SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Watson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V points What are the common components between a router and other computers? CPU RAM ROM Operating System What does a router connect? Multiple networks What does a router do with It determines which interface to use and each packet it receives? What are the 2 types of connections to a router interface? What are the two primary functions of a router? What address does the router use to compare to the routing table? What two processes are used by a router to learn about remote networks and build their routing tables? What are the five components common to all routers? List the 5 different components stored in RAM. What happens to the information in RAM if the router looses power? What are the permanent storage areas in a router? What 3 things are stored in ROM? What is stored in flash? What happens to flash memory when the power is lost? What is stored in NVRAM? What must you do to save changes you have made to a router? What is the most common method used for configuring a router? What is the first thing that happens as the router boots up? forwards the packet on towards its destination LAN Local Area Network WAN Wide Area Network Best Path Determination Forwarding packets toward their destination Destination IP addresss Static Routes Dynamic Routing Protocols Flash, ROM, CPU, RAM, Power Operating System, Running Configuration File, IP Routing Table, ARP Cache, Packet Buffer All information is lost ROM, Flash, and NVRAM The bootstrap instructions Basic diagnostic software Scaled-down version of IOS. Cisco IOS Nothing Startup configuration file Copy the running-config to the startup-config Command Line interface CLI The startup config is copied into RAM
2 1.1.4 What are the 4 phases of the bootup process? What does POST test? What is the main function of the bootstrap program? What are the 2 main places to find the IOS? If a full IOS can not be loaded what does the bootstrap loader do? Where is the startup configuration found? What are the main items stored in the configuration file? Where is the second place that the router looks for the startup config if it is not located in NVRAM? If the router can not locate a startup-config, what mode does it enter? What key command do you press to exit setup mode if you accidentally entered it? What command can be used to help verify and troubleshoot some of the basic hardware and software components of the router? What is the last line displayed in the show version output? What is the default configuration register setting? What does that setting tell the router? What are the two management ports? What is an interface? What must be configured for each interface? What are the two major groups 1. Performing the POST 2. Loading the bootstrap program 3. Locating and loading the Cisco IOS software 4. Locating and loading the startup configuration file or entering setup mode The router hardware Find and load the IOS Flash and TFTP server Loads a scaled down version of the IOS from ROM to RAM NVRAM interface addresses routing information passwords any other configurations saved by the network administrator TFTP server Setup mode Ctrl-C Show version Configuration register 0x2102 attempt to load a Cisco IOS software image from flash memory and load the startup configuration file from NVRAM Console and auxiliary physical connector on the router whose main purpose is to receive and forward packets Each interface must be configured with an IP address and subnet mask of a different network LAN interfaces - such as Ethernet and
3 of router interfaces? What OSI layer does a router operate at? What is the router interface that connects to a LAN called? What is the process that each router uses to determine where to send the packet? What are the four essential information elements to include in the topology diagram? What are the basic tasks to perform when configuring a router? What is the prompt for the user mode? What is the command to enter the privileged EXEC mode? What is the prompt for privileged EXEC mode? What is the command to enter the global configuration mode? What is the command to enter the hostname of a router? What happens to the prompt after you press enter? What is the command used to enter the password to enter the privileged EXEC mode? List the commands to set the password for the console port? List the commands to set the password for the Telnet lines? List the commands to enter the Banner Message of the Day (motd). FastEthernet WAN interfaces - such as serial, ISDN, and Frame Relay Layer 3 Default Gateway decapsulation, searching the routing table, and then re-encapsulation Device names Interfaces used in the design IP addresses and subnet masks Default gateway addresses for end devices, such as PCs Naming the router Setting passwords Configuring interfaces Configuring a banner Saving changes on a router Verifying basic configuration and router operations Router> Enable Router# Router#config t Router(config)#hostname R1 The prompt changes to the hostname R1(config) enable secret class R1(config)#line console 0 R1(config-line)#password cisco R1(config-line)#login R1(config)#line vty 0 4 R1(config-line)#password cisco R1(config-line)#login R1(config)#banner motd # Enter TEXT message. End with the character '#'. ****************************************** WARNING!! Unauthorized Access Prohibited!! ****************************************** #
4 What should the banner show? Warning to unauthorized users What is the command to enter R1(config)#interface Serial0/0 the interface configuration mode? What is the command to set the IP address and subnet mask R1(config-if)#ip address for an interface? What is the command to enter a description for the interface? Router(config-if)#description Ciruit#VBN (help desk: ) What is the command to turn Router(config-if)#no shutdown on an interface? What is the command to view R1#show running-config the running-configuration file? What is the command to save R1#copy running-config startup-config the current config in NVRAM? What command will display the R1#show ip route routing table? What command displays all of R1#show interfaces the interface configuration parameters and statistics? What command displays R1#show ip interface brief abbreviated interface configuration information, including IP address and interface status? Where is the routing table RAM stored? What is a directly connected network? a network that is directly attached to one of the router interfaces What is a remote network? a network that is not directly connected to the What would a C in the first column of a routing table mean? What additional information is included when the destination is a remote network? What command reveals the configured or acquired default gateway, connected, loopback, multicast, and broadcast networks? How does a PC determine which network it belongs to? What command will activate a router interface? What routes does a router know before any static or dynamic routing is configured? router Directly connected the routing metric and the administrative distance Route print uses the subnet mask No shut Directly connected networks
5 1.3.3 What denotes a static route in the routing table? What are the three items that must be included in a static route? When should static routes be used? What are dynamic routing protocols used for? What are 2 of the activities that dynamic routing protocols perform? What is network discovery? What are some dynamic routing protocols? What are the three routing principles? What is asymmetric routing? What does a router compare to select the best path to place in the routing table? What is a metric? What is the best path? The number of routers that a packet must travel through before reaching its destination is called? The data capacity of a link, sometimes referred to as the speed of the link? S Network address and subnet mask of the remote network IP address of the next hop router or the exit interface Network consists of only a few routers A network is connected to the Internet through a single ISP A large network is configured in a hub-andspoke topology share information about the reachability and status of remote networks Network discovery Updating and maintaining routing tables the ability of a routing protocol to share information about the networks that it knows about with other routers that are also using the same routing protocol RIP (Routing Information Protocol) IGRP (Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) IS-IS (Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System) BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) 1. Every router makes its decision alone, based on the information it has in its own routing table. 2. The fact that one router has certain information in its routing table does not mean that other routers have the same information. 3. Routing information about a path from one network to another does not provide routing information about the reverse, or return, path. A packet can take different routes to and from Routing metric the quantitative value used to measure the distance to a given route The path with the lowest metric Hop count Bandwidth
6 1.4.3 What is it called when two paths to a destination have exactly the same metric? What is equal cost load balancing? What are the two functions of packet forwarding? What is the process used by a router to accept a packet on one interface and forward it out another interface called? What are the three major steps a router performs on a packet? What happens to the value of the TTL as a packet moves through a network? Which address does not change as the packet moves through the network? Which address changes as the packet moves through the network? How does a PC determine which network it belongs to? How does it determine if the destination is on the same network? Where does the PC send the packet if the destination is not on its own network? Where does the PC look for the default gateway MAC address? What does the PC do if the MAC address is not in the ARP table? Excellent description of how a packet travels from one pc to another. Make certain you understand the steps. Note any questions you have about the process. Equal cost metric When a router can use multiple interfaces to reach a single network address. Path determination function Switching function Switching 1. Decapsulates the Layer 3 packet by removing the Layer 2 frame header and trailer. 2. Examines the destination IP address of the IP packet to find the best path in the routing table. 3. Encapsulates Layer 3 packet into a new Layer 2 frame and forwards the frame out the exit interface. It is decremented each hop. Goes down IP address MAC address It ands its IP address and subnet mask After anding the packet it compares the network address to its own To the default gateway In its ARP table It sends an ARP request
7 Extra: * What are the primary functions of a route? (Can you list 3?) - read the section on Router Paths and Packet Switching D - * You need to know the components of route and its related functions: - RAM: What is stored in RAM? Can you list the names and its functions? - ROM: What is stored in ROM? Can you list the names and its functions? - FLASH: What is stored in FLASH? Can you list the names and its functions? - NVRAM: What is stored in NVRAM? Can you list the names and its functions? - POST: What is the purpose of POST? * What is the running-config file and what is startup-config? What is the difference between these 2 files? * What is the purpose of show running-config command? * What is the purpose of show startup-config command? * How do you save the running-config file? What command can be used to save the file? * You need to know all the situations of router loading sequences and backup loading sequences (***). - Default complete (IOS and configuration file) loading sequence - Default and backup IOS loading sequence - Default and backup configuration file loading sequence - What happen when router cannot find the valid IOS file? - What happen when router cannot find the startup configuration file?
8 * How many places that you can figure passwords on the router and what are those interfaces? - Do you know the commands needed to configure the console password? - Do you know the commands needed to configure the telnet password? - Do you know the commands needed to configure all 5 lines of telnet password? - Do you know the commands needed to configure the unsecure privileged password? - Do you know the commands needed to configure the secure privileged password? * What is the purpose of service password-encryption command? - What is the router output looks like before executing the command? - What is the router output looks like after executing the command? * In relations to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through a router and designated to another network? - What happen to the layer 2 information? - What happen to the layer 3 information? - Refers to the diagram shown below, what information (field) remain constant and does not get change during the transmission. - Refers to the diagram shown below, what information (field) does not remain constant and does get change all the time during the transmission. - Refers to the diagram shown below, you need to be able to identify all the information about: What is your source MAC address? What is your destination MAC address? What is your source IP address? What is your destination IP address?
9 * From the figure shown below: - Which interface can be used for LAN connection? - Which interface can be used for WAN connection? - Which interface must be used for initial router configuration? - Which interface can be used when there is no network access is available? - What type of cable need to be used to inter-connect 2 routers together with their fastethernet ports? * What is the definition of the term load balance? - What type of routing protocols support load balancing? * What is the definition of the term unequal cost load balance? - What type of routing protocols support unequal cost load balancing? * Based on the following show ip route output, can you explain the following: - What is C stands for? What do you do to produce this C entry? - Do you have enough information to figure out how many interface do you have on the router? - What happen when the router received a packet with the destination IP address of ? (drop or forward? If it forward, where does it forward to?)
10 - What happen when the router received a packet with the destination IP address of ? (drop or forward? If it forward, where does it forward to?) * You have configured the IP addresses on all the router interfaces, but it is still not working. Why? (see graphic listed below) * Please list 3 required commands needed to configure the S0 interface of Sydney router. So, the Sydney router can communicate with Melbourne router. * Analyze the following network, and choose the appropriate outgoing interface - What happen when RouterA want to send a packet to network /24 - What happen when RouterA want to send a packet to network /24 - What happen when RouterB want to send a packet to network /24 - What happen when RouterB want to send a packet to network /24 - What happen when RouterC want to send a packet to network /24 - What happen when RouterC want to send a packet to network /24
11 * Can you figure out what is wrong of the following figure?
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding
 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate the ability
Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Routing Protocols and Concepts 1 Objectives Identify a router as a computer with an OS and hardware designed for the routing process. Demonstrate the ability
Final exam study Guide
 Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS
 QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
Chapter 4: Routing Concepts. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 4: Routing Concepts Routing & Switching Routers are Computers Routers are specialized computers containing the following required components to operate: Central processing unit (CPU) Operating
Chapter 4: Routing Concepts Routing & Switching Routers are Computers Routers are specialized computers containing the following required components to operate: Central processing unit (CPU) Operating
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS. Cisco Lab Øvelse Af Kim Donnerborg / RTS. Side 0 af 8
 KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Chapter 6: Network Layer
 Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
CCNA2 Chapter 1 Practice
 CCNA2 Chapter 1 Practice Where should a crossover UTP cable be used? (Choose 2) To connect two PCs together directly. To connect a router to an Ethernet switch. To connect a PC to an Ethernet switch. To
CCNA2 Chapter 1 Practice Where should a crossover UTP cable be used? (Choose 2) To connect two PCs together directly. To connect a router to an Ethernet switch. To connect a PC to an Ethernet switch. To
Smart Serial. Show interfaces. Shut down. logging synchronous
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
Lab Using the CLI to Gather Network Device Information Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
CCNA EXPLORATION V4.0 ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND CONCEPTS ACCESSIBLE INSTRUCTOR MATERIALS POWERPOINT OBJECTIVES
 CCNA EXPLORATION V4.0 ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND CONCEPTS ACCESSIBLE INSTRUCTOR MATERIALS Prepared by Cisco Learning Institute June 23, 2008 Chapter 1 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Objectives
CCNA EXPLORATION V4.0 ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND CONCEPTS ACCESSIBLE INSTRUCTOR MATERIALS Prepared by Cisco Learning Institute June 23, 2008 Chapter 1 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Objectives
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP
 Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
CCNA 1 Chapter 6 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013
 CCNA 1 Chapter 6 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1 After troubleshooting a router, the network administrator wants to save the router configuration so that it will be used automatically the next time that the router
CCNA 1 Chapter 6 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1 After troubleshooting a router, the network administrator wants to save the router configuration so that it will be used automatically the next time that the router
Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE3080F tutor to get assigned to your routers.
 EEE00F Lab Basics of the Network Lab Student Lab Manual Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE00F tutor to get assigned to your routers. Contents. Resources used in the labs...
EEE00F Lab Basics of the Network Lab Student Lab Manual Before you start the lab exercises see the lab administrator or EEE00F tutor to get assigned to your routers. Contents. Resources used in the labs...
Cisco IOS Configuration Basics
 Cisco IOS Configuration Basics Switching Router Overview Router configuration controls the operation of the router s: Interface IP address and netmask Routing information (static, dynamic or default) Boot
Cisco IOS Configuration Basics Switching Router Overview Router configuration controls the operation of the router s: Interface IP address and netmask Routing information (static, dynamic or default) Boot
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
 Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Antonio Cianfrani. Packet Tracer
 Antonio Cianfrani Packet Tracer Packet Tracer (1/2) Packet Tracer? Cisco Packet Tracer is a software able to emulate CISCO networking devices. Packet Tracer features: Allows to create network topologies
Antonio Cianfrani Packet Tracer Packet Tracer (1/2) Packet Tracer? Cisco Packet Tracer is a software able to emulate CISCO networking devices. Packet Tracer features: Allows to create network topologies
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers %
 CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100% 1. Which two features are characteristics of flash memory? (Choose two.) Flash provides nonvolatile storage. Flash receives a copy of the IOS from RAM when
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100% 1. Which two features are characteristics of flash memory? (Choose two.) Flash provides nonvolatile storage. Flash receives a copy of the IOS from RAM when
(ii) Simei(config)#line console 0 Simei(config-line)#password Networking Simei(config-line)#exit
 Sep 2008 Section A 1. Any of the following 2: a. Frame relay b. ISDN c. PPP d. HDLC 2. (i) RAM copy running-config startup-config 3. hardware platform, feature set, file format, version 4. (i) Cisco Discovery
Sep 2008 Section A 1. Any of the following 2: a. Frame relay b. ISDN c. PPP d. HDLC 2. (i) RAM copy running-config startup-config 3. hardware platform, feature set, file format, version 4. (i) Cisco Discovery
8. Refer to the exhibit. The ORL router is unable to form a neighbor relationship with the JAX router. What is a possible cause of this problem?
 1. Refer to the exhibit. A new PC was deployed in the Sales network. It was given the host address of 192.168.10.31 with a default gateway of 192.168.10.17. The PC is not communicating with the network
1. Refer to the exhibit. A new PC was deployed in the Sales network. It was given the host address of 192.168.10.31 with a default gateway of 192.168.10.17. The PC is not communicating with the network
Lab: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Lab: Basic Static Route onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab: Basic Static Route onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 5 Router and IOS Basics
 Chapter 5 Router and IOS Basics Benefits of Routing Routers provide Packet filtering Connections between local networks Traffic control Wide area network (WAN) connections Routers operate at the Network
Chapter 5 Router and IOS Basics Benefits of Routing Routers provide Packet filtering Connections between local networks Traffic control Wide area network (WAN) connections Routers operate at the Network
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013
 CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1. Refer to the exhibit. A switch was configured as shown. A ping to the default gateway was issued, but the ping was not successful. Other switches in the same
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1. Refer to the exhibit. A switch was configured as shown. A ping to the default gateway was issued, but the ping was not successful. Other switches in the same
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma
 BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Unit 9 Computer Network Routing and Routing Protocols BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Introduction to Routing Routing is the process that a router uses to forward packets toward
BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Unit 9 Computer Network Routing and Routing Protocols BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma Introduction to Routing Routing is the process that a router uses to forward packets toward
1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services?
 CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network
 CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network 11.1.1 What is the system software in Cisco devices? The Cisco IOS provides devices with what network services? How is the IOS generally accessed?
CCNA Explorer 1 Chapter 11 Configuring & Testing Your Network 11.1.1 What is the system software in Cisco devices? The Cisco IOS provides devices with what network services? How is the IOS generally accessed?
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Chapter 6: Network Layer
 Chapter 6: Network Layer CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 Chapter 6 - Sections & Objectives 6.1 Network Layer Protocols Explain how network layer protocols and services support
Chapter 6: Network Layer CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction to Networks v6.0 Chapter 6 - Sections & Objectives 6.1 Network Layer Protocols Explain how network layer protocols and services support
CISCO EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 100-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 35.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: CCNA Interconnecting
CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 100-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 35.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: CCNA Interconnecting
GuideTorrent. The best excellent exam certification guide torrent and dumps torrent provider
 GuideTorrent http://www.guidetorrent.com The best excellent exam certification guide torrent and dumps torrent provider Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor
GuideTorrent http://www.guidetorrent.com The best excellent exam certification guide torrent and dumps torrent provider Exam : 200-125 Title : CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) Vendor
Static Routing. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2. ITE PC v4.0 Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine directly
Static Routing Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 2 1 Objectives Define the general role a router plays in networks. Describe the directly connected networks, different router interfaces Examine directly
CCNA 4 - Final Exam (B)
 CCNA 4 - Final Exam (B) 1. Identify the factors that contribute to congestion on an Ethernet LAN. (Choose three.) improper placement of enterprise level servers addition of hosts to a physical segment
CCNA 4 - Final Exam (B) 1. Identify the factors that contribute to congestion on an Ethernet LAN. (Choose three.) improper placement of enterprise level servers addition of hosts to a physical segment
outing and Switching Elective : Le
 Routing and Switching Elective : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan Chapters covered: Cabling Router Configuration
Routing and Switching Elective : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan Chapters covered: Cabling Router Configuration
Chapter 11. Configuring and Testing Your Network
 Chapter 11 Configuring and Testing Your Network CCNA1-1 Chapter 11 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Chapter 11 Configuring and Testing Your Network CCNA1-1 Chapter 11 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
CCNA 1 Chapter 11 V4.0 Answers
 CCNA 1 Chapter 11 V4.0 Answers 1. Refer to the exhibit. What command will place the router into the correct mode to configure an appropriate interface to connect to a LAN? UBAMA# configure terminal UBAMA(config)#
CCNA 1 Chapter 11 V4.0 Answers 1. Refer to the exhibit. What command will place the router into the correct mode to configure an appropriate interface to connect to a LAN? UBAMA# configure terminal UBAMA(config)#
Lab Manual. ISC 350 (Networks and Telecommunication) Information Technology Solutions. Prepared by: Eng. Altaf Al Farhan.
 Kuwait University Information Technology Solutions College of Computing Sciences and Engineering Department of Information Science Lab Manual ISC 350 (Networks and Telecommunication) Prepared by: Eng.
Kuwait University Information Technology Solutions College of Computing Sciences and Engineering Department of Information Science Lab Manual ISC 350 (Networks and Telecommunication) Prepared by: Eng.
Lab Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems
 Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Lab 1. CLI Navigation. Scenario. Initial Configuration for R1
 Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
CS IT ports switch basic configuration. Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee.
 Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
Basic IOS Command Structure. Router#disable Router>
 Router#disable Router> Basic IOS Command Structure Each IOS command has specific format or syntax and is executed at the appropriate prompt. The general syntax for a command is the command followed by
Router#disable Router> Basic IOS Command Structure Each IOS command has specific format or syntax and is executed at the appropriate prompt. The general syntax for a command is the command followed by
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to answer the following questions:
 CHAPTER 1 Routing Concepts Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to answer the following questions: What are the primary functions and features of a router? How do you connect devices
CHAPTER 1 Routing Concepts Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to answer the following questions: What are the primary functions and features of a router? How do you connect devices
Module 9, Assignment 7
 Module 9, Assignment 7 7.2.3 Control Router via Console (in Packet Tracer) 1. Prepare a Cisco 1841 Router (see figure 6-9). 2. Prepare a PC for administration. 3. Prepare a console cable and plug the serial
Module 9, Assignment 7 7.2.3 Control Router via Console (in Packet Tracer) 1. Prepare a Cisco 1841 Router (see figure 6-9). 2. Prepare a PC for administration. 3. Prepare a console cable and plug the serial
CISCO SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION (41)
 CISCO SYSTEM ADMININSTRATION PAGE 1 OF 11 CONTESTANT ID# Time Rank CISCO SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION (41) Regional 2012 TOTAL POINTS (500) Failure to adhere to any of the following rules will result in disqualification:
CISCO SYSTEM ADMININSTRATION PAGE 1 OF 11 CONTESTANT ID# Time Rank CISCO SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION (41) Regional 2012 TOTAL POINTS (500) Failure to adhere to any of the following rules will result in disqualification:
Which of the following are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.) - packet switching - path selection
 Which three statements are true regarding the encapsulation and de-encapsulation of packets when traveling through a router? (Choose three.) - The router modifies the TTL field, decrementing it by one.
Which three statements are true regarding the encapsulation and de-encapsulation of packets when traveling through a router? (Choose three.) - The router modifies the TTL field, decrementing it by one.
Chapter 6: Network Layer. Introduction to Networks v5.1
 Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks v5.1 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Network Layer Protocols 6.2 Routing 6.3 Routers 6.4 Configure a Cisco Router 6.5 Summary 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All
Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks v5.1 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Network Layer Protocols 6.2 Routing 6.3 Routers 6.4 Configure a Cisco Router 6.5 Summary 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All
Chapter 6: Network Layer
 Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks v5.1 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Network Layer Protocols 6.2 Routing 6.3 Routers 6.4 Configure a Cisco Router 6.5 Summary 2 Upon completion of this section, you
Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks v5.1 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Network Layer Protocols 6.2 Routing 6.3 Routers 6.4 Configure a Cisco Router 6.5 Summary 2 Upon completion of this section, you
LAB 3 Basic Switch Configuration Commands
 LAB 3 Basic Switch Configuration Commands This lab explains basic switch configuration commands in detail with examples. Configuration and commands explained in this tutorial are essential commands to
LAB 3 Basic Switch Configuration Commands This lab explains basic switch configuration commands in detail with examples. Configuration and commands explained in this tutorial are essential commands to
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
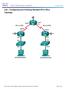 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
2. Which two functions of the OSI model occur at layer two? (Choose two.) physical addressing encoding routing cabling media access control
 1. Which of the following are the address ranges of the private IP addresses? (Choose three.) 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 200.100.50.0 to 200.100.25.255 150.150.0.0 to 150.150.255.255 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
1. Which of the following are the address ranges of the private IP addresses? (Choose three.) 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 200.100.50.0 to 200.100.25.255 150.150.0.0 to 150.150.255.255 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.2
 CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.2 January 12th, 2012AdminLeave a commentgo to comments 1. When must a router serial interface be configured with the clock rate command? when the interface is functioning
CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.2 January 12th, 2012AdminLeave a commentgo to comments 1. When must a router serial interface be configured with the clock rate command? when the interface is functioning
CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.1
 CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.1 January 12th, 2012AdminLeave a commentgo to comments Which of the following are the address ranges of the private IP addresses? (Choose three.) 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers UPDATE 2012 eg.1 January 12th, 2012AdminLeave a commentgo to comments Which of the following are the address ranges of the private IP addresses? (Choose three.) 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
Hochschule Bremen Networking Lab
 Hochschule Bremen Networking Lab User Manual Welcome to the Hochschule Bremen networking lab. This manual will give you a brief introduction on how to use the PCs and networking hardware in the lab. The
Hochschule Bremen Networking Lab User Manual Welcome to the Hochschule Bremen networking lab. This manual will give you a brief introduction on how to use the PCs and networking hardware in the lab. The
Chapter 8: Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client
 Chapter 8: Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Chapter 8: Lab B: Configuring a Remote Access VPN Server and Client Topology IP Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 FA0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
exam. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min CISCO Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND)
 100-105.exam Number: 100-105 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min CISCO 100-105 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Exam A QUESTION 1 Which route source code represents the routing
100-105.exam Number: 100-105 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min CISCO 100-105 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Exam A QUESTION 1 Which route source code represents the routing
Cisco Network Academy CCNA 1 Introduction to Networks
 Cisco Network Academy CCNA 1 Introduction to Networks Packet Tracer Practice with Dans Sample http://www.danscourses.com/ In this lab, you will learn how to configure the following tasks: IPv4 Addressing
Cisco Network Academy CCNA 1 Introduction to Networks Packet Tracer Practice with Dans Sample http://www.danscourses.com/ In this lab, you will learn how to configure the following tasks: IPv4 Addressing
configuring and connecting 24
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
MiPDF.COM. 3. Which procedure is used to access a Cisco 2960 switch when performing an initial configuration in a secure environment?
 CCNA1 v6.0 Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2017 (100%) MiPDF.COM 1. What is the function of the kernel of an operating software? It provides a user interface that allows users to request a specific task. The kernel
CCNA1 v6.0 Chapter 2 Exam Answers 2017 (100%) MiPDF.COM 1. What is the function of the kernel of an operating software? It provides a user interface that allows users to request a specific task. The kernel
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses
 Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA 2: Routers
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
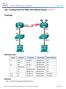 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM
 Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Lab Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration
 Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Lab Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity
 Lab 9.2.5 Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.252
Lab 9.2.5 Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.252
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (2 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (18 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (2 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (18 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Packet Tracer - Configuring Initial Switch Settings
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Verify the Default Switch Configuration Part 2: Configure a Basic Switch Configuration Part 3: Configure a MOTD Banner Part 4: Save Configuration Files to NVRAM Part 5: Configure
Topology Objectives Part 1: Verify the Default Switch Configuration Part 2: Configure a Basic Switch Configuration Part 3: Configure a MOTD Banner Part 4: Save Configuration Files to NVRAM Part 5: Configure
Router Configuration. Router Fundamentals Connecting to the Console Port Router Modes -- User EXEC Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC Lab #9 Goals
 Router Configuration Router Fundamentals Connecting to the Console Port Router Modes -- User EXEC Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC Lab #9 Goals Router Fundamentals Here, we will examine two types of networks:
Router Configuration Router Fundamentals Connecting to the Console Port Router Modes -- User EXEC Router Modes -- Privileged EXEC Lab #9 Goals Router Fundamentals Here, we will examine two types of networks:
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication Topology
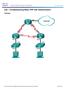 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0 3.1.1 What are the four routing RIP, RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPFv2 protocols that are the focus of this course? 3.1.1.2 What are routing protocols?
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 3 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols V 4.0 3.1.1 What are the four routing RIP, RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPFv2 protocols that are the focus of this course? 3.1.1.2 What are routing protocols?
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT
 Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Powering On the Cisco VG224 Voice Gateway
 CHAPTER 4 To power on your Cisco VG224 voice gateway, perform the following tasks in the order listed, as required: Checklist for Power-On, page 4-1 Power-On Procedure, page 4-1 Initial Configuration Procedures,
CHAPTER 4 To power on your Cisco VG224 voice gateway, perform the following tasks in the order listed, as required: Checklist for Power-On, page 4-1 Power-On Procedure, page 4-1 Initial Configuration Procedures,
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab 9.3.7 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with debug Instructor Version 2500 Objective Utilize a systematic OSI troubleshooting process to diagnose routing problems. Use various show commands to gather
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Lab Configuring Basic RIPv2 (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
(Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
DESIGN AND CONFIGURATION OF WIRED AND WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK USING CISCO PACKET TRACER
 DESIGN AND CONFIGURATION OF WIRED AND WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK USING CISCO PACKET TRACER Khin AyeThu 1, Soe Soe Mon 2, Thida Soe 3 1 First Author, Lecturer, Faculty of Computer Systems and Technologies,
DESIGN AND CONFIGURATION OF WIRED AND WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK USING CISCO PACKET TRACER Khin AyeThu 1, Soe Soe Mon 2, Thida Soe 3 1 First Author, Lecturer, Faculty of Computer Systems and Technologies,
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv2
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Securing Network Devices
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3
4(b): Assign the IP address on the Serial interface of Router. Console Cable
 Lab#4 Router Basic IOS 4(a). Router Basic Commands & Configuration 4(b) Assign the IP address on the Serial interface of Router Console Cable R1 PC1 Objectives Be familiar with use of different Configuration
Lab#4 Router Basic IOS 4(a). Router Basic Commands & Configuration 4(b) Assign the IP address on the Serial interface of Router Console Cable R1 PC1 Objectives Be familiar with use of different Configuration
cisco. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min.
 300-101.cisco Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 Examine the following output of the show ip ospf interface command. What would be the effect of executing the auto-cost
300-101.cisco Number: 300-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min Exam A QUESTION 1 Examine the following output of the show ip ospf interface command. What would be the effect of executing the auto-cost
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
CCNA Questions/Answers Routing Protocols
 Refer to the exhibit and configuration shown above. Routers R1 and R2 are properly configured with eigrp 976 protocol and are able to ping interfaces fa0/1 and fa0/2, respectively. Which commands are necessary
Refer to the exhibit and configuration shown above. Routers R1 and R2 are properly configured with eigrp 976 protocol and are able to ping interfaces fa0/1 and fa0/2, respectively. Which commands are necessary
IOS and Configuration Basics
 APPENDIX C This appendix contains basic information about the Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS) software and includes the following sections: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation Getting Context-Sensitive
APPENDIX C This appendix contains basic information about the Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS) software and includes the following sections: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation Getting Context-Sensitive
Lab - Building a Switch and Router Network
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
Router Startup and Configuration
 Router Startup and Configuration Router Startup In general, the boot process follows these steps: Test hardware (POST) Load the bootstrap program Locate and load the Cisco IOS Locate and load the router
Router Startup and Configuration Router Startup In general, the boot process follows these steps: Test hardware (POST) Load the bootstrap program Locate and load the Cisco IOS Locate and load the router
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Configure Initial Router Settings on Cisco 4000 Series ISRs
 Configure Initial Router Settings on Cisco 4000 Series ISRs This chapter describes how to perform the initial configuration on Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs). It contains the following
Configure Initial Router Settings on Cisco 4000 Series ISRs This chapter describes how to perform the initial configuration on Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs). It contains the following
