MSC. IP Network SGSN. Affected by EDGE BSS Base Station Subsystem HLR Home Location Register
|
|
|
- Muriel Brittany Robertson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Performance Evaluation of TCP/IP over EDGE Hwee Pink Tan 1,Anthony Lo 2, and Winston K. G. Seah 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, National University of Singapore, 10 Kent Ridge Crescent, Singapore 60 2 Centre for Wireless Communications???, National University of Singapore, 20 Science Park Road, #02-34/3 TeleTech Park, Singapore Science Park II, Singapore 64 floanthony, winstong@cwc.nus.edu.sg Abstract. Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution (EDGE) provides an evolutionary path from existing cellular systems such as Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) for delivering higher bit rate services that facilitate wireless Internet access. Thus, EDGE only denes a new radio access technology to achieve higher bit rates. This paper investigates the performance of Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) over the enhanced packet-switched transmission mode of EDGE, i.e., Enhanced General Packet Radio Service (EGPRS). The Network Simulator (ns) tool was used in the simulation. The performance of TCP was examined under various channel conditions with and without the link adaptation scheme of EGPRS. The link adaptation scheme improves the TCP performance under poor channel conditions. In the simulation, two dierent methods, BLock Error Rate (BLER) and the average of measured Carrier-to-Interference ratio (C/I), were employed to determine the channel quality and subsequently to select the most appropriate coding scheme to maximize the TCP throughput. The TCP throughput obtained using the BLER method is higher under poor channel conditions, while the throughput based on the average of measured C/I out-performs BLER under good channel conditions. As a result, we proposed a hybrid method, which selects the BLER method for poor channel conditions and the average measured C/I for good channel conditions. The simulation results show that the throughput obtained using the hybrid method is superior compared to the individual method. 1 Introduction Presently, the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) supports not only speech but data services with user bit rates up to.6 kbps. However, this data rate is not adequate for many Internet applications, especially those that have a large amount of trac to transfer, such as a le transfer. To ameliorate this situation, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has standardized High Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD) [1] and General??? CWC is a national R & D centre funded by the Singapore National Science and Development Board.
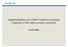
2 2 HPTan et al. Packet Radio Service (GPRS) [2] to achieve higher bit rate. Both standards are evolved from the GSM technology. Since HSCSD and GPRS are based on the original Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) modulation, the increase of bit rate is moderate and below the International Mobile Telecommunications in Year 2000 (IMT-2000) requirement set by International Telecommunication Union (ITU), which is 384 kbps for high-users mobility with wide-area coverage. Thus, ETSI is developing the Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution (EDGE) [3] to enhance both circuit-switched and packet-switched transmission modes of GSM. The enhancements dened in EDGE are basically in the physical and data link layers to eciently providing the required bit rate. EDGE reuses existing GSM/GPRS infrastructure including carrier bandwidth and Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) structure. The Internet is the most popular and widely used packet-switched network that provides applications like File Transfer Protocol (FTP), World Wide Web (WWW), , etc. These Internet applications rely on two commonly used protocols, namely, Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol (IP) (TCP/IP) [4], to reliably transport data across heterogeneous networks. IP is concerned with routing data from source to destination host through one or more networks connected by routers, while TCP provides a reliable end-to-end data transfer service. A number of studies can be found in the literature (e.g., [, 6]) have shown that TCP performs poorly over wireless links. However, these studies are primarily focused on Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs), e.g., WaveLAN. WLANs are diered from cellular networks such as EDGE in a number of ways. Firstly, EDGE provides sophisticated and reliable radio and link layers. Secondly, EDGE is for wide-area coverage and high-speed user mobility. As the main goal of EDGE is to provide wireless Internet access, it is important to evaluate the performance of TCP over EDGE. This paper evaluates the performance of TCP over EDGE through a simulation study using the Network Simulator (ns) [] jointly developed by the University of California - Berkeley, University of Southern California (USC) and Xerox PARC. 2 Overview of EDGE EDGE [3] provides an evolutionary path from Second-Generation (2G) systems (such as GSM) for delivering Third-Generation (3G) services including Internet access, which demand higher bandwidth and quality. As such, EDGE only de- nes a new radio access technology to achieve higher bit rates and reuses the infrastructure of GSM/GPRS. The parts in the GSM/GPRS system, which are aected by EDGE introduction, are the Mobile Station (MS) and the Base Station Subsystem (BSS), as illustrated in Fig. 1. EDGE oers enhancements to packet-switched and circuit-switched transmission modes of GSM, which refer to as Enhanced GPRS (EGPRS) and Enhanced Circuit-Switched Data (ECSD) [8], respectively. EGPRS is the main focus of this paper because it oers packet services and higher user bit rates than ECSD.
3 Lecture Notes in Computer Science 3 HLR VLR EIR MS BSS MSC GMSC PSTN/ISDN EDGE-enabled MS SGSN IP Network GGSN External IP Network Legend: Affected by EDGE BSS Base Station Subsystem HLR Home Location Register EIR Equipment Identity Register MS Mobile Station GGSN Gateway GPRS Support Node MSC Mobile Switching Centre GMSC Gateway Mobile Switching Centre SGSN Serving GPRS Support Node Fig. 1. EDGE Architecture In order to increase the radio gross bit rate, a linear high-level modulation, i.e., 8-Phase Shift Keying (8-PSK) is introduced for EDGE. 8-PSK is chosen because it provides high data rates and high spectral eciency. Many EDGE physical layer parameters are identical to those of GSM. The carrier spacing is 200kHz and GSM's TDMA frame structure is unchanged. Also, the GSM burst structure and period, which is equal to 6:2sec remained. In addition to the physical layer, EDGE also makes enhancements to the Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol. EDGE RLC protocol is somewhat dierent from the corresponding GPRS RLC protocol due to higher bit rate and the need to adapt the data protection to channel quality. The main changes are related to improvements in link quality control scheme. Presently, EDGE includes two link quality control techniques [3], namely, Link Adaptation (LA) and Incremental Redundancy (IR). The LA scheme estimates the link quality and subsequently selects the most appropriate coding scheme for coming transmissions in order to maximize the throughput. EDGE denes six dierent coding schemes (PCS-1 to PCS-6) on top of those of GPRS (CS-1 to CS-4) as described in Table 1. The coding schemes have dierent radio interface rates and robustness, and are therefore optimal for use in dierent linkquality regions. The LA scheme ensures that the most ecient scheme is always selected. In other words, a more robust scheme is employed for bad channel conditions and a less robust one (e.g., PCS-6) for good channel conditions. LA requires feedback information from the receiver to the transmitter about the link conditions in order to select the most appropriate
4 4 HPTan et al. Table 1. Channel Coding Schemes for EGPRS/EDGE Coding Scheme Code Rate Modulation Radio Interface Rate per Timeslot PCS PSK kbps PCS PSK kbps PCS PSK 41.2 kbps PCS PSK 1.60 kbps PCS PSK.3 kbps PCS PSK 6.20 kbps CS GMSK.20 kbps CS GMSK 14.0 kbps CS GMSK 16.0 kbps CS-4 1 GMSK kbps coding scheme. Normally, such information consists of parameters such as mean Carrier-to-Interference ratio (C/I) or Signal-to-Noise Ratio (S/N). In the simulation study, we use the C/I parameter to determine the link quality. However, it is impossible to know C/I beforehand, and can only be estimated. Two dierent methods [] can be employed to estimate C/I and both methods were used and compared in the simulation. In the rst method, the C/I is estimated by averaging the measured C/I over the latest polling interval, which is a number of RLC blocks. This estimation is used to select the coding scheme providing the highest throughput for the given C/I. The throughput (Sn) per time slot for each codingscheme, n, can be determined from the following equation [10]: Sn = Rn:(1 ; BLERn(C=I)) (1) where the radio interface rates (Rn) are given in Table 1, and the BLock Error Rate (BLERn) for a given C/I can be obtained from []. The task of LA is to always select the coding scheme, n, which maximizes Sn according to Eq.(1). The second method uses BLER to indicate the C/I level. For each polling interval, the BLERn for the coding scheme, n, is computed as follows: BLERn = Number of Erroneous Blocks T otal Number ofblocks per Interval (2) If the BLERn lies above a certain threshold, a more robust coding scheme than the current one should be used, otherwise a weaker scheme should be chosen. Both methods always start with the weakest coding scheme, i.e., PCS-6. In the IR scheme, information is rst sent with very little coding, yielding a high bit rate if decoding is immediately successful. If if decoding fails, additional coded bits are sent until decoding succeeds. As a result, the bit rate is lower and the delay increases.
5 3 Simulation Environment Lecture Notes in Computer Science As mentioned, the focus of the paper is on the enhanced packet-switched transmission mode of EDGE, i.e., EGPRS for wireless Internet access. Thus, the performance of TCP is simulated over EGPRS. The simulation was carried out using the ns and its wireless extensions from the Carnegie Mellon University's MONARCH Project [12]. The network conguration used for the simulation study is depicted in Fig. 2(a), which shows end-to-end communications between a single MS and a Fixed Host (FH). Each of the logical entities in the conguration can be realized as an ns node and links are dened to connect these nodes. As illustrated in Fig. 2(b), the FH, GGSN, and SGSN were dened as ns wired nodes, which in turn connected by duplex links. The BSS and MS were dened as ns wireless nodes and they are linked via a wireless channel. Delays and packet losses introduced by the IP network can be modelled in ns by attaching an Error Model (see Fig. 2(b)) on the link between FH and GGSN. The model species the link mean packet loss rate and mean delay. The protocol layers dened for each node is shown in Fig. 2(c). The application layer was implemented by attaching an application object, e.g., FTP, to the TCP agent dened for the end nodes (MS or FH). In the simulation, the FTP object was dened at FH to support uni-directional transfer of bulk data from FH to MS. TCP Agents (source or sink) were dened at the end nodes to implement end-to-end ow control. In the simulation, one-way TCP Tahoe version was used. The EDGE and TCP/IP parameters used in the simulation are summarized in Table 2. Table 2. Simulation Parameters Parameter Value Parameter Value Simulation Time 2000 seconds C/I range 6-30dB TCP version Tahoe RLC Polling Interval 10 blocks TCP Packet Size 12 bytes Frequency Hopping Ideal TCP Window Size 16 segments Modulation Schemes 8-PSK, GMSK Mean Internet Delay 100 s Number of Timeslot(TS) 1 Mean Internet Loss 0.01 Number of MS 1 Coding Schemes PCS-1 to PCS-6, Environment Typical urban, CS-1 to CS-4 low mobility (user speed 3km/hr) 4 Simulation Results and Observations End-to-end TCP performance over EGPRS was evaluated for bulk data transfer from FH to MS based on the scenario in Fig. 2(a) under various channel conditions. Trace agents were attached to the TCP source and sink so that arrival and departure time of each packet was recorded on the packet header. The
6 6 HPTan et al. EDGE-enabled MS BSS SGSN GGSN IP Network (a) Fixed Host Error Model EDGEenabled MS BSS SGSN GGSN Fixed Host Wireless Node Wired Node (b) Application Application TCP Agent TCP Agent TCP/UDP TCP/UDP IP IP Relay IP Relay IP Relay IP SNDCP/LLC SNDCP/LLC RLC/MAC RLC/MAC PHL PHL EDGE-enabled MS BSS SGSN GGSN Fixed Host Error Model Flow Control Wireless Link Wired Link (c) Fig. 2. (a) Top-Level Simulation Environment (b) Realization of the Top-Level Simulation Environment inns (c) Protocol Structure in ns
7 Lecture Notes in Computer Science TCP throughput is then computed from the trace output. In the simulation, the throughput was measured for each EGPRS coding scheme under various channel conditions with and without the LA scheme. Firstly, we will consider the throughput without the LA scheme. Fig. 3(a) depicts the simulated throughput without the LA scheme and Fig. 3(b) illustrates the theoretical throughput determined using Eq.(1). By comparing Figs. 3(a) and 3(b), the simulated throughput levels are signicantly lower than the corresponding theoretical values under all channel conditions. This is because the throughput computed using Eq.(1) assumes that most of the RLC blocks are successfully transmitted on the rst attempt. However, for EGPRS coding schemes, which are highly sensitive to noise, signicant retansmissions occur that can contribute to additional latency, resulting in throughput degradation. If we take latency into account then Eq.(1) can be re-written as follows: Sn = Rn:(1 ; BLERn(C=I)) (1 + BLERn(C=I)) The theoretical throughput, which is computed using Eq.(3) is shown in Fig. 3(c) and the peak throughput levels under good channel conditions are in agreement with the simulated throughput as in Fig. 3(a). For the throughput performance with the LA scheme, there are two methods that can be used to estimate C/I as described in Section 2. Both methods were considered in the simulation. Figs. 4(a) and 4(b) depict the throughput obtained byaveraging the measured C/I and BLER, respectively. In addition, both gures show the maximum simulated throughput in the case of ideal link adaptation, which is determined by selecting the maximum throughput at each C/I over all the coding schemes. For the case where C/I is estimated by averaging the measured C/I, the throughput approximates the performance of the ideal link adaptation under very good channel conditions (when C/I > 2 db) but fails to deliver useful throughput as channel conditons deteriorate. The BLER method, on the other hand, achieves throughput performance of the ideal link adaptation for bad channel conditions (when C/I < 12 db) but unable to reach theideal link adaptation performance when channel conditions improve. Hence, we propose a hybrid method, which selects the BLER method for bad channel conditions and the average measured C/I method for good channel conditions. The throughput obtained using this hybrid method is plotted in Fig. 4(c) and compared with the average measured C/I and BLER. As shown in the gure, the throughput performance of the hybrid method is superior compared to the individual method. (3) Conclusions EDGE is a radio-access technology capable of providing wireless Internet access within the framework of 3G. It reuses GSM technology and oers higher bit rates. In this paper, we investigated the performance of TCP/IP over EDGE using the ns simulation tool. We presented the simulated TCP throughput results with and
8 8 HPTan et al (a) (b) (c) CS-1 CS-2 CS-3 CS-4 PCS-1 PCS-2 PCS-3 PCS-4 PCS- PCS-6 CS-1 CS-2 CS-3 CS-4 PCS-1 PCS-2 PCS-3 PCS-4 PCS- PCS-6 CS-1 CS-2 CS-3 CS-4 PCS-1 PCS-2 PCS-3 PCS-4 PCS- PCS-6 Fig. 3. (a) Simulated Throughput (b) Theoretical Throughput (computed using Eq.(1)) (c) Theoretical Throughput (computed using Eq.(3))
9 Lecture Notes in Computer Science Actual LA Ideal LA (a) Actual LA Ideal LA (b) Ideal LA BLER Estimated C/I Hybrid (c) Fig. 4. (a) Simulated Throughput obtained using Estimated C/I Method (b) Simulated Throughput obtained using BLER Method (c) Simulated Throughput obtained using Hybrid Method
10 10 HPTan et al. without the link adaptation scheme and compared with the theoretical results. The simulated throughput results without link adaptation scheme are comparable to the theoretical one. However, the throughput deteriorates under poor channel conditions. Hence, the link adaptation scheme is designed to cope with poor channel conditions. The link adaptation scheme uses the C/I parameter to determine the link quality and subsequently selects the most appropriate coding scheme. In the simulation, the link adaptation employs two methods, BLER and the average of measured C/I, to determine the link quality. The throughput obtained using the BLER method is higher under poor channel conditions. On the other hand, the average measured C/I out-performs BLER under good channel conditions. As a result, we proposed a hybrid method, which selects the BLER method for poor channel conditions and the average measured C/I for good channel conditions. The simulation results show that the throughput obtained using the hybrid method is superior to the individual method. References 1. ETSI. GSM 03.34: Digital Cellular Telecommunications System (phase 2+) High Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD) Stage 2, ETSI. GSM 03.64: Digital Cellular Telecommunications System (phase 2+) General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Overall Description of the GPRS Radio Interface Stage 2, A. Furuskar et al. \EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates for GSM and TDMS/6 Evolution". IEEE Personal Communications Magazine, pages 6{66, June W. Stevens. TCP/IP Illustrated, Vol. 1. Addison Wesley, Reading, MA, 14.. R. Caceres and L. Iftode. \Improving the Performance of Reliable Transport Protocols in Mobile Computing Environments". IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, ():80{8, S. Seshan H. Balakrishnan and R. Katz. \Improving Reliable Transport and Hando Performance in Cellular Wireless Networks". ACM Wireless Networks, 1(4), 1.. K. Fall and K. Varadhan. ns Notes and Documentation. LBNL, January S. Hamiti et al. \EDGE Circuit Switched Data - An Enhancement of GSM Data Services". In IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, pages 143{1441, September 1.. O. Qeuseth et al. \Algorithms for Link Adaptation in GPRS". In IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC), pages 43{4, May A. Furuskar et al. \System Performance of EDGE, a Proposal for Enhanced Data Rates in Existing Digital Cellular Systems". In IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC), pages 1284{128, May 18.. UWCC. UWC-6 RTT Update. TR4.3/ R4, February Carnegie Mellon University. The CMU Monarch Project's Wireless and Mobility Extensions to ns, August 1.
Acknowledgments. TCP Performance over EGPRS/EDGE PAGE- i -
 Acknowledgments I would like to acknowledge and express my appreciation to Dr Anthony Lo and Dr Winston Seah (Centre for Wireless Communications, National University of Singapore) for their invaluable
Acknowledgments I would like to acknowledge and express my appreciation to Dr Anthony Lo and Dr Winston Seah (Centre for Wireless Communications, National University of Singapore) for their invaluable
Implementation of a WAP model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks. Henrik Fållby
 Implementation of a WAP model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks Henrik Fållby Outline Scoop of this thesis Packet switched vs. circuit switched networks Packet Data in GSM radio networks
Implementation of a WAP model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks Henrik Fållby Outline Scoop of this thesis Packet switched vs. circuit switched networks Packet Data in GSM radio networks
Chapter 2 The 3G Mobile Communications
 Chapter 2 The 3G Mobile Communications 2.1 The Vision for Third Generation (3G) Mobile Communication Systems: The vision for the emerging mobile and personal communication services for the new century
Chapter 2 The 3G Mobile Communications 2.1 The Vision for Third Generation (3G) Mobile Communication Systems: The vision for the emerging mobile and personal communication services for the new century
An Efficient DECT-Mobile IP Interworking for Mobile Computing
 An Efficient DECT-Mobile IP Interworking for Mobile Computing Anthony Lo *, Winston Seah * and Edwin Schreuder + * Centre for Wireless Communications 1, National University of Singapore, 20 Science Park
An Efficient DECT-Mobile IP Interworking for Mobile Computing Anthony Lo *, Winston Seah * and Edwin Schreuder + * Centre for Wireless Communications 1, National University of Singapore, 20 Science Park
Implementation of a WAP model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks
 Implementation of a model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks Henrik Fållby Outline Scoop of this thesis switched vs. circuit switched networks Data in GSM radio networks Wireless Application
Implementation of a model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks Henrik Fållby Outline Scoop of this thesis switched vs. circuit switched networks Data in GSM radio networks Wireless Application
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 13 GPRS
 GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 13 GPRS 1 Two switching modes Circuit Switching Packet switching 2 Circuit switching A connection first sets up Then the entire data transmits through the path that
GSM and Similar Architectures Lesson 13 GPRS 1 Two switching modes Circuit Switching Packet switching 2 Circuit switching A connection first sets up Then the entire data transmits through the path that
GPRS and UMTS T
 GPRS and UMTS T-110.2100 Global Packet Radio Service GPRS uses the time slots not used for circuit switched services Data rate depends on the availability of free time slots GPRS uses the multislot technique,
GPRS and UMTS T-110.2100 Global Packet Radio Service GPRS uses the time slots not used for circuit switched services Data rate depends on the availability of free time slots GPRS uses the multislot technique,
Evaluation of End-to-End TCP performance over WCDMA
 Evaluation of End-to-End TCP performance over WCDMA Liang Hu Department of Communications, Optics & Materials Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark Email:{lh}@com.dtu.dk Abstract this article
Evaluation of End-to-End TCP performance over WCDMA Liang Hu Department of Communications, Optics & Materials Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark Email:{lh}@com.dtu.dk Abstract this article
Base Station Subsystem Key Performance Indicators in EGPRS
 Base Station Subsystem Key Performance Indicators in EGPRS Anders Arte Supervisor: Prof. Sven-Gustav Häggman Instructor: M.Sc. Leo Bhebhe Content Introduction Objectives and Methodology EGPRS EGPRS Fundamentals
Base Station Subsystem Key Performance Indicators in EGPRS Anders Arte Supervisor: Prof. Sven-Gustav Häggman Instructor: M.Sc. Leo Bhebhe Content Introduction Objectives and Methodology EGPRS EGPRS Fundamentals
INTRODUCTION TO GSM DATA SERVICES. ETI25111 Monday, April 3, 2017
 INTRODUCTION TO GSM DATA SERVICES ETI25111 Monday, April 3, 2017 BASIC GSM SERVICES 1. Teleservices (a) Voice full-rate (13kbs) (b) Voice Half-rate (6.5 kbps) (c) SMS (up to 160 characters) (d) MMS (e)
INTRODUCTION TO GSM DATA SERVICES ETI25111 Monday, April 3, 2017 BASIC GSM SERVICES 1. Teleservices (a) Voice full-rate (13kbs) (b) Voice Half-rate (6.5 kbps) (c) SMS (up to 160 characters) (d) MMS (e)
On the Importance of Using Appropriate Link-to-System Level Interfaces for the Study of Link Adaptation
 On the Importance of Using Appropriate Link-to-System Level Interfaces for the Study of Link Adaptation Javier Gozalvez and John Dunlop Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of
On the Importance of Using Appropriate Link-to-System Level Interfaces for the Study of Link Adaptation Javier Gozalvez and John Dunlop Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of
GPRS System Architecture
 1 LECTURE 6 GPRS What is GPRS? 2 General Packet Radio Service is an overlay on top of GSM physical layer and network entities It extends data capabilities of GSM and provides connection to external packet
1 LECTURE 6 GPRS What is GPRS? 2 General Packet Radio Service is an overlay on top of GSM physical layer and network entities It extends data capabilities of GSM and provides connection to external packet
GSM. Course requirements: Understanding Telecommunications book by Ericsson (Part D PLMN) + supporting material (= these slides) GPRS
 GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
GSM Example of a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) At present most successful cellular mobile system (over 200 million subscribers worldwide) Digital (2 nd Generation) cellular mobile system operating
Performance of LLC and TCP on GPRS Uplink with RLC Slot Level Retransmission
 Performance of LLC and TCP on GPRS Uplink with RLC Slot Level Retransmission K. Premkumar and A. Chockalingam Wireless Research Lab (http://wrl.ece.iisc.ernet.in) Department of Electrical Communication
Performance of LLC and TCP on GPRS Uplink with RLC Slot Level Retransmission K. Premkumar and A. Chockalingam Wireless Research Lab (http://wrl.ece.iisc.ernet.in) Department of Electrical Communication
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR GPRS WITH PRIORITIZED AND NON-PRIORITIZED MOBILITY MANAGEMENT PROCEDURES
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR GPRS WITH PRIORITIZED AND NON-PRIORITIZED MOBILITY MANAGEMENT PROCEDURES Karann Chew, Rahim Tafazolli University of Surrey, United Kingdom Abstract - GPRS is part of the evolution
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR GPRS WITH PRIORITIZED AND NON-PRIORITIZED MOBILITY MANAGEMENT PROCEDURES Karann Chew, Rahim Tafazolli University of Surrey, United Kingdom Abstract - GPRS is part of the evolution
Lecture overview. Modifications and derivatives of GSM Data transmission in GSM: HSCSD GPRS part one EDGE
 Lecture overview Modifications and derivatives of GSM Data transmission in GSM: HSCSD GPRS part one EDGE Modifications and derivatives of GSM Introduction of half-rate speech coding (BR 6.5 kb/s) Two users
Lecture overview Modifications and derivatives of GSM Data transmission in GSM: HSCSD GPRS part one EDGE Modifications and derivatives of GSM Introduction of half-rate speech coding (BR 6.5 kb/s) Two users
Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. part 1: General considerations. Mobile Telephony Networks
 Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. part 1: General considerations Mobile Telephony Networks 1 The Evolution of Mobile Telephony 1st Generation 2nd 3rd 4th Analogue Voice
Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. part 1: General considerations Mobile Telephony Networks 1 The Evolution of Mobile Telephony 1st Generation 2nd 3rd 4th Analogue Voice
SIMULATION FRAMEWORK MODELING
 CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION FRAMEWORK MODELING 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter starts with the design and development of the universal mobile communication system network and implementation of the TCP congestion
CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION FRAMEWORK MODELING 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter starts with the design and development of the universal mobile communication system network and implementation of the TCP congestion
TCP PERFORMANCE FOR FUTURE IP-BASED WIRELESS NETWORKS
 TCP PERFORMANCE FOR FUTURE IP-BASED WIRELESS NETWORKS Deddy Chandra and Richard J. Harris School of Electrical and Computer System Engineering Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology Melbourne, Australia
TCP PERFORMANCE FOR FUTURE IP-BASED WIRELESS NETWORKS Deddy Chandra and Richard J. Harris School of Electrical and Computer System Engineering Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology Melbourne, Australia
Backbone Router. Base Station. Fixed Terminal. Wireless Terminal. Fixed Terminal. Base Station. Backbone Router. Wireless Terminal. time.
 Combining Transport Layer and Link Layer Mechanisms for Transparent QoS Support of IP based Applications Georg Carle +, Frank H.P. Fitzek, Adam Wolisz + Technical University Berlin, Sekr. FT-2, Einsteinufer
Combining Transport Layer and Link Layer Mechanisms for Transparent QoS Support of IP based Applications Georg Carle +, Frank H.P. Fitzek, Adam Wolisz + Technical University Berlin, Sekr. FT-2, Einsteinufer
Wireless Communication Systems. Lesson Outline
 Wireless Communication Systems Kimmo Raatikainen kimmo.raatikainen@cs.helsinki.fi Petrozavodsk Kimmo Raatikainen September 7, 2004 Lesson Outline GSM Data GPRS High Speed Circuit Switched Data Wireless
Wireless Communication Systems Kimmo Raatikainen kimmo.raatikainen@cs.helsinki.fi Petrozavodsk Kimmo Raatikainen September 7, 2004 Lesson Outline GSM Data GPRS High Speed Circuit Switched Data Wireless
GSM System Overview. Ph.D. Phone Lin.
 GSM System Overview Phone Lin Ph.D. Email: plin@csie.ntu.edu.tw 1 Outlines Introduction GSM Architecture Location Tracking and Call Setup Security GSM Data Services Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
GSM System Overview Phone Lin Ph.D. Email: plin@csie.ntu.edu.tw 1 Outlines Introduction GSM Architecture Location Tracking and Call Setup Security GSM Data Services Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
Evolution from GSM to UMTS
 2 Evolution from GSM to UMTS Evolution is one of the most common terms used in the context of UMTS. Generally it is understood to mean the technical evolution, i.e. how and what kind of equipment and in
2 Evolution from GSM to UMTS Evolution is one of the most common terms used in the context of UMTS. Generally it is understood to mean the technical evolution, i.e. how and what kind of equipment and in
Analysis QoS Parameters for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols: Under Group Mobility Model
 2009 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications IPCSIT vol.2 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Analysis QoS Parameters for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols: Under Group
2009 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications IPCSIT vol.2 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Analysis QoS Parameters for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols: Under Group
Internal. GSM Fundamentals.
 Internal GSM Fundamentals www.huawei.com HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Chapter 1 GSM System Overview Chapter 2 GSM Network Structure Chapter 3 Service Area and Number Planning Chapter
Internal GSM Fundamentals www.huawei.com HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Chapter 1 GSM System Overview Chapter 2 GSM Network Structure Chapter 3 Service Area and Number Planning Chapter
Evaluating the Eifel Algorithm for TCP in a GPRS Network
 Evaluating the Eifel Algorithm for TCP in a GPRS Network Andrei Gurtov University of Helsinki Finland e-mail: Andrei.Gurtov@cs.Helsinki.FI Reiner Ludwig Ericsson Research Germany e-mail: Reiner.Ludwig@Ericsson.com
Evaluating the Eifel Algorithm for TCP in a GPRS Network Andrei Gurtov University of Helsinki Finland e-mail: Andrei.Gurtov@cs.Helsinki.FI Reiner Ludwig Ericsson Research Germany e-mail: Reiner.Ludwig@Ericsson.com
No ARQ ARQ with 2 ReTX ARQ with 9 ReTX RPA DPA BSS. BSS EGPRS Network E-GSN. Music Server E-GSN E-GSN. E-GSN Public Internet Backbone BSS
 Transmission of Streaming Data over an EGPRS Wireless Network Kapil Chawla, Peter F. Driessen and Xiaoxin Qiu AT&T Laboratories - Research 100 Schulz Drive, Red Bank, NJ 07701, USA Email: fkapil,pfd,xqiug@research.att.com
Transmission of Streaming Data over an EGPRS Wireless Network Kapil Chawla, Peter F. Driessen and Xiaoxin Qiu AT&T Laboratories - Research 100 Schulz Drive, Red Bank, NJ 07701, USA Email: fkapil,pfd,xqiug@research.att.com
ANALYTICAL PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF INTERNET ACCESS OVER GPRS AND ITS COMPARISON WITH SIMULATION RESULTS
 ANALYTICAL PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF INTERNET ACCESS OVER GPRS AND ITS COMPARISON WITH SIMULATION RESULTS Tim Irnich, Peter Stuckmann Aachen University of Technology (RWTH), Chair of Communication Networks
ANALYTICAL PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF INTERNET ACCESS OVER GPRS AND ITS COMPARISON WITH SIMULATION RESULTS Tim Irnich, Peter Stuckmann Aachen University of Technology (RWTH), Chair of Communication Networks
Due to the many benefits provided by both the third-generation (3G) mobile networks and the IEEE wireless local area networks (WLANs), it is
 Performance of UMTS/WLAN Integration at Hot-Spot Locations Using OPNET Marwan Abu-Amara, Ashraf Mahmoud, Tarek Sheltami, Adel Al-Shahrani, Khalid Al-Otaibi, S.M.Rehman, and Taha Anwar {marwan, ashraf,
Performance of UMTS/WLAN Integration at Hot-Spot Locations Using OPNET Marwan Abu-Amara, Ashraf Mahmoud, Tarek Sheltami, Adel Al-Shahrani, Khalid Al-Otaibi, S.M.Rehman, and Taha Anwar {marwan, ashraf,
WIRELESS LANs: THE DECT APPROACH
 WIRELESS LANs: THE DECT APPROACH Anthony Lo Centre for Wireless Communications National University of Singapore 20 Science Park Road #02-34/37 TeleTech Park Singapore Science Park II Singapore 117674 Email:
WIRELESS LANs: THE DECT APPROACH Anthony Lo Centre for Wireless Communications National University of Singapore 20 Science Park Road #02-34/37 TeleTech Park Singapore Science Park II Singapore 117674 Email:
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION FUNDAMENTALS
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE& NAME: IT1403 MOBILE COMPUTING YEAR / SEM : IV / VIII UNIT-1 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION FUNDAMENTALS PART A (2MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE& NAME: IT1403 MOBILE COMPUTING YEAR / SEM : IV / VIII UNIT-1 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION FUNDAMENTALS PART A (2MARKS)
Performance Analysis of Cell Switching Management Scheme in Wireless Packet Communications
 Performance Analysis of Cell Switching Management Scheme in Wireless Packet Communications Jongho Bang Sirin Tekinay Nirwan Ansari New Jersey Center for Wireless Telecommunications Department of Electrical
Performance Analysis of Cell Switching Management Scheme in Wireless Packet Communications Jongho Bang Sirin Tekinay Nirwan Ansari New Jersey Center for Wireless Telecommunications Department of Electrical
Performance and Configuration of Link Adaptation Algorithms with Mobile Speed
 Performance and Configuration of Link Adaptation Algorithms with Mobile Speed Javier Gozalvez* and John Dunlop** *Now with the Signal Theory and Communications Division at the University Miguel Hernández
Performance and Configuration of Link Adaptation Algorithms with Mobile Speed Javier Gozalvez* and John Dunlop** *Now with the Signal Theory and Communications Division at the University Miguel Hernández
Real-World Experience with a Mobile Broadband Network
 Real-World Experience with a Mobile Broadband Network Dr. Jin Yang Verizon Wireless jin.yang@ieee.org September 23, 2004 IEEE Communications Society Oakland-East Bay Chapter, CA Outline Introduction Overview
Real-World Experience with a Mobile Broadband Network Dr. Jin Yang Verizon Wireless jin.yang@ieee.org September 23, 2004 IEEE Communications Society Oakland-East Bay Chapter, CA Outline Introduction Overview
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY QUESTION BANK UNIT I PART A (2MARKS)
 DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY QUESTION BANK Subject Code : IT1402 Subject Name : Mobile Computing Year / Sem : IV / VII UNIT I PART A (2MARKS) 1.What are the 3 fundamental propagation behaviors
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY QUESTION BANK Subject Code : IT1402 Subject Name : Mobile Computing Year / Sem : IV / VII UNIT I PART A (2MARKS) 1.What are the 3 fundamental propagation behaviors
Nexus8610 Traffic Simulation System. Intersystem Handover Simulation. White Paper
 Traffic Simulation System Intersystem Handover Simulation White Paper Notice Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this document was accurate at the time of printing. However, the
Traffic Simulation System Intersystem Handover Simulation White Paper Notice Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this document was accurate at the time of printing. However, the
Mobile Systems Challenges in Next Generation Networks
 International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking 15 Mobile Systems Challenges in Next Generation Networks Seyed Ali Alavian, Jahangir Dadkhah Chimeh Faculty of Applied Science of
International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking 15 Mobile Systems Challenges in Next Generation Networks Seyed Ali Alavian, Jahangir Dadkhah Chimeh Faculty of Applied Science of
Trillium 3G Wireless Software
 White Paper Feburary 2010 Trillium 3G Wireless Software By Ravi Raj Bhat, Vice President of Engineering This white paper presents an overview of technology trends in the wireless market, a historical overview
White Paper Feburary 2010 Trillium 3G Wireless Software By Ravi Raj Bhat, Vice President of Engineering This white paper presents an overview of technology trends in the wireless market, a historical overview
UMTS & New Technologies «Wireless data world»
 EPFL Section Systèmes de Communication Cours Mobile Networks UMTS & New Technologies «Wireless data world» Alexandre LEHERICEY Radio Access Engineering 21/12/2004 mailto: alexandre.lehericey@orange.ch
EPFL Section Systèmes de Communication Cours Mobile Networks UMTS & New Technologies «Wireless data world» Alexandre LEHERICEY Radio Access Engineering 21/12/2004 mailto: alexandre.lehericey@orange.ch
Cross-layer TCP Performance Analysis in IEEE Vehicular Environments
 24 Telfor Journal, Vol. 6, No. 1, 214. Cross-layer TCP Performance Analysis in IEEE 82.11 Vehicular Environments Toni Janevski, Senior Member, IEEE, and Ivan Petrov 1 Abstract In this paper we provide
24 Telfor Journal, Vol. 6, No. 1, 214. Cross-layer TCP Performance Analysis in IEEE 82.11 Vehicular Environments Toni Janevski, Senior Member, IEEE, and Ivan Petrov 1 Abstract In this paper we provide
Talk 4: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks
 Talk 4: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks IEEE Wireless Communication, Oct. 2002 Presented by Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering
Talk 4: WLAN-GPRS Integration for Next-Generation Mobile Data Networks IEEE Wireless Communication, Oct. 2002 Presented by Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering
SERVICE DISCIPLINES PERFORMANCE FOR GPRS WITH LINK ADAPTATION AND HETEROGENEOUS TRAFFIC
 SERVICE DISCIPLINES PERFORMANCE FOR GPRS WITH LINK ADAPTATION AND HETEROGENEOUS TRAFFIC Josep Bada and Fernando Casadevall Universitat Politécnica de Catalunya, Jordi Girona 1-3, 08034 Barcelona- Spain,
SERVICE DISCIPLINES PERFORMANCE FOR GPRS WITH LINK ADAPTATION AND HETEROGENEOUS TRAFFIC Josep Bada and Fernando Casadevall Universitat Politécnica de Catalunya, Jordi Girona 1-3, 08034 Barcelona- Spain,
FROM GSM TO LTE-ADVANCED: AN INTRODUCTION TO MOBILE NETWORKS AND MOBILE BROADBAND 2. GENERAL PACKET RADIO SERVICE (GPRS) AND EDGE
 FROM GSM TO LTE-ADVANCED: AN INTRODUCTION TO MOBILE NETWORKS AND MOBILE BROADBAND 2. GENERAL PACKET RADIO SERVICE (GPRS) AND EDGE GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) Enhance GSM to transport data in an
FROM GSM TO LTE-ADVANCED: AN INTRODUCTION TO MOBILE NETWORKS AND MOBILE BROADBAND 2. GENERAL PACKET RADIO SERVICE (GPRS) AND EDGE GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) Enhance GSM to transport data in an
Cellular Networks and Mobility
 Cellular Networks and Mobility Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Cellular Networks GSM 2G/3G Architecture 3/20 2G Standard 4/20 GSM: combined FDM/TDM divide into 200 khz
Cellular Networks and Mobility Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Cellular Networks GSM 2G/3G Architecture 3/20 2G Standard 4/20 GSM: combined FDM/TDM divide into 200 khz
Ch.16 - Wireless WAN System Architectures
 Ch.16 - Wireless WAN System Architectures 1 Wireless WAN 2 GSM via PSTN 3 GSM via ISDN 4 GPRS 5 Mobitex 6 CDPD 7 PPDC 8 UMTS 9 Future Systems 10 Systems Summary 1 11 Systems Summary 2 1 This section will
Ch.16 - Wireless WAN System Architectures 1 Wireless WAN 2 GSM via PSTN 3 GSM via ISDN 4 GPRS 5 Mobitex 6 CDPD 7 PPDC 8 UMTS 9 Future Systems 10 Systems Summary 1 11 Systems Summary 2 1 This section will
End-to-end IP Service Quality and Mobility - Lecture #5 -
 End-to-end IP Service Quality and Mobility - Lecture #5 - Special Course in Networking Technology S-38.215 vilho.raisanen@nokia.com Planned contents & draft schedule 1. Introduction Jan 13th 2. Characteristics
End-to-end IP Service Quality and Mobility - Lecture #5 - Special Course in Networking Technology S-38.215 vilho.raisanen@nokia.com Planned contents & draft schedule 1. Introduction Jan 13th 2. Characteristics
Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control
 Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control Qinqing Zhang, Hsuan-Jung Su Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies Holmdel, NJ 77 Abstract- The Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol in Universal Mobile Telecommunication
Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control Qinqing Zhang, Hsuan-Jung Su Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies Holmdel, NJ 77 Abstract- The Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol in Universal Mobile Telecommunication
RADIO AWARE SCTP EXTENSION FOR HANDOVER DATA IN EGPRS
 RADIO AWARE SCTP EXTENSION FOR HANDOVER DATA IN EGPRS Mériem Afif 1, Philippe Martins 2, Sami Tabbane 3 and Philippe Godlewski 4 1, 3, Mediatron, Ecole Supérieure des Communications de Tunis (Sup'Com),
RADIO AWARE SCTP EXTENSION FOR HANDOVER DATA IN EGPRS Mériem Afif 1, Philippe Martins 2, Sami Tabbane 3 and Philippe Godlewski 4 1, 3, Mediatron, Ecole Supérieure des Communications de Tunis (Sup'Com),
Enhancements and Performance Evaluation of Wireless Local Area Networks
 Enhancements and Performance Evaluation of Wireless Local Area Networks Jiaqing Song and Ljiljana Trajkovic Communication Networks Laboratory Simon Fraser University Burnaby, BC, Canada E-mail: {jsong,
Enhancements and Performance Evaluation of Wireless Local Area Networks Jiaqing Song and Ljiljana Trajkovic Communication Networks Laboratory Simon Fraser University Burnaby, BC, Canada E-mail: {jsong,
WIRELESS SYSTEM AND NETWORKING
 LECTURE 6 WIRELESS SYSTEM AND NETWORKING References: Rappaport (Chapter 9 and 10) Bernhard (Chapter 3, 4 and 5) Garg (Chapter 8 and 9) Kaarenen (Chapter 1-5 and 9) WIRELESS EVOLUTION Japan Europe Americas
LECTURE 6 WIRELESS SYSTEM AND NETWORKING References: Rappaport (Chapter 9 and 10) Bernhard (Chapter 3, 4 and 5) Garg (Chapter 8 and 9) Kaarenen (Chapter 1-5 and 9) WIRELESS EVOLUTION Japan Europe Americas
E2-E3: CONSUMER MOBILITY. CHAPTER-5 CDMA x OVERVIEW (Date of Creation: )
 E2-E3: CONSUMER MOBILITY CHAPTER-5 CDMA 2000 1x OVERVIEW (Date of Creation: 01-04.2011) Page: 1 CDMA 2000 1X Overview Introduction CDMA (code division multiple access) is a mobile digital radio technology
E2-E3: CONSUMER MOBILITY CHAPTER-5 CDMA 2000 1x OVERVIEW (Date of Creation: 01-04.2011) Page: 1 CDMA 2000 1X Overview Introduction CDMA (code division multiple access) is a mobile digital radio technology
Mobile and Sensor Systems
 Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
Mobile and Sensor Systems Lecture 2: Mobile Medium Access Control Protocols and Wireless Systems Dr Cecilia Mascolo In this lecture We will describe medium access control protocols and wireless systems
VIRTUAL CONNECTION TREE FOR 3G WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 VIRTUAL CONNECTION TREE FOR 3G WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Rajinder Kumar Department of Computer Science and Engineering Punjab Engineering College,Chandigarh raajinderkumar@gmail.com Abstract This
VIRTUAL CONNECTION TREE FOR 3G WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Rajinder Kumar Department of Computer Science and Engineering Punjab Engineering College,Chandigarh raajinderkumar@gmail.com Abstract This
Improving Reliable Transport and Handoff Performance in Cellular Wireless Networks
 Improving Reliable Transport and Handoff Performance in Cellular Wireless Networks H. Balakrishnan, S. Seshan, and R. H. Katz ACM Wireless Networks Vol. 1, No. 4, pp. 469-482 Dec. 1995 P. 1 Introduction
Improving Reliable Transport and Handoff Performance in Cellular Wireless Networks H. Balakrishnan, S. Seshan, and R. H. Katz ACM Wireless Networks Vol. 1, No. 4, pp. 469-482 Dec. 1995 P. 1 Introduction
Discriminating Congestion Losses from Wireless Losses using. Inter-Arrival Times at the Receiver. Texas A&M University.
 Discriminating Congestion Losses from Wireless Losses using Inter-Arrival Times at the Receiver Saad Biaz y Nitin H. Vaidya Department of Computer Science Texas A&M University College Station, TX 7784-,
Discriminating Congestion Losses from Wireless Losses using Inter-Arrival Times at the Receiver Saad Biaz y Nitin H. Vaidya Department of Computer Science Texas A&M University College Station, TX 7784-,
On the Optimizing of LTE System Performance for SISO and MIMO Modes
 2015 Third International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation On the Optimizing of LTE System Performance for SISO and MIMO Modes Ali Abdulqader Bin Salem, Yung-Wey Chong, Sabri
2015 Third International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation On the Optimizing of LTE System Performance for SISO and MIMO Modes Ali Abdulqader Bin Salem, Yung-Wey Chong, Sabri
Signaling System 7 (SS7) By : Ali Mustafa
 Signaling System 7 (SS7) By : Ali Mustafa Contents Types of Signaling SS7 Signaling SS7 Protocol Architecture SS7 Network Architecture Basic Call Setup SS7 Applications SS7/IP Inter-working VoIP Network
Signaling System 7 (SS7) By : Ali Mustafa Contents Types of Signaling SS7 Signaling SS7 Protocol Architecture SS7 Network Architecture Basic Call Setup SS7 Applications SS7/IP Inter-working VoIP Network
Packet or Circuit Switched Voice Radio Bearers - A Capacity Evaluation for GERAN
 Packet or Circuit Switched Voice Radio Bearers - A Capacity Evaluation for GERAN Mats Arvedson, Magnus Edlund, Ola Eriksson, Andreas Nordin and Anders Furuskär Radio Communications Systems, S3, Royal Institute
Packet or Circuit Switched Voice Radio Bearers - A Capacity Evaluation for GERAN Mats Arvedson, Magnus Edlund, Ola Eriksson, Andreas Nordin and Anders Furuskär Radio Communications Systems, S3, Royal Institute
Delay Performance of the New Explicit Loss Notification TCP Technique for Wireless Networks
 Delay Performance of the New Explicit Loss Notification TCP Technique for Wireless Networks Wenqing Ding and Abbas Jamalipour School of Electrical and Information Engineering The University of Sydney Sydney
Delay Performance of the New Explicit Loss Notification TCP Technique for Wireless Networks Wenqing Ding and Abbas Jamalipour School of Electrical and Information Engineering The University of Sydney Sydney
Improving TCP End to End Performance in Wireless LANs with Snoop Protocol
 Improving TCP End to End Performance in Wireless LANs with Snoop Protocol Dejan Jaksic, Zeljko Ilic and Alen Bazant Department of Telecommunications, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Unska
Improving TCP End to End Performance in Wireless LANs with Snoop Protocol Dejan Jaksic, Zeljko Ilic and Alen Bazant Department of Telecommunications, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Unska
The effect of Mobile IP handoffs on the performance of TCP
 Mobile Networks and Applications 4 (1999) 131 135 131 The effect of Mobile IP handoffs on the performance of TCP Anne Fladenmuller a and Ranil De Silva b a Alcatel CIT, Software Department, Route de Nozay,
Mobile Networks and Applications 4 (1999) 131 135 131 The effect of Mobile IP handoffs on the performance of TCP Anne Fladenmuller a and Ranil De Silva b a Alcatel CIT, Software Department, Route de Nozay,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 11, November-2013 ISSN
 7 Location Management Strategies in Mobile Networks Vivek Kumar Department of Computer Science & Engineering Graphic Era University, Dehradun, INDIA vivekror7@gmail.com Narayan Chaturvedi Department of
7 Location Management Strategies in Mobile Networks Vivek Kumar Department of Computer Science & Engineering Graphic Era University, Dehradun, INDIA vivekror7@gmail.com Narayan Chaturvedi Department of
UNIVERSITY OF CYPRUS DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
 Master s Thesis Coverage and Capacity Planning in Enhanced UMTS Josephine Antoniou UNIVERSITY OF CYPRUS DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE June 2004 UNIVERSITY OF CYPRUS DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 1 Table
Master s Thesis Coverage and Capacity Planning in Enhanced UMTS Josephine Antoniou UNIVERSITY OF CYPRUS DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE June 2004 UNIVERSITY OF CYPRUS DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 1 Table
Communication Systems for the Mobile Information Society
 Communication Systems for the Mobile Information Society Martin Sauter Nortel Networks, Germany John Wiley Si Sons, Ltd Contents Preface List of Figures List of Tables List of Abbreviations xi xiii xix
Communication Systems for the Mobile Information Society Martin Sauter Nortel Networks, Germany John Wiley Si Sons, Ltd Contents Preface List of Figures List of Tables List of Abbreviations xi xiii xix
Signaling Protocol Structure in GSM
 GSM Signaling Protocol Structure in GSM Signaling Protocol Structure in GSM Layer 1 is the physical layer which uses the channel structures over the air interface. Layer 2 is the data link layer and across
GSM Signaling Protocol Structure in GSM Signaling Protocol Structure in GSM Layer 1 is the physical layer which uses the channel structures over the air interface. Layer 2 is the data link layer and across
SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK
 Chapter - 6 SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK The entire Research Work on On-Demand Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Mobile Ad hoc Networks has been presented in simplified and easy-to-read form in six
Chapter - 6 SUMMERY, CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK The entire Research Work on On-Demand Routing in Multi-Hop Wireless Mobile Ad hoc Networks has been presented in simplified and easy-to-read form in six
On the Performance of TCP Vegas over UMTS/WCDMA Channels with Large Round-Trip Time Variations
 On the Performance of TCP Vegas over UMTS/WCDMA Channels with Large Round-Trip Time Variations Anthony Lo 1, Geert Heijenk 2, and Ignas Niemegeers 1 1 Delft University of Technology, POBox5031, 2600 GA
On the Performance of TCP Vegas over UMTS/WCDMA Channels with Large Round-Trip Time Variations Anthony Lo 1, Geert Heijenk 2, and Ignas Niemegeers 1 1 Delft University of Technology, POBox5031, 2600 GA
Wireless Networks (CSC-7602) Lecture 1 (27 Aug 2007)
 Wireless Networks (CSC-7602) Lecture 1 (27 Aug 2007) Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark 1 Handouts Class information Schedule (check online frequently) 2 1 Goals Principles on Wireless
Wireless Networks (CSC-7602) Lecture 1 (27 Aug 2007) Seung-Jong Park (Jay) http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~sjpark 1 Handouts Class information Schedule (check online frequently) 2 1 Goals Principles on Wireless
COMP327 Mobile Computing Session: Lecture Set 5 - Wireless Communication Part 2
 COMP327 Mobile Computing Session: 2016-2017 Lecture Set 5 - Wireless Communication Part 2 51 SIM (Subscriber Identity Modules) Smart cards that are inserted into the GSM phone to identify the user Stores
COMP327 Mobile Computing Session: 2016-2017 Lecture Set 5 - Wireless Communication Part 2 51 SIM (Subscriber Identity Modules) Smart cards that are inserted into the GSM phone to identify the user Stores
Delayed ACK Approach for TCP Performance Improvement for Ad Hoc Networks Using Chain Topology
 Delayed ACK Approach for TCP Performance Improvement for Ad Hoc Networks Using Chain Topology Prashant Kumar Gupta M.Tech. Scholar, Computer Networks, Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg (C.G.), India
Delayed ACK Approach for TCP Performance Improvement for Ad Hoc Networks Using Chain Topology Prashant Kumar Gupta M.Tech. Scholar, Computer Networks, Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg (C.G.), India
Performance Analysis of TCP LBA and TCP TAHOE Approaches in g Standard Savreet KaurBrar 1, Sandeep Singh Kang 2
 Performance Analysis of TCP LBA and TCP TAHOE Approaches in 802.11g Standard Savreet KaurBrar 1, Sandeep Singh Kang 2 1 (MTechCSE Student, Chandigarh Engineering College Landran,India) 2 (Associate Professor
Performance Analysis of TCP LBA and TCP TAHOE Approaches in 802.11g Standard Savreet KaurBrar 1, Sandeep Singh Kang 2 1 (MTechCSE Student, Chandigarh Engineering College Landran,India) 2 (Associate Professor
Wireless Data Mobile Network Architecture and Technology
 Wireless Data Mobile Network Architecture and Technology 2001. 2. 15. yclee@sktelecom.com SK Telecom Wireless Data Mobile Network cdma2000 1X gmsgprs umtsgprs GPRS & Mobile IP EDGE & 1X EV-DO/DV EDGE 1X
Wireless Data Mobile Network Architecture and Technology 2001. 2. 15. yclee@sktelecom.com SK Telecom Wireless Data Mobile Network cdma2000 1X gmsgprs umtsgprs GPRS & Mobile IP EDGE & 1X EV-DO/DV EDGE 1X
ENSC 835: HIGH-PERFORMANCE NETWORKS CMPT 885: SPECIAL TOPICS: HIGH-PERFORMANCE NETWORKS
 ENSC 835: HIGH-PERFORMANCE NETWORKS CMPT 885: SPECIAL TOPICS: HIGH-PERFORMANCE NETWORKS GPRS: Wireless links, multiple base transmitter stations, base station controller and cell update Fall 2003 Final
ENSC 835: HIGH-PERFORMANCE NETWORKS CMPT 885: SPECIAL TOPICS: HIGH-PERFORMANCE NETWORKS GPRS: Wireless links, multiple base transmitter stations, base station controller and cell update Fall 2003 Final
Appeal Decision. Appeal No USA ALCATEL-LUCENT USA LTD. Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo, Japan
 Appeal Decision Appeal No. 2014-5131 USA Appellant ALCATEL-LUCENT USA LTD. Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney OKABE, Yuzuru Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney YOSHIZAWA, Hiroshi The case of appeal against the examiner's
Appeal Decision Appeal No. 2014-5131 USA Appellant ALCATEL-LUCENT USA LTD. Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney OKABE, Yuzuru Tokyo, Japan Patent Attorney YOSHIZAWA, Hiroshi The case of appeal against the examiner's
TCP over Wireless Networks Using Multiple. Saad Biaz Miten Mehta Steve West Nitin H. Vaidya. Texas A&M University. College Station, TX , USA
 TCP over Wireless Networks Using Multiple Acknowledgements (Preliminary Version) Saad Biaz Miten Mehta Steve West Nitin H. Vaidya Department of Computer Science Texas A&M University College Station, TX
TCP over Wireless Networks Using Multiple Acknowledgements (Preliminary Version) Saad Biaz Miten Mehta Steve West Nitin H. Vaidya Department of Computer Science Texas A&M University College Station, TX
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF TCP OVER ROUTING PROTOCOLS FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF TCP OVER ROUTING PROTOCOLS FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS Md. Abdullah-Al-Mamun, M. Mahbubur Rahman Department of Information and Communication Engineering Islamic University Kushtia
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF TCP OVER ROUTING PROTOCOLS FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS Md. Abdullah-Al-Mamun, M. Mahbubur Rahman Department of Information and Communication Engineering Islamic University Kushtia
Radio Resource Management in GPRS with Quality of Service
 Radio Resource Management in GPRS with Quality of Service Josep Bada, Ferran Casadevall, Javier Jiménez and Eduardo Medrano Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), Dept. of Signal Theory and Communications,
Radio Resource Management in GPRS with Quality of Service Josep Bada, Ferran Casadevall, Javier Jiménez and Eduardo Medrano Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), Dept. of Signal Theory and Communications,
Maximum bitrate for uplink Maximum bitrate for downlink 20, 40, 72 kbps
 An Enhanced Quality Of Service Method for Guaranteed rate Services over Shared Channels in EGPRS Systems Daniel Fernández and Héctor Montes Nokia Networks, C/ Severo Ochoa, s/n Edif. de Inst. Universitarios,
An Enhanced Quality Of Service Method for Guaranteed rate Services over Shared Channels in EGPRS Systems Daniel Fernández and Héctor Montes Nokia Networks, C/ Severo Ochoa, s/n Edif. de Inst. Universitarios,
B.E. ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SEMESTER - VII EC WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
 B.E. ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SEMESTER - VII EC2401 - WIRELESS COMMUNICATION Question Bank (ALL UNITS) UNIT-I: SERVICES & TECHNICAL CHALLENGES PART A 1. What are the types of Services? (Nov.
B.E. ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SEMESTER - VII EC2401 - WIRELESS COMMUNICATION Question Bank (ALL UNITS) UNIT-I: SERVICES & TECHNICAL CHALLENGES PART A 1. What are the types of Services? (Nov.
UMTS System Architecture and Protocol Architecture
 UMTS System Architecture and Protocol Architecture Overview on overall system architecture UMTS network architecture and elements Mobile station High-level functions UMTS domains and strata UMTS/GPRS protocol
UMTS System Architecture and Protocol Architecture Overview on overall system architecture UMTS network architecture and elements Mobile station High-level functions UMTS domains and strata UMTS/GPRS protocol
Internet. 1) Internet basic technology (overview) 3) Quality of Service (QoS) aspects
 Internet 1) Internet basic technology (overview) 2) Mobility aspects 3) Quality of Service (QoS) aspects Relevant information: these slides (overview) course textbook (Part H) www.ietf.org (details) IP
Internet 1) Internet basic technology (overview) 2) Mobility aspects 3) Quality of Service (QoS) aspects Relevant information: these slides (overview) course textbook (Part H) www.ietf.org (details) IP
EDGE Capabilities, Technology, and Applications
 EDGE Capabilities, Technology, and Applications devcentral White Paper Document Number 13218 Revision 1.0 Revision Date 9/16/2003 AT&T Wireless Developer Program 2003 AT&T Wireless. All rights reserved.
EDGE Capabilities, Technology, and Applications devcentral White Paper Document Number 13218 Revision 1.0 Revision Date 9/16/2003 AT&T Wireless Developer Program 2003 AT&T Wireless. All rights reserved.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 9, September-2016 ISSN
 ISSN 2229-5518 1044 Communication Requirements and Analysis of UMTS Based Smart Grids Distribution Networks Dr. Rajaa Aldeen Abd Khalid, Teba Adil Jihad Abstract- A smart grid (SG), an enhancement of the
ISSN 2229-5518 1044 Communication Requirements and Analysis of UMTS Based Smart Grids Distribution Networks Dr. Rajaa Aldeen Abd Khalid, Teba Adil Jihad Abstract- A smart grid (SG), an enhancement of the
IP Mobility vs. Session Mobility
 IP Mobility vs. Session Mobility Securing wireless communication is a formidable task, something that many companies are rapidly learning the hard way. IP level solutions become extremely cumbersome when
IP Mobility vs. Session Mobility Securing wireless communication is a formidable task, something that many companies are rapidly learning the hard way. IP level solutions become extremely cumbersome when
E1-E2 UPGRADATION COURSE CONSUMER MOBILITY. 3G Concept
 E1-E2 UPGRADATION COURSE CONSUMER MOBILITY 3G Concept Page 1 CHAPTER-TWO 3 G CONCEPT UMTS and the information society Rapid advancements in Information and Communications Technology (ICT) have already
E1-E2 UPGRADATION COURSE CONSUMER MOBILITY 3G Concept Page 1 CHAPTER-TWO 3 G CONCEPT UMTS and the information society Rapid advancements in Information and Communications Technology (ICT) have already
Rab Nawaz Jadoon. Cellular Systems - II DCS. Assistant Professor. Department of Computer Science. COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
 Cellular Systems - II Rab Nawaz Jadoon DCS Assistant Professor COMSATS IIT, Abbottabad Pakistan COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Mobile Communication UMTS Architecture A UMTS network consist
Cellular Systems - II Rab Nawaz Jadoon DCS Assistant Professor COMSATS IIT, Abbottabad Pakistan COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Mobile Communication UMTS Architecture A UMTS network consist
Abbreviations. Coding Scheme
 Managing Service Level Quality: Across Wireless And Fixed Networks. Peter Massam Copyright 2003 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. ISBN: 0-470-84848-0 Abbreviations 3GPP AF AGCH ARM AS ASK ASN AuC 3rd Generation
Managing Service Level Quality: Across Wireless And Fixed Networks. Peter Massam Copyright 2003 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. ISBN: 0-470-84848-0 Abbreviations 3GPP AF AGCH ARM AS ASK ASN AuC 3rd Generation
Examining Mobile-IP Performance in Rapidly Mobile Environments: The Case of a Commuter Train.
 Examining Mobile-IP Performance in Rapidly Mobile Environments: The Case of a Commuter Train. Edwin Hernandez and Abdelsalam (Sumi) Helal Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering
Examining Mobile-IP Performance in Rapidly Mobile Environments: The Case of a Commuter Train. Edwin Hernandez and Abdelsalam (Sumi) Helal Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering
The Effects of Asymmetry on TCP Performance
 The Effects of Asymmetry on TCP Performance Hari Balakrishnan Venkata N. Padmanabhan Randy H. Katz University of California at Berkeley Daedalus/BARWAN Retreat June 1997 Outline Overview Bandwidth asymmetry
The Effects of Asymmetry on TCP Performance Hari Balakrishnan Venkata N. Padmanabhan Randy H. Katz University of California at Berkeley Daedalus/BARWAN Retreat June 1997 Outline Overview Bandwidth asymmetry
Concurrent-MAC: Increasing Concurrent Transmissions in Dense Wireless LANs
 Concurrent-MAC: Increasing Concurrent Transmissions in Dense Wireless LANs Ghazale Hosseinabadi and Nitin Vaidya Department of ECE and Coordinated Science Lab. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Concurrent-MAC: Increasing Concurrent Transmissions in Dense Wireless LANs Ghazale Hosseinabadi and Nitin Vaidya Department of ECE and Coordinated Science Lab. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
EXPERIMENT N0: 06 AIM:TO DESIGN UMTS NETWORK USING OPNET MODELER APPARATUS: OPNET MODELER 14.0
 EXPERIMENT N0: 06 AIM:TO DESIGN UMTS NETWORK USING OPNET MODELER APPARATUS: OPNET MODELER 14.0 THEORY:Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a Third Generation (3G) wireless protocol that
EXPERIMENT N0: 06 AIM:TO DESIGN UMTS NETWORK USING OPNET MODELER APPARATUS: OPNET MODELER 14.0 THEORY:Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a Third Generation (3G) wireless protocol that
QOS ANALYSIS OF 3G AND 4G. Khartoum, Sudan 2 unversity of science and Technology, Khartoum, Sudan
 QOS ANALYSIS OF 3G AND 4G Doaa Hashim Osman 1, Amin Babiker 2 and Khalid hammed Bellal 1 Department of Communication, Faculty of Engineering, AL Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan 2 unversity of science
QOS ANALYSIS OF 3G AND 4G Doaa Hashim Osman 1, Amin Babiker 2 and Khalid hammed Bellal 1 Department of Communication, Faculty of Engineering, AL Neelain University, Khartoum, Sudan 2 unversity of science
CS 268: Wireless Transport Protocols. Kevin Lai Feb 13, 2002
 CS 268: Wireless Transport Protocols Kevin Lai Feb 13, 2002 Motivation! Wireless connectivity proliferating - Satellite, line-of-sight microwave, line-of-sight laser, cellular data (CDMA, GPRS, 3G), wireless
CS 268: Wireless Transport Protocols Kevin Lai Feb 13, 2002 Motivation! Wireless connectivity proliferating - Satellite, line-of-sight microwave, line-of-sight laser, cellular data (CDMA, GPRS, 3G), wireless
E3-E4 (CM MODULE) CDMA x & EV-DO. For internal circulation of BSNL only
 E3-E4 (CM MODULE) CDMA 2000 1x & EV-DO WELCOME This is a presentation for the E3-E4 Technical (CM- Module)fortheTopic:CDMA20001x&EV-DO Eligibility: Those who have got the upgradation frome3toe4. This presentation
E3-E4 (CM MODULE) CDMA 2000 1x & EV-DO WELCOME This is a presentation for the E3-E4 Technical (CM- Module)fortheTopic:CDMA20001x&EV-DO Eligibility: Those who have got the upgradation frome3toe4. This presentation
Short Message Service (SMS)
 TECQUI Ayra M.-B. Short Message Service (SMS) Introduction Short message service is a mechanism of delivery of short messages over the mobile networks. It is a store and forward way of transmitting messages
TECQUI Ayra M.-B. Short Message Service (SMS) Introduction Short message service is a mechanism of delivery of short messages over the mobile networks. It is a store and forward way of transmitting messages
COST/FIT Seminar in Micronova, Otaniemi, Spectroscopy of the uplink Um interface of GPRS/GSM
 COST/FIT Seminar in Micronova, Otaniemi, 10.2.2004. 1 Spectroscopy of the uplink Um interface of GPRS/GSM Jorma Kilpi P.O.Box 1202, 02044 VTT, FINLAND Email: Jorma.Kilpi@vtt.fi 20th February 2004 COST/FIT
COST/FIT Seminar in Micronova, Otaniemi, 10.2.2004. 1 Spectroscopy of the uplink Um interface of GPRS/GSM Jorma Kilpi P.O.Box 1202, 02044 VTT, FINLAND Email: Jorma.Kilpi@vtt.fi 20th February 2004 COST/FIT
PCS. Reference. Wireless and Mobile Network Architectures Y-Bing Lin and Imrich Chlamtac Wiley Computer Publishing
 PCS 1 Reference Wireless and Mobile Network Architectures Y-Bing Lin and Imrich Chlamtac Wiley Computer Publishing 2 Outlines Introduction PCS Architecture Cellular Telephony Cordless Telephony and Low-Tier
PCS 1 Reference Wireless and Mobile Network Architectures Y-Bing Lin and Imrich Chlamtac Wiley Computer Publishing 2 Outlines Introduction PCS Architecture Cellular Telephony Cordless Telephony and Low-Tier
ENSC 894: COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Simulation of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Network Final Project Spring 2014 Sathappan Kathiresan
 ENSC 894: COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Simulation of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Network Final Project Spring 2014 Sathappan Kathiresan Email address, skathire@sfu.ca April 20, 2014 1 Abstract In this
ENSC 894: COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Simulation of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Network Final Project Spring 2014 Sathappan Kathiresan Email address, skathire@sfu.ca April 20, 2014 1 Abstract In this
Throughput Performance Analysis for VOIP over UMTS Networks
 International Journal of Engineering Sciences Paradigms and Researches () Throughput Performance Analysis for VOIP over UMTS Networks Atyaf Mohamed Abdalwahad Mohamed 1, Dr. Khalid Hamid Bilal 2 and Dr.
International Journal of Engineering Sciences Paradigms and Researches () Throughput Performance Analysis for VOIP over UMTS Networks Atyaf Mohamed Abdalwahad Mohamed 1, Dr. Khalid Hamid Bilal 2 and Dr.
DRAFT - QoS Sensitive Roaming Principles 1.0 August 2004
 Official Document IR.68 DRAFT - QoS Sensitive Roaming Principles 1.0 August 2004 This is a binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (See next page):
Official Document IR.68 DRAFT - QoS Sensitive Roaming Principles 1.0 August 2004 This is a binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (See next page):
