Routing Bottlenecks in the Internet: Causes, Exploits, and Countermeasures. ECE Department and CyLab, Carnegie Mellon University
|
|
|
- May Douglas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Routing Bottlenecks in the Internet: Causes, Exploits, and Countermeasures Min Suk Kang Virgil D. Gligor ECE Department and CyLab, Carnegie Mellon University Nov 4, 2014
2 2 Route Diversity is Critical to Resiliency of Internet Connectivity link-flooding attack rest of the world geographic area with poor route diversity
3 3 Fortunately, most countries have enough route diversity # of ISPs with direct international connectivity (source: Most countries have 10+ ISPs with international connections => good Internet route diversity Then, do we need to worry about the link-flooding attacks? Unfortunately, YES.
4 4 Despite high route diversity, Internet connectivity of countries can be degraded Why? routing bottleneck the vast majority of Internet routes to chosen destinations concentrated on a small set of links Paper illustrates 1. pervasive phenomenon of routing bottlenecks 2. causes of routing bottlenecks 3. impact of targeted attacks & countermeasures
5 5 Mincut and Routing Bottleneck mincut, M(S,D) sources (S) routing bottleneck, B destinations (D) geographic area B M(S,D) e.g routing bottleneck bandwidth bottleneck
6 Normalized Link Occurrence 6 Routing Bottlenecks in the current Internet 250 nodes in PlanetLab (in 164 cities in 39 countries) sources (S) M(S,D) B traceroute Link Occurrence 1,000 randomly selected working servers destinations (D) geographic area (ratio) measurement for a country B (0.80) high rank low rank Rank of Links in M(S,D)
7 Normalized link occurrence 7 Routing Bottlenecks 0.4 in 15 Countries link occurrence is accurately modeled by a power-law Tested Countries (alphabetical) Brazil Egypt France Germany India Iran Israel Italy Japan Romania Russia S. Korea Taiwan Turkey UK Country1 Country2 Country3 Country4 Country5 Country6 Country7 Country8 Country9 Country10 Country11 Country12 Country13 Country14 Country15 Country1 Country2 Country3 Country4 Country5 Country6 Country7 Country8 Country9 Country10 Country11 Country12 Country13 Country14 Country15 Country15 α = Rank of Link Country1 (β = 7.8) α = 1.31 Zipf-Mandelbrot distribution f(k) = 1 (k + β) α
8 Normalized link occurrence Routing Bottlenecks 0.25 in 15 Large Cities link occurrence is accurately modeled by a power-law Tested Cities (alphabetical) Beijing Berlin Chicago Guangzhou Houston London Los Angeles Moscow New York Paris Philadelphia Rome Shanghai Shenzhen Tianjin City15 α =2.17 City1 City2 City3 City4 City5 City6 City7 City8 City9 City10 City11 City12 City13 City14 City15 City1 City2 City3 City4 City5 City6 City7 City8 City Rank of Link City1 (β = 7.8) α = 1.38 Zipf-Mandelbrot distribution f(k) = 1 (k + β) α
9 9 Causes? An Analogy w/ Word Occurrence Distribution sentence construction: Principle of least effort [Zipf 49, Mandelbrot 53] ==> Z-M distribution of word occurrence Speaker route construction: Internet routers policies word1 word2 wordn conjecture: route-cost minimization ==> Z-M distribution of link occurrence link1 link2 linkn
10 Norm. Link Occurrence 10 Evidence for Inter-Domain Routing Policy: route-cost minimization BGP favors minimum-cost link => AS-level route concentration Test: policy I: favors min-cost links policy II: distribute routes uniformly AS* $$$? AS AS $ AS AS (*) AS: autonomous system Rank of Inter-AS Links
11 Norm. Link Occurrence 11 Evidence for Intra-Domain Routing Practice: route-cost minimization hierarchical topology + shortest path routing => route concentration at backbones Test: all possible ingress/egress routes clear Zipf-Mandelbrot distribution AS Rank of Intra-AS Links
12 12 Link Types of Routing Bottlenecks 3 link locations: intra-as inter-as IXP AS 1 AS 2 IXP (Internet exchange points) AS 3 AS 4 3 AS categories: Tier-1 Tier-2 Tier-2 Tier-3 Tier-3 Tier-3 Tier-3 (Global Transits/ National Backbones) (regional providers) (customers)
13 Link IXP (N/D: Types not determined) of Routing Bottlenecks < Avg. link types of 50 bottleneck links of 15 countries (percentage) > INTRA-AS (N/D: not determined) N/D N/D inter (N/D) IXP inter (Tier2-Tier3) inter (N/D) (Tier2-Tier2) inter (Tier2-Tier3) (Tier1-Tier3) inter (Tier2-Tier2) (Tier1-Tier2) inter (Tier1-Tier3) (Tier1-Tier1) inter intra (Tier1-Tier2) (Tier2) inter intra Tier-1 (Tier1-Tier1) (Tier1) INTER-AS 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% (N/D: not determined) Tier-2 intra (Tier2) intra (Tier1) (N/D: not determined) intra (Tier1) various link types: intra (30%), inter (30%), and IXP (20%) N/D (N/D: not determined) IXP N/D inter (N/D) IXP inter (Tier2-Tier3) inter N/D (N/D) inter (Tier2-Tier2) inter IXP IXP inter (Tier2-Tier3) (Tier1-Tier3) inter N/D inter (Tier2-Tier2) (N/D) (Tier1-Tier2) inter IXP inter (Tier1-Tier3) (Tier2-Tier3) (Tier1-Tier1) inter N/D intra (Tier2) (Tier1-Tier2) (Tier2-Tier2) (N/D) inter IXP intra (Tier1) (Tier1-Tier1) (Tier1-Tier3) (Tier2-Tier3) intra inter N/D Tier2-Tier2 (Tier2) (Tier1-Tier2) (Tier2-Tier2) (N/D) intra Tier2-Tier3 inter IXP (Tier1) (Tier1-Tier1) (Tier1-Tier3) (Tier2-Tier3) Not intra inter Determined (Tier2) (Tier1-Tier2) (Tier2-Tier2) (N/D) inter (Tier1-Tier1) (Tier1-Tier3) (Tier2-Tier3) intra inter (Tier2) (Tier1-Tier2) (Tier2-Tier2) intra inter (Tier1) (Tier1-Tier1) (Tier1-Tier3) intra inter (Tier2) (Tier1-Tier2) (N/D: not determined) (N/D: not determined) (N/D: not determined) 91% of inter/intra-as links are owned by Tier-1/Tier-2 Not Deter. 13
14 14 Routing-Bottleneck Exploits Massive Link Flooding e.g., Crossfire attack [IEEE S&P 2013] Link-flooding with indistinguishable attack flows Botnets low-rate attack flows routing-bottleneck link Decoy Servers several hops away (e.g., 40 Gbps = 4 Kbps x 10K bots x 1K decoys) Target Geographic area
15 Degradation Ratio 15 Connectivity Degradation in 15 Countries Country15 α = Country1 α = 1.31 (β = 7.8) Country1 Country2 Country3 Country4 Country5 Country6 Country7 Country8 Country9 Country10 Country11 Country12 Country13 Country14 Country Number of Links to Flood
16 Degradation Ratio 16 Connectivity Degradation in 15 Large Cities City15 α = City1 α = 1.38 (β = 7.8) City1 City2 City3 City4 City5 City6 City7 City8 City9 City10 City11 City12 City13 City14 City Number of Links to Flood
17 17 Countermeasures Inter-domain links Load balancing across parallel links between two ASes [ATC 07] Load balancing across links to different ASes [SIGCOMM 06] AS2 AS1 AS2 AS1 AS3 AS4
18 18 Countermeasures Intra-domain links Equal-cost multipath (ECMP) Needs real-time link-weight re-adjustment MPLS tunnels Needs real-time MPLS traffic enginnering (unknown if recent SDN-based solutions can be applied here) AS AS
19 Reduction of degradation ratio (%) 19 Effectiveness of Countermeasures 4 implementation alternatives: Inter-AS links Intra-AS links Tier-1 ASes Tier-1&2 ASes one type fits all countermeasures are not very effective countermeasures at large ISPs (Tier-1&2) are most effective
20 20 Related Work Internet topology studies; e.g., CAIDA, DIMES, etc. Power-law in Internet connectivity; e.g., [SIGCOMM 99, NATURE 00] Link-flooding attacks; e.g., Coremelt [ESORICS 09], Crossfire [S&P 13]
21 21 Conclusions Notion of the routing bottlenecks they are pervasive (in 15 countries and 15 cities) Causes: route-cost minimization very desirable feature of Internet routing Countermeasures effective when implemented in large ISPs
22 22 Thank You Min Suk Kang
Routing Bottlenecks in the Internet: Causes, Exploits, and Countermeasures
 Routing Bottlenecks in the Internet: Causes, Exploits, and Countermeasures ABSTRACT Min Suk Kang ECE and CyLab Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA USA minsukkang@cmu.edu How pervasive is the vulnerability
Routing Bottlenecks in the Internet: Causes, Exploits, and Countermeasures ABSTRACT Min Suk Kang ECE and CyLab Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA USA minsukkang@cmu.edu How pervasive is the vulnerability
CoDef: Collaborative Defense against Large-Scale Link-Flooding Attacks
 CoDef: Collaborative Defense against Large-Scale Link-Flooding Attacks Soo Bum Lee *, Min Suk Kang, Virgil D. Gligor CyLab, Carnegie Mellon University * Qualcomm Dec. 12, 2013 Large Scale Link-Flooding
CoDef: Collaborative Defense against Large-Scale Link-Flooding Attacks Soo Bum Lee *, Min Suk Kang, Virgil D. Gligor CyLab, Carnegie Mellon University * Qualcomm Dec. 12, 2013 Large Scale Link-Flooding
Achieving scale: Large scale active measurements from PlanetLab
 Achieving scale: Large scale active measurements from PlanetLab Marc-Olivier Buob, Jordan Augé (UPMC) 4th PhD School on Traffic Monitoring and Analysis (TMA) April 15th, 2014 London, UK OneLab FUTURE INTERNET
Achieving scale: Large scale active measurements from PlanetLab Marc-Olivier Buob, Jordan Augé (UPMC) 4th PhD School on Traffic Monitoring and Analysis (TMA) April 15th, 2014 London, UK OneLab FUTURE INTERNET
Early detection of Crossfire attacks using deep learning
 Early detection of Crossfire attacks using deep learning Saurabh Misra, Mengxuan Tan, Mostafa Rezazad, Ngai-Man Cheung Singapore University of Technology and Design Content The Crossfire Attack A brief
Early detection of Crossfire attacks using deep learning Saurabh Misra, Mengxuan Tan, Mostafa Rezazad, Ngai-Man Cheung Singapore University of Technology and Design Content The Crossfire Attack A brief
Israel Internet Security Threat Profile
 Israel Internet Security Threat Profile Worldwide Ranking.%.%.%.%.%.%.%.%.%.%.% Overall Average Spam Zombies Malicious Code Phishing Hosts Bots Network Attacking Countries Copyright Symantec Corporation.
Israel Internet Security Threat Profile Worldwide Ranking.%.%.%.%.%.%.%.%.%.%.% Overall Average Spam Zombies Malicious Code Phishing Hosts Bots Network Attacking Countries Copyright Symantec Corporation.
CoDef: Collaborative Defense Against Large-Scale Link-Flooding Attacks
 CoDef: Collaborative Defense Against Large-Scale Link-Flooding Attacks Soo Bum Lee Min Suk Kang Qualcomm ECE and CyLab San Diego, CA USA Carnegie Mellon University soobuml@qti.qualcomm.com Pittsburgh,
CoDef: Collaborative Defense Against Large-Scale Link-Flooding Attacks Soo Bum Lee Min Suk Kang Qualcomm ECE and CyLab San Diego, CA USA Carnegie Mellon University soobuml@qti.qualcomm.com Pittsburgh,
Hurricane Electric What do around 12,000 IPv6 users actually do?
 Hurricane Electric What do around 12,000 IPv6 users actually do? IPv6 Native Backbone Massive Peering! APNIC-26 Christchurch, New Zealand 27 th August 2008 Martin J. Levy, Director IPv6 Strategy Hurricane
Hurricane Electric What do around 12,000 IPv6 users actually do? IPv6 Native Backbone Massive Peering! APNIC-26 Christchurch, New Zealand 27 th August 2008 Martin J. Levy, Director IPv6 Strategy Hurricane
BGP. Daniel Zappala. CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University
 Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/20 Scaling Routing for the Internet scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes in routing tables
Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/20 Scaling Routing for the Internet scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes in routing tables
Minimizing Collateral Damage by Proactive Surge Protection
 Minimizing Collateral Damage by Proactive Surge Protection Jerry Chou, Bill Lin University of California, San Diego Subhabrata Sen, Oliver Spatscheck AT&T Labs-Research ACM SIGCOMM LSAD Workshop, Kyoto,
Minimizing Collateral Damage by Proactive Surge Protection Jerry Chou, Bill Lin University of California, San Diego Subhabrata Sen, Oliver Spatscheck AT&T Labs-Research ACM SIGCOMM LSAD Workshop, Kyoto,
Virtual Multi-homing: On the Feasibility of Combining Overlay Routing with BGP Routing
 Virtual Multi-homing: On the Feasibility of Combining Overlay Routing with BGP Routing Zhi Li, Prasant Mohapatra, and Chen-Nee Chuah University of California, Davis, CA 95616, USA {lizhi, prasant}@cs.ucdavis.edu,
Virtual Multi-homing: On the Feasibility of Combining Overlay Routing with BGP Routing Zhi Li, Prasant Mohapatra, and Chen-Nee Chuah University of California, Davis, CA 95616, USA {lizhi, prasant}@cs.ucdavis.edu,
COM-208: Computer Networks - Homework 6
 COM-208: Computer Networks - Homework 6. (P22) Suppose you are interested in detecting the number of hosts behind a NAT. You observe that the IP layer stamps an identification number sequentially on each
COM-208: Computer Networks - Homework 6. (P22) Suppose you are interested in detecting the number of hosts behind a NAT. You observe that the IP layer stamps an identification number sequentially on each
Outlook for Lodging. Amherst. University of Massachusetts Amherst. Charlie Ballard TripAdvisor
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Tourism Travel and Research Association: Advancing Tourism Research Globally 2015 Marketing Outlook Forum - Outlook for 2016 Outlook for Lodging
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Tourism Travel and Research Association: Advancing Tourism Research Globally 2015 Marketing Outlook Forum - Outlook for 2016 Outlook for Lodging
Understanding the effect of streaming overlay construction on AS level traffic
 Understanding the effect of streaming overlay construction on AS level traffic Reza Motamedi and Reza Rejaie Information and Computer Science Department University of Oregon e-mail: {reza.motamedi,reza}@cs.uoregon.edu
Understanding the effect of streaming overlay construction on AS level traffic Reza Motamedi and Reza Rejaie Information and Computer Science Department University of Oregon e-mail: {reza.motamedi,reza}@cs.uoregon.edu
Jaal: Towards Network Intrusion Detection at ISP Scale
 Jaal: Towards Network Intrusion Detection at ISP Scale A. Aqil, K. Khalil, A. Atya, E. Paplexakis, S. Krishnamurthy, KK. Ramakrishnan University of California Riverside T. Jaeger Penn State University
Jaal: Towards Network Intrusion Detection at ISP Scale A. Aqil, K. Khalil, A. Atya, E. Paplexakis, S. Krishnamurthy, KK. Ramakrishnan University of California Riverside T. Jaeger Penn State University
IP Addressing & Interdomain Routing. Next Topic
 IP Addressing & Interdomain Routing Next Topic IP Addressing Hierarchy (prefixes, class A, B, C, subnets) Interdomain routing Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical Scalability
IP Addressing & Interdomain Routing Next Topic IP Addressing Hierarchy (prefixes, class A, B, C, subnets) Interdomain routing Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical Scalability
Flooding Attacks by Exploiting Persistent Forwarding Loops
 Flooding Attacks by Exploiting Persistent Forwarding Loops Jianhong Xia, Lixin Gao and Teng Fei University of Massachusetts, Amherst MA 01003, USA Email: {jxia, lgao, tfei}@ecs.umass.edu Introduction Routing
Flooding Attacks by Exploiting Persistent Forwarding Loops Jianhong Xia, Lixin Gao and Teng Fei University of Massachusetts, Amherst MA 01003, USA Email: {jxia, lgao, tfei}@ecs.umass.edu Introduction Routing
Internet Architecture and Experimentation
 Internet Architecture and Experimentation Today l Internet architecture l Principles l Experimentation A packet switched network Modern comm. networks are packet switched Data broken into packets, packet
Internet Architecture and Experimentation Today l Internet architecture l Principles l Experimentation A packet switched network Modern comm. networks are packet switched Data broken into packets, packet
Internet measurements: topology discovery and dynamics. Renata Teixeira MUSE Team Inria Paris-Rocquencourt
 Internet measurements: topology discovery and dynamics Renata Teixeira MUSE Team Inria Paris-Rocquencourt Why measure the Internet topology? Network operators Assist in network management, fault diagnosis
Internet measurements: topology discovery and dynamics Renata Teixeira MUSE Team Inria Paris-Rocquencourt Why measure the Internet topology? Network operators Assist in network management, fault diagnosis
Inter-domain Routing. Outline. Border Gateway Protocol
 Inter-domain Routing Outline Border Gateway Protocol Internet Structure Original idea CS 640 2 Internet Structure Today CS 640 3 Route Propagation in the Internet Autonomous System (AS) corresponds to
Inter-domain Routing Outline Border Gateway Protocol Internet Structure Original idea CS 640 2 Internet Structure Today CS 640 3 Route Propagation in the Internet Autonomous System (AS) corresponds to
BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma
 BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Unit 9 Computer Network Routing and Routing Protocols BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Introduction to Routing Routing is the process that a router uses to forward packets toward
BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Unit 9 Computer Network Routing and Routing Protocols BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Introduction to Routing Routing is the process that a router uses to forward packets toward
Cloud DNS Phone: (877)
 Cloud DNS Phone: (877) 937-4236 Email: info@cdnetworks.com CDNetworks Inc., 1500 Valley Vista Dr. Diamond Bar, CA 91765, USA Table of Content Introduction... 3 Cloud DNS Global Points of Presence...3 CDNetworks
Cloud DNS Phone: (877) 937-4236 Email: info@cdnetworks.com CDNetworks Inc., 1500 Valley Vista Dr. Diamond Bar, CA 91765, USA Table of Content Introduction... 3 Cloud DNS Global Points of Presence...3 CDNetworks
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP
 Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore CS 3103: Compute Networks and Protocols Inter-Domain Routing Internet is a network of networks Hierarchy
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore CS 3103: Compute Networks and Protocols Inter-Domain Routing Internet is a network of networks Hierarchy
Top 10 Global Threat Rank by Source
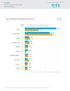 Symantec Internet Security Threat Report, Volume 21 1 Top 10 Threat by Source WORLD RANK PERCENTAGE OF GLOBAL DETECTIONS China 1 2 10.6% 23.7% United States 2 1 18.9% 20.7% India Netherlands Taiwan Turkey
Symantec Internet Security Threat Report, Volume 21 1 Top 10 Threat by Source WORLD RANK PERCENTAGE OF GLOBAL DETECTIONS China 1 2 10.6% 23.7% United States 2 1 18.9% 20.7% India Netherlands Taiwan Turkey
Lecture 13: Traffic Engineering
 Lecture 13: Traffic Engineering CSE 222A: Computer Communication Networks Alex C. Snoeren Thanks: Mike Freedman, Nick Feamster Lecture 13 Overview Evolution of routing in the ARPAnet Today s TE: Adjusting
Lecture 13: Traffic Engineering CSE 222A: Computer Communication Networks Alex C. Snoeren Thanks: Mike Freedman, Nick Feamster Lecture 13 Overview Evolution of routing in the ARPAnet Today s TE: Adjusting
Link State Routing & Inter-Domain Routing
 Link State Routing & Inter-Domain Routing CS640, 2015-02-26 Announcements Assignment #2 is due Tuesday Overview Link state routing Internet structure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Path vector routing Inter
Link State Routing & Inter-Domain Routing CS640, 2015-02-26 Announcements Assignment #2 is due Tuesday Overview Link state routing Internet structure Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Path vector routing Inter
MAPPING PEERING INTERCONNECTIONS TO A FACILITY
 MAPPING PEERING INTERCONNECTIONS TO A FACILITY Vasileios Giotsas 1 Georgios Smaragdakis 2 Bradley Huffaker 1 Matthew Luckie 3 kc claffy 1 vgiotsas@caida.org WIE 2015 1 UCSD/CAIDA 2 MIT/TU Berlin 3 University
MAPPING PEERING INTERCONNECTIONS TO A FACILITY Vasileios Giotsas 1 Georgios Smaragdakis 2 Bradley Huffaker 1 Matthew Luckie 3 kc claffy 1 vgiotsas@caida.org WIE 2015 1 UCSD/CAIDA 2 MIT/TU Berlin 3 University
PoP Level Mapping And Peering Deals
 PoP Level Mapping And Peering Deals Mapping Internet Methodology Data Collection IP Classification to PoP PoP Geolocation PoP locations on Peering estimations Outline Internet Service Providers ISPs are
PoP Level Mapping And Peering Deals Mapping Internet Methodology Data Collection IP Classification to PoP PoP Geolocation PoP locations on Peering estimations Outline Internet Service Providers ISPs are
Outline. EL736 Communications Networks II: Design and Algorithms. Class3: Network Design Modelling Yong Liu 09/19/2006
 EL736 Communications Networks II: Design and Algorithms Class3: Network Design Modelling Yong Liu 09/19/2006 1 Outline Examples Basic Problems Routing Restriction 2 1 Example: Intra-Domain Traffic Engineering
EL736 Communications Networks II: Design and Algorithms Class3: Network Design Modelling Yong Liu 09/19/2006 1 Outline Examples Basic Problems Routing Restriction 2 1 Example: Intra-Domain Traffic Engineering
Important Lessons From Last Lecture Computer Networking. Outline. Routing Review. Routing hierarchy. Internet structure. External BGP (E-BGP)
 Important Lessons From Last Lecture 15-441 Computer Networking Inter-Domain outing BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Every router needs to be able to forward towards any destination Forwarding table must be
Important Lessons From Last Lecture 15-441 Computer Networking Inter-Domain outing BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Every router needs to be able to forward towards any destination Forwarding table must be
A configuration-only approach to shrinking FIBs. Prof Paul Francis (Cornell)
 A configuration-only approach to shrinking FIBs Prof Paul Francis (Cornell) 1 Virtual Aggregation An approach to shrinking FIBs (and RIBs) In routers, not in route reflectors Works with legacy routers
A configuration-only approach to shrinking FIBs Prof Paul Francis (Cornell) 1 Virtual Aggregation An approach to shrinking FIBs (and RIBs) In routers, not in route reflectors Works with legacy routers
J. A. Drew Hamilton, Jr., Ph.D. Director, Information Assurance Laboratory and Associate Professor Computer Science & Software Engineering
 Auburn Information Assurance Laboratory J. A. Drew Hamilton, Jr., Ph.D. Director, Information Assurance Laboratory and Associate Professor Computer Science & Software Engineering 107 Dunstan Hall Auburn
Auburn Information Assurance Laboratory J. A. Drew Hamilton, Jr., Ph.D. Director, Information Assurance Laboratory and Associate Professor Computer Science & Software Engineering 107 Dunstan Hall Auburn
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP
 Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Brad Karp UCL Computer Science (drawn mostly from lecture notes by Hari Balakrishnan and Nick Feamster, MIT) CS 3035/GZ01 4 th December 2014 Outline Context: Inter-Domain Routing
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Brad Karp UCL Computer Science (drawn mostly from lecture notes by Hari Balakrishnan and Nick Feamster, MIT) CS 3035/GZ01 4 th December 2014 Outline Context: Inter-Domain Routing
Interdomain Routing Design for MobilityFirst
 Interdomain Routing Design for MobilityFirst October 6, 2011 Z. Morley Mao, University of Michigan In collaboration with Mike Reiter s group 1 Interdomain routing design requirements Mobility support Network
Interdomain Routing Design for MobilityFirst October 6, 2011 Z. Morley Mao, University of Michigan In collaboration with Mike Reiter s group 1 Interdomain routing design requirements Mobility support Network
Toward an Atlas of the Physical Internet
 Toward an Atlas of the Physical Internet Winter 2014 Paul Barford Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin!! Motivation pb@cs.wisc.edu 1 Objectives of our work Create and maintain a comprehensive catalog
Toward an Atlas of the Physical Internet Winter 2014 Paul Barford Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin!! Motivation pb@cs.wisc.edu 1 Objectives of our work Create and maintain a comprehensive catalog
Routing on the Internet. Routing on the Internet. Hierarchical Routing. Computer Networks. Lecture 17: Inter-domain Routing and BGP
 Routing on the Internet Computer Networks Lecture 17: Inter-domain Routing and BGP In the beginning there was the ARPANET: route using GGP (Gateway-to-Gateway Protocol), a distance vector routing protocol
Routing on the Internet Computer Networks Lecture 17: Inter-domain Routing and BGP In the beginning there was the ARPANET: route using GGP (Gateway-to-Gateway Protocol), a distance vector routing protocol
ENHANCED INTERIOR GATEWAY ROUTING PROTOCOL STUB ROUTER FUNCTIONALITY
 APPLICATION NOTE ENHANCED INTERIOR GATEWAY ROUTING PROTOCOL STUB ROUTER FUNCTIONALITY OVERVIEW Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP).Stub Router functionality, which Cisco introduced in Cisco
APPLICATION NOTE ENHANCED INTERIOR GATEWAY ROUTING PROTOCOL STUB ROUTER FUNCTIONALITY OVERVIEW Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP).Stub Router functionality, which Cisco introduced in Cisco
MAPPING PEERING INTERCONNECTIONS TO A FACILITY
 MAPPING PEERING INTERCONNECTIONS TO A FACILITY Vasileios Giotsas 1 Georgios Smaragdakis 2 Bradley Huffaker 1 Matthew Luckie 3 kc claffy 1 vgiotsas@caida.org CoNEXT 2015 1 UCSD/CAIDA 2 MIT/TU Berlin 3 University
MAPPING PEERING INTERCONNECTIONS TO A FACILITY Vasileios Giotsas 1 Georgios Smaragdakis 2 Bradley Huffaker 1 Matthew Luckie 3 kc claffy 1 vgiotsas@caida.org CoNEXT 2015 1 UCSD/CAIDA 2 MIT/TU Berlin 3 University
! Distance vector routing! Link state routing.! Path vector routing! BGP: Border Gateway Protocol! Route aggregation
 ! Distance vector routing! Link state routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi! IGP and EGP Intra-domain routing protocol, inter-domain routing protocol! Path vector routing! BGP: Border Gateway
! Distance vector routing! Link state routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi! IGP and EGP Intra-domain routing protocol, inter-domain routing protocol! Path vector routing! BGP: Border Gateway
Partitioning the Internet
 Partitioning the Internet Matthias Wachs Christian Grothoff 1 Ramakrishna Thurimella 2 Technische Universität München 1 University of Denver 2 CRiSIS 2012, Cork, Ireland FSNSG (TUM) Partitioning the Internet
Partitioning the Internet Matthias Wachs Christian Grothoff 1 Ramakrishna Thurimella 2 Technische Universität München 1 University of Denver 2 CRiSIS 2012, Cork, Ireland FSNSG (TUM) Partitioning the Internet
Finish Network Layer Start Transport Layer. CS158a Chris Pollett Apr 25, 2007.
 Finish Network Layer Start Transport Layer CS158a Chris Pollett Apr 25, 2007. Outline OSPF BGP IPv6 Transport Layer Services Sockets Example Socket Program OSPF We now look at routing in the internet.
Finish Network Layer Start Transport Layer CS158a Chris Pollett Apr 25, 2007. Outline OSPF BGP IPv6 Transport Layer Services Sockets Example Socket Program OSPF We now look at routing in the internet.
Policy-Compliant Path Diversity and Bisection Bandwidth
 Policy-Compliant Path Diversity and Bisection Bandwidth Rowan Klöti1, Vasileios Kotronis1, Bernhard Ager1, Xenofontas Dimitropoulos2,1 1 ETH Zurich, Switzerland 2 University of Crete / FORTH, Greece 1
Policy-Compliant Path Diversity and Bisection Bandwidth Rowan Klöti1, Vasileios Kotronis1, Bernhard Ager1, Xenofontas Dimitropoulos2,1 1 ETH Zurich, Switzerland 2 University of Crete / FORTH, Greece 1
Dig into MPLS: Transit Tunnel Diversity
 January 2015 Dig into MPLS: Transit Tunnel Diversity Yves VANAUBEL Pascal MÉRINDOL Jean-Jacques PANSIOT Benoit DONNET Summary Motivations MPLS Background Measurement Campaign Label Pattern Recognition
January 2015 Dig into MPLS: Transit Tunnel Diversity Yves VANAUBEL Pascal MÉRINDOL Jean-Jacques PANSIOT Benoit DONNET Summary Motivations MPLS Background Measurement Campaign Label Pattern Recognition
Lecture 7: Data Center Networks
 Lecture 7: Data Center Networks CSE 222A: Computer Communication Networks Alex C. Snoeren Thanks: Nick Feamster Lecture 7 Overview Project discussion Data Centers overview Fat Tree paper discussion CSE
Lecture 7: Data Center Networks CSE 222A: Computer Communication Networks Alex C. Snoeren Thanks: Nick Feamster Lecture 7 Overview Project discussion Data Centers overview Fat Tree paper discussion CSE
Croatian Internet exchange. and Regional Perspective
 and Regional Perspective 4th SEE Telecom Arena Zagreb, 18. 19. March 2008 Ivan Marić, Deputy Director / CTO University Computing Centre - SRCE 1 Agenda Internet architecture & topology Peering & IXP IXP
and Regional Perspective 4th SEE Telecom Arena Zagreb, 18. 19. March 2008 Ivan Marić, Deputy Director / CTO University Computing Centre - SRCE 1 Agenda Internet architecture & topology Peering & IXP IXP
Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing
 Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi 1 Outline Continued from previous lecture on: Distance vector routing Link state routing IGP and EGP Interior gateway protocol, Exterior
Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi 1 Outline Continued from previous lecture on: Distance vector routing Link state routing IGP and EGP Interior gateway protocol, Exterior
Scalable Multipath Routing (towards)
 Scalable Multipath Routing (towards) 71st Meeting of the IFIP WG 10.4 Working Group on Dependability and Security Ian Welch, School of Engineering and Computer Science; Victoria University of Wellington
Scalable Multipath Routing (towards) 71st Meeting of the IFIP WG 10.4 Working Group on Dependability and Security Ian Welch, School of Engineering and Computer Science; Victoria University of Wellington
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example Configuring Active Flow Monitoring Version 9 Modified: 2017-01-18 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net All
Network Configuration Example Configuring Active Flow Monitoring Version 9 Modified: 2017-01-18 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000 www.juniper.net All
Internet Measurements. Motivation
 Internet Measurements Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 2004 Motivation Types of measurements Understand the topology of the Internet Measure performance characteristics Tools: BGP Tables Traceroute measurements
Internet Measurements Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 2004 Motivation Types of measurements Understand the topology of the Internet Measure performance characteristics Tools: BGP Tables Traceroute measurements
Why Are You Still Using Shortest Path? - Path Selection Strategy Utilizing High-functional Nodes -
 Why Are You Still Using Shortest Path? - Path Selection Strategy Utilizing High-functional Nodes - Taro HASHIMOTO, Katsunori YAMAOKA and Yoshinori SAKAI Tokyo Institute of Technology Live streaming media
Why Are You Still Using Shortest Path? - Path Selection Strategy Utilizing High-functional Nodes - Taro HASHIMOTO, Katsunori YAMAOKA and Yoshinori SAKAI Tokyo Institute of Technology Live streaming media
Wholesale Solutions. Connectivity without compromise
 Wholesale Solutions Connectivity without compromise IP Transit Enterprise level service everywhere in Europe At M24Seven, our fastest growing network, capability and geographical coverage in the UK and
Wholesale Solutions Connectivity without compromise IP Transit Enterprise level service everywhere in Europe At M24Seven, our fastest growing network, capability and geographical coverage in the UK and
CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing. Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 16, 2017
 CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 16, 2017 1 Hierarchical routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat not true in
CS 43: Computer Networks Internet Routing Kevin Webb Swarthmore College November 16, 2017 1 Hierarchical routing Our routing study thus far - idealization all routers identical network flat not true in
Hirochika Asai U. Tokyo Hiroshi Esaki U. Tokyo Tsuyoshi Momose Cisco Systems
 Hirochika Asai , U. Tokyo Hiroshi Esaki , U. Tokyo Tsuyoshi Momose , Cisco Systems July 28 th, 2010, P2P RG, IETF 78 The Internet Autonomous
Hirochika Asai , U. Tokyo Hiroshi Esaki , U. Tokyo Tsuyoshi Momose , Cisco Systems July 28 th, 2010, P2P RG, IETF 78 The Internet Autonomous
Network Layer (Routing)
 Network Layer (Routing) Border Gateway Protocol Structure of the Internet Networks (ISPs, CDNs, etc.) group with IP prefixes Networks are richly interconnected, often using IXPs Prefix E1 Net E IXP Prefix
Network Layer (Routing) Border Gateway Protocol Structure of the Internet Networks (ISPs, CDNs, etc.) group with IP prefixes Networks are richly interconnected, often using IXPs Prefix E1 Net E IXP Prefix
Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing
 Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi 1 Outline! Distance vector routing! Link state routing! IGP and EGP Intra-domain routing protocol, inter-domain routing protocol!
Routing(2) Inter-domain Routing Information Network I Youki Kadobayashi 1 Outline! Distance vector routing! Link state routing! IGP and EGP Intra-domain routing protocol, inter-domain routing protocol!
Network Layer, Part 2 Routing. Terminology
 Network Layer, Part Routing These slides are created by Dr. Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang s courses at GMU can make a single machine readable copy and print a single
Network Layer, Part Routing These slides are created by Dr. Huang of George Mason University. Students registered in Dr. Huang s courses at GMU can make a single machine readable copy and print a single
Lecture 19: Network Layer Routing in the Internet
 Lecture 19: Network Layer Routing in the Internet COMP 332, Spring 2018 Victoria Manfredi Acknowledgements: materials adapted from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition: 1996-2016, J.F
Lecture 19: Network Layer Routing in the Internet COMP 332, Spring 2018 Victoria Manfredi Acknowledgements: materials adapted from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition: 1996-2016, J.F
Outline Computer Networking. Inter and Intra-Domain Routing. Internet s Area Hierarchy Routing hierarchy. Internet structure
 Outline 15-441 15-441 Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 10: Inter-Domain outing Border Gateway Protocol -BGP Peter Steenkiste Fall 2016 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f16 outing hierarchy Internet structure
Outline 15-441 15-441 Computer Networking 15-641 Lecture 10: Inter-Domain outing Border Gateway Protocol -BGP Peter Steenkiste Fall 2016 www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441-f16 outing hierarchy Internet structure
ROUTING PROTOCOLS. Mario Baldi Routing - 1. see page 2
 ROUTING PROTOCOLS Mario Baldi www.baldi.info Routing - 1 Copyright Notice This set of transparencies, hereinafter referred to as slides, is protected by copyright laws and provisions of International Treaties.
ROUTING PROTOCOLS Mario Baldi www.baldi.info Routing - 1 Copyright Notice This set of transparencies, hereinafter referred to as slides, is protected by copyright laws and provisions of International Treaties.
On Quantifying Performance Enhancement of Distributed SDN Architecture
 On Quantifying Performance Enhancement of Distributed SDN Architecture Ziyao (Spike) Zhang Imperial College London Liang Ma IBM US Kin K. Leung Imperial College London September 2017 DAIS-ITA Annual Fall
On Quantifying Performance Enhancement of Distributed SDN Architecture Ziyao (Spike) Zhang Imperial College London Liang Ma IBM US Kin K. Leung Imperial College London September 2017 DAIS-ITA Annual Fall
CS 640: Introduction to Computer Networks. Intra-domain routing. Inter-domain Routing: Hierarchy. Aditya Akella
 CS 640: Introduction to Computer Networks Aditya Akella Lecture 11 - Inter-Domain Routing - BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Intra-domain routing The Story So Far Routing protocols generate the forwarding
CS 640: Introduction to Computer Networks Aditya Akella Lecture 11 - Inter-Domain Routing - BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Intra-domain routing The Story So Far Routing protocols generate the forwarding
ISP-Aided Neighbor Selection for P2P Systems
 ISP-Aided Neighbor Selection for P2P Systems Anja Feldmann Vinay Aggarwal, Obi Akonjang, Christian Scheideler (TUM) Deutsche Telekom Laboratories TU-Berlin 1 P2P traffic
ISP-Aided Neighbor Selection for P2P Systems Anja Feldmann Vinay Aggarwal, Obi Akonjang, Christian Scheideler (TUM) Deutsche Telekom Laboratories TU-Berlin 1 P2P traffic
Resilient IP Backbones. Debanjan Saha Tellium, Inc.
 Resilient IP Backbones Debanjan Saha Tellium, Inc. dsaha@tellium.com 1 Outline Industry overview IP backbone alternatives IP-over-DWDM IP-over-OTN Traffic routing & planning Network case studies Research
Resilient IP Backbones Debanjan Saha Tellium, Inc. dsaha@tellium.com 1 Outline Industry overview IP backbone alternatives IP-over-DWDM IP-over-OTN Traffic routing & planning Network case studies Research
Review for Chapter 4 R1,R2,R3,R7,R10,R11,R16,R17,R19,R22,R24, R26,R30 P1,P2,P4,P7,P10,P11,P12,P14,P15,P16,P17,P22,P24,P29,P30
 Review for Chapter 4 R1,R2,R3,R7,R10,R11,R16,R17,R19,R22,R24, R26,R30 P1,P2,P4,P7,P10,P11,P12,P14,P15,P16,P17,P22,P24,P29,P30 R1. Let s review some of the terminology used in this textbook. Recall that
Review for Chapter 4 R1,R2,R3,R7,R10,R11,R16,R17,R19,R22,R24, R26,R30 P1,P2,P4,P7,P10,P11,P12,P14,P15,P16,P17,P22,P24,P29,P30 R1. Let s review some of the terminology used in this textbook. Recall that
Routing. Routing. Overview. Overview. Routing vs. Forwarding. Why Routing
 Routing Dr. Arjan Durresi Department of Computer Science Louisiana State University Overview Routing vs. Forwarding Routing Algorithms, Distance Vector, Link State Dijkstra s Algorithm ARPAnet Routing
Routing Dr. Arjan Durresi Department of Computer Science Louisiana State University Overview Routing vs. Forwarding Routing Algorithms, Distance Vector, Link State Dijkstra s Algorithm ARPAnet Routing
Lecture 16: Interdomain Routing. CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage
 Lecture 16: Interdomain Routing CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage Overview Autonomous Systems Each network on the Internet has its own goals Path-vector Routing Allows scalable, informed route selection
Lecture 16: Interdomain Routing CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage Overview Autonomous Systems Each network on the Internet has its own goals Path-vector Routing Allows scalable, informed route selection
Master Course Computer Networks IN2097
 Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Stephan Günther
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Prof. Carle Department of Computer Science TU München Master Course Computer Networks IN2097 Prof. Dr.-Ing. Georg Carle Christian Grothoff, Ph.D. Stephan Günther
Interdomain Routing and Connectivity
 Interdomain Routing and Connectivity Brighten Godfrey CS 538 February 28 2018 slides 2010-2018 by Brighten Godfrey unless otherwise noted Routing Choosing paths along which messages will travel from source
Interdomain Routing and Connectivity Brighten Godfrey CS 538 February 28 2018 slides 2010-2018 by Brighten Godfrey unless otherwise noted Routing Choosing paths along which messages will travel from source
CS 43: Computer Networks. 24: Internet Routing November 19, 2018
 CS 43: Computer Networks 24: Internet Routing November 19, 2018 Last Class Link State + Fast convergence (reacts to events quickly) + Small window of inconsistency Distance Vector + + Distributed (small
CS 43: Computer Networks 24: Internet Routing November 19, 2018 Last Class Link State + Fast convergence (reacts to events quickly) + Small window of inconsistency Distance Vector + + Distributed (small
Planning for Information Network
 Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Planning for Information Network Lecture 8: Network Routing Protocols Assistant Teacher Samraa Adnan Al-Asadi 1 Routing protocol features There are many ways to characterize routing protocols, including
Best Practices for Determining the Traffic Matrix in IP Networks
 Best Practices for Determining the Traffic Matrix in IP Networks Apricot 2005 - Kyoto, Japan Thursday February 24, 2005 Internet Routing and Backbone Operations Session C5-4 Thomas Telkamp, Cariden Technologies,
Best Practices for Determining the Traffic Matrix in IP Networks Apricot 2005 - Kyoto, Japan Thursday February 24, 2005 Internet Routing and Backbone Operations Session C5-4 Thomas Telkamp, Cariden Technologies,
Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer)
 Routing Basics 1 Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, 2014 Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer) Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 3 IPv4
Routing Basics 1 Small additions by Dr. Enis Karaarslan, 2014 Purdue - Aaron Jarvis (Network Engineer) Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 3 IPv4
AS Router Connectedness Based on Multiple Vantage Points and the Resulting Topologies
 AS Router Connectedness Based on Multiple Vantage Points and the Resulting Topologies Steven Fisher University of Nevada, Reno CS 765 Steven Fisher (UNR) CS 765 CS 765 1 / 62 Table of Contents 1 Introduction
AS Router Connectedness Based on Multiple Vantage Points and the Resulting Topologies Steven Fisher University of Nevada, Reno CS 765 Steven Fisher (UNR) CS 765 CS 765 1 / 62 Table of Contents 1 Introduction
Dynamics of Hot-Potato Routing in IP Networks
 Dynamics of Hot-Potato Routing in IP Networks Jennifer Rexford AT&T Labs Research http://www.research.att.com/~jrex Joint work with Renata Teixeira (UCSD), Aman Shaikh (AT&T), and Timothy Griffin (Intel)
Dynamics of Hot-Potato Routing in IP Networks Jennifer Rexford AT&T Labs Research http://www.research.att.com/~jrex Joint work with Renata Teixeira (UCSD), Aman Shaikh (AT&T), and Timothy Griffin (Intel)
The Flattening Internet Topology:
 The Flattening Internet Topology: Natural Evolution, Unsightly Barnacles or Contrived Collapse? Phillipa Gill Martin Arlitt Zongpeng Li Anirban Mahanti U of Calgary HP Labs/ U of Calgary IIT Delhi U of
The Flattening Internet Topology: Natural Evolution, Unsightly Barnacles or Contrived Collapse? Phillipa Gill Martin Arlitt Zongpeng Li Anirban Mahanti U of Calgary HP Labs/ U of Calgary IIT Delhi U of
NET ID. CS519, Prelim (March 17, 2004) NAME: You have 50 minutes to complete the test. 1/17
 CS519, Prelim (March 17, 2004) NAME: You have 50 minutes to complete the test. 1/17 Q1. 2 points Write your NET ID at the top of every page of this test. Q2. X points Name 3 advantages of a circuit network
CS519, Prelim (March 17, 2004) NAME: You have 50 minutes to complete the test. 1/17 Q1. 2 points Write your NET ID at the top of every page of this test. Q2. X points Name 3 advantages of a circuit network
IPC Financial Markets Network
 Why trading firms choose... IPC Financial Markets Network worldwide connectivity you can count on throughout the trade lifecycle Strength for Voice and and Data Services Today s trading global, faster,
Why trading firms choose... IPC Financial Markets Network worldwide connectivity you can count on throughout the trade lifecycle Strength for Voice and and Data Services Today s trading global, faster,
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP
 Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Stefano Vissicchio UCL Computer Science CS 3035/GZ01 Agenda We study how to route over the Internet 1. Context The Internet, a network of networks Relationships between ASes 2.
Inter-Domain Routing: BGP Stefano Vissicchio UCL Computer Science CS 3035/GZ01 Agenda We study how to route over the Internet 1. Context The Internet, a network of networks Relationships between ASes 2.
Sanctuary Trail: Refuge from Internet DDoS Entrapment
 Sanctuary Trail: Refuge from Internet DDoS Entrapment Hsu-Chun Hsiao, Tiffany Hyun-Jin Kim, Sangjae Yoo, Xin Zhang, Soo Bum Lee, Virgil Gligor, and Adrian Perrig June 7, 2012 CMU-CyLab-12-013 CyLab Carnegie
Sanctuary Trail: Refuge from Internet DDoS Entrapment Hsu-Chun Hsiao, Tiffany Hyun-Jin Kim, Sangjae Yoo, Xin Zhang, Soo Bum Lee, Virgil Gligor, and Adrian Perrig June 7, 2012 CMU-CyLab-12-013 CyLab Carnegie
Peering and Network Deployment at 10G. Nigel Titley
 Peering and Network Deployment at 10G Nigel Titley Introductions Thanks very much for inviting me to speak to you Currently Head of Peering and Transit at Easynet Ltd RIPE NCC Board Chairman Peering Coordinator
Peering and Network Deployment at 10G Nigel Titley Introductions Thanks very much for inviting me to speak to you Currently Head of Peering and Transit at Easynet Ltd RIPE NCC Board Chairman Peering Coordinator
Internet Routing : Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace
 Internet Routing 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Looking Ahead Lab #2 just due Quiz #2
Internet Routing 14-740: Fundamentals of Computer Networks Bill Nace Material from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach, 6 th edition. J.F. Kurose and K.W. Ross Looking Ahead Lab #2 just due Quiz #2
The Shape of the Internet. Slides assembled by Jeff Chase Duke University (thanks to Vishal Misra and C. Faloutsos)
 The Shape of the Internet Slides assembled by Jeff Chase Duke University (thanks to Vishal Misra and C. Faloutsos) The Shape of the Network Characterizing shape : AS-level topology: who connects to whom
The Shape of the Internet Slides assembled by Jeff Chase Duke University (thanks to Vishal Misra and C. Faloutsos) The Shape of the Network Characterizing shape : AS-level topology: who connects to whom
Cloud Load Balancer CDNetworks Inc. All rights reserved.
 Cloud Load Balancer Phone: (877) 937-4236 Email: info@cdnetworks.com 2019 CDNetworks Inc. All rights reserved. Table of Content DNS-based Global Load Balancing... 3 Key Features and Benefits... 4 POP Map...
Cloud Load Balancer Phone: (877) 937-4236 Email: info@cdnetworks.com 2019 CDNetworks Inc. All rights reserved. Table of Content DNS-based Global Load Balancing... 3 Key Features and Benefits... 4 POP Map...
IATF Stakeholder Conference
 IATF Stakeholder Conference 13 September 2017 Oberursel, Germany Rüdiger Funke (BMW Group) Number of certified sites against ISO/TS 16949 (and IATF 16949) 70,000 60,000 50,000 40,000 30,000 30,156 50,071
IATF Stakeholder Conference 13 September 2017 Oberursel, Germany Rüdiger Funke (BMW Group) Number of certified sites against ISO/TS 16949 (and IATF 16949) 70,000 60,000 50,000 40,000 30,000 30,156 50,071
Distributed Clustering Method for Large-Scaled Wavelength Routed Networks
 Distributed Clustering Method for Large-Scaled Wavelength Routed Networks Yukinobu Fukushima Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, Osaka University - Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 60-08, Japan
Distributed Clustering Method for Large-Scaled Wavelength Routed Networks Yukinobu Fukushima Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, Osaka University - Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 60-08, Japan
BGP and inter-as economic relationships
 BGP and inter-as economic relationships E. Gregori 1, A. Improta 2,1, L. Lenzini 2, L. Rossi 1, L. Sani 3 1 Institute of Informatics and Telematics, Italian National Research Council Pisa, Italy 2 Information
BGP and inter-as economic relationships E. Gregori 1, A. Improta 2,1, L. Lenzini 2, L. Rossi 1, L. Sani 3 1 Institute of Informatics and Telematics, Italian National Research Council Pisa, Italy 2 Information
Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan. Computer Networks II Border Gateway protocol (BGP) By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri
 Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan Computer Networks II Border Gateway protocol (BGP) By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri Internet structure: network of networks local ISP Tier
Department of Computer and IT Engineering University of Kurdistan Computer Networks II Border Gateway protocol (BGP) By: Dr. Alireza Abdollahpouri Internet structure: network of networks local ISP Tier
Network Security: Routing security. Aapo Kalliola T Network security Aalto University, Nov-Dec 2012
 Network Security: Routing security Aapo Kalliola T-110.5241 Network security Aalto University, Nov-Dec 2012 Outline 1. Structure of internet 2. Routing basics 3. Security issues 4. Attack 5. Solutions
Network Security: Routing security Aapo Kalliola T-110.5241 Network security Aalto University, Nov-Dec 2012 Outline 1. Structure of internet 2. Routing basics 3. Security issues 4. Attack 5. Solutions
Contents. 4 Challenges for AP-IS Network. 1 Introduction of Network Design
 Contents 1 Introduction of Network Design 2 Current Status of International Backbone Network in ASEAN 3 Potential AP-IS Network in ASEAN 4 Challenges for AP-IS Network 5 Collaboration 01 Introduction of
Contents 1 Introduction of Network Design 2 Current Status of International Backbone Network in ASEAN 3 Potential AP-IS Network in ASEAN 4 Challenges for AP-IS Network 5 Collaboration 01 Introduction of
Internet Architecture and Experimentation
 Internet Architecture and Experimentation To do q q q Internet architecture Principles Experimentation A bit of history Early days ~1960 ARPA sponsored research on networking to let researchers share computers
Internet Architecture and Experimentation To do q q q Internet architecture Principles Experimentation A bit of history Early days ~1960 ARPA sponsored research on networking to let researchers share computers
Internet Routing. Shortest-Path Routing. Intra-Domain Routing and Traffic Engineering. Two-Tiered Internet Routing System
 Intra-Domain Routing and Traffic Engineering Review of Internet routing paradigm and routing algorithms/protocols Intra-domain routing design topology design, convergence, stability, Traffic Engineering
Intra-Domain Routing and Traffic Engineering Review of Internet routing paradigm and routing algorithms/protocols Intra-domain routing design topology design, convergence, stability, Traffic Engineering
No Direction Home: The True Cost of Routing Around Decoys
 No Direction Home: The True Cost of Routing Around Decoys Amir Houmansadr The University of Texas at Austin Edmund L. Wong Meraki, Inc. Vitaly Shmatikov The University of Texas at Austin Abstract Decoy
No Direction Home: The True Cost of Routing Around Decoys Amir Houmansadr The University of Texas at Austin Edmund L. Wong Meraki, Inc. Vitaly Shmatikov The University of Texas at Austin Abstract Decoy
Achieving Fast BGP Reroute with Traffic Engineering Using Multiple Routing Planes
 Achieving Fast BGP Reroute with Traffic Engineering Using Multiple Routing Planes Yu Guo, Ning Wang, Kin-Hon Ho, Michael Howarth, and George Pavlou 2 Centre for Communication Systems Research, University
Achieving Fast BGP Reroute with Traffic Engineering Using Multiple Routing Planes Yu Guo, Ning Wang, Kin-Hon Ho, Michael Howarth, and George Pavlou 2 Centre for Communication Systems Research, University
A Random Walk through Cyber Security
 A Random Walk through Cyber Security Dr. Edward G. Amoroso Chief Executive Officer, TAG Cyber LLC Adjunct Professor, Stevens Institute and NYU Senior Advisor, APL/JHU; 2010 AT&T Labs Fellow eamoroso@tag-cyber.com
A Random Walk through Cyber Security Dr. Edward G. Amoroso Chief Executive Officer, TAG Cyber LLC Adjunct Professor, Stevens Institute and NYU Senior Advisor, APL/JHU; 2010 AT&T Labs Fellow eamoroso@tag-cyber.com
Peering at the Internet s Frontier:
 Peering at the Internet s Frontier: A First Look at ISP Interconnectivity in Africa Arpit Gupta Georgia Tech Matt Calder (USC), Nick Feamster (Georgia Tech), Marshini Chetty (Maryland), Enrico Calandro
Peering at the Internet s Frontier: A First Look at ISP Interconnectivity in Africa Arpit Gupta Georgia Tech Matt Calder (USC), Nick Feamster (Georgia Tech), Marshini Chetty (Maryland), Enrico Calandro
Peering THINK. A Guide
 Peering THINK A Guide Purpose of This Guide To demonstrate the features and benefits of Peering as a resource, and how it helps businesses connect faster, operate more efficiently and lower costs. Contents
Peering THINK A Guide Purpose of This Guide To demonstrate the features and benefits of Peering as a resource, and how it helps businesses connect faster, operate more efficiently and lower costs. Contents
Interdomain routing CSCI 466: Networks Keith Vertanen Fall 2011
 Interdomain routing CSCI 466: Networks Keith Vertanen Fall 2011 Overview Business relationships between ASes Interdomain routing using BGP Advertisements Routing policy Integration with intradomain routing
Interdomain routing CSCI 466: Networks Keith Vertanen Fall 2011 Overview Business relationships between ASes Interdomain routing using BGP Advertisements Routing policy Integration with intradomain routing
70 CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET
 70 CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET one of these packets arrives to a packet switch, what information in the packet does the switch use to determine the link onto which the packet is forwarded?
70 CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET one of these packets arrives to a packet switch, what information in the packet does the switch use to determine the link onto which the packet is forwarded?
Service Provider Multihoming
 Service Provider Multihoming ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last
Service Provider Multihoming ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last
Why dynamic route? (1)
 Routing Why dynamic route? (1) Static route is ok only when Network is small There is a single connection point to other network No redundant route 2 Why dynamic route? (2) Dynamic Routing Routers update
Routing Why dynamic route? (1) Static route is ok only when Network is small There is a single connection point to other network No redundant route 2 Why dynamic route? (2) Dynamic Routing Routers update
Network Layer: Routing
 Network Layer: Routing The Problem A B R 1 R 2 R 4 R 3 Goal: for each destination, compute next hop 1 Lecture 9 2 Basic Assumptions Trivial solution: Flooding Dynamic environment: links and routers unreliable:
Network Layer: Routing The Problem A B R 1 R 2 R 4 R 3 Goal: for each destination, compute next hop 1 Lecture 9 2 Basic Assumptions Trivial solution: Flooding Dynamic environment: links and routers unreliable:
