Chapter 3: VLANs. Routing & Switching
|
|
|
- Doris Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3: VLANs Routing & Switching
2 VLAN Definitions A VLAN is a logical partition of a Layer 2 network. VLANs logically group hosts, regardless of physical location. Multiple partitions can be created, allowing for multiple VLANs to co-exist. Each VLAN is a broadcast domain, usually with its own IP network. Devices in one VLAN do not hear the broadcasts from devices in another VLAN. VLANs are mutually isolated and packets can only pass between them via a router. The partitioning of the Layer 2 network takes place inside a Layer 2 device, usually via a switch. The hosts grouped within a VLAN are unaware of the VLAN s existence. After the initial boot of an unconfigured switch, all ports are members of the default VLAN. 2
3 VLAN Definitions 3
4 Benefits of VLANs Security Cost reduction Better performance Shrink broadcast domains Improved IT staff efficiency Simpler project and application management 4
5 Types of VLANs Data VLAN is a VLAN that is configured to carry user-generated traffic. Default VLAN contains all unconfigured switch ports after the initial boot up of a switch loading the default configuration and are part of the same broadcast domain. Native VLAN is assigned to an 802.1Q trunk port. Trunk ports are the links between switches that support the transmission of traffic associated with more than one VLAN (both tagged and untagged traffic) Management VLAN is any VLAN that is configured to access management features of the switch. 5
6 Voice VLANs VoIP traffic is time-sensitive and requires: Assured bandwidth to ensure voice quality. Transmission priority over other types of network traffic. Ability to be routed around congested areas on the network. Delay of less than 150 ms across the network. The voice VLAN feature enables access ports to carry IP voice traffic from an IP phone. The switch can connect to a Cisco IP phones and carry IP voice traffic. The sound quality of an IP phone call can deteriorate if the data is unevenly sent; the switch supports quality of service (QoS). 6
7 Voice VLANs The Cisco IP phone has two RJ-45 ports that each support connections to external devices. Network Port (10/100 SW) - Use this port to connect the phone to the network. The phone can also obtain inline power from the Cisco Catalyst switch over this connection. Access Port (10/100 PC) - Use this port to connect a network device, such as a computer, to the phone. 7
8 Voice VLANs 8
9 VLAN Trunks A VLAN trunk carries more than one VLAN. A VLAN trunk is usually established between switches so same-vlan devices can communicate, even if physically connected to different switches. A VLAN trunk is not associated to any VLANs; neither is the trunk ports used to establish the trunk link. Cisco IOS supports IEEE802.1Q, a popular VLAN trunk protocol. Types of point-to-point connections that utilize VLAN trunking: between two switches that utilize multiple VLANs between a switch and a server that has an 802.1Q NIC 9
10 VLAN Trunks 10
11 Controlling Broadcast Domains with VLANs VLANs can be used to limit the reach of broadcast frames. A VLAN is a broadcast domain of its own. A broadcast frame sent by a device in a specific VLAN is forwarded within that VLAN only. VLANs help control the reach of broadcast frames and their impact in the network. Unicast and multicast frames are forwarded within the originating VLAN. 11
12 Tagging Ethernet Frames for VLAN Identification Frame tagging is the process of adding a VLAN identification header to the frame. It is used to properly transmit multiple VLAN frames through a trunk link. Switches tag frames to identify the VLAN to that they belong. Different tagging protocols exist; IEEE 802.1Q is a vey popular example. The protocol defines the structure of the tagging header added to the frame. Switches add VLAN tags to the frames before placing them into trunk links and remove the tags before forwarding frames through nontrunk ports. When properly tagged, the frames can transverse any number of switches via trunk links and still be forwarded within the correct VLAN at the destination. 12
13 Tagging Ethernet Frames for VLAN Identification 13
14 Tagging Ethernet Frames for VLAN Identification A frame is traveling between PC-A and PC-B through the switch. What VLAN tagging is added to the frame? No VLAN tag is added to the frame 14
15 Native VLANs and 802.1Q Tagging Frames that belong to the native VLAN are not tagged. Frames received untagged remain untagged and are placed in the native VLAN when forwarded. If there are no ports associated to the native VLAN and no other trunk links, an untagged frame is dropped. In Cisco switches, the native VLAN is VLAN 1, by default. Two types of point-to-point connections utilize VLAN trunking: between two switches that utilize multiple VLANs between a switch and a server that has an 802.1Q NIC An 802.1Q trunk port, with a native VLAN assigned, supports both tagged and untagged traffic. 15
16 Voice VLAN Tagging 16
17 VLAN Ranges on Catalyst Switches Cisco Catalyst 2960 and 3560 Series switches support over 4,000 VLANs. VLANs are split into two categories: Normal range VLANs VLAN numbers from 1 to 1,005 Configurations stored in the vlan.dat (in the flash memory) VTP can only learn and store normal range VLANs Extended Range VLANs VLAN numbers from 1,006 to 4,096 Configurations stored in the running configuration (NVRAM) VTP does not learn extended range VLANs 17
18 Resetting a Switch How do you clear all VLAN information from the switch? 1. Delete the startup configuration 2. Delete the vlan.dat file in the flash memory 3. Reboot the switch 18
19 Creating a VLAN 19
20 Assigning Ports to VLANs 20
21 Assigning Ports to VLANs What is the effect of issuing a switchport access vlan 20 command on the Fa0/18 port of a switch that does not have this VLAN in the VLAN database? VLAN 20 will be created automatically 21
22 Assigning a Voice VLAN 22
23 Changing VLAN Port Membership Port Fa0/11 on a switch is assigned to VLAN 30. If the command no switchport access vlan 30 is entered on the Fa0/11 interface, what will happen? Port Fa0/11 will be returned to VLAN 1 23
24 Changing VLAN Port Membership What must the network administrator do to remove Fast Ethernet port fa0/1 from VLAN 2 and assign it to VLAN 3? Enter the switchport access vlan 3 command in interface configuration mode. 24
25 Deleting VLANs What happens to a port that is associated with VLAN 20 when the administrator deletes VLAN 20 from the switch? The port becomes inactive. 25
26 Verifying VLAN Information The show vlan command displays the VLAN assignment for all ports as well as the existing VLANs on the switch. 26
27 Verifying VLAN Information 27
28 Verifying VLAN Information Which command displays the encapsulation type, the voice VLAN ID, and the access mode VLAN for the Fa0/1 interface? show interfaces Fa0/1 switchport 28
29 Verifying VLAN Information PC-C broadcasts a packet. Which PCs will receive the broadcast sent by PC-C? PC-D, PC-E 29
30 Configuring IEEE 802.1q Trunk Links A Cisco switch currently allows traffic tagged with VLANs 10 and 20 across trunk port Fa0/5. What is the effect of issuing a switchport trunk allowed vlan 30 command on Fa0/5? It allows only VLAN 30 on Fa0/5 30
31 Resetting the Trunk To Default State 31
32 Resetting the Trunk To Default State 32
33 Verifying Trunk Configuration What VLANs are allowed across a trunk when the range of allowed VLANs is set to the default value? All VLANs will be allowed across the trunk. 33
34 Troubleshooting VLANs DLS1 is connected to another switch, DLS2, via a trunk link. A host that is connected to DLS1 is not able to communicate to a host that is connected to DLS2, even though they are both in VLAN 99. Which command should be added to Fa0/1 on DLS1 to correct the problem? switchport trunk native vlan 66 34
35 Troubleshooting VLANs PC-A and PC-B are both in VLAN 60. PC-A is unable to communicate with PC-B. What is the problem? The VLAN that is used by PC-A is not in the list of allowed VLANs on the trunk. 35
36 Troubleshooting VLANs Interface Fa0/1 is connected to a PC. Fa0/2 is a trunk link to another switch. All other ports are unused. Which security best practice did the administrator forget to configure? All user ports are associated with VLANs distinct from VLAN 1 and distinct from the 'black-hole' VLAN. 36
37 Introduction to Dynamic Trunking Protocol Switch ports can be manually configured to form trunks. Switch ports can also be configured to negotiate and establish a trunk link with a connected peer. The Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) manages trunk negotiation. DTP is a Cisco proprietary protocol and is enabled, by default, in Cisco Catalyst 2960 and 3560 switches. If the port on the neighbor switch is configured in a trunk mode that supports DTP, it manages the negotiation. The default DTP configuration for Cisco Catalyst 2960 and 3560 switches is dynamic auto. 37
38 Dynamic Trunking Protocol Cisco Catalyst 2960 and 3560 support the following trunk modes: Switchport mode dynamic auto makes the interface become a trunk interface if the neighboring interface is set to trunk or desirable mode. Switchport mode dynamic desirable makes the interface actively attempt to convert the link to a trunk link. Switchport mode trunk puts the interface into permanent trunking mode and negotiates to convert the neighboring link into a trunk link. Switchport mode nonegotiate prevents the interface from generating DTP frames. 38
39 Dynamic Trunking Protocol Under which two occasions should an administrator disable DTP while managing a local area network? When connecting a Cisco switch to a non-cisco switch On links that should not be trunking Which command should the network administrator implement to prevent the transfer of DTP frames between a Cisco switch and a non-cisco switch? S1(config-if)# switchport nonegotiate 39
40 IP Addressing Issues with VLAN It is a common practice to associate a VLAN with an IP network. Because different IP networks only communicate through a router, all devices within a VLAN must be part of the same IP network to communicate. The figure displays that PC1 cannot communicate to the server because it has a wrong IP address configured. 40
41 Common Problems with Trunks Trunking issues are usually associated with incorrect configurations. The most common type of trunk configuration errors are: Native VLAN mismatches Trunk mode mismatches Allowed VLANs on trunks If a trunk problem is detected, the best practice guidelines recommend to troubleshoot in the order shown above. 41
42 Trunk Mode Mismatches If a port on a trunk link is configured with a trunk mode that is incompatible with the neighboring trunk port, a trunk link fails to form between the two switches. Use the show interfaces trunk command to check the status of the trunk ports on the switches. To fix the problem, configure the interfaces with proper trunk modes. 42
43 Incorrect VLAN List VLANs must be allowed in the trunk before their frames can be transmitted across the link. Use the switchport trunk allowed vlan command to specify which VLANs are allowed in a trunk link. Use the show interfaces trunk command to ensure the correct VLANs are permitted in a trunk. 43
44 Incorrect VLAN List PC-A and PC-B are both in VLAN 60. PC-A is unable to communicate with PC-B. What is the problem? The VLAN that is used by PC-A is not in the list of allowed VLANs on the trunk 44
45 Incorrect VLAN List DLS1 is connected to another switch, DLS2, via a trunk link. A host that is connected to DLS1 is not able to communicate to a host that is connected to DLS2, even though they are both in VLAN 99. Which command should be added to Fa0/1 on DLS1 to correct the problem? switchport trunk native vlan 66 45
46 Switch Spoofing Attack There are a number of different types of VLAN attacks in modern switched networks; VLAN hopping is one example. The default configuration of the switch port is dynamic auto. In a basic VLAN hopping attack, attackers take advantage of the default automatic trunking configuration switch feature. By configuring a host to act as a switch and form a trunk, an attacker could gain access to any VLAN in the network. Because the attacker is now able to access other VLANs, this is called a VLAN hopping attack. To prevent a basic switch spoofing attack, turn off trunking on all ports, except the ones that specifically require trunking. Change the native VLAN number to one that is distinct from all user VLANs and is not VLAN 1 Disable DTP auto negotiation on end-user ports. 46
47 PVLAN Edge The Private VLAN (PVLAN) Edge feature, also known as protected ports, ensures that there is no exchange of unicast, broadcast, or multicast traffic between protected ports on the switch. Local relevancy only. A protected port only exchanges traffic with unprotected ports. A protected port does not exchange traffic with another protected port. 47
48 Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) Switch 1 Configuration Switch# conf t Switch(config)# spanning-tree mode pvst Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 4096 Switch(config)# interface FastEthernet0/2 Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 2 Switch(config-if)# interface FastEthernet0/21 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Switch(config-if)# interface FastEthernet0/22 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Switch(config-if)# interface FastEthernet0/23 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Switch(config-if)# interface FastEthernet0/24 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Switch(config-if)# interface GigabitEthernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Switch(config-if)# interface GigabitEthernet0/2 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) maintains a spanning tree instance for each VLAN configured in the network. It uses ISL Trunking and allows a VLAN trunk to be forwarding for some VLANs while blocking for other VLANs. Since PVST treats each VLAN as a separate network, it has the ability to load balance traffic (at layer-2) by forwarding some VLANs on one trunk and other Vlans on another trunk without causing a Spanning Tree loop. 48
49 VLAN Design Guidelines Move all ports from VLAN 1 and assign them to a not-in-use VLAN Shut down all unused switch ports. Separate management and user data traffic. Change the management VLAN to a VLAN other than VLAN 1. (The same goes to the native VLAN.) Ensure that only devices in the management VLAN can connect to the switches. The switch should only accept SSH connections. Disable autonegotiation on trunk ports. Do not use the auto or desirable switch port modes. 49
50 Inter-VLAN Routing Switch Configuration Switch# conf t Switch(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk Switch(config-if)# interface FastEthernet0/3 Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10 Switch(config-if)# interface FastEthernet0/5 Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 20 Switch(config-if)# interface FastEthernet0/7 Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 30 Switch(config-if)# interface Vlan1 Switch(config-if)# ip address Switch(config-if)# ip default-gateway
51 Inter-VLAN Routing Router Configuration Router# conf t Router(config)# interface FastEthernet0/0.1 Router(config-if)# description Management VLAN 1 Router(config-if)# encapsulation dot1q 1 native Router(config-if)# ip address Router(config-if)# interface FastEthernet0/0.10 Router(config-if)# description Accounting VLAN 10 Router(config-if)# encapsulation dot1q 10 Router(config-if)# ip address Router(config-if)# interface FastEthernet0/0.20 Router(config-if)# description Marketing VLAN 20 Router(config-if)# encapsulation dot1q 20 Router(config-if)# ip address Router(config-if)# interface FastEthernet0/0.30 Router(config-if)# description Engineering VLAN 30 Router(config-if)# encapsulation dot1q 30 Router(config-if)# ip address
52 Virtual Trunking Protocol (VTP) Switch 2 Configuration Switch(config)#int vlan 1 Switch(config-if)#ip address Switch(config-if)#no shut Switch(config)# vtp mode server Switch(config)# vtp domain group1 Switch(config)# vtp password cisco Switch(config)#int fa0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode trunk Add VLANs to this switch Switch 2 Configuration Switch(config)#int vlan 1 Switch(config-if)#ip address Switch(config-if)#no shut Switch(config)# vtp mode client Switch(config)# vtp domain group1 Switch(config)# vtp password cisco Switch(config)#int fa0/1 Switch(config-if)#switchport mode trunk 52
53 53
CHAPTER 1: VLANS. Routing & Switching
 CHAPTER 1: VLANS Routing & Switching CHAPTER 1 1.1 VLAN Segmentation 1.2 VLAN Implementation 1.3 VLAN Security and Design 1.4 Summary CHAPTER 1 : OBJECTIVES Explain the purpose of VLANs in a switched network.
CHAPTER 1: VLANS Routing & Switching CHAPTER 1 1.1 VLAN Segmentation 1.2 VLAN Implementation 1.3 VLAN Security and Design 1.4 Summary CHAPTER 1 : OBJECTIVES Explain the purpose of VLANs in a switched network.
1. Which two statements are true about VLAN implementation? (Choose two.)
 CCNA 2 Chapter 3 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Which two statements are true about VLAN implementation? (Choose two.) The size of the collision domain is reduced. The number of required switches in
CCNA 2 Chapter 3 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Which two statements are true about VLAN implementation? (Choose two.) The size of the collision domain is reduced. The number of required switches in
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
7 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco MWR 2941 router. It includes information about VLAN
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification. Comparing ISL and 802.1Q. VLAN Trunking
 Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Maintaining Specific VLAN Identification Specifically developed for multi-vlan interswitch communications Places a unique identifier in each frame Functions at Layer 2 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. It includes information
Cisco Exploration 3 Module 3 LAN Switching and Wireless Jim Johnston Class Notes September 9, 2008
 Cisco Exploration 3 Module 3 LAN Switching and Wireless Jim Johnston Class Notes September 9, 2008 VLAN is a logically separate IP subnetwork. This allows multiple networks to exist on a switch and provide
Cisco Exploration 3 Module 3 LAN Switching and Wireless Jim Johnston Class Notes September 9, 2008 VLAN is a logically separate IP subnetwork. This allows multiple networks to exist on a switch and provide
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN modes and the VLAN Membership
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
VLAN Configuration. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the CGR 2010 ESM. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring VLAN Trunks
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Sybex CCENT Chapter 11: VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing. Instructor & Todd Lammle
 Sybex CCENT 100-101 Chapter 11: VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 11 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: LAN Switching Technologies Describe how VLANs
Sybex CCENT 100-101 Chapter 11: VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing Instructor & Todd Lammle Chapter 11 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: LAN Switching Technologies Describe how VLANs
Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Configuring Private VLANs
 36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
Ch. 9 VTP (Trunking, VTP, Inter-VLAN Routing) CCNA 3 version 3.0
 Ch. 9 VTP (Trunking, VTP, Inter-VLAN Routing) CCNA 3 version 3.0 Overview Explain the origins and functions of VLAN trunking Describe how trunking enables the implementation of VLANs in a large network
Ch. 9 VTP (Trunking, VTP, Inter-VLAN Routing) CCNA 3 version 3.0 Overview Explain the origins and functions of VLAN trunking Describe how trunking enables the implementation of VLANs in a large network
CCENT Study Guide. Chapter 11 VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing
 CCENT Study Guide Chapter 11 VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing Chapter 11 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies 2.4 Configure, verify, and troubleshoot
CCENT Study Guide Chapter 11 VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing Chapter 11 Objectives The CCENT Topics Covered in this chapter include: 2.0 LAN Switching Technologies 2.4 Configure, verify, and troubleshoot
VLANs. CCNA Exploration Semester 3 Chapter Sep-13
 VLANs CCNA Exploration Semester 3 Chapter 3 1 Topics The role of VLANs in a network Trunking VLANs Configure VLANs on switches Troubleshoot common VLAN problems 2 Semester 3 LAN Design Basic Switch Concepts
VLANs CCNA Exploration Semester 3 Chapter 3 1 Topics The role of VLANs in a network Trunking VLANs Configure VLANs on switches Troubleshoot common VLAN problems 2 Semester 3 LAN Design Basic Switch Concepts
VLANs and Trunking C H A P T E R. 6-1: VLAN Configuration. Section 6-1
 C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
C H A P T E R 6 Section 6-1 VLANs and Trunking See the following sections for configuration information about these topics: 6-1: VLAN Configuration Describes the method for configuring, creating, and configuring
Chapter 3. Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) Part II
 Chapter 3 Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) Part II CCNA3-1 Chapter 3-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Chapter 3 Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) Part II CCNA3-1 Chapter 3-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 일년무료업데이트서비스제공
 itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. VLANs, Trunking, & VTP. VLANs Overview
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp VLANs, Trunking, & VTP http:// VLANs Overview Virtual Local Area Network Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain Switches create a separate CAM table
Configuring Interface Characteristics
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. The
CHAPTER 10 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. The
Introduction to Switched Networks Routing And Switching
 Introduction to Switched Networks Routing And Switching 1 Converged Networks Growing Complexity of Networks Our digital world is changing Information must be accessed from anywhere in the world Networks
Introduction to Switched Networks Routing And Switching 1 Converged Networks Growing Complexity of Networks Our digital world is changing Information must be accessed from anywhere in the world Networks
For information about configuring these settings from Cluster Management Suite (CMS), refer to the online help.
 Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring VLANs This chapter provides information about configuring virtual LANs (VLANs). It includes command-line interface (CLI) procedures for using commands that have been specifically created or
Configuring Interface Characteristics
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Catalyst 3750 switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch
CHAPTER 11 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Catalyst 3750 switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch
Configuring Voice VLAN
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure the voice VLAN feature on the Catalyst 3750 switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch stack. Voice VLAN
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure the voice VLAN feature on the Catalyst 3750 switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch stack. Voice VLAN
Configuring Cisco IP Phone Support
 CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure support for Cisco IP phones on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
CHAPTER 16 This chapter describes how to configure support for Cisco IP phones on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer
VLANs Level 3 Unit 9 Computer Networks
 VLANs Some Requirements of LANs Need to split up broadcast domains to make good use of bandwidth People in different departments may need to be grouped together for access to servers Security: restrict
VLANs Some Requirements of LANs Need to split up broadcast domains to make good use of bandwidth People in different departments may need to be grouped together for access to servers Security: restrict
Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.)
 Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Volume: 149 Questions Question No : 1 Which three of these statements regarding 802.1Q trunking are correct? (Choose three.) A. 802.1Q native VLAN frames are untagged by default. B. 802.1Q trunking ports
Configuring Interface Characteristics
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter defines the types of Catalyst 2975 interfaces and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch stack. Understanding
CHAPTER 12 This chapter defines the types of Catalyst 2975 interfaces and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and a switch stack. Understanding
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling
 CHAPTER 26 This chapter describes how to configure IEEE 802.1Q tunneling in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS
CHAPTER 26 This chapter describes how to configure IEEE 802.1Q tunneling in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. Understanding Interface Types, page 9-1 Using Interface Configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. Understanding Interface Types, page 9-1 Using Interface Configuration
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 7 Monitoring VLANs, page 19 Where to Go Next,
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
 34 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on the Catalyst 4500 series switches. SPAN selects network traffic for analysis by a network
34 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on the Catalyst 4500 series switches. SPAN selects network traffic for analysis by a network
: Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks
 Exam : Cisco 642-812 Title : Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks Version : Demo Cheat-Test,help you pass any IT exam! Q: 1 Which three statements about the Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol
Exam : Cisco 642-812 Title : Building Cisco Multilayer Switched Networks Version : Demo Cheat-Test,help you pass any IT exam! Q: 1 Which three statements about the Multiple Spanning Tree (MST) protocol
Configuring Private VLANs
 36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
36 CHAPTER This chapter describes private VLANs (PVLANs) on Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides restrictions, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major
Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces
 Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces Ethernet interfaces can be configured either as access ports or trunk ports. Trunks carry the traffic of multiple VLANs over a single link and allow you to extend
Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces Ethernet interfaces can be configured either as access ports or trunk ports. Trunks carry the traffic of multiple VLANs over a single link and allow you to extend
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
 41 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on the Catalyst 4500 series switches. SPAN selects network traffic for analysis by a network
41 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on the Catalyst 4500 series switches. SPAN selects network traffic for analysis by a network
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
 CHAPTER 32 This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on the Catalyst 3750-X or 3560-X switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a Catalyst
CHAPTER 32 This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on the Catalyst 3750-X or 3560-X switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a Catalyst
Configuring SPAN. Understanding SPAN CHAPTER. This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and on the Catalyst 2960 switch.
 CHAPTER 23 This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and on the Catalyst 2960 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see
CHAPTER 23 This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and on the Catalyst 2960 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see
Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
 CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
CHAPTER 14 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling With Release 12.1(13)E and later, the Catalyst 6500 series switches support IEEE 802.1Q tunneling and Layer 2 protocol tunneling.
Configuring Private VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for Private VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for Private VLANs, on page 1 Information About Private VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure Private VLANs, on
Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for Private VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for Private VLANs, on page 1 Information About Private VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure Private VLANs, on
Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for SPAN and RSPAN, page 1 Restrictions for SPAN and RSPAN, page 2 Information About SPAN and RSPAN, page 3 How to Configure SPAN and RSPAN, page 14 Monitoring
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for SPAN and RSPAN, page 1 Restrictions for SPAN and RSPAN, page 2 Information About SPAN and RSPAN, page 3 How to Configure SPAN and RSPAN, page 14 Monitoring
Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
 24 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for
24 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure Switched Port Analyzer (SPAN) and Remote SPAN (RSPAN) on your Catalyst 2950 or Catalyst 2955 switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for
Switches running the LAN Base feature set support only static routing on SVIs.
 Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, on page 2 Information About VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure VLANs, on page 6 Monitoring VLANs, on page
Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, on page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, on page 2 Information About VLANs, on page 2 How to Configure VLANs, on page 6 Monitoring VLANs, on page
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
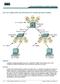 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Implement VTP. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 4 Modified by Tony Chen 10/01/2008
 Implement VTP LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 4 Modified by Tony Chen 10/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake on my PowerPoint
Implement VTP LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 4 Modified by Tony Chen 10/01/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake on my PowerPoint
Understanding and Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes private VLANs on the Catalyst 4000 family switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major sections:
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes private VLANs on the Catalyst 4000 family switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major sections:
Configuring Interface Characteristics
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1 How to Configure Interface Characteristics, page 11 Monitoring Interface Characteristics, page 28 Configuration Examples for Interface Characteristics,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Information About, page 1 How to Configure Interface Characteristics, page 11 Monitoring Interface Characteristics, page 28 Configuration Examples for Interface Characteristics,
Configuring VLANs. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for VLANs
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 8 Monitoring VLANs, page 22 Where to Go Next,
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLANs, page 1 Restrictions for VLANs, page 2 Information About VLANs, page 2 How to Configure VLANs, page 8 Monitoring VLANs, page 22 Where to Go Next,
Note: Use two 2960 switches for ALS1 and ALS2 and two 3560 switches for DLS1 and DLS2
 LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS
 Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
The following graphic shows a single switch VLAN configuration.
 7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
7.1. VLAN A Virtual LAN (VLAN) can be defined as: Broadcast domains defined by switch port rather than network address. A grouping of devices based on service need, protocol, or other criteria rather than
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Table of Contents. Cisco Using One DHCP Server for Voice and Data Networks
 Table of Contents Using One DHCP Server for Voice and Data Networks1 Document ID: 19580..1 Introduction.1 Prerequisites1 Requirements1 Components Used..1 Conventions..1 Problem.2 Solution.2 The Network
Table of Contents Using One DHCP Server for Voice and Data Networks1 Document ID: 19580..1 Introduction.1 Prerequisites1 Requirements1 Components Used..1 Conventions..1 Problem.2 Solution.2 The Network
Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
 Prerequisites for SPAN and RSPAN, page 1 Restrictions for SPAN and RSPAN, page 1 Information About SPAN and RSPAN, page 3 How to Configure SPAN and RSPAN, page 14 Monitoring SPAN and RSPAN Operations,
Prerequisites for SPAN and RSPAN, page 1 Restrictions for SPAN and RSPAN, page 1 Information About SPAN and RSPAN, page 3 How to Configure SPAN and RSPAN, page 14 Monitoring SPAN and RSPAN Operations,
CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0)
 200-125 - CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) 1.What is one benefit of PVST+? A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops. B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches
200-125 - CCNA Cisco Certified Network Associate CCNA (v3.0) 1.What is one benefit of PVST+? A. PVST+ supports Layer 3 load balancing without loops. B. PVST+ reduces the CPU cycles for all the switches
Interface and Hardware Components Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 9300 Switches)
 Interface and Hardware Components Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 9300 Switches) First Published: 2017-07-31 Last Modified: 2017-11-03 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc.
Interface and Hardware Components Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.x (Catalyst 9300 Switches) First Published: 2017-07-31 Last Modified: 2017-11-03 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc.
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
Configuring Link Aggregation
 Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 1 (GUI), page 3 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 4 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 1 (GUI), page 3 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 4 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
VLANs. LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 3. Version Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1
 VLANs LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 3 Version 4.0 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Explain the role of VLANs in a converged network. Explain the role of trunking
VLANs LAN Switching and Wireless Chapter 3 Version 4.0 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Explain the role of VLANs in a converged network. Explain the role of trunking
Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
 CHAPTER 22 This chapter describes how to configure the port-based traffic control features on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
CHAPTER 22 This chapter describes how to configure the port-based traffic control features on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in
Lab 5: Basic VLAN Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Configuring EtherChannels
 27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel on Layer 2 interfaces. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links between switches, routers, and servers. You can use it to increase
27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannel on Layer 2 interfaces. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links between switches, routers, and servers. You can use it to increase
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Advance Networks Laboratory Exp.4 Inter-VLAN Routing
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Advance Networks Laboratory 0907529 Exp.4 Inter-VLAN Routing Objectives 1. Describe the three primary options for
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Advance Networks Laboratory 0907529 Exp.4 Inter-VLAN Routing Objectives 1. Describe the three primary options for
Lab Configuring EtherChannel
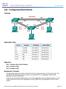 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Configuring Port Security
 33 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure port security on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It provides an overview of port security on the Catalyst 4500 series switch and details the configuration
33 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure port security on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. It provides an overview of port security on the Catalyst 4500 series switch and details the configuration
Configuring SmartPort Macros
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure and apply SmartPort macros on your switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the switch commands used in this chapter, look at the Cisco
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure and apply SmartPort macros on your switch. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the switch commands used in this chapter, look at the Cisco
Configuring Flex Links
 CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master
CHAPTER 18 This chapter describes how to configure Flex Links in Cisco IOS Release 12.2SX. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, see the Cisco IOS Master
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Configuring VTP. Understanding VTP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3560 switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) and the VLAN database for managing VLANs with the Catalyst 3560 switch. For complete syntax and usage information for the commands
CCIE Foundation. WorkBooks.com. Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP. 3550/3560 Switching. Answers
 CCIE Foundation The GAP from CCNP to CCIE WWW.Net WorkBooks.com Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP 3550/3560 Switching Answers CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 1 of
CCIE Foundation The GAP from CCNP to CCIE WWW.Net WorkBooks.com Narbik Kocharians CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SP 3550/3560 Switching Answers CCIE Foundation by Narbik Kocharians Switching Lab Page 1 of
Configuring Private VLANs Using NX-OS
 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on Cisco NX-OS devices. Private VLANs provide additional protection at the Layer 2 level. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature
This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on Cisco NX-OS devices. Private VLANs provide additional protection at the Layer 2 level. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior
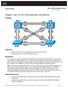 Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objectives Background Observe the behavior of a separate spanning tree instance per VLAN. Change spanning tree mode to rapid spanning tree. Four
Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0)
 CertBus.com 300-115 Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) Pass Cisco 300-115 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee
CertBus.com 300-115 Q&As Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH v2.0) Pass Cisco 300-115 Exam with 100% Guarantee Free Download Real Questions & Answers PDF and VCE file from: 100% Passing Guarantee
CCNA( ) Dumps V2.0( ) CCNA
 CCNA(200-125) Dumps V2.0(2018.1.3) CCNA 200-125 QUESTION 1 Which technology supports the stateless assignment of IPv6 addresses?(choose two.) A. DNS B. DHCPv6 C. DHCP D. autoconfiguration Correct Answer:
CCNA(200-125) Dumps V2.0(2018.1.3) CCNA 200-125 QUESTION 1 Which technology supports the stateless assignment of IPv6 addresses?(choose two.) A. DNS B. DHCPv6 C. DHCP D. autoconfiguration Correct Answer:
the larger the number of users and devices, the more broadcasts and packets each switch must handle.
 VLANs Introduction By default, routers allow broadcasts to occur only within the originating network, while switches forward broadcasts to all segments. Flat network = one broadcast domain. that the largest
VLANs Introduction By default, routers allow broadcasts to occur only within the originating network, while switches forward broadcasts to all segments. Flat network = one broadcast domain. that the largest
Configuring Link Aggregation
 Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 2 (GUI), page 4 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 5 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 2 (GUI), page 4 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 5 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
examcollection.premium.exam.157q. Exam code: Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks. Version 15.0
 300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.157q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 15.0 Question
300-115.examcollection.premium.exam.157q Number: 300-115 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 15.0 Exam code: 300-115 Exam name: Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Version 15.0 Question
Exam Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH)
 Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Exam 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) Multiple Choice Questions (2018-05-08 Updated) (300-115) Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
Cisco Certified Network Professional (CCNP) Exam 300-115 Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks (SWITCH) Multiple Choice Questions (2018-05-08 Updated) (300-115) Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트
 PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
 CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to use Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. REP is a Cisco proprietary protocol that provides an alternative to Spanning Tree Protocol
CHAPTER 19 This chapter describes how to use Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP) on the Catalyst 4500 series switch. REP is a Cisco proprietary protocol that provides an alternative to Spanning Tree Protocol
VLAN Configuration via CLI on 300/500 Series Managed Switches
 Article ID: 4986 4986 - VLAN Configuration via CLI on 300/500 Series Managed Switches Objective VLANs allow you to logically segment a LAN into different broadcast domains. In scenarios where sensitive
Article ID: 4986 4986 - VLAN Configuration via CLI on 300/500 Series Managed Switches Objective VLANs allow you to logically segment a LAN into different broadcast domains. In scenarios where sensitive
