Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection Via Maximizing the Expected Throughput Efficiency of ARQ Protocol
|
|
|
- Jasper Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection Via aximizing the Expected Throughput Efficiency of AQ Protocol Xiang Li 1,2,*, an-tian Li 1, Zhen-Guo Gao 2, and Li-Ning Sun 1 1 obot esearch Institute, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 0001, China 2 College of Computer Science and Technology, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, 0001, China {leexiang, gag}@hrbeu.edu.cn, {limt, lnsun}@hit.edu.cn Abstract. Bluetooth provides different kinds of data packet types with different sizes and error correction mechanisms, thus adapter layer can choose the most suitable packet to be transmitted according to the error rate on the link and application requirements. Based on the acknowledgement history of the most recently transmitted packets, an adaptive algorithm is proposed to choose the suitable Bluetooth data packet for transmission through maximizing the expected throughput efficiency of AQ protocol on Bluetooth ACL data communication link. Simulation results indicate that this method works very well with a short observation history and also show special performance of D and DH data packet transmission. Keywords: Bluetooth, Piconet, AQ, ACL, Throughput Efficiency. 1 Introduction Bluetooth (BT [1,2] is a short-range radio link intended to be a cable replacement between portable and/or fixed electronic devices. Two types of transmission links, SCO and ACL links are used. SCO link is a symmetric point to point link supporting time-bounded voice traffic. SCO packets are transmitted over reserved intervals without being polled. ACL link is a point to multipoint link between master and all slaves in the piconet and can use all the remaining slots of the channel not used for SCO link. Bluetooth is a frequency hopping system which can support multiple communication channels in a common area (each channel is defined by a unique frequency hopping sequence. Frequency hopping is used in such a way that the radio is turned to the same frequency for the entire duration of the packet, but then changes to a different frequency each time it transmits a new packet or retransmits an erroneous packet. Since the fading and interference in the new frequency channel will be significantly different than that of the previous one, the use of frequency hopping with AQ provides an effective method of diversity. Automatic epeat equest (AQ protocols are designed to remove transmission errors from data communications systems. When used over relatively high bit-error rate (BE links (e.g., 10-5 or higher such as wireless or satellite links, their performance is * Supported by the Harbin Engineering University Foundation (HEUFT060.. Bubak et al. (Eds.: ICCS 2008, Part I, LNCS 5101, pp , Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2008
2 560 X. Li et al. sensitive to the packet size used in the transmission. When too large a packet size is employed, there is an increased need for retransmissions, while too small a packet size is inefficient because of the fixed overhead required per packet. When an AQ scheme is to be used at the link layer over a relatively high error-rate link, the packet size should be chosen based on the error-rate [3]. The optimal communication problem in Bluetooth has been investigated in some documents. In [4], a solution is proposed to enhance the Bluetooth link layer to make use of channel state information and adopt the suitable Bluetooth packet type to enhance TCP throughput. The throughput of the six Bluetooth ACL packets that use AQ as a function of channel symbol SN are derived in [5], then optimal packet type can be selected at different SNs. Document [6] provides algorithms to maximize the throughput under lossy transmission conditions in a piconet with one or more slaves by selecting the packet lengths optimally in accordance with the channel conditions for different frequencies. All these works are concentrating on throughput under different channel conditions, such as BE or SN, which are not easy to know ahead. In this paper, we concern with choosing optimal packet payload length on the Bluetooth ACL data communication links, in terms of maximizing the throughput efficiency of AQ protocol based on the acknowledgement history of the most recently transmitted packets. That is, given the number of packets that required retransmission, an estimate of the channel BE is made, based on which a packet size is chosen to maximizes the expected throughput efficiency of the data link protocol. 2 Bluetooth Data Packets In Bluetooth, the data on the piconet channel is conveyed in packets. The general packet format is shown in Fig.1. Each packet consists of 3 entities: the access code, the header, and the payload. In Fig. 1, the number of bits per entity is indicated [1]. Fig. 1. Standard Packet Format The access code and header are of fixed size: 72 bits and 54 bits respectively. The payload length can range from zero to a maximum of 2745 bits. Different packet types have been defined. Packets may consist of the (shortened access code only, of the access code header, or of the access code header payload. Data in Bluetooth can be transmitted asynchronously using ACL packets. In this paper, we mainly focus on ACL packets data transfer used in asynchronously connections. Seven ACL packet types are defined in the Bluetooth. D stands for Data- edium rate, DH for Data-High rate. D packets are all 2/3-FEC encoded to tolerate possible transmission errors. Not encoded by FEC, DH packets are more errorvulnerable, but it can carry more information.
3 Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection Adaptive Packet Selection Algorithm 3.1 Throughput Efficiency of AQ Protocol A protocol performance is usually characterized by many parameters which are defined by the communication system requirements. The most important parameters are the probability of receiving a message without errors and the protocol throughput efficiency. There are several definitions of the protocol throughput efficiency. ost frequently it is defined as the ratio of the mean number of information bits successfully accepted by the receiver to the number of bits that could have been transmitted during the same time interval [7]. To do so we must first derive an expression for the throughput efficiency of the AQ protocol. The expressions derived in this section assume the use of an optimal AQ protocol in that only packets containing errors are retransmitted. The throughput efficiency of AQ scheme that uses packets having n bits of information bits k is determined by [8]: k η = ( / (1 n where, the first term k/n of the above expression represents the ratio of information bits to total bits in a packet, and represents the average number of transmission attempts per packet. Assuming that the AQ scheme retransmits a packet until the acknowledgement of a successful reception, the average number of attempts,, needed to successfully transmit one packet is given by [4]: =1 1-p+2 p 1-p+3 p p 1-p+ = 1 (2 1 p where, p is the packet error rate. So, for a given p, the throughput efficiency of AQ that uses packets having n bits of information bits k is given by: k η = ( ( 1- p (3 n 3.2 Choosing Packet Size Via aximizing the Expected Throughput Efficiency of AQ Protocol When a perfect retransmission algorithm (A perfect retransmission algorithm is one that only retransmits packets that are in error and can continuously transmit new packets as long as no errors occur. The selective repeat protocol is an example of a perfect retransmission algorithm is employed, the optimal packet size to be used by the data link protocol is given by [3]: 2 2 hln(1 b 4hln(1 b + h ln(1 b k opt = (4 2ln(1 b where b is the known channel BE and h is the number of overhead bits per packet(these bits are used for control, error detection, and framing.
4 562 X. Li et al. When h equals to 126the optimal packet size under different channel BE can be displayed in Fig. 2 by formula (4. Fig. 2 shows that the optimal packet size decreases according to the increase of the channel BE. This change trends meets to the real application requirement because when a much larger packet size is used the efficiency of the protocol would drop dramatically while the channel BE is much higher. Therefore a much smaller packet size is efficient under a much higher channel BE because a small packet has low packet error rate. On the contrary, a much larger packet size makes efficient use of the channel when the channel BE is much lower. Fig. 2. Optimal packet size under different channel bit error rate In Bluetooth, in order to guarantee reliable transmission AQ mechanism is adopted. That is, the receiving side sends back special control frame as the acknowledgement or negative acknowledgement (ACK/NACK to the input. In case of drop frame or acknowledgement message, the timer will send out timeout signal when the timer has expired, and to remind other sides that some problems have happened and this frame must be retransmitted. At the same time, receiver must be capable of distinguishing between retransmitted and new frame. With an AQ scheme in Bluetooth specification, D, DH and the data field of DV packets are transmitted and retransmitted until acknowledgement of a successful reception is returned by the destination (or timeout is exceeded. The acknowledgement information is included in the header of the return packet, so-called piggy-backing. To determine whether the payload is correct or not, a CC code is added to the packet. The AQ scheme only works on the payload in the packet (only that payload which has a CC. The packet header and the voice payload are not protected by the AQ. Depending on the packet retransmission records on the current link, an adaptive method to select the best packet for data transmission is proposed to improve the performance of Bluetooth system. The basic idea behind this scheme is that a large packet has low overheads and is advantageous when the BE is relatively low, while a small packet has a low packet error rate and thus is advantageous when the BE is high. So, depending on channel BE, every type of Bluetooth ACL data packet has different performance. Without any bit error, the DH5 packet would give the best performance since it carries the most information bit per unit time. However, as the BE increases, the packet error rate of DH5 increases faster than smaller packets. Thus, there exists a problem to how to select suitable packet to adapt to the current channel conditions. However, it is difficult to estimate the channel BE in a short time when the link is operating under error detection with retransmission [9], but we can acquire the packet retransmission history easily.
5 Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection 563 This paper proposes a simple algorithm to choose the packet size such that the conditional efficiency of the protocol is maximized under different channel BEs based on packet transmission record. Supposed the BE is b, and, the number of retransmission requests out of the last packet transmissions, by averaging the above expression over all possible values of b and using the conditional distribution of b given (assuming that b is constant over the period of interest. The resulting expression is given by [3]: η ( k ηp( b db (5 = 1 0 where P(b, is the conditional probability of b given that out of the last packets required retransmission. We now wish to choose the value of k that maximizes η. To do so we must first express the conditional probability of b given. The conditional probability of b given, P(b, can be expressed as follows: b, ] b] b] P [ b ] = = (6 ] ] Solving for the above conditional probability requires knowledge of a prior distribution of b. In the absence of a prior, we assume a uniform prior, that is b]=1. This approach, in essence, is the same as a maximum likelihood approach where a uniform prior is assumed, except that here we associate a cost function with the estimates of b. With this approach we get and so P [ ] b] db (7 = b] b] db = b ] = 1 0 b] b] db In wireless communication, we generally assume that channels are independent and same distribution model, that is, assume that error rates on the channel are independent of each other and commonly kept invariable. Given packet error rate p, the probability that packets contain errors and therefore require retransmission is the probability that out of packet are in error. Since packet errors are independent from packet to packet, this probability can be expressed according to the binomial distribution with parameter p, therefore b] can be expressed as: The packet error rate, p, for DH packets is: b] = ( p (1 p (9 k (8 p = 1 (1 b (10 ecalling that D packets are protected by a (,10 Hamming code (encoded with a 2/3 block FEC, i.e., in every block, bits are used to encode 10 bits of data, which is capable of correcting one bit error per bit code block. The payload is correctly decoded provided that all code blocks contain one or fewer errors. The packet error rate, p, for D packets can be approximated as:
6 564 X. Li et al. p = 1 ((1 b + b(1 b 14 k / Hence, for DH packets, b] can be expressed as: (11 k ' k '( b] = ( (1 (1 b (1 b (12 For D packets, b] can be expressed as: 14 k'/ 14 k'( / b] = ( (1 ((1 b + b (1 b ((1 b + b (1 b (13 where k' is the payload size used in the previous transmissions. Combining equations (5 (13, we can get η (k for DH and D packets respectively as: ( 1 ( 0 η ( k (1 ((1 b (1 ((1 b k (1 b [ n k = ( 0 + b(1 b + b(1 b ( 14 k' / 14 k' / (1 (1 b (1 (1 b k ' k ' ((1 b ((1 b (1 b (1 b k ' ( k '( + b(1 b + b(1 b ] db db 14 k'( / 14 k'( / ]db db (14 ( + = 1 14 k/ k((1 b b(1 b η (k [ 0 n where n=k+126. It is now possible to choose the value of k, the payload length to be used in future transmissions, so that the throughput efficiency of the AQ protocol is maximized. This can be done by choosing the value of k that maximizes equation (14 or ( for a value of that is equal to the number of retransmission requests that occurred during the previous transmissions using the payload size k '. 4 Simulation esults Usually, the solution way of the maximization problem for η (k in equation (7 or (8 is difficult; However, for specific values of, and k ' equation (7 or (8 can be solved numerically. An optimal value for k can now be found using numerical search algorithms. Since the numerical evaluation of this integral is very intensive, a comprehensive search for the optimal value of k is not practical. Instead, a restricted search using select values for k can be performed. Such a search, for example, can consider values of k that are a multiple of 100; thereby significantly reducing the complexity of the search. Such a restricted search has little impact on the performance of the protocol since values of k that are within 100 bits of the optimal block size should result in near-optimal performance. Here, analysis of equation (14 or ( is taken using atlab7.0, where k is always valued as the multiple of 100 and the pace of b is In fig. 3, we plot the optimal payload size when a history of 50 previously transmitted 00 bit packets payload is considered. As can be seen from the fig. 3 (a, for DH
7 Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection 565 packets transmission, when the previous fifty transmissions resulted in no errors the payload length can be maximized to 2744 bits (the maximization throughput efficiency can be gotten at payload length of 3200 bits. When one and two errors occurred the payload length can be increased to 2100 and 1700 bits respectively. When three errors occurred the payload length can be kept at 00 bits and when more than three errors occur the payload length is reduced. As depicted in fig. 3 (b, for D packets transmission, when the previous fifty transmissions resulted in no errors the payload length can be maximized to be 2745 bits (the maximization throughput efficiency can be gotten at packet payload length of 4400 bits. When one, two and three errors occurred the payload length can be increased to 2500, 1900 and 1600 bits respectively and when more than three errors occur the payload length is reduced. (etransmisssion Packets (a DH packet Optimal payload length (etransmisssion Packets (b D packet Optimal payload length Fig. 3. Optimal packet size selection based on retransmission history Let k be the optimal packet size chosen for a given value of out of the last packet transmissions. The efficiency of the AQ protocol with that value of k can be computed according to equation (3 combined with equation (10 or (11. Then it can be averaged over the distribution of given b to yield the performance of AQ for a given value of b. Fig. 4 shows the mean throughput efficiency of AQ with various values of and b, and a previous packet payload length of 00 bits. As can be seen from the figure, whether it is DH or D packets transmission, good performance is obtained with a history of just bits payload size (50 packets at packet payload size of 00 bits. When b is higher than 10-5, more of history is required to obtain a reasonable estimate of throughput efficiency for D packets transmission; but for DH packets transmission, the situation is quite different, only few or the least history of packets transfer is required to obtain high throughput efficiency. The throughput efficiency can be computed according to equation (3 using the optimal packet size obtained from the formula (4 under different channel BE. In the previous fifty packets transmission with payload length of 00 bits, the mean throughput efficiency of DH is calculated based on the select optimizing packet size under different retransmission packets. Fig. 5 compares mean throughout efficiency of DH packets transmission based on retransmission history and the optimal packets transmission (opt according to formula (4 for various b. As can be seen from the
8 566 X. Li et al. Fig. 4. ean throughput efficiency of algorithm for various b Fig. 5, both mean throughout efficiency increase against the decrease of b. The mean throughout efficiency of DH packets based on retransmission packets is always below to the optimal packets transmission (opt, but the difference is not so great. Similarly, the mean throughput efficiency of D is calculated based on the select optimizing packet size under different numbers of retransmission packets. Fig. 6 compares mean throughout efficiency of D packets transmission based on retransmission history and the optimal packets transmission (opt according to formula (4 for various b. As can be seen from the figure, both mean throughout efficiency increase by the decrease of b. The mean throughout efficiency of Bluetooth D packets based on retransmission packets becomes mild while the b is less than 10-3, which is close to When b is large than 10-3, the mean throughout efficiency of D packets based on retransmission packets is larger than the optimal packets transmission (opt. Hence, the larger throughout efficiency can be gained by using D packets transmission with AQ protocol when the channel BE is high. In the previous fifty packets transmission with payload length of 00 bits, select optimizing packet size under different retransmission packets, fig. 7 compares mean throughout efficiency of AQ during DH and D packets transmission for various b. Fig. 5. Comparing mean throughput efficiency of DH and optimal packets transmission (opt
9 Bluetooth ACL Packet Selection 567 Fig. 6. Comparing mean throughput efficiency of D and optimal packets transmission (opt It is important to note that the performance of AQ is much more vulnerable to DH packets when b is high. That is, when b is high the use of DH or D packet type can have a disastrous effect on the throughput efficiency, and D packets transfer can produce higher throughput efficiency than DH packets. When b is low, small variations in the throughput efficiency from the different bit error rate b, packet types (DH/D. So in a high error rate environment, it is better to take D packets as data transmission, which accords with the capability of D to tolerate high transmission error rate. Oppositely, in a low error rate environment, it is better to take DH packets as data transmission, it is because not decoded by 2/3-FEC DH packets have relatively higher data transfer rate than D packets data transmission. DH D Fig. 7. Comparing mean throughput efficiency of DH and D packets transmission 5 Conclusion This paper introduces a method to select the optimal packet payload length used by Bluetooth ACL data link layer. The throughput efficiency of AQ protocol is given based on retransmission history. So, given packet transmission record we can choose the packet size such that the expected throughput efficiency of the AQ protocol is maximized under different channel BEs. Simulation results show that the method works very well even with a short observation history (50 packets at size of 00 bits payload, total bits payload transfer. In a high error rate environment, it is
10 568 X. Li et al. better to take D packets as data transmission; but in a low error rate environment, it is better to take DH packets as data transmission to improve the data transfer rate. eferences 1. Bluetooth V1.1 Core Specifications, 2. Harrtsen, J.: The bluetooth radio system. IEEE Personal Communicatios 7(1, ( odiano, E.: An adaptive algorithm for optimizing the packet size used in wireless AQ protocols. Wireless Networks 5, ( Chen, L.J., Kapoor,., Sanadidi,.Y., Gerla,.: Enhancing bluetooth TCP throughput via link layer packet adaptation. In: Proc. of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC 2004, pp IEEE Press, Paris ( Valenti,.C., obert,., eed, J.H.: On the throughput of bluetooth data transmissions. In: Proc. of the IEEE Wireless Commun. and Networking Conf., pp IEEE Press, Orlando ( Sarkar, S.: Optimal Communication in Bluetooth Piconets. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 54(2, ( Turin, W.: Throughput analysis of the Go-Back-N protocol in fading radio channels. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 17(5, ( Pribylov, V.P., Chernetsky, G.A.: Throughput efficiency of automatic repeat request algorithm with selective reject in communication links with great signal propagation delay. In: Proc. of the 3-rd IEEE-ussia Conferences icrowave Electronics: easurements, Identification (EIA 2001, pp IEEE Press, Novosibirsk ( Jesung, J., Yujin, L., Yongsuk, K., Joong, S..: An adaptive segmentation scheme for the Bluetooth-based wireless channel. In: Proc. of the 10th International Conference on Computer communications and networks, pp IEEE Press, Scottsdale (2001
Optimizing Packet Size via Maximizing Throughput Efficiency of ARQ on Bluetooth ACL Data Communication Link
 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED INFOATICS and COUNICATIONS, alta, September -7, 25 (pp24-28 Optimizing Pacet Size via aximizing Throughput Efficiency of AQ on Bluetooth ACL Data Communication
Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on APPLIED INFOATICS and COUNICATIONS, alta, September -7, 25 (pp24-28 Optimizing Pacet Size via aximizing Throughput Efficiency of AQ on Bluetooth ACL Data Communication
Data Link Control Protocols
 Protocols : Introduction to Data Communications Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Prepared by Steven Gordon on 23 May 2012 Y12S1L07, Steve/Courses/2012/s1/its323/lectures/datalink.tex,
Protocols : Introduction to Data Communications Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Prepared by Steven Gordon on 23 May 2012 Y12S1L07, Steve/Courses/2012/s1/its323/lectures/datalink.tex,
IEEE P Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks TM
 IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks TM SCORT - An Alternative to the Bluetooth SCO Link for Voice Operation in an Interference Environment Slide 1 Bluetooth SCO Link The Bluetooth
IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks TM SCORT - An Alternative to the Bluetooth SCO Link for Voice Operation in an Interference Environment Slide 1 Bluetooth SCO Link The Bluetooth
Improving Simultaneous Voice and Data Performance in Bluetooth Systems
 Improving Simultaneous Voice and Data Performance in Bluetooth Systems Abstract In the Bluetooth system, isochronous applications, such as voice and audio, are carried by Synchronous Connection Oriented
Improving Simultaneous Voice and Data Performance in Bluetooth Systems Abstract In the Bluetooth system, isochronous applications, such as voice and audio, are carried by Synchronous Connection Oriented
UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore.
 Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Communication Switching Techniques UNIT 5 P.M.Arun Kumar, Assistant Professor, Department of IT, Sri Krishna College of Engineering and Technology, Coimbatore. Bluetooth Techniques References 1. Wireless
Correct Bluetooth EDR FEC Performance with SEC-DAEC Decoding
 Correct Bluetooth EDR FEC Performance with SEC-DAEC Decoding R. Razavi, M. Fleury and M. Ghanbari By selecting from Bluetooth s Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) packet types according to channel conditions, optimal
Correct Bluetooth EDR FEC Performance with SEC-DAEC Decoding R. Razavi, M. Fleury and M. Ghanbari By selecting from Bluetooth s Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) packet types according to channel conditions, optimal
CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING
 Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2010 April 21, 2010, Rolla, Missouri CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Chaitri Aroskar caa279@mst.edu Y.R.Zheng
Proceedings of the 4th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2010 April 21, 2010, Rolla, Missouri CROSS-LAYER APPROACHES TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Chaitri Aroskar caa279@mst.edu Y.R.Zheng
Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control
 Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control Qinqing Zhang, Hsuan-Jung Su Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies Holmdel, NJ 77 Abstract- The Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol in Universal Mobile Telecommunication
Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control Qinqing Zhang, Hsuan-Jung Su Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies Holmdel, NJ 77 Abstract- The Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol in Universal Mobile Telecommunication
Enhancing Bluetooth TCP Throughput via Link Layer Packet Adaptation
 Enhancing Bluetooth TCP Throughput via Link Layer Packet Adaptation Ling-Jyh Chen, Rohit Kapoor, M. Y. Sanadidi, Mario Gerla UCLA Computer Science Department, Los Angeles, CA 995, USA {cclljj, rohitk,
Enhancing Bluetooth TCP Throughput via Link Layer Packet Adaptation Ling-Jyh Chen, Rohit Kapoor, M. Y. Sanadidi, Mario Gerla UCLA Computer Science Department, Los Angeles, CA 995, USA {cclljj, rohitk,
e-pg Pathshala Quadrant 1 e-text
 e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
e-pg Pathshala Subject : Computer Science Module: Bluetooth Paper: Computer Networks Module No: CS/CN/37 Quadrant 1 e-text In our journey on networks, we are now exploring wireless networks. We looked
CHAPTER 5 PROPAGATION DELAY
 98 CHAPTER 5 PROPAGATION DELAY Underwater wireless sensor networks deployed of sensor nodes with sensing, forwarding and processing abilities that operate in underwater. In this environment brought challenges,
98 CHAPTER 5 PROPAGATION DELAY Underwater wireless sensor networks deployed of sensor nodes with sensing, forwarding and processing abilities that operate in underwater. In this environment brought challenges,
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS. M. Subramani and M. Ilyas
 SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
SIMULATION BASED ANALYSIS OF BLUETOOTH NETWORKS M. Subramani and M. Ilyas College of Engineering Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton, Florida 33431 {msubrama@cse.fau.edu, ilyas@fau.edu} Abstract Many
Improving Bluetooth EDR Data Throughput Using FEC and Interleaving
 Improving Bluetooth EDR Data Throughput Using FEC and Interleaving Ling-Jyh Chen 1, Tony Sun 2, and Yung-Chih Chen 1 1 Institute of Information Science, Academia Sinica, Taipei 11529, Taiwan {cclljj, ycchen}@iis.sinica.edu.tw
Improving Bluetooth EDR Data Throughput Using FEC and Interleaving Ling-Jyh Chen 1, Tony Sun 2, and Yung-Chih Chen 1 1 Institute of Information Science, Academia Sinica, Taipei 11529, Taiwan {cclljj, ycchen}@iis.sinica.edu.tw
Energy Evaluation for Bluetooth Link Layer Packet Selection Scheme
 European Wireless 29 1 Energy Evaluation for Bluetooth Link Layer Packet Selection Scheme Gian Paolo Perrucci and Morten V. Pedersen and Tatiana K. Madsen and Frank H.P. Fitzek Department of Electronic
European Wireless 29 1 Energy Evaluation for Bluetooth Link Layer Packet Selection Scheme Gian Paolo Perrucci and Morten V. Pedersen and Tatiana K. Madsen and Frank H.P. Fitzek Department of Electronic
ADAPTIVE PACKET SELECTION ALGORITHM FOR BLUETOOTH DATA PACKETS
 Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Applied Computer Science, Hangzhou, China, April 15-17, 2007 160 ADAPTIVE PACKET SELECTION ALGORITHM FOR BLUETOOTH DATA PACKETS RADOSVETA SOKULLU
Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Applied Computer Science, Hangzhou, China, April 15-17, 2007 160 ADAPTIVE PACKET SELECTION ALGORITHM FOR BLUETOOTH DATA PACKETS RADOSVETA SOKULLU
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
Guide to Wireless Communications, 3 rd Edition Chapter 5 Wireless Personal Area Networks Objectives Describe a wireless personal area network (WPAN) List the different WPAN standards and their applications
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets
 A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
A Routing Protocol and Energy Efficient Techniques in Bluetooth Scatternets Balakrishna J. Prabhu and A. Chockalingam Department of Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
WITH the evolution and popularity of wireless devices,
 Network Coding with Wait Time Insertion and Configuration for TCP Communication in Wireless Multi-hop Networks Eiji Takimoto, Shuhei Aketa, Shoichi Saito, and Koichi Mouri Abstract In TCP communication
Network Coding with Wait Time Insertion and Configuration for TCP Communication in Wireless Multi-hop Networks Eiji Takimoto, Shuhei Aketa, Shoichi Saito, and Koichi Mouri Abstract In TCP communication
Delayed ACK Approach for TCP Performance Improvement for Ad Hoc Networks Using Chain Topology
 Delayed ACK Approach for TCP Performance Improvement for Ad Hoc Networks Using Chain Topology Prashant Kumar Gupta M.Tech. Scholar, Computer Networks, Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg (C.G.), India
Delayed ACK Approach for TCP Performance Improvement for Ad Hoc Networks Using Chain Topology Prashant Kumar Gupta M.Tech. Scholar, Computer Networks, Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg (C.G.), India
Module 6 STILL IMAGE COMPRESSION STANDARDS
 Module 6 STILL IMAGE COMPRESSION STANDARDS Lesson 19 JPEG-2000 Error Resiliency Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to: 1. Name two different types of lossy
Module 6 STILL IMAGE COMPRESSION STANDARDS Lesson 19 JPEG-2000 Error Resiliency Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to: 1. Name two different types of lossy
Multiple Access Protocols
 Multiple Access Protocols Computer Networks Lecture 2 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 Multiple Access to a Shared Channel The medium (or its sub-channel) may be shared by multiple stations (dynamic allocation) just
Multiple Access Protocols Computer Networks Lecture 2 http://goo.gl/pze5o8 Multiple Access to a Shared Channel The medium (or its sub-channel) may be shared by multiple stations (dynamic allocation) just
Reliable Communication using Packet Coding for Underwater Acoustic Channels
 Reliable Communication using Packet Coding for Underwater Acoustic Channels Rameez Ahmed and Milica Stojanovic Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA Email: rarameez@ece.neu.edu, millitsa@ece.neu.edu
Reliable Communication using Packet Coding for Underwater Acoustic Channels Rameez Ahmed and Milica Stojanovic Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA Email: rarameez@ece.neu.edu, millitsa@ece.neu.edu
Master. Slave. Master. Slaves. TCP/IP Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology. Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3
 / Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
/ Traffic with Efficient Bluetooth Technology Shafqat Hameed 1, Umar F.Khan 2, *Muhammad Saleem 3 1,3 National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST), Pakistan 2 University of Bradford, Bradford,
Politecnico di Milano Scuola di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione. Link Layer. Fundamentals of Communication Networks
 Politecnico di Milano Scuola di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione Link Layer Fundamentals of Communication Networks Data Link layer o It is the first logical layer in the protocol stack o Functions
Politecnico di Milano Scuola di Ingegneria Industriale e dell Informazione Link Layer Fundamentals of Communication Networks Data Link layer o It is the first logical layer in the protocol stack o Functions
Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference
 Vol:1, No:3, 27 Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference Radosveta Sokullu and Engin Karatepe International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering
Vol:1, No:3, 27 Performance Evaluation of Bluetooth Links in the Presence of Specific Types of Interference Radosveta Sokullu and Engin Karatepe International Science Index, Electrical and Computer Engineering
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks
 CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
CS263: Wireless Communications and Sensor Networks Matt Welsh Lecture 6: Bluetooth and 802.15.4 October 12, 2004 2004 Matt Welsh Harvard University 1 Today's Lecture Bluetooth Standard for Personal Area
November 1998 doc.: IEEE /378 IEEE P Wireless LANs Extension of Bluetooth and Direct Sequence Interference Model.
 IEEE P802.11 Wireless LANs Extension of Bluetooth and 802.11 Direct Sequence Interference Model Date: November 11, 1998 Author: Jim Zyren Harris Semiconductor Melbourne, FL, USA Phone: (407)729-4177 Fax:
IEEE P802.11 Wireless LANs Extension of Bluetooth and 802.11 Direct Sequence Interference Model Date: November 11, 1998 Author: Jim Zyren Harris Semiconductor Melbourne, FL, USA Phone: (407)729-4177 Fax:
SENSOR-MAC CASE STUDY
 SENSOR-MAC CASE STUDY Periodic Listen and Sleep Operations One of the S-MAC design objectives is to reduce energy consumption by avoiding idle listening. This is achieved by establishing low-duty-cycle
SENSOR-MAC CASE STUDY Periodic Listen and Sleep Operations One of the S-MAC design objectives is to reduce energy consumption by avoiding idle listening. This is achieved by establishing low-duty-cycle
An Efficient Tool for the Evaluation of the Impact of WiFi Interference on Bluetooth Performance
 1 An Efficient Tool for the Evaluation of the Impact of WiFi Interference on Bluetooth Performance Madani Zeghdoud 1, Pascal Cordier 1, and Michel Terré 2 1 France Telecom R&D, Issy les Moulineaux, France.
1 An Efficient Tool for the Evaluation of the Impact of WiFi Interference on Bluetooth Performance Madani Zeghdoud 1, Pascal Cordier 1, and Michel Terré 2 1 France Telecom R&D, Issy les Moulineaux, France.
A Dynamic Slot Assignment Scheme for Slave-to-Slave and Multicast-like Communication in Bluetooth Personal Area Networks
 A Dynamic Slot Assignment Scheme for Slave-to-Slave and Multicast-like Communication in Bluetooth Personal Area Networks Carlos Cordeiro, Sachin Abhyankar, and Dharma P. Agrawal OBR Center for Distributed
A Dynamic Slot Assignment Scheme for Slave-to-Slave and Multicast-like Communication in Bluetooth Personal Area Networks Carlos Cordeiro, Sachin Abhyankar, and Dharma P. Agrawal OBR Center for Distributed
Energy Efficiency Maximization for Wireless Sensor Networks
 Energy Efficiency Maximization for Wireless Sensor Networks Inwhee Joe College of Information and Communications Hanyang University Seoul, Korea iwjoe@hanyang.ac.kr Abstract. Because of the remote nature
Energy Efficiency Maximization for Wireless Sensor Networks Inwhee Joe College of Information and Communications Hanyang University Seoul, Korea iwjoe@hanyang.ac.kr Abstract. Because of the remote nature
CHAPTER 6 PILOT/SIGNATURE PATTERN BASED MODULATION TRACKING
 CHAPTER 6 PILOT/SIGNATURE PATTERN BASED MODULATION TRACKING 6.1 TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER Each modulated signal is preceded by a unique N bit pilot sequence (Manton, JH 2001). A switch in the transmitter
CHAPTER 6 PILOT/SIGNATURE PATTERN BASED MODULATION TRACKING 6.1 TRANSMITTER AND RECEIVER Each modulated signal is preceded by a unique N bit pilot sequence (Manton, JH 2001). A switch in the transmitter
UAMAC: Unidirectional-Link Aware MAC Protocol for Heterogeneous Ad Hoc Networks
 UAMAC: Unidirectional-Link Aware MAC Protocol for Heterogeneous Ad Hoc Networks Sung-Hee Lee, Jong-Mu Choi, and Young-Bae Ko College of Information and Communication, Ajou University, South Korea shlee@dmc.ajou.ac.kr,
UAMAC: Unidirectional-Link Aware MAC Protocol for Heterogeneous Ad Hoc Networks Sung-Hee Lee, Jong-Mu Choi, and Young-Bae Ko College of Information and Communication, Ajou University, South Korea shlee@dmc.ajou.ac.kr,
FORWARD ERROR CORRECTION CODING TECHNIQUES FOR RELIABLE COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 FORWARD ERROR CORRECTION CODING TECHNIQUES FOR RELIABLE COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Jyoti Sharma Department of ECE Sri Sai College of Engg. & Technology, Badhani, Punjab, India Priya Department of ECE Sri Sai
FORWARD ERROR CORRECTION CODING TECHNIQUES FOR RELIABLE COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Jyoti Sharma Department of ECE Sri Sai College of Engg. & Technology, Badhani, Punjab, India Priya Department of ECE Sri Sai
Wireless Communications
 4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
4. Medium Access Control Sublayer DIN/CTC/UEM 2018 Why do we need MAC for? Medium Access Control (MAC) Shared medium instead of point-to-point link MAC sublayer controls access to shared medium Examples:
Communication Networks I December 4, 2001 Agenda Graph theory notation Trees Shortest path algorithms Distributed, asynchronous algorithms Page 1
 Communication Networks I December, Agenda Graph theory notation Trees Shortest path algorithms Distributed, asynchronous algorithms Page Communication Networks I December, Notation G = (V,E) denotes a
Communication Networks I December, Agenda Graph theory notation Trees Shortest path algorithms Distributed, asynchronous algorithms Page Communication Networks I December, Notation G = (V,E) denotes a
Introduction to Bluetooth
 Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Introduction to Bluetooth Kirsten Matheus The idea behind Bluetooth The problems when trying to realize the idea The solutions used in Bluetooth How well the solutions work 12.06.2003 1 he Idea Behind
Ad hoc and Sensor Networks Chapter 6: Link layer protocols. Holger Karl
 Ad hoc and Sensor Networks Chapter 6: Link layer protocols Holger Karl Goals of this chapter Link layer tasks in general Framing group bit sequence into packets/frames Important: format, size Error control
Ad hoc and Sensor Networks Chapter 6: Link layer protocols Holger Karl Goals of this chapter Link layer tasks in general Framing group bit sequence into packets/frames Important: format, size Error control
Wireless multipoint communication for optical sensors in the industrial environment using the new Bluetooth standard
 Wireless multipoint communication for optical sensors in the industrial environment using the new Bluetooth standard Stephan Hussmann*a, Wing Yan Laua, Terry ChUa, Markus Grothofb aschool of Engineering,
Wireless multipoint communication for optical sensors in the industrial environment using the new Bluetooth standard Stephan Hussmann*a, Wing Yan Laua, Terry ChUa, Markus Grothofb aschool of Engineering,
Wireless Sensornetworks Concepts, Protocols and Applications. Chapter 5b. Link Layer Control
 Wireless Sensornetworks Concepts, Protocols and Applications 5b Link Layer Control 1 Goals of this cha Understand the issues involved in turning the radio communication between two neighboring nodes into
Wireless Sensornetworks Concepts, Protocols and Applications 5b Link Layer Control 1 Goals of this cha Understand the issues involved in turning the radio communication between two neighboring nodes into
Local Area Networks NETW 901
 Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
Local Area Networks NETW 901 Lecture 6 IEEE 802.15.1 - Bluetooth Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 The 802.15 Family Target environment: communication of personal
PROPOSAL OF MULTI-HOP WIRELESS LAN SYSTEM FOR QOS GUARANTEED TRANSMISSION
 PROPOSAL OF MULTI-HOP WIRELESS LAN SYSTEM FOR QOS GUARANTEED TRANSMISSION Phuc Khanh KIEU, Shinichi MIYAMOTO Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University 2-1 Yamada-oka, Suita, Osaka, 565-871 JAPAN
PROPOSAL OF MULTI-HOP WIRELESS LAN SYSTEM FOR QOS GUARANTEED TRANSMISSION Phuc Khanh KIEU, Shinichi MIYAMOTO Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University 2-1 Yamada-oka, Suita, Osaka, 565-871 JAPAN
Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth
 Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth Vishwanath Sinha, D. Raveendra Babu Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur - 08 06, INDIA vsinha@iitk.ernet.in,
Class-based Packet Scheduling Policies for Bluetooth Vishwanath Sinha, D. Raveendra Babu Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur - 08 06, INDIA vsinha@iitk.ernet.in,
4. Error correction and link control. Contents
 //2 4. Error correction and link control Contents a. Types of errors b. Error detection and correction c. Flow control d. Error control //2 a. Types of errors Data can be corrupted during transmission.
//2 4. Error correction and link control Contents a. Types of errors b. Error detection and correction c. Flow control d. Error control //2 a. Types of errors Data can be corrupted during transmission.
Investigation on OLSR Routing Protocol Efficiency
 Investigation on OLSR Routing Protocol Efficiency JIRI HOSEK 1, KAROL MOLNAR 2 Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication, Brno University of Technology Purkynova
Investigation on OLSR Routing Protocol Efficiency JIRI HOSEK 1, KAROL MOLNAR 2 Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication, Brno University of Technology Purkynova
A Modified Medium Access Control Algorithm for Systems with Iterative Decoding
 A Modified Medium Access Control Algorithm for Systems with Iterative Decoding Inkyu Lee Carl-Erik W. Sundberg Sunghyun Choi Dept. of Communications Eng. Korea University Seoul, Korea inkyu@korea.ac.kr
A Modified Medium Access Control Algorithm for Systems with Iterative Decoding Inkyu Lee Carl-Erik W. Sundberg Sunghyun Choi Dept. of Communications Eng. Korea University Seoul, Korea inkyu@korea.ac.kr
TOPOLOGY CONTROL IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS WITH COOPERATIVE COMMUNICATIONS
 IEEE 2012 Transactions on Wireless Communications, Volume: 9, Issue: 2 TOPOLOGY CONTROL IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS WITH COOPERATIVE COMMUNICATIONS Abstract Cooperative communication has received tremendous
IEEE 2012 Transactions on Wireless Communications, Volume: 9, Issue: 2 TOPOLOGY CONTROL IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS WITH COOPERATIVE COMMUNICATIONS Abstract Cooperative communication has received tremendous
By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela
 By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela 1 Agenda Introduction WPAN WLAN Simulation Models Simulation results Concluding remarks 2 Introduc.on Coexistence of WPAN and WLAN Performance evaluation WLAN
By N.Golmie Presented by: Sushanth Divvela 1 Agenda Introduction WPAN WLAN Simulation Models Simulation results Concluding remarks 2 Introduc.on Coexistence of WPAN and WLAN Performance evaluation WLAN
By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
ABSTRACT The seemingly endless entanglement of data wires connecting today s electronic devices has become slightly less jumbled with the introduction of Bluetooth technology and the creation of a wireless
Chapter 4: Implicit Error Detection
 4. Chpter 5 Chapter 4: Implicit Error Detection Contents 4.1 Introduction... 4-2 4.2 Network error correction... 4-2 4.3 Implicit error detection... 4-3 4.4 Mathematical model... 4-6 4.5 Simulation setup
4. Chpter 5 Chapter 4: Implicit Error Detection Contents 4.1 Introduction... 4-2 4.2 Network error correction... 4-2 4.3 Implicit error detection... 4-3 4.4 Mathematical model... 4-6 4.5 Simulation setup
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer. Part II TDMA and Polling
 Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Ad Hoc Nets - MAC layer Part II TDMA and Polling More MAC Layer protocols Bluetooth Piconet: a polling/tdma scheme Cluster TDMA: based on TDMA (with random access and reserved slots) research protocol
Video Streaming Over Multi-hop Wireless Networks
 Video Streaming Over Multi-hop Wireless Networks Hao Wang Dept. of Computer Information System, Cameron University hwang@cameron.edu Andras Farago, Subbarayan Venkatesan Dept. of Computer Science, The
Video Streaming Over Multi-hop Wireless Networks Hao Wang Dept. of Computer Information System, Cameron University hwang@cameron.edu Andras Farago, Subbarayan Venkatesan Dept. of Computer Science, The
Performance Simulation of TCP/IP over a Bluetooth Ad-hoc Network
 Performance Simulation of TCP/IP over a Bluetooth Ad-hoc Network Niklas Johansson, Maria Kihl and Ulf Körner Department of Communication Systems, Lund University, Sweden (niklasj, maria, ulfk)@telecom.lth.se
Performance Simulation of TCP/IP over a Bluetooth Ad-hoc Network Niklas Johansson, Maria Kihl and Ulf Körner Department of Communication Systems, Lund University, Sweden (niklasj, maria, ulfk)@telecom.lth.se
UDP-Lite Enhancement Through Checksum Protection
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS UDP-Lite Enhancement Through Checksum Protection To cite this article: Suherman et al 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 180
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS UDP-Lite Enhancement Through Checksum Protection To cite this article: Suherman et al 2017 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 180
Dynamic Traffic Congestion Control Scheme in MANET with Cooperative Communication
 Dynamic Traffic Congestion Control Scheme in MANET with Cooperative Communication P.Deepa 1, Dr. P.S.K Patra 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, 2 Head of the Department, Agni College of
Dynamic Traffic Congestion Control Scheme in MANET with Cooperative Communication P.Deepa 1, Dr. P.S.K Patra 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, 2 Head of the Department, Agni College of
Improvement of Buffer Scheme for Delay Tolerant Networks
 Improvement of Buffer Scheme for Delay Tolerant Networks Jian Shen 1,2, Jin Wang 1,2, Li Ma 1,2, Ilyong Chung 3 1 Jiangsu Engineering Center of Network Monitoring, Nanjing University of Information Science
Improvement of Buffer Scheme for Delay Tolerant Networks Jian Shen 1,2, Jin Wang 1,2, Li Ma 1,2, Ilyong Chung 3 1 Jiangsu Engineering Center of Network Monitoring, Nanjing University of Information Science
Bhopal, , India 3 M.Tech Scholor,Department Of Computer Science, BIST Bhopal. Bhopal, , India
 Indirect Mobile Data Transfer Under Bluetooth Protocol 1 Pramod Kumar Maurya, 2 Gireesh Dixit, 3 Jay Prakash Maurya 1 M.Tech Scholor, 2 HOD, Department Of Computer Science, MPM, Bhopal, Bhopal, 462021,
Indirect Mobile Data Transfer Under Bluetooth Protocol 1 Pramod Kumar Maurya, 2 Gireesh Dixit, 3 Jay Prakash Maurya 1 M.Tech Scholor, 2 HOD, Department Of Computer Science, MPM, Bhopal, Bhopal, 462021,
Channel Adaptive ACK Mechanism in IEEE Wireless Personal Area Networks
 Channel Adaptive ACK Mechanism in IEEE 802.15.3 Wireless Personal Area Networks Jong-In Lee 28 August 2008 Broadband Communication Laboratory Korea University FISC 2008 Outline Introduction System model
Channel Adaptive ACK Mechanism in IEEE 802.15.3 Wireless Personal Area Networks Jong-In Lee 28 August 2008 Broadband Communication Laboratory Korea University FISC 2008 Outline Introduction System model
A Study of Wireless Compressed Digitalaudio
 A Study of Wireless Compressed Digital Transmission Andreas Floros 1, Marios Koutroubas 2, Nicolas-Alexander Tatlas 2 and John Mourjopoulos 2 1 ATMEL Hellas S.A., Patras Science Park, Platani, 26 500 Patras,
A Study of Wireless Compressed Digital Transmission Andreas Floros 1, Marios Koutroubas 2, Nicolas-Alexander Tatlas 2 and John Mourjopoulos 2 1 ATMEL Hellas S.A., Patras Science Park, Platani, 26 500 Patras,
Exercises TCP/IP Networking With Solutions
 Exercises TCP/IP Networking With Solutions Jean-Yves Le Boudec Fall 2009 3 Module 3: Congestion Control Exercise 3.2 1. Assume that a TCP sender, called S, does not implement fast retransmit, but does
Exercises TCP/IP Networking With Solutions Jean-Yves Le Boudec Fall 2009 3 Module 3: Congestion Control Exercise 3.2 1. Assume that a TCP sender, called S, does not implement fast retransmit, but does
Real-time and Reliable Video Transport Protocol (RRVTP) for Visual Wireless Sensor Networks (VSNs)
 Real-time and Reliable Video Transport Protocol (RRVTP) for Visual Wireless Sensor Networks (VSNs) Dr. Mohammed Ahmed Abdala, Mustafa Hussein Jabbar College of Information Engineering, Al-Nahrain University,
Real-time and Reliable Video Transport Protocol (RRVTP) for Visual Wireless Sensor Networks (VSNs) Dr. Mohammed Ahmed Abdala, Mustafa Hussein Jabbar College of Information Engineering, Al-Nahrain University,
Bluetooth. Bluetooth Radio
 Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Bluetooth Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol stack for low-power, short-range wireless data communications between fixed and mobile devices, and can be used to create Personal Area Networks (PANs).
Improving Wireless Link Throughput via Interleaved FEC
 Improving Wireless Link Throughput via Interleaved FEC Ling-Jyh Chen, Tony Sun, M. Y. Sanadidi, Mario Gerla UCLA Computer Science Department, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA {cclljj, tonysun, medy, gerla}@cs.ucla.edu
Improving Wireless Link Throughput via Interleaved FEC Ling-Jyh Chen, Tony Sun, M. Y. Sanadidi, Mario Gerla UCLA Computer Science Department, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA {cclljj, tonysun, medy, gerla}@cs.ucla.edu
Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009
 I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
I. Overview of Bluetooth Introduction to Wireless Networking ECE 401WN Spring 2009 Lecture 6: Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 Chapter 15 Bluetooth and IEEE 802.15 What is Bluetooth? An always-on, short-range
A Rate-adaptive MAC Protocol Based on TCP Throughput for Ad Hoc Networks in fading channels
 A Rate-adaptive MAC Protocol Based on TCP Throughput for Ad Hoc Networks in fading channels Shoko Uchida, Katsuhiro Naito, Kazuo Mori, and Hideo Kobayashi Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering,
A Rate-adaptive MAC Protocol Based on TCP Throughput for Ad Hoc Networks in fading channels Shoko Uchida, Katsuhiro Naito, Kazuo Mori, and Hideo Kobayashi Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering,
CHAPTER 4 CROSS LAYER INTERACTION
 38 CHAPTER 4 CROSS LAYER INTERACTION The cross layer interaction techniques used in the lower layers of the protocol stack, solve the hidden and exposed terminal problems of wireless and ad hoc networks.
38 CHAPTER 4 CROSS LAYER INTERACTION The cross layer interaction techniques used in the lower layers of the protocol stack, solve the hidden and exposed terminal problems of wireless and ad hoc networks.
CS4/MSc Computer Networking. Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth
 CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
CS4/MSc Computer Networking Lecture 13: Personal Area Networks Bluetooth Computer Networking, Copyright University of Edinburgh 2005 BlueTooth Low cost wireless connectivity for Personal Area Networks
Simulation of Bluetooth Network
 Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Simulation of Bluetooth Network Lennart Lagerstedt Stockholm, 2003 Master of Science Thesis Project The Department of Microelectronics and Information Technology, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) Lennart
Interference Mitigation Technique for Performance Enhancement in Coexisting Bluetooth and WLAN
 2012 International Conference on Information and Computer Networks (ICICN 2012) IPCSIT vol. 27 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Interference Mitigation Technique for Performance Enhancement in Coexisting
2012 International Conference on Information and Computer Networks (ICICN 2012) IPCSIT vol. 27 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Interference Mitigation Technique for Performance Enhancement in Coexisting
Performance Comparison of Mobility Generator C4R and MOVE using Optimized Link State Routing (OLSR)
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 11 (November. 2016), V1 PP 25-29 www.iosrjen.org Performance Comparison of Mobility Generator and MOVE using
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 06, Issue 11 (November. 2016), V1 PP 25-29 www.iosrjen.org Performance Comparison of Mobility Generator and MOVE using
original standard a transmission at 5 GHz bit rate 54 Mbit/s b support for 5.5 and 11 Mbit/s e QoS
 IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
IEEE 802.11 The standard defines a wireless physical interface and the MAC layer while LLC layer is defined in 802.2. The standardization process, started in 1990, is still going on; some versions are:
Queuing Delay and Achievable Throughput in Random Access Wireless Ad Hoc Networks
 Queuing Delay and Achievable Throughput in Random Access Wireless Ad Hoc Networks Nabhendra Bisnik and Alhussein Abouzeid Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Troy, NY bisnin@rpi.edu, abouzeid@ecse.rpi.edu
Queuing Delay and Achievable Throughput in Random Access Wireless Ad Hoc Networks Nabhendra Bisnik and Alhussein Abouzeid Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Troy, NY bisnin@rpi.edu, abouzeid@ecse.rpi.edu
An Adaptive Scheduling Algorithm for Bluetooth Ad-hoc Networks
 An Adaptive Scheduling Algorithm for Bluetooth Ad-hoc Networks Raymond Y.L. Lee and Vincent W.S. Wong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of British Columbia,Vancouver, BC,
An Adaptive Scheduling Algorithm for Bluetooth Ad-hoc Networks Raymond Y.L. Lee and Vincent W.S. Wong Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of British Columbia,Vancouver, BC,
Effect of Payload Length Variation and Retransmissions on Multimedia in a WLANs
 Effect of Payload Length Variation and Retransmissions on Multimedia in 8.a WLANs Sayantan Choudhury Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering sayantan@ece.ucsb.edu Jerry D. Gibson Dept. of Electrical
Effect of Payload Length Variation and Retransmissions on Multimedia in 8.a WLANs Sayantan Choudhury Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering sayantan@ece.ucsb.edu Jerry D. Gibson Dept. of Electrical
CC-SCTP: Chunk Checksum of SCTP for Enhancement of Throughput in Wireless Network Environments
 CC-SCTP: Chunk Checksum of SCTP for Enhancement of Throughput in Wireless Network Environments Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) uses the 32-bit checksum in the common header, by which a corrupted
CC-SCTP: Chunk Checksum of SCTP for Enhancement of Throughput in Wireless Network Environments Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) uses the 32-bit checksum in the common header, by which a corrupted
Dynamic Power Control MAC Protocol in Mobile Adhoc Networks
 Dynamic Power Control MAC Protocol in Mobile Adhoc Networks Anita Yadav Y N Singh, SMIEEE R R Singh Computer Science and Engineering Electrical Engineering Computer Science and Engineering Department Department
Dynamic Power Control MAC Protocol in Mobile Adhoc Networks Anita Yadav Y N Singh, SMIEEE R R Singh Computer Science and Engineering Electrical Engineering Computer Science and Engineering Department Department
Error Control in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Cross Layer Analysis
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln CSE Journal Articles Computer Science and Engineering, Department of 2009 Error Control in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Cross
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln CSE Journal Articles Computer Science and Engineering, Department of 2009 Error Control in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Cross
Optimizing Joint Erasure- and Error-Correction Coding for Wireless Packet Transmissions
 Optimizing Joint Erasure- and Error-Correction Coding for Wireless Packet Transmissions 2007 IEEE Communication Theory Workshop Christian R. Berger 1, Shengli Zhou 1, Yonggang Wen 2, Peter Willett 1 and
Optimizing Joint Erasure- and Error-Correction Coding for Wireless Packet Transmissions 2007 IEEE Communication Theory Workshop Christian R. Berger 1, Shengli Zhou 1, Yonggang Wen 2, Peter Willett 1 and
SIMULATION FRAMEWORK MODELING
 CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION FRAMEWORK MODELING 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter starts with the design and development of the universal mobile communication system network and implementation of the TCP congestion
CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION FRAMEWORK MODELING 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter starts with the design and development of the universal mobile communication system network and implementation of the TCP congestion
RD-TCP: Reorder Detecting TCP
 RD-TCP: Reorder Detecting TCP Arjuna Sathiaseelan and Tomasz Radzik Department of Computer Science, King s College London, Strand, London WC2R 2LS {arjuna,radzik}@dcs.kcl.ac.uk Abstract. Numerous studies
RD-TCP: Reorder Detecting TCP Arjuna Sathiaseelan and Tomasz Radzik Department of Computer Science, King s College London, Strand, London WC2R 2LS {arjuna,radzik}@dcs.kcl.ac.uk Abstract. Numerous studies
Bluetooth Demystified
 Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth Demystified S-72.4210 Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications Er Liu liuer@cc.hut.fi -10 Content Outline Bluetooth History Bluetooth Market and Applications Bluetooth Protocol Stacks Radio
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication
 Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Bluetooth: Short-range Wireless Communication Wide variety of handheld devices Smartphone, palmtop, laptop Need compatible data communication interface Complicated cable/config. problem Short range wireless
Performance Evaluation of Modified IEEE MAC for Multi-Channel Multi-Hop Ad Hoc Network *
 Performance Evaluation of Modified IEEE 802.11 MAC for Multi-Channel Multi-Hop Ad Hoc Network * Jiandong LI ISN Lab., Xidian University JL384@cornell.edu Zygmunt J. Haas Cornell University haas@ece.cornell.edu
Performance Evaluation of Modified IEEE 802.11 MAC for Multi-Channel Multi-Hop Ad Hoc Network * Jiandong LI ISN Lab., Xidian University JL384@cornell.edu Zygmunt J. Haas Cornell University haas@ece.cornell.edu
Inside Bluetooth. Host. Bluetooth. Module. Application RFCOMM SDP. Transport Interface. Transport Bus. Host Controller Interface
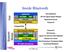 Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Inside Bluetooth Application Host Application Host Audio (SCO) RFCOMM SDP Data (ACL) Control API and Legacy Support Modules Bluetooth HCI Driver Transport Interface Physical I/F Transport Bus Bluetooth
Makidis Michael.
 Makidis Michael mmakidis05@aueb.gr RLC protocol overview procedures Simulation setup Performance of applications without contention Performance of applications with contention Performance of CBR Media
Makidis Michael mmakidis05@aueb.gr RLC protocol overview procedures Simulation setup Performance of applications without contention Performance of applications with contention Performance of CBR Media
MAC Protocol Proposal for Fixed BWA Networks Based on DOCSIS. Re: Medium Access Control Task Group Call for Contributions Session #4
 Project Title Date Submitted IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group MAC Protocol Proposal for Fixed BWA Networks Based on DOCSIS 1999-10-29 Source Phil Guillemette SpaceBridge Networks Corporation
Project Title Date Submitted IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group MAC Protocol Proposal for Fixed BWA Networks Based on DOCSIS 1999-10-29 Source Phil Guillemette SpaceBridge Networks Corporation
554 IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL. 13, NO. 3, JUNE Ian F. Akyildiz, Fellow, IEEE, Özgür B. Akan, Member, IEEE, and Giacomo Morabito
 554 IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL 13, NO 3, JUNE 2005 A Rate Control Scheme for Adaptive Real-Time Applications in IP Networks With Lossy Links and Long Round Trip Times Ian F Akyildiz, Fellow,
554 IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING, VOL 13, NO 3, JUNE 2005 A Rate Control Scheme for Adaptive Real-Time Applications in IP Networks With Lossy Links and Long Round Trip Times Ian F Akyildiz, Fellow,
Maximizing the Lifetime of Clustered Wireless Sensor Network VIA Cooperative Communication
 Vol., Issue.3, May-June 0 pp--7 ISSN: - Maximizing the Lifetime of Clustered Wireless Sensor Network VIA Cooperative Communication J. Divakaran, S. ilango sambasivan Pg student, Sri Shakthi Institute of
Vol., Issue.3, May-June 0 pp--7 ISSN: - Maximizing the Lifetime of Clustered Wireless Sensor Network VIA Cooperative Communication J. Divakaran, S. ilango sambasivan Pg student, Sri Shakthi Institute of
Impact of IEEE MAC Packet Size on Performance of Wireless Sensor Networks
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 10, Issue 3, Ver. IV (May - Jun.2015), PP 06-11 www.iosrjournals.org Impact of IEEE 802.11
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 10, Issue 3, Ver. IV (May - Jun.2015), PP 06-11 www.iosrjournals.org Impact of IEEE 802.11
On the Importance of Using Appropriate Link-to-System Level Interfaces for the Study of Link Adaptation
 On the Importance of Using Appropriate Link-to-System Level Interfaces for the Study of Link Adaptation Javier Gozalvez and John Dunlop Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of
On the Importance of Using Appropriate Link-to-System Level Interfaces for the Study of Link Adaptation Javier Gozalvez and John Dunlop Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of
Comparing Bluetooth HDP and SPP for Mobile Health Devices
 Comparing Bluetooth HDP and SPP for Mobile Health Devices Jad Noueihed, Robert Diemer, Samarjit Chakraborty and Stefanie Biala Institute for Real-Time Computer Systems, TU Munich Vodafone Group R&D Germany,
Comparing Bluetooth HDP and SPP for Mobile Health Devices Jad Noueihed, Robert Diemer, Samarjit Chakraborty and Stefanie Biala Institute for Real-Time Computer Systems, TU Munich Vodafone Group R&D Germany,
Adaptive QoS Platform in Multimedia Networks
 Adaptive QoS Platform in Multimedia Networks Mahmoud Sherif, Ibrahim Habib, Mahmoud Naghshineh, and Parviz Kermani CUNY Graduate School and Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New
Adaptive QoS Platform in Multimedia Networks Mahmoud Sherif, Ibrahim Habib, Mahmoud Naghshineh, and Parviz Kermani CUNY Graduate School and Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New
An Efficient Bandwidth Estimation Schemes used in Wireless Mesh Networks
 An Efficient Bandwidth Estimation Schemes used in Wireless Mesh Networks First Author A.Sandeep Kumar Narasaraopeta Engineering College, Andhra Pradesh, India. Second Author Dr S.N.Tirumala Rao (Ph.d)
An Efficient Bandwidth Estimation Schemes used in Wireless Mesh Networks First Author A.Sandeep Kumar Narasaraopeta Engineering College, Andhra Pradesh, India. Second Author Dr S.N.Tirumala Rao (Ph.d)
Random Assignment Protocols
 Random Assignment Protocols Random assignment strategies attempt to reduce problem occur in fixed assignment strategy by eliminating pre allocation of bandwidth to communicating nodes. Random assignment
Random Assignment Protocols Random assignment strategies attempt to reduce problem occur in fixed assignment strategy by eliminating pre allocation of bandwidth to communicating nodes. Random assignment
ENGI 4557 Digital Communications Practice Problems 2017 (Part 2)
 ENGI 4557 Digital Communications Practice Problems 207 (Part 2) H = n p i log 2 ( ) p i C = W log 2 ( + S N ) SNR = 6m + 0 log 0 ( 3σ2 x V ) 2 SNR = 6m 0 ( ) n n! = k k!(n k)! x = σ 2 = + + x p(x)dx (x
ENGI 4557 Digital Communications Practice Problems 207 (Part 2) H = n p i log 2 ( ) p i C = W log 2 ( + S N ) SNR = 6m + 0 log 0 ( 3σ2 x V ) 2 SNR = 6m 0 ( ) n n! = k k!(n k)! x = σ 2 = + + x p(x)dx (x
TCP PERFORMANCE FOR FUTURE IP-BASED WIRELESS NETWORKS
 TCP PERFORMANCE FOR FUTURE IP-BASED WIRELESS NETWORKS Deddy Chandra and Richard J. Harris School of Electrical and Computer System Engineering Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology Melbourne, Australia
TCP PERFORMANCE FOR FUTURE IP-BASED WIRELESS NETWORKS Deddy Chandra and Richard J. Harris School of Electrical and Computer System Engineering Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology Melbourne, Australia
2. Modelling of telecommunication systems (part 1)
 2. Modelling of telecommunication systems (part ) lect02.ppt S-38.45 - Introduction to Teletraffic Theory - Fall 999 2. Modelling of telecommunication systems (part ) Contents Telecommunication networks
2. Modelling of telecommunication systems (part ) lect02.ppt S-38.45 - Introduction to Teletraffic Theory - Fall 999 2. Modelling of telecommunication systems (part ) Contents Telecommunication networks
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0002906A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0002906A1 Rune (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2001 (54) METHOD AND ARRANGEMENT INA COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2001.0002906A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0002906A1 Rune (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 7, 2001 (54) METHOD AND ARRANGEMENT INA COMMUNICATION NETWORK (75) Inventor:
Design and Simulation of an Underwater Acoustic Local Area Network
 Design and Simulation of an Underwater Acoustic Local Area Network Ethem M. Sozer, Milica Stojanovic, and John G. Proakis Northeastern University, Communications and Digital Signal Processing Center 409
Design and Simulation of an Underwater Acoustic Local Area Network Ethem M. Sozer, Milica Stojanovic, and John G. Proakis Northeastern University, Communications and Digital Signal Processing Center 409
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology
 Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
Introduction to Bluetooth Wireless Technology Jon Inouye Staff Software Engineer Mobile Platforms Group Intel Corporation Bluetooth Bluetooth is is a a trademark trademark owned owned by by Bluetooth Bluetooth
