Lab 5. Spanning Tree. Overview. JNCIS-ENT Bootcamp
|
|
|
- Shona Watkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab 5 Spanning Tree Overview This lab demonstrates basic configuration and monitoring tasks when implementing spanning tree and some related protection features on EX Series switches. In this lab, you use the command-line interface (CLI) to configure and monitor RSTP as well as bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) and loop protection. All devices are connected to a common management network which facilitates access to the CLI. These exercises assume you already have some basic understanding of the JUNOS CLI interfaces or you have read the JNCIA-JUNOS documentation or similar. Note that your lab login (password given to you separately) grants you all permissions needed to complete this lab; however, some restrictions have been made to prevent loss of connectivity to the devices. Please be careful, and have fun! By completing this lab, you will perform the following tasks: Update the existing configuration. Configure and monitor RSTP. Configure and monitor BPDU protection. Please refer to the next page lab diagram to perform this exercise: 1
2 Lab Diagram Lab 5: Implementing Spanning Tree Bridge Priority: 4K Bridge Priority: 8K / /24 srxx-1 ge-0/0/1 ge-0/0/2 srxx / /24 ge-0/0/8 ge-0/0/10 ge-0/0/10 ge-0/0/8 Bridge Priority: 32K (default) ge-0/0/9 exx-1 exx-2 Bridge Priority: 32K (default) ge-0/0/9 VLAN: v /24 vr11 ge-0/0/6 ge-0/0/7 VLAN: v /24 vr12 Virtual Routers VLAN: v /24 vr21 ge-0/0/6 ge-0/0/7 VLAN: v /24 vr22 2
3 Part 1: Logging In Using the CLI The goal of this lab part is to become familiar with the access details for your pod of routers & switches and to log in through the CLI. To perform this lab you will have to login in 2x EX switches and 2x SRX devices. 4 sessions in total! srxx-1, srxx-2, exx-1 & exx-2 (being X the initial of the POD being assigned to you) Note Please do NOT delete interface ge-0/0/0 or me0 as this is your management interface which provides access to your session!! Do NOT delete either the security section of your configurations. This allows your system to allow any traffic in/out. Note 2 It is recommended that you use the console connection to access your assigned station. Using the console connection ensures persistent connectivity even when the management network access is unavailable. If needed, review the instructions about how to connect to your system using the console port. Having said that, you can also use the management IP address to perform this lab. Chose the one you want Note 3 Remember that the exercise proposed in this documentation is generic and the examples given here apply only to one particular pod of devices. Please adapt the example to your assigned set of devices (srxa-1, srxa-2, exa-1 & exa-2 or srxb-1, srxb-2, exb-1 & exb-2 or srxc-1, srxc-2, exc-1 & exc-2 or srxd-1, srxd-2, exd-1 & exd2). Look at you lab diagram and mind the pod of systems that you have been assigned! Step 1.1 Log in to both EX systems with the username lab using the password given to you. Note that both the name and password are case-sensitive. You can connect to your SRX or EX Series devices either using the console connection through the terminal server or through a Telnet or SSH session using the SRX Series device s management IP address. Use the one access method that you prefer. Here is an example on how to login via console into your exx-1 switch. Please open a similar session to the pairing switch exx-2 [luis@js2 ~]$ telnet Trying Connected to ( ). Escape character is '^]'. 3
4 exa-1 (ttyu0) login: lab Password: Enter configuration mode and load the lab5-start configuration from the /var/home/lab/jncis/ directory. Commit your changes when complete. {master:0 configure Entering configuration mode {master:0[edit] load override jncis/lab5-start load complete {master:0[edit] commit configuration check succeeds commit complete {master:0[edit] Repeat the same for the other switch exx-2. Login in the system, load the lab5-start configuration file, etc. ~]$ telnet Step 1.2 Open a separate session to your two assigned SRX Series devices. Note you can connect to your SRX Series device using the console connection through the terminal server or through a Telnet or SSH session using the SRX Series device s management IP address. [luis@js2 ~]$ telnet Trying Connected to ( ). Escape character is '^]'. login: lab Password: --- JUNOS 12.1R1.9 built :12:49 UTC lab@srxa-1> 4
5 Enter configuration mode and load the lab5-start configuration from the /var/home/lab/jncis/ directory. Commit your changes when complete. configure Entering configuration mode [edit] load override jncis/lab5-start load complete [edit] commit commit complete Exiting configuration mode Note Not likely, but if you happen to get a message like this: lab@host1-a# commit warning: You have changed mpls flow mode. You have to reboot the system for your change to take effect. If you have deployed a cluster, be sure to reboot all nodes. commit complete As the message suggest, please reboot the machine by issuing a request system reboot and keep going. Ignore this note if you do not receive a warning of this kind Repeat the same for the other SRX srxx-2. Login in the system, load the lab5-start.config configuration file, etc. [luis@js2 ~]$ telnet Part 2: Modifying the existing configuration Step 2.1 In this lab part, you will modify the configuration to prepare for subsequent lab parts. Refer to network diagram for this lab for topological and configuration details. Return to your assigned EX switch. From your assigned ESX switch, navigate to the [edit vlans] hierarchy level and add the VLANs assigned to virtual routers attached to the remote team s switch. Once this step is done, you should see a total of four VLANs defined on your switch; v11, v12, v21, and v22. 5
6 {master:0[edit] edit vlans {master:0[edit vlans] show v11 { vlan-id 11; l3-interface vlan.11; v12 { vlan-id 12; l3-interface vlan.12; {master:0[edit vlans] lab@exa-1# set remote-network1-vlan-name vlan-id remote-network1-vlan-id {master:0[edit vlans] lab@exa-1# set remote-network2-vlan-name vlan-id remote-network2-vlan-id {master:0[edit vlans] lab@exa-1# show v11 { vlan-id 11; l3-interface vlan.11; v12 { vlan-id 12; l3-interface vlan.12; v21 { vlan-id 21; v22 { vlan-id 22; Step 2.2 Navigate to the [edit interfaces] hierarchy and associate ge-0/0/8.0 with all vlans. {master:0[edit vlans] lab@exa-1# top edit interfaces {master:0[edit interfaces] lab@exa-1# show ge-0/0/8 unit 0 { family ethernet-switching { port-mode trunk; vlan { members [ v11 v12 ]; 6
7 {master:0[edit interfaces] delete ge-0/0/8 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan {master:0[edit interfaces] lab@exa-1# set ge-0/0/8 unit 0 family ethernet-switching vlan members all {master:0[edit interfaces] lab@exa-1# show ge-0/0/8 unit 0 { family ethernet-switching { port-mode trunk; vlan { members all; Step 2.3 Use the copy command to replicate the configuration associated with ge-0/0/8 to the ge-0/0/10 interface. {master:0[edit interfaces] lab@exa-1# copy ge-0/0/8 to ge-0/0/10 {master:0[edit interfaces] lab@exa-1# show ge-0/0/10 unit 0 { family ethernet-switching { port-mode trunk; vlan { members all; Step 2.4 Activate the configuration changes using the commit command. Next, issue the run show ethernet-switching interfaces command. Note Do NOT forget to follow these steps again and configure the other switch exx-2!! {master:0[edit interfaces] lab@exa-1# commit configuration check succeeds commit complete 7
8 {master:0[edit interfaces] run show ethernet-switching interfaces Interface State VLAN members Tag Tagging Blocking ge-0/0/1.0 down default untagged unblocked ge-0/0/6.0 up v11 11 untagged unblocked ge-0/0/7.0 up v12 12 untagged unblocked ge-0/0/8.0 up v11 11 tagged unblocked v12 12 tagged unblocked v21 21 tagged unblocked v22 22 tagged unblocked ge-0/0/10.0 up v11 11 tagged unblocked v12 12 tagged unblocked v21 21 tagged unblocked v22 22 tagged unblocked Based on the resulting output, are any of the listed interfaces currently blocking traffic? As shown in the sample output, you should see all interfaces in the unblocked blocking state, which means all interfaces should be forwarding traffic rather than blocking traffic. Part 3: Configuring and Monitoring RSTP In this lab part, you will configure and monitor RSTP. First, you will perform some ping tests on your SRX Series device to identify the need for spanning tree within a Layer 2 network. Next, you will configure RSTP on your assigned devices. Finally, you will verify the effects of enabling RSTP in a Layer 2 network with redundant paths. You will need to refer to the network diagram for this lab for some of the configuration tasks performed in this lab part. Step 3.1 Note The next lab steps are performed on your assigned SRX Series devices. If needed, refer to the management network diagram for access details. Return to one of your assigned SRX Series device. From your assigned SRX Series device, attempt to ping the IP addresses assigned to the VLAN interfaces defined on your EX Series switch. That is the network1-address and network2-address or the addresses of the vr devices. Refer to the network diagram for this lab, if needed. 8
9 [edit] run ping PING ( ): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=9.501 ms 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=0 ttl=63 time= ms (DUP!) 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.937 ms 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.798 ms 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.769 ms ^C ping statistics packets transmitted, 4 packets received, +1 duplicates, 50% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.769/10.992/39.953/ ms [edit] lab@srxa-1# run ping count 5 PING ( ): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=2.765 ms 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=3.678 ms (DUP!) 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=2.201 ms 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=3.558 ms (DUP!) 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=7.214 ms 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=8.276 ms (DUP!) 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=4.154 ms 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=5.055 ms (DUP!) 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=2.223 ms ping statistics packets transmitted, 5 packets received, +4 duplicates, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 2.201/4.347/8.276/2.024 ms [edit] lab@srxa-1# run ping PING ( ): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=9.370 ms 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=0 ttl=63 time= ms (DUP!) 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.751 ms 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.797 ms 64 bytes from : icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.734 ms ^C ping statistics packets transmitted, 8 packets received, +1 duplicates, 30% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.734/6.872/40.006/ ms Do the ping tests succeed? What might these result indicate? 9
10 Your results may vary from those shown above. In the sample output, the ping tests are not clearly successful. In some situations you may not see any response while in other situations you may see some intermittent replies; including duplicate ICMP echo replies. These results are often indicative of a Layer 2 loop. Step 3.2 Activate the RSTP configuration on both SRX devices (the protocol is actually preconfigured in your device but not activated). Issue the commit and-quit command to activate the change and return to operational mode. [edit] lab@srxa-1# show protocols inactive: rstp { bridge-priority 4k; [edit] lab@srxa-1# activate protocols rstp [edit] lab@srxa-1# commit and-quit commit complete Exiting configuration mode lab@srxa-1> Note Do NOT forget to follow these steps again and configure the other srxx-2!! Step 3.3 Return to your assigned EX Series switches. On your assigned EX Series switches, enable the RSTP protocol. Next, activate the configuration changes and return to operational mode. {master:0[edit interfaces] lab@exa-1# top set protocols rstp {master:0[edit interfaces] lab@exa-1# commit and-quit configuration check succeeds commit complete Exiting configuration mode Based on the priority values listed on the network diagram for this lab, can you predict which device will be elected the root bridge? 10
11 Based on the assigned priority values, srxx-1, where X represents your assigned pod value, should be elected the root bridge. Step 3.4 Issue the show spanning-tree bridge command. {master:0 lab@exa-1> show spanning-tree bridge STP bridge parameters Context ID : 0 Enabled protocol : RSTP Root ID : :26:88:02:74:90 Root cost : Root port : ge-0/0/8.0 Hello time : 2 seconds Maximum age : 20 seconds Forward delay : 15 seconds Message age : 1 Number of topology changes : 2 Time since last topology change : 61 seconds Topology change initiator : ge-0/0/8.0 Topology change last recvd. from : 00:26:88:e9:d2:88 Local parameters Bridge ID : :23:9c:13:a8:41 Extended system ID : 0 Internal instance ID : 0 What is your switch s bridge ID? The answer will vary. In the sample output, the bridge ID is :23:9c:13:a8:41. Remember that the bridge ID is created by combining the bridge priority (32K by default) and the system MAC address. The system MAC address is typically the same as the public base address for the device. The public base address can be viewed on EX Series switches using the following command: {master:0 lab@exa-1> show chassis mac-addresses FPC 0 MAC address information: Public base address 00:23:9c:13:a8:40 Public count 64 11
12 Can you determine which device is elected as the root bridge? The srxx-1 device, where X represents your assigned pod value, should be elected as the root bridge based on the bridge priority value of Which interface on your switch has been selected as the root port? The answer depends on the device you check it. On switch exx-1, where X represents your assigned pod value, you should see ge-0/0/8.0 elected as the root port. On switch exx-2, where X represents your assigned pod value, you should see ge-0/0/10.0 elected as the root port. A sample capture taken from exx-2 follows: {master:0 lab@exa-2> show spanning-tree bridge STP bridge parameters Context ID : 0 Enabled protocol : RSTP Root ID : :26:88:02:74:90 Root cost : Root port : ge-0/0/10.0 Hello time : 2 seconds Maximum age : 20 seconds Forward delay : 15 seconds Message age : 1 Number of topology changes : 2 Time since last topology change : 340 seconds Topology change initiator : ge-0/0/10.0 Topology change last recvd. from : 00:26:88:e9:d2:8a Local parameters Bridge ID : :23:9c:13:91:81 Extended system ID : 0 Internal instance ID : 0 What is the cumulative cost to the root bridge from your designated switch? Regardless of your assigned switch, the cumulative cost to the root bridge should be based on the active topology. 12
13 Step 3.5 Issue the show spanning-tree interface command to determine the state and role of each switch port. {master:0 show spanning-tree interface Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0 Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role port ID bridge ID Cost ge-0/0/ : : c13a FWD DESG ge-0/0/ : : c13a FWD DESG ge-0/0/ : : FWD ROOT ge-0/0/ : : b BLK ALT Does your switch currently have any ports in the blocking (BLK) state? If so, which interface? Regardless of the switch you look at, you should have one switch port in the blocking (BLK) state. The actual interface in the blocking state will depend on your device. If you look at switch exx-1, where X represents your assigned pod value, you should see ge-0/0/10.0 in the blocking state. If you look at switch is exx-2, you should see ge- 0/0/8.0 in the blocking state. A sample capture taken from exx-2 follows: {master:0 lab@exa-2> show spanning-tree interface Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0 Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role port ID bridge ID Cost ge-0/0/ : : c FWD DESG ge-0/0/ : : c FWD DESG ge-0/0/ : : b BLK ALT ge-0/0/ : : FWD ROOT Why are all the port costs the same for all interfaces? They are all the same because they are using the default port cost for 1 Gbps Ethernet. If a port has been changed to influence root port election you might see something like 13
14 the following output where the influenced port and path have a lower value than the default for 1 Gbps Ethernet: {master:0 lab@exa-1> show spanning-tree interface Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0 Interface Port ID Designated Designated Port State Role port ID bridge ID Cost ge-0/0/ : : c13a FWD DESG ge-0/0/ : : c13a FWD DESG ge-0/0/ : : FWD ROOT ge-0/0/ : : b BLK ALT Step 3.6 Issue the show ethernet-switching interfaces command to view the effects of the spanning tree calculations on Ethernet switching interfaces. {master:0 lab@exa-1> show ethernet-switching interfaces Interface State VLAN members Tag Tagging Blocking ge-0/0/1.0 down default untagged blocked by STP ge-0/0/6.0 up v11 11 untagged unblocked ge-0/0/7.0 up v12 12 untagged unblocked ge-0/0/8.0 up v11 11 tagged unblocked v12 12 tagged unblocked v21 21 tagged unblocked v22 22 tagged unblocked ge-0/0/10.0 up v11 11 tagged blocked by STP v12 12 tagged blocked by STP v21 21 tagged blocked by STP v22 22 tagged blocked by STP Are any Ethernet switching interfaces now in the blocking state? If so, which interfaces and why? Regardless of the switch you look at, you should have two Ethernet switching ports in the blocking state. In all cases, ge-0/0/1.0 should be blocked by STP because it is not physically up. The second interface in the blocking state will depend on the device. If you look at exx-1, where X represents your assigned pod value, you should see ge- 0/0/10.0 in the blocking state. If you look at exx-2, where X represents your assigned pod value, you should see ge-0/0/8.0 in the blocking state. The second interface is also being blocked by STP due to the least cost path calculation to the root bridge. 14
15 Step 3.7 Issue the show spanning-tree interface ge-0/0/y detail command for the interface currently designated as the root port (where y is either ge-0/0/8 or ge-0/0/10 depending on the switch you are checking). {master:0 lab@exa-1> show spanning-tree interface ge-0/0/8 detail Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0 Interface name : ge-0/0/8.0 Port identifier : Designated port ID : Port cost : Port state : Forwarding Designated bridge ID : :26:88:02:74:90 Port role : Root Link type : Pt-Pt/NONEDGE Boundary port : NA Edge delay while expiry count : 1 Rcvd info while expiry count : 0 What is the Link type for this interface? The Link type for the root port should be Pt-Pt/NONEDGE. This is the default link type for an interface operating in full-duplex that receives BPDUs. Step 3.8 Issue the show spanning-tree interface ge-0/0/6 detail command. {master:0 lab@exa-1> show spanning-tree interface ge-0/0/6 detail Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0 Interface name : ge-0/0/6.0 Port identifier : Designated port ID : Port cost : Port state : Forwarding Designated bridge ID : :23:9c:13:a8:41 Port role : Designated Link type : Pt-Pt/EDGE Boundary port : NA Edge delay while expiry count : 1 Rcvd info while expiry count : 0 15
16 What is the Link type for this interface? Can you explain why it is different than the root port? The Link type for ge-0/0/6 should be Pt-Pt/EDGE. This is the expected link type for this interface because it is operating in full-duplex and is not receiving BPDUs from the connected virtual router. For an interface operating in half-duplex mode, you see a link type of shared rather than point-to-point. The following output confirms the current duplex setting for ge-0/0/6: {master:0 lab@exa-1> show interfaces ge-0/0/6 extensive match "Link mode" Link mode: Full-duplex, Flow control: None, Remote fault: OK, Step 3.9 Return to your assigned SRX Series devices. On one of your assigned SRX Series device, use the ping utility and attempt to ping the IP addresses assigned to the VLAN interfaces defined on your EX Series switch (the same ones as in step 3.1). Refer to the network diagram for this lab, if needed. lab@srxa-1> ping count 10 rapid PING ( ): 56 data bytes!!!!!!!!!! ping statistics packets transmitted, 10 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.560/1.825/2.337/0.293 ms lab@srxa-1> ping count 10 rapid PING ( ): 56 data bytes!!!!!!!!!! ping statistics packets transmitted, 10 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.234/1.343/1.551/0.098 ms lab@srxa-1> ping count 10 rapid PING ( ): 56 data bytes!!!!!!!!!! ping statistics packets transmitted, 10 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 1.633/2.045/2.742/0.343 ms 16
17 Do the ping tests succeed? Yes, at this time the ping tests should succeed Part 4: Configuring and Monitoring BPDU Protection Step 4.1 In this lab part, you will enable some protection features. First, you will enable the ge-0/0/9.0 interface for Layer 2 operations as an edge port. Next, you will configure BPDU protection and monitor the effects of this protection feature. Finally, you will administratively clear a BPDU error condition. This lab section could be performed on the srxx-1 and exx-1 pair of devices only. Return to your assigned EX Series switches. On your EX Series switches, enter configuration mode and navigate to the [edit interfaces] hierarchy level. {master:0 lab@exa-1> configure Entering configuration mode {master:0[edit] lab@exa-1# edit interfaces Enable ge-0/0/9 for Layer 2 operations as an access port for the default VLAN {master:0[edit interfaces] lab@exa-1# set ge-0/0/9 unit 0 family ethernet-switching Step 4.2 Navigate to the [edit protocols rstp] hierarchy. Define ge-0/0/9.0 as an edge port. Next, issue the commit command to activate the configuration changes. {master:0[edit interfaces] lab@exa-1# top edit protocols rstp {master:0[edit protocols rstp] lab@exa-1# set interface ge-0/0/9.0 edge {master:0[edit protocols rstp] lab@exa-1# commit configuration check succeeds commit complete 17
18 Step 4.3 Issue the run show spanning-tree interface ge-0/0/9.0 detail command. {master:0[edit protocols rstp] run show spanning-tree interface ge-0/0/9.0 detail Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0 Interface name : ge-0/0/9.0 Port identifier : Designated port ID : Port cost : Port state : Forwarding Designated bridge ID : :23:9c:13:a8:41 Port role : Designated Link type : Pt-Pt/EDGE Boundary port : NA Edge delay while expiry count : 1 Rcvd info while expiry count : 0 Is ge-0/0/9.0 designated as an edge port? Yes, ge-0/0/9.0 should now be designated as a point-to-point edge (Pt-PT/EDGE) interface as shown in the sample output. What is the state and role of ge-0/0/9.0? At this time the newly added interface should be present in the generated output and should assume the forwarding state and designated role. Step 4.4 Enable the BPDU protection feature under the [edit protocols rstp] hierarchy and activate the configuration change using the commit command. {master:0[edit protocols rstp] lab@exa-1# set bpdu-block-on-edge {master:0[edit protocols rstp] lab@exa-1# commit 18
19 configuration check succeeds commit complete Step 4.5 Issue the run show ethernet-switching interfaces command. {master:0[edit protocols rstp] run show ethernet-switching interfaces Interface State VLAN members Tag Tagging Blocking ge-0/0/1.0 down default untagged blocked by STP ge-0/0/6.0 up v11 11 untagged unblocked ge-0/0/7.0 up v12 12 untagged unblocked ge-0/0/8.0 up v11 11 tagged unblocked v12 12 tagged unblocked v21 21 tagged unblocked v22 22 tagged unblocked ge-0/0/9.0 up default untagged unblocked ge-0/0/10.0 up v11 11 tagged blocked by STP v12 12 tagged blocked by STP v21 21 tagged blocked by STP v22 22 tagged blocked by STP What are the interface and blocking states for ge-0/0/9.0? The interface and blocking states for interface ge-0/0/9.0 should be up and unblocked respectively. Step 4.6 Return to your assigned SRX Series device. On your SRX Series device, enter configuration mode and navigate to the [edit interfaces] hierarchy level. configure Entering configuration mode [edit] edit interfaces [edit interfaces] Activate the ge-0/0/9 interface. Next, issue the commit command to activate the configuration change. 19
20 [edit interfaces] show ge-0/0/9 ## ## inactive: interfaces ge-0/0/9 ## unit 0 { family ethernet-switching { port-mode trunk; vlan { members all; [edit interfaces] lab@srxa-1# activate ge-0/0/9 [edit interfaces] lab@srxa-1# commit commit complete Step 4.7 Return to your assigned EX Series switch. On your EX Series switch, issue the run show ethernet-switching interfaces command to determine the current state of the ge-0/0/9.0 interface. {master:0[edit protocols rstp] lab@exa-1# run show ethernet-switching interfaces Interface State VLAN members Tag Tagging Blocking ge-0/0/1.0 down default untagged blocked by STP ge-0/0/6.0 up v11 11 untagged unblocked ge-0/0/7.0 up v12 12 untagged unblocked ge-0/0/8.0 up v11 11 tagged unblocked v12 12 tagged unblocked v21 21 tagged unblocked v22 22 tagged unblocked ge-0/0/9.0 down default untagged Disabled by bpdu-control ge-0/0/10.0 up v11 11 tagged blocked by STP v12 12 tagged blocked by STP v21 21 tagged blocked by STP v22 22 tagged blocked by STP What are the interface and blocking states for ge-0/0/9.0? The interface and blocking states for interface ge-0/0/9.0 should be down and disabled by bpdu-control respectively. 20
21 Step 4.8 Issue the run show spanning-tree interface ge-0/0/9.0 detail command. {master:0[edit protocols rstp] run show spanning-tree interface ge-0/0/9.0 detail Spanning tree interface parameters for instance 0 Interface name : ge-0/0/9.0 Port identifier : Designated port ID : Port cost : Port state : Blocking Designated bridge ID : :23:9c:13:a8:41 Port role : Disabled (Bpdu-Inconsistent) Link type : Pt-Pt/EDGE Boundary port : NA Edge delay while expiry count : 2 Rcvd info while expiry count : 0 What is the state and role of ge-0/0/9.0? Currently, the ge-0/0/9.0 interface should show the Blocking state and Disabled (Bpdu-Inconsistent) port role. Step 4.9 Return to your assigned SRX Series device. On your SRX Series device, deactivate again the ge-0/0/9 interface. Next, issue the commit and-quit command to activate the configuration change and return to operational mode. [edit interfaces] lab@srxa-1# deactivate ge-0/0/9 [edit interfaces] lab@srxa-1# show ge-0/0/9 ## ## inactive: interfaces ge-0/0/9 ## unit 0 { family ethernet-switching { port-mode trunk; vlan { members all; 21
22 [edit interfaces] commit and-quit commit complete Exiting configuration mode Step 4.10 Return to your assigned EX Series switch. On your EX Series switch, clear the current BPDU error condition. Next, issue the run show ethernet-switching interfaces ge-0/0/9.0 command to verify the error condition has been cleared. {master:0[edit protocols rstp] run clear ethernet-switching bpdu-error {master:0[edit protocols rstp] run show ethernet-switching interfaces ge-0/0/9.0 Interface State VLAN members Tag Tagging Blocking ge-0/0/9.0 up default untagged unblocked Has the error condition been administratively removed? Step 4.11 Yes, as shown in the sample output, the error condition should now be gone thanks to the illustrated clear command. If the error condition persists, check the configurations on your assigned devices. Log out of all your assigned EX Series switches and SRX devices. {master:0[edit protocols rstp] top {master:0[edit] exit Exiting configuration mode {master:0 exit exa-1 (ttyu0) login: STOP You have completed Lab 5! 22
Lab 2. Spanning Tree Protocols. Overview. JNCIS-ENT++ Bootcamp
 Lab 2 Spanning Tree Protocols Overview This lab demonstrates basic configuration and monitoring tasks when implementing spanning tree and some related protection features on EX Series switches. In this
Lab 2 Spanning Tree Protocols Overview This lab demonstrates basic configuration and monitoring tasks when implementing spanning tree and some related protection features on EX Series switches. In this
Lab 4. Firewall Filters and Class of Service. Overview. Introduction to JUNOS Software & Routing Essentials
 Lab 4 Firewall Filters and Class of Service Overview This lab demonstrates configuration and monitoring of Firewall Filters and Class of Service on JUNOS devices. In this lab, you use the Command Line
Lab 4 Firewall Filters and Class of Service Overview This lab demonstrates configuration and monitoring of Firewall Filters and Class of Service on JUNOS devices. In this lab, you use the Command Line
Junos Enterprise Switching
 Junos Enterprise Switching Chapter 6: Device Security and Firewall Filters 2011 Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. www.juniper.net Worldwide Education Services Chapter Objectives After successfully
Junos Enterprise Switching Chapter 6: Device Security and Firewall Filters 2011 Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. www.juniper.net Worldwide Education Services Chapter Objectives After successfully
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING
 Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior
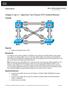 Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe the default behavior of STP. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Default Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe the default behavior of STP. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches
Chapter 4 Configuring Switching
 Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Using the Switching Tab The navigation tabs on the top of the home page include a Switching tab that lets you manage your GS108T Gigabit Smart Switch using features under
Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Using the Switching Tab The navigation tabs on the top of the home page include a Switching tab that lets you manage your GS108T Gigabit Smart Switch using features under
Configuring STP and RSTP
 7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
7 CHAPTER Configuring STP and RSTP This chapter describes the IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and the ML-Series implementation of the IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP). It also explains
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1
 CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
 13 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Contents Overview.................................................... 13-2 How Spanning Tree Operates.................................
13 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Contents Overview.................................................... 13-2 How Spanning Tree Operates.................................
Lab 1. JUNOS CLI & Initial Configuration. Overview. Introduction to JUNOS Software & Routing Essentials
 Lab 1 JUNOS CLI & Initial Configuration Overview This lab introduces you to the JUNOS software command-line interface (CLI). In this lab, you will familiarize yourself with various CLI operational-mode
Lab 1 JUNOS CLI & Initial Configuration Overview This lab introduces you to the JUNOS software command-line interface (CLI). In this lab, you will familiarize yourself with various CLI operational-mode
Lab 5.5.2: Challenge Spanning Tree Protocol
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Creating private Megaport connections using Juniper MX and EX series devices
 devices 1 Creating private Megaport connections using Juniper MX and EX series devices In this article, we will document, how to create a Point-to-Point connection between two end-points on Megaport Backbone.
devices 1 Creating private Megaport connections using Juniper MX and EX series devices In this article, we will document, how to create a Point-to-Point connection between two end-points on Megaport Backbone.
GuideTorrent. The best excellent exam certification guide torrent and dumps torrent provider
 GuideTorrent http://www.guidetorrent.com The best excellent exam certification guide torrent and dumps torrent provider Exam : JN0-343 Title : Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT)
GuideTorrent http://www.guidetorrent.com The best excellent exam certification guide torrent and dumps torrent provider Exam : JN0-343 Title : Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT)
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Configuring vpcs, page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 25 vpc Default
Configuring STP and Prestandard IEEE 802.1s MST
 20 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and prestandard IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol on Catalyst 6500 series switches. Note The IEEE 802.1s
20 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and prestandard IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol on Catalyst 6500 series switches. Note The IEEE 802.1s
Index. Numerics. Index p priority (QoS) definition Q VLAN standard w as a region 5-54
 Index Numerics 802.1p priority (QoS) 802.1Q VLAN standard 5-7 802.1w as a region 5-54 A active path 5-5 address IP 7-8 advertisement 3-3 applicable products 1-ii ARP age setting 7-10 cache 7-4 cache table
Index Numerics 802.1p priority (QoS) 802.1Q VLAN standard 5-7 802.1w as a region 5-54 A active path 5-5 address IP 7-8 advertisement 3-3 applicable products 1-ii ARP age setting 7-10 cache 7-4 cache table
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs vpc Overview Information About vpcs, on page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, on page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, on page
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs vpc Overview Information About vpcs, on page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, on page 11 Verifying the vpc Configuration, on page
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 Configuring Virtual Port Channels This chapter describes how to configure virtual port channels (vpcs) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page
Configuring Virtual Port Channels This chapter describes how to configure virtual port channels (vpcs) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example Configuring a Two-Tiered Virtualized Data Center for Large Enterprise Networks Release NCE 33 Modified: 2016-08-01 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California
Network Configuration Example Configuring a Two-Tiered Virtualized Data Center for Large Enterprise Networks Release NCE 33 Modified: 2016-08-01 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California
Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch
 Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch Requirements EX Series switches use bridging and virtual LANs (VLANs) to connect network devices in a LAN desktop computers, IP telephones,
Example: Setting Up Basic Bridging and a VLAN for an EX Series Switch Requirements EX Series switches use bridging and virtual LANs (VLANs) to connect network devices in a LAN desktop computers, IP telephones,
The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on the IEEE 802.1s standard.
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco implementation of the IEEE 802.1s Multiple STP (MSTP) on the IE 3010 switch. Note The multiple spanning-tree (MST) implementation is based on
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS
 Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
References: tates-roles.html
 Volume: 65 Questions Question No: 1 What are three RSTP port states? (Choose three.) A. learning B. forwarding C. listening D. blocking E. discarding Answer: A,B,E Explanation: Port States in STP and RSTP
Volume: 65 Questions Question No: 1 What are three RSTP port states? (Choose three.) A. learning B. forwarding C. listening D. blocking E. discarding Answer: A,B,E Explanation: Port States in STP and RSTP
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5
 Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
Implement Spanning Tree Protocols LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 5 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Explain the role of redundancy in a converged
SWP-0208G, 8+2SFP. 8-Port Gigabit Web Smart Switch. User s Manual
 SWP-0208G 1 SWP-0208G, 8+2SFP 8-Port Gigabit Web Smart Switch User s Manual Version: 3.4 April 1, 2008 2 TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 MAIN FEATURES...4 1.2 START TO MANAGE THIS SWITCH...6
SWP-0208G 1 SWP-0208G, 8+2SFP 8-Port Gigabit Web Smart Switch User s Manual Version: 3.4 April 1, 2008 2 TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 MAIN FEATURES...4 1.2 START TO MANAGE THIS SWITCH...6
Configuring Virtual Port Channels
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 11 vpc Default Settings, page 16 Configuring
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About vpcs, page 1 Guidelines and Limitations for vpcs, page 10 Verifying the vpc Configuration, page 11 vpc Default Settings, page 16 Configuring
PASS4TEST. IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! We offer free update service for one year
 PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 351-001 Title : CCIE Cisco Certified InterNetworking Expert Vendors : Cisco
PASS4TEST IT Certification Guaranteed, The Easy Way! \ http://www.pass4test.com We offer free update service for one year Exam : 351-001 Title : CCIE Cisco Certified InterNetworking Expert Vendors : Cisco
Configuring STP. Understanding Spanning-Tree Features CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on your switch. For information about the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Understanding and Configuring STP
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on a Catalyst 4500 series switch. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configuring EtherChannel. Topology. Objective. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv6 Switch. Configure EtherChannel.
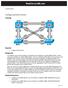 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
Spanning Tree Protocol
 For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
For conceptual information about, see the Using the with the EtherSwitch Network Module section of the EtherSwitch Network feature module. Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1
Management Software AT-S101. User s Guide. For use with the AT-GS950/8POE Gigabit Ethernet WebSmart Switch. Version Rev.
 Management Software AT-S101 User s Guide For use with the AT-GS950/8POE Gigabit Ethernet WebSmart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-000985 Rev. A Copyright 2008 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part
Management Software AT-S101 User s Guide For use with the AT-GS950/8POE Gigabit Ethernet WebSmart Switch Version 1.0.0 613-000985 Rev. A Copyright 2008 Allied Telesis, Inc. All rights reserved. No part
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices using Cisco Data Center Manager (DCNM) for LAN. For more information about the Cisco
BLADE 802.1s Spanning Tree and Interoperability with Cisco
 BLADE 802.1s Spanning Tree and Interoperability with Cisco Technical Brief Industry-standard 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol with Cisco interoperability for HP GbE2/GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switches
BLADE 802.1s Spanning Tree and Interoperability with Cisco Technical Brief Industry-standard 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol with Cisco interoperability for HP GbE2/GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switches
AT-S41 Version 1.1.7C Management Software for the AT-8326GB and AT-8350GB Series Fast Ethernet Switches. Software Release Notes
 AT-S41 Version 1.1.7C Management Software for the AT-8326GB and AT-8350GB Series Fast Ethernet Switches Software Release Notes Please read this document before you begin to use the AT-S41 management software.
AT-S41 Version 1.1.7C Management Software for the AT-8326GB and AT-8350GB Series Fast Ethernet Switches Software Release Notes Please read this document before you begin to use the AT-S41 management software.
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for STP, page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, page 2 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, page 14 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, page
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for STP, page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, page 2 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, page 14 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, page
Configuring Rapid PVST+
 This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
This chapter contains the following sections: Information About Rapid PVST+, page 1, page 16 Verifying the Rapid PVST+ Configuration, page 24 Information About Rapid PVST+ The Rapid PVST+ protocol is the
Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy
 Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1
Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1
Spanning-Tree Protocol
 Spanning-Tree Protocol Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Objectives Redundancy in a converged network Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) STP Operation
Spanning-Tree Protocol Malin Bornhager Halmstad University Session Number 2002, Svenska-CNAP Halmstad University 1 Objectives Redundancy in a converged network Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) STP Operation
Index. Numerics. Index 1
 Index Numerics 802.1p priority (QoS) definition 8-6 802.1q VLAN in mesh 7-23 802.1Q VLAN standard 6-6 802.1w as a region 6-54 802.1x, mesh, not supported 7-5 A ABC enabled on edge switch 7-26 in mesh domain
Index Numerics 802.1p priority (QoS) definition 8-6 802.1q VLAN in mesh 7-23 802.1Q VLAN standard 6-6 802.1w as a region 6-54 802.1x, mesh, not supported 7-5 A ABC enabled on edge switch 7-26 in mesh domain
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces (J-Web Procedure)
 Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces (J-Web Procedure) An Ethernet interface must be configured for optimal performance in a high-traffic network. To configure properties on a Gigabit Ethernet interface
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces (J-Web Procedure) An Ethernet interface must be configured for optimal performance in a high-traffic network. To configure properties on a Gigabit Ethernet interface
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Introduction to lab assignments with GNS3
 Politecnico di Torino TSR/CNTS, PRL, PAR Introduction to lab assignments with GNS3 User guide and helpful tips Roberto Bonafiglia, Fulvio Risso October 27, 2017 Contents 1 Requirements 4 2 Access to GNS3
Politecnico di Torino TSR/CNTS, PRL, PAR Introduction to lab assignments with GNS3 User guide and helpful tips Roberto Bonafiglia, Fulvio Risso October 27, 2017 Contents 1 Requirements 4 2 Access to GNS3
Configuring Port-Based and Client-Based Access Control (802.1X)
 9 Configuring Port-Based and Client-Based Access Control (802.1X) Contents Overview..................................................... 9-3 Why Use Port-Based or Client-Based Access Control?............
9 Configuring Port-Based and Client-Based Access Control (802.1X) Contents Overview..................................................... 9-3 Why Use Port-Based or Client-Based Access Control?............
Chapter 5: STP. * What is STP? How does STP work?
 Chapter 5: STP * What is STP? How does STP work? * What would be the worst case scenario that could happen to a redundant path switched network with the STP is disabled? When multiple paths exist between
Chapter 5: STP * What is STP? How does STP work? * What would be the worst case scenario that could happen to a redundant path switched network with the STP is disabled? When multiple paths exist between
Deployment Guide for SRX Series Services Gateways in Chassis Cluster Configuration
 Deployment Guide for SRX Series Services Gateways in Chassis Cluster Configuration Version 1.2 June 2013 Juniper Networks, 2013 Contents Introduction... 3 Chassis Cluster Concepts... 4 Scenarios for Chassis
Deployment Guide for SRX Series Services Gateways in Chassis Cluster Configuration Version 1.2 June 2013 Juniper Networks, 2013 Contents Introduction... 3 Chassis Cluster Concepts... 4 Scenarios for Chassis
Junos OS. 2nd edition FOR. Walter Goralski, Cathy Gadecki, and Michael Bushong. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. WILEY
 Junos OS FOR 2nd edition Walter Goralski, Cathy Gadecki, and Michael Bushong WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Table of Contents tllii(tii«es9«9i
Junos OS FOR 2nd edition Walter Goralski, Cathy Gadecki, and Michael Bushong WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Table of Contents tllii(tii«es9«9i
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
Peplink SD Switch User Manual. Published on October 25th, 2018
 Peplink SD Switch User Manual Published on October 25th, 2018 1 Table of Contents Switch Layout 4 Specifications 5 Hardware Overview 6 Quick Start Functions 7 Reset Switch 7 Connect Ethernet 7 Connect
Peplink SD Switch User Manual Published on October 25th, 2018 1 Table of Contents Switch Layout 4 Specifications 5 Hardware Overview 6 Quick Start Functions 7 Reset Switch 7 Connect Ethernet 7 Connect
Junos OS Release 12.1X47 Feature Guide
 Junos OS Release 12.1X47 Feature Guide Junos OS Release 12.1X47-D15 19 November 2014 Revision 1 This feature guide accompanies Junos OS Release 12.1X47-D15. This guide contains detailed information about
Junos OS Release 12.1X47 Feature Guide Junos OS Release 12.1X47-D15 19 November 2014 Revision 1 This feature guide accompanies Junos OS Release 12.1X47-D15. This guide contains detailed information about
Management Software AT-S79. User s Guide. For use with the AT-GS950/16 and AT-GS950/24 Smart Switches. Version Rev.
 Management Software AT-S79 User s Guide For use with the AT-GS950/16 and AT-GS950/24 Smart Switches Version 1.0.0 613-000207 Rev. A Copyright 2005 Allied Telesyn, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this
Management Software AT-S79 User s Guide For use with the AT-GS950/16 and AT-GS950/24 Smart Switches Version 1.0.0 613-000207 Rev. A Copyright 2005 Allied Telesyn, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this
ICND2. Rapid Spanning-Tree Protocol. These exercises utilize build on the previous ones used in the last class sessions.
 ICND2 Rapid Spanning-Tree Protocol TOPOLOGY 5x2950 (Layer 2 Switches) These exercises utilize build on the previous ones used in the last class sessions. Lab Exercise 1: Rapid Spanning-Tree Configuration
ICND2 Rapid Spanning-Tree Protocol TOPOLOGY 5x2950 (Layer 2 Switches) These exercises utilize build on the previous ones used in the last class sessions. Lab Exercise 1: Rapid Spanning-Tree Configuration
Lab Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype
 Lab 7.3.3 Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype Device Designation Device Name IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0.1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1 BR4 Fa0/0.10 10.10.10.254 255.255.255.0
Lab 7.3.3 Configuring and Testing the Rapid Spanning Tree Prototype Device Designation Device Name IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0.1 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1 BR4 Fa0/0.10 10.10.10.254 255.255.255.0
JN0-343 Q&As. Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Pass Juniper JN0-343 Exam with 100% Guarantee
 JN0-343 Q&As Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Pass Juniper JN0-343 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee
JN0-343 Q&As Juniper Networks Certified Internet Specialist (JNCIS-ENT) Pass Juniper JN0-343 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee
Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s)
 Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s) Document ID: 24248 Introduction Where to Use MST PVST+ Case Standard 802.1q Case MST Case MST Region MST Configuration and MST Region Region Boundary
Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s) Document ID: 24248 Introduction Where to Use MST PVST+ Case Standard 802.1q Case MST Case MST Region MST Configuration and MST Region Region Boundary
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 7 This chapter descibes how to configure Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on the Cisco wireless mobile interface card (WMIC). Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Configuring STP Extensions
 Configuring STP Extensions This chapter describes the configuration of extensions to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It includes the following sections: About STP
Configuring STP Extensions This chapter describes the configuration of extensions to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. It includes the following sections: About STP
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway. Ports Assignment Network
 Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Felix Rohrer Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Cisco Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1
 Cisco Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1 Table of Contents Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s)...1 Introduction...1 Where to use MST...2 PVST+ Case...2 Standard 802.1q
Cisco Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1 Table of Contents Understanding Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s)...1 Introduction...1 Where to use MST...2 PVST+ Case...2 Standard 802.1q
Example: Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling on EX Series Switches
 Example: Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling on EX Series Switches Requirements Layer 2 protocol tunneling (L2PT) allows you to send Layer 2 protocol data units (PDUs) across a service provider network
Example: Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling on EX Series Switches Requirements Layer 2 protocol tunneling (L2PT) allows you to send Layer 2 protocol data units (PDUs) across a service provider network
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
 Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
Restrictions for STP Restrictions for STP, on page 1 Information About Spanning Tree Protocol, on page 1 How to Configure Spanning-Tree Features, on page 13 Monitoring Spanning-Tree Status, on page 25
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
Index. Numerics. Index 1
 Index Numerics 3DES 7-3, 8-3 802.1x See port-based access control. A aaa authentication 5-8 aaa authenticaton web browser 6-11 aaa port-access See Web or MAC Authentication. access levels, authorized IP
Index Numerics 3DES 7-3, 8-3 802.1x See port-based access control. A aaa authentication 5-8 aaa authenticaton web browser 6-11 aaa port-access See Web or MAC Authentication. access levels, authorized IP
Lab Network Baseline Discovery
 Lab 1.2.6 Network Baseline Discovery Objective In this lab, the student will establish the baseline for the configuration and operation of the network. The student will complete the following tasks: Job
Lab 1.2.6 Network Baseline Discovery Objective In this lab, the student will establish the baseline for the configuration and operation of the network. The student will complete the following tasks: Job
LAB. Spanning Tree Protocol
 LAB Spanning Tree Protocol Scenario 1 Attention to the switch model 10.0.0.2/24 10.0.0.1/24 10.0.0.3/24 Scenario 1 Configuration 1. Define the scenario according to the figure. Be careful when selecting
LAB Spanning Tree Protocol Scenario 1 Attention to the switch model 10.0.0.2/24 10.0.0.1/24 10.0.0.3/24 Scenario 1 Configuration 1. Define the scenario according to the figure. Be careful when selecting
Example: Configuring DHCP Snooping, DAI, and MAC Limiting on an EX Series Switch with Access to a DHCP Server Through a Second Switch
 Example: Configuring DHCP Snooping, DAI, and MAC Limiting on an EX Series Switch with Access to a DHCP Server Through a Second Switch Requirements You can configure DHCP snooping, dynamic ARP inspection
Example: Configuring DHCP Snooping, DAI, and MAC Limiting on an EX Series Switch with Access to a DHCP Server Through a Second Switch Requirements You can configure DHCP snooping, dynamic ARP inspection
Peplink SD Switch User Manual
 Peplink SD Switch User Manual Peplink Products: Peplink SD Switch 8-ports/24-ports/48-ports Peplink SD Switch Firmware 1.2.0 Published on December 10, 2018 Copyright & Trademarks Copyright & trademark
Peplink SD Switch User Manual Peplink Products: Peplink SD Switch 8-ports/24-ports/48-ports Peplink SD Switch Firmware 1.2.0 Published on December 10, 2018 Copyright & Trademarks Copyright & trademark
BraindumpsIT. BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf!
 BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol
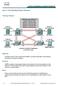 Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
Network Configuration Example
 Network Configuration Example Configuring RSVP-Signaled Point-to-Multipoint LSPs on Logical Systems Modified: 2017-01-18 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
Network Configuration Example Configuring RSVP-Signaled Point-to-Multipoint LSPs on Logical Systems Modified: 2017-01-18 Juniper Networks, Inc. 1133 Innovation Way Sunnyvale, California 94089 USA 408-745-2000
5. Write a capture filter for question 4.
 Pre-Lab 2: Single Segment IP Networks 1. Review Linux man pages for arp at www.linuxmanpages.com (in both Sections 7 and 8), the ARP RFC (RFC 826) at www.ietf.org, and Section 3.4 of the IBM Red Book.
Pre-Lab 2: Single Segment IP Networks 1. Review Linux man pages for arp at www.linuxmanpages.com (in both Sections 7 and 8), the ARP RFC (RFC 826) at www.ietf.org, and Section 3.4 of the IBM Red Book.
Abstract. GAK; Reviewed: WCH 8/14/2003. Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes 2003 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Rapid Reconfiguration Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1w Sample Configurations for Avaya P882/P580 Gigabit Ethernet Switches with Third Party Vendors including Cisco, HP and Foundry - Issue 1.0 Abstract
Rapid Reconfiguration Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) 802.1w Sample Configurations for Avaya P882/P580 Gigabit Ethernet Switches with Third Party Vendors including Cisco, HP and Foundry - Issue 1.0 Abstract
Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise?
 Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Volume: 283 Questions Question No: 1 What is the maximum number of switches that can be stacked using Cisco StackWise? A. 4 B. 5 C. 8 D. 9 E. 10 F. 13 Answer: D Question No: 2 A network engineer wants
Abstract. Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab
 Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for Configuring Avaya C363T RSTP to Interoperate with Extreme Networks MSTP to Support Avaya Communication Manager and Avaya G650 Media Gateway
Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes for Configuring Avaya C363T RSTP to Interoperate with Extreme Networks MSTP to Support Avaya Communication Manager and Avaya G650 Media Gateway
Sections Describing Standard Software Features
 30 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using automatic-qos (auto-qos) commands or by using standard QoS commands. With QoS, you can give preferential treatment to
30 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using automatic-qos (auto-qos) commands or by using standard QoS commands. With QoS, you can give preferential treatment to
Configuring MST Using Cisco NX-OS
 This chapter describes how to configure Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About MST, page
This chapter describes how to configure Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About MST, page
Configuring STP Extensions
 This chapter contains the following sections: Overview, page 1 Overview Cisco has added extensions to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) that make convergence more efficient. In some cases, even though similar
This chapter contains the following sections: Overview, page 1 Overview Cisco has added extensions to Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) that make convergence more efficient. In some cases, even though similar
CCNA Security 1.0 Student Packet Tracer Manual
 1.0 Student Packet Tracer Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
1.0 Student Packet Tracer Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
DEPLOYING A STACK OF DELL M-SERIES BLADE SWITCHES IN SIMPLE SWITCH MODE (SSM)
 Deploying DEPLOYING A STACK OF DELL M-SERIES BLADE SWITCHES IN SIMPLE SWITCH MODE (SSM) Victor Lama DELL Network Sales Engineer Banking and Securities v1.0 5 APR 2012 A detailed case study of a client
Deploying DEPLOYING A STACK OF DELL M-SERIES BLADE SWITCHES IN SIMPLE SWITCH MODE (SSM) Victor Lama DELL Network Sales Engineer Banking and Securities v1.0 5 APR 2012 A detailed case study of a client
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Managed Ethernet Switch User s Manual
 Managed Ethernet Switch User s Manual Information Coding: UM00D908 Version: V1.1 Product version: all Product Name: Managed Industrial Ethernet Switches on DIN Rail and Rack. Applicable to: Technical Support
Managed Ethernet Switch User s Manual Information Coding: UM00D908 Version: V1.1 Product version: all Product Name: Managed Industrial Ethernet Switches on DIN Rail and Rack. Applicable to: Technical Support
Spanning Tree Protocol(STP)
 Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create
Introduction Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on bridges and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE 802.1D. The main purpose of STP is to ensure that you do not create
Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series ISR
 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series First Published: 2015-04-06 Last Modified: 2017-12-21 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer
Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer 2 Gigabit EtherSwitch Network Interface Module Configuration Guide for Cisco 4000 Series First Published: 2015-04-06 Last Modified: 2017-12-21 Cisco 4-Port and 8-Port Layer
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial
 STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial Introduction: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on switches. It was first introduced as CST (Common Spanning
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) - Step by Step Configuration Tutorial Introduction: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 protocol that runs on switches. It was first introduced as CST (Common Spanning
VERTICAL HORIZON VH-2402S FAST ETHERNET SWITCH MANAGEMENT GUIDE
 VERTICAL HORIZON VH-2402S FAST ETHERNET SWITCH MANAGEMENT GUIDE 9033645-01 Notice Only qualified personnel should perform installation procedures. NOTICE Enterasys Networks reserves the right to make
VERTICAL HORIZON VH-2402S FAST ETHERNET SWITCH MANAGEMENT GUIDE 9033645-01 Notice Only qualified personnel should perform installation procedures. NOTICE Enterasys Networks reserves the right to make
Actual4Test. Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams
 Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : JN0-102 Title : Juniper Networks Certified Internet Associate, Junos (JNCIA-Junos) Vendor : Juniper
Actual4Test http://www.actual4test.com Actual4test - actual test exam dumps-pass for IT exams Exam : JN0-102 Title : Juniper Networks Certified Internet Associate, Junos (JNCIA-Junos) Vendor : Juniper
Managing Network Spanning Trees
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and how to use and configure Cisco s proprietary spanning-tree protocols, Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), Multiple Spanning
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes, the IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and how to use and configure Cisco s proprietary spanning-tree protocols, Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST), Multiple Spanning
CCNA Layer 2 switching. Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03
 CCNA 640-801 Layer 2 switching Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 What is Switching? It breaks the Collision Domain It takes the packet and forwards to destined port without any modification. Network still remains
CCNA 640-801 Layer 2 switching Revision no.: PPT/2K605/03 What is Switching? It breaks the Collision Domain It takes the packet and forwards to destined port without any modification. Network still remains
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Communication Redundancy User s Manual
 User s Manual Fifth Edition, June 2015 www.moxa.com/product 2015 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved. User s Manual The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used
User s Manual Fifth Edition, June 2015 www.moxa.com/product 2015 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved. User s Manual The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used
Chapter 32 VSRP Commands
 Chapter 32 VSRP Commands activate Activates a VSRP VRID. NOTE: This command is equivalent to the enable command. ProCurveRS(config)# vlan 200 ProCurveRS(config-vlan-200)# tag ethernet 1/1 to 1/8 ProCurveRS(config-vlan-200)#
Chapter 32 VSRP Commands activate Activates a VSRP VRID. NOTE: This command is equivalent to the enable command. ProCurveRS(config)# vlan 200 ProCurveRS(config-vlan-200)# tag ethernet 1/1 to 1/8 ProCurveRS(config-vlan-200)#
Figure 7-1 Unicast Static FDB window
 7. Layer 2 Features FDB VLAN Spanning Tree Loopback Detection Link Aggregation L2 Multicast Control LLDP FDB Static FDB Unicast Static FDB This window is used to view and configure the static unicast forwarding
7. Layer 2 Features FDB VLAN Spanning Tree Loopback Detection Link Aggregation L2 Multicast Control LLDP FDB Static FDB Unicast Static FDB This window is used to view and configure the static unicast forwarding
Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree
 Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Layer 2 Engineering Spanning Tree Campus Network Design & Operations Workshop These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Bridging Transmitting Non-IP Traffic or Merging Two Networks
 10 Bridging Transmitting Non-IP Traffic or Merging Two Networks Contents Overview..................................................... 10-3 Transmitting Non-IP Traffic..................................
10 Bridging Transmitting Non-IP Traffic or Merging Two Networks Contents Overview..................................................... 10-3 Transmitting Non-IP Traffic..................................
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Five Designing a Network Topology Original slides copyright by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Network Topology Design Issues Hierarchy Redundancy Modularity Well-defined
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Five Designing a Network Topology Original slides copyright by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Network Topology Design Issues Hierarchy Redundancy Modularity Well-defined
 switch# switch#configure terminal switch(config)#spanning-tree mode pvst switch(config)#spanning-tree extend system-id switch(config)#vtp mode transparent switch(config)#vlan 4093 Switch(config-vlan)#exit
switch# switch#configure terminal switch(config)#spanning-tree mode pvst switch(config)#spanning-tree extend system-id switch(config)#vtp mode transparent switch(config)#vlan 4093 Switch(config-vlan)#exit
