IWAN Under the Hood - Next Gen Performance Routing and DMVPN. David Prall, Communication Architect CCIE 6508 (R&S/SP/Security)
|
|
|
- Paula Price
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 IWAN Under the Hood - Next Gen Performance Routing and DMVPN David Prall, Communication Architect CCIE 6508 (R&S/SP/Security) dprall@cisco.com
3 Agenda Introduction Intelligent Path Control PfRv3 Operations Deployment Considerations Troubleshooting Key Takeaways
4 Intelligent Path Control Performance Routing v3
5 Intelligent WAN Solution Components Unified Branch MPLS 3G/4G-LTE Private Cloud Virtual Private Cloud Internet Public Cloud Management Automation Transport Independent Intelligent Path Control Application Optimisation Secure Connectivity Simplified Application Enhanced Application Comprehensive Hybrid WAN Aware Routing Visibility and Performance Threat Defence
6 Hybrid WAN: Intelligent Path Control Leveraging the Internet Voice/Video/Critical take the best delay, jitter, and/or loss path MPLS Private Cloud Branch Other traffic is load balanced to maximise bandwidth Internet PfR monitors network performance and routes applications based on application performance policies PfR load balances traffic based upon link utilisation levels to efficiently utilise all available WAN bandwidth Virtual Private Cloud Voice/Video/Critical will be rerouted if the current path degrades below policy thresholds
7 How PfR Works Key Operations MC Traffic Classes BR Learning Active TCs BR MC MC BR Performance Measurements BR MC Best Path BR BR MC+BR MC+BR MC+BR MC+BR MC+BR MC+BR MC+BR MC+BR MC+BR MC+BR BR MC+BR Define Your Traffic Policy Learn the Traffic Measurement Path Enforcement Define Traffic Classes and service level Policies based on Applications or DSCP Border Routers learn current traffic classes going to the WAN based on classifier definitions Measure the traffic flow and network performance and report metrics to the Master Controller Master Controller commands path changes based on traffic class policy definitions
8 IOS-XE 3.15 IOS 15.5(2)T Advanced Topology IWAN POP1 DC1 DCI WAN Core DC2 IWAN POP2 R10 R10 R11 R12 R13 R14 R21 R22 R23 R / /8 Support for multiple BRs per cloud Horizontal scaling Support for Multiple POPs Different Prefix Common Prefix DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET R31 R41 R51 R / / / / /8
9 PfRv3 Operations
10 IWAN Solution Components PfR path selection policies AVC/QoS PfR intelligent routing AVC/QoS Overlay routing over tunnels Overlay tunnels - DMVPN Transport routing Perimeter Security Internet Routing Perimeter Security MPLS-VPN Routing IWAN Layered Solution leveraging point to multipoint WAN connections with secure tunnel overlay architecture and intelligent policy routing to provide cost optimisation and dynamic load balancing
11 IWAN Domain DMVPN IWAN Prescriptive Design Transport Independent Design based on DMVPN Branch spoke sites establish an IPsec tunnel to and register with the hub site Data traffic flows over the DMVPN tunnels WAN interface IP address used for the tunnel source address (in a Front-door VRF) One tunnel per user inside VRF Overlay Routing BGP or EIGRP are typically used for scalability IP routing exchanges prefix information for each site Per-tunnel QOS is applied to prevent hub site oversubscription to spoke sites IWAN POP1 R10 R11 R12 R21 R22 R31 ATBT MPLS R41 DCI WAN Core ISLAND INET R51 IWAN POP / / /24 R20 R52
12 Which Routing Protocol Should I Use? IWAN Profiles are based upon ibgp and EIGRP for scalability and optimal Intelligent Path Control Intelligent Path Control: PfR can be used with any routing protocols by relying on the routing table (RIB). Requires all valid WAN paths be ECMP so that each valid path is in the RIB. For BGP and EIGRP, PfR can look into protocol s topology information to determine both best paths and secondary paths thus, ECMP is not required. PfRv3 always checks for a parent route before being able to control a Traffic Class. Parent route check is done as follows: Check to see if there is an NHRP shortcut route If not Check in the order of BGP, EIGRP, Static and RIB Make sure that all Border Routers have a route over each external path to the destination sites, PfR will NOT be able to effectively control traffic otherwise.
13 Performance Monitoring Passive Monitoring SITE1 CPE1 2 MPLS 3 3 CPE12 CPE11 SITE2 Dual CPE CPE2 2 INET CPE10 SITE3 Single CPE Bandwidth on egress Per Traffic Class (dest-prefix, DSCP, AppName) Performance Monitor Collect Performance Metrics Per Channel - Per DSCP - Per Source and Destination Site - Per Interface
14 Performance Monitoring Smart Probing SITE1 CPE1 2 MPLS 3 3 CPE12 CPE11 SITE2 Dual CPE CPE2 INET CPE10 SITE3 Single CPE Integrated Smart Probes Traffic driven intelligent on/off Site to site and per DSCP Performance Monitor Collect Performance Metrics Per Channel - Per DSCP - Per Source and Destination Site - Per Interface
15 PfR Components The Decision Maker: Master Controller (MC) Apply policy, verification, reporting No packet forwarding/ inspection required Standalone of combined with a BR VRF Aware IPv4 only (IPv6 Future) The Forwarding Path: Border Router (BR) Gain network visibility in forwarding path (Learn, measure) Enforce MC s decision (path enforcement) VRF aware IPv4 only (IPv6 Future) Central Sites Branch Sites MC1 BR1 MC/BR MC/BR BR2 Branch Sites BR
16 IWAN Domain Collection of sites that share the same set of policies An IWAN domain includes: A mandatory Hub site, Optional Transit sites, As well as Branch sites. Each site has a unique identifier (Site-Id) Derived from the loopback address of the local MC Central and headquarter sites play a significant role in PfR and are called an IWAN Point of Presence (POP). Each of these sites will have a unique identifier called a POP-ID Each site runs PfR and gets its path control configuration and policies from the logical IWAN domain controller through the IWAN Peering Service R10 R11 R12 R21 R22 R31 R41 R51 R52 Site ID DC-East Site ID PATH1 Site ID DCI WAN Core PATH2 DC-West Site ID Site ID R20
17 IWAN Sites Hub Site Located in an enterprise central site or headquarter location. Can act as a transit site to access servers in the datacentres or for spoke-to-spoke traffic Only one Hub site exists per IWAN domain The logical domain controller functionality resides on this site s master controller (Hub MC). Transit Site Located in an enterprise central site or headquarter location. Can act as a Transit site The local MC peers with the Hub MC Branch Site DMVPN spoke, and are a stub site where traffic transit is not allowed. The local MC peers with the Hub MC
18 Hub Site One central site is assigned the role of Hub Site Each central site is allocated a unique POP- ID in the entire domain. POP-ID = 0 for the Hub Site The MC is assigned the Domain Controller (DC) role DC + MC = Hub Master Controller Central point of provisioning for PfR policies Listen for incoming peering request BRs are Hub BRs Peer with the local MC HUB SITE Site ID = R10 POP-ID 0 R /16 R11 R12 R21 R22 R31 DMVPN MPLS R41 DMVPN INET R51 R / / /24
19 R10 PfR Deployment Hub domain IWAN vrf default master hub source-interface Loopback0 enterprise-prefix prefix-list ENTERPRISE_PREFIX site-prefixes prefix-list SITE1_PREFIX Policies Monitors HUB SITE Site ID = R10 POP-ID 0 R11 domain IWAN vrf default border master source-interface Loopback0! interface Tunnel100 description -- Primary Path -- domain IWAN path MPLS path-id 1 Site Prefix: static definition of prefixes for a site MANDATORY Path MPLS Id 1 R11 R12 Path INET Id R12 domain IWAN vrf default border master source-interface Loopback0! interface Tunnel200 description Secondary Path -- domain IWAN path INET path-id 2 Performance Monitors instances (PMI) Monitor1 Site Prefix Learning (egress direction) Monitor2 Aggregate Bandwidth per Traffic Class (egress direction) Monitor3 Performance measurements (ingress direction)
20 Enterprise Prefix List The main use of the enterprise prefix list is to determine the enterprise boundary. With enterprise-prefix If a prefix doesn't match any site-prefix but matches enterprise-prefix then the prefix belongs to a site that is not participating in PfRv3 but it does belong to the enterprise. PfR will not influence traffic towards sites that have NOT enabled PFR. Without enterprise-prefix All the traffic that would be going towards a spoke that is NOT PfR enabled will be learnt as internet traffic class and therefore subjected to load balancing. domain IWAN vrf default master hub source-interface Loopback0 enterprise-prefix prefix-list ENTERPRISE_PREFIX! ip prefix-list ENTERPRISE_PREFIX seq 10 permit /8
21 Redundant MC Anycast IP What happens when a MC fails? Traffic forwarded based on routing information IE: no drop What happens when the Hub MC fails? Branch MCs keep their configuration and policies Continue to optimise traffic A backup MC can be defined on the hub. Using the same IP address as the primary Routing Protocol is used to make sure BRs and branch MC connect to the primary Stateless redundancy Backup MC will re-learn the traffic R10 Hub MC /32 R11 DMVPN MPLS HUB SITE R100 Backup Hub MC /31 R12 DMVPN INET R31 R41 R51 R52
22 Transit Site Introduce Transit Site" concept for the 2nd Central site Up to 63 in theory Each POP is allocated a unique POP-ID in the entire domain POP-ID configured Transit MC Behaves like a Hub MC without provisioning Peers with the Hub MC Transit BRs Similar as a Hub BR Peer with the local MC HUB SITE Site ID = R10 TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R /16 R11 R12 R21 R22 R31 DMVPN MPLS R41 DMVPN INET R51 POP-ID / / /24 IOS-XE 3.15 IOS 15.5(2)T R52
23 R20 PfR Deployment Transit Site domain IWAN vrf default master transit 1 source-interface Loopback0 site-prefixes prefix-list SITE2_PREFIX hub TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R20 POP-ID /16 R21 domain IWAN vrf default border master source-interface Loopback0! interface Tunnel100 description -- Primary Path -- domain IWAN path MPLS path-id 1 R22 domain IWAN vrf default border master source-interface Loopback0! interface Tunnel200 description Secondary Path -- domain IWAN path INET path-id 2 Site Prefix: static definition of prefixes for a site MANDATORY Path MPLS Id 1 R21 Performance Monitors instances (PMI) 2 3 Monitor1 Site Prefix Learning (egress direction) 1 R22 Path INET Id 2 Monitor2 Aggregate Bandwidth per Traffic Class (egress direction) Monitor3 Performance measurements (ingress direction)
24 Branch Sites Hub MC listening for incoming requests Branch MC connects to Hub MC Service Exchange Timers Policies and Monitor configurations Site Prefixes MC Peering HUB SITE Site ID = R10 TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R /16 R11 R12 R21 R22 DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET BRANCH SITE Site3 Site ID = R31 R41 R51 R / / /24
25 PfR Deployment Single CPE Branch HUB SITE Site ID = TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R31 R41 domain IWAN vrf default master branch source-interface Loopback0 hub border master local source-interface Loopback0 R10 R /16 R11 R12 R21 R22 DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET Single CPE Branch Sites Branch MCs connect to the Hub R31 R41 R51 R / / /24
26 PfR Deployment Dual CPE Branch R51 domain IWAN vrf default master branch source-interface Loopback0 hub border master local source-interface Loopback0 HUB SITE Site ID = R10 TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R /16 R11 R12 R21 R22 R52 domain IWAN vrf default border master source-interface Loopback0 DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET Dual CPE Branch Sites Branch MCs connect to the Hub BRs directly connected (mandatory) R31 R41 R51 R / / /24
27 Automatic Interface Discovery Transit BRs have path names manually defined, ie MPLS and INET Transit BRs send Discovery Packet with path names from to all discovered sites Discovery probes generated from the Hub/Transit Border Routers R10 MPLS Path-Id 1 HUB SITE Site ID = R20 R11 R12 R21 R22 INET Path-ID 2 MPLS Path-ID 1 TRANSIT SITE Site ID = INET Path-Id 2 DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET WAN Path is detected on the branch - Path Name - Path Id - DSCP R31 R41 R51 R / / /24
28 WAN Interface Performance Monitors Apply 3 Performance Monitors instances (PMI) over external interfaces Monitor1 Site Prefix Learning (egress direction) Monitor2 Aggregate Bandwidth per Traffic Class (egress direction) Monitor3 Performance measurements (ingress direction) R31
29 Site Prefix Discovery HUB SITE Site ID = Every MC in the domain owns a Site Prefix database Gives the mapping between site and prefixes 2 options: Static Automatic Learning R10 R11 MPLS R12 INET R31 R41 R51 R / / /24
30 Site Prefix Discovery HUB SITE Site ID = Source Prefix and Mask collected from Performance Monitor R10 SAF - Site 3 Monitor interval is 30 sec /24 R11 R12 BR send to its local MC MC send information to all peers via Peering MPLS INET Source Destination DSCP App AF41 AppXY SAF - Site /24 SAF - Site 3 SAF- Site / /24 1 R31 R41 R51 R52 R10 MC Site-Pfx Mask / / / /24
31 Site Prefix Discovery HUB SITE Site ID = TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R10 R /16 Site Prefix List Site1 Site /16 Site /24 Site /24 Site /24 R11 R12 R21 R22 DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET R31 R41 R51 R / / /24
32 Site Prefixes Static Configuration This allows configuring site-prefix manually instead of learning. This configuration should be used at the site if the site is used for transit. For example, Site A reaches Site B via Hub-Site, where Hub-Site is transit site. The configuration is used to prevent learning of Site A prefix as Hub-Site prefix when it is transiting from Hub. MC1 Hub MC /32 BR1 IWAN POP1 BR2 domain IWAN vrf default master hub source-interface Loopback0 site-prefixes prefix-list DC1_PREFIX! ip prefix-list DC1_PREFIX seq 10 permit /16! Source Destination DSCP App AF41 AppXY
33 Define PfR Traffic Policies CLASS MATCH ADMIN PERFORMANCE Define your Traffic Policy Identify Traffic Classes based on Application or DSCP Performance thresholds (loss, delay and Jitter), Preferred Path Centralised on a Domain Controller Voice Interactive Video Critical Data DSCP Application DSCP Application DSCP Application Preferred: MPLS Fallback: INET Next Fallback: 4G Preferred: MPLS Fallback: INET Preferred: MPLS Fallback: INET Delay threshold Loss threshold Jitter threshold Delay threshold Loss threshold Jitter threshold Delay threshold Loss threshold Jitter threshold Best Effort DSCP Application - Delay threshold Loss threshold Jitter threshold
34 IWAN Policies DSCP or App Based domain IWAN vrf default master hub load-balance class MEDIA sequence 10 match application <APP-NAME1> policy real-time-video match application <APP-NAME2> policy custom priority 1 one-way-delay threshold 200 priority 2 loss threshold 1 path-preference MPLS fallback INET class VOICE sequence 20 match dscp <DSCP-VALUE> policy voice path-preference MPLS fallback INET class CRITICAL sequence 30 match dscp af31 policy low-latency-data Policies: DSCP or Application Based Policies (NBAR2) DSCP marking can be used with NBAR2 on the LAN interface (ingress on BR) Default Class is load balanced Custom thresholds Pre-defined thresholds R10
35 Built-in Policy Templates Pre-defined Template Threshold Definition Voice priority 1 one-way-delay threshold 150 threshold 150 (msec) priority 2 packet-loss-rate threshold 1 (%) priority 2 byte-loss-rate threshold 1 (%) priority 3 jitter 30 (msec) Real-time-video priority 1 packet-loss-rate threshold 1 (%) priority 1 byte-loss-rate threshold 1 (%) Low-latency-data priority 2 one-way-delay threshold 150 (msec) priority 3 jitter 20 (msec) priority 1 one-way-delay threshold 100 (msec) priority 2 byte-loss-rate threshold 5 (%) priority 2 packet-loss-rate threshold 5 (%) Predefined Template Bulk-data Best-effort scavenger Threshold Definition priority 1 one-way-delay threshold 300 (msec) priority 2 byte-loss-rate threshold 5 (%) priority 2 packet-loss-rate threshold 5 (%) priority 1 one-way-delay threshold 500 (msec) priority 2 byte-loss-rate threshold 10 (%) priority 2 packet-loss-rate threshold 10 (%) priority 1 one-way-delay threshold 500 (msec) priority 2 byte-loss-rate threshold 50 (%) priority 2 packet-loss-rate threshold 50 (%)
36 PfRv3 works on Traffic Class DSCP Based DSCP Based Policies Prefix DSCP AppID Dest Site Next- Hop /24 EF N/A Site 3? /24 AF41 N/A Site 3? /24 AF31 N/A Site 3? /24 0 N/A Site 3? /24 EF N/A Site 4? /24 AF41 N/A Site 4? /24 AF31 N/A Site 4? /24 0 N/A Site 4? /24 EF N/A Site 5? /24 AF41 N/A Site 5? /24 AF31 N/A Site 5? /24 0 N/A Site 5? HUB SITE Site ID = R10 TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R /16 R11 R12 R21 R22 DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET Traffic with EF, AF41, AF31 and 0 Traffic Class Destination Prefix DSCP Value Application (N/A when DSCP policies used) R31 R41 R51 R / / /24
37 PfRv3 works on Traffic Class Application Based Application based Policies Prefix DSCP AppID Dest Site Next-Hop /24 EF N/A Site 3? /24 AF41 App1 Site 3? /24 AF41 App2 Site 3? /24 AF41 N/A Site 3? /24 AF31 N/A Site 3? /24 0 N/A Site 3? /24 EF N/A Site 4? /24 AF41 App1 Site 4? /24 AF31 N/A Site 4? /24 0 N/A Site 4? /24 EF N/A Site 5? /24 AF41 App2 Site 5? /24 AF31 N/A Site 5? /24 0 N/A Site 5? Traffic with EF, AF41, AF31 and 0 App1, App2, etc Traffic Class Destination Prefix DSCP Value Application (N/A when DSCP policies used) HUB SITE Site ID = R10 TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R11 R12 R21 R22 R31 R /16 DMVPN MPLS R41 DMVPN INET R / / /24 R52
38 Channels from Branch to Central Sites IWAN POP MC1 Hub MC /32 Present Channel 10 Site 1 MPLS Path 1 DSCP AF41 Present Channel 11 Site 1 MPLS Path 2 DSCP AF41 BR1 MPLS BR2 BR3 INET Backup Channel 12 Site 1 INET Path 3 DSCP AF41 R10 R11 R12 R / / /24
39 Channel Between Branch Sites MC1 Hub MC /32 BR1 IWAN POP BR2 Between Any Pair of Sites that has traffic! Present Channel 13 Site 4 MPLS DSCP EF MPLS INET Backup Channel 14 Site 4 INET DSCP EF R31 R41 R51 R / / /24
40 Channel Monitoring performance per channel Channel per destination site, DSCP, Path Name and Path Id Destination Prefix from Site Prefix database Include all sites advertising that prefix Load balance may be done between POPs if prefix is shared between multiple transit sites Track individual BR performance on the hub A PfR-label uniquely identify a path between sites across clouds (embedded in GRE encapsulation) POP-ID PATH-ID POP-ID PATH-ID R10 Path MPLS Id /16 HUB SITE Site ID = R11 R12 R21 R22 R /16 Path INET Id 2 DMVPN MPLS /16 TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R20 Path MPLS Id 1 DMVPN INET IOS-XE 3.15 IOS 15.5(2)T Path INET Id /16
41 TC to Channel Mapping Channel created for each destination site, path name, next-hop (path identifier) and DSCP. Destination Prefix announced by destination site TC => Destination Prefix, DSCP => Mapped to the corresponding Channel R31-Site3-Spoke#sh domain IWAN master channel dscp ef Channel Id: 53 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: MPLS DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:1 0:0 [0x10000] TCs: 1 Channel Created: 3w5d ago Provisional R31-Site3-Spoke#sh State: Initiated and domain open IWAN master channel dscp ef Operational state: Available Channel to hub: Channel TRUE Id: 57 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: INET DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:2 0:0 [0x20000] TCs: Site Prefix 0 List /32 Channel (Routable) Created: 3w5d ago Provisional (Active) State: Initiated and open /16 Operational (Routable) state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) /16 (Routable)
42 Destination Site: Collecting Performance Metrics Smart Probes Without actual traffic 20 pps for channel without traffic IOS-XE: BR sends 10 probes spaced 20ms apart in the first 500ms and another similar 10 probes in the next 500ms IOS: BR sends one packet every 50ms With actual traffic Lower frequency when real traffic is observed over the channel Probes sent every 1/3 of [Monitor Interval], ie every 10 sec by default Measured by Performance Monitor just like other data traffic
43 Performance Violation Performance notification exported ONLY when there is a violation on a specific channel Generated from ingress monitor attached on destination BRs to the source site MC Based on Monitor interval (30 sec default, configurable) Via all available external interfaces. R31 TCA Delay DSCP AF41 Path MPLS HUB SITE Site ID = R10 TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R /16 R11 R12 R21 R22 DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET R31 R41 R51 R / / /24
44 Policy Decision and Path Enforcement Search MC database for TC to site R31 with DSCP EF going over path MPLS Auto Tunnel between Border Routers Option1: next hop is local to the BR Option2: next hop is another BR, forward through the auto-tunnel (GRE encap used) R10 Flow Auto-tunnel mgre interface Option2 HUB SITE Site ID = R11 R12 Option1 MPLS INET
45 Deployment Considerations
46 IWAN 2.0 Hub/Transit MC Scaling ASR 1002-X 2000 sites ASR 1001-X 1000 sites ISR sites ISR sites CSR1000v 1 vcpu 200 sites CSR1000v 2 vcpu 500 sites
47 IWAN Application Policies NBAR2: Asymmetric routing issue Some applications require DPI to see both sides of the flow Inherent to all DPI engines Workaround HSRP Master PBR statement on the return path R10 HUB SITE Site ID = TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R20 R11 R12 R21 R22 DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET R51 R52
48 Unreachable Timer HUB SITE Site ID = TRANSIT SITE Site ID = Channel Unreachable PfRv3 considers a channel reachable as long as the site receives a PACKET on that channel A channel is declared unreachable in both directions if There is NO traffic on the Channel, probes are the only way of detecting unreachability. So if no probe is received within 1 sec, PfR detects unreachability. When there IS traffic on the channel, if PfR does not see any packet for more than a second on a channel PfR detects unreachability. Default: 1 Sec Recommended: 4 sec Advanced options with (3)S / 15.5(3)M channel-unreachable-timer 4 R10 Path MPLS Id 1 R11 R12 R21 R22 Path INET Id 2 DMVPN MPLS R /24 R20 Path MPLS Id 1 DMVPN INET Path INET Id 2
49 Failover Time HUB SITE Site ID = TRANSIT SITE Site ID = Ingress Performance Violation detected Delay, loss or jitter thresholds Based on Monitor-interval Default 30 Seconds Single Fast Monitor Interval Configurable domain IWAN vrf default master hub monitor-interval 4 dscp ef monitor-interval 4 dscp af41 monitor-interval 4 dscp cs4 monitor-interval 4 dscp af31 R10 Path MPLS Id 1 R20 R11 R12 R21 R22 Path INET Id 2 DMVPN MPLS R /24 Path MPLS Id 1 DMVPN INET Path INET Id 2
50 Load Balancing Current Situation - Load balancing works on physical links - Load sharing on NH on the same DMVPN network (XE and IOS 15.5(3)M1) : - between R11 and R21 - Between R12 and R22 Default Classes TCs - Load balancing at any time (not only at creation time). - TC will be moved to ensure bandwidth on all links is within the defined range Performance TCs - Initial load-balancing while placing the TCs, on a per TC basis. PfR does not account for the TCs getting fatter. R10 Path MPLS Id /16 HUB SITE Site ID = R11 R12 R21 R22 Path INET Id 2 MPLS R31 TRANSIT SITE Site ID = R20 Path MPLS Id 1 INET Path INET Id /16
51 Path Selection Direction from POPs to Spokes Each POP is a unique site by itself and so it will only control traffic towards the spoke on the WAN s that belong to that POP. PfRv3 will NOT be redirecting traffic between POP across the DCI or WAN Core. If it is required that all the links are considered from POP to spoke, then the customer will need to use a single MC. Only one next hop (on branch) per DMVPN network No PfR control between Transit Sites R10 Path MPLS Id 1 HUB SITE Site ID = Hub MC POP-ID 0 R20 R11 R12 R21 R22 Path INET Id 2 DMVPN MPLS R /24 Path MPLS Id 1 TRANSIT SITE Site ID = DMVPN INET Transit MC POP-ID 1 Path INET Id 2
52 Path Selection Direction from Spokes to POPs The spoke considers all the paths (multiple NH s) towards the POPs The concept of "active" and "standby" next hops based on routing metrics and advertised mask length in routing is used to gather information about the preferred POP for a given prefix. Example: If the best metric for a given prefix is on DC1 then all the next hops on that DC for all the ISPs are tagged as active (only for that prefix). R10 Path MPLS Id 1 DC1 Site ID = R20 R11 R12 R21 R22 Path INET Id 2 DMVPN MPLS R /24 Path MPLS Id 1 DC2 Site ID = / /24 DMVPN INET Path INET Id 2 LP LP LP 3000 LP 400
53 Next Hop Status for Prefix Active next hop: A next hop is considered active if it is located at the POP site which has the next hop with the best routing metric for a given prefix Standby next hop: A next hop is considered standby if it is located at the POP site which advertises a route for prefix but does not have any next hop with best metric. Routable* next hop: A next hop is considered routable for a given prefix if it advertises one or more routes for the prefix and it was not a candidate channel for any traffic class Unreachable next hop: A next hop is considered unreachable for a given prefix if it is down or does not advertise any route for the prefix The sorting for active/standby considers all the channels/next hops on all WAN interfaces which are Routable. Note: Routable is a new status visible starting from XE /15.5(3)M1. On the border prior to XE /15.5(3)M1 active, standby and unreachable were supported.
54 PfRv3 Routing Definitions Best Metric A next hop in a given list is considered to have a best metric based on following metrics/criteria: Advertised mask length ( ) BGP: Weight( ), Local-Preference ( ) EIGRP : FD ( ), Successor FD ( ) Mask length takes precedence. Only if advertised mask lengths are equal, the protocol specific metrics are used.
55 Channels DC1 Site ID = DC2 Site ID = Channel to all next-hops, per DSCP Depending on the routing prefix advertisements, metrics and PfR Site Prefix List, destination-prefix will be active/standby/routable R10 R11 R12 R21 R22 Path MPLS Id 1 Path INET Id 2 R20 Path MPLS Id 1 Path INET Id 2 CHANNEL PATH NEXT HOPS PREFIX STATUS 1 MPLS R11? 2 INET R12? 3 MPLS R21? 4 INET R22? Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4 R /24
56 Use Case #1 Separate Prefix BGP Site1 advertises and /8 Site2 advertises /16 and /8 R10 SITE1 PfR Site-Prefix R20 SITE2 PfR Site-Prefix / /16 PfR: Site1 Site-Prefix: Site2 Site-Prefix: /16 BGP R11 Path MPLS Id 1 R12 R21 R22 Path INET Id 2 Path MPLS Id 1 Path INET Id 2 BGP CHANNEL PATH NEXT HOP PREFIX STATUS 1 MPLS R11 Active /8 Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch / /8 2 INET R12 Active 3 MPLS R /16 Active 4 INET R /16 Active R /24
57 Path Selection SITE1 PfR Site-Prefix SITE2 PfR Site-Prefix /16 R10 R /16 BGP R11 R12 R21 R22 BGP / / /8 R31 PfR View PREFIX PATH PREFERENCE NEXT-HOPS ORDER Status DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET MPLS Preferred INET Fallback R11 R12 Active Active No Preference R11, R12 Active R /24
58 Channels Site1 R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master channel dscp ef Channel Id: 5 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: MPLS DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:1 0:0 [0x10000] TCs: 1 Channel Created: 00:03:56 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) Label 0:1 POP 0 Path-ID 1 R11 Channel Id: 6 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: INET DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:2 0:0 [0x20000] TCs: 0 Channel Created: 00:03:56 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) Label 0:2 POP 0 Path-ID 2 R12 [Output omitted for brevity]
59 Channels Site2 R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master channel dscp ef Channel Id: 15 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: MPLS DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 1:1 0:0 [0x ] TCs: 1 Channel Created: 00:02:26 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) /16 (Active) Label 1:1 POP 1 Path-ID 1 R21 Channel Id: 16 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: INET DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 1:2 0:0 [0x ] TCs: 0 Channel Created: 00:02:26 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) /16 (Active) Label 1:2 POP 1 Path-ID 2 R22 [Output omitted for brevity]
60 Use Case #2 Shared Prefix DC Stickiness with more Specific Prefix Dual datacentre Same prefixes shared across Site1/Site2 Site1 preferred for Site2 preferred for /16 R31 PfR View CHANNEL PATH NEXT HOP PREFIX STATUS 1 MPLS R11 2 INET R12 3 MPLS R21 4 INET R / / / /16 Active Standby Active Standby Standby Active Standby Active BGP R10 R /8 Path MPLS Id 1 SITE1 PfR Site-Prefix /16 R20 SITE2 PfR Site-Prefix /16 R12 R21 R22 Path INET Id /16 Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4 R /24 Path MPLS Id 1 Path INET Id / /8 BGP
61 Path Selection R10 SITE1 PfR Site-Prefix / /16 R20 SITE2 PfR Site-Prefix /16 R31 PfR View R11 Path MPLS Id 1 R12 R21 R22 Path INET Id 2 Path MPLS Id 1 Path INET Id 2 PREFIX PATH PREFERENCE MPLS Preferred INET Fallback NEXT-HOPS ORDER R11 R12 R21 R22 Status Active Active Standby Standby Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4 No Preference R11, R12 R21, R22 Active Standby R /24
62 Channels Site1 R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master channel dscp ef Channel Id: 5 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: MPLS DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:1 0:0 [0x10000] TCs: 1 Channel Created: 00:17:25 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) /16 (Standby) Label 0:1 POP 0 Path-ID 1 R11 Channel Id: 6 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: INET DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:2 0:0 [0x20000] TCs: 0 Channel Created: 00:17:25 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) /16 (Standby) Label 0:2 POP 0 Path-ID 2 R12 [Output omitted for brevity]
63 Channels Site2 R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master channel dscp ef Channel Id: 15 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: MPLS DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 1:1 0:0 [0x ] TCs: 1 Channel Created: 00:15:55 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Standby) /16 (Active) Label 1:1 POP 1 Path-ID 1 R21 Channel Id: 16 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: INET DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 1:2 0:0 [0x ] TCs: 0 Channel Created: 00:15:55 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Standby) /16 (Active) Label 1:2 POP 1 Path-ID 2 R22 [Output omitted for brevity]
64 Use Case #3 Shared Prefix DC Stickiness with Different Metrics BGP: Both Site1 and Site2 advertise and /16 DC preference can be determined per branch R31 PfR View CHANNEL PATH NEXT HOP PREFIX STATUS 1 MPLS R11 2 INET R12 3 MPLS R21 4 INET R / / / /16 Active Active Active Active Standby Standby Standby Standby BGP / /8 R10 R11 LP SITE1 PfR Site-Prefix /16 LP /16 R20 R12 R21 R22 R /24 LP 3000 Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4 SITE2 PfR Site-Prefix /16 LP 400 BGP / /8
65 Path Selection Transit Site Affinity introduced in 15.5(3)M1 and XE R10 SITE1 PfR Site-Prefix / /16 R20 SITE2 PfR Site-Prefix /16 R11 R12 R21 R22 R31 PfR View PREFIX PATH PREFERENCE NEXT-HOPS ORDER Status BGP / /8 LP LP LP 3000 LP 400 BGP / /8 MPLS Preferred INET Fallback R11 R12 R21 R22 Active Active Standby Standby Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4 No Preference R11, R12 R21, R22 Active Standby R /24
66 Channels Site1 R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master channel dscp ef Channel Id: 73 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: MPLS DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:1 0:0 [0x10000] TCs: 2 Channel Created: 00:03:47 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) /16 (Active) Label 0:1 POP 0 Path-ID 1 R11 Channel Id: 82 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: INET DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:2 0:0 [0x20000] TCs: 0 Channel Created: 00:03:10 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) /16 (Active) Label 0:2 POP 0 Path-ID 2 R12 [Output omitted for brevity]
67 Channels Site2 R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master channel dscp ef Channel Id: 79 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: MPLS DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 1:1 0:0 [0x ] TCs: 0 Channel Created: 00:03:17 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Standby) /16 (Standby) Label 1:1 POP 1 Path-ID 1 R21 Channel Id: 86 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: INET DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 1:2 0:0 [0x ] TCs: 0 Channel Created: 00:02:41 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Standby) /16 (Standby) Label 1:2 POP 1 Path-ID 2 R22 [Output omitted for brevity]
68 Use Case #4 No DC Stickiness Dual Central Sites Same Prefix To disable and come back to previous default: R31 PfR View domain IWAN vrf default master hub advanced no transit-site-affinity CHANNEL PATH NEXT HOP PREFIX STATUS 1 MPLS R11 Active BGP / /8 R10 R11 LP 1000 SITE1 PfR Site-Prefix /16 R20 R12 R21 R22 LP 1000 LP 1000 Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4 SITE2 PfR Site-Prefix LP 1000 BGP / /8 2 INET R12 Active 3 MPLS R21 Active 4 INET R22 Active R /24
69 Path Selection R10 SITE1 PfR Site-Prefix / /16 R20 SITE2 PfR Site-Prefix /16 R11 R12 R21 R22 R31 PfR View PREFIX PATH PREFERENCE MPLS Preferred INET Fallback No Preference NEXT-HOPS ORDER R11, R21 R12, R22 R11, R12, R21, R22 Status Active, Active Active, Active Active, Active, Active, Active BGP /8 LP LP LP 3000 Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4 R /24 LP /8 BGP
70 Channels Site1 R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master channel dscp ef Channel Id: 90 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: MPLS DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:1 0:0 [0x10000] TCs: 1 Channel Created: 00:01:57 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) /16 (Active) Label 0:1 POP 0 Path-ID 1 R11 Channel Id: 91 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: INET DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:2 0:0 [0x20000] TCs: 0 Channel Created: 00:01:57 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) /16 (Active) Label 0:2 POP 0 Path-ID 2 R12 [Output omitted for brevity]
71 Channels Site2 R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master channel dscp ef Channel Id: 92 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: MPLS DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 1:1 0:0 [0x ] TCs: 1 Channel Created: 00:01:57 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) /16 (Active) Label 1:1 POP 1 Path-ID 1 R21 Channel Id: 93 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: INET DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 1:2 0:0 [0x ] TCs: 0 Channel Created: 00:01:57 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) /16 (Active) Label 1:2 POP 1 Path-ID 2 R22 [Output omitted for brevity] [Output omitted for brevity]
72 Use Case #5 Path of Last Resort Path of last resort (PLR) option for metered links PLR Channels muted when in standby mode Once it is active, smart probes will only be sent on dscp 0 (zero sla) to conserve bandwidth Smart probe frequency will be reduced to 1 packet every 10 secs from 20 packets per secs. Unreachable detection will be extended to 60 secs R10 R11 SITE1 Site ID = R12 R13 R21 R22 DMVPN MPLS DMVPN INET R20 SITE2 Site ID = DMVPN LTE R23 R13 R23 interface Tunnel300 description LTE Path -- domain IWAN path LTE path-id 3 path-last-resort R /24
73 Troubleshooting
74 Check Traffic Classes Summary R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master traffic-classes summary APP - APPLICATION, TC-ID - TRAFFIC-CLASS-ID, APP-ID - APPLICATION-ID SP - SERVICE PROVIDER, PC = PRIMARY CHANNEL ID, BC - BACKUP CHANNEL ID, BR - BORDER, EXIT - WAN INTERFACE UC - UNCONTROLLED, PE - PICK-EXIT, CN - CONTROLLED, UK - UNKNOWN Dst-Site-Pfx Dst-Site-Id APP DSCP TC-ID APP-ID State SP PC/BC BR/EXIT /28 Internet N/A af21 10 N/A CN INET 19/NA /Tunnel / N/A ef 7 N/A CN MPLS 13/ /Tunnel N/A default 9 N/A CN INET 3/ /Tunnel N/A ef 8 N/A CN MPLS 4/ /Tunnel100 Total Traffic Classes: 4 Site: 3 Internet: 1 R31-Site3-Spoke# Traffic Class Controlled Path Information - Channels
75 Check Traffic Classes Details R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master traffic-classes dscp ef Dst-Site-Prefix: DSCP: ef [46] Traffic class id:8 Clock Time: 15:46:41 (EST) 01/15/2016 TC Learned: 00:20:40 ago Present State: CONTROLLED Current Performance Status: in-policy Current Service Provider: MPLS since 00:20:10 Previous Service Provider: Unknown BW Used: 20 Kbps Present WAN interface: Tunnel100 in Border Present Channel (primary): 4 MPLS pfr-label:0:1 0:0 [0x10000] Backup Channel: 5 INET pfr-label:0:2 0:0 [0x20000] Destination Site ID bitmap: 1 Destination Site ID: Class-Sequence in use: 10 Class Name: VOICE using policy User-defined priority 2 packet-loss-rate threshold 5.0 percent priority 1 one-way-delay threshold 150 msec priority 2 byte-loss-rate threshold 5.0 percent BW Updated: 00:00:10 ago Reason for Latest Route Change: Delay Check Traffic Class Voice for site 1 Active Path used Check Channels used (Primary and Backup) Path name and Path Id (Next Hop) reason for last change
76 Check Traffic Classes Details R31-Site3-Spoke#show domain IWAN master traffic-classes dscp ef [Output omitted for brevity] Reason for Latest Route Change: Delay Route Change History: Date and Time Previous Exit Current Exit Reason 1: 15:50:27 (EST) 01/15/16 MPLS(0:1 0:0)/ /Tu100 (Ch:4) INET(0:2 0:0)/ /Tu200 (Ch:5) Out-of-Policy (One Way Delay : 283 msec) 2: 15:26:31 (EST) 01/15/16 None(0:0 0:0)/ /None (Ch:0) MPLS(0:1 0:0)/ /Tu100 (Ch:4) Uncontrolled to Controlled Transition History of Route Changes: Last 5 reasons Route change from MPLS to INET due to Delay
77 Monitoring Channels R31-Site3-Spoke#sh domain IWAN master channels dscp ef Channel Id: 4 Dst Site-Id: Link Name: MPLS DSCP: ef [46] pfr-label: 0:1 0:0 [0x10000] TCs: 0 Channel Created: 22:05:08 ago Provisional State: Initiated and open Operational state: Available Channel to hub: TRUE Interface Id: 15 Supports Zero-SLA: Yes Muted by Zero-SLA: No Estimated Channel Egress Bandwidth: 40 Kbps Immitigable Events Summary: Total Performance Count: 0, Total BW Count: 0 Site Prefix List /32 (Routable) (Active) ODE Statistics: Received: 484 [SNIP]
78 Monitoring Channels (Cont d) ODE [CONTD] ODE Stats Bucket Number: 1 Last Updated : 00:00:01 ago Packet Count : 38 Byte Count : 3192 One Way Delay : 283 msec* Loss Rate Pkts: 0.0 % Loss Rate Byte: 0.0 % Jitter Mean : 4783 usec Unreachable : FALSE ODE Stats Bucket Number: 2 Last Updated : 00:00:03 ago Packet Count : 37 Byte Count : 3108 One Way Delay : 284 msec* Loss Rate Pkts: 0.0 % Loss Rate Byte: 0.0 % Jitter Mean : 5081 usec Unreachable : FALSE On Demand Export (ODE) Delay Out of Policy
79 Monitoring Channels (Cont d) TCA [CONTD] TCA Statistics: Received: 441 ; Processed: 128 ; Unreach_rcvd: 0 ; Local Unreach_rcvd: 0 TCA lost byte rate: 0 TCA lost packet rate: 7 TCA one-way-delay: 0 TCA network-delay: 434 TCA jitter mean: 0 Latest TCA Bucket Last Updated : 00:00:03 ago One Way Delay : 284 msec* Loss Rate Pkts: NA Loss Rate Byte: NA Jitter Mean : NA Unreachability: FALSE Threshold Crossing Alert (TCA) One Way Delay OOP
80 Key Takeaways
81 Performance Routing Phases Summary IWAN 2.0 PfR version 3 IOS 15.4(3)M IOS-XE 3.13 PfR version 3 IOS 15.5(1)T IOS-XE 3.14 PfR version 3 IOS 15.5(2)T IOS-XE 3.15 PfR version 3 IOS 15.5(3)M IOS-XE 3.16 IWAN 2.1 PfR version 3 IOS 15.5(3)M1 IOS-XE PfR Domain One touch provisioning Auto Discovery of sites NBAR2 support Passive Monitoring (performance monitor) Smart Probing VRF Awareness IPv4/IPv6 (Future) <10 lines of configuration and centralised Zero SLA WCCP Support Transit Sites Multiple Next Hop per DMVPN Multiple POPs Syslog (TCA) Show last 5 TCA Path of Last Resort EIGRP IWAN Simplification (Stub site) POP Affinity Blackout ~ sub second Brownout ~ 2 sec Scale 2000 sites
82 Performance Routing Platform Support Cisco CSR-1000 Cisco ASR-1000 MC BR* Cisco ISR G2 family 3900-AX 2900-AX 1900-AX 890 Cisco ISR MC BR MC BR MC BR * BR support 3.18
83 Key Takeaways IWAN Intelligent Path Control pillar is based upon Performance Routing (PfR) Maximises WAN bandwidth utilisation Protects applications from performance degradation Enables the Internet as a viable WAN transport Provides multisite coordination to simplify network wide provisioning. Application-based policy driven framework and is tightly integrated with existing AVC components. Smart and Scalable multi-sites solution to enforce application SLAs while optimising network resources utilisation. PfRv3 is the 3 rd generation Multi-Site aware Bandwidth and Path Control/Optimisation solution for WAN/Cloud based applications. Available on ASR1k, ISR4k, and ISR-G2
84 More Information Cisco.com IWAN and PfRv3 Page: DocWiki dcloud dcloud IWAN 4D Lab: CVD IWAN 2.x WAN CVD s Intelligent WAN Technology Design Guide - February 2016: Intelligent WAN Configuration Files Guide - February 2016: IWAN Security for Remote Site DIA and Guest Wireless Design Guide March 2015: IWAN Application Optimisation using Cisco WAAS and Akamai Connect Technology Design Guide - March 2015:
85 IWAN Book Pre-order available VIRL lab available
86 Q & A
87 Complete Your Online Session Evaluation Give us your feedback and receive a Cisco 2016 T-Shirt by completing the Overall Event Survey and 5 Session Evaluations. Directly from your mobile device on the Cisco Live Mobile App By visiting the Cisco Live Mobile Site Visit any Cisco Live Internet Station located throughout the venue T-Shirts can be collected Friday 11 March at Registration Learn online with Cisco Live! Visit us online after the conference for full access to session videos and presentations.
88 Thank you
89
PfRv3 Zero SLA Support
 The Performance Routing v3 (PfRv3) Zero SLA Support feature enables users to reduce probing frequency on various ISP links, such as 3G, 4G, and LTE When the Zero SLA (0-SLA) feature is configured on an
The Performance Routing v3 (PfRv3) Zero SLA Support feature enables users to reduce probing frequency on various ISP links, such as 3G, 4G, and LTE When the Zero SLA (0-SLA) feature is configured on an
Intelligent WAN 2.0 Traffic Independent Design and Intelligent Path Selection
 Intelligent WAN 2.0 Traffic Independent Design and Intelligent Path Selection Tech-WAN Jaromír Pilař Consulting Systems Engineer, CCIE #2910 Cisco Intelligent WAN (IWAN) AVC Private Cloud ISR-AX 3G/4G-LTE
Intelligent WAN 2.0 Traffic Independent Design and Intelligent Path Selection Tech-WAN Jaromír Pilař Consulting Systems Engineer, CCIE #2910 Cisco Intelligent WAN (IWAN) AVC Private Cloud ISR-AX 3G/4G-LTE
Návrh inteligentní WAN sítě
 Návrh inteligentní WAN sítě EN2 Jaromír Pilař, CSE Agenda Úvod a základní pilíře inteligentní WAN sítě Tranport Independent Design Inteligentní výběr cesty Shrnutí Presentation Title: Intelligent WAN:
Návrh inteligentní WAN sítě EN2 Jaromír Pilař, CSE Agenda Úvod a základní pilíře inteligentní WAN sítě Tranport Independent Design Inteligentní výběr cesty Shrnutí Presentation Title: Intelligent WAN:
Implementing Next Generation Performance Routing PfRv3
 Implementing Next Generation Performance Routing PfRv3 Jean-Marc Barozet Technical Leader IWAN Solution Group Agenda Business Trends PfRv3 Principles Monitoring Details The Life of a Packet Path Enforcement
Implementing Next Generation Performance Routing PfRv3 Jean-Marc Barozet Technical Leader IWAN Solution Group Agenda Business Trends PfRv3 Principles Monitoring Details The Life of a Packet Path Enforcement
Performance Routing Version 3 Configuration Guide
 First Published: 2014-07-22 Last Modified: 2016-04-20 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387)
First Published: 2014-07-22 Last Modified: 2016-04-20 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387)
PfRv3 Inter-DC Optimization
 The PfRv3-Inter-DC-Optimization feature provides support by routing traffic from a hub site to another for specific traffic types such as data, voice, video, etc. Feature Information for PfRv3-Inter-DC-Optimization,
The PfRv3-Inter-DC-Optimization feature provides support by routing traffic from a hub site to another for specific traffic types such as data, voice, video, etc. Feature Information for PfRv3-Inter-DC-Optimization,
PfRv3 Path of Last Resort
 The PfRv3 path of last resort feature allows the traffic to be routed to the path of last resort. Feature Information for, page 1 Restrictions for, page 2 Information About, page 2 How to Configure, page
The PfRv3 path of last resort feature allows the traffic to be routed to the path of last resort. Feature Information for, page 1 Restrictions for, page 2 Information About, page 2 How to Configure, page
Intelligent WAN : CVU update
 Intelligent WAN : CVU update Deliver enhanced mobile experience at the branch with Intelligent WAN Soren D. Andreasen (sandreas@cisco.com) Technical Solution Architect CCIE# 3252 Agenda IWAN 2.0/2.1 overview
Intelligent WAN : CVU update Deliver enhanced mobile experience at the branch with Intelligent WAN Soren D. Andreasen (sandreas@cisco.com) Technical Solution Architect CCIE# 3252 Agenda IWAN 2.0/2.1 overview
Intelligent WAN Multiple Data Center Deployment Guide
 Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Multiple Data Center Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1 Deploying
Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Multiple Data Center Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1 Deploying
Intelligent WAN Multiple VRFs Deployment Guide
 Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Multiple VRFs Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deploying the Cisco IWAN Multiple VRFs...
Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Multiple VRFs Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deploying the Cisco IWAN Multiple VRFs...
Cisco Intelligent WAN
 Cisco Intelligent WAN Ľuboš Lontoš Systems Engineer SP/R&S ALEF NULA a.s. Agenda Cisco iwan Architecture Overview Tranport Independent Design Intelligent Path Control- PfRv3 Product PorMolio Tradi4onal
Cisco Intelligent WAN Ľuboš Lontoš Systems Engineer SP/R&S ALEF NULA a.s. Agenda Cisco iwan Architecture Overview Tranport Independent Design Intelligent Path Control- PfRv3 Product PorMolio Tradi4onal
Cisco recommends that you have basic knowledge of Performance Routing (PfR).
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations R3 Master Hub Router R4 Hub Border Router R5 Hub Border Router R9 Branch Master Router R10 Branch
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Configure Network Diagram Configurations R3 Master Hub Router R4 Hub Border Router R5 Hub Border Router R9 Branch Master Router R10 Branch
Intelligent WAN (IWAN) Design and Deployment
 Intelligent WAN (IWAN) Design and Deployment Adam Groudan, Technical Solutions Architect David Prall, Communications Architect BRKCRS-2002 Cisco Spark How Questions? Use Cisco Spark to communicate with
Intelligent WAN (IWAN) Design and Deployment Adam Groudan, Technical Solutions Architect David Prall, Communications Architect BRKCRS-2002 Cisco Spark How Questions? Use Cisco Spark to communicate with
Chapter H through R. loss (PfR), page 28. load-balance, page 23 local (PfR), page 24 logging (PfR), page 26
 Chapter H through R holddown (PfR), page 3 host-address (PfR), page 5 hub, page 7 inside bgp (PfR), page 8 interface (PfR), page 10 interface tunnel (global configuration), page 12 jitter (PfR), page 13
Chapter H through R holddown (PfR), page 3 host-address (PfR), page 5 hub, page 7 inside bgp (PfR), page 8 interface (PfR), page 10 interface tunnel (global configuration), page 12 jitter (PfR), page 13
Deploying Performance Routing
 Deploying Performance Routing KRST-2362 Jean-Marc Barozet Technical Leader Application Visibility and Control Network Operating Systems Technology Group Introducing Performance Routing (PfR) Application
Deploying Performance Routing KRST-2362 Jean-Marc Barozet Technical Leader Application Visibility and Control Network Operating Systems Technology Group Introducing Performance Routing (PfR) Application
Help! BRKRST Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 2
 Help! 2 Understanding and Troubleshooting Intelligent Path Control in IWAN Brandon Lynch Network Engineer, Core Software Group Richard Furr Technical Leader, Technical Services Agenda Introduction PfRv3
Help! 2 Understanding and Troubleshooting Intelligent Path Control in IWAN Brandon Lynch Network Engineer, Core Software Group Richard Furr Technical Leader, Technical Services Agenda Introduction PfRv3
IWAN APIC-EM Application Cisco Intelligent WAN
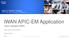 IWAN APIC-EM Application Cisco Intelligent WAN René og Per Cisco DK SE s Feb 23 th 2016 AVC MPLS Private Cloud 3G/4G-LTE Virtual Private Cloud Branch WAAS PfR Internet Public Cloud Control, Management,
IWAN APIC-EM Application Cisco Intelligent WAN René og Per Cisco DK SE s Feb 23 th 2016 AVC MPLS Private Cloud 3G/4G-LTE Virtual Private Cloud Branch WAAS PfR Internet Public Cloud Control, Management,
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example
 FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Cisco IOS Performance Routing Version 3 Command Reference
 First Published: 2017-04-07 Last Modified: 2017-04-07 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387)
First Published: 2017-04-07 Last Modified: 2017-04-07 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS (6387)
Intelligent WAN High Availability and Scalability Deployment Guide
 Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN High Availability and Scalability Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1
Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN High Availability and Scalability Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1
Performance Routing Version 3 Commands
 Performance Routing Version 3 Commands advanced, page 3 bandwidth (interface configuration), page 4 border (VRF configuration), page 7 class (master controller configuration), page 8 collector, page 9
Performance Routing Version 3 Commands advanced, page 3 bandwidth (interface configuration), page 4 border (VRF configuration), page 7 class (master controller configuration), page 8 collector, page 9
ARCHIVED DOCUMENT. - The topics in the document are now covered by more recent content.
 ARCHIVED DOCUMENT This document is archived and should only be used as a historical reference and should not be used for new deployments for one of the following reasons: - The topics in the document are
ARCHIVED DOCUMENT This document is archived and should only be used as a historical reference and should not be used for new deployments for one of the following reasons: - The topics in the document are
Intelligent WAN Design Summary
 Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Design Summary September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents WAN Strategy... 1 IWAN Introduction... 4 Business Use Cases for IWAN...4 Business Use Cases for
Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Design Summary September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents WAN Strategy... 1 IWAN Introduction... 4 Business Use Cases for IWAN...4 Business Use Cases for
Intelligent WAN Deployment Guide
 Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1 Configuring DMVPN Hub Router...2
Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1 Configuring DMVPN Hub Router...2
Cisco Service Advertisement Framework Deployment Guide
 Cisco Service Advertisement Framework Deployment Guide What You Will Learn Cisco Service Advertisement Framework (SAF) is a network-based, scalable, bandwidth-efficient approach to service advertisement
Cisco Service Advertisement Framework Deployment Guide What You Will Learn Cisco Service Advertisement Framework (SAF) is a network-based, scalable, bandwidth-efficient approach to service advertisement
IWAN Intelligent WAN, Next Generation Branch Architecture. Lars Thoren Technical Marketing Engineer, ENG
 IWAN Intelligent WAN, Next Generation Branch Architecture Lars Thoren Technical Marketing Engineer, ENG Mobile Device Network Traffic Average Number of Apps per Device* Average App Size** OS Update File
IWAN Intelligent WAN, Next Generation Branch Architecture Lars Thoren Technical Marketing Engineer, ENG Mobile Device Network Traffic Average Number of Apps per Device* Average App Size** OS Update File
Optimized Edge Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.1MT
 Optimized Edge Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.1MT Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800
Optimized Edge Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15.1MT Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800
Pressures on the WAN
 IWAN Radek Boch, Systems Engineer, Cisco, rboch@cisco.com CCIE#7095 14.11.2013 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 The Application Landscape Is Changing Applications Are
IWAN Radek Boch, Systems Engineer, Cisco, rboch@cisco.com CCIE#7095 14.11.2013 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 The Application Landscape Is Changing Applications Are
DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458
 DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 BRKCCIE-3003 @CCIE6458 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since
DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 BRKCCIE-3003 @CCIE6458 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since
Performance Routing (PfR) Master Controller Redundancy Configuration
 Performance Routing (PfR) Master Controller Redundancy Configuration This application note provides an overview on how to configure a Performance Routing (PfR) master controller in a redundant configuration.
Performance Routing (PfR) Master Controller Redundancy Configuration This application note provides an overview on how to configure a Performance Routing (PfR) master controller in a redundant configuration.
WAN Edge MPLSoL2 Service
 4 CHAPTER While Layer 3 VPN services are becoming increasing popular as a primary connection for the WAN, there are a much larger percentage of customers still using Layer 2 services such Frame-Relay (FR).
4 CHAPTER While Layer 3 VPN services are becoming increasing popular as a primary connection for the WAN, there are a much larger percentage of customers still using Layer 2 services such Frame-Relay (FR).
Deploying and Administering Cisco s Digital Network Architecture (DNA) and Intelligent WAN (IWAN) (DNADDC)
 Deploying and Administering Cisco s Digital Network Architecture (DNA) and Intelligent WAN (IWAN) (DNADDC) COURSE OVERVIEW: Deploying and Administering Cisco s Digital Network Architecture (DNA) and Intelligent
Deploying and Administering Cisco s Digital Network Architecture (DNA) and Intelligent WAN (IWAN) (DNADDC) COURSE OVERVIEW: Deploying and Administering Cisco s Digital Network Architecture (DNA) and Intelligent
Cisco Performance Routing
 Cisco Performance Routing As enterprise organizations grow their businesses, the demand for real-time application performance and a better application experience for users increases. For example, voice
Cisco Performance Routing As enterprise organizations grow their businesses, the demand for real-time application performance and a better application experience for users increases. For example, voice
Cloud Intelligent Network
 Dubrovnik, Croatia, South East Europe 20-22 May, 2013 Cloud Intelligent Network Mitko Vasilev CIN Lead Central Europe mitko@cisco.com 2011 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 1 New Application
Dubrovnik, Croatia, South East Europe 20-22 May, 2013 Cloud Intelligent Network Mitko Vasilev CIN Lead Central Europe mitko@cisco.com 2011 2012 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 1 New Application
GRE and DM VPNs. Understanding the GRE Modes Page CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 You can configure Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) and Dynamic Multipoint (DM) VPNs that include GRE mode configurations. You can configure IPsec GRE VPNs for hub-and-spoke, point-to-point,
CHAPTER 23 You can configure Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) and Dynamic Multipoint (DM) VPNs that include GRE mode configurations. You can configure IPsec GRE VPNs for hub-and-spoke, point-to-point,
SD-WAN Deployment Guide (CVD)
 SD-WAN Deployment Guide (CVD) All Cisco Meraki security appliances are equipped with SD-WAN capabilities that enable administrators to maximize network resiliency and bandwidth efficiency. This guide introduces
SD-WAN Deployment Guide (CVD) All Cisco Meraki security appliances are equipped with SD-WAN capabilities that enable administrators to maximize network resiliency and bandwidth efficiency. This guide introduces
IWAN Security for Remote Site Direct Internet Access and Guest Wireless
 IWAN Security for Remote Site Direct Internet Access and Guest Wireless Technology Design Guide (ISR4K) March 2015 Table of Contents Preface...1 CVD Navigator...2 Use Cases... 2 Scope... 2 Proficiency...
IWAN Security for Remote Site Direct Internet Access and Guest Wireless Technology Design Guide (ISR4K) March 2015 Table of Contents Preface...1 CVD Navigator...2 Use Cases... 2 Scope... 2 Proficiency...
Configuring Basic Performance Routing
 Performance Routing (PfR) provides additional intelligence to classic routing technologies to track the performance of, or verify the quality of, a path between two devices over a Wide Area Networking
Performance Routing (PfR) provides additional intelligence to classic routing technologies to track the performance of, or verify the quality of, a path between two devices over a Wide Area Networking
REFERENCE NETWORK ARCHITECTURE
 REFERENCE NETWORK ARCHITECTURE CISCO VALIDATED DESIGN Intelligent WAN Technology Design Guide February 2016 REFERENCE NETWORK ARCHITECTURE Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Technology
REFERENCE NETWORK ARCHITECTURE CISCO VALIDATED DESIGN Intelligent WAN Technology Design Guide February 2016 REFERENCE NETWORK ARCHITECTURE Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Technology
Intelligent WAN. Technology Design Guide
 Intelligent WAN Technology Design Guide January 2015 Table of Contents Preface... 1 CVD Navigator... 2 Use Cases...2 Scope...2 Proficiency...2 Introduction... 3 Technology Use Cases...3 Use Case: Secure
Intelligent WAN Technology Design Guide January 2015 Table of Contents Preface... 1 CVD Navigator... 2 Use Cases...2 Scope...2 Proficiency...2 Introduction... 3 Technology Use Cases...3 Use Case: Secure
Cisco recommends that you have basic knowledge of Performance Routing (PfR).
 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Passive Monitoring Active Monitoring Hybrid Mode Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Passive
Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Passive Monitoring Active Monitoring Hybrid Mode Configure Network Diagram Relevant Configuration Verify Passive
Setting Up OER Network Components
 Setting Up OER Network Components First Published: January 29, 2007 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes the concepts and tasks to help you set up the network components required for an
Setting Up OER Network Components First Published: January 29, 2007 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes the concepts and tasks to help you set up the network components required for an
MPLS VPN over mgre. Finding Feature Information. Last Updated: November 1, 2012
 MPLS VPN over mgre Last Updated: November 1, 2012 The MPLS VPN over mgre feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity
MPLS VPN over mgre Last Updated: November 1, 2012 The MPLS VPN over mgre feature overcomes the requirement that a carrier support multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) by allowing you to provide MPLS connectivity
Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN: Simple and Secure Branch-to-Branch Communications
 Data Sheet Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN: Simple and Secure Branch-to-Branch Communications Product Overview Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) is a Cisco IOS Software-based security solution for building
Data Sheet Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN: Simple and Secure Branch-to-Branch Communications Product Overview Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) is a Cisco IOS Software-based security solution for building
Performance Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS Release 15M&T
 First Published: November 29, 2012 Last Modified: March 25, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS
First Published: November 29, 2012 Last Modified: March 25, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000 800 553-NETS
CVP Enterprise Cisco SD-WAN Retail Profile (Hybrid WAN, Segmentation, Zone-Based Firewall, Quality of Service, and Centralized Policies)
 CVP CVP Enterprise Cisco SD-WAN Retail Profile (Hybrid WAN, Segmentation, Zone-Based Firewall, Quality of Service, and Centralized Policies) 2018 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This
CVP CVP Enterprise Cisco SD-WAN Retail Profile (Hybrid WAN, Segmentation, Zone-Based Firewall, Quality of Service, and Centralized Policies) 2018 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This
IWAN AVC/QoS Design. Kelly Fleshner, Communications Architect. CCIE # years BRKRST-2043
 IWAN AVC/QoS Design Kelly Fleshner, Communications Architect CCIE #1852 21 years BRKRST-2043 Cisco Spark How Questions? Use Cisco Spark to chat with the speaker after the session 1. Find this session in
IWAN AVC/QoS Design Kelly Fleshner, Communications Architect CCIE #1852 21 years BRKRST-2043 Cisco Spark How Questions? Use Cisco Spark to chat with the speaker after the session 1. Find this session in
DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates
 DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 BRKCCIE-3003 @CCIE6458 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since
DMVPN for R&S CCIE Candidates Johnny Bass CCIE #6458 BRKCCIE-3003 @CCIE6458 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public About the Presenter Johnny Bass Networking industry since
Network Automation and Branch Agility The Network Helps Enable Digital Business. Rajinder Singh Product Sales Specialist June 2016
 Network Automation and Branch Agility The Network Helps Enable Digital Business Rajinder Singh Product Sales Specialist June 2016 Agenda WAN Market Drivers Cisco Intelligent WAN (IWAN) Cisco Intelligent
Network Automation and Branch Agility The Network Helps Enable Digital Business Rajinder Singh Product Sales Specialist June 2016 Agenda WAN Market Drivers Cisco Intelligent WAN (IWAN) Cisco Intelligent
Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN: Simple and Secure Branch-to-Branch Communications
 Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN: Simple and Secure Branch-to-Branch Communications Product Overview Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) is a Cisco IOS Software-based security solution for building scalable
Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN: Simple and Secure Branch-to-Branch Communications Product Overview Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) is a Cisco IOS Software-based security solution for building scalable
BGP Inbound Optimization Using Performance Routing
 BGP Inbound Optimization Using Performance Routing The PfR BGP Inbound Optimization feature introduced support for the best entrance selection for traffic that originates from prefixes outside an autonomous
BGP Inbound Optimization Using Performance Routing The PfR BGP Inbound Optimization feature introduced support for the best entrance selection for traffic that originates from prefixes outside an autonomous
MPLS VPN Inter-AS Option AB
 First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
First Published: December 17, 2007 Last Updated: September 21, 2011 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol
Migrating Your Existing WAN to Cisco s IWAN
 Migrating Your Existing WAN to Cisco s IWAN BRKCRS-2007 Brad Edgeworth, CCIE#31574, Systems Engineer @BradEdgeworth Mani Ganesan, CCIE#27200, Consulting Systems Engineer @Mani_Cisco Introduction Housekeeping
Migrating Your Existing WAN to Cisco s IWAN BRKCRS-2007 Brad Edgeworth, CCIE#31574, Systems Engineer @BradEdgeworth Mani Ganesan, CCIE#27200, Consulting Systems Engineer @Mani_Cisco Introduction Housekeeping
MPLS VPN--Inter-AS Option AB
 The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
The feature combines the best functionality of an Inter-AS Option (10) A and Inter-AS Option (10) B network to allow a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) service provider
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Last Updated: December 14, 2011 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Last Updated: December 14, 2011 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier Using LDP and an IGP Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) enables one MPLS VPN-based service provider
Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Firewall and NAT
 Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Firewall and NAT The Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Firewall and NAT feature supports the forwarding of packets from a standby
Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Firewall and NAT The Interchassis Asymmetric Routing Support for Zone-Based Firewall and NAT feature supports the forwarding of packets from a standby
Cisco Group Encrypted Transport VPN
 Cisco Group Encrypted Transport VPN Q. What is Cisco Group Encrypted Transport VPN? A. Cisco Group Encrypted Transport is a next-generation WAN VPN solution that defines a new category of VPN, one that
Cisco Group Encrypted Transport VPN Q. What is Cisco Group Encrypted Transport VPN? A. Cisco Group Encrypted Transport is a next-generation WAN VPN solution that defines a new category of VPN, one that
VeloCloud Cloud-Delivered WAN Fast. Simple. Secure. KUHN CONSULTING GmbH
 VeloCloud Cloud-Delivered WAN Fast. Simple. Secure. 1 Agenda 1. Overview and company presentation 2. Solution presentation 3. Main benefits to show to customers 4. Deployment models 2 VeloCloud Company
VeloCloud Cloud-Delivered WAN Fast. Simple. Secure. 1 Agenda 1. Overview and company presentation 2. Solution presentation 3. Main benefits to show to customers 4. Deployment models 2 VeloCloud Company
Enterprise SD-WAN Financial Profile (Hybrid WAN, Segmentation, Quality of Service, Centralized Policies)
 CVP CVP Enterprise SD-WAN Financial Profile (Hybrid WAN, Segmentation, Quality of Service, Centralized Policies) 2018 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
CVP CVP Enterprise SD-WAN Financial Profile (Hybrid WAN, Segmentation, Quality of Service, Centralized Policies) 2018 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks
 Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
Shortcut Switching Enhancements for NHRP in DMVPN Networks Routers in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) Phase 3 network use Next Hop Resolution Protocol (NHRP) Shortcut Switching to discover shorter paths
Configuring FlexVPN Spoke to Spoke
 Last Published Date: March 28, 2014 The FlexVPN Spoke to Spoke feature enables a FlexVPN client to establish a direct crypto tunnel with another FlexVPN client leveraging virtual tunnel interfaces (VTI),
Last Published Date: March 28, 2014 The FlexVPN Spoke to Spoke feature enables a FlexVPN client to establish a direct crypto tunnel with another FlexVPN client leveraging virtual tunnel interfaces (VTI),
COURSE OUTLINE: Course: CCNP Route Duration: 40 Hours
 COURSE OUTLINE: Course: CCNP Route 300-101 Duration: 40 Hours CCNP Route Training Day 1: Connecting Remote Locations Principles of Static Routing Configuring an IPv4 Static Route Configuring a Static Default
COURSE OUTLINE: Course: CCNP Route 300-101 Duration: 40 Hours CCNP Route Training Day 1: Connecting Remote Locations Principles of Static Routing Configuring an IPv4 Static Route Configuring a Static Default
Intelligent WAN Remote Site 4G LTE Deployment Guide
 Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Remote Site 4G LTE Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1 Deploying Remote
Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Remote Site 4G LTE Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deployment Details...1 Deploying Remote
DNA SA Border Node Support
 Digital Network Architecture (DNA) Security Access (SA) is an Enterprise architecture that brings together multiple building blocks needed for a programmable, secure, and highly automated fabric. Secure
Digital Network Architecture (DNA) Security Access (SA) is an Enterprise architecture that brings together multiple building blocks needed for a programmable, secure, and highly automated fabric. Secure
LiveAction IWAN Management
 LIVEACTION, INC. LiveAction IWAN Management LiveAction, Inc. 3500 WEST BAYSHORE ROAD PALO Copyright ALTO, CA 2016 94303 LiveAction, Inc. All rights reserved. LiveAction, LiveNX, LiveUX, the LiveAction
LIVEACTION, INC. LiveAction IWAN Management LiveAction, Inc. 3500 WEST BAYSHORE ROAD PALO Copyright ALTO, CA 2016 94303 LiveAction, Inc. All rights reserved. LiveAction, LiveNX, LiveUX, the LiveAction
Advanced Concepts of DMVPN (Dynamic Multipoint VPN)
 Advanced Concepts of DMVPN (Dynamic Multipoint VPN) Mike Sullenberger Distinguished Engineer Agenda DMVPN Design Overview DMVPN General IWAN Specific NHRP Details NHRP Overview NHRP Registrations/Resolutions/Redirects
Advanced Concepts of DMVPN (Dynamic Multipoint VPN) Mike Sullenberger Distinguished Engineer Agenda DMVPN Design Overview DMVPN General IWAN Specific NHRP Details NHRP Overview NHRP Registrations/Resolutions/Redirects
VRF, MPLS and MP-BGP Fundamentals
 VRF, MPLS and MP-BGP Fundamentals Jason Gooley, CCIEx2 (RS, SP) #38759 Twitter: @ccie38759 LinkedIn: http://www.linkedin.com/in/jgooley Agenda Introduction to Virtualization VRF-Lite MPLS & BGP Free Core
VRF, MPLS and MP-BGP Fundamentals Jason Gooley, CCIEx2 (RS, SP) #38759 Twitter: @ccie38759 LinkedIn: http://www.linkedin.com/in/jgooley Agenda Introduction to Virtualization VRF-Lite MPLS & BGP Free Core
IPv6 Switching: Provider Edge Router over MPLS
 Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is deployed by many service providers in their IPv4 networks. Service providers want to introduce IPv6 services to their customers, but changes to their existing IPv4
Enterprise. Nexus 1000V. L2/L3 Fabric WAN/PE. Customer VRF. MPLS Backbone. Service Provider Data Center-1 Customer VRF WAN/PE OTV OTV.
 2 CHAPTER Cisco's Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) architecture supports virtual data centers that consist of a collection of geographically-dispersed data center locations. Since data centers are
2 CHAPTER Cisco's Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) architecture supports virtual data centers that consist of a collection of geographically-dispersed data center locations. Since data centers are
Exam Questions Demo Cisco. Exam Questions CCIE SP CCIE Service Provider Written Exam
 Cisco Exam Questions 400-201 CCIE SP CCIE Service Provider Written Exam Version:Demo 1. Which is one difference between H-VPLS and VPLS? A. VPLS is a point-to-point Layer-2 services and H-VPLS is a multipoint
Cisco Exam Questions 400-201 CCIE SP CCIE Service Provider Written Exam Version:Demo 1. Which is one difference between H-VPLS and VPLS? A. VPLS is a point-to-point Layer-2 services and H-VPLS is a multipoint
Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela) Migration, QoS and Advanced Policies Hands-on Lab
 Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela) Migration, QoS and Advanced Policies Hands-on Lab Ali Shaikh Technical Leader Faraz Shamim Sr. Technical Leader Mossaddaq Turabi Distinguished ENgineer Cisco Spark How Questions?
Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela) Migration, QoS and Advanced Policies Hands-on Lab Ali Shaikh Technical Leader Faraz Shamim Sr. Technical Leader Mossaddaq Turabi Distinguished ENgineer Cisco Spark How Questions?
Cisco SD-WAN and DNA-C
 Cisco SD-WAN and DNA-C SD-WAN Cisco SD-WAN Intent-based networking for the branch and WAN 4x Improved application experience Better user experience Deploy applications in minutes on any platform with consistent
Cisco SD-WAN and DNA-C SD-WAN Cisco SD-WAN Intent-based networking for the branch and WAN 4x Improved application experience Better user experience Deploy applications in minutes on any platform with consistent
CCIE Routing & Switching
 CCIE Routing & Switching Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert Routing and Switching (CCIE Routing and Switching) certifies the skills required of expert-level network engineers to plan, operate and troubleshoot
CCIE Routing & Switching Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert Routing and Switching (CCIE Routing and Switching) certifies the skills required of expert-level network engineers to plan, operate and troubleshoot
Performing Path Traces
 About Path Trace, page 1 Performing a Path Trace, page 13 Collecting QoS and Interface Statistics in a Path Trace, page 15 About Path Trace With Path Trace, the controller reviews and collects network
About Path Trace, page 1 Performing a Path Trace, page 13 Collecting QoS and Interface Statistics in a Path Trace, page 15 About Path Trace With Path Trace, the controller reviews and collects network
Adaptive QoS over DMVPN
 Adaptive QoS over Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) ensures effective bandwidth management using dynamic shapers based on available bandwidth. This feature enables various QoS features to adapt to non service-level
Adaptive QoS over Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) ensures effective bandwidth management using dynamic shapers based on available bandwidth. This feature enables various QoS features to adapt to non service-level
Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN
 Platformă de e-learning și curriculă e-content pentru învățământul superior tehnic Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN MPLS VPN 5-ian-2010 What this lecture is about: IP
Platformă de e-learning și curriculă e-content pentru învățământul superior tehnic Securizarea Calculatoarelor și a Rețelelor 32. Tehnologia MPLS VPN MPLS VPN 5-ian-2010 What this lecture is about: IP
CCIE R&S LAB CFG H2/A5 (Jacob s & Jameson s)
 Contents Section 1 Layer 2 Technologies... 2 1.1 Jameson s Datacenter: Access port... 2 1.2 Jameson s Datacenter: Trunk ports... 4 1.3 Jameson s Datacenter: Link bundling... 5 1.4 Jameson s Branch Offices...
Contents Section 1 Layer 2 Technologies... 2 1.1 Jameson s Datacenter: Access port... 2 1.2 Jameson s Datacenter: Trunk ports... 4 1.3 Jameson s Datacenter: Link bundling... 5 1.4 Jameson s Branch Offices...
VPN WAN. Technology Design Guide
 VPN WAN Technology Design Guide December 2013 Table of Contents Preface...1 CVD Navigator...2 Use Cases... 2 Scope... 2 Proficiency... 2 Introduction...3 Related Reading... 3 Technology Use Cases... 3
VPN WAN Technology Design Guide December 2013 Table of Contents Preface...1 CVD Navigator...2 Use Cases... 2 Scope... 2 Proficiency... 2 Introduction...3 Related Reading... 3 Technology Use Cases... 3
CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 7 & 21: Wide Area Networks
 CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 7 & 21: Wide Area Networks Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 21 objectives The ICND2 topics covered in this chapter include: 2 Chapter 21 objectives (con
CCNA Routing and Switching Study Guide Chapters 7 & 21: Wide Area Networks Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 21 objectives The ICND2 topics covered in this chapter include: 2 Chapter 21 objectives (con
LABRST-2099 iwan Deployment using NSO
 LABRST-2099 iwan Deployment using NS Intelligent WAN (IWAN) enables businesses to switch smoothly between different WAN transports with no compromise in terms of application performance, reliability, or
LABRST-2099 iwan Deployment using NS Intelligent WAN (IWAN) enables businesses to switch smoothly between different WAN transports with no compromise in terms of application performance, reliability, or
Cisco Virtual Office High-Scalability Design
 Solution Overview Cisco Virtual Office High-Scalability Design Contents Scope of Document... 2 Introduction... 2 Platforms and Images... 2 Design A... 3 1. Configure the ACE Module... 3 2. Configure the
Solution Overview Cisco Virtual Office High-Scalability Design Contents Scope of Document... 2 Introduction... 2 Platforms and Images... 2 Design A... 3 1. Configure the ACE Module... 3 2. Configure the
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
 The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (L3VPN) services, over an IP core network, using L2TPv3 multipoint tunneling instead of MPLS. This allows L2TPv3 tunnels
The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (L3VPN) services, over an IP core network, using L2TPv3 multipoint tunneling instead of MPLS. This allows L2TPv3 tunnels
Monitoring MPLS Services
 CHAPTER 17 The following topics describe how to view and manage aspects of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) services using Cisco Prime Network Vision (Prime Network Vision), including the MPLS service
CHAPTER 17 The following topics describe how to view and manage aspects of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) services using Cisco Prime Network Vision (Prime Network Vision), including the MPLS service
Add Path Support in EIGRP
 The feature enables hubs in a single Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) domain to advertise multiple best paths to connected spokes when the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is the routing
The feature enables hubs in a single Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) domain to advertise multiple best paths to connected spokes when the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is the routing
MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP. BGP IPv4 Label Session
 MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session The MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session feature provides a method to advertise explicit null in a Border Gateway
MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session The MPLS VPN Explicit Null Label Support with BGP IPv4 Label Session feature provides a method to advertise explicit null in a Border Gateway
Managing Site-to-Site VPNs: The Basics
 CHAPTER 23 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
CHAPTER 23 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Foundation Learning Guide Foundation learning for the ROUTE 642-902 Exam Diane Teare Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, IN 46240 Implementing Cisco IP
Migrating from Dynamic Multipoint VPN Phase 2 to Phase 3: Why and How to Migrate to the Next Phase
 Migration Guide Migrating from Dynamic Multipoint VPN Phase 2 to Phase 3: Why and How to Migrate to the Next Phase This guide shows how a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) deployment can be migrated to make
Migration Guide Migrating from Dynamic Multipoint VPN Phase 2 to Phase 3: Why and How to Migrate to the Next Phase This guide shows how a Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) deployment can be migrated to make
Remote Access MPLS-VPNs
 First Published: August 12, 2002 Last Updated: May 4, 2009 The feature allows the service provider to offer a scalable end-to-end Virtual Private Network (VPN) service to remote users. This feature integrates
First Published: August 12, 2002 Last Updated: May 4, 2009 The feature allows the service provider to offer a scalable end-to-end Virtual Private Network (VPN) service to remote users. This feature integrates
MPLS VPN Multipath Support for Inter-AS VPNs
 The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
The feature supports Virtual Private Network (VPN)v4 multipath for Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs) in the interautonomous system (Inter-AS) Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) VPN environment.
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution
 MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature lets you configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes and Multiprotocol
MPLS VPN Carrier Supporting Carrier IPv4 BGP Label Distribution This feature lets you configure your carrier supporting carrier network to enable Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to transport routes and Multiprotocol
ibgp Multipath Load Sharing
 This feature module describes the feature. This feature enables the BGP speaking router to select multiple ibgp paths as the best paths to a destination. The best paths or multipaths are then installed
This feature module describes the feature. This feature enables the BGP speaking router to select multiple ibgp paths as the best paths to a destination. The best paths or multipaths are then installed
Technology Overview. Overview CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 2 Revised: July 29, 2013, This overview of AVC technology includes the following topics: Overview, page 2-1 AVC Features and Capabilities, page 2-2 AVC Architecture, page 2-4 Interoperability of
CHAPTER 2 Revised: July 29, 2013, This overview of AVC technology includes the following topics: Overview, page 2-1 AVC Features and Capabilities, page 2-2 AVC Architecture, page 2-4 Interoperability of
Flexible Dynamic Mesh VPN draft-detienne-dmvpn-00
 Flexible Dynamic Mesh VPN draft-detienne-dmvpn-00 Fred Detienne, Cisco Systems Manish Kumar, Cisco Systems Mike Sullenberger, Cisco Systems What is Dynamic Mesh VPN? DMVPN is a solution for building VPNs
Flexible Dynamic Mesh VPN draft-detienne-dmvpn-00 Fred Detienne, Cisco Systems Manish Kumar, Cisco Systems Mike Sullenberger, Cisco Systems What is Dynamic Mesh VPN? DMVPN is a solution for building VPNs
Managing Site-to-Site VPNs: The Basics
 CHAPTER 21 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
CHAPTER 21 A virtual private network (VPN) consists of multiple remote peers transmitting private data securely to one another over an unsecured network, such as the Internet. Site-to-site VPNs use tunnels
Highly Available Wide Area Network Design
 Highly Available Wide Area Network Design David Prall, Communications Architect dprall@cisco.com CCIE #6508 (R&S/SP/Security) BRKRST-2042 Agenda Introduction Cisco IOS and IP Routing Convergence Techniques
Highly Available Wide Area Network Design David Prall, Communications Architect dprall@cisco.com CCIE #6508 (R&S/SP/Security) BRKRST-2042 Agenda Introduction Cisco IOS and IP Routing Convergence Techniques
BGP Link Bandwidth. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for BGP Link Bandwidth
 The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Link Bandwidth feature is used to advertise the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community. This feature is configured for links between directly
