Adaptive Approach of DSR and OLSR Routing Protocols Using Optimal Probabilistic Logical Key Hierarchy in MANET
|
|
|
- Malcolm Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
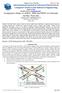
1 Bonfring International Journal of Networking Technologies and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, June Adaptive Approach of DSR and OLSR Routing Protocols Using Optimal Probabilistic Logical Key Hierarchy in MANET Harshit Prakash Patidar and Neetu Sharma Abstract--- Wireless network with ad-hoc behaviour consists of mobile nodes which facilitates a fundamental architecture for communication without any support of traditional, steady and fixed-positioned routers. However, the architecture must preserve communicating routes and hosts have mobile nature and their restricted transmission range. There are several protocols for managing the routing in the mobility atmosphere. In the MANET, the mobile nodes can perform the roles of both hosts and routers. Various MANET applications are used for Military strategic communications and Disaster recovery mostly depend on secure node communication. For Secure Communication, we use several Logical Hierarchy Key protocols in Mobile Ad-hoc Network but the group key administration looks upon many problems assuming due to unreliable media, mobile node failure and less energy resources. In this paper, we analyze new logical key with Optimal Probabilistic Technique in DSR and OLSR routing protocols in Mobile Ad-hoc Network. In this key, all nodes are shaped in a tree structure. OPLKH decreases the Rekey Cost and several routing energy consumptions in Mobile Ad-hoc Network. In simulation, we calculate the amount of Rekeys Cost, Energy Consumption for Data Transmission, Energy Consumption for Routing and Energy Consumption for Key Generation in the network. Keywords--- Automatic-Configuring Infrastructure, Energy Consumption, Rekey Cost. W I. INTRODUCTION IRELESS communication technology is not practical with a particular architecture for all wireless networks because of fixed behaviour of wireless nodes or devices. Wireless communication technology is growing at high speed. Wireless networks with mobile nodes such as ad-hoc wireless networks must have functionality to be self-organized and self-configured because of the mobile nature of devices and networks. On these networks, mobile devices or hosts have a limited transmission range to communicate with other hosts. If a host wants to send data to another host which is not within the transmission range of the source node, then the data must be Harshit Prakash Patidar, Department of Computer Science, Govt. Engg. College, Ajmer, Rajasthan. harshitprakash@gmail.com Neetu Sharma, Department of Computer Science, Govt. Engg. College, Ajmer, Rajasthan. neetucom10@gmail.com DOI: / BIJNTA.8131 expressed through the network using other nodes which can play the role of routers in delivering the message all over the network. Broadcasting must be used for sending messages by the mobile hosts and host nodes should be in tremendously activate mode for accepting any message that it has received. Hosts can be single directional that can transmit only in one direction at a time in the ad-hoc network so that the communication is not bidirectional as usually in wireless communication systems. [1] Figure 1: Infrastructure Less Network Routing Protocols should have the capability of handling many numbers of hosts with their limiting energy resources and limiting bandwidths in Wireless Ad-hoc Networks. Host mobility is the main challenge for routing protocols. By the management of mobility systems, hosts can appear and disappear at various locations in the network. Although in adhoc networks, all hosts in the network perform their role as routers and must have participated in route maintenance and route discovery for other nodes or hosts in the network. It is also essential for ad-hoc routing protocols to reduce routing message overhead, growing mobility and number of hosts. Routing tables must be kept smaller because increasing the routing table size will interrupt control packets of host sent on the network and will eventually increase the large link overhead. [1] [2] II. OVERVIEW OF OLSR AND DSR ROUTING PROTOCOLS Routing protocols find the shortest path from source to destination and are categorized into two categories based on time taken for route discovery and when to discover the routes. One of the main routing protocols of Proactive Routing Protocol is OLSR. It s one of the major functionalities is to
2 Bonfring International Journal of Networking Technologies and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, June maintain recent reflecting routing information by sending control messages, recurring at regular intervals between the hosts which updates their routing tables. All the updates are forwarded all over the network if any changes are found in the structure. Link state routing algorithms are used by the Proactive Routing Protocols to flood frequently the link information about its adjacent nodes. On-demand routing protocols are other routing protocols in which it generates routes when they have exigency of the source hosts and route maintenance as it is required. Such protocols use distance vector routing algorithms. These protocols have vectors that contain selective information about the path to the destination and the cost. Whenever nodes interchange vectors of their information, each host transforms possessed routing information when they have a requirement. Optimal Link State Routing Protocol is the example of Proactive Routing Protocol. Optimal Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR) Proactive routing protocol interchanges routing statics with other hosts in the network. Multi Point Relays (MPRs) are the key idea used in OLSR. MPR is used to decrease the number of control packets required for the data transmission. To forward traffic of data in the network, a host picks its single hop symmetric neighbors termed as MPRs set that protects all hosts that are two hop away. MPR hosts or nodes have responsibility for forwarding control traffic in OLSR while in the classical link state algorithm, all the nodes forward the messages. Battery consumptions can be reduced in OLSR using other existing link state algorithm. [7] [8] Figure 2: Classification of Routing Protocols 2.1. Proactive (Table-Driven) Routing Protocols Proactive Routing Protocols are table driven routing protocols to broadcast the data packets, every node has its routing table and every node needs to step up connections to some other existing hosts of the networks. All the nodes of the network maintain their records related to all existing destinations, required number of hops mandatory to get in at every recorded destination in the tabular form. All the entries in the routing table are labeled with a particular sequence number that are produced by the destination nodes. For the stability retaining, every source node broadcasts and transforms its table of routing regularly. On the basis of routing tables, how many numbers of hops are required to reach from a specific source node to a destination node are calculated and which stations are receptacle is measured by the broadcasting of packets among the nodes. Every broadcasting data node contains a new number with sequence and for every new route node, maintains the information as given below. [5] Number of hops obligatory to reach a specific destination node. New sequence number for every destination and Contains destination address. Basically, table driven routing protocols are more beneficial for the networks that contain the least number of hosts in the network because all the hosts need to inform their node entries to all other hosts on the network. There is additional bandwidth Consumption in the routing table and the higher routing overhead problem is classified. [6] Figure 3: OLSR Routing Protocol 2.2. Reactive (On-Demand) Routing Protocol On-demand routing protocols determine routes on-demand that is the reason of the reactive routing protocol has less overhead problems as compared to proactive routing protocols. This type of protocols uses global searching (flooding) conception. In on-demand technique, consistent updates in routing tables with newer rout topology is not desired. In on-demand routing protocols, it looks for the routing in proactive method and create the link. In order to send and accept the packets from a source host or node to a destination node, the route discovery method is applied by the flooding or oversupplying the RREQ (route request) packets all over the network. [9] DSR and AODV are the example of Reactive Routing Protocol. Dynamic Source Routing Protocol (DSR) DSR is one of the on-demand routing protocols when a source node floods packets; the transmitter node hives up hopby-hop route to the recipient node. It applies source routing concept. The list of routes is cached in a source cache. Source routes are kept in the packet header by the data packets. Dynamic source routing follows the route discovery method to send the data packets from sender node to the receiver node for which it does not intimate discovery process to actively accretion such a route. In route discovery, DSR works by spreading the data packets in network with RREQ (route request) packets. In DSR protocol, Periodic hello message
3 Bonfring International Journal of Networking Technologies and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, June transmission is not required. Dynamic Source Routing (DSR) is beaconless on-demand routing protocol. RREQ packets are found by all closer nodes and continue the flood spreading process by retransmission of RREQ packets unless it acquires destination host or its route cache consists of a route for the destination node, such as a host responds to the RREQ with a RREP (route reply) packet that is routed back to the actual source node. Source routing applies route request RREQ and route reply RREP packets. The RREQ establishes the path traversed all over the network. The route reply (RREP) packets, routes themselves back to the source by traversing this path towards the back. The source hives up backward route by RREP packets for forthcoming use. If any connection on a source route is intoxicated, a route error (RERR) packet is apprised to the source host. [9] Figure 4: DSR Routing Protocol III. DESCRIPTION OF MOBILITY MODEL In mobility model, the Random Waypoint Mobility Model is a random model for the movement of mobile nodes explaining how their location, velocity and acceleration changes over the time. Mobility models are used for simulation purposes when any new network protocols are estimated. The random waypoint mobility model was first proposed by Maltz and Johnson. It is one of the most popular mobility models to calculate Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) routing protocols because of its simplicity and wide availability. In random-based mobility simulation models, the mobile nodes move randomly and independently without any restrictions. To be more specific, the destination, speed and the way are all chosen randomly and independently of the other nodes. This type of model has been used in many simulation projects. Figure 5: Random Waypoint Mobility Model The Random Walk Mobility Model and the Random Direction Mobility Model are two different kinds of variants of the Random Waypoint Mobility Model. [10] IV. ENERGY CONSUMPTION MODEL We have calculated the energy consumption for data transmission and receiving as proposed by Dongkyun Kim (Dongkyun Kim. Et al. 2002) and for key generation proposed by Potlapally Nachiketh (Nachiketh R. et al. 2003) The energy consumption required to transmit a packet p then the energy E(p)=i*v*t p Joules where i is new value, v is the voltage and t p is the time occupied to transmit the packet p. Energy consumption for the key setup phase using AES of 128-bit key is 7.83 uj/key. We use symmetric key of AES of 128-bit length for simulation. [11] V. OUR APPROACH We analyze OPLKH methods which are basically used for the optimization for PLKH resulting reduced the Rekey cost more. We also establish the LKH tree structure regarding the member Rekey Probabilities as opposed to the cumulative probability of PLKH. We emphasis on the decreasing of number of Rekeys that are caused due to member compromise or eviction. [12] In the tree structure, members are as leaf nodes which are same as in PLKH. We assemble it for a new insert operation which places the members either as a leaf node or as an internal node in the LKH tree structure which is based on their probabilities. When any new member C joins the group, member C is placed at a position such that all the ancestors of C will have higher probability and all the descendants of C will have lesser probability. [12] [13] Figure 6: CPUT Operation The LKH scheme aims to reduce the cost of a negotiation recovery process by adding extra encryption keys into the system. The members of the group are organized as the leaves of a logical key tree structure preserved by the key manager. The internal nodes in this tree structure are rational entities which do not relate to any real life entities of the multicast group but are used for key distribution purpose only. There is a key linked with each node in the tree structure and each member holds a replica of every key on the path from its corresponding leaf node to the root node of the tree structure. [14] [15]. When a fellow node leaves the group, its related corresponding physical node is required to be removed from
4 Bonfring International Journal of Networking Technologies and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, June the tree structure. The physical node may be an internal node or an external node based on how it is injected and whether it has any dependent nodes at present. In OPLKH scheme, physical node is removed by delete procedure only if it is a leaf node otherwise delete operation sets its type as consumable and refresh affected keys. [14] [15] With the development of the centralized key management, the tree structure key scheme is improved and the cost of Rekeying from Probability 0 (m) to 0 (log m) is reduced where m denotes the group size. MANET accepted the OPLKH method and analyzed the Rekey Cost and energy consumption for key generation, data transmission and routing in the network. [17] [18] VI. PROPOSED METHODOLOGY FOR THE MANET In this method, we have concentrated on reducing the cost of Rekey of LKH based protocols by organizing the tree structure based on Rekey Probabilities of nodes. In OPLKH scheme, we have implemented all the logical actions of OPLKH into MANET atmosphere. In MANET, we have chosen clusterhead as a key-server because there is no key-server. Weighted clustering algorithm (WCA) is used for selecting clusterhead. As Rekey Probability is one of the major things to cause Re-clustering, we have considered Rekey Probability to be another factor in Weighted Clustering Algorithm. [16] The WCA has the softness of taking combined effect of the degree and assigning different weights of ideality, node mobility, battery power and transmission power. The updated WCA algorithm as follows: Clusterhead Selection Technique Step 1: Find the neighbours of each node v (i.e. nodes within its broadcast range). This gives the degree, d v, of this node. H is number of nodes, a clusterhead can handle. Step 2: Calculate the degree-difference, D v = d v H, for every node v. Step 3: For every node, compute the sum of the distances, S v, with all its neighbours. Step 4: Calculate the running average of the speed for every node v. This provides the mobility of the node v and is denoted by M v. Step 5: Calculate the consumed battery power, T v. Since we assume that consumption of battery power is more for a clusterhead than for an ordinary node. Step 6: Calculate a combined weight I v = c 1 * D v + c 2 * S v + c 3 * M v + c 4 * T v, for each node v. The coefficients c 1, c 2, c 3 and c 4 are the weighting factors for the corresponding system parameters. Step 7: Calculate the average weights of all nodes, AI, and also compute the average Rekey Probabilities of all nodes, ARP. Step 8: Now check for each node v. If (weight I v < AI and corresponding Rekey Probability, RP v < ARP). Then Calculate the new weight NI v = I v * RP v. Step 9: Choose the node with minimum NI v to be the cluster head. (Key-server). By using the improved WCA algorithm, primarily we choose the best node as clusterhead from the existing nodes to escape Re-clustering. The following key features are considered in this Weighted Clustering Algorithma) The clusterhead selection method is a periodic and is invoked as barely as possible. It reduces system updates and reduces computational and communicational costs. b) To confirm efficient MAC functioning, each clusterhead can ideally support a pre-defined system threshold node. By optimizing or limiting the number of nodes in each cluster, the systems high throughput can be achieved. c) The battery power can be skillfully used within certain transmission range. If a node works as a clusterhead rather than an ordinary node, consumption of the battery power is extra. [16] VII. SIMULATION RESULT AND ANALYSIS Optimal Probabilistic Logical Key is simulated in Mobile Ad-hoc Network. C++ language is used for simulation. Groups of 128, 256, 512, 768 and 1024 nodes are experiments for implementing. For each experiment, we have produced the joining/leaving of nodes arbitrarily, in addition, some members may leave because of power exhaustion and some members may join/leave based on connection failure or availability. For each join/leave operation, we have documented the numbers of Rekeys generated and energy consumption for key generation. In OPLKH method, we have categorized three categories namely static, semi-dynamic and dynamic based on number of leaves and Rekey Probabilities. But in MANET, we added some extra parameters to classify these categories. The additional parameters are pause time, node mobility and updating interval time. The additional parameters are listed in Table 1. In simulation, for every updating interval time, we have updated the node positions and routing tables. Table 1: Simulation Parameter Simulation Static Semi- Dynamic Parameters Dynamic Mobility 0-5 m/s 0-10 m/s 0-20 m/s Packet Size 256 bytes 256 bytes 256 bytes Mobility Model Random Waypoint Random Waypoint Random Waypoint Pause Time 0-10 s 0-5 s 0 s Updating 10 s 5 s 1 s Interval Time No. of Leaves ¼ of Group Size ½ of Group Size ¾ of Group Size Area (in sq. m) 800x x x800 Energy J J J
5 Bonfring International Journal of Networking Technologies and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, June Simulation Results In simulation results, we have calculated the numbers of Rekeys and energy consumption for routing, data transmission and key generation in static, semi-dynamic and dynamic scenarios for each group size of 128, 256, 512, 768 and 1024 nodes. it is a Reactive Routing Protocol and establishes routes only when required. Here, Energy Consumption is very less. Figure 7: Graph between Number of Nodes and Number of Rekeys in case of DSR Figure 7 shows Number of Nodes versus Number of Rekeys in the network in the case of Dynamic Source Routing Protocol. In DSR protocol, Rekey operation i.e. number of joining/leaving in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Rekey operation i.e. number of joining/leaving in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Figure 9: Graph between Number of Nodes and Energy Consumption for Routing in case of DSR Figure 9 shows Number of Nodes versus Energy Consumption for Routing in the network in case of Dynamic Source Routing Protocol. In DSR protocol, Energy Consumption for Routing in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Energy Consumption for Routing in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Energy Consumption for Routing is smaller in case of DSR as compared to OLSR. Figure 8: Graph between Number of Nodes and Energy Consumption at Server in case of DSR Figure 8 shows Number of Nodes versus Energy Consumption at Server in the network in case of Dynamic Source Routing Protocol. In DSR protocol, Energy Consumption at Server in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Energy Consumption at Server in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Energy Consumption at Server occurs because of key distribution and key generation. In case of DSR protocol, Figure 10: Graph between Number of Nodes and energy Consumption for Data Transmission in case of DSR Figure 10 shows Number of Nodes versus Energy Consumption for Data Transmission in the network in case of Dynamic Source Routing Protocol. In DSR protocol, Energy Consumption for Data Transmission in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Energy Consumption for Data Transmission in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Energy Consumption for Data Transmission is smaller in case of DSR as compared to OLSR.
6 Bonfring International Journal of Networking Technologies and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, June Figure 11: Graph between Number of Nodes and energy Consumption for Key Generation in case of DSR Figure 11 shows Number of Nodes versus Energy Consumption for Key Generation in the network in case of Dynamic Source Routing Protocol. In DSR protocol, Energy Consumption for Key Generation in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Energy Consumption for Key Generation in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Here, it is observed that if number of Rekeys increase, the Energy Consumption for Key Generation also increases. Figure 13: Graph between Number of Nodes and Number of Rekeys in case of OLSR Figure 13 shows Number of Nodes versus Number of Rekeys in the network in case of Optimal Link State Routing Protocol. In OLSR protocol, Rekey operation i.e. number of joining/leaving in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Rekey operation i.e. number of joining/leaving in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Figure 12: Graph between Number of Nodes and Total Energy Consumption in Network in case of DSR Figure 12 shows Number of Nodes verses Total Energy Consumption in Network in case of Dynamic Source Routing Protocol. In DSR protocol, Total Energy Consumption in Network in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Total Energy Consumption in Network in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Total Energy Consumption in Network is the sum of Energy Consumption for Routing, Energy Consumption for Key Generation and Energy Consumption for Data Transmission. Figure 14: Graph between Number of Nodes and Energy Consumption at Server in case of OLSR Figure 14 shows Number of Nodes versus Energy Consumption at Server in the network in case of Optimal Link State Routing Protocol. In OLSR protocol, Energy Consumption at Server in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Energy Consumption at Server in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Energy Consumption at Server occurs because of key distribution and key generation. In case of OLSR protocol, it is a Proactive Routing Protocol and computes routes to each node. It causes more energy depletion in the network.
7 Bonfring International Journal of Networking Technologies and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, June Figure 15: Graph between Number of Nodes and Energy Consumption for Routing in case of OLSR Figure 15 shows Number of Nodes versus Energy Consumption for Routing in the network in case of Optimal Link State Routing Protocol. In OLSR protocol, Energy Consumption for Routing in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Energy Consumption for Routing in the Semi- Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Energy Consumption for Routing is bigger in case of OLSR as compared to DSR. Figure 17: Graph between Number of Nodes and Energy Consumption for Key Generation in case of OLSR Figure 17 shows Number of Nodes versus Energy Consumption for Key Generation in the network in case of Optimal Link State Routing Protocol. In OLSR protocol, Energy Consumption for Key Generation in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Energy Consumption for Key Generation in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Here, it is observed that if number of Rekeys increase, the Energy Consumption for Key Generation also increases. Figure 16: Graph between Number of Nodes and Energy Consumption for Data Transmission in case of OLSR Figure 16 shows Number of Nodes versus Energy Consumption for Data Transmission in the network in case of Optimal Link State Routing Protocol. In OLSR protocol, Energy Consumption for Data Transmission in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Energy Consumption for Data Transmission in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Energy consumption for Data Transmission is bigger in case of OLSR as compared to DSR. Figure 18: Graph between Number of Nodes and Total Energy Consumption in Network in case of OLSR Figure 18 shows Number of Nodes versus Total Energy Consumption in Network in case of Optimal Link State Routing Protocol. In OLSR protocol, Total Energy Consumption in Network in the Static categories is less as compared to the Semi-Dynamic categories and Dynamic categories. Similarly, Total Energy Consumption in Network in the Semi-Dynamic categories is less as compared to the Dynamic categories. Total Energy Consumption in Network is sum of Energy Consumption for Routing, Energy Consumption for Key Generation and Energy Consumption for Data Transmission.
8 Bonfring International Journal of Networking Technologies and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, June VIII. CONCLUSION Secure Group Communication is the most challenging issue in Mobile Ad-hoc Network. Reason behind this serious problem of centralization of administration, power consumptions and lack of fixed infrastructure. Power resources are limited for nodes in Mobile Ad-hoc Network. We have analyzed the logic of Optimal Probabilistic Logical Key Hierarchy which reduces Rekey Cost. Reduction of Rekey Cost reduces the cost of energy data transmission and consumption of energy which increases the longer existence of Mobile Ad-hoc Network. REFERENCES [1] X. Hong, K. Xu and M. Gerla, Scalable routing protocols for mobile ad hoc networks, IEEE network, Vol. 16, No. 4, Pp , [2] K. Huishan, C. Huimin and K.Y. Nam, Routing Protocols in Ad-hoc Wireless Networks, National University of Singapore, [3] T. Lin, S.F. Midkiff and J.S. Park, A framework for wireless ad hoc routing protocols, IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking, Vol. 2, Pp , [4] J. Macker, Mobile ad hoc networking (MANET): Routing protocol performance issues and evaluation considerations, RFC 2501, IETF Network Working Group, [5] T. Clausen and P. Jacquet, Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR), RFC 3626, IETF Network Working Group, [6] Y. Ge, T. Kunz and L. Lamont, Quality of service routing in ad-hoc networks using OLSR, IEEE 36th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Pp. 1-9, [7] P. Jacquet, P. Muhlethaler, T. Clausen, A. Laouiti, A. Qayyum and L. Viennot, Optimized link state routing protocol for ad hoc networks, IEEE International Conference on Multi Topic, IEEE INMIC Technology for the 21st Century, Pp , [8] A. Laouti, P. Mühlethaler, A. Najid and E. Plakoo, Simulation results of the olsr routing protocol for wireless network, Doctoral dissertation, INRIA, [9] S.S. Kaushik and P.R. Deshmukh, Comparison of effectiveness of AODV, DSDV and DSR Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad hoc Networks, International Journal of Information Technology and Knowledge Management, Vol. 2, No. 2, Pp , [10] [11] N.R. Potlapally, S. Ravi, A. Raghunathan and N.K. Jha, Analyzing the energy consumption of security protocols, In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Low power electronics and design, Pp , [12] A.M. Hegland, E. Winjum, S.F. Mjolsnes, C. Rong, O. Kure and P. Spilling, A survey of key management in ad hoc networks, IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, Vol. 8, No. 3, Pp , [13] J. Li, G. Cui, X. Fu, Z. Liu and L. Su, A secure group key management scheme in ad hoc networks, IEEE International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Vol. 2, Pp , [14] J. Biswas and S.K. Nandy, Efficient Key Management and Distribution for MANET, IEEE International Conference on Communications, Vol. 5, Pp , [15] K. Gomathi and B. Parvathavarthini, An efficient cluster based key management scheme for MANET with authentication, IEEE Trendz in Information Sciences & Computing (TISC), Pp , [16] M. Chatterjee, S.K. Das and D. Turgut, An on-demand weighted clustering algorithm (WCA) for ad hoc networks, IEEE Conference on Global Telecommunications, Vol. 3, Pp , [17] A.R. Pais and S. Joshi, A new probabilistic rekeying method for secure multicast groups, International Journal of Information Security, Vol. 9, No. 4, Pp , [18] A.A. Selçuk and D. Sidhu, Probabilistic optimization techniques for multicast key management, Computer Networks, Vol. 40, No. 2, Pp , 2002.
Re-Clustering Approach using WCA in DSR and OLSR Routing Protocols in MANET
 Bonfring International Journal of Networking Technologies and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2016 4 Re-Clustering Approach using WCA in DSR and OLSR Routing Protocols in MANET Harshit Prakash Patidar
Bonfring International Journal of Networking Technologies and Applications, Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2016 4 Re-Clustering Approach using WCA in DSR and OLSR Routing Protocols in MANET Harshit Prakash Patidar
Adoptive Approach of DSR and OLSR Routing Protocols using Optimal Probabilistic Logical Key Hierarchy in MANET
 International Journal of Computer Engineering and Information Technology VOL. 8, NO. 5, May 2016, 71 78 Available online at: www.ijceit.org E-ISSN 2412-8856 (Online) Adoptive Approach of DSR and OLSR Routing
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Information Technology VOL. 8, NO. 5, May 2016, 71 78 Available online at: www.ijceit.org E-ISSN 2412-8856 (Online) Adoptive Approach of DSR and OLSR Routing
Performance Of OLSR Routing Protocol Under Different Route Refresh Intervals In Ad Hoc Networks
 Performance Of OLSR Routing Protocol Under Different Route Refresh Intervals In Ad Hoc Networks P.Suganthi Research Scholar Mother Teresa Women s University Kodaikanal, TamilNadu, India Dr.A.Tamilarasi
Performance Of OLSR Routing Protocol Under Different Route Refresh Intervals In Ad Hoc Networks P.Suganthi Research Scholar Mother Teresa Women s University Kodaikanal, TamilNadu, India Dr.A.Tamilarasi
Simulation & Performance Analysis of Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocol
 Simulation & Performance Analysis of Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocol V.S.Chaudhari 1, Prof.P.N.Matte 2, Prof. V.P.Bhope 3 Department of E&TC, Raisoni College of Engineering, Ahmednagar Abstract:-
Simulation & Performance Analysis of Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocol V.S.Chaudhari 1, Prof.P.N.Matte 2, Prof. V.P.Bhope 3 Department of E&TC, Raisoni College of Engineering, Ahmednagar Abstract:-
2013, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 85
 Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Overview of
Volume 3, Issue 12, December 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Overview of
Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET
 208 Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET Jaya Jacob 1,V.Seethalakshmi 2 1 II MECS,Sri Shakthi Institute of Science and Technology, Coimbatore, India 2 Associate Professor-ECE, Sri
208 Performance Evaluation of Various Routing Protocols in MANET Jaya Jacob 1,V.Seethalakshmi 2 1 II MECS,Sri Shakthi Institute of Science and Technology, Coimbatore, India 2 Associate Professor-ECE, Sri
Estimate the Routing Protocols for Internet of Things
 Estimate the Routing Protocols for Internet of Things 1 Manjushree G, 2 Jayanthi M.G 1,2 Dept. of Computer Network and Engineering Cambridge Institute of Technology Bangalore, India Abstract Internet of
Estimate the Routing Protocols for Internet of Things 1 Manjushree G, 2 Jayanthi M.G 1,2 Dept. of Computer Network and Engineering Cambridge Institute of Technology Bangalore, India Abstract Internet of
Routing Protocols in MANETs
 Chapter 4 Routing Protocols in MANETs 4.1 Introduction The main aim of any Ad Hoc network routing protocol is to meet the challenges of the dynamically changing topology and establish a correct and an
Chapter 4 Routing Protocols in MANETs 4.1 Introduction The main aim of any Ad Hoc network routing protocol is to meet the challenges of the dynamically changing topology and establish a correct and an
Performance Analysis and Enhancement of Routing Protocol in Manet
 Vol.2, Issue.2, Mar-Apr 2012 pp-323-328 ISSN: 2249-6645 Performance Analysis and Enhancement of Routing Protocol in Manet Jaya Jacob*, V.Seethalakshmi** *II MECS, Sri Shakthi Institute of Engineering and
Vol.2, Issue.2, Mar-Apr 2012 pp-323-328 ISSN: 2249-6645 Performance Analysis and Enhancement of Routing Protocol in Manet Jaya Jacob*, V.Seethalakshmi** *II MECS, Sri Shakthi Institute of Engineering and
Performance Analysis of MANET Routing Protocols OLSR and AODV
 VOL. 2, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 211 Performance Analysis of MANET Routing Protocols OLSR and AODV Jiri Hosek Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication, Brno University of Technology Email: hosek@feec.vutbr.cz
VOL. 2, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 211 Performance Analysis of MANET Routing Protocols OLSR and AODV Jiri Hosek Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication, Brno University of Technology Email: hosek@feec.vutbr.cz
Routing Protocols in MANET: Comparative Study
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 7, July 2014, pg.119
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 7, July 2014, pg.119
Impact of Hello Interval on Performance of AODV Protocol
 Impact of Hello Interval on Performance of AODV Nisha Bhanushali Priyanka Thakkar Prasanna Shete ABSTRACT The multi-hop ad hoc networks are self organizing networks with dynamic topology. The reactive
Impact of Hello Interval on Performance of AODV Nisha Bhanushali Priyanka Thakkar Prasanna Shete ABSTRACT The multi-hop ad hoc networks are self organizing networks with dynamic topology. The reactive
A COMPARISON OF IMPROVED AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL BASED ON IEEE AND IEEE
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 4, No. 2 (2009) 132-141 School of Engineering, Taylor s University College A COMPARISON OF IMPROVED AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL BASED ON IEEE 802.11 AND IEEE
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 4, No. 2 (2009) 132-141 School of Engineering, Taylor s University College A COMPARISON OF IMPROVED AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL BASED ON IEEE 802.11 AND IEEE
Investigation on OLSR Routing Protocol Efficiency
 Investigation on OLSR Routing Protocol Efficiency JIRI HOSEK 1, KAROL MOLNAR 2 Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication, Brno University of Technology Purkynova
Investigation on OLSR Routing Protocol Efficiency JIRI HOSEK 1, KAROL MOLNAR 2 Department of Telecommunications Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication, Brno University of Technology Purkynova
Performance of Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols in Different Network Sizes
 Performance of Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols in Different Network Sizes Sudheer Kumar 1, Akhilesh Yadav 2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Kanpur Institute of Technology, Kanpur sudheerkr21@gmail.co
Performance of Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols in Different Network Sizes Sudheer Kumar 1, Akhilesh Yadav 2 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Kanpur Institute of Technology, Kanpur sudheerkr21@gmail.co
Performance Analysis of Wireless Mobile ad Hoc Network with Varying Transmission Power
 , pp.1-6 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsacs.2015.3.1.01 Performance Analysis of Wireless Mobile ad Hoc Network with Varying Transmission Power Surabhi Shrivastava, Laxmi Shrivastava and Sarita Singh Bhadauria
, pp.1-6 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsacs.2015.3.1.01 Performance Analysis of Wireless Mobile ad Hoc Network with Varying Transmission Power Surabhi Shrivastava, Laxmi Shrivastava and Sarita Singh Bhadauria
Performance Analysis of Proactive and Reactive Routing Protocols for QOS in MANET through OLSR & AODV
 MIT International Journal of Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering, Vol. 3, No. 2, August 2013, pp. 57 61 57 Performance Analysis of Proactive and Reactive Routing Protocols for QOS in MANET through
MIT International Journal of Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering, Vol. 3, No. 2, August 2013, pp. 57 61 57 Performance Analysis of Proactive and Reactive Routing Protocols for QOS in MANET through
QoS Routing By Ad-Hoc on Demand Vector Routing Protocol for MANET
 2011 International Conference on Information and Network Technology IPCSIT vol.4 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore QoS Routing By Ad-Hoc on Demand Vector Routing Protocol for MANET Ashwini V. Biradar
2011 International Conference on Information and Network Technology IPCSIT vol.4 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore QoS Routing By Ad-Hoc on Demand Vector Routing Protocol for MANET Ashwini V. Biradar
OLSR Protocol with Cross Layer Design in MANET
 OLSR Protocol with Cross Layer Design in MANET 1 Janakkumar Patel, 2 Mitesh Thakkar Department Of Computer Engineering L.J. Institute of Engineering & Technology, Ahmedabad-382210, India 1 janakp005@gmail.com
OLSR Protocol with Cross Layer Design in MANET 1 Janakkumar Patel, 2 Mitesh Thakkar Department Of Computer Engineering L.J. Institute of Engineering & Technology, Ahmedabad-382210, India 1 janakp005@gmail.com
Comparative Study on Performance Evaluation of Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols Navpreet Chana 1, Navjot Kaur 2, Kuldeep Kumar 3, Someet Singh 4
 Comparative Study on Performance Evaluation of Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols Navpreet Chana 1, Navjot Kaur 2, Kuldeep Kumar 3, Someet Singh 4 1 Research Scholar, Computer Science and Engineering, Lovely
Comparative Study on Performance Evaluation of Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols Navpreet Chana 1, Navjot Kaur 2, Kuldeep Kumar 3, Someet Singh 4 1 Research Scholar, Computer Science and Engineering, Lovely
Shortcut Tree Routing using Neighbor Table in ZigBee Wireless Networks
 Shortcut Tree Routing using Neighbor Table in ZigBee Wireless Networks Salmu K.P 1, Chinchu James 2 1,2 Department of Computer Science, IIET, Nellikuzhi Abstract- ZigBee is a worldwide standard for wireless
Shortcut Tree Routing using Neighbor Table in ZigBee Wireless Networks Salmu K.P 1, Chinchu James 2 1,2 Department of Computer Science, IIET, Nellikuzhi Abstract- ZigBee is a worldwide standard for wireless
Figure 1: Ad-Hoc routing protocols.
 Performance Analysis of Routing Protocols for Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Sukhchandan Lally and Ljiljana Trajković Simon Fraser University Vancouver, British Columbia Canada E-mail: {lally, ljilja}@sfu.ca
Performance Analysis of Routing Protocols for Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks Sukhchandan Lally and Ljiljana Trajković Simon Fraser University Vancouver, British Columbia Canada E-mail: {lally, ljilja}@sfu.ca
Routing in Ad Hoc Wireless Networks PROF. MICHAEL TSAI / DR. KATE LIN 2014/05/14
 Routing in Ad Hoc Wireless Networks PROF. MICHAEL TSAI / DR. KATE LIN 2014/05/14 Routing Algorithms Link- State algorithm Each node maintains a view of the whole network topology Find the shortest path
Routing in Ad Hoc Wireless Networks PROF. MICHAEL TSAI / DR. KATE LIN 2014/05/14 Routing Algorithms Link- State algorithm Each node maintains a view of the whole network topology Find the shortest path
Throughput Analysis of Many to One Multihop Wireless Mesh Ad hoc Network
 Throughput Analysis of Many to One Multihop Wireless Mesh Ad hoc Network Dr.S.Senthil Kumar,Assistant Professor, Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Government College of Engineering, Salem,India
Throughput Analysis of Many to One Multihop Wireless Mesh Ad hoc Network Dr.S.Senthil Kumar,Assistant Professor, Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Government College of Engineering, Salem,India
A Survey - Energy Efficient Routing Protocols in MANET
 , pp. 163-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijfgcn.2016.9.5.16 A Survey - Energy Efficient Routing Protocols in MANET Jyoti Upadhyaya and Nitin Manjhi Department of Computer Science, RGPV University Shriram
, pp. 163-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijfgcn.2016.9.5.16 A Survey - Energy Efficient Routing Protocols in MANET Jyoti Upadhyaya and Nitin Manjhi Department of Computer Science, RGPV University Shriram
A Highly Effective and Efficient Route Discovery & Maintenance in DSR
 A Highly Effective and Efficient Route Discovery & Maintenance in DSR Shiva Prakash 1, Rajeev Kumar 2, Brijesh Nayak 3, Manindar Kumar Yadav 4 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Madan Mohan
A Highly Effective and Efficient Route Discovery & Maintenance in DSR Shiva Prakash 1, Rajeev Kumar 2, Brijesh Nayak 3, Manindar Kumar Yadav 4 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Madan Mohan
ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENT REACTIVE, PROACTIVE & HYBRID ROUTING PROTOCOLS: A REVIEW
 ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENT REACTIVE, PROACTIVE & HYBRID ROUTING PROTOCOLS: A REVIEW Kirandeep Kaur 1, Mr.Pawan Luthra 2, Er.Gagandeep 3 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shaheed Bhagat Singh
ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENT REACTIVE, PROACTIVE & HYBRID ROUTING PROTOCOLS: A REVIEW Kirandeep Kaur 1, Mr.Pawan Luthra 2, Er.Gagandeep 3 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Shaheed Bhagat Singh
MANET is considered a collection of wireless mobile nodes that are capable of communicating with each other. Research Article 2014
 Throughput Analysis of Proactive and Reactive MANET Routing Protocols Kiranveer Kaur 1 Surinderjit Kaur 2 Vikramjit Singh 3 Department of Computer Science, University College of Engineering, Department
Throughput Analysis of Proactive and Reactive MANET Routing Protocols Kiranveer Kaur 1 Surinderjit Kaur 2 Vikramjit Singh 3 Department of Computer Science, University College of Engineering, Department
Impact of Node Velocity and Density on Probabilistic Flooding and its Effectiveness in MANET
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 12, December 2014,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 12, December 2014,
A COMPARISON OF REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS DSR, AODV AND TORA IN MANET
 ISSN: 2278 1323 All Rights Reserved 2016 IJARCET 296 A COMPARISON OF REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS DSR, AODV AND TORA IN MANET Dr. R. Shanmugavadivu 1, B. Chitra 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer
ISSN: 2278 1323 All Rights Reserved 2016 IJARCET 296 A COMPARISON OF REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS DSR, AODV AND TORA IN MANET Dr. R. Shanmugavadivu 1, B. Chitra 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer
Comparative Study of Routing Protocols in MANET
 Comparative Study of Routing Protocols in MANET First Author-PrernaYadav 1 Student,Second Author-ShubhraSaxena 2 Professor Abstract-An ad hoc network is basically a collection of wireless nodes not having
Comparative Study of Routing Protocols in MANET First Author-PrernaYadav 1 Student,Second Author-ShubhraSaxena 2 Professor Abstract-An ad hoc network is basically a collection of wireless nodes not having
Zone-based Proactive Source Routing Protocol for Ad-hoc Networks
 2014 IJSRSET Volume i Issue i Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Science Zone-based Proactive Source Routing Protocol for Ad-hoc Networks Dr.Sangheethaa.S 1, Dr. Arun Korath
2014 IJSRSET Volume i Issue i Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Science Zone-based Proactive Source Routing Protocol for Ad-hoc Networks Dr.Sangheethaa.S 1, Dr. Arun Korath
Performance Evaluation of Two Reactive and Proactive Mobile Ad Hoc Routing Protocols
 www.ijcsi.org 551 Performance Evaluation of Two Reactive and Proactive Mobile Ad Hoc Routing Protocols Kashif Ibrahim Qazi Javed Ahmed Abdul Qudoos Mirza Aamir Mehmood Department of Computer Science, Balochistan
www.ijcsi.org 551 Performance Evaluation of Two Reactive and Proactive Mobile Ad Hoc Routing Protocols Kashif Ibrahim Qazi Javed Ahmed Abdul Qudoos Mirza Aamir Mehmood Department of Computer Science, Balochistan
Performance Comparison of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR MANET Routing Protocols
 Performance Comparison of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR MANET Routing Protocols Akshay Shankar, Lavanya Chelle Information Science Engineering RNS Institute of Technology Bangalore, India Abstract- A Mobile
Performance Comparison of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR MANET Routing Protocols Akshay Shankar, Lavanya Chelle Information Science Engineering RNS Institute of Technology Bangalore, India Abstract- A Mobile
Mobile Communications. Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks
 Ad-hoc+mesh-net 1 Mobile Communications Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Ad-hoc+mesh-net 2 What is an ad-hoc network? What are differences between
Ad-hoc+mesh-net 1 Mobile Communications Ad-hoc and Mesh Networks Manuel P. Ricardo Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Ad-hoc+mesh-net 2 What is an ad-hoc network? What are differences between
A Comparative study of On-Demand Data Delivery with Tables Driven and On-Demand Protocols for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network
 A Comparative study of On-Demand Data Delivery with Tables Driven and On-Demand Protocols for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Humayun Bakht Research Fellow, London School of Commerce, United Kingdom humayunbakht@yahoo.co.uk
A Comparative study of On-Demand Data Delivery with Tables Driven and On-Demand Protocols for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Humayun Bakht Research Fellow, London School of Commerce, United Kingdom humayunbakht@yahoo.co.uk
6367(Print), ISSN (Online) Volume 4, Issue 2, March April (2013), IAEME & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET)
 INTERNATIONAL International Journal of Computer JOURNAL Engineering OF COMPUTER and Technology ENGINEERING (IJCET), ISSN 0976- & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET) ISSN 0976 6367(Print) ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4,
INTERNATIONAL International Journal of Computer JOURNAL Engineering OF COMPUTER and Technology ENGINEERING (IJCET), ISSN 0976- & TECHNOLOGY (IJCET) ISSN 0976 6367(Print) ISSN 0976 6375(Online) Volume 4,
Content. 1. Introduction. 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm. 3. Simulation and Results. 4. Future Work. 5.
 Rahem Abri Content 1. Introduction 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm Path Discovery Reverse Path Setup Forward Path Setup Route Table Management Path Management Local Connectivity Management
Rahem Abri Content 1. Introduction 2. The Ad-hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm Path Discovery Reverse Path Setup Forward Path Setup Route Table Management Path Management Local Connectivity Management
Performance evaluation of reactive and proactive routing protocol in IEEE ad hoc network
 Author manuscript, published in "ITCom 6 - next generation and sensor networks, Boston : United States (26)" DOI :.7/2.68625 Performance evaluation of reactive and proactive routing protocol in IEEE 82.
Author manuscript, published in "ITCom 6 - next generation and sensor networks, Boston : United States (26)" DOI :.7/2.68625 Performance evaluation of reactive and proactive routing protocol in IEEE 82.
ROUTE STABILITY MODEL FOR DSR IN WIRELESS ADHOC NETWORKS
 ROUTE STABILITY MODEL FOR DSR IN WIRELESS ADHOC NETWORKS Ganga S 1, Binu Chandran R 2 1, 2 Mohandas College Of Engineering And Technology Abstract: Wireless Ad-Hoc Network is a collection of wireless mobile
ROUTE STABILITY MODEL FOR DSR IN WIRELESS ADHOC NETWORKS Ganga S 1, Binu Chandran R 2 1, 2 Mohandas College Of Engineering And Technology Abstract: Wireless Ad-Hoc Network is a collection of wireless mobile
[Kamboj* et al., 5(9): September, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116
![[Kamboj* et al., 5(9): September, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116 [Kamboj* et al., 5(9): September, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/92/109489555.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY NOVEL REVIEW OF MANET ROUTING PROTOCOLS Nippun Kamboj*, Dr. Munishwar Rai Department of Computer Applications Maharishi Markandeshwar
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY NOVEL REVIEW OF MANET ROUTING PROTOCOLS Nippun Kamboj*, Dr. Munishwar Rai Department of Computer Applications Maharishi Markandeshwar
Analysis of Black-Hole Attack in MANET using AODV Routing Protocol
 Analysis of Black-Hole Attack in MANET using Routing Protocol Ms Neha Choudhary Electronics and Communication Truba College of Engineering, Indore India Dr Sudhir Agrawal Electronics and Communication
Analysis of Black-Hole Attack in MANET using Routing Protocol Ms Neha Choudhary Electronics and Communication Truba College of Engineering, Indore India Dr Sudhir Agrawal Electronics and Communication
Behaviour of Routing Protocols of Mobile Adhoc Netwok with Increasing Number of Groups using Group Mobility Model
 Behaviour of Routing Protocols of Mobile Adhoc Netwok with Increasing Number of Groups using Group Mobility Model Deepak Agrawal, Brajesh Patel Department of CSE Shri Ram Institute of Technology Jabalpur,
Behaviour of Routing Protocols of Mobile Adhoc Netwok with Increasing Number of Groups using Group Mobility Model Deepak Agrawal, Brajesh Patel Department of CSE Shri Ram Institute of Technology Jabalpur,
PNR: New Position based Routing Algorithm for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
 PNR: New Position based Routing Algorithm for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Hossein Ashtiani, Shahpour Alirezaee, seyed mohsen mir hosseini, HamidKhosravi Abstract An ad hoc network (MANET) has no fixed networking
PNR: New Position based Routing Algorithm for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Hossein Ashtiani, Shahpour Alirezaee, seyed mohsen mir hosseini, HamidKhosravi Abstract An ad hoc network (MANET) has no fixed networking
Improved Performance of Mobile Adhoc Network through Efficient Broadcasting Technique
 Improved Performance of Mobile Adhoc Network through Efficient Broadcasting Technique Vijay J Parmar Department of Computer Engineering,Sarvajanic College of Engineering and Technology Surat, Gujrat (India),E-mail
Improved Performance of Mobile Adhoc Network through Efficient Broadcasting Technique Vijay J Parmar Department of Computer Engineering,Sarvajanic College of Engineering and Technology Surat, Gujrat (India),E-mail
Optimizing Performance of Routing against Black Hole Attack in MANET using AODV Protocol Prerana A. Chaudhari 1 Vanaraj B.
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Optimizing Performance of Routing against Black Hole Attack in MANET using AODV Protocol
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Optimizing Performance of Routing against Black Hole Attack in MANET using AODV Protocol
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS AMANDEEP University College of Engineering, Punjabi University Patiala, Punjab, India amandeep8848@gmail.com GURMEET KAUR University College of Engineering,
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF AODV ROUTING PROTOCOL IN MANETS AMANDEEP University College of Engineering, Punjabi University Patiala, Punjab, India amandeep8848@gmail.com GURMEET KAUR University College of Engineering,
Performance Evaluation Of Ad-Hoc On Demand Routing Protocol (AODV) Using NS-3 Simulator
 Performance Evaluation Of Ad-Hoc On Demand Routing Protocol (AODV) Using NS-3 Simulator Dr. S. K. Singh Professor, Department of EC, India Dr. R. Gupta Asst. Prof. Department of EC, India Abstract: The
Performance Evaluation Of Ad-Hoc On Demand Routing Protocol (AODV) Using NS-3 Simulator Dr. S. K. Singh Professor, Department of EC, India Dr. R. Gupta Asst. Prof. Department of EC, India Abstract: The
Performance Evaluation of MANET through NS2 Simulation
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 1 (2014), pp. 25-30 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Performance Evaluation
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174, Volume 7, Number 1 (2014), pp. 25-30 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Performance Evaluation
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 3, March ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 3, March-2015 1464 Performance Evaluation of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols through Clustering in MANETS Prof. A Rama Rao, M
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 3, March-2015 1464 Performance Evaluation of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols through Clustering in MANETS Prof. A Rama Rao, M
Varying Overhead Ad Hoc on Demand Vector Routing in Highly Mobile Ad Hoc Network
 Journal of Computer Science 7 (5): 678-682, 2011 ISSN 1549-3636 2011 Science Publications Varying Overhead Ad Hoc on Demand Vector Routing in Highly Mobile Ad Hoc Network 1 V. Balaji and 2 V. Duraisamy
Journal of Computer Science 7 (5): 678-682, 2011 ISSN 1549-3636 2011 Science Publications Varying Overhead Ad Hoc on Demand Vector Routing in Highly Mobile Ad Hoc Network 1 V. Balaji and 2 V. Duraisamy
Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Networks Lesson 05 Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Routing Algorithms Part 2
 Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Networks Lesson 05 Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Routing Algorithms Part 2 Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Temporally ordered routing algorithm (TORA) A reactive
Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Networks Lesson 05 Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Routing Algorithms Part 2 Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Temporally ordered routing algorithm (TORA) A reactive
Review paper on performance analysis of AODV, DSDV, OLSR on the basis of packet delivery
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661, p- ISSN: 2278-8727Volume 11, Issue 1 (May. - Jun. 2013), PP 51-55 Review paper on performance analysis of AODV, DSDV, OLSR on the basis
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661, p- ISSN: 2278-8727Volume 11, Issue 1 (May. - Jun. 2013), PP 51-55 Review paper on performance analysis of AODV, DSDV, OLSR on the basis
Quantitative Performance Evaluation of DSDV and OLSR Routing Protocols in Wireless Ad-hoc Networks
 Quantitative Performance Evaluation of DSDV and OLSR Routing Protocols in Wireless Ad-hoc Networks E. Suresh Babu P S V Srinivasa Rao M Srinivasa Rao C Nagaraju Assoc. Prof. of CSE K L University, Vijayawada.
Quantitative Performance Evaluation of DSDV and OLSR Routing Protocols in Wireless Ad-hoc Networks E. Suresh Babu P S V Srinivasa Rao M Srinivasa Rao C Nagaraju Assoc. Prof. of CSE K L University, Vijayawada.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR ADVANCE RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY WINGS TO YOUR THOUGHTS..
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR ADVANCE RESEARCH An Overview of Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks: Architecture, Routing and Challenges Avadhesh Kumar 1 Sonali Yadav 2 Kamalesh Chandra Maurya 3 1 Assistant Professor, avadhesh@iul.ac.in
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL FOR ADVANCE RESEARCH An Overview of Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks: Architecture, Routing and Challenges Avadhesh Kumar 1 Sonali Yadav 2 Kamalesh Chandra Maurya 3 1 Assistant Professor, avadhesh@iul.ac.in
Power aware Multi-path Routing Protocol for MANETS
 Power aware Multi-path Routing Protocol for MANETS Shruthi P Murali 1,Joby John 2 1 (ECE Dept, SNGCE, India) 2 (ECE Dept, SNGCE, India) Abstract: Mobile Adhoc Network consists of a large number of mobile
Power aware Multi-path Routing Protocol for MANETS Shruthi P Murali 1,Joby John 2 1 (ECE Dept, SNGCE, India) 2 (ECE Dept, SNGCE, India) Abstract: Mobile Adhoc Network consists of a large number of mobile
Evaluation of Routing Protocols for Mobile Ad hoc Networks
 International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) Evaluation of Routing Protocols for Mobile Ad hoc Networks Abstract Mobile Ad hoc network is a self-configuring infrastructure less network
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) Evaluation of Routing Protocols for Mobile Ad hoc Networks Abstract Mobile Ad hoc network is a self-configuring infrastructure less network
Simulation and Performance Analysis of OLSR Routing Protocol Using OPNET
 Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2012 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: Simulation and Performance Analysis
Volume 2, Issue 2, February 2012 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: Simulation and Performance Analysis
Simulation and Comparative Analysis of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR Routing Protocol in MANET Abstract Keywords:
 Volume-9 Number-1 Jan -June 2017 pp. 16-21 available online at www.csjournalss.com Simulation and Comparative Analysis of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR Routing Protocol in MANET Sachin Lalar, Arun Kumar Yadav
Volume-9 Number-1 Jan -June 2017 pp. 16-21 available online at www.csjournalss.com Simulation and Comparative Analysis of AODV, DSR, DSDV and OLSR Routing Protocol in MANET Sachin Lalar, Arun Kumar Yadav
Performance Evaluation of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocol in wireless sensor network Environment
 2012 International Conference on Computer Networks and Communication Systems (CNCS 2012) IPCSIT vol.35(2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Evaluation of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocol in wireless
2012 International Conference on Computer Networks and Communication Systems (CNCS 2012) IPCSIT vol.35(2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Evaluation of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocol in wireless
Anil Saini Ph.D. Research Scholar Department of Comp. Sci. & Applns, India. Keywords AODV, CBR, DSDV, DSR, MANETs, PDF, Pause Time, Speed, Throughput.
 Volume 6, Issue 7, July 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Performance Analysis
Volume 6, Issue 7, July 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Performance Analysis
Simulation and Performance Analysis of Throughput and Delay on Varying Time and Number of Nodes in MANET
 International Journal of Recent Research and Review, Vol. VII, Issue 2, June 2014 ISSN 2277 8322 Simulation and Performance Analysis of and on Varying and Number of Nodes in MANET Arun Jain 1, Ramesh Bharti
International Journal of Recent Research and Review, Vol. VII, Issue 2, June 2014 ISSN 2277 8322 Simulation and Performance Analysis of and on Varying and Number of Nodes in MANET Arun Jain 1, Ramesh Bharti
Performance Analysis of DSDV, AODV, DSR and OLSR MANET Routing Protocols
 International Journal of Applied Science & Technology Research Excellence Vol. 5 Issue 1, Jan.- Feb. 215, Performance Analysis of,, and MANET Routing Protocols Sunil Malik #1, Dr. K.P Yadav *2, #1 Research
International Journal of Applied Science & Technology Research Excellence Vol. 5 Issue 1, Jan.- Feb. 215, Performance Analysis of,, and MANET Routing Protocols Sunil Malik #1, Dr. K.P Yadav *2, #1 Research
Implementation and simulation of OLSR protocol with QoS in Ad Hoc Networks
 Implementation and simulation of OLSR protocol with QoS in Ad Hoc Networks Mounir FRIKHA, Manel MAAMER Higher School of Communication of Tunis (SUP COM), Network Department, m.frikha@supcom.rnu.tn ABSTRACT
Implementation and simulation of OLSR protocol with QoS in Ad Hoc Networks Mounir FRIKHA, Manel MAAMER Higher School of Communication of Tunis (SUP COM), Network Department, m.frikha@supcom.rnu.tn ABSTRACT
Ad Hoc Routing Protocols and Issues
 Ad Hoc Routing Protocols and Issues Stefano Basagni ECE Dept Northeastern University Boston, Jan 2003 Ad hoc (AD-HAHK or AD-HOKE)-Adjective a) Concerned with a particular end or purpose, and b) formed
Ad Hoc Routing Protocols and Issues Stefano Basagni ECE Dept Northeastern University Boston, Jan 2003 Ad hoc (AD-HAHK or AD-HOKE)-Adjective a) Concerned with a particular end or purpose, and b) formed
To enhance Routing in ZigBee Wireless Networks
 To enhance Routing in ZigBee Wireless Networks P.Chanthiya Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Dr.Sivanthi Aditanar College of Engineering, Tiruchendur, India Abstract The
To enhance Routing in ZigBee Wireless Networks P.Chanthiya Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Dr.Sivanthi Aditanar College of Engineering, Tiruchendur, India Abstract The
Performance Evaluation of AODV DSDV and OLSR Routing Protocols with Varying FTP Connections in MANET
 Performance Evaluation of AODV DSDV and OLSR Protocols with Varying FTP Connections in MANET Alok Upadhyay, Rupali Phatak Research Scholar, Asst. Professor -Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
Performance Evaluation of AODV DSDV and OLSR Protocols with Varying FTP Connections in MANET Alok Upadhyay, Rupali Phatak Research Scholar, Asst. Professor -Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
Scalability Performance of AODV, TORA and OLSR with Reference to Variable Network Size
 Lovekesh Kumar / International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: Scalability Performance of AODV, TORA and OLSR with Reference to Variable Network Size Lovekesh Kumar* *(Department
Lovekesh Kumar / International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN: Scalability Performance of AODV, TORA and OLSR with Reference to Variable Network Size Lovekesh Kumar* *(Department
AODV-PA: AODV with Path Accumulation
 -PA: with Path Accumulation Sumit Gwalani Elizabeth M. Belding-Royer Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara fsumitg, ebeldingg@cs.ucsb.edu Charles E. Perkins Communications
-PA: with Path Accumulation Sumit Gwalani Elizabeth M. Belding-Royer Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara fsumitg, ebeldingg@cs.ucsb.edu Charles E. Perkins Communications
Mitigating Superfluous Flooding of Control Packets MANET
 Mitigating Superfluous Flooding of Control Packets MANET B.Shanmugha Priya 1 PG Student, Department of Computer Science, Park College of Engineering and Technology, Kaniyur, Coimbatore, India 1 Abstract:
Mitigating Superfluous Flooding of Control Packets MANET B.Shanmugha Priya 1 PG Student, Department of Computer Science, Park College of Engineering and Technology, Kaniyur, Coimbatore, India 1 Abstract:
Experiment and Evaluation of a Mobile Ad Hoc Network with AODV Routing Protocol
 Experiment and Evaluation of a Mobile Ad Hoc Network with AODV Routing Protocol Kalyan Kalepu, Shiv Mehra and Chansu Yu, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University 2121
Experiment and Evaluation of a Mobile Ad Hoc Network with AODV Routing Protocol Kalyan Kalepu, Shiv Mehra and Chansu Yu, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cleveland State University 2121
Performance Comparison of DSDV, AODV, DSR, Routing protocols for MANETs
 2012 International Conference on Computer Networks and Communication Systems (CNCS 2012) IPCSIT vol.35(2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Comparison of DSDV, AODV, DSR, Routing protocols
2012 International Conference on Computer Networks and Communication Systems (CNCS 2012) IPCSIT vol.35(2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Comparison of DSDV, AODV, DSR, Routing protocols
An Efficient Zone-Based Multicast Routing Protocol for Ad Hoc Network
 An Efficient Zone-Based Multicast Routing Protocol for Ad Hoc Network Tain-Sao Chang 1 Jyh-Horng Wen 2* and Tzu-Ting Wu 3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering National Chung Cheng University No. 168
An Efficient Zone-Based Multicast Routing Protocol for Ad Hoc Network Tain-Sao Chang 1 Jyh-Horng Wen 2* and Tzu-Ting Wu 3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering National Chung Cheng University No. 168
A Comparative Analysis of Energy Preservation Performance Metric for ERAODV, RAODV, AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in MANET
 A Comparative Analysis of Energy Preservation Performance Metric for ERAODV, RAODV, AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in MANET Bhabani Sankar Gouda Department of Computer Science & Engineering National Institute
A Comparative Analysis of Energy Preservation Performance Metric for ERAODV, RAODV, AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in MANET Bhabani Sankar Gouda Department of Computer Science & Engineering National Institute
Analysis QoS Parameters for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols: Under Group Mobility Model
 2009 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications IPCSIT vol.2 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Analysis QoS Parameters for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols: Under Group
2009 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications IPCSIT vol.2 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Analysis QoS Parameters for Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Routing Protocols: Under Group
Comprehensive Study and Review Various Routing Protocols in MANET
 126 Comprehensive Study and Review Various Routing Protocols in MANET Prabhjot Kaur 1, Preet Bala 2 M-Tech Student(CSE), GZS PTU CAMPUS, Bathinda Prabhjot6996@gmail.com Dr. Shaveta Rani, Dr. Paramjeet
126 Comprehensive Study and Review Various Routing Protocols in MANET Prabhjot Kaur 1, Preet Bala 2 M-Tech Student(CSE), GZS PTU CAMPUS, Bathinda Prabhjot6996@gmail.com Dr. Shaveta Rani, Dr. Paramjeet
REVIEW ON ROUTING PROTOCOLS FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
 REVIEW ON ROUTING PROTOCOLS FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS G. Poornima 1, Mr. M. Rajasenathipathi 2, 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science, NGM College, Pollachi 2 Assistant Professor, Department
REVIEW ON ROUTING PROTOCOLS FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS G. Poornima 1, Mr. M. Rajasenathipathi 2, 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science, NGM College, Pollachi 2 Assistant Professor, Department
Simulation and Analysis of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Vehicular Adhoc Networks using Random Waypoint Mobility Model
 Simulation and Analysis of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Vehicular Adhoc Networks using Random Waypoint Mobility Model 1 R. Jeevitha, 2 M. Chandra Kumar 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer
Simulation and Analysis of AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Vehicular Adhoc Networks using Random Waypoint Mobility Model 1 R. Jeevitha, 2 M. Chandra Kumar 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer
A Comparative Study between AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks using Network Simulator NS2
 A Comparative Study between AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks using Network Simulator NS2 Marwan Aziz Mohammed Dept. of Software Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Koya University,
A Comparative Study between AODV and DSDV Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks using Network Simulator NS2 Marwan Aziz Mohammed Dept. of Software Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Koya University,
Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network
 International Journal of Computer Science & Management Studies, Vol. 12, Issue 02, April 2012 Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Sachin Minocha M. Tech Student, Vaish College of Engineering, Rohtak, Haryana
International Journal of Computer Science & Management Studies, Vol. 12, Issue 02, April 2012 Protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Network Sachin Minocha M. Tech Student, Vaish College of Engineering, Rohtak, Haryana
MODIFICATION AND COMPARISON OF DSDV AND DSR PROTOCOLS
 MODIFICATION AND COMPARISON OF DSDV AND DSR PROTOCOLS Department of computer science Thadomal Shahani engineering college Mumbai-400051, ABSTRACT: In this era of mobile devices, mobile ad-hoc network (MANET)
MODIFICATION AND COMPARISON OF DSDV AND DSR PROTOCOLS Department of computer science Thadomal Shahani engineering college Mumbai-400051, ABSTRACT: In this era of mobile devices, mobile ad-hoc network (MANET)
Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Networks Lesson 04 Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Routing Algorithms Part 1
 Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Networks Lesson 04 Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Routing Algorithms Part 1 Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Ad-hoc networks deployment For routing, target detection,
Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Networks Lesson 04 Mobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) Routing Algorithms Part 1 Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Ad-hoc networks deployment For routing, target detection,
Effects of Caching on the Performance of DSR Protocol
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, p-issn: 2278-8719, Volume 2, Issue 9 (September 2012), PP 07-11 Effects of Caching on the Performance of DSR Protocol Narinderjeet Kaur 1, Maninder
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, p-issn: 2278-8719, Volume 2, Issue 9 (September 2012), PP 07-11 Effects of Caching on the Performance of DSR Protocol Narinderjeet Kaur 1, Maninder
' INRIA Rocquencourt, Domaine de Voluceau
 OPTIMIZED FLOODING AND INTERFERENCE-AWARE QOS ROUTING IN OLSR* Dang Quan ~ ~ u ~ and e n Pascale ' ~inet' ' INRIA Rocquencourt, Domaine de Voluceau Rocquencourt - B.P 105 78153 Le Chesnay Cedex, France
OPTIMIZED FLOODING AND INTERFERENCE-AWARE QOS ROUTING IN OLSR* Dang Quan ~ ~ u ~ and e n Pascale ' ~inet' ' INRIA Rocquencourt, Domaine de Voluceau Rocquencourt - B.P 105 78153 Le Chesnay Cedex, France
Analysis of Routing Protocols in MANETs
 Analysis of Routing Protocols in MANETs Musica Supriya, Rashmi, Nishchitha, Ashwini C Shetty, Sharath Kumar Student, Dept. of CSE, SMVITM Bantakal, Karnataka, India Student, Dept. of CSE, SMVITM Bantakal,
Analysis of Routing Protocols in MANETs Musica Supriya, Rashmi, Nishchitha, Ashwini C Shetty, Sharath Kumar Student, Dept. of CSE, SMVITM Bantakal, Karnataka, India Student, Dept. of CSE, SMVITM Bantakal,
Kapitel 5: Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Characteristics. Applications of Ad Hoc Networks. Wireless Communication. Wireless communication networks types
 Kapitel 5: Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Mobilkommunikation 2 WS 08/09 Wireless Communication Wireless communication networks types Infrastructure-based networks Infrastructureless networks Ad hoc networks Prof.
Kapitel 5: Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Mobilkommunikation 2 WS 08/09 Wireless Communication Wireless communication networks types Infrastructure-based networks Infrastructureless networks Ad hoc networks Prof.
A SURVEY OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
 Journal homepage: www.mjret.in ISSN:2348-6953 A SURVEY OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS Ms. Amruta Kodole 1, Prof. P. M. Agarkar 2 Computer Engineering Dr. D. Y. Patil School Of Engineering
Journal homepage: www.mjret.in ISSN:2348-6953 A SURVEY OF ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS Ms. Amruta Kodole 1, Prof. P. M. Agarkar 2 Computer Engineering Dr. D. Y. Patil School Of Engineering
Keywords VANET, Routing protocols, AODV, DSR, DSDV.
 Volume 5, Issue 5, May 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Comparative Study
Volume 5, Issue 5, May 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Comparative Study
UCS-805 MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2011 TOPIC 8. ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala.
 Mobile Ad Hoc Networks: Routing TOPIC 8 UCS-805 MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2011 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET) Introduction
Mobile Ad Hoc Networks: Routing TOPIC 8 UCS-805 MOBILE COMPUTING Jan-May,2011 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET) Introduction
A Review Paper on Secure Routing Technique for MANETs
 A Review Paper on Secure Routing Technique for MANETs Sonali Sharma 1, Simranjit Kaur 2 1M.Tech student, Dept. of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Sri Sai College of Engineering and Technology(Badhani),
A Review Paper on Secure Routing Technique for MANETs Sonali Sharma 1, Simranjit Kaur 2 1M.Tech student, Dept. of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Sri Sai College of Engineering and Technology(Badhani),
Unicast Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. Dr. Ashikur Rahman CSE 6811: Wireless Ad hoc Networks
 Unicast Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks 1 Routing problem 2 Responsibility of a routing protocol Determining an optimal way to find optimal routes Determining a feasible path to a destination based on
Unicast Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks 1 Routing problem 2 Responsibility of a routing protocol Determining an optimal way to find optimal routes Determining a feasible path to a destination based on
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DSR USING A NOVEL APPROACH
 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DSR USING A NOVEL APPROACH 1. Prof.S.P. Setti 2. Narasimha Raju K 3. Naresh Kumar K CS&SE Dept., CS&SE Dept., CS&SE Dept., AU College of Engineering, AU College of Engineering,
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF DSR USING A NOVEL APPROACH 1. Prof.S.P. Setti 2. Narasimha Raju K 3. Naresh Kumar K CS&SE Dept., CS&SE Dept., CS&SE Dept., AU College of Engineering, AU College of Engineering,
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS AND STUDY OF DIFFERENT QOS PARAMETERS OF WIRELESS AD-HOC NETWORK
 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS AND STUDY OF DIFFERENT QOS PARAMETERS OF WIRELESS AD-HOC NETWORK Nalin Gahlaut 1, Jaya sharma 2, Pankaj Kumar 3, Kaushal Kumar 4 1 Doctoral Candidate, Uttarakhand Technical University,
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS AND STUDY OF DIFFERENT QOS PARAMETERS OF WIRELESS AD-HOC NETWORK Nalin Gahlaut 1, Jaya sharma 2, Pankaj Kumar 3, Kaushal Kumar 4 1 Doctoral Candidate, Uttarakhand Technical University,
A Survey on Wireless Routing Protocols (AODV, DSR, DSDV)
 RESEARCH ARTICLE International Journal of Computer Techniques - Volume 2 Issue 1, 2015 OPEN ACCESS A Survey on Wireless Routing Protocols (AODV, DSR, DSDV) Sejal D Mello 1, Priyanka B. Patil 2, Tarannum
RESEARCH ARTICLE International Journal of Computer Techniques - Volume 2 Issue 1, 2015 OPEN ACCESS A Survey on Wireless Routing Protocols (AODV, DSR, DSDV) Sejal D Mello 1, Priyanka B. Patil 2, Tarannum
Performance Analysis of Routing Protocols in MANET
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661, p- ISSN: 2278-8727Volume 16, Issue 2, Ver. XI (Mar-Apr. 2014), PP 89-94 Performance Analysis of Routing Protocols in MANET Mohamed Otmani
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661, p- ISSN: 2278-8727Volume 16, Issue 2, Ver. XI (Mar-Apr. 2014), PP 89-94 Performance Analysis of Routing Protocols in MANET Mohamed Otmani
An Extensive Simulation Analysis of AODV Protocol with IEEE MAC for Chain Topology in MANET
 An Extensive Simulation Analysis of AODV Protocol with IEEE 802.11 MAC for Chain Topology in MANET V.K.Taksande 1, Dr.K.D.Kulat 2 1 Department of Electronics & Communication, Nagpur University Priyadarshini
An Extensive Simulation Analysis of AODV Protocol with IEEE 802.11 MAC for Chain Topology in MANET V.K.Taksande 1, Dr.K.D.Kulat 2 1 Department of Electronics & Communication, Nagpur University Priyadarshini
IMPACT OF MOBILITY SPEED ON PROACTIVE AND REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE ADHOC NETWORKS
 IMPACT OF MOBILITY SPEED ON PROACTIVE AND REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE ADHOC NETWORKS E. Gnanamanoharan and R. Bensraj Department of Electrical Engineering, Annamalai University, Tamil Nadu, India
IMPACT OF MOBILITY SPEED ON PROACTIVE AND REACTIVE ROUTING PROTOCOLS IN MOBILE ADHOC NETWORKS E. Gnanamanoharan and R. Bensraj Department of Electrical Engineering, Annamalai University, Tamil Nadu, India
Computation of Multiple Node Disjoint Paths
 Chapter 5 Computation of Multiple Node Disjoint Paths 5.1 Introduction In recent years, on demand routing protocols have attained more attention in mobile Ad Hoc networks as compared to other routing schemes
Chapter 5 Computation of Multiple Node Disjoint Paths 5.1 Introduction In recent years, on demand routing protocols have attained more attention in mobile Ad Hoc networks as compared to other routing schemes
Backward Aodv: An Answer To Connection Loss In Mobile Adhoc Network (Manet)
 Backward Aodv: An Answer To Connection Loss In Mobile Adhoc Network (Manet) Dr. Naveen Kr. Singh Ms. Neetu Sharma Ms. Shweta Agarwal Asso. Prof. Asstt. Prof. Asstt. Prof. ABES Engineering College ABES
Backward Aodv: An Answer To Connection Loss In Mobile Adhoc Network (Manet) Dr. Naveen Kr. Singh Ms. Neetu Sharma Ms. Shweta Agarwal Asso. Prof. Asstt. Prof. Asstt. Prof. ABES Engineering College ABES
ENERGY EFFICIENT MULTIPATH ROUTING FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
 ENERGY EFFICIENT MULTIPATH ROUTING FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS May Cho Aye and Aye Moe Aung Faculty of Information and Communication Technology, University of Technology (Yatanarpon Cyber City), Pyin Oo
ENERGY EFFICIENT MULTIPATH ROUTING FOR MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS May Cho Aye and Aye Moe Aung Faculty of Information and Communication Technology, University of Technology (Yatanarpon Cyber City), Pyin Oo
