Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition. Chapter 7: Network Hardware in Depth
|
|
|
- Brianna Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition Chapter 7: Network Hardware in Depth
2 Objectives Describe the advanced features and operation of network switches Describe routing table properties and discuss routing protocols Explain basic and advanced wireless access point features Select the most suitable NIC bus and features for a computer Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 2
3 Network Switches in Depth Switches work at the Data Link layer (Layer 2) Receive frames on one port and forward them out the port where the destination device can be found Switches send broadcast frames out all ports Each switch port is considered a collision domain (see figure on next slide) Switches do not forward collision information to any other ports Switch ports can operate in full-duplex mode Allows connected devices to transmit and receive simultaneously, eliminating the possibility of a collision Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3
4 Network Switches in Depth Each switch port is a collision domain Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 4
5 Switch Port Modes of Operation Ports on a typical 10/100 Mbps switch can usually operate in these modes: 10 Mbps half-duplex 100 Mbps half-duplex 10 Mbps full-duplex 100 Mbps full-duplex Most switches run in auto-negotiate mode, which means the switch sets the mode to the highest performance setting the connected device supports Auto-MDIX mode switches transmit and receive pairs automatically so a straight-through or crossover cable can be used Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5
6 Creating the Switching Table A switching table holds MAC address/port pairs that tell the switch where to forward a frame, based on the destination MAC address When a switch is first powered on, its table is empty As network devices send frames, the switch reads each frame s source address and adds it to the table along with the port it was received from If a frame s destination address isn t found in the switching table, the switch forwards the frame out all ports Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 6
7 Creating the Switching Table Switching tables can contain multiple MAC addresses per port Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7
8 Creating the Switching Table Most switches include a number that indicates the number of MAC addresses the switch can hold in its table (8K MAC addresses supported) Switching tables prevent stale entries by including a timestamp when an entry is created When a switch receives a frame from a device already in its table, it updates the entry with a new timestamp The period of time a table keeps a MAC address is called the aging time If the timestamp isn t updated within the aging time, the entry expires and is removed from the table Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 8
9 Frame Forwarding Methods Cut-through switching switch reads only enough of the incoming frame to determine the frame s source and destination address (fastest method) Disadvantage: no error checking Store-and-forward switching switch reads the entire frame into its buffers before forwarding it Switch examines the FCS field to make sure it contains no errors before forwarding the frame Fragment-free switching switch reads enough of the frame to guarantee that it s at least the minimum size for the network type Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 9
10 Advanced Switch Features High-end switches, often referred to as smart switches and managed switches, can help make a network more efficient and reliable The following slides are an overview of the most common features found in smart switches Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 10
11 Advanced Switch Features Multicast processing Switches process multicast frames in one of two ways By treating them as broadcasts and sending them out all ports Used by low-end switches or those that have not been configured for it By forwarding the frames only to ports that have registered the multicast address Used by switches that support Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Multicast MAC addresses always begin with 01:00:5E, leaving the rest of the address to identify a particular multicast application Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 11
12 Advanced Switch Features Spanning Tree Protocol Enables switches to detect when there is a potential for a switching loop (occurs when a frame is forwarded from one switch to another in an infinite loop) When a possible loop is detected, one of the switch ports goes into blocking mode, preventing it from forwarding frames that would create a loop If the loop configuration is broken, the switch that was in blocking mode resumes forwarding frames The next slide shows an example of a switching loop Simulation 15 STP prevents switching loops Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 12
13 Advanced Switch Features Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 13
14 Advanced Switch Features Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANS) enable you to configure one or more switch ports into separate broadcast domains It s like separating a switch into two or more switches that aren t connected to one another A router is needed to communicate between VLANs Improves management and security of the network and gives more control of broadcast frames Allows administrators to group users and resources logically instead of by physical location Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14
15 Advanced Switch Features VLANs logically group users and resources from different physical locations A trunk port is a switch Port configured to carry Traffic from all VLANs to another switch or router Simulation 16 How switches use trunk ports with VLANs Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 15
16 Advanced Switch Features Factors to consider before using VLANs Overuse of VLANs can end up costing you more than it benefits you More VLANs mean more logical networks so your network will be more complicated Every VLAN you create requires a corresponding router interface Routers are slower devices, so performance can decrease with the addition of more VLANs More router interfaces mean additional IP networks, which is likely to require subnetting your existing network Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 16
17 Advanced Switch Features Switch Port Security In some public buildings, network jacks with connections to switches are often available to public users, who can easily plug in a laptop that contain viruses, hacker tools, and other malware A switch with port security features can help prevent this type of connection Enables an administrator to limit how many and which MAC addresses can connect to a port If an unauthorized computer attempts to connect, the port can be disabled and a message can be sent to the administrator to alert them of the intrusion Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 17
18 Routers in Depth Routers operate at the Network layer (Layer 3) and work with packets Connect separate logical networks to form an internetwork Broadcast frames are not forwarded to other router ports (other networks) Routers can be used to create complex internetworks with multiple paths creating fault tolerance and load sharing All processing done by routers depends on the following features found on most routers: Router interfaces Routing tables Routing protocols Access control lists Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 18
19 Routers in Depth Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 19
20 Router Interfaces Routers must have two or more interfaces (ports) in order to take packets coming from one network and forward them to another network When a router interface receives a frame, it compares the destination MAC address with the interface s MAC address If they match, the router strips the frame header and trailer and reads the packet s destination IP address If the IP address matches it processes the packet If the IP address does not match, the router consults its routing table to determine how to get the packet to the its destination The process of moving a packet from the incoming interface to the outgoing interface is called packet forwarding Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 20
21 Router Interfaces Packets are forwarded from one network to another Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 21
22 Routing Tables Routing tables are composed of network address and interface pairs that tell the router which interface a packet should be forwarded to Most routing tables contain the following for each entry: Destination network: Usually expressed in CIDR notation such as /16 Next hop: The next hop indicates an interface name or the address of the next router in the path to the destination Total number of routers a packet must travel through is called the hop count Metric: Numeric value that tells the router how far away the destination network is (also called cost or distance) Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 22
23 Routing Tables Contents of routing tables (cont.): How the route is derived: This field tells you how the route gets into the routing table (one of 3 ways) Network is connected directly Administrator enters the route information manually (called a static route) Route information is entered dynamically, via a routing protocol Timestamp: Tells the router how long it has been since the routing protocol updated the dynamic route Simulation 17 Routers use multiple paths in an internetwork Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 23
24 Routing Tables Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 24
25 Routing Protocols Routing protocol A set of rules that routers use to exchange information so that all routers have accurate information about an internetwork to populate their routing tables Two main types of routing protocols Distance-vector protocols share information about an internetwork s status by copying a router s routing table to other routers (routers sharing a network are called neighbors) Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and RIPv2 are most common Link-state protocols share information with other routers by sending the status of all their interface links to other routers Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is most common Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 25
26 Routing Protocols Distance-vector versus link-state routing protocols Speed of convergence refers to how fast the routing tables of all routers in an internetwork are updated when a change in the network occurs Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 26
27 Routing Protocols Routing protocols are not a necessity in all situations, as static routes can be entered in a routing table manually. Consider the following: Does the network change often? If so, a routing protocol is probably a good choice Are there several alternate paths to many of the networks in the internetwork? If so, a routing protocol can reroute around down links or congested routes automatically Is the internetwork large? A routing protocol builds and maintains routing tables automatically Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 27
28 Access Control Lists Access Control List (ACL) A set of rules configured on a router s interface for specifying which addresses and which protocols can pass through an interface and to which destinations When an ACL blocks a packet it is called packet filtering Usually configured to block traffic based on: Source address Destination address Protocol Addresses can be specific IP addresses or network numbers and filtering can be done on either source or destination address or both Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 28
29 Wireless Access Points in Depth Basic wireless settings on most APs define the settings a client wireless device needs to connect to an AP: Wireless network mode: allows you to choose which standard the AP should operate under Wireless network name (SSID): when an AP is shipped, the SSID is set to a default value it is recommended that you change it upon setup Wireless channel: recommended that you set your channels five channels apart, such as 1, 6, and 11 SSID broadcast status: by default, APs are configured to transmit the SSID so that any wireless device in range can see the network Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 29
30 Wireless Security Options Most APs offer the following security options: Encryption Authentication MAC filtering AP isolation Encryption all private networks should use this Most common protocols are Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA), and Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) Use the highest level of security your systems support (all devices must use the same protocol) Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 30
31 Wireless Security Options Authentication If used, users must enter a username and password to access the wireless network APs that support authentication usually support the Remote Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) protocol MAC filtering enables you to restrict which devices can connect to your AP Add the MAC addresses of the wireless devices allowed to access your network to a list on the AP AP isolation creates a separate virtual network for each client connection Clients can access the Internet but can t communicate with each other Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 31
32 Advanced Wireless Settings Common advanced settings: Adjustable transmit power: Lets you control the power and range of the wireless network signal Multiple SSIDs: Two or more wireless networks can be created with different security settings VLAN support: To assign wireless networks to wired VLANs Traffic priority: If your AP is configured for multiple networks you can assign a priority to packets coming from each network Wi-Fi Multimedia: Provides Quality of Service (QoS) settings for multimedia traffic, giving priority to streaming audio or video AP modes: An AP can be set to operate as a traditional access point, a repeater, or a wireless bridge Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 32
33 Network Interface Cards in Depth PC Bus Options a bus makes the connections between a computer s vital components The faster the bus, the faster data can be transferred between these components, which makes for a faster system NICs are considered I/O devices and can be built into the motherboard or added as an expansion card Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus became the default bus standard Most implementations are 32-bit and operate at 33 MHz with a maximum data transfer rate of 133 MBps First bus to accommodate the Microsoft Plug-and-Play architecture Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 33
34 Network Interface Cards in Depth PC Bus Options (continued): PCI-X is backward-compatible with PCI but supports speeds from 66 MHz to 533 MHz, providing data transfers from 500 MBps to more than 4 GBps Accommodated developments in faster network cards PCIe uses a high-speed serial communication protocol of one or more lines or lanes Each lane can operate at 250 MBps in each direction PCIe 2.0 provides data rates of 500 MBps PCIe is now the dominant bus technology Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 34
35 Network Interface Cards in Depth PC Bus Options (continued): PCMCIA: credit card-sized expansion cards used mainly to add functionality to laptop computers Cardbus operates at 33 MHz and provides up to 132 MBps data transfer rates ExpressCard uses PCIe technology to provide data transfer rates up to 500 MBps USB: Universal Serial Bus comes in three versions: USB 1.0, USB 2.0, USB 3.0 and is now a standard interface on PCs and MACs Data rates increased with the release of each version Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 35
36 Advanced Features of NICs If a NIC is slow, it can limit network performance When selecting a network adapter, first identify the physical characteristics the card must match (type of bus, type of network technology, type of connector needed to connect to media) Hardware-enhancement options: Shared adapter memory: the adapter s buffers map directly to RAM on the computer Shared system memory: a NIC s onboard processor selects a region of RAM on the computer and writes to it as though it were buffer space on the adapter Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 36
37 Advanced Features of NICs Hardware-enhancement options (continued): Bus mastering: permits a network adapter to take control of the computer s bus to initiate and manage data transfers to and from the computer s memory RAM buffering: means a NIC includes additional memory to provide temporary storage for incoming and outgoing network data that arrives at the NIC faster than it can be sent out Onboard co-processors: enable the card to process incoming and outgoing network data without requiring service from the CPU QOS: allows prioritizing time-sensitive data Automatic link aggregation: enables you to install multiple NICs in one computer and aggregate the bandwidth Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 37
38 Advanced Features of NICs Hardware-enhancement options (continued): Improved fault tolerance by installing a second NIC Failure of the primary NIC shifts network traffic to the second NIC Advanced Configuration Power Management Interface (ACPI) offers wake-on LAN, which allows an administrator to power on a PC remotely by accessing the NIC through the network Preboot Execution Environment (PXE) allow a computer to download an OS instead of booting it from a local hard drive Used on diskless workstations ( thin clients ) that do not store the OS locally Typical desktop computers with basic features are usually adequate. Servers do warrant some of these high-end features Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 38
39 Chapter Summary Network switches use auto-negotiate mode to determine the link speed and duplex mode Switching tables can hold many more MAC addresses than ports Switches forward frames by using a variety of methods: cut-through, fragment-free, and store-and-forward Advanced features, such as VLANs, STP, multicast support, and port security are found on smart switches Routing tables contain destination networks, next hop addresses, metrics, methods used to derive routes, and timestamps Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 39
40 Chapter Summary Routing protocols populate routing tables dynamically. The most common type of routing protocols are distancevector and link-state Access points have the following basic settings: wireless mode, SSID, and wireless channel Higher-end APs can support advanced features, such as multiple SSIDs, adjustable transmit power, VLANs, QoS, and repeater and bridge modes NIC selection includes the PC bus Some advanced NIC features to consider include RAM buffering, onboard co-processors, automatic link aggregation, and multiple ports for fault tolerance Copyright 2012 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 40
Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition. Chapter 7: Network Hardware in Depth
 Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition Chapter 7: Network Hardware in Depth Objectives Describe the advanced features and operation of network switches Describe routing table properties and discuss
Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition Chapter 7: Network Hardware in Depth Objectives Describe the advanced features and operation of network switches Describe routing table properties and discuss
Full file at
 Guide to Networking Essentials, Sixth Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Network Hardware Essentials At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives Tips Quick Quizzes Class Discussion Topics
Guide to Networking Essentials, Sixth Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Network Hardware Essentials At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives Tips Quick Quizzes Class Discussion Topics
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Original slides by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Selection Criteria for Switching and Routing Protocols Network traffic
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Original slides by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Selection Criteria for Switching and Routing Protocols Network traffic
Chapter 2. Switch Concepts and Configuration. Part I
 Chapter 2 Switch Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 2-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Chapter 2 Switch Concepts and Configuration Part I CCNA3-1 Chapter 2-1 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor,
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies
 1. Explain different network devices in detail. Or Explain NIC (Network Interface Card) in detail. Network interface cards are add on cards as hardware cards on the motherboard. This is additional hardware
1. Explain different network devices in detail. Or Explain NIC (Network Interface Card) in detail. Network interface cards are add on cards as hardware cards on the motherboard. This is additional hardware
Basic Wireless Settings on the CVR100W VPN Router
 Basic Wireless Settings on the CVR100W VPN Router Objective A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) utilizes radio communication to connect wireless devices to a LAN. An example is a Wi-Fi hotspot at a cafe.
Basic Wireless Settings on the CVR100W VPN Router Objective A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) utilizes radio communication to connect wireless devices to a LAN. An example is a Wi-Fi hotspot at a cafe.
More on LANS. LAN Wiring, Interface
 More on LANS Chapters 10-11 LAN Wiring, Interface Mostly covered this material already NIC = Network Interface Card Separate processor, buffers incoming/outgoing data CPU might not be able to keep up network
More on LANS Chapters 10-11 LAN Wiring, Interface Mostly covered this material already NIC = Network Interface Card Separate processor, buffers incoming/outgoing data CPU might not be able to keep up network
Interface The exit interface a packet will take when destined for a specific network.
 The Network Layer The Network layer (also called layer 3) manages device addressing, tracks the location of devices on the network, and determines the best way to move data, which means that the Network
The Network Layer The Network layer (also called layer 3) manages device addressing, tracks the location of devices on the network, and determines the best way to move data, which means that the Network
Cisco CCNA (ICND1, ICND2) Bootcamp
 Cisco CCNA (ICND1, ICND2) Bootcamp Course Duration: 5 Days Course Overview This five-day course covers the essential topics of ICND1 and ICND2 in an intensive Bootcamp format. It teaches students the skills
Cisco CCNA (ICND1, ICND2) Bootcamp Course Duration: 5 Days Course Overview This five-day course covers the essential topics of ICND1 and ICND2 in an intensive Bootcamp format. It teaches students the skills
Chapter 4 Configuring Switching
 Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Using the Switching Tab The navigation tabs on the top of the home page include a Switching tab that lets you manage your GS108T Gigabit Smart Switch using features under
Chapter 4 Configuring Switching Using the Switching Tab The navigation tabs on the top of the home page include a Switching tab that lets you manage your GS108T Gigabit Smart Switch using features under
Network+ Guide to Networks 7 th Edition
 Network+ Guide to Networks 7 th Edition Chapter 10 Network Segmentation and Virtualization 2016 Cengage Learning. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in
Network+ Guide to Networks 7 th Edition Chapter 10 Network Segmentation and Virtualization 2016 Cengage Learning. May not be scanned, copied or duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in
A+ Certification Guide. Chapter 16 (Part B) Networking
 A+ Certification Guide Chapter 16 (Part B) Networking Chapter 16 (Part B) Objectives Installing and Configuring Network Interface Cards Networking Configuration for Small Network Switches and Routers Setting
A+ Certification Guide Chapter 16 (Part B) Networking Chapter 16 (Part B) Objectives Installing and Configuring Network Interface Cards Networking Configuration for Small Network Switches and Routers Setting
Computer to Network Connection
 Computer to Network Connection Network Installation Steps Having a clear understanding of all the steps required to physically building a network improves the success of a project. You may need to install
Computer to Network Connection Network Installation Steps Having a clear understanding of all the steps required to physically building a network improves the success of a project. You may need to install
CN1047 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKING CHAPTER 5 OSI MODEL NETWORK LAYER
 CN1047 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKING CHAPTER 5 OSI MODEL NETWORK LAYER Network Layer Network layer manages options pertaining to host and network addressing, managing subnetworks, and internetworking.
CN1047 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORKING CHAPTER 5 OSI MODEL NETWORK LAYER Network Layer Network layer manages options pertaining to host and network addressing, managing subnetworks, and internetworking.
3. What could you use if you wanted to reduce unnecessary broadcast, multicast, and flooded unicast packets?
 Nguyen The Nhat - Take Exam Exam questions Time remaining: 00: 00: 51 1. Which command will give the user TECH privileged-mode access after authentication with the server? username name privilege level
Nguyen The Nhat - Take Exam Exam questions Time remaining: 00: 00: 51 1. Which command will give the user TECH privileged-mode access after authentication with the server? username name privilege level
Hubs. twisted pair. hub. 5: DataLink Layer 5-1
 Hubs Hubs are essentially physical-layer repeaters: bits coming from one link go out all other links at the same rate no frame buffering no CSMA/CD at : adapters detect collisions provides net management
Hubs Hubs are essentially physical-layer repeaters: bits coming from one link go out all other links at the same rate no frame buffering no CSMA/CD at : adapters detect collisions provides net management
CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0)
 CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0) 1. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function
CCENT Practice Certification Exam # 2 - CCNA Exploration: Accessing the WAN (Version 4.0) 1. Data is being sent from a source PC to a destination server. Which three statements correctly describe the function
Chapter 5 Local Area Networks. Computer Concepts 2013
 Chapter 5 Local Area Networks Computer Concepts 2013 5 Chapter Contents Section A: Network Building Blocks Section B: Wired and Wireless Technologies Section C: Network Setup Section D: Sharing Files Section
Chapter 5 Local Area Networks Computer Concepts 2013 5 Chapter Contents Section A: Network Building Blocks Section B: Wired and Wireless Technologies Section C: Network Setup Section D: Sharing Files Section
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
Chapter Seven. Local Area Networks: Part 1. Data Communications and Computer Networks: A Business User s Approach Seventh Edition
 Chapter Seven Local Area Networks: Part 1 Data Communications and Computer Networks: A Business User s Approach Seventh Edition After reading this chapter, you should be able to: State the definition of
Chapter Seven Local Area Networks: Part 1 Data Communications and Computer Networks: A Business User s Approach Seventh Edition After reading this chapter, you should be able to: State the definition of
CS610- Computer Network Solved Subjective From Midterm Papers
 Solved Subjective From Midterm Papers May 08,2012 MC100401285 Moaaz.pk@gmail.com Mc100401285@gmail.com PSMD01 CS610- Computer Network Midterm Examination - Fall 2011 1. Where are destination and source
Solved Subjective From Midterm Papers May 08,2012 MC100401285 Moaaz.pk@gmail.com Mc100401285@gmail.com PSMD01 CS610- Computer Network Midterm Examination - Fall 2011 1. Where are destination and source
Switching & ARP Week 3
 Switching & ARP Week 3 Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White lbwhite@wit.ie Office : 324 Many Slides courtesy of Tony Chen 1 Ethernet Using Switches In the last few years, switches have quickly
Switching & ARP Week 3 Module : Computer Networks Lecturer: Lucy White lbwhite@wit.ie Office : 324 Many Slides courtesy of Tony Chen 1 Ethernet Using Switches In the last few years, switches have quickly
Introducing Campus Networks
 Cisco Enterprise Architecture Introducing Campus Networks 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. BCMSN v2.0 2-2 Campus Data Center Combines switching
Cisco Enterprise Architecture Introducing Campus Networks 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. BCMSN v2.0 2-2 Campus Data Center Combines switching
Top-Down Network Design, Ch. 7: Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols. Top-Down Network Design. Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Seven Selecting Switching and Routing Protocols Copyright 2010 Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer 1 Switching 2 Page 1 Objectives MAC address table Describe the features
A. ARPANET was an early packet switched network initially connecting 4 sites (Stanford, UC Santa Barbara, UCLA, and U of Utah).
 Volume: 245 Questions Question No: 1 Which of the following statements best describes ARPANET? A. ARPANET was an early packet switched network initially connecting 4 sites (Stanford, UC Santa Barbara,
Volume: 245 Questions Question No: 1 Which of the following statements best describes ARPANET? A. ARPANET was an early packet switched network initially connecting 4 sites (Stanford, UC Santa Barbara,
Network Security Fundamentals. Network Security Fundamentals. Roadmap. Security Training Course. Module 2 Network Fundamentals
 Network Security Fundamentals Security Training Course Dr. Charles J. Antonelli The University of Michigan 2013 Network Security Fundamentals Module 2 Network Fundamentals Roadmap Network Fundamentals
Network Security Fundamentals Security Training Course Dr. Charles J. Antonelli The University of Michigan 2013 Network Security Fundamentals Module 2 Network Fundamentals Roadmap Network Fundamentals
Chapter 6 Connecting Device
 Computer Networks Al-Mustansiryah University Elec. Eng. Department College of Engineering Fourth Year Class Chapter 6 Connecting Device 6.1 Functions of network devices Separating (connecting) networks
Computer Networks Al-Mustansiryah University Elec. Eng. Department College of Engineering Fourth Year Class Chapter 6 Connecting Device 6.1 Functions of network devices Separating (connecting) networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
The Network Layer and Routers
 The Network Layer and Routers Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/18 Network Layer deliver packets from sending host to receiving host must be on every host, router in
The Network Layer and Routers Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University 2/18 Network Layer deliver packets from sending host to receiving host must be on every host, router in
Layer 2 functionality bridging and switching
 Layer 2 functionality bridging and switching BSAD 141 Dave Novak Sources: Network+ Guide to Networks, Dean 2013 Overview Layer 2 functionality Error detection Bridges Broadcast and collision domains How
Layer 2 functionality bridging and switching BSAD 141 Dave Novak Sources: Network+ Guide to Networks, Dean 2013 Overview Layer 2 functionality Error detection Bridges Broadcast and collision domains How
SWP-0208G, 8+2SFP. 8-Port Gigabit Web Smart Switch. User s Manual
 SWP-0208G 1 SWP-0208G, 8+2SFP 8-Port Gigabit Web Smart Switch User s Manual Version: 3.4 April 1, 2008 2 TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 MAIN FEATURES...4 1.2 START TO MANAGE THIS SWITCH...6
SWP-0208G 1 SWP-0208G, 8+2SFP 8-Port Gigabit Web Smart Switch User s Manual Version: 3.4 April 1, 2008 2 TABLE OF CONTENT 1.0 INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 MAIN FEATURES...4 1.2 START TO MANAGE THIS SWITCH...6
Networking Devices. Punch_down panels
 Networking Devices Punch_down panels Hubs Switches Bridges Routes Gateways Network Interface Cards (NICs) Wireless access points Modems 1 Punch_down panels Wiring closets Labeling schemes 2 1 Hubs The
Networking Devices Punch_down panels Hubs Switches Bridges Routes Gateways Network Interface Cards (NICs) Wireless access points Modems 1 Punch_down panels Wiring closets Labeling schemes 2 1 Hubs The
Image courtesy Cisco Systems, Inc. Illustration of a Cisco Catalyst switch
 by Jeff Tyson If you have read other HowStuffWorks articles on networking or the Internet, then you know that a typical network consists of nodes (computers), a connecting medium (wired or wireless) and
by Jeff Tyson If you have read other HowStuffWorks articles on networking or the Internet, then you know that a typical network consists of nodes (computers), a connecting medium (wired or wireless) and
Introduction to Switched Networks Routing And Switching
 Introduction to Switched Networks Routing And Switching 1 Converged Networks Growing Complexity of Networks Our digital world is changing Information must be accessed from anywhere in the world Networks
Introduction to Switched Networks Routing And Switching 1 Converged Networks Growing Complexity of Networks Our digital world is changing Information must be accessed from anywhere in the world Networks
Chapter 4 NETWORK HARDWARE
 Chapter 4 NETWORK HARDWARE 1 Network Devices As Organizations grow, so do their networks Growth in number of users Geographical Growth Network Devices : Are products used to expand or connect networks.
Chapter 4 NETWORK HARDWARE 1 Network Devices As Organizations grow, so do their networks Growth in number of users Geographical Growth Network Devices : Are products used to expand or connect networks.
CISCO SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION (41)
 CISCO SYSTEM ADMININSTRATION PAGE 1 OF 11 CONTESTANT ID# Time Rank CISCO SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION (41) Regional 2012 TOTAL POINTS (500) Failure to adhere to any of the following rules will result in disqualification:
CISCO SYSTEM ADMININSTRATION PAGE 1 OF 11 CONTESTANT ID# Time Rank CISCO SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION (41) Regional 2012 TOTAL POINTS (500) Failure to adhere to any of the following rules will result in disqualification:
Configuring Interface Characteristics
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. The
CHAPTER 10 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the switch and describes how to configure them. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. The
Wireless g AP. User s Manual
 Wireless 802.11g AP User s Manual Version 1.8 User s Guide 0 Copyright Statement No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means,
Wireless 802.11g AP User s Manual Version 1.8 User s Guide 0 Copyright Statement No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means,
Introduction to Networking Devices
 Introduction to Networking Devices Objectives Explain the uses, advantages, and disadvantages of repeaters, hubs, wireless access points, bridges, switches, and routers Define the standards associated
Introduction to Networking Devices Objectives Explain the uses, advantages, and disadvantages of repeaters, hubs, wireless access points, bridges, switches, and routers Define the standards associated
Trademarks. Statement of Conditions by NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved.
 2004 by NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks @2004 NETGEAR, Inc. NETGEAR, the Netgear logo, The Gear Guy and Everybody s connecting are trademarks of Netgear, Inc. in the United States and/or
2004 by NETGEAR, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks @2004 NETGEAR, Inc. NETGEAR, the Netgear logo, The Gear Guy and Everybody s connecting are trademarks of Netgear, Inc. in the United States and/or
EEC-684/584 Computer Networks
 EEC-684/584 Computer Networks Lecture 14 wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Outline 2 Review of last lecture Internetworking
EEC-684/584 Computer Networks Lecture 14 wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Outline 2 Review of last lecture Internetworking
Chapter 4 Advanced Settings and Features
 Chapter 4 Advanced Settings and Features This chapter describes the features you can configure or view under Advanced in the main menu of your WiFi range extender. Advanced Wireless Settings Note: The
Chapter 4 Advanced Settings and Features This chapter describes the features you can configure or view under Advanced in the main menu of your WiFi range extender. Advanced Wireless Settings Note: The
Growth. Individual departments in a university buy LANs for their own machines and eventually want to interconnect with other campus LANs.
 Internetworking Multiple networks are a fact of life: Growth. Individual departments in a university buy LANs for their own machines and eventually want to interconnect with other campus LANs. Fault isolation,
Internetworking Multiple networks are a fact of life: Growth. Individual departments in a university buy LANs for their own machines and eventually want to interconnect with other campus LANs. Fault isolation,
Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition. Chapter 6: Network Reference Models and Standards
 Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition Chapter 6: Network Reference Models and Standards Objectives Explain the OSI reference model layers and their relationship to hardware and software Explain
Guide to Networking Essentials, 6 th Edition Chapter 6: Network Reference Models and Standards Objectives Explain the OSI reference model layers and their relationship to hardware and software Explain
Hands-On Network Security: Practical Tools & Methods
 Hands-On Network Security: Practical Tools & Methods Security Training Course Dr. Charles J. Antonelli The University of Michigan 2012 Hands-On Network Security Module 2 Network Fundamentals Roadmap Network
Hands-On Network Security: Practical Tools & Methods Security Training Course Dr. Charles J. Antonelli The University of Michigan 2012 Hands-On Network Security Module 2 Network Fundamentals Roadmap Network
Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS)
 Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS) CHAPTERS 1. Configure Basic Wireless Parameters 2. Configure Wireless Client Parameters 3. Configure Wireless AP Parameters 4. Configure Multi-SSID 5.
Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS) CHAPTERS 1. Configure Basic Wireless Parameters 2. Configure Wireless Client Parameters 3. Configure Wireless AP Parameters 4. Configure Multi-SSID 5.
Computer Networking. December 2004 CEN CN
 Computer Networking CEN CN 1 Layer 2 - Bridge Frame Header Data Bridge Trailer Data Link Layer Physical Layer More complex than repeat, it requires hardware and software Bridges have diminished because
Computer Networking CEN CN 1 Layer 2 - Bridge Frame Header Data Bridge Trailer Data Link Layer Physical Layer More complex than repeat, it requires hardware and software Bridges have diminished because
IT114 NETWORK+ Learning Unit 1 Objectives: 1, 2 Time In-Class Time Out-Of-Class Hours 2-3. Lectures: Course Introduction and Overview
 IT114 NETWORK+ Course Objectives Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Identify the devices and elements of computer networks; 2. Diagram network models using the appropriate
IT114 NETWORK+ Course Objectives Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: 1. Identify the devices and elements of computer networks; 2. Diagram network models using the appropriate
Distributed Queue Dual Bus
 Distributed Queue Dual Bus IEEE 802.3 to 802.5 protocols are only suited for small LANs. They cannot be used for very large but non-wide area networks. IEEE 802.6 DQDB is designed for MANs It can cover
Distributed Queue Dual Bus IEEE 802.3 to 802.5 protocols are only suited for small LANs. They cannot be used for very large but non-wide area networks. IEEE 802.6 DQDB is designed for MANs It can cover
CISCO EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 100-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 35.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: CCNA Interconnecting
CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 100-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 35.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 100-101 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: CCNA Interconnecting
- Hubs vs. Switches vs. Routers -
 1 Layered Communication - Hubs vs. Switches vs. Routers - Network communication models are generally organized into layers. The OSI model specifically consists of seven layers, with each layer representing
1 Layered Communication - Hubs vs. Switches vs. Routers - Network communication models are generally organized into layers. The OSI model specifically consists of seven layers, with each layer representing
1. IPv6 is the latest version of the TCP/IP protocol. What are some of the important IPv6 requirements?
 95 Chapter 7 TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP Addressing This chapter presents an overview of the TCP/IP Protocol Suite. It starts with the history and future of TCP/IP, compares the TCP/IP protocol model
95 Chapter 7 TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP Addressing This chapter presents an overview of the TCP/IP Protocol Suite. It starts with the history and future of TCP/IP, compares the TCP/IP protocol model
Some portions courtesy Srini Seshan or David Wetherall
 CSE 123 Computer Networks Fall 2009 Lecture 6: Data-Link III: Hubs, Bridges and Switches Some portions courtesy Srini Seshan or David Wetherall Misc Homework solutions have been posted I ll post a sample
CSE 123 Computer Networks Fall 2009 Lecture 6: Data-Link III: Hubs, Bridges and Switches Some portions courtesy Srini Seshan or David Wetherall Misc Homework solutions have been posted I ll post a sample
A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC, 8th Edition. Chapter 16 Networking Types, Devices, and Cabling
 A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC, Chapter 16 Networking Types, Devices, and Cabling Objectives Learn about network types and topologies Learn about the hardware used to build local networks Learn
A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC, Chapter 16 Networking Types, Devices, and Cabling Objectives Learn about network types and topologies Learn about the hardware used to build local networks Learn
Configuring Basic Wireless Settings on the RV130W
 Article ID: 5027 Configuring Basic Wireless Settings on the RV130W Objective Wireless networking operates by sending information over radio waves, which can be more vulnerable to intruders than a traditional
Article ID: 5027 Configuring Basic Wireless Settings on the RV130W Objective Wireless networking operates by sending information over radio waves, which can be more vulnerable to intruders than a traditional
Networking Fundamentals Tom Brett
 Networking Fundamentals Tom Brett Data Before we look at networking, it is important for us to understand what Data is and how it is stored and represented Data According to Webopedia, data is distinct
Networking Fundamentals Tom Brett Data Before we look at networking, it is important for us to understand what Data is and how it is stored and represented Data According to Webopedia, data is distinct
What is a Network? A connection of two or more computers so that they can share resources.
 NETWORKS What is a Network? A connection of two or more computers so that they can share resources. Network Benefits Remote access Sharing files & resources Communication Cost Maintenance Communication
NETWORKS What is a Network? A connection of two or more computers so that they can share resources. Network Benefits Remote access Sharing files & resources Communication Cost Maintenance Communication
Lecture 9. Reminder: Homework 3, Programming Project 2 due today. Questions? Thursday, September 22 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 9 1
 Lecture 9 Reminder: Homework 3, Programming Project 2 due today. Questions? Thursday, September 22 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 9 1 Outline Chapter 3 - Internetworking 3.1 Switching and Bridging 3.2 Basic
Lecture 9 Reminder: Homework 3, Programming Project 2 due today. Questions? Thursday, September 22 CS 475 Networks - Lecture 9 1 Outline Chapter 3 - Internetworking 3.1 Switching and Bridging 3.2 Basic
More on Link Layer. Recap of Last Class. Interconnecting Nodes in LAN (Local-Area Network) Interconnecting with Hubs. Computer Networks 9/21/2009
 More on Link Layer Kai Shen Recap of Last Class Ethernet dominant link layer technology for local-area l networks Ethernet frame structure Ethernet multiple access control CSMA/CD, exponential back-off
More on Link Layer Kai Shen Recap of Last Class Ethernet dominant link layer technology for local-area l networks Ethernet frame structure Ethernet multiple access control CSMA/CD, exponential back-off
EEC-484/584 Computer Networks
 EEC-484/584 Computer Networks Lecture 13 wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Outline 2 Review of lecture 12 Routing Congestion
EEC-484/584 Computer Networks Lecture 13 wenbing@ieee.org (Lecture nodes are based on materials supplied by Dr. Louise Moser at UCSB and Prentice-Hall) Outline 2 Review of lecture 12 Routing Congestion
Powered by Accton. ES Port Gigabit Web-Smart Switch. Management Guide.
 Powered by Accton ES4324 24-Port Gigabit Web-Smart Switch Management Guide www.edge-core.com Management Guide 24-Port Gigabit Web-Smart Switch with 24 1000BASE-T (RJ-45) Ports, and 4 Combination (RJ-45/SFP)
Powered by Accton ES4324 24-Port Gigabit Web-Smart Switch Management Guide www.edge-core.com Management Guide 24-Port Gigabit Web-Smart Switch with 24 1000BASE-T (RJ-45) Ports, and 4 Combination (RJ-45/SFP)
Switching and Forwarding Reading: Chapter 3 1/30/14 1
 Switching and Forwarding Reading: Chapter 3 1/30/14 1 Switching and Forwarding Next Problem: Enable communication between hosts that are not directly connected Fundamental Problem of the Internet or any
Switching and Forwarding Reading: Chapter 3 1/30/14 1 Switching and Forwarding Next Problem: Enable communication between hosts that are not directly connected Fundamental Problem of the Internet or any
exam. Number: Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min CISCO Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND)
 100-105.exam Number: 100-105 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min CISCO 100-105 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Exam A QUESTION 1 Which route source code represents the routing
100-105.exam Number: 100-105 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min CISCO 100-105 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 1 (ICND) Exam A QUESTION 1 Which route source code represents the routing
7010INT Data Communications Lecture 7 The Network Layer
 Introduction 7010INT Data Communications Lecture 7 The Layer Internetworking & Devices Connecting LANs Routing Backbone networks Virtual LANs Addressing Application Presentation Session Data Link Physical
Introduction 7010INT Data Communications Lecture 7 The Layer Internetworking & Devices Connecting LANs Routing Backbone networks Virtual LANs Addressing Application Presentation Session Data Link Physical
Understanding Networking Fundamentals
 Understanding Networking Fundamentals Training Details Training Time : 5 Days Capacity : 12 Prerequisites : There are no prerequisites for this course. About Training About Training A strong foundation
Understanding Networking Fundamentals Training Details Training Time : 5 Days Capacity : 12 Prerequisites : There are no prerequisites for this course. About Training About Training A strong foundation
CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam 2014
 CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam 2014 1 Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router: R1# copy running-config tftp Address or name of remote host [ ]? When the
CCNA 1 v5.0 R&S ITN Final Exam 2014 1 Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator enters these commands into the R1 router: R1# copy running-config tftp Address or name of remote host [ ]? When the
1. What type of network cable is used between a terminal and a console port? cross-over straight-through rollover patch cable 2.
 1. What type of network cable is used between a terminal and a console port? cross-over straight-through rollover patch cable 2. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has decided to use packet
1. What type of network cable is used between a terminal and a console port? cross-over straight-through rollover patch cable 2. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has decided to use packet
CCNA 1 Chapter 5 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013
 CCNA 1 Chapter 5 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1 2 A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in its ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination
CCNA 1 Chapter 5 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1 2 A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in its ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination
Sections Describing Standard Software Features
 30 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using automatic-qos (auto-qos) commands or by using standard QoS commands. With QoS, you can give preferential treatment to
30 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using automatic-qos (auto-qos) commands or by using standard QoS commands. With QoS, you can give preferential treatment to
CCNA. Course Catalog
 CCNA Course Catalog 2012-2013 This course is intended for the following audience: Network Administrator Network Engineer Systems Engineer CCNA Exam Candidates Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA 640-802)
CCNA Course Catalog 2012-2013 This course is intended for the following audience: Network Administrator Network Engineer Systems Engineer CCNA Exam Candidates Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA 640-802)
HP 5120 SI Switch Series
 HP 5120 SI Switch Series Layer 2 - LAN Switching Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-1807 Software version: Release 1513 Document version: 6W100-20130830 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
HP 5120 SI Switch Series Layer 2 - LAN Switching Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-1807 Software version: Release 1513 Document version: 6W100-20130830 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
2. What is a characteristic of a contention-based access method?
 CCNA 1 Chapter 5 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Which statement is true about MAC addresses? MAC addresses are implemented by software. A NIC only needs a MAC address if connected to a WAN. The first
CCNA 1 Chapter 5 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 (100%) 1. Which statement is true about MAC addresses? MAC addresses are implemented by software. A NIC only needs a MAC address if connected to a WAN. The first
Cisco CISCO Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Exam (ICND) Practice Test. Version
 Cisco 640-811 CISCO 640-811 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Exam (ICND) Practice Test Version 1.3 QUESTION NO: 1 Cisco 640-811: Practice Exam What is the purpose of the OSPF router ID in a DR/BDR
Cisco 640-811 CISCO 640-811 Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Exam (ICND) Practice Test Version 1.3 QUESTION NO: 1 Cisco 640-811: Practice Exam What is the purpose of the OSPF router ID in a DR/BDR
MTA_98-366_Vindicator930
 MTA_98-366_Vindicator930 Number: 98-366 Passing Score: 700 Time Limit: 45 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Microsoft Technology Associate Networking Fundamentals MTA 98-366 Exam A QUESTION
MTA_98-366_Vindicator930 Number: 98-366 Passing Score: 700 Time Limit: 45 min File Version: 1.0 http://www.gratisexam.com/ Microsoft Technology Associate Networking Fundamentals MTA 98-366 Exam A QUESTION
Prepared by Agha Mohammad Haidari Network Manager ICT Directorate Ministry of Communication & IT
 Network Basics Prepared by Agha Mohammad Haidari Network Manager ICT Directorate Ministry of Communication & IT E-mail :Agha.m@mcit.gov.af Cell:0700148122 After this lesson,you will be able to : Define
Network Basics Prepared by Agha Mohammad Haidari Network Manager ICT Directorate Ministry of Communication & IT E-mail :Agha.m@mcit.gov.af Cell:0700148122 After this lesson,you will be able to : Define
TestsDumps. Latest Test Dumps for IT Exam Certification
 TestsDumps http://www.testsdumps.com Latest Test Dumps for IT Exam Certification Exam : 200-105 Title : Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2 v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest
TestsDumps http://www.testsdumps.com Latest Test Dumps for IT Exam Certification Exam : 200-105 Title : Interconnecting Cisco Networking Devices Part 2 (ICND2 v3.0) Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest
Fundamental Questions to Answer About Computer Networking, Jan 2009 Prof. Ying-Dar Lin,
 Fundamental Questions to Answer About Computer Networking, Jan 2009 Prof. Ying-Dar Lin, ydlin@cs.nctu.edu.tw Chapter 1: Introduction 1. How does Internet scale to billions of hosts? (Describe what structure
Fundamental Questions to Answer About Computer Networking, Jan 2009 Prof. Ying-Dar Lin, ydlin@cs.nctu.edu.tw Chapter 1: Introduction 1. How does Internet scale to billions of hosts? (Describe what structure
SYSTEMS ADMINISTRATION USING CISCO (315)
 Page 1 of 10 Contestant Number: Time: Rank: SYSTEMS ADMINISTRATION USING CISCO (315) REGIONAL 2014 TOTAL POINTS (500) Failure to adhere to any of the following rules will result in disqualification: 1.
Page 1 of 10 Contestant Number: Time: Rank: SYSTEMS ADMINISTRATION USING CISCO (315) REGIONAL 2014 TOTAL POINTS (500) Failure to adhere to any of the following rules will result in disqualification: 1.
Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP)
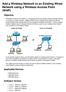 Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP) Objective A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a networking device that allows wireless-capable devices to connect to
Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP) Objective A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a networking device that allows wireless-capable devices to connect to
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트
 PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
PASS4TEST IT 인증시험덤프전문사이트 http://www.pass4test.net 일년동안무료업데이트 Exam : 640-802 Title : Cisco Certified Network Associate(CCNA) Vendors : Cisco Version : DEMO 1 / 10 Get Latest & Valid 640-802 Exam's Question
Section 1. General Networking Theory
 Section 1 General Networking Theory This chapter ensures you are prepared for questions in the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert (CCIE) written exam that deal with general networking theories. General
Section 1 General Networking Theory This chapter ensures you are prepared for questions in the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert (CCIE) written exam that deal with general networking theories. General
Traditional network management methods have typically
 Advanced Configuration for the Dell PowerConnect 5316M Blade Server Chassis Switch By Surendra Bhat Saurabh Mallik Enterprises can take advantage of advanced configuration options for the Dell PowerConnect
Advanced Configuration for the Dell PowerConnect 5316M Blade Server Chassis Switch By Surendra Bhat Saurabh Mallik Enterprises can take advantage of advanced configuration options for the Dell PowerConnect
Management Software AT-S67 AT-S68. User s Guide FOR USE WITH AT-FS7016 AND AT-FS7024 SMART SWITCHES VERSION PN Rev A
 Management Software AT-S67 AT-S68 User s Guide FOR USE WITH AT-FS7016 AND AT-FS7024 SMART SWITCHES VERSION 1.0.0 PN 613-50494-00 Rev A Copyright 2003 Allied Telesyn, Inc. 960 Stewart Drive Suite B, Sunnyvale,
Management Software AT-S67 AT-S68 User s Guide FOR USE WITH AT-FS7016 AND AT-FS7024 SMART SWITCHES VERSION 1.0.0 PN 613-50494-00 Rev A Copyright 2003 Allied Telesyn, Inc. 960 Stewart Drive Suite B, Sunnyvale,
CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks
 CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks Link Layer, Switches, VLANS, MPLS, Data Centers Sec 6.4 to 6.7 Prof. Lina Battestilli Fall 2017 Chapter 6 Outline Link layer and LANs: 6.1 introduction,
CSC 401 Data and Computer Communications Networks Link Layer, Switches, VLANS, MPLS, Data Centers Sec 6.4 to 6.7 Prof. Lina Battestilli Fall 2017 Chapter 6 Outline Link layer and LANs: 6.1 introduction,
1-Port Gigabit Ethernet Network Card - PCI Express, Intel I210 NIC
 1-Port Gigabit Ethernet Network Card - PCI Express, Intel I210 NIC Product ID: ST1000SPEXI Boost the performance and capabilities of your server or desktop computer by adding a Gigabit Ethernet port through
1-Port Gigabit Ethernet Network Card - PCI Express, Intel I210 NIC Product ID: ST1000SPEXI Boost the performance and capabilities of your server or desktop computer by adding a Gigabit Ethernet port through
Top-Down Network Design
 Top-Down Network Design Chapter Five Designing a Network Topology Original slides copyright by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Network Topology Design Issues Hierarchy Redundancy Modularity Well-defined
Top-Down Network Design Chapter Five Designing a Network Topology Original slides copyright by Cisco Press & Priscilla Oppenheimer Network Topology Design Issues Hierarchy Redundancy Modularity Well-defined
VLANs Level 3 Unit 9 Computer Networks
 VLANs Some Requirements of LANs Need to split up broadcast domains to make good use of bandwidth People in different departments may need to be grouped together for access to servers Security: restrict
VLANs Some Requirements of LANs Need to split up broadcast domains to make good use of bandwidth People in different departments may need to be grouped together for access to servers Security: restrict
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS
 Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring Rapid PVST+ Using NX-OS This chapter describes how to configure the Rapid per VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST+) protocol on Cisco NX-OS devices. This chapter includes the following sections:
Configuring QoS. Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for QoS
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for QoS, page 1 Restrictions for QoS, page 3 Information About QoS, page 4 How to Configure QoS, page 28 Monitoring Standard QoS, page 80 Configuration
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for QoS, page 1 Restrictions for QoS, page 3 Information About QoS, page 4 How to Configure QoS, page 28 Monitoring Standard QoS, page 80 Configuration
Light Mesh AP. User s Guide. 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft
 Light Mesh AP User s Guide 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft i FCC Certifications This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Light Mesh AP User s Guide 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft i FCC Certifications This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Sections Describing Standard Software Features
 27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using automatic-qos (auto-qos) commands or by using standard QoS commands. With QoS, you can give preferential treatment to
27 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure quality of service (QoS) by using automatic-qos (auto-qos) commands or by using standard QoS commands. With QoS, you can give preferential treatment to
LAN Interconnection and Other Link Layer Protocols
 LAN Interconnection and Other Link Layer Protocols Ethernet dominant link layer technology for local-area networks Ethernet frame structure Kai Shen Dept. of Computer Science, University of Rochester Ethernet
LAN Interconnection and Other Link Layer Protocols Ethernet dominant link layer technology for local-area networks Ethernet frame structure Kai Shen Dept. of Computer Science, University of Rochester Ethernet
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE 400, Experiment # 2
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE 400, Experiment # 2 IP Addressing and Subnetting: Establishing Elementary Networks using Hubs, Switches and Routers. Objectives:
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Electrical Engineering Department EE 400, Experiment # 2 IP Addressing and Subnetting: Establishing Elementary Networks using Hubs, Switches and Routers. Objectives:
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter defines the types of interfaces on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch and describes how to configure them. The chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Types,
Product features. Applications
 Applications Layer 2+ VLAN static routing application The managed switch features a built-in, robust IPv4/IPv6 Layer 3 traffic static routing protocol to ensure reliable routing between VLANs and network
Applications Layer 2+ VLAN static routing application The managed switch features a built-in, robust IPv4/IPv6 Layer 3 traffic static routing protocol to ensure reliable routing between VLANs and network
 Seite von 7 05.0.200 Close Window Assessment System Exam Viewer - CCNA Practice Certification Exam # - (Version 4.0) Below you will find the assessment items as presented on the exam as well as the scoring
Seite von 7 05.0.200 Close Window Assessment System Exam Viewer - CCNA Practice Certification Exam # - (Version 4.0) Below you will find the assessment items as presented on the exam as well as the scoring
CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer
 CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer LOCAL CISCO ACADEMY ELSYS TU INSTRUCTOR: STELA STEFANOVA 1 Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission; Objectives Describe how the
CCNA Exploration1 Chapter 7: OSI Data Link Layer LOCAL CISCO ACADEMY ELSYS TU INSTRUCTOR: STELA STEFANOVA 1 Explain the role of Data Link layer protocols in data transmission; Objectives Describe how the
CH : 15 LOCAL AREA NETWORK OVERVIEW
 CH : 15 LOCAL AREA NETWORK OVERVIEW P. 447 LAN (Local Area Network) A LAN consists of a shared transmission medium and a set of hardware and software for interfacing devices to the medium and regulating
CH : 15 LOCAL AREA NETWORK OVERVIEW P. 447 LAN (Local Area Network) A LAN consists of a shared transmission medium and a set of hardware and software for interfacing devices to the medium and regulating
Procedure: You can find the problem sheet on the Desktop of the lab PCs.
 University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Advance Networks Laboratory 907529 Lab.3 WLAN Security Objectives 1. Configure administrator accounts.
University of Jordan Faculty of Engineering & Technology Computer Engineering Department Computer Advance Networks Laboratory 907529 Lab.3 WLAN Security Objectives 1. Configure administrator accounts.
Chapter 5 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to:
 Chapter 5 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the operation of the Ethernet sublayers. Identify the major fields of the Ethernet frame. Describe the purpose
Chapter 5 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe the operation of the Ethernet sublayers. Identify the major fields of the Ethernet frame. Describe the purpose
