interface This chapter describes how to use the Cisco IOS software CLI to configure the Cisco
CHAPTER 4 Configuring the Cisco 3825 Mobile Wireless Edge Router in a RAN-O Solution with the Command-Line Interface This chapter describes how to use the Cisco IOS software CLI to configure the Cisco
Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1 E1 Interfaces
 Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1 E1 Interfaces This chapter describes how to implement the Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1/E1 Interfaces with the AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 Module feature. This card provides
Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1 E1 Interfaces This chapter describes how to implement the Integrated Voice and Data WAN on T1/E1 Interfaces with the AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 Module feature. This card provides
Configuring T1/E1 Interfaces
 This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
This chapter provides information about configuring the T1/E1 interface module on the chassis. It includes the following sections: For information about managing your system images and configuration files,
Implementing T1 CAS for VoIP
 This chapter describes how to implement the T1 Channel-Associated Signaling (CAS) for VoIP feature. This feature adds support for T1 CAS and E1 R2 signaling with the voice feature card (VFC). The T1 CAS
This chapter describes how to implement the T1 Channel-Associated Signaling (CAS) for VoIP feature. This feature adds support for T1 CAS and E1 R2 signaling with the voice feature card (VFC). The T1 CAS
Multicast Music-on-Hold Support on Cisco UBE
 First Published: July 22, 2011 Last Updated: July 22, 2011 The Multicast Music-on-Hold (MMOH) feature enables you to subscribe to a music streaming service when you are using a Cisco Unified Border Element.
First Published: July 22, 2011 Last Updated: July 22, 2011 The Multicast Music-on-Hold (MMOH) feature enables you to subscribe to a music streaming service when you are using a Cisco Unified Border Element.
Configuring Cisco Integrated Data Service Unit/Channel Service Unit (DSU/CSU) Modules and WAN Interface Cards
 Configuring Cisco Integrated Data Service Unit/Channel Service Unit (DSU/CSU) Modules and WAN Interface Cards Document ID: 10265 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device.
Configuring Cisco Integrated Data Service Unit/Channel Service Unit (DSU/CSU) Modules and WAN Interface Cards Document ID: 10265 Interactive: This document offers customized analysis of your Cisco device.
Integrated Services Routers 4000 Series Digital Voice Configuration Example
 Integrated Services Routers 4000 Series Digital Voice Configuration Example Document ID: 118792 Contributed by Karan Moudgil, Cisco TAC Engineer. Feb 27, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Integrated Services Routers 4000 Series Digital Voice Configuration Example Document ID: 118792 Contributed by Karan Moudgil, Cisco TAC Engineer. Feb 27, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Circuit Emulation over IP
 (CEoIP) provides a virtual circuit through an IP network--similar to a leased line--to integrate solutions that require a time-sensitive, bit-transparent transport into IP networks. Data, with proprietary
(CEoIP) provides a virtual circuit through an IP network--similar to a leased line--to integrate solutions that require a time-sensitive, bit-transparent transport into IP networks. Data, with proprietary
Cisco 1- and 2-port T1/E1 Multiflex Voice/WAN Interface Cards for the Cisco 1751 and Cisco 1760 Routers
 Cisco 1- and 2-port T1/E1 Multiflex Voice/WAN Interface Cards for the Cisco 1751 and Cisco 1760 Routers This document describes the Cisco 1- and 2-port T1/E1 multiflex interface cards, and provides instructions
Cisco 1- and 2-port T1/E1 Multiflex Voice/WAN Interface Cards for the Cisco 1751 and Cisco 1760 Routers This document describes the Cisco 1- and 2-port T1/E1 multiflex interface cards, and provides instructions
Configuring Modem Transport Support for VoIP
 Configuring Modem Transport Support for VoIP This chapter explains how to configure modem transport support for Voice over IP (VoIP) and contains the following sections: Modem Transport Support Overview,
Configuring Modem Transport Support for VoIP This chapter explains how to configure modem transport support for Voice over IP (VoIP) and contains the following sections: Modem Transport Support Overview,
Cisco 7206 Series Router-PBX Interoperability: Lucent Definity G3r PBX and VXC-2TE1+ Port Adapter Card with E1 ISDN PRI Signaling
 Cisco 7206 Series Router-PBX Interoperability: Lucent Definity G3r PBX and VXC-2TE1+ Port Adapter Card with E1 ISDN PRI This document describes the interoperability and configuration of a Cisco 7200 series
Cisco 7206 Series Router-PBX Interoperability: Lucent Definity G3r PBX and VXC-2TE1+ Port Adapter Card with E1 ISDN PRI This document describes the interoperability and configuration of a Cisco 7200 series
No Service Password-Recovery
 No Service Password-Recovery Last Updated: January 18, 2012 The No Service Password-Recovery feature is a security enhancement that prevents anyone with console access from accessing the router configuration
No Service Password-Recovery Last Updated: January 18, 2012 The No Service Password-Recovery feature is a security enhancement that prevents anyone with console access from accessing the router configuration
AIM-ATM, AIM-VOICE-30, and AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 on the Cisco 2600 Series and Cisco 3660
 AIM-ATM, AIM-VOICE-30, and AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 on the Cisco 2600 Series and Cisco 3660 Feature History Release 12.2(2)XA 12.2(2)XB Modification The High-Performance ATM Advanced Integration Module (AIM-ATM)
AIM-ATM, AIM-VOICE-30, and AIM-ATM-VOICE-30 on the Cisco 2600 Series and Cisco 3660 Feature History Release 12.2(2)XA 12.2(2)XB Modification The High-Performance ATM Advanced Integration Module (AIM-ATM)
This feature was introduced.
 Feature History Release 12.2(11)T Modification This feature was introduced. This document describes the QSIG for TCL IVR (Tool Language Interactive Voice Response) 2.0 feature in and includes the following
Feature History Release 12.2(11)T Modification This feature was introduced. This document describes the QSIG for TCL IVR (Tool Language Interactive Voice Response) 2.0 feature in and includes the following
Overview of Circuit Emulation
 Circuit Emulation (CEM) is a technology that provides a protocol-independent transport over IP/MPLS networks. It s proprietary or legacy applications to be carried transparently to the destination, similar
Circuit Emulation (CEM) is a technology that provides a protocol-independent transport over IP/MPLS networks. It s proprietary or legacy applications to be carried transparently to the destination, similar
Lucent/Avaya Definity G3si V9 PBX with CallManager using the Cisco 3640-T1 PRI as an MGCP Gateway
 Application te Lucent/Avaya Definity G3si V9 PBX with CallManager using the Cisco 3640-T1 PRI as an MGCP Gateway This application note discusses the integration of the Lucent/Avaya Definity G3si V9 PBX
Application te Lucent/Avaya Definity G3si V9 PBX with CallManager using the Cisco 3640-T1 PRI as an MGCP Gateway This application note discusses the integration of the Lucent/Avaya Definity G3si V9 PBX
Configuring the SS7 Port Adapter
 CHAPTER 4 To continue your SS7 Port Adapter installation, you must configure the card type as either T1 or E1 and then configure the interfaces. This chapter contains the following sections: Using the
CHAPTER 4 To continue your SS7 Port Adapter installation, you must configure the card type as either T1 or E1 and then configure the interfaces. This chapter contains the following sections: Using the
Integrated Data and Voice Services for ISDN PRI Interfaces on Multiservice Access Routers
 Integrated Data and Voice Services for ISDN PRI Interfaces on Multiservice Access Routers This chapter describes how to configure ISDN PRI interfaces to support the integration of data and voice calls
Integrated Data and Voice Services for ISDN PRI Interfaces on Multiservice Access Routers This chapter describes how to configure ISDN PRI interfaces to support the integration of data and voice calls
Integrated Data and Voice Services for ISDN PRI Interfaces on Multiservice Access Routers
 Integrated Data and Voice Services for ISDN PRI Interfaces on Multiservice Access Routers This chapter describes how to configure ISDN PRI interfaces to support the integration of data and voice calls
Integrated Data and Voice Services for ISDN PRI Interfaces on Multiservice Access Routers This chapter describes how to configure ISDN PRI interfaces to support the integration of data and voice calls
Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Router T1/E1 Voice and WAN Network Interface Modules Data Sheet
 Data Sheet Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Router T1/E1 Voice and WAN Network Interface Modules Data Sheet These flexible interface cards support multiple integrated data and voice applications,
Data Sheet Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Router T1/E1 Voice and WAN Network Interface Modules Data Sheet These flexible interface cards support multiple integrated data and voice applications,
ATM Software Segmentation and Reassembly
 Feature History Release Modification 12.2(2)XB Cisco 2600 Series T1/E1 ATM and Cisco 3660 T1 Inverse Multiplexing over ATM (IMA) ATM Adaption Layer 2 (AAL2) Support was introduced. 12.2(8)T This feature
Feature History Release Modification 12.2(2)XB Cisco 2600 Series T1/E1 ATM and Cisco 3660 T1 Inverse Multiplexing over ATM (IMA) ATM Adaption Layer 2 (AAL2) Support was introduced. 12.2(8)T This feature
Multichannel STM-1 Port Adapter for the Cisco 7500 Series Router
 Multichannel STM-1 Port Adapter for the Cisco 7500 Series Router This feature module describes the Multichannel STM-1 Port Adapter (PA-MC-STM-1). It includes information on the benefits of this port adapter,
Multichannel STM-1 Port Adapter for the Cisco 7500 Series Router This feature module describes the Multichannel STM-1 Port Adapter (PA-MC-STM-1). It includes information on the benefits of this port adapter,
Configuring the SM-1-STM1
 4 CHAPTER To continue your SM-1-STM1 service module installation, you must configure the STM-1 interface. This chapter contains the following sections: Configuring the Interface, page 4-1 Checking the
4 CHAPTER To continue your SM-1-STM1 service module installation, you must configure the STM-1 interface. This chapter contains the following sections: Configuring the Interface, page 4-1 Checking the
Configuring FXS Ports for Basic Calls
 Configuring FXS Ports for Basic Calls First Published: October 2, 2008 Last updated: March 19, 2010 This module describes how to configure analog Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) ports on a Cisco Integrated
Configuring FXS Ports for Basic Calls First Published: October 2, 2008 Last updated: March 19, 2010 This module describes how to configure analog Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) ports on a Cisco Integrated
IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (QnQ) and L2PT on L2 Ports
 Revised: November 11, 2011, OL-20468-01 First Published: November 11, 2011 Last Updated: November 11, 2011 This feature provides Layer 2 Tunneling support for QnQ and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT)
Revised: November 11, 2011, OL-20468-01 First Published: November 11, 2011 Last Updated: November 11, 2011 This feature provides Layer 2 Tunneling support for QnQ and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling (L2PT)
Configuring the 1-Port Channelized OC-3/STM-1 SPA
 CHAPTER 12 Configuring the 1-Port Channelized OC-3/STM-1 SPA This chapter provides information about configuring the 1-Port Channelized OC-3/STM-1 SPA on Cisco 12000 Series Routers. It includes the following
CHAPTER 12 Configuring the 1-Port Channelized OC-3/STM-1 SPA This chapter provides information about configuring the 1-Port Channelized OC-3/STM-1 SPA on Cisco 12000 Series Routers. It includes the following
Configure IOS-XE to display full show running-config for users with low Privilege Levels
 Configure IOS-XE to display full show running-config for users with low Privilege Levels Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configuration Problem Configuration Solution and
Configure IOS-XE to display full show running-config for users with low Privilege Levels Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configuration Problem Configuration Solution and
IPsec Anti-Replay Window: Expanding and Disabling
 IPsec Anti-Replay Window: Expanding and Disabling First Published: February 28, 2005 Last Updated: March 24, 2011 Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker
IPsec Anti-Replay Window: Expanding and Disabling First Published: February 28, 2005 Last Updated: March 24, 2011 Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker
Private Line Automatic Ringdown for Trading Turrets
 Private Line Automatic Ringdown for Trading Turrets The Private Line Automatic Ringdown for Trading Turrets feature improves connection service for turrets in the financial industry primarily for corporations
Private Line Automatic Ringdown for Trading Turrets The Private Line Automatic Ringdown for Trading Turrets feature improves connection service for turrets in the financial industry primarily for corporations
Configuring the Cisco IPICS RMS Component
 Configuring the Cisco IPICS RMS Component APPENDIXA This appendix describes the configuration steps that you must follow to configure the RMS router for use with the Cisco IPICS server. The Cisco IPICS
Configuring the Cisco IPICS RMS Component APPENDIXA This appendix describes the configuration steps that you must follow to configure the RMS router for use with the Cisco IPICS server. The Cisco IPICS
Configuring the E1 + G.703 and T1 + DSX-1 Modules
 9 Configuring the E1 + G.703 and T1 + DSX-1 Modules Contents Using an E1- or T1-Carrier Line for Data and Voice................... 9-3 Drop-and-Insert Modules..................................... 9-3 Standards
9 Configuring the E1 + G.703 and T1 + DSX-1 Modules Contents Using an E1- or T1-Carrier Line for Data and Voice................... 9-3 Drop-and-Insert Modules..................................... 9-3 Standards
Clock Recovery System
 The recovers the service clock using Adaptive Clock Recovery (ACR) and Differential Clock Recovery (DCR). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About Clock Recovery, page 1 Prerequisites for
The recovers the service clock using Adaptive Clock Recovery (ACR) and Differential Clock Recovery (DCR). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About Clock Recovery, page 1 Prerequisites for
Overview of Circuit Emulation
 Circuit Emulation (CEM) is a technology that provides a protocol-independent transport over IP/MPLS networks. It s proprietary or legacy applications to be carried transparently to the destination, similar
Circuit Emulation (CEM) is a technology that provides a protocol-independent transport over IP/MPLS networks. It s proprietary or legacy applications to be carried transparently to the destination, similar
Configuring the Eight-Port FXS RJ-21 Module
 CHAPTER 7 Configuring the Eight-Port FXS RJ-21 Module The Eight-port RJ-21 FXS Module is a high-density analog phone and fax relay interface. By providing service to analog phones and fax machines, the
CHAPTER 7 Configuring the Eight-Port FXS RJ-21 Module The Eight-port RJ-21 FXS Module is a high-density analog phone and fax relay interface. By providing service to analog phones and fax machines, the
IP Communications High Density Digital Voice/Fax Network Module
 IP Communications High Density Digital Voice/Fax Network Module Document ID: 65356 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Key Features Hardware
IP Communications High Density Digital Voice/Fax Network Module Document ID: 65356 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Key Features Hardware
Configuring Secure Shell
 Configuring Secure Shell Last Updated: October 24, 2011 The Secure Shell (SSH) feature is an application and a protocol that provides a secure replacement to the Berkeley r-tools. The protocol secures
Configuring Secure Shell Last Updated: October 24, 2011 The Secure Shell (SSH) feature is an application and a protocol that provides a secure replacement to the Berkeley r-tools. The protocol secures
Logging to Local Nonvolatile Storage (ATA Disk)
 Logging to Local Nonvolatile Storage (ATA Last Updated: October 12, 2011 The Logging to Local Nonvolatile Storage (ATA feature enables system logging messages to be saved on an advanced technology attachment
Logging to Local Nonvolatile Storage (ATA Last Updated: October 12, 2011 The Logging to Local Nonvolatile Storage (ATA feature enables system logging messages to be saved on an advanced technology attachment
Clock Recovery System
 The recovers the service clock using Adaptive Clock Recovery (ACR) and Differential Clock Recovery (DCR). Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Information About Clock Recovery, on page 1 Prerequisites
The recovers the service clock using Adaptive Clock Recovery (ACR) and Differential Clock Recovery (DCR). Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Information About Clock Recovery, on page 1 Prerequisites
t1 through tug-2 e1 unframed
 t1 through tug-2 e1 unframed t1, page 3 t1 bert, page 5 t1/e1 cem-group, page 8 t1 clock source, page 9 t1 external, page 11 t1 fdl ansi, page 13 t1 framing, page 15 t1 linecode, page 18 t1 logging-events,
t1 through tug-2 e1 unframed t1, page 3 t1 bert, page 5 t1/e1 cem-group, page 8 t1 clock source, page 9 t1 external, page 11 t1 fdl ansi, page 13 t1 framing, page 15 t1 linecode, page 18 t1 logging-events,
Configure Q.SIG PRI Trunks between Call Manager and Avaya S8700/G650 with Unity Voice Mail Integration
 Configure Q.SIG PRI Trunks between Call Manager and Avaya S8700/G650 with Unity Voice Mail Integration Document ID: 63790 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Test
Configure Q.SIG PRI Trunks between Call Manager and Avaya S8700/G650 with Unity Voice Mail Integration Document ID: 63790 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Test
Tech Note: Configuring Q.SIG PRI trunk between Cisco Call Manager and Avaya S8700/G650 with Cisco Unity Voice Mail integration
 Tech Note: Configuring Q.SIG PRI trunk between Cisco Call Manager and Avaya S8700/G650 with Cisco Unity Voice Mail integration The objective of this document is to provide Cisco s customers and business
Tech Note: Configuring Q.SIG PRI trunk between Cisco Call Manager and Avaya S8700/G650 with Cisco Unity Voice Mail integration The objective of this document is to provide Cisco s customers and business
RADIUS Route Download
 The feature allows users to configure their network access server (NAS) to direct RADIUS authorization. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 1 Information About, page 1 How to Configure,
The feature allows users to configure their network access server (NAS) to direct RADIUS authorization. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 1 Information About, page 1 How to Configure,
AAA Dead-Server Detection
 The feature allows you to configure the criteria to be used to mark a RADIUS server as dead. If no criteria are explicitly configured, the criteria are computed dynamically on the basis of the number of
The feature allows you to configure the criteria to be used to mark a RADIUS server as dead. If no criteria are explicitly configured, the criteria are computed dynamically on the basis of the number of
Cisco 2621 Gateway-PBX Interoperability: Lucent/Avaya Definity G3si with T1 PRI Signaling
 Cisco 2621 Gateway-PBX Interoperability: Lucent/Avaya Definity G3si with T1 PRI Signaling This document describes the interoperability and configuration of a Cisco 2621 voice gateway with a Lucent/Avaya
Cisco 2621 Gateway-PBX Interoperability: Lucent/Avaya Definity G3si with T1 PRI Signaling This document describes the interoperability and configuration of a Cisco 2621 voice gateway with a Lucent/Avaya
ECMP Load Balancing. MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3S (Cisco ASR 900 Series) 1
 Equal-cost multi-path routing (ECMP) is a routing strategy where next-hop packet forwarding to a single destination can occur over multiple "best paths" which tie for top place in routing metric calculations.
Equal-cost multi-path routing (ECMP) is a routing strategy where next-hop packet forwarding to a single destination can occur over multiple "best paths" which tie for top place in routing metric calculations.
Configuring Clear Channel T3/E3 and Channelized T3 and T1/E1 Controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 Configuring Clear Channel T3/E3 and Channelized T3 and T1/E1 Controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the configuration of clear channel T3/E3 controllers and channelized T3
Configuring Clear Channel T3/E3 and Channelized T3 and T1/E1 Controllers on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the configuration of clear channel T3/E3 controllers and channelized T3
Lab Configuring Basic RIPv2 (Solution)
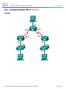 (Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
(Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
Router-Shelf Redundancy for the Cisco AS5800
 This document describes router-shelf redundancy for the Cisco AS5800 universal access server. It includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Feature Overview, page 1 Prerequisites,
This document describes router-shelf redundancy for the Cisco AS5800 universal access server. It includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Feature Overview, page 1 Prerequisites,
IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling
 IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker duplicating encrypted packets by assigning a unique sequence
IPsec Anti-Replay Window Expanding and Disabling Cisco IP security (IPsec) authentication provides anti-replay protection against an attacker duplicating encrypted packets by assigning a unique sequence
Interface Commands. Configuring Logical Interfaces chapter in the. Cisco IOS Interface Configuration Guide. Cisco IOS Interface Configuration Guide
 Interface Commands This book describes the basic commands that can be used on different types of interfaces. These commands correspond to the interface configuration tasks included in the Cisco IOS configuration
Interface Commands This book describes the basic commands that can be used on different types of interfaces. These commands correspond to the interface configuration tasks included in the Cisco IOS configuration
CONFIGURATION DU SWITCH
 Current configuration : 2037 bytes version 12.2 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Switch no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero
Current configuration : 2037 bytes version 12.2 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Switch no aaa new-model ip subnet-zero
Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source
 Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce a new compression technique
Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce a new compression technique
Lab Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 Static Routes (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD
 G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD This document describes the Multirate Symmetrical High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL) feature supported on the Cisco IAD2420 series integrated
G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD This document describes the Multirate Symmetrical High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL) feature supported on the Cisco IAD2420 series integrated
Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source
 Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce a new compression technique
Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce a new compression technique
Single-router APS for the Cisco Series Router
 Single-router APS for the Cisco 12000 Series Router This feature provides 1+1 single-router automatic protection switching (SR-APS) for the Cisco 12000 series ISE ATM line cards (Engine 3) installed in
Single-router APS for the Cisco 12000 Series Router This feature provides 1+1 single-router automatic protection switching (SR-APS) for the Cisco 12000 series ISE ATM line cards (Engine 3) installed in
Using the setup Command Facility
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to use the setup command facility to configure your Cisco integrated access device (IAD). The setup command facility prompts you to enter information needed to start
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to use the setup command facility to configure your Cisco integrated access device (IAD). The setup command facility prompts you to enter information needed to start
Configuring Pseudowire
 This chapter provides information about configuring pseudowire features on the Cisco ASR 920 Series Router. Pseudowire Overview, on page 1 CEM Configuration, on page 2 CEM Configuration Guidelines and
This chapter provides information about configuring pseudowire features on the Cisco ASR 920 Series Router. Pseudowire Overview, on page 1 CEM Configuration, on page 2 CEM Configuration Guidelines and
Encrypted Vendor-Specific Attributes
 Encrypted Vendor-Specific Attributes Last Updated: January 15, 2012 The Encrypted Vendor-Specific Attributes feature provides users with a way to centrally manage filters at a RADIUS server and supports
Encrypted Vendor-Specific Attributes Last Updated: January 15, 2012 The Encrypted Vendor-Specific Attributes feature provides users with a way to centrally manage filters at a RADIUS server and supports
Configuring Local Authentication and Authorization
 Configuring Local Authentication and Authorization Finding Feature Information, page 1 How to Configure Local Authentication and Authorization, page 1 Monitoring Local Authentication and Authorization,
Configuring Local Authentication and Authorization Finding Feature Information, page 1 How to Configure Local Authentication and Authorization, page 1 Monitoring Local Authentication and Authorization,
L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients
 L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients The L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients feature allows mulitple Windows client to connect to an IPsec-enabled Cisco IOS Layer 2 Tunneling
L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients The L2TP IPsec Support for NAT and PAT Windows Clients feature allows mulitple Windows client to connect to an IPsec-enabled Cisco IOS Layer 2 Tunneling
Configuring System MTU
 Restrictions for System MTU, on page 1 Information About the MTU, on page 1 How to Configure MTU, on page 2 Configuration Examples for System MTU, on page 4 Additional References for System MTU, on page
Restrictions for System MTU, on page 1 Information About the MTU, on page 1 How to Configure MTU, on page 2 Configuration Examples for System MTU, on page 4 Additional References for System MTU, on page
Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source
 Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source Last Updated: April 17, 2012 The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce
Lossless Compression R1 ATM Cell Switching and External BITS Clocking Source Last Updated: April 17, 2012 The Lossless Compression R1, ATM Cell Switching, and External BITS Clocking Source features introduce
VoIP with Channel Associated Signaling (CAS)
 VoIP with Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) Document ID: 14078 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions T1 Signaling: CCS and CAS CCS CAS Configure
VoIP with Channel Associated Signaling (CAS) Document ID: 14078 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions T1 Signaling: CCS and CAS CCS CAS Configure
Using the Setup Script
 APPENDIX A Using the Setup Script The information herein applies to the Cisco AS5350, Cisco AS5400, and Cisco AS5400HPX universal gateways that the latter requires use of Cisco IOS release 122(2)XB or
APPENDIX A Using the Setup Script The information herein applies to the Cisco AS5350, Cisco AS5400, and Cisco AS5400HPX universal gateways that the latter requires use of Cisco IOS release 122(2)XB or
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Solution)
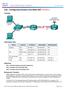 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Gateway G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.201.18 255.255.255.252 N/A ISP S0/0/0 (DCE)
Configuring Embedded Resource Manager-MIB
 The Embedded Resource Manager (ERM)-MIB feature introduces MIB support for the ERM feature. The ERM feature tracks resource usage information for every registered resource owner and resource user. The
The Embedded Resource Manager (ERM)-MIB feature introduces MIB support for the ERM feature. The ERM feature tracks resource usage information for every registered resource owner and resource user. The
Encrypted Vendor-Specific Attributes
 The feature provides users with a way to centrally manage filters at a RADIUS server and supports the following types of string vendor-specific attributes (VSAs): Tagged String VSA, on page 2 (similar
The feature provides users with a way to centrally manage filters at a RADIUS server and supports the following types of string vendor-specific attributes (VSAs): Tagged String VSA, on page 2 (similar
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI
 ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI Feature History Release 12.1(T) 12.1(5)XM2 Modification This feature was introduced. Support was added for the Cisco AS5350 and Cisco AS5400 universal gateways. This
ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI Feature History Release 12.1(T) 12.1(5)XM2 Modification This feature was introduced. Support was added for the Cisco AS5350 and Cisco AS5400 universal gateways. This
Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme. Topology. Objectives. Background / Scenario
 CSNB214 Packet Tracer Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Network Requirements Part 2: Design the VLSM Address Scheme Part 3: Cable and Configure
CSNB214 Packet Tracer Lab Designing and Implementing a VLSM Addressing Scheme Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Network Requirements Part 2: Design the VLSM Address Scheme Part 3: Cable and Configure
Lab Configuring Dynamic and Static NAT (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
channel-group through cut-through
 channel-group, page 2 channel-group (interface), page 7 clear counters, page 13 clear lacp counters, page 17 cut-through, page 18 1 channel-group channel-group To configure serial WAN on a T1 or E1 interface,
channel-group, page 2 channel-group (interface), page 7 clear counters, page 13 clear lacp counters, page 17 cut-through, page 18 1 channel-group channel-group To configure serial WAN on a T1 or E1 interface,
Lab Configuring Port Address Translation (PAT) (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD
 G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD This document describes the Multirate Symmetrical High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL) feature supported on the Cisco IAD2420 series integrated
G.SHDSL Symmetric DSL Support for Cisco IAD2420 Series IAD This document describes the Multirate Symmetrical High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (G.SHDSL) feature supported on the Cisco IAD2420 series integrated
Auto In-Service State for Ports
 This document describes the Auto In-Service State (AINS) feature on the port. Effective Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.1, the Cisco NCS 4200 Series support management of equipment and port state model in two
This document describes the Auto In-Service State (AINS) feature on the port. Effective Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.1, the Cisco NCS 4200 Series support management of equipment and port state model in two
Voice over IP Q.SIG Network Transparency
 Voice over IP Q.SIG Network Transparency Feature History Release 12.0(7)T 12.1(5)XM2 Modification This feature was introduced Support was added for the Cisco AS5350 and Cisco AS5400 universal gateways.
Voice over IP Q.SIG Network Transparency Feature History Release 12.0(7)T 12.1(5)XM2 Modification This feature was introduced Support was added for the Cisco AS5350 and Cisco AS5400 universal gateways.
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
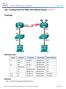 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Using Cisco Discovery Protocol
 Using Cisco Discovery Protocol First Published: February 1, 1995 Last Updated: August 12, 2010 Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Layer 2 media-independent and network-independent protocol that runs on
Using Cisco Discovery Protocol First Published: February 1, 1995 Last Updated: August 12, 2010 Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a Layer 2 media-independent and network-independent protocol that runs on
Remote Access MPLS-VPNs
 First Published: August 12, 2002 Last Updated: May 4, 2009 The feature allows the service provider to offer a scalable end-to-end Virtual Private Network (VPN) service to remote users. This feature integrates
First Published: August 12, 2002 Last Updated: May 4, 2009 The feature allows the service provider to offer a scalable end-to-end Virtual Private Network (VPN) service to remote users. This feature integrates
BGP Event-Based VPN Import
 BGP Event-Based VPN Import Last Updated: April 13, 2012 The BGP Event-Based VPN Import feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced
BGP Event-Based VPN Import Last Updated: April 13, 2012 The BGP Event-Based VPN Import feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced
Sample Business Ready Branch Configuration Listings
 APPENDIX A Sample Business Ready Branch Configuration Listings The following is a sample configuration of a Business Ready Branch. There are many permutations of feature combinations when setting up the
APPENDIX A Sample Business Ready Branch Configuration Listings The following is a sample configuration of a Business Ready Branch. There are many permutations of feature combinations when setting up the
E and M Signals over MPLS
 This chapter provides information about peer-to-peer transport of receive and transmit (E and M) signals and voice data over MPLS on the Cisco ASR 903 Router. E and M Signaling Overview, page 1 Restrictions,
This chapter provides information about peer-to-peer transport of receive and transmit (E and M) signals and voice data over MPLS on the Cisco ASR 903 Router. E and M Signaling Overview, page 1 Restrictions,
Configuring the Physical Subscriber Line for RADIUS Access and Accounting
 Configuring the Physical Subscriber Line for RADIUS Access and Accounting Last Updated: December 5, 2011 Configuring a physical subscriber line for RADIUS Access and Accounting enables an L2TP access concentrator
Configuring the Physical Subscriber Line for RADIUS Access and Accounting Last Updated: December 5, 2011 Configuring a physical subscriber line for RADIUS Access and Accounting enables an L2TP access concentrator
Contextual Configuration Diff Utility
 Contextual Configuration Diff Utility Last Updated: November 29, 2011 The Contextual Configuration Diff Utility feature provides the ability to perform a line-by-line comparison of any two configuration
Contextual Configuration Diff Utility Last Updated: November 29, 2011 The Contextual Configuration Diff Utility feature provides the ability to perform a line-by-line comparison of any two configuration
AT&T IP Flexible Reach Service and AT&T IP Toll-Free on AT&T VPN Service
 AT&T IP Flexible Reach Service and AT&T IP Toll-Free on AT&T VPN Service TDM Gateway Customer Configuration Guide for AT&T IP Flexible Reach Service and AT&T IP Toll-Free on AT&T VPN Service as the Underlying
AT&T IP Flexible Reach Service and AT&T IP Toll-Free on AT&T VPN Service TDM Gateway Customer Configuration Guide for AT&T IP Flexible Reach Service and AT&T IP Toll-Free on AT&T VPN Service as the Underlying
EHWIC-4SHDSL-EA module Fixed ISR G2 routers like C888EA-K9 work in both CO and CPE modes with Cisco IOS Software 15.2(2)T2 and later releases.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Configurations ATM mode EFM mode Introduction This document describes configuration steps required to implement a back-to-back
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Configurations ATM mode EFM mode Introduction This document describes configuration steps required to implement a back-to-back
Configuring DHCP Option 60 and Option 82 with VPN-ID Support for Transparent Automatic Logon
 Configuring DHCP Option 60 and Option 82 with VPN-ID Support for Transparent Automatic Logon Intelligent Services Gateway (ISG) is a Cisco software feature set that provides a structured framework in which
Configuring DHCP Option 60 and Option 82 with VPN-ID Support for Transparent Automatic Logon Intelligent Services Gateway (ISG) is a Cisco software feature set that provides a structured framework in which
Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
 The feature allows different flows of traffic over a Gigabit EtherChannel (GEC) interface to be identified based on the packet header and then mapped to the different member links of the port channel.
The feature allows different flows of traffic over a Gigabit EtherChannel (GEC) interface to be identified based on the packet header and then mapped to the different member links of the port channel.
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Implementing Traffic Filters for IPv6 Security
 Implementing Traffic Filters for IPv6 Security Last Updated: November 14, 2011 This module describes how to configure Cisco IOS XE IPv6 traffic filter and firewall features for your Cisco networking devices.
Implementing Traffic Filters for IPv6 Security Last Updated: November 14, 2011 This module describes how to configure Cisco IOS XE IPv6 traffic filter and firewall features for your Cisco networking devices.
Voice Performance Statistics on Cisco Gateways
 Voice Performance Statistics on Cisco Gateways The Voice Performance Statistics on Cisco Gateways feature enables the collection of voice call signaling statistics and VoIP AAA accounting statistics based
Voice Performance Statistics on Cisco Gateways The Voice Performance Statistics on Cisco Gateways feature enables the collection of voice call signaling statistics and VoIP AAA accounting statistics based
QoS: Child Service Policy for Priority Class
 QoS: Child Service Policy for Priority Class First Published: November, 2006 Last Updated: March 2, 2009 The QoS: Child Service Policy for Priority Class feature allows you to configure a child service
QoS: Child Service Policy for Priority Class First Published: November, 2006 Last Updated: March 2, 2009 The QoS: Child Service Policy for Priority Class feature allows you to configure a child service
RPR+ on Cisco 7500 Series Routers
 RPR+ on Cisco 7500 Series Routers Feature History 12.0(19)ST1 12.0(22)S 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(22)S. This feature was integrated
RPR+ on Cisco 7500 Series Routers Feature History 12.0(19)ST1 12.0(22)S 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(22)S. This feature was integrated
