Distributed Computing over Communication Networks: Leader Election
|
|
|
- Samson Simmons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Distributed Computing over Communication Networks: Leader Election
2 Motivation Reasons for electing a leader? Reasons for not electing a leader?
3 Motivation Reasons for electing a leader? Once elected, coordination tasks may become simpler For example: wireless medium access (break symmetry) Reasons for not electing a leader? Reduced parallelism? Self-stabilization needed: re-election when leader dies Leader bottleneck / single point of failure?
4 How to elect a leader in a ring?
5 Model Synchronous Local Algorithm : Round Send receive compute.
6 Anonymous Ring Anonymous System Anonymous nodes do not have identifiers. Theorem In an anonymous ring, leader election is impossible! Why?
7 Impossibility in Synchronous Ring Theorem In an anonymous ring, leader election is impossible! First, note the following lemma: Lemma After round k of any deterministic algorithm on an anonymous ring, each node is in the same state s k. Proof idea?! By induction: all nodes start in same state, and each round consists of sending, receiving and performing local computations. All nodes send the same messages, receive the same messages, and do the same computations. So they always stay in same state... QED So when a node decides to become a leader, then all others do too.
8 Discussion What is the basic problem? Symmetry... How could it be broken? - How to elect a leader in a star? - Randomization? - What if nodes have IDs?
9 Asynchronous Ring Let s assume: Uniform System Nodes do not know n. - non-anonymous nodes with unique IDs - asynchronous ring - uniform ring: n unknown! - no message losses etc. How to elect a leader now?
10 Asynchronous Ring Let s assume: - non-anonymous nodes with unique IDs - asynchronous ring How to evaluate? Criteria? Asynchronous time?! Algorithm Clockwise each node v does the following: v sends a message with its ID v to clockwise neighbor (unless v already received a message with ID w>v) if v receives message w with w>v then v forwards w to clockwise neighbor v decides not to be the leader else if v receives its own ID v then v decides to be the leader
11 Evaluation Time Complexity Number of rounds (for asynchronous, assume max delay of one unit). Message Complexity Number of messages sent. Local Complexity Local computations... For our algorithm?!
12 Clockwise Algorithm Theorem Algo is correct, time complexity O(n), message complexity O(n 2 ). Proof idea? Correctness: Let z be max ID. No other node can swallow z s ID, so z will get the message back. So z becomes leader. Every other node declares non-leader when forwarding z (the latest!). Message complexity: Each node forwards at most n messages (n IDs in total). Time complexity: Message circles around cycle (depending on model, at most twice: once to wake up z, and then until z becomes leader). QED Can we do better?! Time? Messages?...
13 Radius Growth Algorithm Radius Growth each node v does the following: Initially, all nodes are active (can still become leader) Whenever a node v sees a message with w>v, it decides not to be a leader and becomes passive Active nodes search in an exponentially growing neighborhood (clockwise and counterclockwise) for nodes with higher IDs by sending out probe messages: a probe includes sender s ID, a leader bit saying whether original sender can still become a leader, and TTL (initially =1). All nodes w receiving a probe decrement TTL and foward to next neighbor; if w s ID is larger than original sender s ID, the leader bit is set to zero. If TTL=0, return message to sender (reply msg) including leader bit. If leader bit is still 1, double the TTL, and two new probes are sent (for both neighbors); otherwise node becomes passive. If v receives its own probe message (not the reply): it becomes leader.
14 Radius Growth Am I leader here?
15 Radius Growth Am I leader here?
16 Radius Growth Am I leader here? How to analyze? Complexities?
17 Radius Growth Theorem Algo is correct, time complexity O(n), message complexity O(n log n). Proof idea? Correctness: Like clockwise algo. Time complexity: O(n) since node with max identifier sends messages with round trip times 2, 4, 8,..., 2 k with k O(log n). The sum constitutes a geometric series and is hence linear in n. Message complexity: Only one node can survive phase p that covers a distance of 2 p. So less than n/2 p nodes are active in round p+1. Being active in round p costs roughly 2 p messages, so it s around O(n) per round over all active nodes. As we have a logarithmic number of phases, the claim follows. QED
18 Can we do better?!
19 Or how can we prove that we cannot? Lower bounds!
20 Lower Bound (1) Take-Away In message passing systems, lower bounds can often be proved by arguing about messages that need to be exchanged! Concepts: 1. Generally, we need some definitions to characterize the class of algorithms for which the lower bound holds. 2. Moreover, in distributed systems, a (hypothetical) scheduler determines sequence of events... Execution An execution of a distributed algorithm is a list of events, sorted by time. An event is a record (time, node, type, message) where type is send or receive.
21 Lower Bound (2) Assumptions: - Asynchronous ring: nodes wake up at arbitrary times but always when receiving a packet - nodes have IDs, and node with max ID should become leader - every node must know ID of leader - uniform algorithm: n is not known - arbitrary scheduler but links are FIFO For our lower bound proof, we define the concept of open schedules: Open Schedule Schedule chosen by scheduler. Open if there is an open edge in the ring. Edge is open if no message traversing edge has been received so far.
22 Lower Bound by Induction Proof by induction: 2-node Ring Given a ring R with two nodes, we can construct an open schedule in which at least one message is received. The nodes cannot distinguish this schedule from one on a larger ring with all other nodes being where the open edge is. Proof of Lemma: u and v cannot distinguish between the two scenarios! open edge: no messages received v vs u Open schedule? v u
23 Proof of Lemma: Open Schedule 2-node Ring Given a ring R with two nodes, we can construct an open schedule in which at least one message is received. The nodes cannot distinguish this schedule from one on a larger ring with all other nodes being where the open edge is. Open schedule for 2-node ring? In any leader election algorithm, the two nodes must learn about each other! We stop execution when first message is received (on whatever link). We can do this because it s an asynchronous world (no simultaneous arrivals)... open edge So other edge is open: Nodes don t know, is it an edge, or is it more? v u QED
24 Open Schedules for Larger Rings? n-node Lemma Ring 2 By gluing together two rings of size n/2 for which we have open schedules, an open schedule can be constructed on a ring of size n. Let M(n/2) denote the number of messages used in each of these schedules by some algorithm ALG. Then, in the entire ring 2M(n/2)+n/4 messages have to be exchanged to solve leader election. Proof? Open schedule? u v
25 Assume ALG needs M(n/2) messages here how many for the whole ring? Open schedule for larger ring? Idea: take two times smaller ring and close one edge...
26 Proof of Lemma: By Induction - Consider the ring of size n and divide it in two subrings R1 and R2. As long as no message comes from outside, nodes cannot distinguish these two rings from two rings of size n/2. (Just delay messages accordingly: all other messages of algorithm are sent.) - So nodes exchange 2*M(n/2) messages (induction hypothesis) in the subrings before learning anything about the other subring. Wlog assume R1 has max ID. So each node in R2 must learn that ID, which requires at least n/2 message receptions. - So there must be an edge connecting the two rings that produces (= triggers, but not necessarily transmits!) at least n/4 messages. Schedule/close this edge and leave other open... => open schedule for larger ring! And enough messages! M(n/2) M(n/2) R1 R2
27 Open Schedules for Larger Rings? Theorem Any algo needs at least Ω(n log n) messages. Proof by induction: Claim follows from maths... So we are optimal. Can we do better?
28 Breaking the Lower Bound Take-Away In synchronous systems, not receiving a message is also information! Idea for message complexity n? E.g., find minimum ID in environment where nodes have unique but arbitrary integer IDs (but n known)... Sync Leader Election each node v does the following: - Divide time into phases of n steps (leaves time for lower-id nodes to broadcast...) - If phase = v and did not get a message: - v becomes leader - v sends I am leader! to everybody! Breaks message lower bound but we may wait long! Runtime O(n*minID)? What is the time message tradeoff?
29 Literature for further reading: - Attiya/Welch (Alg. 3.1 for example) - Peleg s book (as always ) End of lecture
DD2451 Parallel and Distributed Computing --- FDD3008 Distributed Algorithms
 DD2451 Parallel and Distributed Computing --- FDD3008 Distributed Algorithms Lecture 8 Leader Election Mads Dam Autumn/Winter 2011 Previously... Consensus for message passing concurrency Crash failures,
DD2451 Parallel and Distributed Computing --- FDD3008 Distributed Algorithms Lecture 8 Leader Election Mads Dam Autumn/Winter 2011 Previously... Consensus for message passing concurrency Crash failures,
Distributed Computing
 Principles of Distributed Computing Roger Wattenhofer wattenhofer@tik.ee.ethz.ch Assistant: Christoph Lenzen (lenzen@tik.ee.ethz.ch) Spring 2010 2 Introduction What is Distributed Computing? In the last
Principles of Distributed Computing Roger Wattenhofer wattenhofer@tik.ee.ethz.ch Assistant: Christoph Lenzen (lenzen@tik.ee.ethz.ch) Spring 2010 2 Introduction What is Distributed Computing? In the last
Distributed Systems Leader election & Failure detection
 Distributed Systems Leader election & Failure detection He Sun School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Leader of a computation Many distributed computations need a coordinator of server processors
Distributed Systems Leader election & Failure detection He Sun School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Leader of a computation Many distributed computations need a coordinator of server processors
GIAN Course on Distributed Network Algorithms. Spanning Tree Constructions
 GIAN Course on Distributed Network Algorithms Spanning Tree Constructions Stefan Schmid @ T-Labs, 2011 Spanning Trees Attactive infrastructure : sparse subgraph ( loop-free backbone ) connecting all nodes.
GIAN Course on Distributed Network Algorithms Spanning Tree Constructions Stefan Schmid @ T-Labs, 2011 Spanning Trees Attactive infrastructure : sparse subgraph ( loop-free backbone ) connecting all nodes.
Throughout this course, we use the terms vertex and node interchangeably.
 Chapter Vertex Coloring. Introduction Vertex coloring is an infamous graph theory problem. It is also a useful toy example to see the style of this course already in the first lecture. Vertex coloring
Chapter Vertex Coloring. Introduction Vertex coloring is an infamous graph theory problem. It is also a useful toy example to see the style of this course already in the first lecture. Vertex coloring
Leader Election in Rings
 Leader Election Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 2003 Leader Election in Rings Under different models: Synchronous vs. asynchronous Anonymous vs. non-anonymous (knowledge of unique id) Knowledge of n (non-uniform)
Leader Election Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 2003 Leader Election in Rings Under different models: Synchronous vs. asynchronous Anonymous vs. non-anonymous (knowledge of unique id) Knowledge of n (non-uniform)
GIAN Course on Distributed Network Algorithms. Spanning Tree Constructions
 GIAN Course on Distributed Network Algorithms Spanning Tree Constructions Stefan Schmid @ T-Labs, 2011 Spanning Trees Attactive infrastructure : sparse subgraph ( loop-free backbone ) connecting all nodes.
GIAN Course on Distributed Network Algorithms Spanning Tree Constructions Stefan Schmid @ T-Labs, 2011 Spanning Trees Attactive infrastructure : sparse subgraph ( loop-free backbone ) connecting all nodes.
CSc Leader Election
 CSc72010 Leader Election Reading Skim 3.5 Read 3.6, General synchronous networks Read 4.1 Leader election algorithms Lelann/Chang/Roberts: O(n) time complexity O(n 2 ) message complexity Hirschberg/Sinclair
CSc72010 Leader Election Reading Skim 3.5 Read 3.6, General synchronous networks Read 4.1 Leader election algorithms Lelann/Chang/Roberts: O(n) time complexity O(n 2 ) message complexity Hirschberg/Sinclair
Algorithms for COOPERATIVE DS: Leader Election in the MPS model
 Algorithms for COOPERATIVE DS: Leader Election in the MPS model 1 Leader Election (LE) problem In a DS, it is often needed to designate a single processor (i.e., a leader) as the coordinator of some forthcoming
Algorithms for COOPERATIVE DS: Leader Election in the MPS model 1 Leader Election (LE) problem In a DS, it is often needed to designate a single processor (i.e., a leader) as the coordinator of some forthcoming
Distributed Algorithms 6.046J, Spring, Nancy Lynch
 Distributed Algorithms 6.046J, Spring, 205 Nancy Lynch What are Distributed Algorithms? Algorithms that run on networked processors, or on multiprocessors that share memory. They solve many kinds of problems:
Distributed Algorithms 6.046J, Spring, 205 Nancy Lynch What are Distributed Algorithms? Algorithms that run on networked processors, or on multiprocessors that share memory. They solve many kinds of problems:
Distributed minimum spanning tree problem
 Distributed minimum spanning tree problem Juho-Kustaa Kangas 24th November 2012 Abstract Given a connected weighted undirected graph, the minimum spanning tree problem asks for a spanning subtree with
Distributed minimum spanning tree problem Juho-Kustaa Kangas 24th November 2012 Abstract Given a connected weighted undirected graph, the minimum spanning tree problem asks for a spanning subtree with
21. Distributed Algorithms
 21. Distributed Algorithms We dene a distributed system as a collection of individual computing devices that can communicate with each other [2]. This denition is very broad, it includes anything, from
21. Distributed Algorithms We dene a distributed system as a collection of individual computing devices that can communicate with each other [2]. This denition is very broad, it includes anything, from
All-to-All Communication
 Network Algorithms All-to-All Communication Thanks to Thomas Locher from ABB Research for basis of slides! Stefan Schmid @ T-Labs, 2011 Repetition Tree: connected graph without cycles Spanning subgraph:
Network Algorithms All-to-All Communication Thanks to Thomas Locher from ABB Research for basis of slides! Stefan Schmid @ T-Labs, 2011 Repetition Tree: connected graph without cycles Spanning subgraph:
MAC Theory. Chapter 7. Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks Roger Wattenhofer
 MAC Theory Chapter 7 7/1 Seeing Through Walls! [Wilson, Patwari, U. Utah] Schoolboy s dream, now reality thank to sensor networks... 7/2 Rating Area maturity First steps Text book Practical importance
MAC Theory Chapter 7 7/1 Seeing Through Walls! [Wilson, Patwari, U. Utah] Schoolboy s dream, now reality thank to sensor networks... 7/2 Rating Area maturity First steps Text book Practical importance
Verteilte Systeme/Distributed Systems Ch. 5: Various distributed algorithms
 Verteilte Systeme/Distributed Systems Ch. 5: Various distributed algorithms Holger Karl Computer Networks Group Universität Paderborn Goal of this chapter Apart from issues in distributed time and resulting
Verteilte Systeme/Distributed Systems Ch. 5: Various distributed algorithms Holger Karl Computer Networks Group Universität Paderborn Goal of this chapter Apart from issues in distributed time and resulting
Maximal Independent Set
 Chapter 4 Maximal Independent Set In this chapter we present a first highlight of this course, a fast maximal independent set (MIS) algorithm. The algorithm is the first randomized algorithm that we study
Chapter 4 Maximal Independent Set In this chapter we present a first highlight of this course, a fast maximal independent set (MIS) algorithm. The algorithm is the first randomized algorithm that we study
Maximal Independent Set
 Chapter 0 Maximal Independent Set In this chapter we present a highlight of this course, a fast maximal independent set (MIS) algorithm. The algorithm is the first randomized algorithm that we study in
Chapter 0 Maximal Independent Set In this chapter we present a highlight of this course, a fast maximal independent set (MIS) algorithm. The algorithm is the first randomized algorithm that we study in
6.852: Distributed Algorithms Fall, Instructor: Nancy Lynch TAs: Cameron Musco, Katerina Sotiraki Course Secretary: Joanne Hanley
 6.852: Distributed Algorithms Fall, 2015 Instructor: Nancy Lynch TAs: Cameron Musco, Katerina Sotiraki Course Secretary: Joanne Hanley What are Distributed Algorithms? Algorithms that run on networked
6.852: Distributed Algorithms Fall, 2015 Instructor: Nancy Lynch TAs: Cameron Musco, Katerina Sotiraki Course Secretary: Joanne Hanley What are Distributed Algorithms? Algorithms that run on networked
The Power of Locality
 GIAN Course on Distributed Network Algorithms The Power of Locality Case Study: Graph Coloring Stefan Schmid @ T-Labs, 2011 Case Study: Graph Coloring Case Study: Graph Coloring Assign colors to nodes.
GIAN Course on Distributed Network Algorithms The Power of Locality Case Study: Graph Coloring Stefan Schmid @ T-Labs, 2011 Case Study: Graph Coloring Case Study: Graph Coloring Assign colors to nodes.
Broadcast: Befo re 1
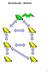 Broadcast: Before 1 After 2 Spanning Tree ffl assume fixed spanning tree ffl asynchronous model 3 Processor State parent terminated children 4 Broadcast: Step One parent terminated children 5 Broadcast:Step
Broadcast: Before 1 After 2 Spanning Tree ffl assume fixed spanning tree ffl asynchronous model 3 Processor State parent terminated children 4 Broadcast: Step One parent terminated children 5 Broadcast:Step
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014
 Suggested Reading: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014 Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning: The Junction
Suggested Reading: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014 Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning: The Junction
A synchronizer generates sequences of clock pulses at each node of the network satisfying the condition given by the following definition.
 Chapter 8 Synchronizers So far, we have mainly studied synchronous algorithms because generally, asynchronous algorithms are often more di cult to obtain and it is substantially harder to reason about
Chapter 8 Synchronizers So far, we have mainly studied synchronous algorithms because generally, asynchronous algorithms are often more di cult to obtain and it is substantially harder to reason about
Distributed Algorithms 6.046J, Spring, 2015 Part 2. Nancy Lynch
 Distributed Algorithms 6.046J, Spring, 2015 Part 2 Nancy Lynch 1 This Week Synchronous distributed algorithms: Leader Election Maximal Independent Set Breadth-First Spanning Trees Shortest Paths Trees
Distributed Algorithms 6.046J, Spring, 2015 Part 2 Nancy Lynch 1 This Week Synchronous distributed algorithms: Leader Election Maximal Independent Set Breadth-First Spanning Trees Shortest Paths Trees
Relationships Between Broadcast and Shared Memory in Reliable Anonymous Distributed Systems
 Relationships Between Broadcast and Shared Memory in Reliable Anonymous Distributed Systems James Aspnes, Yale University Faith Ellen Fich, University of Toronto Eric Ruppert, York University Anonymity
Relationships Between Broadcast and Shared Memory in Reliable Anonymous Distributed Systems James Aspnes, Yale University Faith Ellen Fich, University of Toronto Eric Ruppert, York University Anonymity
Initial Assumptions. Modern Distributed Computing. Network Topology. Initial Input
 Initial Assumptions Modern Distributed Computing Theory and Applications Ioannis Chatzigiannakis Sapienza University of Rome Lecture 4 Tuesday, March 6, 03 Exercises correspond to problems studied during
Initial Assumptions Modern Distributed Computing Theory and Applications Ioannis Chatzigiannakis Sapienza University of Rome Lecture 4 Tuesday, March 6, 03 Exercises correspond to problems studied during
Online Algorithms. Lecture 11
 Online Algorithms Lecture 11 Today DC on trees DC on arbitrary metrics DC on circle Scheduling K-server on trees Theorem The DC Algorithm is k-competitive for the k server problem on arbitrary tree metrics.
Online Algorithms Lecture 11 Today DC on trees DC on arbitrary metrics DC on circle Scheduling K-server on trees Theorem The DC Algorithm is k-competitive for the k server problem on arbitrary tree metrics.
Stability Analysis of M-Dimensional Asynchronous Swarms With a Fixed Communication Topology
 76 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 48, NO. 1, JANUARY 2003 Stability Analysis of M-Dimensional Asynchronous Swarms With a Fixed Communication Topology Yang Liu, Member, IEEE, Kevin M. Passino,
76 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON AUTOMATIC CONTROL, VOL. 48, NO. 1, JANUARY 2003 Stability Analysis of M-Dimensional Asynchronous Swarms With a Fixed Communication Topology Yang Liu, Member, IEEE, Kevin M. Passino,
Distributed Leader Election Algorithms in Synchronous Networks
 Distributed Leader Election Algorithms in Synchronous Networks Mitsou Valia National Technical University of Athens School of Applied Mathematics and Physics 1/66 Distributed Computing Distributed computing
Distributed Leader Election Algorithms in Synchronous Networks Mitsou Valia National Technical University of Athens School of Applied Mathematics and Physics 1/66 Distributed Computing Distributed computing
DO NOT RE-DISTRIBUTE THIS SOLUTION FILE
 Professor Kindred Math 104, Graph Theory Homework 2 Solutions February 7, 2013 Introduction to Graph Theory, West Section 1.2: 26, 38, 42 Section 1.3: 14, 18 Section 2.1: 26, 29, 30 DO NOT RE-DISTRIBUTE
Professor Kindred Math 104, Graph Theory Homework 2 Solutions February 7, 2013 Introduction to Graph Theory, West Section 1.2: 26, 38, 42 Section 1.3: 14, 18 Section 2.1: 26, 29, 30 DO NOT RE-DISTRIBUTE
Distributed Computing
 Principles of Distributed Computing Roger Wattenhofer wattenhofer@ethz.ch Spring 2014 Contents 1 Vertex Coloring 5 1.1 Problem & Model........................... 5 1.2 Coloring Trees............................
Principles of Distributed Computing Roger Wattenhofer wattenhofer@ethz.ch Spring 2014 Contents 1 Vertex Coloring 5 1.1 Problem & Model........................... 5 1.2 Coloring Trees............................
CSE 486/586 Distributed Systems
 CSE 486/586 Distributed Systems Mutual Exclusion Steve Ko Computer Sciences and Engineering University at Buffalo CSE 486/586 Recap: Consensus On a synchronous system There s an algorithm that works. On
CSE 486/586 Distributed Systems Mutual Exclusion Steve Ko Computer Sciences and Engineering University at Buffalo CSE 486/586 Recap: Consensus On a synchronous system There s an algorithm that works. On
Algorithm 23 works. Instead of a spanning tree, one can use routing.
 Chapter 5 Shared Objects 5.1 Introduction Assume that there is a common resource (e.g. a common variable or data structure), which different nodes in a network need to access from time to time. If the
Chapter 5 Shared Objects 5.1 Introduction Assume that there is a common resource (e.g. a common variable or data structure), which different nodes in a network need to access from time to time. If the
Graph Algorithms. Many problems in networks can be modeled as graph problems.
 Graph Algorithms Graph Algorithms Many problems in networks can be modeled as graph problems. - The topology of a distributed system is a graph. - Routing table computation uses the shortest path algorithm
Graph Algorithms Graph Algorithms Many problems in networks can be modeled as graph problems. - The topology of a distributed system is a graph. - Routing table computation uses the shortest path algorithm
Geometric Routing: Of Theory and Practice
 Geometric Routing: Of Theory and Practice PODC 03 F. Kuhn, R. Wattenhofer, Y. Zhang, A. Zollinger [KWZ 02] [KWZ 03] [KK 00] Asymptotically Optimal Geometric Mobile Ad-Hoc Routing Worst-Case Optimal and
Geometric Routing: Of Theory and Practice PODC 03 F. Kuhn, R. Wattenhofer, Y. Zhang, A. Zollinger [KWZ 02] [KWZ 03] [KK 00] Asymptotically Optimal Geometric Mobile Ad-Hoc Routing Worst-Case Optimal and
Treewidth and graph minors
 Treewidth and graph minors Lectures 9 and 10, December 29, 2011, January 5, 2012 We shall touch upon the theory of Graph Minors by Robertson and Seymour. This theory gives a very general condition under
Treewidth and graph minors Lectures 9 and 10, December 29, 2011, January 5, 2012 We shall touch upon the theory of Graph Minors by Robertson and Seymour. This theory gives a very general condition under
Concepts. Techniques for masking faults. Failure Masking by Redundancy. CIS 505: Software Systems Lecture Note on Consensus
 CIS 505: Software Systems Lecture Note on Consensus Insup Lee Department of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania CIS 505, Spring 2007 Concepts Dependability o Availability ready
CIS 505: Software Systems Lecture Note on Consensus Insup Lee Department of Computer and Information Science University of Pennsylvania CIS 505, Spring 2007 Concepts Dependability o Availability ready
Consensus. Chapter Two Friends. 2.3 Impossibility of Consensus. 2.2 Consensus 16 CHAPTER 2. CONSENSUS
 16 CHAPTER 2. CONSENSUS Agreement All correct nodes decide for the same value. Termination All correct nodes terminate in finite time. Validity The decision value must be the input value of a node. Chapter
16 CHAPTER 2. CONSENSUS Agreement All correct nodes decide for the same value. Termination All correct nodes terminate in finite time. Validity The decision value must be the input value of a node. Chapter
Network Algorithms. Distributed Sorting
 Network Algorithms Distributed Sorting Stefan Schmid @ T-Labs, 2 Sorting Distributed Sorting Graph with n nodes {v,,v n } and n values. Goal: node vi should store i-th smallest value. v 6 v 2 2 v 3 7 v
Network Algorithms Distributed Sorting Stefan Schmid @ T-Labs, 2 Sorting Distributed Sorting Graph with n nodes {v,,v n } and n values. Goal: node vi should store i-th smallest value. v 6 v 2 2 v 3 7 v
Network Layer: Routing
 Network Layer: Routing The Problem A B R 1 R 2 R 4 R 3 Goal: for each destination, compute next hop 1 Lecture 9 2 Basic Assumptions Trivial solution: Flooding Dynamic environment: links and routers unreliable:
Network Layer: Routing The Problem A B R 1 R 2 R 4 R 3 Goal: for each destination, compute next hop 1 Lecture 9 2 Basic Assumptions Trivial solution: Flooding Dynamic environment: links and routers unreliable:
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #6: Mining Data Streams Seoul National University 1 Outline Overview Sampling From Data Stream Queries Over Sliding Window 2 Data Streams In many data mining situations,
Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #6: Mining Data Streams Seoul National University 1 Outline Overview Sampling From Data Stream Queries Over Sliding Window 2 Data Streams In many data mining situations,
Treaps. 1 Binary Search Trees (BSTs) CSE341T/CSE549T 11/05/2014. Lecture 19
 CSE34T/CSE549T /05/04 Lecture 9 Treaps Binary Search Trees (BSTs) Search trees are tree-based data structures that can be used to store and search for items that satisfy a total order. There are many types
CSE34T/CSE549T /05/04 Lecture 9 Treaps Binary Search Trees (BSTs) Search trees are tree-based data structures that can be used to store and search for items that satisfy a total order. There are many types
Instructions. Notation. notation: In particular, t(i, 2) = 2 2 2
 Instructions Deterministic Distributed Algorithms, 10 21 May 2010, Exercises http://www.cs.helsinki.fi/jukka.suomela/dda-2010/ Jukka Suomela, last updated on May 20, 2010 exercises are merely suggestions
Instructions Deterministic Distributed Algorithms, 10 21 May 2010, Exercises http://www.cs.helsinki.fi/jukka.suomela/dda-2010/ Jukka Suomela, last updated on May 20, 2010 exercises are merely suggestions
Lecture 2: Leader election algorithms.
 Distributed Algorithms M.Tech., CSE, 0 Lecture : Leader election algorithms. Faculty: K.R. Chowdhary : Professor of CS Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny reserved for
Distributed Algorithms M.Tech., CSE, 0 Lecture : Leader election algorithms. Faculty: K.R. Chowdhary : Professor of CS Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny reserved for
15-451/651: Design & Analysis of Algorithms November 4, 2015 Lecture #18 last changed: November 22, 2015
 15-451/651: Design & Analysis of Algorithms November 4, 2015 Lecture #18 last changed: November 22, 2015 While we have good algorithms for many optimization problems, the previous lecture showed that many
15-451/651: Design & Analysis of Algorithms November 4, 2015 Lecture #18 last changed: November 22, 2015 While we have good algorithms for many optimization problems, the previous lecture showed that many
Distributed Sorting. Chapter Array & Mesh
 Chapter 9 Distributed Sorting Indeed, I believe that virtually every important aspect of programming arises somewhere in the context of sorting [and searching]! Donald E. Knuth, The Art of Computer Programming
Chapter 9 Distributed Sorting Indeed, I believe that virtually every important aspect of programming arises somewhere in the context of sorting [and searching]! Donald E. Knuth, The Art of Computer Programming
memoization or iteration over subproblems the direct iterative algorithm a basic outline of dynamic programming
 Dynamic Programming 1 Introduction to Dynamic Programming weighted interval scheduling the design of a recursive solution memoizing the recursion 2 Principles of Dynamic Programming memoization or iteration
Dynamic Programming 1 Introduction to Dynamic Programming weighted interval scheduling the design of a recursive solution memoizing the recursion 2 Principles of Dynamic Programming memoization or iteration
Distributed Objects with Sense of Direction
 Distributed Objects with Sense of Direction G. V. BOCHMANN University of Ottawa P. FLOCCHINI Université de Montréal D. RAMAZANI Université de Montréal Introduction An object system consists of a collection
Distributed Objects with Sense of Direction G. V. BOCHMANN University of Ottawa P. FLOCCHINI Université de Montréal D. RAMAZANI Université de Montréal Introduction An object system consists of a collection
Dr. Amotz Bar-Noy s Compendium of Algorithms Problems. Problems, Hints, and Solutions
 Dr. Amotz Bar-Noy s Compendium of Algorithms Problems Problems, Hints, and Solutions Chapter 1 Searching and Sorting Problems 1 1.1 Array with One Missing 1.1.1 Problem Let A = A[1],..., A[n] be an array
Dr. Amotz Bar-Noy s Compendium of Algorithms Problems Problems, Hints, and Solutions Chapter 1 Searching and Sorting Problems 1 1.1 Array with One Missing 1.1.1 Problem Let A = A[1],..., A[n] be an array
Byzantine Consensus in Directed Graphs
 Byzantine Consensus in Directed Graphs Lewis Tseng 1,3, and Nitin Vaidya 2,3 1 Department of Computer Science, 2 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and 3 Coordinated Science Laboratory
Byzantine Consensus in Directed Graphs Lewis Tseng 1,3, and Nitin Vaidya 2,3 1 Department of Computer Science, 2 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and 3 Coordinated Science Laboratory
Analyze the obvious algorithm, 5 points Here is the most obvious algorithm for this problem: (LastLargerElement[A[1..n]:
![Analyze the obvious algorithm, 5 points Here is the most obvious algorithm for this problem: (LastLargerElement[A[1..n]: Analyze the obvious algorithm, 5 points Here is the most obvious algorithm for this problem: (LastLargerElement[A[1..n]:](/thumbs/90/104324109.jpg) CSE 101 Homework 1 Background (Order and Recurrence Relations), correctness proofs, time analysis, and speeding up algorithms with restructuring, preprocessing and data structures. Due Thursday, April
CSE 101 Homework 1 Background (Order and Recurrence Relations), correctness proofs, time analysis, and speeding up algorithms with restructuring, preprocessing and data structures. Due Thursday, April
Asynchronous Resource Discovery in Peer to Peer Networks 1
 Asynchronous Resource Discovery in Peer to Peer Networks 1 Shay Kutten Faculty of Industrial Eng. & Management The Technion Haifa 32000, Israel kutten@ie.technion.ac.il David Peleg Dept. of Computer Science
Asynchronous Resource Discovery in Peer to Peer Networks 1 Shay Kutten Faculty of Industrial Eng. & Management The Technion Haifa 32000, Israel kutten@ie.technion.ac.il David Peleg Dept. of Computer Science
Introduction to the Analysis of Algorithms. Algorithm
 Introduction to the Analysis of Algorithms Based on the notes from David Fernandez-Baca Bryn Mawr College CS206 Intro to Data Structures Algorithm An algorithm is a strategy (well-defined computational
Introduction to the Analysis of Algorithms Based on the notes from David Fernandez-Baca Bryn Mawr College CS206 Intro to Data Structures Algorithm An algorithm is a strategy (well-defined computational
COMP Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
 COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Approximation Algorithms CLRS 35.1-35.5 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures 1 / 30 Approaching
COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Approximation Algorithms CLRS 35.1-35.5 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures 1 / 30 Approaching
High Dimensional Indexing by Clustering
 Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland Recall that, our discussion so far has assumed that the dimensionality d is moderately high, such that it can be regarded as a constant. This means that d should
Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland Recall that, our discussion so far has assumed that the dimensionality d is moderately high, such that it can be regarded as a constant. This means that d should
6.852 Lecture 10. Minimum spanning tree. Reading: Chapter 15.5, Gallager-Humblet-Spira paper. Gallager-Humblet-Spira algorithm
 6.852 Lecture 10 Gallager-Humblet-Spira algorithm Reading: Chapter 15.5, Gallager-Humblet-Spira paper Assume undirected graph (i.e., bidirectional communication) distinct edge weights size and diameter
6.852 Lecture 10 Gallager-Humblet-Spira algorithm Reading: Chapter 15.5, Gallager-Humblet-Spira paper Assume undirected graph (i.e., bidirectional communication) distinct edge weights size and diameter
Definition For vertices u, v V (G), the distance from u to v, denoted d(u, v), in G is the length of a shortest u, v-path. 1
 Graph fundamentals Bipartite graph characterization Lemma. If a graph contains an odd closed walk, then it contains an odd cycle. Proof strategy: Consider a shortest closed odd walk W. If W is not a cycle,
Graph fundamentals Bipartite graph characterization Lemma. If a graph contains an odd closed walk, then it contains an odd cycle. Proof strategy: Consider a shortest closed odd walk W. If W is not a cycle,
arxiv: v1 [cs.dc] 6 May 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cs.dc] 6 May 2014 arxiv: v1 [cs.dc] 6 May 2014](/thumbs/83/87084720.jpg) Consensus with an Abstract MAC Layer Calvin Newport Georgetown University cnewport@cs.georgetown.edu arxiv:1405.1382v1 [cs.dc] 6 May 2014 Abstract In this paper, we study distributed consensus in the radio
Consensus with an Abstract MAC Layer Calvin Newport Georgetown University cnewport@cs.georgetown.edu arxiv:1405.1382v1 [cs.dc] 6 May 2014 Abstract In this paper, we study distributed consensus in the radio
Gathering of Six Robots on Anonymous Symmetric Rings
 Author manuscript, published in "Structural Information and Communication Complexity 6796 (2011) 174-185" DOI : 10.1007/978-3-642-22212-2_16 Gathering of Six Robots on Anonymous Symmetric Rings Gianlorenzo
Author manuscript, published in "Structural Information and Communication Complexity 6796 (2011) 174-185" DOI : 10.1007/978-3-642-22212-2_16 Gathering of Six Robots on Anonymous Symmetric Rings Gianlorenzo
How many leaves on the decision tree? There are n! leaves, because every permutation appears at least once.
 Chapter 8. Sorting in Linear Time Types of Sort Algorithms The only operation that may be used to gain order information about a sequence is comparison of pairs of elements. Quick Sort -- comparison-based
Chapter 8. Sorting in Linear Time Types of Sort Algorithms The only operation that may be used to gain order information about a sequence is comparison of pairs of elements. Quick Sort -- comparison-based
Deadlock Wednesday, October 13, :08 PM
 Deadlock Page 1 Deadlock Wednesday, October 13, 2004 8:08 PM Deadlock Other side of spectrum (from race conditions) Common forms Circular dependencies. Resource saturation. All symptoms of roughly the
Deadlock Page 1 Deadlock Wednesday, October 13, 2004 8:08 PM Deadlock Other side of spectrum (from race conditions) Common forms Circular dependencies. Resource saturation. All symptoms of roughly the
The Increase of the Instability of Networks due to Quasi-Static Link Capacities
 The Increase of the Instability of Networks due to Quasi-Static Link Capacities D. Koukopoulos a,,m.mavronicolas b, P. Spirakis c a RACTI, 61 Riga Fereou, 26221 Patras, Greece. b Department of Computer
The Increase of the Instability of Networks due to Quasi-Static Link Capacities D. Koukopoulos a,,m.mavronicolas b, P. Spirakis c a RACTI, 61 Riga Fereou, 26221 Patras, Greece. b Department of Computer
Notes for Recitation 8
 6.04/8.06J Mathematics for Computer Science October 5, 00 Tom Leighton and Marten van Dijk Notes for Recitation 8 Build-up error Recall a graph is connected iff there is a path between every pair of its
6.04/8.06J Mathematics for Computer Science October 5, 00 Tom Leighton and Marten van Dijk Notes for Recitation 8 Build-up error Recall a graph is connected iff there is a path between every pair of its
Exam Principles of Distributed Computing
 Distributed Computing FS 2015 Prof. Dr. Roger Wattenhofer P. Bissig, P. Brandes, S. Brandt, K.T. Förster, B. Keller, M. König, L. Peer, J. Seidel, D. Stolz, J. Uitto Exam Principles of Distributed Computing
Distributed Computing FS 2015 Prof. Dr. Roger Wattenhofer P. Bissig, P. Brandes, S. Brandt, K.T. Förster, B. Keller, M. König, L. Peer, J. Seidel, D. Stolz, J. Uitto Exam Principles of Distributed Computing
Efficient Universal Recovery in Broadcast Networks
 Efficient Universal Recovery in Broadcast Networks Thomas Courtade and Rick Wesel UCLA September 30, 2010 Courtade and Wesel (UCLA) Efficient Universal Recovery Allerton 2010 1 / 19 System Model and Problem
Efficient Universal Recovery in Broadcast Networks Thomas Courtade and Rick Wesel UCLA September 30, 2010 Courtade and Wesel (UCLA) Efficient Universal Recovery Allerton 2010 1 / 19 System Model and Problem
Self Stabilization. CS553 Distributed Algorithms Prof. Ajay Kshemkalyani. by Islam Ismailov & Mohamed M. Ali
 Self Stabilization CS553 Distributed Algorithms Prof. Ajay Kshemkalyani by Islam Ismailov & Mohamed M. Ali Introduction There is a possibility for a distributed system to go into an illegitimate state,
Self Stabilization CS553 Distributed Algorithms Prof. Ajay Kshemkalyani by Islam Ismailov & Mohamed M. Ali Introduction There is a possibility for a distributed system to go into an illegitimate state,
Compact Sets. James K. Peterson. September 15, Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University
 Compact Sets James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 15, 2017 Outline 1 Closed Sets 2 Compactness 3 Homework Closed Sets
Compact Sets James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University September 15, 2017 Outline 1 Closed Sets 2 Compactness 3 Homework Closed Sets
Models of distributed computing: port numbering and local algorithms
 Models of distributed computing: port numbering and local algorithms Jukka Suomela Adaptive Computing Group Helsinki Institute for Information Technology HIIT University of Helsinki FMT seminar, 26 February
Models of distributed computing: port numbering and local algorithms Jukka Suomela Adaptive Computing Group Helsinki Institute for Information Technology HIIT University of Helsinki FMT seminar, 26 February
11.1 Facility Location
 CS787: Advanced Algorithms Scribe: Amanda Burton, Leah Kluegel Lecturer: Shuchi Chawla Topic: Facility Location ctd., Linear Programming Date: October 8, 2007 Today we conclude the discussion of local
CS787: Advanced Algorithms Scribe: Amanda Burton, Leah Kluegel Lecturer: Shuchi Chawla Topic: Facility Location ctd., Linear Programming Date: October 8, 2007 Today we conclude the discussion of local
Graph Algorithms. Many problems in networks can be modeled as graph problems.
 Graph Algorithms Many problems in networks can be modeled as graph problems. - The topology of a distributed system is a graph. - Routing table computation uses the shortest path algorithm - Efficient
Graph Algorithms Many problems in networks can be modeled as graph problems. - The topology of a distributed system is a graph. - Routing table computation uses the shortest path algorithm - Efficient
On Fractional Dynamic Faults with Threshold
 On Fractional Dynamic Faults with Threshold Stefan Dobrev 1, Rastislav Královič 2, Richard Královič 2, and Nicola Santoro 3 1 School of Information Technology and Engineering, University of Ottawa, Ottawa,
On Fractional Dynamic Faults with Threshold Stefan Dobrev 1, Rastislav Královič 2, Richard Královič 2, and Nicola Santoro 3 1 School of Information Technology and Engineering, University of Ottawa, Ottawa,
Lecture 1: Introduction to distributed Algorithms
 Distributed Algorithms M.Tech., CSE, 2016 Lecture 1: Introduction to distributed Algorithms Faculty: K.R. Chowdhary : Professor of CS Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny
Distributed Algorithms M.Tech., CSE, 2016 Lecture 1: Introduction to distributed Algorithms Faculty: K.R. Chowdhary : Professor of CS Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny
γ(ɛ) (a, b) (a, d) (d, a) (a, b) (c, d) (d, d) (e, e) (e, a) (e, e) (a) Draw a picture of G.
 MAD 3105 Spring 2006 Solutions for Review for Test 2 1. Define a graph G with V (G) = {a, b, c, d, e}, E(G) = {r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z} and γ, the function defining the edges, is given by the table ɛ
MAD 3105 Spring 2006 Solutions for Review for Test 2 1. Define a graph G with V (G) = {a, b, c, d, e}, E(G) = {r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z} and γ, the function defining the edges, is given by the table ɛ
Cuckoo Hashing for Undergraduates
 Cuckoo Hashing for Undergraduates Rasmus Pagh IT University of Copenhagen March 27, 2006 Abstract This lecture note presents and analyses two simple hashing algorithms: Hashing with Chaining, and Cuckoo
Cuckoo Hashing for Undergraduates Rasmus Pagh IT University of Copenhagen March 27, 2006 Abstract This lecture note presents and analyses two simple hashing algorithms: Hashing with Chaining, and Cuckoo
Randomized Rumor Spreading in Social Networks
 Randomized Rumor Spreading in Social Networks Benjamin Doerr (MPI Informatics / Saarland U) Summary: We study how fast rumors spread in social networks. For the preferential attachment network model and
Randomized Rumor Spreading in Social Networks Benjamin Doerr (MPI Informatics / Saarland U) Summary: We study how fast rumors spread in social networks. For the preferential attachment network model and
Algorithms, Games, and Networks February 21, Lecture 12
 Algorithms, Games, and Networks February, 03 Lecturer: Ariel Procaccia Lecture Scribe: Sercan Yıldız Overview In this lecture, we introduce the axiomatic approach to social choice theory. In particular,
Algorithms, Games, and Networks February, 03 Lecturer: Ariel Procaccia Lecture Scribe: Sercan Yıldız Overview In this lecture, we introduce the axiomatic approach to social choice theory. In particular,
Theorem 2.9: nearest addition algorithm
 There are severe limits on our ability to compute near-optimal tours It is NP-complete to decide whether a given undirected =(,)has a Hamiltonian cycle An approximation algorithm for the TSP can be used
There are severe limits on our ability to compute near-optimal tours It is NP-complete to decide whether a given undirected =(,)has a Hamiltonian cycle An approximation algorithm for the TSP can be used
09 B: Graph Algorithms II
 Correctness and Complexity of 09 B: Graph Algorithms II CS1102S: Data Structures and Algorithms Martin Henz March 19, 2010 Generated on Thursday 18 th March, 2010, 00:20 CS1102S: Data Structures and Algorithms
Correctness and Complexity of 09 B: Graph Algorithms II CS1102S: Data Structures and Algorithms Martin Henz March 19, 2010 Generated on Thursday 18 th March, 2010, 00:20 CS1102S: Data Structures and Algorithms
Lecture 2 The k-means clustering problem
 CSE 29: Unsupervised learning Spring 2008 Lecture 2 The -means clustering problem 2. The -means cost function Last time we saw the -center problem, in which the input is a set S of data points and the
CSE 29: Unsupervised learning Spring 2008 Lecture 2 The -means clustering problem 2. The -means cost function Last time we saw the -center problem, in which the input is a set S of data points and the
A O (log n ) Distributed Algorithm to Construct Routing Structures for Pub/Sub Systems. Volker Turau. November 6th, 2018
 A O (log n ) Distributed Algorithm to Construct Routing Structures for Pub/Sub Systems Volker Turau 20th Int. Symposium on Stabilization, Safety, and Security of Distributed Systems November 6th, 2018
A O (log n ) Distributed Algorithm to Construct Routing Structures for Pub/Sub Systems Volker Turau 20th Int. Symposium on Stabilization, Safety, and Security of Distributed Systems November 6th, 2018
Dijkstra s algorithm for shortest paths when no edges have negative weight.
 Lecture 14 Graph Algorithms II 14.1 Overview In this lecture we begin with one more algorithm for the shortest path problem, Dijkstra s algorithm. We then will see how the basic approach of this algorithm
Lecture 14 Graph Algorithms II 14.1 Overview In this lecture we begin with one more algorithm for the shortest path problem, Dijkstra s algorithm. We then will see how the basic approach of this algorithm
Scheduling Algorithms to Minimize Session Delays
 Scheduling Algorithms to Minimize Session Delays Nandita Dukkipati and David Gutierrez A Motivation I INTRODUCTION TCP flows constitute the majority of the traffic volume in the Internet today Most of
Scheduling Algorithms to Minimize Session Delays Nandita Dukkipati and David Gutierrez A Motivation I INTRODUCTION TCP flows constitute the majority of the traffic volume in the Internet today Most of
Message-Optimal Connected Dominating Sets in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
 Message-Optimal Connected Dominating Sets in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Khaled M. Alzoubi Department of Computer Science Illinois Institute of Technology Chicago, IL 6066 alzoubi@cs.iit.edu Peng-Jun Wan Department
Message-Optimal Connected Dominating Sets in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Khaled M. Alzoubi Department of Computer Science Illinois Institute of Technology Chicago, IL 6066 alzoubi@cs.iit.edu Peng-Jun Wan Department
CSCI 5454, CU Boulder Samriti Kanwar Lecture April 2013
 1. Byzantine Agreement Problem In the Byzantine agreement problem, n processors communicate with each other by sending messages over bidirectional links in order to reach an agreement on a binary value.
1. Byzantine Agreement Problem In the Byzantine agreement problem, n processors communicate with each other by sending messages over bidirectional links in order to reach an agreement on a binary value.
Solutions to the Second Midterm Exam
 CS/Math 240: Intro to Discrete Math 3/27/2011 Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek Solutions to the Second Midterm Exam Problem 1 This question deals with the following implementation of binary search. Function
CS/Math 240: Intro to Discrete Math 3/27/2011 Instructor: Dieter van Melkebeek Solutions to the Second Midterm Exam Problem 1 This question deals with the following implementation of binary search. Function
Packet Efficient Implementation of the Omega Failure Detector
 Packet Efficient Implementation of the Omega Failure Detector Quentin Bramas, Dianne Foreback, Mikhail Nesterenko, Sébastien Tixeuil To cite this version: Quentin Bramas, Dianne Foreback, Mikhail Nesterenko,
Packet Efficient Implementation of the Omega Failure Detector Quentin Bramas, Dianne Foreback, Mikhail Nesterenko, Sébastien Tixeuil To cite this version: Quentin Bramas, Dianne Foreback, Mikhail Nesterenko,
Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS
 Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS Distributed Computing Group Mobile Computing Summer 2004 Overview Motivation Dominating Set Connected Dominating Set The Greedy Algorithm The Tree Growing Algorithm The Marking
Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS Distributed Computing Group Mobile Computing Summer 2004 Overview Motivation Dominating Set Connected Dominating Set The Greedy Algorithm The Tree Growing Algorithm The Marking
Distributed Algorithms. The Leader Election Problem. 1.2 The Network Model. Applications. 1 The Problem and the Model. Lesson two Leader Election
 The Problem and the Model Distributed Algorithms Lesson two Leader Election. The problem What is a leader A leader is a member that all other nodes acknowledge as being distinguished to perform some special
The Problem and the Model Distributed Algorithms Lesson two Leader Election. The problem What is a leader A leader is a member that all other nodes acknowledge as being distinguished to perform some special
Coordination 1. To do. Mutual exclusion Election algorithms Next time: Global state. q q q
 Coordination 1 To do q q q Mutual exclusion Election algorithms Next time: Global state Coordination and agreement in US Congress 1798-2015 Process coordination How can processes coordinate their action?
Coordination 1 To do q q q Mutual exclusion Election algorithms Next time: Global state Coordination and agreement in US Congress 1798-2015 Process coordination How can processes coordinate their action?
Distributed Systems. coordination Johan Montelius ID2201. Distributed Systems ID2201
 Distributed Systems ID2201 coordination Johan Montelius 1 Coordination Coordinating several threads in one node is a problem, coordination in a network is of course worse: failure of nodes and networks
Distributed Systems ID2201 coordination Johan Montelius 1 Coordination Coordinating several threads in one node is a problem, coordination in a network is of course worse: failure of nodes and networks
2 A Plane Sweep Algorithm for Line Segment Intersection
 EECS 396/496: Computational Geometry Fall 2017 Lecturer: Huck Bennett Lecture 2: Line Segment Intersection In this lecture, we will study the problem of computing all intersections of a set of line segmentn
EECS 396/496: Computational Geometry Fall 2017 Lecturer: Huck Bennett Lecture 2: Line Segment Intersection In this lecture, we will study the problem of computing all intersections of a set of line segmentn
Lecture 1 August 31, 2017
 CS 388R: Randomized Algorithms Fall 017 Lecture 1 August 31, 017 Prof. Eric Price Scribe: Garrett Goble, Daniel Brown NOTE: THESE NOTES HAVE NOT BEEN EDITED OR CHECKED FOR CORRECTNESS 1 Randomized Algorithms
CS 388R: Randomized Algorithms Fall 017 Lecture 1 August 31, 017 Prof. Eric Price Scribe: Garrett Goble, Daniel Brown NOTE: THESE NOTES HAVE NOT BEEN EDITED OR CHECKED FOR CORRECTNESS 1 Randomized Algorithms
Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS
 Distributed Computing Group Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS Mobile Computing Summer 2004 Overview Motivation Dominating Set Connected Dominating Set The Greedy Algorithm The Tree Growing Algorithm The Marking
Distributed Computing Group Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS Mobile Computing Summer 2004 Overview Motivation Dominating Set Connected Dominating Set The Greedy Algorithm The Tree Growing Algorithm The Marking
Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning
 Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 / 29 Y Tao Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning In this lecture, we
Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 / 29 Y Tao Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning In this lecture, we
Draft Notes 1 : Scaling in Ad hoc Routing Protocols
 Draft Notes 1 : Scaling in Ad hoc Routing Protocols Timothy X Brown University of Colorado April 2, 2008 2 Introduction What is the best network wireless network routing protocol? This question is a function
Draft Notes 1 : Scaling in Ad hoc Routing Protocols Timothy X Brown University of Colorado April 2, 2008 2 Introduction What is the best network wireless network routing protocol? This question is a function
Chapter 1 Programming: A General Overview
 Introduction Chapter 1 Programming: A General Overview This class is an introduction to the design, implementation, and analysis of algorithms. examples: sorting large amounts of data organizing information
Introduction Chapter 1 Programming: A General Overview This class is an introduction to the design, implementation, and analysis of algorithms. examples: sorting large amounts of data organizing information
CPSC 536N: Randomized Algorithms Term 2. Lecture 5
 CPSC 536N: Randomized Algorithms 2011-12 Term 2 Prof. Nick Harvey Lecture 5 University of British Columbia In this lecture we continue to discuss applications of randomized algorithms in computer networking.
CPSC 536N: Randomized Algorithms 2011-12 Term 2 Prof. Nick Harvey Lecture 5 University of British Columbia In this lecture we continue to discuss applications of randomized algorithms in computer networking.
Multi-Cluster Interleaving on Paths and Cycles
 Multi-Cluster Interleaving on Paths and Cycles Anxiao (Andrew) Jiang, Member, IEEE, Jehoshua Bruck, Fellow, IEEE Abstract Interleaving codewords is an important method not only for combatting burst-errors,
Multi-Cluster Interleaving on Paths and Cycles Anxiao (Andrew) Jiang, Member, IEEE, Jehoshua Bruck, Fellow, IEEE Abstract Interleaving codewords is an important method not only for combatting burst-errors,
Λέων-Χαράλαμπος Σταματάρης
 Λέων-Χαράλαμπος Σταματάρης INTRODUCTION Two classical problems of information dissemination in computer networks: The broadcasting problem: Distributing a particular message from a distinguished source
Λέων-Χαράλαμπος Σταματάρης INTRODUCTION Two classical problems of information dissemination in computer networks: The broadcasting problem: Distributing a particular message from a distinguished source
by conservation of flow, hence the cancelation. Similarly, we have
 Chapter 13: Network Flows and Applications Network: directed graph with source S and target T. Non-negative edge weights represent capacities. Assume no edges into S or out of T. (If necessary, we can
Chapter 13: Network Flows and Applications Network: directed graph with source S and target T. Non-negative edge weights represent capacities. Assume no edges into S or out of T. (If necessary, we can
CSE 421 Applications of DFS(?) Topological sort
 CSE 421 Applications of DFS(?) Topological sort Yin Tat Lee 1 Precedence Constraints In a directed graph, an edge (i, j) means task i must occur before task j. Applications Course prerequisite: course
CSE 421 Applications of DFS(?) Topological sort Yin Tat Lee 1 Precedence Constraints In a directed graph, an edge (i, j) means task i must occur before task j. Applications Course prerequisite: course
