OSPF Virtual Link. Contents. Prerequisites. Document ID: Requirements. Components Used
|
|
|
- MargaretMargaret French
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
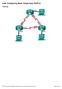
1 OSPF Virtual Link Document ID: Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations How the Virtual Link Operates Calculate the Shortest Path Using a GRE Tunnel Instead of a Virtual Link Verify Examine the OSPF Database Troubleshoot Troubleshoot Commands Related Information Introduction All areas in an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) autonomous system must be physically connected to the backbone area (Area 0). In some cases, where this is not possible, you can use a virtual link to connect to the backbone through a non backbone area. You can also use virtual links to connect two parts of a partitioned backbone through a non backbone area. The area through which you configure the virtual link, known as a transit area, must have full routing information. The transit area cannot be a stub area. This document examines the OSPF database in a virtual link environment. You can read more about virtual links in the OSPF Design Guide. Prerequisites Requirements Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics: Configuring OSPF OSPF Inter Area Routing Components Used This document is not restricted to specific software or hardware versions. The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
2 Conventions Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions. Configure In this section, you are presented with the information to configure the features described in this document. Note: Use the Command Lookup Tool (registered customers only) to find more information on the commands used in this document. Network Diagram This document uses this network setup: Configurations This document uses these configurations: Router Router Router Current configuration: hostname Router Router interface Loopback0 ip address interface Ethernet2/0/0 ip address interface Serial2/1/0 ip address router ospf 2 network area 0 network area 1
3 area 1 virtual link ! Area 1 is the transit area.! IP address is the router! ID of the router between Area 1! and Area 2 (Router ). See! the next Note. end Note: The OSPF router ID is usually the highest IP address on the box or the highest loopback address, if one exists. The router ID is only calculated at boot time or at any time that the OSPF process is restarted. Issue the show ip ospf interface command to find the router ID. Current configuration: hostname Router Router interface Loopback0 ip address interface Serial0/1/0 ip address interface ATM1/0.20 point to point ip address router ospf 2 network area 1 network area 1 end Current configuration: hostname Router Router interface Loopback0 ip address interface Ethernet0/0 ip address interface ATM2/0.20 point to point ip address router ospf 2 network area 2 network area 1 area 1 virtual link ! Area 1 is the transit area.! IP address is the router! ID of the router between Area 1! and Area 0 (Router ). end
4 How the Virtual Link Operates Initially, the virtual link is down because Router does not know how to reach Router (the other end of the virtual link). All of the link state advertisements (LSAs) in Area 1 need to be flooded, and the shortest path first (SPF) algorithm must be run within Area 1 by all three routers, for Router to know how to reach Router through Area 1. After the routers know how to reach each other through the transit area, they try to form adjacency across the virtual link. The OSPF packets between the two ends of the virtual link are not multicast packets. They are tunneled packets from source to the destination , because they are tunneled to the other end of the virtual link. It is important to note that if there is a firewall in between the virtual link routers, you need to enable the OSPF (IP protocol 89) port between the virtual link tunnel outgoing interface IPs that are between and Once the routers become adjacent on the virtual link, Router considers itself an area border router (ABR), because it now has a link in Area 0. As a result, Router creates a summary LSA for /8 in Area 0 and in Area 1. If the virtual link is misconfigured for some reason, then Router does not consider itself an ABR because it does not have any interfaces in Area 0. If this is the case, it does not create summary LSAs or advertise /8 into Area 1. Note: OSPF runs on top of IP and uses protocol number 89. OSPF does not rely on any other transport protocols, such as TCP and UDP. Calculate the Shortest Path This section calculates the shortest path from the perspective of Router Router looks in its own LSA and sees that Router is a neighbor. It then looks at the LSA of Router to verify that Router sees Router as a neighbor. If both routers see each other as neighbors, then they are considered reachable. Each router also checks its local neighbor table (which you can see with the show ip ospf neighbor command) to verify that its interface and the interface of the neighbor are on a common IP subnet. Note: This check is not performed on an unnumbered interface. If they are on a common subnet, the routers install routes for any stub networks listed in the router LSA of their neighbor. In this example, /8 is the only stub network listed in the LSA of Router in Area 1, to which Router is already directly connected. Router does the same examination for the LSA of Router , but there are not any useful stub networks in the LSA of Router After all of the reachable router LSAs in Area 1 are examined, Router looks at summary LSAs in the database. It finds two summary LSAs for /8 in Area 1 and chooses the one with the lowest total cost, which is the metric to reach the advertising router plus the metric of the summary LSA. Router can reach through Router with a cost of = 139. Router can reach through Router with a cost of = 11. Router installs a route in its routing table through Router with a metric of 11.
5 This output shows the OSPF routes in the routing table of each router previously described: Router #show ip route ospf! Output suppressed. O /8 [110/65] via , 00:38:12, Serial2/1/0 O IA /8 [110/75] via , 00:38:02, Serial2/1/0 Router #show ip route ospf! Output suppressed. O IA /8 [110/74] via , 00:38:08, Serial0/1/0 O IA /8 [110/11] via , 00:38:12, ATM1/0.20! This is the route in this example. Router #show ip route ospf! Output suppressed. O O /8 [110/75] via , 00:38:18, ATM2/ /8 [110/65] via , 00:38:28, ATM2/0.20 Using a GRE Tunnel Instead of a Virtual Link You can also build a generic routing encapsulation (GRE) tunnel between Router and Router and put the tunnel in Area 0. The main differences between a GRE tunnel and a virtual link are described in this table: GRE Tunnel All traffic in the tunnel is encapsulated and decapsulated by the tunnel endpoints. Tunnel headers in every packet cause overhead. The tunnel can go through a stub area. Verify Virtual Link The routing updates are tunneled, but the data traffic is sent natively. Data traffic is not subject to any tunnel overhead. The transit area cannot be a stub area, because routers in the stub area do not have routes for external destinations. Because data is sent natively, if a packet destined for an external destination is sent into a stub area which is also a transit area, then the packet is not routed correctly. The routers in the stub area do not have routes for specific external destinations. Use this section to confirm that your configuration works properly.
6 The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT to view an analysis of show command output. show ip ospf database Displays a list of the LSAs and types them into a link state database. This list shows only the information in the LSA header. show ip ospf database [router] [link state id] Displays a list of all of the LSAs of a router in the database. LSAs are produced by every router. These fundamental LSAs list all of the links of the routers or interfaces, along with the states and outgoing costs of the links, and they are flooded only within the area in which they originate. show ip ospf [process id [area id]] database [summary] [link state id] Displays information only about the network summary LSAs in the database. show ip ospf database [summary] [self originate] Displays only self originated LSAs (from the local router). Examine the OSPF Database This is how the OSPF database looks, given this network environment, when you issue the show ip ospf database command. Router #show ip ospf database OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 2) Router Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count x xD5DF (DNA) 0x x Summary Net Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum x xAA (DNA) 0x x7A x xA (DNA) 0x xEA3F (DNA) 0x xF624 Router Link States (Area 1) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count x xDDA x x64DD x xA14C 2 Summary Net Link States (Area 1) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum x x x xEBF x xBF x xF624 Router #show ip ospf database OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 2) Router Link States (Area 1) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count x xDDA x x64DD 4
7 x xA14C 2 Summary Net Link States (Area 1) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum x x x xEBF x xBF x xF624 Router #show ip ospf database OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 2) Router Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count (DNA) 0x xD5DF x x Summary Net Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum (DNA) 0x xAA x x7A (DNA) 0x xA x xEA3F x xF624 Router Link States (Area 1) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count x xDDA x x64DD x xA14C 2 Summary Net Link States (Area 1) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum x x x xEBF x xBF x xF624 Router Link States (Area 2) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count x xCF5 1 Summary Net Link States (Area 2) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum x xEBF x x7A x xEA3F Notice that LSAs learned through the virtual link have the DoNotAge option. The virtual link is treated like a demand circuit. Router #show ip ospf database router OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 2) Router Link States (Area 0)
8 LS age: 1100 LS Type: Router Links Link State ID: ! For router links, Link State ID is always the same as the Advertising Router. Advertising Router: ! This is the router ID of the router that created this LSA. LS Seq Number: Checksum: 0xD5DF Length: 48 Area Border Router! Bit B in the router LSA indicates that this router is an ABR. Number of Links: 2! There are two links in Area 0. Link connected to: a Virtual Link (Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: ! Router ID of the neighbor on the other end of the virtual link. (Link Data) Router Interface address: ! The interface that this router uses to send packets to the neighbor. TOS 0 Metrics: 65! The metric comes from the cost for this router to reach the neighboring router:! the ATM link has a cost of 1 and the serial link has a cost of 64. Link connected to: a Stub Network! This represents the Ethernet segment /8. (Link ID) Network/subnet number: (Link Data) Network Mask: TOS 0 Metrics: 10 Router Link States (Area 1) LS age: 122 LS Type: Router Links Link State ID: Advertising Router: LS Seq Number: Checksum: 0xDBA7 Length: 48 Area Border Router Number of Links: 2! There are two links in Area 1. Link connected to: another Router (point to point) (Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: (Link Data) Router Interface address: TOS 0 Metrics: 64
9 Link connected to: a Stub Network (Link ID) Network/subnet number: (Link Data) Network Mask: TOS 0 Metrics: 64 Router #show ip ospf database router OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 2) Router Link States (Area 1) LS age: 245 LS Type: Router Links Link State ID: Advertising Router: LS Seq Number: Checksum: 0x64DD Length: 72 Number of Links: 4! There are four links in Area 1. Link connected to: another Router (point to point) (Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: (Link Data) Router Interface address: TOS 0 Metrics: 1 Link connected to: a Stub Network (Link ID) Network/subnet number: (Link Data) Network Mask: TOS 0 Metrics: 1 Link connected to: another Router (point to point) (Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: (Link Data) Router Interface address: TOS 0 Metrics: 64 Link connected to: a Stub Network (Link ID) Network/subnet number: (Link Data) Network Mask: TOS 0 Metrics: 64 Router #show ip ospf database router OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 2) Router Link States (Area 0) Routing Bit Set on this LSA LS age: 5 (DoNotAge) LS Type: Router Links Link State ID: Checksum: 0x3990 Length: 36 Area Border Router
10 Number of Links: 1! There is one link in Area 0. Link connected to: a Virtual Link (Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: (Link Data) Router Interface address: TOS 0 Metrics: 65 Router Link States (Area 1) Routing Bit Set on this LSA LS age: 1137 LS Type: Router Links Link State ID: LS Seq Number: Checksum: 0xA14C Length: 48 Area Border Router Number of Links: 2! There are two links in Area 1. Link connected to: another Router (point to point) (Link ID) Neighboring Router ID: (Link Data) Router Interface address: TOS 0 Metrics: 1 Link connected to: a Stub Network (Link ID) Network/subnet number: (Link Data) Network Mask: TOS 0 Metrics: 1 Router considers itself an ABR because it has a link to Area 0 (the virtual link). As a result, it generates a summary LSA for into Area 1 and Area 0, which you can see when you issue the show ip ospf database summary command. Router #show ip ospf database summary OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 2) Summary Net Link States (Area 0) LS age: 1779 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) LS Seq Number: Checksum: 0xF624 TOS: 0 Metric: 10 Summary Net Link States (Area 1) LS age: 1766
11 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) Advertising Router: LS Seq Number: Checksum: 0xBF22 TOS: 0 Metric: 75 LS age: 1781 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) LS Seq Number: Checksum: 0xF624 TOS: 0 Metric: 10 Also, notice that Router creates summary LSAs in Area 2 for all of the information that it learned from Area 0 and Area 1. Router #show ip ospf database summary self originate OSPF Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 2) Summary Net Link States (Area 0) LS age: 155 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) Checksum: 0x7871 TOS: 0 Metric: 65 LS age: 155 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) Checksum: 0xE840 TOS: 0 Metric: 1 LS age: 156 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) Checksum: 0xF425 TOS: 0 Metric: 10 LS age: 157 Summary Net Link States (Area 1)
12 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) Checksum: 0xE9F6 TOS: 0 Metric: 75 LS age: 165 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) Checksum: 0xF425 TOS: 0 Metric: 10 Summary Net Link States (Area 2) LS age: 167 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) Checksum: 0xE9F6 TOS: 0 Metric: 75 LS age: 168 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) Checksum: 0x7871 TOS: 0 Metric: 65 LS age: 168 Link State ID: (summary Network Number) Checksum: 0xE840 TOS: 0 Metric: 1 Troubleshoot Use this section to troubleshoot your configuration. Troubleshoot Commands The Output Interpreter Tool (registered customers only) (OIT) supports certain show commands. Use the OIT
13 to view an analysis of show command output. Note: Refer to Important Information on Debug Commands before you use debug commands. debug ip ospf adjdisplays the events involved to build or break OSPF adjacency. The routers become adjacent and exchange LSAs via the virtual link, similar to a physical link. You can see the adjacency if you examine the router LSA or the output of the debug ip ospf adj command: Router # May 26 17:25:03.089: OSPF: Rcv hello from area 0 from OSPF_VL May 26 17:25:03.091: OSPF: 2 Way Communication to on OSPF_VL3, state 2WAY May 26 17:25:03.091: OSPF: Send DBD to on OSPF_VL3 seq 0xD1C opt 0x62 flag 0x7 len 32 May 26 17:25:03.135: OSPF: End of hello processing May 26 17:25:03.139: OSPF: Rcv DBD from on OSPF_VL3 seq 0x1617 opt 0x22 flag 0x7 len 32 mtu 0 state EXSTART May 26 17:25:03.175: OSPF: First DBD and we are not SLAVE May 26 17:25:03.179: OSPF: Rcv DBD from on OSPF_VL3 seq 0xD1C opt 0x22 flag 0x2 len 172 mtu 0 state EXSTART May 26 17:25:03.183: OSPF: NBR Negotiation Done. We are the MASTER May 26 17:25:03.189: OSPF: Send DBD to on OSPF_VL3 seq 0xD1D opt 0x62 flag 0x3 len 172 May 26 17:25:03.191: OSPF: Database request to May 26 17:25:03.191: OSPF: sent LS REQ packet to , length 36 May 26 17:25:03.263: OSPF: Rcv DBD from on OSPF_VL3 seq 0xD1D opt 0x22 flag 0x0 len 32 mtu 0 state EXCHANGE May 26 17:25:03.267: OSPF: Send DBD to on OSPF_VL3 seq 0xD1E opt 0x62 flag 0x1 len 32 May 26 17:25:03.311: OSPF: Rcv DBD from on OSPF_VL3 seq 0xD1E opt 0x22 flag 0x0 len 32 mtu 0 state EXCHANGE May 26 17:25:03.311: OSPF: Exchange Done with on OSPF_VL3 May 26 17:25:03.315: OSPF: Synchronized with on OSPF_VL3, state FULL May 26 17:25:03.823: OSPF: Build router LSA for area 0, router ID , seq 0x May 26 17:25:03.854: OSPF: Dead event ignored for on demand circuit OSPF_VL3 Router #show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface FULL/ 00:00: ATM2/0.20 Router #show ip ospf virtual links Virtual Link OSPF_VL3 to router is up Run as demand circuit DoNotAge LSA allowed. Transit area 1, via interface ATM2/0.20, Cost of using 65 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT, Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 Hello due in 00:00:01 Adjacency State FULL (Hello suppressed) Index 1/2, retransmission queue length 0, number of retransmission 0 First 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last retransmission scan length is 0, maximum is 0 Last retransmission scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec Notice that adjacencies over virtual links are not displayed in the show ip ospf neighbor command output. The only way to see them is to look at the router LSA and observe debug commands as the adjacency comes
14 up, or issue the show ip ospf virtual links command. Related Information What Are OSPF Areas and Virtual Links? Configuring OSPF Authentication on a Virtual Link Configuring a GRE Tunnel over IPSec with OSPF What Does the show ip ospf interface Command Reveal? How OSPF Propagates External Routes into Multiple Areas OSPF Database Explanation Guide OSPF Support Page IP Routed Protocols Support Page IP Routing Support Page Technical Support & Documentation Cisco Systems Contacts & Feedback Help Site Map Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Terms & Conditions Privacy Statement Cookie Policy Trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. Updated: Jan 04, 2007 Document ID: 47866
OSPF Routers Connected by a Point to Multipoint Link
 OSPF Routers Connected by a Point to Multipoint Link Document ID: 47862 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Examine
OSPF Routers Connected by a Point to Multipoint Link Document ID: 47862 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Examine
Sample Configuration for OSPFv3
 Sample Configuration for OSPFv3 Document ID: 112100 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configuration Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
Sample Configuration for OSPFv3 Document ID: 112100 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configuration Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
OSPF Demand Circuit Feature
 OSPF Demand Circuit Feature Document ID: 5132 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How Is OSPF over Demand Circuit Different from a Normal Circuit? Suppressed Periodic
OSPF Demand Circuit Feature Document ID: 5132 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions How Is OSPF over Demand Circuit Different from a Normal Circuit? Suppressed Periodic
OSPF SNMP ifindex Value for Interface ID in Data Fields
 OSPF SNMP ifindex Value for Interface ID in Data Fields This feature allows you to configure the interface ID value Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) and Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3)
OSPF SNMP ifindex Value for Interface ID in Data Fields This feature allows you to configure the interface ID value Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) and Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3)
OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability
 OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability Contents Introduction Prerequisites Background Information Scenario 1 Network Diagram: Abstract from RFC 2328 Section 16.2 Scenario 2 Network Diagram: Abstract from
OSPF Virtual Links: Transit capability Contents Introduction Prerequisites Background Information Scenario 1 Network Diagram: Abstract from RFC 2328 Section 16.2 Scenario 2 Network Diagram: Abstract from
Networkers 2001, Australia
 Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting OSPF Jono Ladmore 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. Presentation_ID 2 Agenda LSA Details Troubleshooting Commands Common Issues Troubleshooting
Networkers 2001, Australia March 28-30, Brisbane 1 Troubleshooting OSPF Jono Ladmore 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. Presentation_ID 2 Agenda LSA Details Troubleshooting Commands Common Issues Troubleshooting
SNMP ifindex Value for Interface ID in OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 Data Fields
 SNMP ifindex Value for Interface ID in OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 Data Fields This document describes the configuration command that allows you to use either the current interface number or the SNMP MIB-II interface
SNMP ifindex Value for Interface ID in OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 Data Fields This document describes the configuration command that allows you to use either the current interface number or the SNMP MIB-II interface
Configuration and Management of Networks
 onfiguration and Management of Networks SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure multi-area SPF on a r.! Verify multi-area behavior.! reate
onfiguration and Management of Networks SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure multi-area SPF on a r.! Verify multi-area behavior.! reate
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Initial Configurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link
 Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
Initial onfigurations for OSPF over a Point to Point Link Document ID: 13687 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used onventions OSPF over a Point to Point Link with IP Addresses
Config. Router# show ip ospf
 Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, OSPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization
 NPv6 RUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-3, SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization Topology bjectives Background onfigure multi-area SPF on a r. Verify multi-area behavior. reate an SPF virtual link. Summarize an area.
NPv6 RUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-3, SPF Virtual Links and Area Summarization Topology bjectives Background onfigure multi-area SPF on a r. Verify multi-area behavior. reate an SPF virtual link. Summarize an area.
OSPF, MTU and LSA Packing Tech Note
 OSPF, MTU and LSA Packing Tech Note Document ID: 116119 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Jul 29, 2013 Contents Introduction OSPF Packet Size MTU in DBD Packet OSPF Behavior and Packing
OSPF, MTU and LSA Packing Tech Note Document ID: 116119 Contributed by Luc De Ghein, Cisco TAC Engineer. Jul 29, 2013 Contents Introduction OSPF Packet Size MTU in DBD Packet OSPF Behavior and Packing
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication Topology Objectives Background onfigure multiple-area OSPF on a r. Verify multiple-area behavior. onfigure OSPF stub, totally
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPF with Stub Areas and Authentication Topology Objectives Background onfigure multiple-area OSPF on a r. Verify multiple-area behavior. onfigure OSPF stub, totally
OSPF Stub Router Advertisement
 The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
OSPF Not So Stubby Area (NSSA)
 OSPF Not So Stubby Area (NSSA) Document ID: 6208 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions What Is a Type 7 LSA? Configuration Tasks Defining a Not So Stubby Area Defining
OSPF Not So Stubby Area (NSSA) Document ID: 6208 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions What Is a Type 7 LSA? Configuration Tasks Defining a Not So Stubby Area Defining
Configuring IS IS for IP on Cisco Routers
 Configuring IS IS for IP on Cisco Routers Document ID: 13795 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions IS IS Sample Configuration Network Diagram Configurations Monitoring
Configuring IS IS for IP on Cisco Routers Document ID: 13795 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions IS IS Sample Configuration Network Diagram Configurations Monitoring
Configuration and Management of Networks
 onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
Link State. 1 Flooding of link-state information. 5 Routing Table. 3 SPF Algorithm. 2 Building a Topological Database. 4 SPF Tree
 Link State 1 Flooding of link-state information 5 Routing Table 2 Building a Topological Database 3 SPF Algorithm 4 SPF Tree OSPF Hello Protocol OSPF routers send Hellos on OSPF enabled interfaces: Default
Link State 1 Flooding of link-state information 5 Routing Table 2 Building a Topological Database 3 SPF Algorithm 4 SPF Tree OSPF Hello Protocol OSPF routers send Hellos on OSPF enabled interfaces: Default
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF with Multi Area Adjacency Configuration Example
 OSPF with Multi Area Adjacency Configuration Example Document ID: 118879 Contributed by Narra Naukwal, Cisco TAC Engineer. Mar 31, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used
OSPF with Multi Area Adjacency Configuration Example Document ID: 118879 Contributed by Narra Naukwal, Cisco TAC Engineer. Mar 31, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used
Cabrillo College. Rick Graziani, Instructor
 Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution
 Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
OSPF. About OSPF. CLI Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.4 1
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Open Shortest Path First () routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Open Shortest Path First () routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines
The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s
 Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
Review Questions The following questions are designed to test your understanding of this chapter s material. For more information on how to get additional questions, please see www.lammle.com/ccn a. You
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Configuring Networking Protocols
 11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv3 Topology
 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address R1 R2 R3 S0/0/0 (DCE) Lo0 Lo1 Lo2 Lo3 S0/0/0 S0/0/1
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address R1 R2 R3 S0/0/0 (DCE) Lo0 Lo1 Lo2 Lo3 S0/0/0 S0/0/1
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 OSPFv3 2 OSPFv2 Latest revision is RFC 2328 April 1998 OSPF uses a 2 level hierarchical model SPF calculation is performed independently for each area Typically
2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 OSPFv3 2 OSPFv2 Latest revision is RFC 2328 April 1998 OSPF uses a 2 level hierarchical model SPF calculation is performed independently for each area Typically
CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0
 Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
Copyright Information, Inc. All rights reserved. The following publication, CCIE R&S Lab Workbook Volume I Version 5.0, was developed by Internetwork Expert, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
IPv6 Routing: OSPFv3
 Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) is an IPv4 and IPv6 link-state routing protocol that supports IPv6 and IPv4 unicast address families (AFs). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites
Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) is an IPv4 and IPv6 link-state routing protocol that supports IPv6 and IPv4 unicast address families (AFs). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites
Configuring OSPF. Cisco s OSPF Implementation
 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Configuring IS IS over IPv6
 Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN
 Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN Document ID: 23565 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Router Configurations Problem Cause of the LSP Failure
Troubleshooting LSP Failure in MPLS VPN Document ID: 23565 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Router Configurations Problem Cause of the LSP Failure
Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
 ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
Configuring OSPF network management 39 Enabling message logging 39 Enabling the advertisement and reception of opaque LSAs 40 Configuring OSPF to
 Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 OSPF areas 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported OSPF features 17 Protocols and
Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 OSPF areas 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported OSPF features 17 Protocols and
FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 4 1.1 area default-cost...4 1.2 area range...5 1.3 area stub... 6 1.4 auto-cost...7 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...8 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 4 1.1 area default-cost...4 1.2 area range...5 1.3 area stub... 6 1.4 auto-cost...7 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...8 1.6 default-information
Creating Multiple OSPF Areas. 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. 6-1
 Creating Multiple OSPF Areas 6-1 Issues with Maintaining a Large OSPF Network I am only receiving LSAs, no data. OSPF The SPF is running too often for me to route. OSPF OSPF OSPF OSPF My routing table
Creating Multiple OSPF Areas 6-1 Issues with Maintaining a Large OSPF Network I am only receiving LSAs, no data. OSPF The SPF is running too often for me to route. OSPF OSPF OSPF OSPF My routing table
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
OSPFv2 deep dive. Михайловский Василий Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015
 OSPFv2 deep dive Михайловский Василий vamikhai@cisco.com Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015 Содержание TBD OSPFv2 transport Using IP-multicast 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6; Protocol number 89; Unicast for immediate
OSPFv2 deep dive Михайловский Василий vamikhai@cisco.com Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015 Содержание TBD OSPFv2 transport Using IP-multicast 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6; Protocol number 89; Unicast for immediate
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Agenda OSPF Primer OSPF in Service Provider Networks OSPF BCP - Adding Networks OSPF Command Summary 2 OSPF Primer 3
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Agenda OSPF Primer OSPF in Service Provider Networks OSPF BCP - Adding Networks OSPF Command Summary 2 OSPF Primer 3
OSPF Protocol Overview on page 187. OSPF Standards on page 188. OSPF Area Terminology on page 188. OSPF Routing Algorithm on page 190
 Chapter 17 OSPF Protocol Overview The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF uses link-state information
Chapter 17 OSPF Protocol Overview The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF uses link-state information
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information. Contents
 Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
FiberstoreOS. IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 6 1.1 area default-cost... 6 1.2 area range...7 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 6 1.1 area default-cost... 6 1.2 area range...7 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
OSPF External path selection: External Type- 2 (E2) VS NSSA Type-2 (N2)
 OSPF External path selection: External Type- 2 (E2) VS NSSA Type-2 (N2) Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Abstract from RFC 3101 Section 2.5 Abstract
OSPF External path selection: External Type- 2 (E2) VS NSSA Type-2 (N2) Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Information Abstract from RFC 3101 Section 2.5 Abstract
How To Configure Basic OSPFv3 Scenarios
 How To Configure Basic OSPFv3 Scenarios Contents 1. Contents...... 1 2. Introduction...... 2 3. OSPFv3 Basic Configuration...... 3 Commands for basic OSPFv3 configuration... 4 OSPFv3 basic configuration
How To Configure Basic OSPFv3 Scenarios Contents 1. Contents...... 1 2. Introduction...... 2 3. OSPFv3 Basic Configuration...... 3 Commands for basic OSPFv3 configuration... 4 OSPFv3 basic configuration
OSPF Sham-Link Support for MPLS VPN
 Feature History Release Modification 12.2(8)T This feature was introduced. This module describes how to configure and use a sham-link to connect Virtual Private Network (VPN) client sites that run the
Feature History Release Modification 12.2(8)T This feature was introduced. This module describes how to configure and use a sham-link to connect Virtual Private Network (VPN) client sites that run the
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
 OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Open : specification publicly available RFC 1247, RFC 2328 Working group formed in 1988 Goals: Large, heterogeneous internetworks Uses the Link State algorithm Topology
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Open : specification publicly available RFC 1247, RFC 2328 Working group formed in 1988 Goals: Large, heterogeneous internetworks Uses the Link State algorithm Topology
OSPFv2 Segment Routing Strict SPF
 The OSPFv2 Segment Routing Strict Shortest Path First (SPF) feature provides information about the strict SPF segment identifiers (SIDs). Restrictions for, on page 1 Information About, on page 1 Enabling
The OSPFv2 Segment Routing Strict Shortest Path First (SPF) feature provides information about the strict SPF segment identifiers (SIDs). Restrictions for, on page 1 Information About, on page 1 Enabling
Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers
 OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
 OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Open : specification publicly available RFC 1247, RFC 2328 Working group formed in 1988 Goals: Large, heterogeneous internetworks Uses the Link State algorithm Topology
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Open : specification publicly available RFC 1247, RFC 2328 Working group formed in 1988 Goals: Large, heterogeneous internetworks Uses the Link State algorithm Topology
RHI on the Content Switching Module Configuration Example
 RHI on the Content Switching Module Configuration Example Document ID: 60043 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
RHI on the Content Switching Module Configuration Example Document ID: 60043 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example
 Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113153 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Adjust Administrative Distance for Route Selection in Cisco IOS Routers Configuration Example Document ID: 113153 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions. Net412- Network troubleshooting
 Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
OSPF. Unless otherwise noted, OSPF refers to OSPFv2 throughout this document.
 Open Shortest Path First () is a link state based interior gateway protocol developed by the working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). At present, version 2 (RFC2328) is used. Introduction
Open Shortest Path First () is a link state based interior gateway protocol developed by the working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). At present, version 2 (RFC2328) is used. Introduction
Configuring OSPF with CLI
 OSPF Configuring OSPF with CLI This section provides information to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) using the command line interface. Topics in this section include: OSPF Configuration Guidelines
OSPF Configuring OSPF with CLI This section provides information to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) using the command line interface. Topics in this section include: OSPF Configuration Guidelines
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
Explanation: In order to verify proper route redistribution, use the "show ip route" command on all routers
 QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
OSPF. OSPF processs can be enabled on 2 levels
 OSPF UDP port 89 Metic cost Link state protocol Flood the link state information in the entire topology Builds the topology table Stores in LSDB Runs SPF(Djsktra algorithm) for best path to reach destination
OSPF UDP port 89 Metic cost Link state protocol Flood the link state information in the entire topology Builds the topology table Stores in LSDB Runs SPF(Djsktra algorithm) for best path to reach destination
Area Command in Interface Mode for OSPFv2
 This document describes how to enable Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) on a per-interface basis to simplify the configuration of unnumbered interfaces. The ip ospf area command allows you to
This document describes how to enable Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) on a per-interface basis to simplify the configuration of unnumbered interfaces. The ip ospf area command allows you to
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Veryx ATTEST TM. Sample Test cases Overview. Conformance Test Suite. Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2)
 Veryx ATTEST TM Conformance Test Suite Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) Sample Test cases Overview Part Number: T / TCLS OSPFv2 1.0-1110/1.0 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction
Veryx ATTEST TM Conformance Test Suite Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2) Sample Test cases Overview Part Number: T / TCLS OSPFv2 1.0-1110/1.0 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction
CompSci 356: Computer Network Architectures. Lecture 13: Dynamic routing protocols: Link State Chapter 3.3.3, Xiaowei Yang
 CompSci 356: Computer Network Architectures Lecture 13: Dynamic routing protocols: Link State Chapter 3.3.3, 3.2.9 Xiaowei Yang xwy@cs.duke.edu Today Clarification on RIP Link-state routing Algorithm Protocol:
CompSci 356: Computer Network Architectures Lecture 13: Dynamic routing protocols: Link State Chapter 3.3.3, 3.2.9 Xiaowei Yang xwy@cs.duke.edu Today Clarification on RIP Link-state routing Algorithm Protocol:
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
Logging neighbor state changes 38 Configuring OSPF network management 39 Enabling message logging 39 Enabling the advertisement and reception of
 Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 Area based OSPF network partition 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported features
Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 Area based OSPF network partition 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported features
Use NAT to Hide the Real IP Address of CTC to Establish a Session with ONS 15454
 Use NAT to Hide the Real IP Address of CTC to Establish a Session with ONS 15454 Document ID: 65122 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Topology
Use NAT to Hide the Real IP Address of CTC to Establish a Session with ONS 15454 Document ID: 65122 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Topology
EECS 122, Lecture 16. Link Costs and Metrics. Traffic-Sensitive Metrics. Traffic-Sensitive Metrics. Static Cost Metrics.
 EECS 122, Lecture 16 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu Link Costs and Metrics Routing protocols compute shortest/cheapest paths using some optimization criteria Choice of criteria has strong effect
EECS 122, Lecture 16 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu Link Costs and Metrics Routing protocols compute shortest/cheapest paths using some optimization criteria Choice of criteria has strong effect
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration RIP Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
IPv6 Routing Protocols Update
 IPv6 Routing Protocols Update Wim Verrydt Solutions Architect BRKRST-2022 Abstract and Pre-requisite The proposed session provides a comprehensive overview of the main IPv6 routing protocols: IS-IS, OSPFv3,
IPv6 Routing Protocols Update Wim Verrydt Solutions Architect BRKRST-2022 Abstract and Pre-requisite The proposed session provides a comprehensive overview of the main IPv6 routing protocols: IS-IS, OSPFv3,
Vendor: Juniper. Exam Code: JN Exam Name: Enterprise Routing and Switching Support, Professional (JNCSP-ENT) Version: Demo
 Vendor: Juniper Exam Code: JN0-694 Exam Name: Enterprise Routing and Switching Support, Professional (JNCSP-ENT) Version: Demo QUESTION 1 You are implementing Q-in-Q tunneling on an EX Series switch. You
Vendor: Juniper Exam Code: JN0-694 Exam Name: Enterprise Routing and Switching Support, Professional (JNCSP-ENT) Version: Demo QUESTION 1 You are implementing Q-in-Q tunneling on an EX Series switch. You
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example
 FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
FlexVPN HA Dual Hub Configuration Example Document ID: 118888 Contributed by Piotr Kupisiewicz, Wen Zhang, and Frederic Detienne, Cisco TAC Engineers. Apr 08, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting. IPv4 Routing Workflow. IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting http:// IPv4 Routing Workflow IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps Routing lookup Switching method Layer 2 encapsulation
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp IPv4 IGP Troubleshooting http:// IPv4 Routing Workflow IPv4 routing can be subdivided into three discrete steps Routing lookup Switching method Layer 2 encapsulation
Link State Routing. Link State Packets. Link State Protocol. Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and pitfalls
 Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 16.3, 2017/03/09 11:25:31) Tuesday, March 7, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and
Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 16.3, 2017/03/09 11:25:31) Tuesday, March 7, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and
Introduction to OSPF OSPF. Link State Routing. Link State. Fast Convergence. Low Bandwidth Utilisation
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IP Workshops OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 47) Designed for TCP/IP Internet environment Fast convergence
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IP Workshops OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 47) Designed for TCP/IP Internet environment Fast convergence
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Table of Contents. Cisco Introduction to EIGRP
 Table of Contents Introduction to EIGRP...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 What is IGRP?...2 What is EIGRP?...2 How Does EIGRP Work?...2 EIGRP
Table of Contents Introduction to EIGRP...1 Introduction...1 Before You Begin...1 Conventions...1 Prerequisites...1 Components Used...1 What is IGRP?...2 What is EIGRP?...2 How Does EIGRP Work?...2 EIGRP
Network Working Group. Category: Standards Track Stanford University March 1994
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1587 Category: Standards Track R. Coltun RainbowBridge Communications V. Fuller Stanford University March 1994 The OSPF NSSA Option Status of this Memo This
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 1587 Category: Standards Track R. Coltun RainbowBridge Communications V. Fuller Stanford University March 1994 The OSPF NSSA Option Status of this Memo This
OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF
OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF
OSPF Commands on Cisco IOS XR Software
 This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training
 REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
scope scope {global vrf vrf-name} no scope {global vrf vrf-name} Syntax Description
 Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Vanguard Managed Solutions
 Vanguard Managed Solutions Vanguard Applications Ware IP and LAN Feature Protocols Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Notice 2003 Vanguard Managed Solutions, LLC 575 West Street Mansfield, Massachusetts 02048
Vanguard Managed Solutions Vanguard Applications Ware IP and LAN Feature Protocols Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Notice 2003 Vanguard Managed Solutions, LLC 575 West Street Mansfield, Massachusetts 02048
