BGP Best External. Finding Feature Information
|
|
|
- Annabella Leonard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. The feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external neighbors as a backup route. This feature is beneficial in active-backup topologies, where service providers use routing policies that cause a border router to choose a path received over an Interior Border Gateway Protocol (ibgp) session (of another border router) as the best path for a prefix even if it has an Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (ebgp) learned path. This active-backup topology defines one exit or egress point for the prefix in the autonomous system and uses the other points as backups if the primary link or ebgp peering is unavailable. The policy causes the border router to hide the paths learned over its ebgp sessions from the autonomous system because it does not advertise any path for such prefixes. To cope with this situation, some devices advertise one externally learned path called the best external path. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 2 Restrictions for, page 2 Information About, page 3 How to Configure, page 5 Configuration Examples for, page 10 Additional References, page 11 Feature Information for, page 12 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the Feature Information for, on page 12. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to An account on Cisco.com is not required. 1
2 Prerequisites for Prerequisites for The Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) protocol must be enabled to quickly detect link failures. Ensure that the BGP and the Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) network is up and running with the customer site connected to the provider site by more than one path (multihomed). The backup path must have a unique next hop that is not the same as the next hop of the best path. BGP must support lossless switchover between operational paths. Restrictions for The feature will not install a backup path if BGP Multipath is installed and a multipath exists in the BGP table. One of the multipaths automatically acts as a backup for the other paths. The feature is not supported with the following features: MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier MPLS VPN Inter Autonomous Systems, option B MPLS VPN Virtual Routing and Forwarding Label The feature cannot be configured with Multicast or Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) Virtual Routing and Forwarding address families. The feature cannot be configured on route reflectors. The feature does not support Nonstop Forwarding/Stateful Switchover (NSF/SSO). However, In-Service Software Upgrade (ISSU) is supported if both Route Processors have the BGP Best External feature configured. The feature can be configured only on VPNv4, VPNv6, IPv4 VRF, and IPv6 VRF address families. When you configure the feature using the bgp advertise-best-external command, you need not enable the BGP Prefix-Independent Convergence (PIC) feature with the bgp additional-paths install command. The BGP PIC feature is automatically enabled by the BGP Best External feature. When you configure the feature, it will override the functionality of the MPLS VPN--BGP Local Convergence feature. However, you need not remove the protection local-prefixes command from the configuration. 2
3 Information About Information About Overview Service providers use routing policies that cause a border router to choose a path received over an internal BGP (ibgp) session (of another border router) as the best path for a prefix even if it has an external BGP (ebgp) learned path. This practice is popularly known as active-backup topology and is done to define one exit or egress point for the prefix in the autonomous system and to use the other points as backups if the primary link or ebgp peering is unavailable. The policy, though beneficial, causes the border router to hide the paths learned over its ebgp sessions from the autonomous system because the border router does not advertise any path for such prefixes. To cope with this situation, some devices advertise one externally learned path called the best external path. The best external behavior causes the BGP selection process to select two paths to every destination: The best path is selected from the complete set of routes known to that destination. The best external path is selected from the set of routes received from its external peers. BGP advertises the best path to external peers. Instead of withdrawing the best path from its internal peers when it selects an ibgp path as the best path, BGP advertises the best external path to the internal peers. The feature is an essential component of the Prefix-Independent Convergence (PIC) edge for both Internet access and Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN scenarios and makes alternate paths available in the network in the active-backup topology. What the Best External Route Means The feature uses a best external route as a backup path, which, according to draft-marques-idr-best-external, is the most preferred route among those received from external neighbors. The most preferred route from external neighbors can be the following: Two routers in different clusters that have an Interior Border Gateway Protocol (ibgp) session between them. Two routers in different autonomous systems of a confederation that have an External Border Gateway Protocol (ebgp) session between them. The best external route might be different from the best route installed in the Routing Information Base (RIB). The best route could be an internal route. By allowing the best external route to be advertised and stored, in addition to the best route, networks gain faster restoration of connectivity by providing additional paths that may be used if the primary path fails. Feature Operation The feature is based on Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) draft-marques-idr-best-external.txt. The feature advertises a best external route to its internal peers as a backup route. The backup route is stored in the RIB and Cisco Express Forwarding. If the 3
4 Configuration Modes for Enabling primary path fails, the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Prefix-Independent Convergence (PIC) functionality enables the best external path to take over, enabling faster restoration of connectivity. Feature Operation shows a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN using the BGP Best External feature. The network includes the following components: Figure 1: MPLS VPN: Best External at the Edge of MPLS VPN Exterior BGP (ebgp) sessions exist between the provider edge (PE) and customer edge (CE) routers. PE 1 is the primary router and has a higher local preference setting. Traffic from CE 2 uses PE 1 to reach router CE 1. PE 1 has two paths to reach CE 1. CE 1 is dual-homed with PE 1 and PE 2. PE 1 is the primary path and PE 2 is the backup path. In Feature Operation, traffic in the MPLS cloud flows through PE 1 to reach CE 1. Therefore, PE 2 uses PE 1 as the best path and PE 2 as the backup path. PE 1 and PE 2 are configured with the feature. BGP computes both the best path (the PE 1-CE 1 link) and a backup path (PE 2) and installs both paths into the Routing Information Base (RIB) and Cisco Express Forwarding. The best external path (PE 2) is advertised to the peer routers, in addition to the best path. When Cisco Express Forwarding detects a link failure on the PE 1-CE 1 link, Cisco Express Forwarding immediately switches to the backup path PE 2. Traffic is quickly rerouted due to local fast convergence in Cisco Express Forwarding using the backup path. Thus, traffic loss is minimized and fast convergence is achieved. Configuration Modes for Enabling You can enable the feature in different modes, each of which protects Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) in its own way: 4
5 How to Configure If you issue the bgp advertise-best-external command in VPNv4 address family configuration mode, it applies to all IPv4 VRFs. If you issue the command in this mode, you need not issue it for specific VRFs. If you issue the bgp advertise-best-external command in IPv4 address family configuration mode, it applies only to that VRF. How to Configure Configuring the Feature Perform the following task to configure the feature. This task shows how to configure the feature in either an IPv4 or VPNv4 address family. In VPNv4 address family configuration mode, the feature applies to all IPv4 Virtural Routing Forwarding (VRF); you need not configure it for specific VRFs. If you issue the bgp advertise-best-external command in IPv4 VRF address family configuration mode, the feature applies only to that VRF. Before You Begin Configure the MPLS VPN and verify that it is working properly before configuring the BGP Best External feature. See the "Configuring MPLS Layer 3 VPNs" section for more information. Configure multiprotocol VRFs to allow you to share route-target policies (import and export) between IPv4 and IPv6 or configure separate route-target policies for IPv4 and IPv6 VPNs. For information about configuring multiprotocol VRFs, see the "MPLS VPN--VRF CLI for IPv4 and IPv6 VPNs section". Ensure that the customer edge (CE) router is connected to the network by at least two paths. SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. configure terminal 3. router bgp autonomous-system-number 4. Do one of the following: address-family ipv4 [unicast vrf vrf-name] or address-family vpnv4 [unicast] or 5. bgp advertise-best-external 6. neighbor ip-address remote-as autonomous-system-number 7. neighbor ip-address activate 8. neighbor ip-address fall-over [bfd route-map map-name] 9. end 5
6 Configuring the Feature DETAILED STEPS Step 1 Step 2 Command or Action enable Router> enable configure terminal Purpose Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Enters global configuration mode. Step 3 Router# configure terminal router bgp autonomous-system-number Enters router configuration mode for the specified routing process. Router(config)# router bgp Step 4 Do one of the following: address-family ipv4 [unicast vrf vrf-name] or address-family vpnv4 [unicast] or Specifies the IPv4 or VPNv4 address family and enters address family configuration mode. The unicast keyword specifies the IPv4 or VPNv4 unicast address family. The vrf keyword and vrf-name argument specify the name of the VRF instance to associate with subsequent IPv4 address family configuration mode commands. Router(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast Router(config-router)# address-family vpnv4 Step 5 bgp advertise-best-external Router(config-router-af)# bgp advertise-best-external Calculates and uses an external backup path and installs it into the RIB and Cisco Express Forwarding. 6
7 Verifying the Feature Step 6 Step 7 Command or Action neighbor ip-address remote-as autonomous-system-number Router(config-router-af)# neighbor remote-as neighbor ip-address activate Router(config-router-af)# neighbor activate Purpose Adds the IP address of the neighbor in the specified autonomous system to the IPv4 multiprotocol BGP neighbor table of the local router. By default, neighbors that are defined using the neighbor remote-as command in router configuration mode exchange only IPv4 unicast address prefixes. To exchange other address prefix types, neighbors must also be activated using the neighbor activate command in address family configuration mode for the other prefix types. Enables the neighbor to exchange prefixes for the IPv4 unicast address family with the local router. Step 8 neighbor ip-address fall-over [bfd route-map map-name] Router(config-router-af)# neighbor fall-over bfd Configures the BGP peering to use fast session deactivation and enables BFD protocol support for failover. BGP will remove all routes learned through this peer if the session is deactivated. Step 9 end Router(config-router-af)# end (Optional) Exits address family configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. Verifying the Feature Perform the following task to verify that the feature is configured correctly. 7
8 Verifying the Feature SUMMARY STEPS 1. enable 2. show vrf detail 3. show ip bgp ipv4 {mdt {all rd vrf} multicast tunnel unicast} or show ip bgp vpnv4{all rd route-distinguisher vrf vrf-name} [rib-failure] [ip-prefix/length [longer-prefixes]] [network-address [mask] [longer-prefixes]] [cidr-only] [community] [community-list] [dampened-paths] [filter-list] [flap-statistics] [inconsistent-as] [neighbors] [paths [line]] [peer-group] [quote-regexp] [regexp] [summary] [labels] 4. show bgp vpnv4 unicast vrf vrf-name ip-address 5. show ip route vrf vrf-name repair-paths ip-address 6. show ip cef vrf vrf-name ip-address detail DETAILED STEPS Step 1 enable Use this command to enable privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password, if prompted. For example: Router> enable Router# Step 2 show vrf detail Use this command to verify that the feature is enabled. The following show vrf detail command output shows that the feature is enabled. Router# show vrf detail VRF test1 (VRF Id = 1); default RD 400:1; default VPNID <not set> Interfaces: Se4/0 Address family ipv4 (Table ID = 1 (0x1)): Export VPN route-target communities RT:100:1 RT:200:1 RT:300:1 RT:400:1 Import VPN route-target communities RT:100:1 RT:200:1 RT:300:1 RT:400:1 No import route-map No export route-map VRF label distribution protocol: not configured VRF label allocation mode: per-prefix Prefix protection with additional path enabled Address family ipv6 not active. Step 3 show ip bgp ipv4 {mdt {all rd vrf} multicast tunnel unicast} 8
9 Verifying the Feature or show ip bgp vpnv4{all rd route-distinguisher vrf vrf-name} [rib-failure] [ip-prefix/length [longer-prefixes]] [network-address [mask] [longer-prefixes]] [cidr-only] [community] [community-list] [dampened-paths] [filter-list] [flap-statistics] [inconsistent-as] [neighbors] [paths [line]] [peer-group] [quote-regexp] [regexp] [summary] [labels] Use this command to verify that the best external route is advertised. In the command output, the code b indicates a backup path and the code x designates the best external path. Router# show ip bgp vpnv4 all BGP table version is , local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, multipath, b backup-path, x best-external Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path Route Distinguisher: 11:12 (default for vrf blue) *>i / ? * i ? * ? *bx ? * ? Step 4 show bgp vpnv4 unicast vrf vrf-name ip-address Use this command to verify that the best external route is advertised. Router# show bgp vpnv4 unicast vrf vpn BGP routing table entry for 10:10: /32, version 10 Paths: (2 available, best #1, table vpn1) Advertise-best-external Advertised to update-groups: (metric 21) from ( ) Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 200, valid, internal, best Extended Community: RT:1:1 mpls labels in/out 23/ from ( ) Origin incomplete, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, backup/repair, advertise-best-external Extended Community: RT:1:1, recursive-via-connected mpls labels in/out 23/nolabel Step 5 show ip route vrf vrf-name repair-paths ip-address Use this command to display the repair route. Router# show ip route vrf vpn1 repair-paths Routing Table: vpn1 Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 9
10 Configuration Examples for E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set /8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks B /24 [200/0] via , 00:38:33 [RPR][200/0] via , 00:38:33 B /32 [200/0] via , 00:38:33 [RPR][200/0] via , 00:38: /8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks C /24 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 L /32 is directly connected, Ethernet0/0 B /24 [200/0] via , 00:38:33 [RPR][200/0] via , 00:38:33 Step 6 show ip cef vrf vrf-name ip-address detail Use this command to display the best external route. Router# show ip cef vrf test detail /30, epoch 0, flags rib defined all labels recursive via label 35 nexthop Ethernet0/0 label 25 recursive via label 28, repair nexthop Ethernet0/0 label 24 Configuration Examples for Configuring the Feature The following example shows how to configure the feature in VPNv4 mode: vrf definition test1 rd 400:1 route-target export 100:1 route-target export 200:1 route-target export 300:1 route-target export 400:1 route-target import 100:1 route-target import 200:1 route-target import 300:1 route-target import 400:1 address-family ipv4 exit-address-family exit! interface Ethernet1/0 vrf forwarding test1 ip address exit! router bgp no synchronization 10
11 Additional References bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor remote-as neighbor update-source Loopback0 neighbor remote-as neighbor update-source Loopback0 no auto-summary! address-family vpnv4 bgp advertise-best-external neighbor activate neighbor send-community extended neighbor activate neighbor send-community extended exit-address-family! address-family ipv4 vrf test1 no synchronization bgp recursion host neighbor remote-as neighbor fall-over bfd neighbor activate neighbor as-override exit-address-family Additional References Related Documents Related Topic Cisco IOS commands BGP commands Basic MPLS VPNs Multiprotocol VRFs A failover feature that creates a new path after a link or node failure Document Title Cisco IOS Master Command List, All Releases Cisco IOS IP Routing: BGP Command Reference Configuring MPLS Layer 3 VPNs module in the MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs Configuration Guide MPLS VPN VRF CLI for IPv4 and IPv6 VPNs module in the MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs Configuration Guide MPLS VPN--BGP Local Convergence Standards Standard draft-marques-idr-best-external Title, Advertisement of the best external route to ibgp 11
12 Feature Information for MIBs MIB MIBs Link To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: RFCs RFC RFC 1771 RFC 2547 Title A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) BGP/MPLS VPNs Technical Assistance Description The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. Link Feature Information for The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature. Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to. An account on Cisco.com is not required. 12
13 Feature Information for Table 1: Feature Information for Feature Name Releases 12.2(33)SRE 15.2(3)T 15.2(4)S 15.1(1)SY Feature Information The feature provides the network with a backup external route to avoid loss of connectivity of the primary external route. This feature advertises the most preferred route among those received from external neighbors as a backup route. The following commands were introduced or modified: bgp advertise-best-external, bgp recursion host, show ip bgp, show ip bgp vpnv4, show ip cef, show ip cef vrf, show ip route, and show ip route vrf. 13
14 Feature Information for 14
BGP Event-Based VPN Import
 The feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced BGP path import is driven by events; when a BGP path changes, all of its imported copies
The feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced BGP path import is driven by events; when a BGP path changes, all of its imported copies
ibgp Multipath Load Sharing
 ibgp Multipath Load haring Feature History Release 12.2(2)T 12.2(14) Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into. This feature module describes the ibgp Multipath Load haring
ibgp Multipath Load haring Feature History Release 12.2(2)T 12.2(14) Modification This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into. This feature module describes the ibgp Multipath Load haring
MPLS VPN Multipath Support for Inter-AS VPNs
 The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
BGP mvpn BGP safi IPv4
 The BGP mvpn BGP safi 129 IPv4 feature provides the capability to support multicast routing in the service provider s core IPv4 network This feature is needed to support BGP-based MVPNs BGP MVPN provides
The BGP mvpn BGP safi 129 IPv4 feature provides the capability to support multicast routing in the service provider s core IPv4 network This feature is needed to support BGP-based MVPNs BGP MVPN provides
BGP Diverse Path Using a Diverse-Path Route Reflector
 BGP Diverse Path Using a Diverse-Path Route Reflector The feature allows Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to distribute an alternative path other than the best path between BGP speakers when route reflectors
BGP Diverse Path Using a Diverse-Path Route Reflector The feature allows Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to distribute an alternative path other than the best path between BGP speakers when route reflectors
BGP Event-Based VPN Import
 BGP Event-Based VPN Import Last Updated: April 13, 2012 The BGP Event-Based VPN Import feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced
BGP Event-Based VPN Import Last Updated: April 13, 2012 The BGP Event-Based VPN Import feature introduces a modification to the existing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) path import process. The enhanced
BGP-MVPN SAFI 129 IPv6
 Subsequent Address Family Identifier (SAFI) 129, known as VPN Multicast SAFI, provides the capability to support multicast routing in the service provider's core IPv6 network. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Subsequent Address Family Identifier (SAFI) 129, known as VPN Multicast SAFI, provides the capability to support multicast routing in the service provider's core IPv6 network. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Configuring IPv6 Provider Edge over MPLS (6PE)
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family
 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute L2VPN endpoint provisioning information. BGP uses a separate L2VPN
BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute L2VPN endpoint provisioning information. BGP uses a separate L2VPN
BGP Link Bandwidth. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for BGP Link Bandwidth
 The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
Configuring Easy Virtual Network Shared Services
 Configuring Easy Virtual Network Shared Services This chapter describes how to use route replication and redistribution to share services in an Easy Virtual Network (EVN). Finding Feature Information,
Configuring Easy Virtual Network Shared Services This chapter describes how to use route replication and redistribution to share services in an Easy Virtual Network (EVN). Finding Feature Information,
ibgp Multipath Load Sharing
 This feature module describes the feature. This feature enables the BGP speaking router to select multiple ibgp paths as the best paths to a destination. The best paths or multipaths are then installed
This feature module describes the feature. This feature enables the BGP speaking router to select multiple ibgp paths as the best paths to a destination. The best paths or multipaths are then installed
MPLS VPN Half-Duplex VRF
 The feature provides scalable hub-and-spoke connectivity for subscribers of an Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service. This feature addresses the limitations of hub-and-spoke
The feature provides scalable hub-and-spoke connectivity for subscribers of an Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service. This feature addresses the limitations of hub-and-spoke
BGP Cost Community. Prerequisites for the BGP Cost Community Feature
 The feature introduces the cost extended community attribute. The cost community is a non-transitive extended community attribute that is passed to internal BGP (ibgp) and confederation peers but not to
The feature introduces the cost extended community attribute. The cost community is a non-transitive extended community attribute that is passed to internal BGP (ibgp) and confederation peers but not to
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
BGP Link Bandwidth. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for BGP Link Bandwidth
 The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
Configuring Internal BGP Features
 This module describes how to configure internal Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) features. Internal BGP (ibgp) refers to running BGP on networking devices within one autonomous system. BGP is an interdomain
This module describes how to configure internal Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) features. Internal BGP (ibgp) refers to running BGP on networking devices within one autonomous system. BGP is an interdomain
MPLS VPN Inter-AS with ASBRs Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses
 MPLS VPN Inter-AS with ASBRs Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN Inter-AS with Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses feature allows
MPLS VPN Inter-AS with ASBRs Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses The Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN Inter-AS with Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) Exchanging VPN-IPv4 Addresses feature allows
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking Last Updated: November 26, 2012 The BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed.
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking Last Updated: November 26, 2012 The BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed.
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family
 BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family Last Updated: November 21, 2012 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute
BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family Last Updated: November 21, 2012 BGP support for the Layer 2 Virtual Private Network (L2VPN) address family introduces a BGP-based autodiscovery mechanism to distribute
BGP Support for 4-byte ASN
 The Cisco implementation of 4-byte autonomous system (AS) numbers uses asplain (65538, for example) as the default regular expression match and the output display format for AS numbers. However, you can
The Cisco implementation of 4-byte autonomous system (AS) numbers uses asplain (65538, for example) as the default regular expression match and the output display format for AS numbers. However, you can
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider
BGP Next Hop Unchanged
 BGP Next Hop Unchanged Last Updated: September 8, 2011 In an external BGP (ebgp) session, by default, the router changes the next hop attribute of a BGP route (to its own address) when the router sends
BGP Next Hop Unchanged Last Updated: September 8, 2011 In an external BGP (ebgp) session, by default, the router changes the next hop attribute of a BGP route (to its own address) when the router sends
Configuring Scalable Hub-and-Spoke MPLS VPNs
 Configuring Scalable Hub-and-Spoke MPLS VPNs Last Updated: December 15, 2011 This module explains how to ensure that virtual private network (VPN) clients that connect to the same provider edge (PE) router
Configuring Scalable Hub-and-Spoke MPLS VPNs Last Updated: December 15, 2011 This module explains how to ensure that virtual private network (VPN) clients that connect to the same provider edge (PE) router
Configuring BGP: RT Constrained Route Distribution
 Configuring BGP: RT Constrained Route Distribution BGP: RT Constrained Route Distribution is a feature that can be used by service providers in Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 VPNs to reduce
Configuring BGP: RT Constrained Route Distribution BGP: RT Constrained Route Distribution is a feature that can be used by service providers in Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 VPNs to reduce
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Last Updated: December 14, 2011 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Last Updated: December 14, 2011 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one
MPLS VPN Route Target Rewrite
 The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
The feature allows the replacement of route targets on incoming and outgoing Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates Typically, Autonomous System Border Routers (ASBRs) perform the replacement of route targets
BGP NSF Awareness. Finding Feature Information
 Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) awareness allows a device to assist NSF-capable neighbors to continue forwarding packets during a Stateful Switchover (SSO) operation. The feature allows an NSF-aware device that
Nonstop Forwarding (NSF) awareness allows a device to assist NSF-capable neighbors to continue forwarding packets during a Stateful Switchover (SSO) operation. The feature allows an NSF-aware device that
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
MPLS VPN Inter-AS IPv4 BGP Label Distribution
 MPLS VPN Inter-AS IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature enables you to set up a Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider network so that the autonomous system boundary routers (ASBRs) exchange
MPLS VPN Inter-AS IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature enables you to set up a Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider network so that the autonomous system boundary routers (ASBRs) exchange
MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP. BGP IPv4 Label Session
 MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session The MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session feature provides a method to advertise explicit null in a Border Gateway
MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session The MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session feature provides a method to advertise explicit null in a Border Gateway
Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support
 Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support Last Updated: December 23, 2011 The Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support feature enables Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs) used for Multicast VPNs (MVPNs) to span
Configuring Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support Last Updated: December 23, 2011 The Multicast VPN Inter-AS Support feature enables Multicast Distribution Trees (MDTs) used for Multicast VPNs (MVPNs) to span
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
LAB1: BGP IPv4. BGP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
 IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 22, 2013 Last Modified: January 22, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 22, 2013 Last Modified: January 22, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
Information About IPv6 Multicast Address Family Support for. Multiprotocol BGP. Finding Feature Information
 IPv6 Multicast Address Family Support for Multiprotocol BGP Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About IPv6 Multicast Address Family Support for Multiprotocol BGP, page 1 How to Implement IPv6
IPv6 Multicast Address Family Support for Multiprotocol BGP Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About IPv6 Multicast Address Family Support for Multiprotocol BGP, page 1 How to Implement IPv6
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks
 Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature enables you to configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature enables you to configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers
 OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
MPLS over GRE. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for MPLS VPN L3VPN over GRE
 The feature provides a mechanism for tunneling Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets over a non-mpls network. This feature utilizes MPLS over generic routing encapsulation (MPLSoGRE) to encapsulate
The feature provides a mechanism for tunneling Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) packets over a non-mpls network. This feature utilizes MPLS over generic routing encapsulation (MPLSoGRE) to encapsulate
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature lets you configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes and Multiprotocol
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature lets you configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes and Multiprotocol
EIGRP Support for Route Map Filtering
 The feature enables Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) to interoperate with other protocols to leverage additional routing functionality by filtering inbound and outbound traffic based
The feature enables Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) to interoperate with other protocols to leverage additional routing functionality by filtering inbound and outbound traffic based
Multi-VRF Support. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for Multi-VRF Support
 The feature allows you to configure and maintain more than one instance of a routing and forwarding table within the same customer edge (CE) device. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for,
The feature allows you to configure and maintain more than one instance of a routing and forwarding table within the same customer edge (CE) device. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for,
MPLS VPN over mgre. Finding Feature Information. Last Updated: November 1, 2012
 MPLS VPN over mgre Last Updated: November 1, 2012 The MPLS VPN over mgre feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity
MPLS VPN over mgre Last Updated: November 1, 2012 The MPLS VPN over mgre feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity
Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
Configuring a BGP Route Server
 BGP route server is a feature designed for internet exchange (IX) operators that provides an alternative to full ebgp mesh peering among the service providers who have a presence at the IX. The route server
BGP route server is a feature designed for internet exchange (IX) operators that provides an alternative to full ebgp mesh peering among the service providers who have a presence at the IX. The route server
BGP FlowSpec Route-reflector Support
 The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Flowspec (Flow Specification) Route Reflector feature enables service providers to control traffic flows in their network. This helps in filtering traffic and helps in
The BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Flowspec (Flow Specification) Route Reflector feature enables service providers to control traffic flows in their network. This helps in filtering traffic and helps in
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands
 Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
Multiprotocol BGP Extensions for IP Multicast Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor multiprotocol BGP. Multiprotocol BGP is based on RFC 2283, Multiprotocol Extensions for
IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature
 IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature Document ID: 117567 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Apr 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Background Information Implement ibgp PE CE BGP Customer
IOS Implementation of the ibgp PE CE Feature Document ID: 117567 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Apr 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Background Information Implement ibgp PE CE BGP Customer
MPLS Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
 MPLS Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) The IP Virtual Private Network (VPN) feature for Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) allows a Cisco IOS network to deploy scalable IPv4 Layer 3 VPN backbone services.
MPLS Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) The IP Virtual Private Network (VPN) feature for Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) allows a Cisco IOS network to deploy scalable IPv4 Layer 3 VPN backbone services.
Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks
 Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks Document ID: 47807 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Route Leaking from a Global Routing Table into a VRF and Route
Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks Document ID: 47807 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Route Leaking from a Global Routing Table into a VRF and Route
MPLS VPN C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T. BGP Advertising IPv4 Prefixes with a Label
 7 C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T This online supplement of Chapter 7 focuses on two important developments. The first one is Inter-Autonomous. Inter-Autonomous is a concept whereby two service provider
7 C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T This online supplement of Chapter 7 focuses on two important developments. The first one is Inter-Autonomous. Inter-Autonomous is a concept whereby two service provider
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
BGP-VPN Distinguisher Attribute
 The BGP VPN Distinguisher Attribute feature allows a network administrator to keep source route targets (RTs) private from an Autonomous System Border Router (ASBR) in a destination autonomous system.
The BGP VPN Distinguisher Attribute feature allows a network administrator to keep source route targets (RTs) private from an Autonomous System Border Router (ASBR) in a destination autonomous system.
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions.
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configuration DN Bit Verify Troubleshoot Related Cisco Support Community Discussions Introduction
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Configure Network Diagram Configuration DN Bit Verify Troubleshoot Related Cisco Support Community Discussions Introduction
BGP Additional Paths. Finding Feature Information. Information About BGP Additional Paths. Problem That Additional Paths Can Solve
 The feature allows the advertisement of multiple paths through the same peering session for the same prefix without the new paths implicitly replacing any previous paths. This behavior promotes path diversity
The feature allows the advertisement of multiple paths through the same peering session for the same prefix without the new paths implicitly replacing any previous paths. This behavior promotes path diversity
Protecting an EBGP peer when memory usage reaches level 2 threshold 66 Configuring a large-scale BGP network 67 Configuring BGP community 67
 Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Cisco BGP Overview. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for Cisco BGP
 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an interdomain routing protocol designed to provide loop-free routing between separate routing domains that contain independent routing policies (autonomous systems). The
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an interdomain routing protocol designed to provide loop-free routing between separate routing domains that contain independent routing policies (autonomous systems). The
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
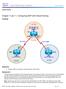 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Implementing Static Routes
 This module describes how to implement static routes. Static routes are user-defined routes that cause packets moving between a source and a destination to take a specified path. Static routes can be important
This module describes how to implement static routes. Static routes are user-defined routes that cause packets moving between a source and a destination to take a specified path. Static routes can be important
MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs: Inter-AS and CSC Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15SY
 MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs: Inter-AS and CSC Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15SY First Published: October 15, 2012 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
MPLS: Layer 3 VPNs: Inter-AS and CSC Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15SY First Published: October 15, 2012 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706
InterAS Option B. Information About InterAS. InterAS and ASBR
 This chapter explains the different InterAS option B configuration options. The available options are InterAS option B, InterAS option B (with RFC 3107), and InterAS option B lite. The InterAS option B
This chapter explains the different InterAS option B configuration options. The available options are InterAS option B, InterAS option B (with RFC 3107), and InterAS option B lite. The InterAS option B
Add Path Support in EIGRP
 The feature enables hubs in a single Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) domain to advertise multiple best paths to connected spokes when the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is the routing
The feature enables hubs in a single Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) domain to advertise multiple best paths to connected spokes when the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is the routing
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
 Feature History Release Modification 12.2(8)T This feature was introduced. This module describes how to configure and use a sham-link to connect Virtual Private Network (VPN) client sites that run the
Feature History Release Modification 12.2(8)T This feature was introduced. This module describes how to configure and use a sham-link to connect Virtual Private Network (VPN) client sites that run the
BGP Commands: M through N
 match additional-paths advertise-set, on page 3 match as-path, on page 6 match community, on page 8 match extcommunity, on page 10 match local-preference, on page 12 match policy-list, on page 14 match
match additional-paths advertise-set, on page 3 match as-path, on page 6 match community, on page 8 match extcommunity, on page 10 match local-preference, on page 12 match policy-list, on page 14 match
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Feature History Release 12.0(14)ST 12.0(16)ST 12.2(8)T 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S 12.0(23)S Modification This feature was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(14)ST. Support
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Feature History Release 12.0(14)ST 12.0(16)ST 12.2(8)T 12.0(21)ST 12.0(22)S 12.0(23)S Modification This feature was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(14)ST. Support
Implementing MPLS Layer 3 VPNs
 A Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (VPN) consists of a set of sites that are interconnected by means of an MPLS provider core network. At each customer site, one or
A Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (VPN) consists of a set of sites that are interconnected by means of an MPLS provider core network. At each customer site, one or
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
 The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (L3VPN) services, over an IP core network, using L2TPv3 multipoint tunneling instead of MPLS. This allows L2TPv3 tunnels
The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (L3VPN) services, over an IP core network, using L2TPv3 multipoint tunneling instead of MPLS. This allows L2TPv3 tunnels
Cisco BGP Overview. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for Cisco BGP. Last Updated: October 19, 2011
 Cisco BGP Overview Last Updated: October 19, 2011 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an interdomain routing protocol designed to provide loop-free routing between separate routing domains that contain independent
Cisco BGP Overview Last Updated: October 19, 2011 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an interdomain routing protocol designed to provide loop-free routing between separate routing domains that contain independent
Configuration prerequisites 45 Configuring BGP community 45 Configuring a BGP route reflector 46 Configuring a BGP confederation 46 Configuring BGP
 Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents. BGP commands 1
 Contents BGP commands 1 address-family ipv4 1 address-family ipv6 2 address-family link-state 3 advertise-rib-active 4 aggregate 5 balance 7 balance as-path-neglect 9 bestroute as-path-neglect 10 bestroute
Contents BGP commands 1 address-family ipv4 1 address-family ipv6 2 address-family link-state 3 advertise-rib-active 4 aggregate 5 balance 7 balance as-path-neglect 9 bestroute as-path-neglect 10 bestroute
BGP Support for IP Prefix Export from a VRF Table into the Global Table
 BGP Support for IP Prefix Export from a VRF Table into the Global Table This feature allows a network administrator to export IP prefixes from a VRF table into the global routing table. Finding Feature
BGP Support for IP Prefix Export from a VRF Table into the Global Table This feature allows a network administrator to export IP prefixes from a VRF table into the global routing table. Finding Feature
Configuring IPv6 VPN Provider Edge over MPLS (6VPE)
 Configuring IPv6 VPN Provider Edge over MPLS (6VPE) Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6VPE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented
Configuring IPv6 VPN Provider Edge over MPLS (6VPE) Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6VPE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented
MPLS VPN: VRF Selection Based on Source IP Address
 MPLS VPN: VRF Selection Based on Source IP Address The VPN Routing and Forwarding (VRF) Selection feature allows a specified interface on a provider edge (PE) router to route packets to different Virtual
MPLS VPN: VRF Selection Based on Source IP Address The VPN Routing and Forwarding (VRF) Selection feature allows a specified interface on a provider edge (PE) router to route packets to different Virtual
Configuring BGP community 43 Configuring a BGP route reflector 44 Configuring a BGP confederation 44 Configuring BGP GR 45 Enabling Guard route
 Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
Contents Configuring BGP 1 Overview 1 BGP speaker and BGP peer 1 BGP message types 1 BGP path attributes 2 BGP route selection 6 BGP route advertisement rules 6 BGP load balancing 6 Settlements for problems
BGP Persistence. Restrictions for BGP Persistence. Information About BGP Persistence
 BGP persistence enables the router to retain routes that it has learnt from the configured neighbor even when the neighbor session is down. BGP persistence is also referred as long lived graceful restart
BGP persistence enables the router to retain routes that it has learnt from the configured neighbor even when the neighbor session is down. BGP persistence is also referred as long lived graceful restart
MPLS VPN--Show Running VRF
 MPLS VPN--Show Running VRF Last Updated: December 15, 2011 The MPLS VPN--Show Running VRF feature provides a Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) option to display a subset of the running configuration
MPLS VPN--Show Running VRF Last Updated: December 15, 2011 The MPLS VPN--Show Running VRF feature provides a Cisco IOS command-line interface (CLI) option to display a subset of the running configuration
Implementing Static Routes on Cisco IOS XR Software
 Implementing Static Routes on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes how to implement static routes. Static routes are user-defined routes that cause packets moving between a source and a destination
Implementing Static Routes on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes how to implement static routes. Static routes are user-defined routes that cause packets moving between a source and a destination
Contents. Introduction. Prerequisites. Configure. Requirements. Components Used
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations CE1 CE2 PE1 PE2 Verify Case 1: Accepting and exchanging customer routes over MP-BGP Case 2: Leaking
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations CE1 CE2 PE1 PE2 Verify Case 1: Accepting and exchanging customer routes over MP-BGP Case 2: Leaking
BGP Dynamic Neighbors
 BGP dynamic neighbor support allows BGP peering to a group of remote neighbors that are defined by a range of IP addresses. Each range can be configured as a subnet IP address. BGP dynamic neighbors are
BGP dynamic neighbor support allows BGP peering to a group of remote neighbors that are defined by a range of IP addresses. Each range can be configured as a subnet IP address. BGP dynamic neighbors are
Layer3 VPN with RIP protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with IP protocol between E-PE Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to
MPLS Layer3 VPN with IP protocol between E-PE Disclaimer This onfiguration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to
EIGRP Route Tag Enhancements
 The feature enables you to specify and display route tags in dotted-decimal format, filter routes using the route tag value with wildcard mask, and set a default route tag for all internal Enhanced Interior
The feature enables you to specify and display route tags in dotted-decimal format, filter routes using the route tag value with wildcard mask, and set a default route tag for all internal Enhanced Interior
Configuring Multicast VPN Extranet Support
 Configuring Multicast VPN Extranet Support First Published: December 4, 2006 Last Updated: June 10, 2011 The Multicast VPN Extranet Support feature (sometimes referred to as the MVPN Extranet Support feature)
Configuring Multicast VPN Extranet Support First Published: December 4, 2006 Last Updated: June 10, 2011 The Multicast VPN Extranet Support feature (sometimes referred to as the MVPN Extranet Support feature)
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 9400 Switches)
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 9400 Switches) First Published: 2017-09-07 Last Modified: 2017-10-30 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems,
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 9400 Switches) First Published: 2017-09-07 Last Modified: 2017-10-30 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems,
Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute
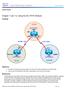 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
scope scope {global vrf vrf-name} no scope {global vrf vrf-name} Syntax Description
 Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
BGP AS-Override Split-Horizon
 The feature enables a Provider Edge (PE) device using split-horizon to avoid advertisement of routes propagated by a Customer Edge (CE) device to the same CE device. The BGP AS-Override Split-Horizon feature
The feature enables a Provider Edge (PE) device using split-horizon to avoid advertisement of routes propagated by a Customer Edge (CE) device to the same CE device. The BGP AS-Override Split-Horizon feature
OSPFv2 Local RIB. Finding Feature Information
 With the feature, each OSPF protocol instance has its own local Routing Information Base (RIB). The OSPF local RIB serves as the primary state for OSPF SPF route computation. The global RIB is not updated
With the feature, each OSPF protocol instance has its own local Routing Information Base (RIB). The OSPF local RIB serves as the primary state for OSPF SPF route computation. The global RIB is not updated
BGP Command Reference for Cisco NCS 5500 Series and Cisco NCS 540 Series Routers
 BGP Command Reference for Cisco NCS 5500 Series and Cisco NCS 540 Series Routers First Published: 2015-12-23 Last Modified: 2018-03-30 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San
BGP Command Reference for Cisco NCS 5500 Series and Cisco NCS 540 Series Routers First Published: 2015-12-23 Last Modified: 2018-03-30 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San
BGP Graceful Shutdown
 The feature reduces or eliminates the loss of traffic along a link being shut down for maintenance. Routers always have a valid route available during the convergence process. This feature is used primarily
The feature reduces or eliminates the loss of traffic along a link being shut down for maintenance. Routers always have a valid route available during the convergence process. This feature is used primarily
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
 26 CHAPTER Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide a secure way for customers to share bandwidth over an ISP backbone network. A VPN is a collection of sites sharing a common routing table. A customer
26 CHAPTER Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide a secure way for customers to share bandwidth over an ISP backbone network. A VPN is a collection of sites sharing a common routing table. A customer
Implementing BGP on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 Implementing BGP on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) that allows you to create loop-free interdomain routing between autonomous systems.
Implementing BGP on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) that allows you to create loop-free interdomain routing between autonomous systems.
BGP Route Reflector Commands
 This chapter provides details of the commands used for configuring Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Route Reflector (RR). address-family (BGP), on page 2 keychain, on page 5 neighbor (BGP), on page 7 remote-as
This chapter provides details of the commands used for configuring Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Route Reflector (RR). address-family (BGP), on page 2 keychain, on page 5 neighbor (BGP), on page 7 remote-as
