Internet data transfer record between CERN and California. Sylvain Ravot (Caltech) Paolo Moroni (CERN)
|
|
|
- Gavin Fletcher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Internet data transfer record between CERN and California Sylvain Ravot (Caltech) Paolo Moroni (CERN)
2 Summary Internet2 Land Speed Record Contest New LSR DataTAG project and network configuration Establishing an LSR: hardware and tuning Conclusions Acknowledgements Ravot - Moroni - 2
3 Internet2 LSR Contest (I) From A minimum of 100 megabytes must be transferred a minimum terrestrial distance of 100 kilometers with a minimum of two router hops in each direction between the source node and the destination node across one or more operational and production-oriented high-performance research and education networks. The contest unit of measurement is [ ] bitmeters/second. Ravot - Moroni - 3
4 Internet2 LSR Contest (II) Instances of all hardware units and software modules used to transfer contest data on the source node, the destination node, the links, and the routers must be offered for commercial sale or as open source software to all U.S. members of the Internet community by their respective vendors or developers prior to or immediately after winning the contest. Award classes: single or multiple TCP streams, on top of IPv4 or IPv6 Generally available networks and equipment, vs. lab prototypes Ravot - Moroni - 4
5 Former LSR TCP/IPv4 single stream By NIKHEF, Caltech and SLAC Established on November 19 th Km of network: Geneva- Amsterdam-Chicago-Sunnyvale 0.93 Gb/sec terabit-meters/second Ravot - Moroni - 5
6 Current LSR TCP/IPv4 single stream By Caltech, CERN, LANL and SLAC, within the DataTAG project framework Established on February 27 th -28 th 2003 by Sylvain Ravot (Caltech) using IPERF Terabit-meters/second Km of network: Geneva-Chicago- Sunnyvale (shorter distance than the former LSR) 2.38 Gb/sec (sustained: a Terabyte of data moved in an hour) Ravot - Moroni - 6
7 DataTAG project Full project title: Research and technological development for a transatlantic GRID IST project (EU funded), supported by the NSF and the DoE (Caltech): Partners: PPARC (UK), INRIA (FR), University of Amsterdam (NL), INFN (IT) and CERN (CH) Researchers also from Caltech, Los Alamos, SLAC and Canada Test-bed kernel: transatlantic STM-16 between Geneva (CERN) and Chicago (StarLight), with interconnected workstations at each side. Test-bed extensions provided by GEANT, SURFnet, VTHD and other partners, in Europe and North America Ravot - Moroni - 7
8 DataTAG as test-bed for LSR Research on TCP as part of the DataTAG programme The Geneva-Chicago link was the main environment for the LSR Network extension made available: Chicago- Sunnyvale STM-64 Router at Sunnyvale 10 GbE interfaces on DataTAG PCs Ravot - Moroni - 8
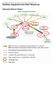
9 Cisco (Cisco loan) LSR network configuration Cisco 7609 (DataTAG) DataTAG network STM-64 (Level3 loan) STM-16 (T-systems) 10 GbE PC (10GbE) (Intel loan) PC (10GbE) (Intel loan) Juniper T640 (TeraGrid) Cisco 7606 (DataTAG) Level3 PoP SUNNYVALE (California USA) StarLight Chicago (Illinois USA) CERN Geneva (Switzerland) Ravot - Moroni - 9
10 Establishing an LSR: hardware (I) No LSR without good hardware A lot of bandwidth: minimum 2.5 Gb/sec on the whole path (thanks to Level3 for the STM-64 on loan between Chicago and Sunnyvale) Powerful routers (Cisco 7600 and GSR, Juniper T640) Powerful Linux PCs on both sides Intel 10 GbE interfaces Ravot - Moroni - 10
11 Establishing an LSR: hardware (II) Linux PC at CERN: Dual Intel Xeon processors, 2.40GHz with 512K L2 cache SuperMicro P4DP8-G2 Motherboard Intel E700 chipset 2 GB RAM,PC2100 ECC Reg. DDR Hard drive: 1 x 140 GB - Maxtor ATA-133 On board Intel 82546EB dual port Gigabit Ethernet controller 4U Rack-mounted server Linux PC at Sunnyvale: Dual Intel Xeon processors, 2.40GHz with 512K L2 cache SuperMicro P4DPE-G2 Motherboard 2 GB RAM, PC2100 ECC Reg. DDR 2* 3ware RAID controllers 16 Western Digital IDE disk drives for RAID and 1 for system 2 Intel fast Ethernet 2*SysKonnect Gigabit Ethernet card SK-9843 SK-NET GE SX 4U Rack-mounted server 480W to run 600W to spin up Ravot - Moroni - 11
12 Establishing an LSR: hardware (III) Intel 10 GbE interfaces: Intel Pro/10 GbE- LR Not yet commercially available when the LSR was set, but announced as commercially available shortly afterwards Ravot - Moroni - 12
13 Establishing an LSR: standard tuning MTU set to 9000 bytes TCP window size increased from the Linux default of 64K: essential over long distance But standard Linux kernel (2.4.20) Standard tuning is not enough for LSR: why? Ravot - Moroni - 13
14 TCP WAN problems Responsiveness to packet losses is proportional to the square of the RTT: R=C*(RTT**2)/2*MSS (where C is the link capacity and MSS is the max segment size). This makes it very difficult to take advantage of full capacity over long-distance WAN: not a real problem for standard traffic on a shared link, but a serious penalty for LSR Slow start mode is too slow using default parameters: they are good for standard traffic, but not for LSR Ravot - Moroni - 14
15 Example: recovering from a packet loss TCP Throughput CERN-Chicago over the 622 Mbit/s link Throughput (Mbit/s) min TCP reactivity Time (s) Time to increase the throughput by 120 Mbit/s is larger than 6 min for a connection between Chicago and CERN. Packet losses is a disaster for the overall throughput Ravot - Moroni - 15
16 Example: slow start vs. congestion avoidance Cwnd average of the last 10 samples. SSTHRESH Cwnd average over the life of the connection to that point Slow start Congestion Avoidance Ravot - Moroni - 16
17 Establishing an LSR: what goes wrong Behaviour of the TCP stack: if C is very small, it keeps the responsiveness low enough for any terrestrial RTT. Therefore modern, fast WAN links are bad for TCP performance TCP tries to increase its window size until something breaks (packet loss, congestion, ); then restarts from a half of the previous value until it breaks again. This gradual approximation process takes very long over long distance and degrades performance Ravot - Moroni - 17
18 Establishing an LSR: further tuning Knowing a priori the available bandwidth, prevent TCP from trying larger windows by restricting the amount of buffers it may use: without buffers, it won t try to use larger windows and packet losses can be avoided The product C*RTT yields the optimal TCP window size for a link of capacity C So, allocate just enough buffers to let TCP squeeze the maximum performance from the existing bandwidth and nothing else Ravot - Moroni - 18
19 Further tuning: Linux implementation Tuning TCP buffers (numbers for STM-16): echo > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_rmem echo > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_wmem echo > /proc/sys/net/core/wmem_max echo > /proc/sys/net/core/rmem_max Tuning the network device buffers: /sbin/ifconfig eth1 txqueuelen /sbin/ifconfig eth1 mtu 9000 Both on sender and receiver Ravot - Moroni - 19
20 Even further tuning: Linux implementation TCP slow start mode vs. congestion avoidance mode is another performance penalty in the sender for the LSR On Linux (sender side only): sysctl -w w net.ipv4.route.flush=1 This prevents TCP from using any previously cached window value, i.e. speeds up slow start mode and gets to congestion avoidance mode at exponential speed (otherwise the growth of the congestion window would start at half of some previously cached value) Ravot - Moroni - 20
21 IPERF parameters On the sender: iperf -c c i i 5 -P P 3 -w w 40M -t t 180 On the receiver: iperf s -w w 128M IPERF is available at Ravot - Moroni - 21
22 Conclusions: how useful in practice? The LSR result cannot be immediately translated into practical general-purpose recommendations: it relies on some a priori knowledge (the physical link speed) dedicated bandwidth ad hoc TCP tuning: good for LSR, not for general- purpose traffic Nevertheless, work is ongoing for a more modern TCP stack: the new LSR demonstrates that fast WAN TCP is possible in practice, by tweaking TCP a bit Ravot - Moroni - 22
23 Conclusions: sustained throughput The LSR definition has only very limited provisioning for requiring sustained throughput (100 Megabytes are not much) However the achieved LSR shows that high sustained throughput is in principle possible with TCP over long distance Former results could sustain the throughput only for seconds, before some TCP feedback mechanism kicked in Ravot - Moroni - 23
24 Other remarks The bottleneck for things like the LSR is now in the end hosts: no non-trivial tuning was needed on the network where the LSR was established Incidentally, although single-stream, the new LSR was also good enough to establish the new LSR for multiple IPv4 streams No TCP packet was lost during the LSR trial window Details of the new record are not published on yet Ravot - Moroni - 24
25 Acknowledgements: people Sylvain Ravot (working for Caltech at CERN) Wu-Chun Feng (LANL) Les Cottrell (SLAC) Ravot - Moroni - 25
26 Acknowledgements: industrial partners Ravot - Moroni - 26
27 Acknowledgements: organisations
High bandwidth, Long distance. Where is my throughput? Robin Tasker CCLRC, Daresbury Laboratory, UK
 High bandwidth, Long distance. Where is my throughput? Robin Tasker CCLRC, Daresbury Laboratory, UK [r.tasker@dl.ac.uk] DataTAG is a project sponsored by the European Commission - EU Grant IST-2001-32459
High bandwidth, Long distance. Where is my throughput? Robin Tasker CCLRC, Daresbury Laboratory, UK [r.tasker@dl.ac.uk] DataTAG is a project sponsored by the European Commission - EU Grant IST-2001-32459
Achieving Record Speed Trans- Atlantic End-to-end TCP Throughput
 Achieving Record Speed Trans- Atlantic End-to-end TCP Throughput Les Cottrell SLAC Prepared for the NANOG meeting, Salt Lake City, June 2003 http://www.slac.stanford.edu/grp/scs/net/talk/nanog-jun03.html
Achieving Record Speed Trans- Atlantic End-to-end TCP Throughput Les Cottrell SLAC Prepared for the NANOG meeting, Salt Lake City, June 2003 http://www.slac.stanford.edu/grp/scs/net/talk/nanog-jun03.html
46PaQ. Dimitris Miras, Saleem Bhatti, Peter Kirstein Networks Research Group Computer Science UCL. 46PaQ AHM 2005 UKLIGHT Workshop, 19 Sep
 46PaQ Dimitris Miras, Saleem Bhatti, Peter Kirstein Networks Research Group Computer Science UCL 46PaQ AHM 2005 UKLIGHT Workshop, 19 Sep 2005 1 Today s talk Overview Current Status and Results Future Work
46PaQ Dimitris Miras, Saleem Bhatti, Peter Kirstein Networks Research Group Computer Science UCL 46PaQ AHM 2005 UKLIGHT Workshop, 19 Sep 2005 1 Today s talk Overview Current Status and Results Future Work
Lighting the Blue Touchpaper for UK e-science - Closing Conference of ESLEA Project The George Hotel, Edinburgh, UK March, 2007
 Working with 1 Gigabit Ethernet 1, The School of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL UK E-mail: R.Hughes-Jones@manchester.ac.uk Stephen Kershaw The School of Physics
Working with 1 Gigabit Ethernet 1, The School of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL UK E-mail: R.Hughes-Jones@manchester.ac.uk Stephen Kershaw The School of Physics
TCP Tuning Domenico Vicinanza DANTE, Cambridge, UK
 TCP Tuning Domenico Vicinanza DANTE, Cambridge, UK domenico.vicinanza@dante.net EGI Technical Forum 2013, Madrid, Spain TCP! Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)! One of the original core protocols of the
TCP Tuning Domenico Vicinanza DANTE, Cambridge, UK domenico.vicinanza@dante.net EGI Technical Forum 2013, Madrid, Spain TCP! Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)! One of the original core protocols of the
Evaluation of Advanced TCP Stacks on Fast Long-Distance Production Networks p. 1
 Evaluation of Advanced TCP Stacks on Fast Long-Distance Production Networks Hadrien Bullot & R. Les Cottrell {hadrien,cottrell}@slac.stanford.edu Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Menlo Park Evaluation
Evaluation of Advanced TCP Stacks on Fast Long-Distance Production Networks Hadrien Bullot & R. Les Cottrell {hadrien,cottrell}@slac.stanford.edu Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Menlo Park Evaluation
Data transfer over the wide area network with a large round trip time
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Data transfer over the wide area network with a large round trip time To cite this article: H Matsunaga et al 1 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 219 656 Recent citations - A two
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Data transfer over the wide area network with a large round trip time To cite this article: H Matsunaga et al 1 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 219 656 Recent citations - A two
Network Design Considerations for Grid Computing
 Network Design Considerations for Grid Computing Engineering Systems How Bandwidth, Latency, and Packet Size Impact Grid Job Performance by Erik Burrows, Engineering Systems Analyst, Principal, Broadcom
Network Design Considerations for Grid Computing Engineering Systems How Bandwidth, Latency, and Packet Size Impact Grid Job Performance by Erik Burrows, Engineering Systems Analyst, Principal, Broadcom
Wide-Area Networking at SLAC. Warren Matthews and Les Cottrell (SCS Network Group) Presented at SLAC, April
 Wide-Area Networking at SLAC Warren Matthews and Les Cottrell (SCS Network Group) Presented at SLAC, April 6 2001. Overview SLAC s Connections to WANs Utilization End-to-end Performance The Future Note:
Wide-Area Networking at SLAC Warren Matthews and Les Cottrell (SCS Network Group) Presented at SLAC, April 6 2001. Overview SLAC s Connections to WANs Utilization End-to-end Performance The Future Note:
High Performance Ethernet for Grid & Cluster Applications. Adam Filby Systems Engineer, EMEA
 High Performance Ethernet for Grid & Cluster Applications Adam Filby Systems Engineer, EMEA 1 Agenda Drivers & Applications The Technology Ethernet Everywhere Ethernet as a Cluster interconnect Ethernet
High Performance Ethernet for Grid & Cluster Applications Adam Filby Systems Engineer, EMEA 1 Agenda Drivers & Applications The Technology Ethernet Everywhere Ethernet as a Cluster interconnect Ethernet
Optimizing 10-Gigabit Ethernet for Networks of Workstations, Clusters, and Grids: A Case Study Λ
 Proc. of ACM/IEEE SC 23: High-Performance Networking and Computing Conference, November 23. Optimizing 1-Gigabit Ethernet for Networks of Workstations, Clusters, and Grids: A Case Study Λ Wu-chun Feng,
Proc. of ACM/IEEE SC 23: High-Performance Networking and Computing Conference, November 23. Optimizing 1-Gigabit Ethernet for Networks of Workstations, Clusters, and Grids: A Case Study Λ Wu-chun Feng,
CMS Data Transfer Challenges and Experiences with 40G End Hosts
 CMS Data Transfer Challenges and Experiences with 40G End Hosts NEXT Technology Exchange Advanced Networking / Joint Techs Indianapolis, October 2014 Azher Mughal, Dorian Kcira California Institute of
CMS Data Transfer Challenges and Experiences with 40G End Hosts NEXT Technology Exchange Advanced Networking / Joint Techs Indianapolis, October 2014 Azher Mughal, Dorian Kcira California Institute of
Transport layer issues
 Transport layer issues Dmitrij Lagutin, dlagutin@cc.hut.fi T-79.5401 Special Course in Mobility Management: Ad hoc networks, 28.3.2007 Contents Issues in designing a transport layer protocol for ad hoc
Transport layer issues Dmitrij Lagutin, dlagutin@cc.hut.fi T-79.5401 Special Course in Mobility Management: Ad hoc networks, 28.3.2007 Contents Issues in designing a transport layer protocol for ad hoc
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP. JY Le Boudec 2014
 1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2014 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2014 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
Gigabyte Bandwidth Enables Global Co-Laboratories
 Gigabyte Bandwidth Enables Global Co-Laboratories Prof. Harvey Newman, Caltech Jim Gray, Microsoft Presented at Windows Hardware Engineering Conference Seattle, WA, 2 May 2004 Credits: This represents
Gigabyte Bandwidth Enables Global Co-Laboratories Prof. Harvey Newman, Caltech Jim Gray, Microsoft Presented at Windows Hardware Engineering Conference Seattle, WA, 2 May 2004 Credits: This represents
ASPERA HIGH-SPEED TRANSFER. Moving the world s data at maximum speed
 ASPERA HIGH-SPEED TRANSFER Moving the world s data at maximum speed ASPERA HIGH-SPEED FILE TRANSFER Aspera FASP Data Transfer at 80 Gbps Elimina8ng tradi8onal bo
ASPERA HIGH-SPEED TRANSFER Moving the world s data at maximum speed ASPERA HIGH-SPEED FILE TRANSFER Aspera FASP Data Transfer at 80 Gbps Elimina8ng tradi8onal bo
TCP on High-Speed Networks
 TCP on High-Speed Networks from New Internet and Networking Technologies for Grids and High-Performance Computing, tutorial given at HiPC 04, Bangalore, India December 22nd, 2004 C. Pham University Lyon,
TCP on High-Speed Networks from New Internet and Networking Technologies for Grids and High-Performance Computing, tutorial given at HiPC 04, Bangalore, India December 22nd, 2004 C. Pham University Lyon,
Sun Lustre Storage System Simplifying and Accelerating Lustre Deployments
 Sun Lustre Storage System Simplifying and Accelerating Lustre Deployments Torben Kling-Petersen, PhD Presenter s Name Principle Field Title andengineer Division HPC &Cloud LoB SunComputing Microsystems
Sun Lustre Storage System Simplifying and Accelerating Lustre Deployments Torben Kling-Petersen, PhD Presenter s Name Principle Field Title andengineer Division HPC &Cloud LoB SunComputing Microsystems
Chapter 4. Routers with Tiny Buffers: Experiments. 4.1 Testbed experiments Setup
 Chapter 4 Routers with Tiny Buffers: Experiments This chapter describes two sets of experiments with tiny buffers in networks: one in a testbed and the other in a real network over the Internet2 1 backbone.
Chapter 4 Routers with Tiny Buffers: Experiments This chapter describes two sets of experiments with tiny buffers in networks: one in a testbed and the other in a real network over the Internet2 1 backbone.
TCP Congestion Control
 TCP Congestion Control What is Congestion The number of packets transmitted on the network is greater than the capacity of the network Causes router buffers (finite size) to fill up packets start getting
TCP Congestion Control What is Congestion The number of packets transmitted on the network is greater than the capacity of the network Causes router buffers (finite size) to fill up packets start getting
TCP Congestion Control
 What is Congestion TCP Congestion Control The number of packets transmitted on the network is greater than the capacity of the network Causes router buffers (finite size) to fill up packets start getting
What is Congestion TCP Congestion Control The number of packets transmitted on the network is greater than the capacity of the network Causes router buffers (finite size) to fill up packets start getting
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP. JY Le Boudec 2014
 1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2014 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2014 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
GÉANT Support for Research Within and Beyond Europe
 GÉANT Support for Research Within and Beyond Europe TNC 2003, Zagreb 19-22 May Marian Garcia, Operations Manager DANTE AGENDA GÉANT Global Research Connectivity Europe, North America and other regions
GÉANT Support for Research Within and Beyond Europe TNC 2003, Zagreb 19-22 May Marian Garcia, Operations Manager DANTE AGENDA GÉANT Global Research Connectivity Europe, North America and other regions
Managing Caching Performance and Differentiated Services
 CHAPTER 10 Managing Caching Performance and Differentiated Services This chapter explains how to configure TCP stack parameters for increased performance ant throughput and how to configure Type of Service
CHAPTER 10 Managing Caching Performance and Differentiated Services This chapter explains how to configure TCP stack parameters for increased performance ant throughput and how to configure Type of Service
CSE 123A Computer Networks
 CSE 123A Computer Networks Winter 2005 Lecture 14 Congestion Control Some images courtesy David Wetherall Animations by Nick McKeown and Guido Appenzeller The bad news and the good news The bad news: new
CSE 123A Computer Networks Winter 2005 Lecture 14 Congestion Control Some images courtesy David Wetherall Animations by Nick McKeown and Guido Appenzeller The bad news and the good news The bad news: new
FAST TCP: From Theory to Experiments
 FAST TCP: From Theory to Experiments C. Jin, D. Wei, S. H. Low G. Buhrmaster, J. Bunn, D. H. Choe, R. L. A. Cottrell, J. C. Doyle W. Feng, O. Martin, H. Newman, F. Paganini, S. Ravot, S. Singh http://netlab.caltech.edu/fast/
FAST TCP: From Theory to Experiments C. Jin, D. Wei, S. H. Low G. Buhrmaster, J. Bunn, D. H. Choe, R. L. A. Cottrell, J. C. Doyle W. Feng, O. Martin, H. Newman, F. Paganini, S. Ravot, S. Singh http://netlab.caltech.edu/fast/
FAST TCP: From Theory to Experiments
 FAST TCP: From Theory to Experiments C. Jin, D. Wei, S. H. Low G. Buhrmaster, J. Bunn, D. H. Choe, R. L. A. Cottrell, J. C. Doyle W. Feng, O. Martin, H. Newman, F. Paganini, S. Ravot, S. Singh http://netlab.caltech.edu/fast/
FAST TCP: From Theory to Experiments C. Jin, D. Wei, S. H. Low G. Buhrmaster, J. Bunn, D. H. Choe, R. L. A. Cottrell, J. C. Doyle W. Feng, O. Martin, H. Newman, F. Paganini, S. Ravot, S. Singh http://netlab.caltech.edu/fast/
Diamond Networks/Computing. Nick Rees January 2011
 Diamond Networks/Computing Nick Rees January 2011 2008 computing requirements Diamond originally had no provision for central science computing. Started to develop in 2007-2008, with a major development
Diamond Networks/Computing Nick Rees January 2011 2008 computing requirements Diamond originally had no provision for central science computing. Started to develop in 2007-2008, with a major development
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP. JY Le Boudec 2015
 1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2015 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
1 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2015 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP. JY Le Boudec 2015
 Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2015 1 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
Congestion Control In The Internet Part 2: How it is implemented in TCP JY Le Boudec 2015 1 Contents 1. Congestion control in TCP 2. The fairness of TCP 3. The loss throughput formula 4. Explicit Congestion
TCP Strategies. Keepalive Timer. implementations do not have it as it is occasionally regarded as controversial. between source and destination
 Keepalive Timer! Yet another timer in TCP is the keepalive! This one is not required, and some implementations do not have it as it is occasionally regarded as controversial! When a TCP connection is idle
Keepalive Timer! Yet another timer in TCP is the keepalive! This one is not required, and some implementations do not have it as it is occasionally regarded as controversial! When a TCP connection is idle
Lecture 21: Congestion Control" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren
 Lecture 21: Congestion Control" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Lecture 21 Overview" How fast should a sending host transmit data? Not to fast, not to slow, just right Should not be faster than
Lecture 21: Congestion Control" CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Lecture 21 Overview" How fast should a sending host transmit data? Not to fast, not to slow, just right Should not be faster than
TCP Performance. EE 122: Intro to Communication Networks. Fall 2006 (MW 4-5:30 in Donner 155) Vern Paxson TAs: Dilip Antony Joseph and Sukun Kim
 TCP Performance EE 122: Intro to Communication Networks Fall 2006 (MW 4-5:30 in Donner 155) Vern Paxson TAs: Dilip Antony Joseph and Sukun Kim http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/ Materials with thanks
TCP Performance EE 122: Intro to Communication Networks Fall 2006 (MW 4-5:30 in Donner 155) Vern Paxson TAs: Dilip Antony Joseph and Sukun Kim http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~ee122/ Materials with thanks
Topics. TCP sliding window protocol TCP PUSH flag TCP slow start Bulk data throughput
 Topics TCP sliding window protocol TCP PUSH flag TCP slow start Bulk data throughput 2 Introduction In this chapter we will discuss TCP s form of flow control called a sliding window protocol It allows
Topics TCP sliding window protocol TCP PUSH flag TCP slow start Bulk data throughput 2 Introduction In this chapter we will discuss TCP s form of flow control called a sliding window protocol It allows
The Future of High-Performance Networking (The 5?, 10?, 15? Year Outlook)
 Workshop on New Visions for Large-Scale Networks: Research & Applications Vienna, VA, USA, March 12-14, 2001 The Future of High-Performance Networking (The 5?, 10?, 15? Year Outlook) Wu-chun Feng feng@lanl.gov
Workshop on New Visions for Large-Scale Networks: Research & Applications Vienna, VA, USA, March 12-14, 2001 The Future of High-Performance Networking (The 5?, 10?, 15? Year Outlook) Wu-chun Feng feng@lanl.gov
Transmission Control Protocol. ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications
 Transmission Control Protocol ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Contents Overview of TCP (Review) TCP and Congestion Control The Causes of Congestion Approaches to Congestion Control TCP Congestion
Transmission Control Protocol ITS 413 Internet Technologies and Applications Contents Overview of TCP (Review) TCP and Congestion Control The Causes of Congestion Approaches to Congestion Control TCP Congestion
UltraLight Network Phase I
 UltraLight Network Phase I Figure 1 UltraLight Network Phase 1 1 UltraLight Network Phase 2 Figure 2 UltraLight Network Phase 2 2 UltraLight Network Phase 3 Figure 3 UltraLight Network Phase 3 3 UltraLight
UltraLight Network Phase I Figure 1 UltraLight Network Phase 1 1 UltraLight Network Phase 2 Figure 2 UltraLight Network Phase 2 2 UltraLight Network Phase 3 Figure 3 UltraLight Network Phase 3 3 UltraLight
Evaluation of TCP Based Congestion Control Algorithms Over High-Speed Networks
 Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Master's Theses Graduate School 2006 Evaluation of TCP Based Congestion Control Algorithms Over High-Speed Networks Yaaser Ahmed Mohammed Louisiana State
Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Master's Theses Graduate School 2006 Evaluation of TCP Based Congestion Control Algorithms Over High-Speed Networks Yaaser Ahmed Mohammed Louisiana State
TCP on High-Speed Networks
 TCP on High-Speed Networks from New Internet and Networking Technologies for Grids and High-Performance Computing, tutorial given at HiPC 04, Bangalore, India December 22nd, 2004 C. Pham University Lyon,
TCP on High-Speed Networks from New Internet and Networking Technologies for Grids and High-Performance Computing, tutorial given at HiPC 04, Bangalore, India December 22nd, 2004 C. Pham University Lyon,
8. TCP Congestion Control
 8. TCP Congestion Control 1 TCP Congestion Control Slow-start increase Multiplicative decrease Congestion avoidance Measurement of variation Exponential timer backoff 2002 Yanghee Choi 2 Congestion Control
8. TCP Congestion Control 1 TCP Congestion Control Slow-start increase Multiplicative decrease Congestion avoidance Measurement of variation Exponential timer backoff 2002 Yanghee Choi 2 Congestion Control
Da t e: August 2 0 th a t 9: :00 SOLUTIONS
 Interne t working, Examina tion 2G1 3 0 5 Da t e: August 2 0 th 2 0 0 3 a t 9: 0 0 1 3:00 SOLUTIONS 1. General (5p) a) Place each of the following protocols in the correct TCP/IP layer (Application, Transport,
Interne t working, Examina tion 2G1 3 0 5 Da t e: August 2 0 th 2 0 0 3 a t 9: 0 0 1 3:00 SOLUTIONS 1. General (5p) a) Place each of the following protocols in the correct TCP/IP layer (Application, Transport,
BicTCP Implemenation in Linux Kernels
 BicTCP Implemenation in Linux Kernels Yee-Ting Li and Doug Leith Hamilton Institute, NUI Maynooth 15th February 2004 Abstract This document describes a bug in BicTCP, which has been implemented into the
BicTCP Implemenation in Linux Kernels Yee-Ting Li and Doug Leith Hamilton Institute, NUI Maynooth 15th February 2004 Abstract This document describes a bug in BicTCP, which has been implemented into the
Lecture 15: Transport Layer Congestion Control
 Lecture 15: Transport Layer Congestion Control COMP 332, Spring 2018 Victoria Manfredi Acknowledgements: materials adapted from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition: 1996-2016, J.F Kurose
Lecture 15: Transport Layer Congestion Control COMP 332, Spring 2018 Victoria Manfredi Acknowledgements: materials adapted from Computer Networking: A Top Down Approach 7 th edition: 1996-2016, J.F Kurose
CS519: Computer Networks. Lecture 5, Part 4: Mar 29, 2004 Transport: TCP congestion control
 : Computer Networks Lecture 5, Part 4: Mar 29, 2004 Transport: TCP congestion control TCP performance We ve seen how TCP the protocol works Sequencing, receive window, connection setup and teardown And
: Computer Networks Lecture 5, Part 4: Mar 29, 2004 Transport: TCP congestion control TCP performance We ve seen how TCP the protocol works Sequencing, receive window, connection setup and teardown And
What is the Future for High-Performance Networking?
 What is the Future for High-Performance Networking? Wu-chun (Wu) Feng feng@lanl.gov RADIANT: Research And Development in Advanced Network Technology http://www.lanl.gov/radiant Computer & Computational
What is the Future for High-Performance Networking? Wu-chun (Wu) Feng feng@lanl.gov RADIANT: Research And Development in Advanced Network Technology http://www.lanl.gov/radiant Computer & Computational
Optical Networking Activities in NetherLight
 Optical Networking Activities in NetherLight TERENA Networking Conference 2003 Zagreb, May 19-22, 2003 Erik Radius Manager Network Services, SURFnet Outline NetherLight What is it Why: the rationale From
Optical Networking Activities in NetherLight TERENA Networking Conference 2003 Zagreb, May 19-22, 2003 Erik Radius Manager Network Services, SURFnet Outline NetherLight What is it Why: the rationale From
Context-Aware Network Stack Optimization
 Context-Aware Network Stack Optimization Olivier Mehani 1,2 Roksana Boreli 2 Thierry Ernst 1 1 Institut National de Rercherche en Informatique et Automatique Équipe-projet Imara name.surname@inria.fr 2
Context-Aware Network Stack Optimization Olivier Mehani 1,2 Roksana Boreli 2 Thierry Ernst 1 1 Institut National de Rercherche en Informatique et Automatique Équipe-projet Imara name.surname@inria.fr 2
Measuring end-to-end bandwidth with Iperf using Web100
 Measuring end-to-end bandwidth with Iperf using Web Ajay Tirumala Les Cottrell Tom Dunigan CS Dept. SLAC CSMD University of Illinois Stanford University ORNL Urbana, IL 6181 Menlo Park, CA 9425 Oak Ridge,
Measuring end-to-end bandwidth with Iperf using Web Ajay Tirumala Les Cottrell Tom Dunigan CS Dept. SLAC CSMD University of Illinois Stanford University ORNL Urbana, IL 6181 Menlo Park, CA 9425 Oak Ridge,
FPGAs and Networking
 FPGAs and Networking Marc Kelly & Richard Hughes-Jones University of Manchester 12th July 27 1 Overview of Work Looking into the usage of FPGA's to directly connect to Ethernet for DAQ readout purposes.
FPGAs and Networking Marc Kelly & Richard Hughes-Jones University of Manchester 12th July 27 1 Overview of Work Looking into the usage of FPGA's to directly connect to Ethernet for DAQ readout purposes.
ICS 351: Networking Protocols
 ICS 351: Networking Protocols IP packet forwarding application layer: DNS, HTTP transport layer: TCP and UDP network layer: IP, ICMP, ARP data-link layer: Ethernet, WiFi 1 Networking concepts each protocol
ICS 351: Networking Protocols IP packet forwarding application layer: DNS, HTTP transport layer: TCP and UDP network layer: IP, ICMP, ARP data-link layer: Ethernet, WiFi 1 Networking concepts each protocol
ClearStream. Prototyping 40 Gbps Transparent End-to-End Connectivity. Cosmin Dumitru! Ralph Koning! Cees de Laat! and many others (see posters)!
 ClearStream Prototyping 40 Gbps Transparent End-to-End Connectivity Cosmin Dumitru! Ralph Koning! Cees de Laat! and many others (see posters)! University of Amsterdam! more data! Speed! Volume! Internet!
ClearStream Prototyping 40 Gbps Transparent End-to-End Connectivity Cosmin Dumitru! Ralph Koning! Cees de Laat! and many others (see posters)! University of Amsterdam! more data! Speed! Volume! Internet!
Title: Collaborative research: End-to-End Provisioned Optical Network Testbed for Large-Scale escience Applications
 Year 1 Activities report for the NSF project EIN-0335190 Title: Collaborative research: End-to-End Provisioned Optical Network Testbed for Large-Scale escience Applications Date: July 29, 2004 (this is
Year 1 Activities report for the NSF project EIN-0335190 Title: Collaborative research: End-to-End Provisioned Optical Network Testbed for Large-Scale escience Applications Date: July 29, 2004 (this is
Using QoS for High Throughput TCP Transport over Fat Long Pipes
 Using QoS for High Throughput TCP Transport over Fat Long Pipes Andrea Di Donato Network Research Engineer add@hep.ucl.ac.uk www.hep.ucl.ac.uk/~add Yee-Ting Li e-science PHD Student ytl@hep.ucl.ac.uk www.hep.ucl.ac.uk/~ytl
Using QoS for High Throughput TCP Transport over Fat Long Pipes Andrea Di Donato Network Research Engineer add@hep.ucl.ac.uk www.hep.ucl.ac.uk/~add Yee-Ting Li e-science PHD Student ytl@hep.ucl.ac.uk www.hep.ucl.ac.uk/~ytl
a. (4pts) What general information is contained in a LSR-PDU update that A might send?
 B1: Networks (25 points) Link State Routing (LSR). (Hint: flooding and Dijkstra s Algorithm). Assume Router A has physical links to Routers W, X, Y, Z. a. (4pts) What general information is contained in
B1: Networks (25 points) Link State Routing (LSR). (Hint: flooding and Dijkstra s Algorithm). Assume Router A has physical links to Routers W, X, Y, Z. a. (4pts) What general information is contained in
A Low Latency Solution Stack for High Frequency Trading. High-Frequency Trading. Solution. White Paper
 A Low Latency Solution Stack for High Frequency Trading White Paper High-Frequency Trading High-frequency trading has gained a strong foothold in financial markets, driven by several factors including
A Low Latency Solution Stack for High Frequency Trading White Paper High-Frequency Trading High-frequency trading has gained a strong foothold in financial markets, driven by several factors including
SharkFest 17 Europe. My TCP ain t your TCP. Simon Lindermann. Stack behavior back then and today. Miele & Cie KG.
 SharkFest 17 Europe My TCP ain t your TCP Stack behavior back then and today 9th November 2017 Simon Lindermann Miele & Cie KG #sf17eu Estoril, Portugal#sf17eu My TCP Estoril, ain tportugal your TCP 7-10
SharkFest 17 Europe My TCP ain t your TCP Stack behavior back then and today 9th November 2017 Simon Lindermann Miele & Cie KG #sf17eu Estoril, Portugal#sf17eu My TCP Estoril, ain tportugal your TCP 7-10
Your Name: Your student ID number:
 CSC 573 / ECE 573 Internet Protocols October 11, 2005 MID-TERM EXAM Your Name: Your student ID number: Instructions Allowed o A single 8 ½ x11 (front and back) study sheet, containing any info you wish
CSC 573 / ECE 573 Internet Protocols October 11, 2005 MID-TERM EXAM Your Name: Your student ID number: Instructions Allowed o A single 8 ½ x11 (front and back) study sheet, containing any info you wish
Cisco Exam Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Version: 12.0 [ Total Questions: 202 ]
![Cisco Exam Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Version: 12.0 [ Total Questions: 202 ] Cisco Exam Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Version: 12.0 [ Total Questions: 202 ]](/thumbs/81/84168691.jpg) s@lm@n Cisco Exam 100-101 Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Version: 12.0 [ Total Questions: 202 ] Topic 7, Troubleshooting Cisco 100-101 : Practice Test Question No : 1 - (Topic
s@lm@n Cisco Exam 100-101 Cisco Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Version: 12.0 [ Total Questions: 202 ] Topic 7, Troubleshooting Cisco 100-101 : Practice Test Question No : 1 - (Topic
Network Management & Monitoring
 Network Management & Monitoring Network Delay These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) End-to-end
Network Management & Monitoring Network Delay These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 Unported license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) End-to-end
End-user systems: NICs, MotherBoards, Disks, TCP Stacks & Applications
 2th-21st June 25 NeSC Edinburgh http://gridmon.dl.ac.uk/nfnn/ End-user systems: NICs, MotherBoards, Disks, TCP Stacks & Applications Richard Hughes-Jones Work reported is from many Networking Collaborations
2th-21st June 25 NeSC Edinburgh http://gridmon.dl.ac.uk/nfnn/ End-user systems: NICs, MotherBoards, Disks, TCP Stacks & Applications Richard Hughes-Jones Work reported is from many Networking Collaborations
Bandwidth Allocation & TCP
 Bandwidth Allocation & TCP The Transport Layer Focus Application Presentation How do we share bandwidth? Session Topics Transport Network Congestion control & fairness Data Link TCP Additive Increase/Multiplicative
Bandwidth Allocation & TCP The Transport Layer Focus Application Presentation How do we share bandwidth? Session Topics Transport Network Congestion control & fairness Data Link TCP Additive Increase/Multiplicative
Multiple unconnected networks
 TCP/IP Life in the Early 1970s Multiple unconnected networks ARPAnet Data-over-cable Packet satellite (Aloha) Packet radio ARPAnet satellite net Differences Across Packet-Switched Networks Addressing Maximum
TCP/IP Life in the Early 1970s Multiple unconnected networks ARPAnet Data-over-cable Packet satellite (Aloha) Packet radio ARPAnet satellite net Differences Across Packet-Switched Networks Addressing Maximum
ETSF10 Internet Protocols Transport Layer Protocols
 ETSF10 Internet Protocols Transport Layer Protocols 2012, Part 2, Lecture 2.1 Kaan Bür, Jens Andersson Transport Layer Protocols Process-to-process delivery [ed.4 ch.23.1] [ed.5 ch.24.1] Transmission Control
ETSF10 Internet Protocols Transport Layer Protocols 2012, Part 2, Lecture 2.1 Kaan Bür, Jens Andersson Transport Layer Protocols Process-to-process delivery [ed.4 ch.23.1] [ed.5 ch.24.1] Transmission Control
Intel SR2612UR storage system
 storage system 1 Table of contents Test description and environment 3 Test topology 3 Test execution 5 Functionality test results 5 Performance test results 6 Stability test results 9 2 Test description
storage system 1 Table of contents Test description and environment 3 Test topology 3 Test execution 5 Functionality test results 5 Performance test results 6 Stability test results 9 2 Test description
Evaluation of the LDC Computing Platform for Point 2
 Evaluation of the LDC Computing Platform for Point 2 SuperMicro X6DHE-XB, X7DB8+ Andrey Shevel CERN PH-AID ALICE DAQ CERN 10 October 2006 Purpose Background: Test the machine (X6DHE-XB) as LDC with 6 D-RORCs
Evaluation of the LDC Computing Platform for Point 2 SuperMicro X6DHE-XB, X7DB8+ Andrey Shevel CERN PH-AID ALICE DAQ CERN 10 October 2006 Purpose Background: Test the machine (X6DHE-XB) as LDC with 6 D-RORCs
Multi-class Applications for Parallel Usage of a Guaranteed Rate and a Scavenger Service
 Department of Computer Science 1/18 Multi-class Applications for Parallel Usage of a Guaranteed Rate and a Scavenger Service Markus Fidler fidler@informatik.rwth-aachen.de Volker Sander sander@fz.juelich.de
Department of Computer Science 1/18 Multi-class Applications for Parallel Usage of a Guaranteed Rate and a Scavenger Service Markus Fidler fidler@informatik.rwth-aachen.de Volker Sander sander@fz.juelich.de
TCP. CSU CS557, Spring 2018 Instructor: Lorenzo De Carli (Slides by Christos Papadopoulos, remixed by Lorenzo De Carli)
 TCP CSU CS557, Spring 2018 Instructor: Lorenzo De Carli (Slides by Christos Papadopoulos, remixed by Lorenzo De Carli) 1 Sources Fall and Stevens, TCP/IP Illustrated Vol. 1, 2nd edition Congestion Avoidance
TCP CSU CS557, Spring 2018 Instructor: Lorenzo De Carli (Slides by Christos Papadopoulos, remixed by Lorenzo De Carli) 1 Sources Fall and Stevens, TCP/IP Illustrated Vol. 1, 2nd edition Congestion Avoidance
Fast Retransmit. Problem: coarsegrain. timeouts lead to idle periods Fast retransmit: use duplicate ACKs to trigger retransmission
 Fast Retransmit Problem: coarsegrain TCP timeouts lead to idle periods Fast retransmit: use duplicate ACKs to trigger retransmission Packet 1 Packet 2 Packet 3 Packet 4 Packet 5 Packet 6 Sender Receiver
Fast Retransmit Problem: coarsegrain TCP timeouts lead to idle periods Fast retransmit: use duplicate ACKs to trigger retransmission Packet 1 Packet 2 Packet 3 Packet 4 Packet 5 Packet 6 Sender Receiver
Q500-P20 performance report
 Q500-P20 performance report Version 0.1 Nov 2013 Table of Contents Revision History... 2 Table of Contents... 3 1. Test bed... 4 1.1 Hardware... 4 1.2 Software... 4 1.3 Storage target settings... 5 2.
Q500-P20 performance report Version 0.1 Nov 2013 Table of Contents Revision History... 2 Table of Contents... 3 1. Test bed... 4 1.1 Hardware... 4 1.2 Software... 4 1.3 Storage target settings... 5 2.
Routers: Forwarding EECS 122: Lecture 13
 Input Port Functions Routers: Forwarding EECS 22: Lecture 3 epartment of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley Physical layer: bit-level reception ata link layer:
Input Port Functions Routers: Forwarding EECS 22: Lecture 3 epartment of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California Berkeley Physical layer: bit-level reception ata link layer:
Toward a Reliable Data Transport Architecture for Optical Burst-Switched Networks
 Toward a Reliable Data Transport Architecture for Optical Burst-Switched Networks Dr. Vinod Vokkarane Assistant Professor, Computer and Information Science Co-Director, Advanced Computer Networks Lab University
Toward a Reliable Data Transport Architecture for Optical Burst-Switched Networks Dr. Vinod Vokkarane Assistant Professor, Computer and Information Science Co-Director, Advanced Computer Networks Lab University
CS268: Beyond TCP Congestion Control
 TCP Problems CS68: Beyond TCP Congestion Control Ion Stoica February 9, 004 When TCP congestion control was originally designed in 1988: - Key applications: FTP, E-mail - Maximum link bandwidth: 10Mb/s
TCP Problems CS68: Beyond TCP Congestion Control Ion Stoica February 9, 004 When TCP congestion control was originally designed in 1988: - Key applications: FTP, E-mail - Maximum link bandwidth: 10Mb/s
Congestion control in TCP
 Congestion control in TCP If the transport entities on many machines send too many packets into the network too quickly, the network will become congested, with performance degraded as packets are delayed
Congestion control in TCP If the transport entities on many machines send too many packets into the network too quickly, the network will become congested, with performance degraded as packets are delayed
The European DataGRID Production Testbed
 The European DataGRID Production Testbed Franck Bonnassieux CNRS/UREC ENS-Lyon France DataGrid Network Work Package Manager Franck.Bonnassieux@ens-lyon.fr Presentation outline General DataGrid project
The European DataGRID Production Testbed Franck Bonnassieux CNRS/UREC ENS-Lyon France DataGrid Network Work Package Manager Franck.Bonnassieux@ens-lyon.fr Presentation outline General DataGrid project
Design a Remote-Office or Branch-Office Data Center with Cisco UCS Mini
 White Paper Design a Remote-Office or Branch-Office Data Center with Cisco UCS Mini February 2015 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Contents
White Paper Design a Remote-Office or Branch-Office Data Center with Cisco UCS Mini February 2015 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Contents
Recap. TCP connection setup/teardown Sliding window, flow control Retransmission timeouts Fairness, max-min fairness AIMD achieves max-min fairness
 Recap TCP connection setup/teardown Sliding window, flow control Retransmission timeouts Fairness, max-min fairness AIMD achieves max-min fairness 81 Feedback Signals Several possible signals, with different
Recap TCP connection setup/teardown Sliding window, flow control Retransmission timeouts Fairness, max-min fairness AIMD achieves max-min fairness 81 Feedback Signals Several possible signals, with different
Investigating the Use of Synchronized Clocks in TCP Congestion Control
 Investigating the Use of Synchronized Clocks in TCP Congestion Control Michele Weigle (UNC-CH) November 16-17, 2001 Univ. of Maryland Symposium The Problem TCP Reno congestion control reacts only to packet
Investigating the Use of Synchronized Clocks in TCP Congestion Control Michele Weigle (UNC-CH) November 16-17, 2001 Univ. of Maryland Symposium The Problem TCP Reno congestion control reacts only to packet
Characterizing Slow Start in High Speed Networks
 Characterizing Slow Start in High Speed Networks Kazumi Kumazoe (HMC), Masato Tsuru, Yuji Oie Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan Mario Gerla University of California, Los Angeles, USA November 17 th,
Characterizing Slow Start in High Speed Networks Kazumi Kumazoe (HMC), Masato Tsuru, Yuji Oie Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan Mario Gerla University of California, Los Angeles, USA November 17 th,
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS
 CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 24: Congestion Control Prof. Alan Mislove (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica,
CS3600 SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Lecture 24: Congestion Control Prof. Alan Mislove (amislove@ccs.neu.edu) Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica,
GÉANT IP Service Description. High Performance IP Services to Support Advanced Research
 GÉANT IP Service Description High Performance IP Services to Support Advanced Research Issue Date: 1 November 2017 GÉANT IP Overview The GÉANT IP service provides high-bandwidth, international Internet
GÉANT IP Service Description High Performance IP Services to Support Advanced Research Issue Date: 1 November 2017 GÉANT IP Overview The GÉANT IP service provides high-bandwidth, international Internet
FAST Kernel: Background Theory and Experimental Results. (Extended Abstract)
 FAST Kernel: Background Theory and Experimental Results (Extended Abstract) C. Jin, D. Wei, S. H. Low G. Buhrmaster, J. Bunn, D. H. Choe, R. L. A. Cottrell J. C. Doyle, H. Newman, F. Paganini, S. Ravot,
FAST Kernel: Background Theory and Experimental Results (Extended Abstract) C. Jin, D. Wei, S. H. Low G. Buhrmaster, J. Bunn, D. H. Choe, R. L. A. Cottrell J. C. Doyle, H. Newman, F. Paganini, S. Ravot,
LANCOM Techpaper IEEE n Indoor Performance
 Introduction The standard IEEE 802.11n features a number of new mechanisms which significantly increase available bandwidths. The former wireless LAN standards based on 802.11a/g enable physical gross
Introduction The standard IEEE 802.11n features a number of new mechanisms which significantly increase available bandwidths. The former wireless LAN standards based on 802.11a/g enable physical gross
PLEASE READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU START
 MIDTERM EXAMINATION #2 NETWORKING CONCEPTS 03-60-367-01 U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R - S c h o o l o f C o m p u t e r S c i e n c e Fall 2011 Question Paper NOTE: Students may take this question
MIDTERM EXAMINATION #2 NETWORKING CONCEPTS 03-60-367-01 U N I V E R S I T Y O F W I N D S O R - S c h o o l o f C o m p u t e r S c i e n c e Fall 2011 Question Paper NOTE: Students may take this question
Improving Packet Processing Performance of a Memory- Bounded Application
 Improving Packet Processing Performance of a Memory- Bounded Application Jörn Schumacher CERN / University of Paderborn, Germany jorn.schumacher@cern.ch On behalf of the ATLAS FELIX Developer Team LHCb
Improving Packet Processing Performance of a Memory- Bounded Application Jörn Schumacher CERN / University of Paderborn, Germany jorn.schumacher@cern.ch On behalf of the ATLAS FELIX Developer Team LHCb
ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKS
 ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKS Congestion Control and Avoidance 1 Lecture-6 Instructor : Mazhar Hussain CONGESTION CONTROL When one part of the subnet (e.g. one or more routers in an area) becomes overloaded,
ADVANCED COMPUTER NETWORKS Congestion Control and Avoidance 1 Lecture-6 Instructor : Mazhar Hussain CONGESTION CONTROL When one part of the subnet (e.g. one or more routers in an area) becomes overloaded,
BlueGene/L. Computer Science, University of Warwick. Source: IBM
 BlueGene/L Source: IBM 1 BlueGene/L networking BlueGene system employs various network types. Central is the torus interconnection network: 3D torus with wrap-around. Each node connects to six neighbours
BlueGene/L Source: IBM 1 BlueGene/L networking BlueGene system employs various network types. Central is the torus interconnection network: 3D torus with wrap-around. Each node connects to six neighbours
Hyper-converged infrastructure with Proxmox VE virtualization platform and integrated Ceph Storage.
 Hyper-converged infrastructure with Proxmox VE virtualization platform and integrated Ceph Storage. To optimize performance in hyper-converged deployments with Proxmox VE and Ceph storage the appropriate
Hyper-converged infrastructure with Proxmox VE virtualization platform and integrated Ceph Storage. To optimize performance in hyper-converged deployments with Proxmox VE and Ceph storage the appropriate
CS4700/CS5700 Fundamentals of Computer Networks
 CS4700/CS5700 Fundamentals of Computer Networks Lecture 15: Congestion Control Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang Alan Mislove amislove at ccs.neu.edu
CS4700/CS5700 Fundamentals of Computer Networks Lecture 15: Congestion Control Slides used with permissions from Edward W. Knightly, T. S. Eugene Ng, Ion Stoica, Hui Zhang Alan Mislove amislove at ccs.neu.edu
Transport layer. UDP: User Datagram Protocol [RFC 768] Review principles: Instantiation in the Internet UDP TCP
![Transport layer. UDP: User Datagram Protocol [RFC 768] Review principles: Instantiation in the Internet UDP TCP Transport layer. UDP: User Datagram Protocol [RFC 768] Review principles: Instantiation in the Internet UDP TCP](/thumbs/88/115916296.jpg) Transport layer Review principles: Reliable data transfer Flow control Congestion control Instantiation in the Internet UDP TCP 1 UDP: User Datagram Protocol [RFC 768] No frills, bare bones Internet transport
Transport layer Review principles: Reliable data transfer Flow control Congestion control Instantiation in the Internet UDP TCP 1 UDP: User Datagram Protocol [RFC 768] No frills, bare bones Internet transport
The 6net project An IPv6 testbed for the European Community Gunter Van de Velde, Cisco Systems
 The 6net project An IPv6 testbed for the European Community Gunter Van de Velde, gvandeve@cisco.com Infrastructure of the 6NET-Project What is the initial goal? To keep initial setup simple Create awareness
The 6net project An IPv6 testbed for the European Community Gunter Van de Velde, gvandeve@cisco.com Infrastructure of the 6NET-Project What is the initial goal? To keep initial setup simple Create awareness
CS 356: Computer Network Architectures Lecture 19: Congestion Avoidance Chap. 6.4 and related papers. Xiaowei Yang
 CS 356: Computer Network Architectures Lecture 19: Congestion Avoidance Chap. 6.4 and related papers Xiaowei Yang xwy@cs.duke.edu Overview More on TCP congestion control Theory Macroscopic behavior TCP
CS 356: Computer Network Architectures Lecture 19: Congestion Avoidance Chap. 6.4 and related papers Xiaowei Yang xwy@cs.duke.edu Overview More on TCP congestion control Theory Macroscopic behavior TCP
EXAM TCP/IP NETWORKING Duration: 3 hours With Solutions
 SCIPER: First name: Family name: EXAM TCP/IP NETWORKING Duration: 3 hours With Solutions Jean-Yves Le Boudec January 2016 INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your solution into this document and return it to us (you
SCIPER: First name: Family name: EXAM TCP/IP NETWORKING Duration: 3 hours With Solutions Jean-Yves Le Boudec January 2016 INSTRUCTIONS 1. Write your solution into this document and return it to us (you
Transport layer. Review principles: Instantiation in the Internet UDP TCP. Reliable data transfer Flow control Congestion control
 Transport layer Review principles: Reliable data transfer Flow control Congestion control Instantiation in the Internet UDP TCP 1 UDP: User Datagram Protocol [RFC 768] No frills, bare bones Internet transport
Transport layer Review principles: Reliable data transfer Flow control Congestion control Instantiation in the Internet UDP TCP 1 UDP: User Datagram Protocol [RFC 768] No frills, bare bones Internet transport
6.1 Internet Transport Layer Architecture 6.2 UDP (User Datagram Protocol) 6.3 TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) 6. Transport Layer 6-1
 6. Transport Layer 6.1 Internet Transport Layer Architecture 6.2 UDP (User Datagram Protocol) 6.3 TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) 6. Transport Layer 6-1 6.1 Internet Transport Layer Architecture The
6. Transport Layer 6.1 Internet Transport Layer Architecture 6.2 UDP (User Datagram Protocol) 6.3 TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) 6. Transport Layer 6-1 6.1 Internet Transport Layer Architecture The
Achieve Optimal Network Throughput on the Cisco UCS S3260 Storage Server
 White Paper Achieve Optimal Network Throughput on the Cisco UCS S3260 Storage Server Executive Summary This document describes the network I/O performance characteristics of the Cisco UCS S3260 Storage
White Paper Achieve Optimal Network Throughput on the Cisco UCS S3260 Storage Server Executive Summary This document describes the network I/O performance characteristics of the Cisco UCS S3260 Storage
Vorlesung Kommunikationsnetze
 Picture 15 13 Vorlesung Kommunikationsnetze Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit B. Wiegel sowie A. Schmeiser und M. Rabel Sommersemester 2009 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen
Picture 15 13 Vorlesung Kommunikationsnetze Prof. Dr. H. P. Großmann mit B. Wiegel sowie A. Schmeiser und M. Rabel Sommersemester 2009 Institut für Organisation und Management von Informationssystemen
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 10
 ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 10 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 28 September 2017 Announcements HW#4 was due HW#5 will be posted. midterm/fall break You
ECE 435 Network Engineering Lecture 10 Vince Weaver http://web.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 28 September 2017 Announcements HW#4 was due HW#5 will be posted. midterm/fall break You
Virtualization Practices:
 Virtualization Practices: Providing a Complete Virtual Solution in a Box Jyh-shing Chen, NetApp Author: Jyh-shing Chen, NetApp SNIA Legal Notice The material contained in this tutorial is copyrighted by
Virtualization Practices: Providing a Complete Virtual Solution in a Box Jyh-shing Chen, NetApp Author: Jyh-shing Chen, NetApp SNIA Legal Notice The material contained in this tutorial is copyrighted by
ECE4110, Internetwork Programming, QUIZ 2 - PRACTICE Spring 2006
 Email Address ECE4110, Internetwork Programming, QUIZ 2 - PRACTICE Spring 2006 Name (Print) Prof. John A. Copeland Practice for April 11, 2006 Tel.: 404-894-5177 E-Mail: copeland@ece.gatech.edu RULES.
Email Address ECE4110, Internetwork Programming, QUIZ 2 - PRACTICE Spring 2006 Name (Print) Prof. John A. Copeland Practice for April 11, 2006 Tel.: 404-894-5177 E-Mail: copeland@ece.gatech.edu RULES.
Report on Transport Protocols over Mismatched-rate Layer-1 Circuits with 802.3x Flow Control
 Report on Transport Protocols over Mismatched-rate Layer-1 Circuits with 82.3x Flow Control Helali Bhuiyan, Mark McGinley, Tao Li, Malathi Veeraraghavan University of Virginia Email: {helali, mem5qf, taoli,
Report on Transport Protocols over Mismatched-rate Layer-1 Circuits with 82.3x Flow Control Helali Bhuiyan, Mark McGinley, Tao Li, Malathi Veeraraghavan University of Virginia Email: {helali, mem5qf, taoli,
