Applying Fuzzy Logic to Admission Control in GPRS/EGPRS Networks
|
|
|
- Eugenia Barton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Applying Fuzzy Logic to Admission Control in GPRS/EGPRS Networks Doru Todinca Department of Computer Science, University Politehnica of Timisoara, Faculty of Computer and Control Engineering, Bd. V. Parvan 2, 1900 Timisoara, Romania, Abstract: We propose a new admission control algorithm for GPRS/EGPRS cellular data networks, based on fuzzy inference. The admission decision is based on system parameters like the network load and users precedence, being expressed in the form of fuzzy if-then rules. Simulation results are presented for the fuzzy admission algorithm, using our model for a GPRS/EGPRS cell and a simplified simulation scenario. Keywords: GPRS, admission control, fuzzy inference 1 Introduction The mobile communications had gained a large acceptance in the recent years, which constitutes very good premises for introducing new applications and services, among which data services are playing a very important role. The need for data services on mobile communications networks had increased because the users of personal computers wanted to have access to the same services and applications when they are mobile, as they have from their office or from home. In this paper we focus on GPRS, the General Packet Radio Service [1], [2], [3], [4], a data service developed over the very popular GSM (Global System for Mobile communications) networks. The evolution of GSM and GPRS towards the 3 rd generation mobile networks (3G) will be based on the EDGE (Enhanced Data Rates for Global Evolution) technology, which is capable to ensure higher data rates. The resulting combination between GPRS and EDGE is called Enhanced GPRS, or EGPRS [7]. In order to satisfy the different Quality of Service (QoS) requirements of the users in a GPRS/EGPRS network, a crucial problem that has to be solved is the resource allocation, with a focus on the allocation of the radio resources. This problem can be split into two main sub problems: admission control (AC), which is the decision to admit or to reject the request of an user for entering into the system, and
2 transmission control, which comprises the algorithms used to share the network (radio) resources among the admitted users. We have addressed the transmission control problem in [18], [19], [5]. In this work, we focus on the admission control problem, proposing a new admission control algorithm based on fuzzy rules. The paper is organized as follows: next section presents the problem of resource allocation in GPRS/EGPRS, including our simulation model for a (E)GPRS cell, section 3 describes the fuzzy admission control algorithm, an evaluation of our AC algorithm appears in section 4, followed by a section of conclusions. 2. The Problem of Resource Allocation in (E)GPRS 2.1 A Brief Description of GPRS GPRS is a packet switching service offered over GSM, that is a circuit switching network. The packet switching offers many advantages for data transfer compared with circuit switching, from both the network and the users perspective [1], [4]. We consider a number of users in a GPRS/EGPRS cell. The users want to send or to receive data, but before transferring data, they have to be admitted in the system (the admission control). The GPRS nodes involved in the admission control process are: the Mobile Station (MS), the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN), the Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN), the leading role in the negotiation between those nodes being taken by the SGSN. The Base Station of the cell where the user is situated is informed about the decision resulting from the admission process and it will have to provide the radio resources to the admitted user. The radio resources for a carrier in a GPRS cell are represented by a number of 8 channels, available every 20 milliseconds. The 8 channels are shared between voice and data traffic, usually the voice having priority over data transmissions. When a channel is allocated for data, it is called Packet Data Traffic Channel (PDTCH). A centralised controller, the Packet Control Unit (PCU), part of the Base Station Sub-system, performs the transmission control, i.e., the algorithms that are used to share the radio resources among the connected users from the cell served by the PCU. 2.2 Our Model for Resource Allocations in GPRS/EGPRS General Aspects The tool used for our model is the discrete event network simulator OMNeT++ [20]. A simulation model in OMNeT++ consists of a number of modules (nodes),
3 the communication between nodes being realised through messages. The model can be hierarchically structured, the basic building blocks of the hierarchy being the simple modules. Their behaviour is described in C++. In our model, each user is a composed module, the other modules in the system being the Packet Control Unit, the user generator, the admission controller and the stat node. The user generator and the stat node have no direct correspondence in a real GPRS or EGPRS network, but they are important for simulation purposes: the user generator is used for creating new users in the system, and the stat node serves for collecting the simulation results. The user generator creates users at certain time intervals and provides the user with their main characteristics: the QoS profile, the amount of data that the users want to transfer in a session and the pattern of the data generation process (users data source), their mobility pattern, etc. Related to users mobility, it is important to know if the user comes from another cell (handoff user) or it begins the connection in the current cell, and how long will the user stay in the current cell. The information about each user created by the user generator is sent to the admission controller, which decides if the user will be admitted in the system or if it will be rejected. If the user is admitted, a start user command is sent to a free user node (a node that is not occupied by another user) The Model for the Users and for the PCU A user is modelled through a compound module consisting mainly of a source node, a file buffer, a data packet buffer and a sink. The source generates a number of files according to the specific traffic pattern. A file in our model can be a real-life file, like in a FTP or transfer, a group of files (for example the content of a web page in a www session), or a part of a file (a frame in a streaming session). The files are stored in the file buffer until the send file command coming from the PCU determines the first file in buffer to be split into data blocks (or radio blocks), according to the coding scheme of that user, and the data blocks are moved into the data packet buffer. The data blocks have a fixed length, of 456 bits, consisting of user s information and the code bits. Depending on the coding scheme (CS) used, the number of user s bits in a data block can vary in GPRS from 181 bits for CS1, to 428 bits for CS4. In EGPRS, there are 9 modulation and coding schemes, MCS1 to MCS9. Depending on the scheduling algorithm used for transmission control, the PCU will inform each user how many data blocks to transfer during the current block cycle of 20ms. In this work the Weighted Round Robin (WRR) algorithm is used for scheduling [18], [19], [5], and the weights are given by the QoS profile of the users: the streaming users are assigned a weight of 8, which means that they are allowed to transfer up to 8 data blocks during a block cycle, the web browsing (www) users can transfer up to 4 data blocks, and the background users (the users
4 that are transferring files through download or FTP) can transfer only 1 data block (their weight is 1). More details about the transmission control algorithms are given in [18], [19] and [5], while the simulation model is described in more detail in [16]. 3. The Fuzzy Admission Control Algorithm 3.1 Motivation The Problem of Admission Control in Cellular Data Networks Admission control (AC) is performed in any type of network that offers certain guarantees on the QoS offered to its users. Admission control has been largely used in ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) networks [13]. User admission plays an important role in mobile cellular networks as well. The first mobile networks were used only for telephony, i.e., they were circuit switching networks. The main problem in that case was to reserve resources for the users that move from one cell to another. It is generally accepted that it is less desirable to drop a call in progress than to reject a new call, and as a consequence, the AC algorithms for cellular networks have two target parameters: the call dropping probability and the call blocking probability. A good AC algorithm tries to minimize the call blocking probability while strictly maintaining the call dropping probability under a certain value. In this way, the research on the AC algorithms had focused very much on mobility prediction and on techniques for resource reservation in the neighbouring cells. The complexity of the AC problem has increased for mobile data networks (like GPRS and EGPRS), compared to mobile telephony networks. In addition to the call dropping and call blocking probabilities, the network has to ensure the negotiated QoS to the admitted users (in terms of delay, throughput, loss, etc) and to maximize the network utilization. Another important aspect is that the traffic patterns for data users are by far more complex than the statistical behaviour of the voice calls, which can be accurately modelled by Poisson processes Research Directions in AC for Cellular Data Networks This section summarizes some of the most interesting research directions in the problem of admission control algorithms for cellular data networks.
5 The works in [8], [11], [14] and [15] propose different admission control methods based on thresholds. Different admission policies are applied for different regions, and the regions are separated by thresholds. The regions can be based either on network load, like in [11], [14] and [15], or on the number of users from each traffic class, like in [8]. Determining the values for the thresholds that separate those regions is a difficult problem. The authors of [8] use complex mathematical techniques in order to determine the thresholds, while the authors of [11] simply assign them heuristic values. The AC algorithm proposed by Stuckmann et al ([14], [15]) divide the available bandwidth into regions that can be shared by users from adjacent traffic classes. The authors of [6] propose a decision-theoretic approach based on Markov Decision Processes (MDP), but for real-life problems, the number of states in the Markov model becomes too large. We can see that the AC methods proposed in the literature for cellular data networks involve complex mathematical methods, which are difficult to apply for real-life problems due to the computational overhead. Moreover, in order to obtain models that are mathematically tractable, numerous assumptions are made, especially concerning the probability distribution functions (pdfs) of the parameters involved in AC. The pdfs for users traffic characteristics, call durations, cell residence times, etc, are assumed to be of Poisson type, or that they can be described by Markov Modulated Poisson Processes (MMDPs). While for voice calls, most of those assumptions are realistic and the models obtained have shown good results, the characteristics of data traffic cannot be accurately modelled through the framework of Poisson processes or through their extensions, the MMDPs Fuzzy Logic: a Possible Solution to AC for Cellular Data Networks We believe that a fuzzy logic based admission control can overcome those difficulties because: 1) Fuzzy sets can be a natural extension of the solutions based on thresholds: instead of trying to find an exact or optimum value for a parameter like network load, or number of users from a certain class, it is much easier to define those parameters as linguistic variables, and to separate their domain in linguistic terms, that are fuzzy sets. In this way, a threshold that separates two different behaviours is transformed into a region that ensures a gradual (smooth) change from one behaviour to another. The solutions presented in [8], [11], [14], [15] can be extended in this manner. 2) A fuzzy based solution does not have to rely on any assumption regarding the probability distribution functions for data traffic, session duration, etc.
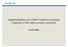
6 3) For real-life problems, the fuzzy logic-based solutions are by far less complex (and hence, less computationally intensive) than the solutions based on Markov models. 4) The expertise of the network operators can be easily and directly transposed into fuzzy if-then rules, without the necessity to use sophisticated mathematical techniques (e.g. queueing or Markov models). Fuzzy logic, sometimes combined with neural networks, has been applied in ATM networks for policing or for admission control [10]. In [9] fuzzy logic was used for admission control in cellular data networks in order to adjust the amount of resources that have to be reserved in a cell for the users that can move onto this cell from the neighbouring cells. 3.2 Implementation of the Fuzzy AC Algorithm For implementing the AC algorithm, we use the general structure of a fuzzy logic controller (FLC) presented in [12], which was modelled and simulated in [17]. The fuzzy rules have in premise the linguistic variables network load and users precedence, and in conclusion the linguistic variable admission decision with the terms strong accept (SA), weak accept (WA), weak reject (WR) and strong reject (SR). The terms for network load and for users precedence are high (H), medium (M) and low (L). The shape of the fuzzy sets describing the linguistic variables in premise and conclusion are shown in Figure 1. The values for the parameters in Figure 1 are: m=63, a1=m/4, a2=m/2, a3=3m/4, b1=8 (SR), b2=24 (WR), b3=40 (WA) and b4=56 (SA). Since the work is in progress, in this paper we present a simplified simulation scenario that includes a simplified form of the fuzzy rules, where only the network load is taken into account in the premise. The set of rules is: 1) If network load is H then admission decision is SR. 2) If network load is M then admission decision is WA. 3) If network load is L then admission decision is SA. µ 1 L M H µ 1 0 a1 a2 a3 m domain 0 b1 b2 b3 b4 m domain Figure 1. The linguistic variables in premise (left) and conclusion (right)
7 The FLC will try to keep the network load close to a target value, which is in this case the middle of the interval [0,m]. If the output of the FLC (the admission decision) is below 31 then the user is rejected, while for a value of the admission decision higher than 31, the user is admitted. 4 Evaluation of Our Fuzzy AC Algorithm 4.1 Simulation Results In this work, we do not consider users mobility and their precedence. The number of channels used for data traffic is always 8. For an easier interpretation of the simulation results, the process of user generation is periodic, not random, as in reality, and we call a step a period of the user generator. In order to generate the initial load of the system, all the users created in the firsts 20 steps of the user generation process are admitted. Figure 2 shows the network load (in the left) and the FLC input and output (in the right) when the target load is 5 and the user generation period is 230ms. The network load is given by the sum of users weights for all the admitted users, over the average number of channels available for data traffic. We can see that in the first 20 steps, when the initial load is generated, the network load increases to values higher than 10, but then the fuzzy AC algorithm manages to keep it close to 5. Actually, the network load never exceeds 5.5 after step 40. Network load Fuzzy admission load load input, output input output steps steps Figure 2. The results of the fuzzy AC algorithm FLC input includes the existing network load plus the extra load given by the user that attempts to be connected, scaled to the interval [0,63]. The output of the FLC shows that, after the initial period, the majority of the users are admitted, but there are also situations when the FLC output is below 31, which means rejection. If the user generation period is smaller, then the FLC oscillates around the middle of the interval, more users being rejected.
8 4.2 Discussion An AC algorithm compares the bandwidth used by the connected users plus the bandwidth required by the user that attempts to be connected with the bandwidth provided by the network. If the available bandwidth can accommodate the new connection, the new user is admitted, otherwise, it is rejected. In (E)GPRS, the network provides a certain number of channels, but the users transfer rates depend on their coding schemes, that can change in time (e.g. because of users mobility), hence a first problem would be how to express the bandwidth (required by users or provided by the network). Our approach is to consider user s assigned weights and, based on them, to determine the network load. A certain network load will determine the delay experienced by the users files, and hence, the QoS provided by the network. In this work, each QoS class has a certain weight, but it is possible that users weights change in time, for example, based on their coding schemes. In such a situation, an average weight should be consider for each QoS class. We mention that we do not consider here applications that are very delay sensitive (e.g., those that correspond to the conversational traffic class) and for which the network has to reserve (radio) resources. Another important aspect is how to determine the average number of PDTCHs (channels available for GPRS) provided by the network, since it depends on the traffic channels allocated for voice calls (in GPRS) or reserved for conversational applications (in EGPRS)? We can compute the average value for a time window, or even combine a long-term value and a short-term value, with different relative weights. A similar problem is how to take into account users activity factor (they do not transfer data all the time when they are connected). For computing the network load, we have considered the weights for all connected users, but we will have to investigate how to combine this approach with considering the weights for the users that are active (that are transferring data in the current block cycle). The users precedence will play an important role, especially if we decide to admit the users with high precedence, even if the network load is high. User s precedence is a conventional value, assigned by the network operator, according to user s QoS class (that can be subscription based, traffic based, or both) and to its mobility situation (if it comes from another cell, or if it is a new call). If we decide to admit all users that come from another cell, like in [8], then it is possible to admit too many users and the network can fall in a congested state. To avoid this, we can use a bandwidth adaptation algorithm (similar to [8]), or to block the allocation of physical resources to low precedence users, even if they are admitted. Conclusions This work describes a new admission control algorithm for GPRS and EGPRS networks, based on fuzzy if-then rules. We have shown the effectiveness of the algorithm in a simple simulation scenario.
9 Our future work will use the result from this paper in order to improve and extend the fuzzy admission control algorithm, taking into account more information about the users and the network (e.g. users precedence, the quality of the radio link, etc). Finally, the algorithm will be tested in more complex simulation scenario, close to real-life situation. References [1] C. Bettstetter, H.-J. Vogel, and J. Ebersacher, GSM phase 2+ General Packet Radio Service GPRS: Architectures, protocols, and air interface, IEEE Communications Surveys, vol. 2, no. 3, [2] G. Brasche and B. Walke, Concepts, services, and protocols of new GSM phase 2+ General Packet Radio Service, IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 35, no. 8, pp , August [3] J. Cai and D.J. Goodman, General Packet Radio Service in GSM, IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 35, no. 10, pp , October [4] B. Ghribi and L. Logrippo, Understanding GPRS: the GSM packet radio service, Computer Networks, vol. 34, pp , [5] H. Graja, P. Perry, D. Todinca, and J. Murphy, Novel GPRS simulator for testing MAC protocols, in Proc of IEE 3G 2003: Fourth International Conference on 3G Mobile Communications Technologies, pp , London, UK, June [6] Z. Haas, L. Halpern, L. Li and S. Wicker, A decision theoretic approach to resource allocation in wireless multimedia networks, in Proc. 4 th International Workshop on Discrete Algorithms and Methods for Mobile Computing and Communications dialm, [7] T. Halonen, J. Romero, and J. Molero (editors), GSM, GPRS and EDGE performance, John Wiley & Sons LTD, [8] S. Kim, T. Kwon and Y. Choi, Call admission control for prioritized adaptive multimedia services in wireless/mobile networks, in Proc of IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC 00 Spring), Tokyo, Japan, [9] Y.-C. Ko, S.-K. Park, C.-Y. Chun, H.-W. Lee and C.-H. Cho, An adaptive QoS provisioning distributed call admission control using fuzzy logic control, in Proc. of IEEE ICC 2001, vol. 2, pp , Helsinki, Finland, [10] H.H. Lim and B. Qiu, A predictive measurement-based fuzzy logic connection admission control, in Proc. of IEEE ICC 2001, vol. 3, pp , Helsinki, Finland, [11] J.R. Moorman, J.R. Lockwood and S.-M. Kang, Real-time prioritized call admission control in a base station scheduler, in Proc. of ACM Wowmom, pp , Boston, MA, USA, 2000.
10 [12] M.J. Patyra, Design Considerations of Digital Fuzzy Logic Controllers, in Fuzzy Logic - Implementation and Applications, pp , edited by M.J. Patyra and D.M. Mlynek, Wiley & Teubner, [13] H.G. Perros and K.M.Elsayed, Call admission control schemes: a review, IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 34, no. 11, pp , Nov, [14] P. Stuckmann, Quality of service management in GPRS-based radio access networks, Telecommunication Systems, vol.19:3,4, pp , [15] P. Stuckmann and O. Mőller, Advanced scheduling and admission control techniques for cellular packet radio networks, in Proc. of European Personal Mobile Communications Conference EPMCC 2003, Glasgow, UK, [16] D. Todinca, Modelling resource allocation techniques for GPRS/EGPRS networks, Periodica Politehnica, Transactions on Automatic Control and Computer Science, vol. 48 (62), pp , [17] D. Todinca, A.M.Badulescu and R.E. Precup, VHDL approach to performance analysis of fuzzy logic controllers, in Proc.of IPMU 2000, Madrid, Spain, [18] D. Todinca, P. Perry and J. Murphy, Algorithms for resource allocation in data transfer over EGPRS networks, in Proc. of ECUMN'2002, pp , Colmar, France, [19] D. Todinca, P. Perry and J. Murphy, Novel prioritised EGPRS medium access regime for reduced transfer delay during congested periods, in Proc. of IEE 3G, pp , London, UK, [20] A. Varga, OMNeT++ Discrete event simulation system. User Manual,
Performance Analysis of Cell Switching Management Scheme in Wireless Packet Communications
 Performance Analysis of Cell Switching Management Scheme in Wireless Packet Communications Jongho Bang Sirin Tekinay Nirwan Ansari New Jersey Center for Wireless Telecommunications Department of Electrical
Performance Analysis of Cell Switching Management Scheme in Wireless Packet Communications Jongho Bang Sirin Tekinay Nirwan Ansari New Jersey Center for Wireless Telecommunications Department of Electrical
On the Importance of Using Appropriate Link-to-System Level Interfaces for the Study of Link Adaptation
 On the Importance of Using Appropriate Link-to-System Level Interfaces for the Study of Link Adaptation Javier Gozalvez and John Dunlop Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of
On the Importance of Using Appropriate Link-to-System Level Interfaces for the Study of Link Adaptation Javier Gozalvez and John Dunlop Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of
DRAFT - QoS Sensitive Roaming Principles 1.0 August 2004
 Official Document IR.68 DRAFT - QoS Sensitive Roaming Principles 1.0 August 2004 This is a binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (See next page):
Official Document IR.68 DRAFT - QoS Sensitive Roaming Principles 1.0 August 2004 This is a binding permanent reference document of the GSM Association. Security Classification Category (See next page):
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR GPRS WITH PRIORITIZED AND NON-PRIORITIZED MOBILITY MANAGEMENT PROCEDURES
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR GPRS WITH PRIORITIZED AND NON-PRIORITIZED MOBILITY MANAGEMENT PROCEDURES Karann Chew, Rahim Tafazolli University of Surrey, United Kingdom Abstract - GPRS is part of the evolution
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR GPRS WITH PRIORITIZED AND NON-PRIORITIZED MOBILITY MANAGEMENT PROCEDURES Karann Chew, Rahim Tafazolli University of Surrey, United Kingdom Abstract - GPRS is part of the evolution
A New Call Admission Control scheme for Real-time traffic in Wireless Networks
 A New Call Admission Control scheme for Real-time traffic in Wireless Networks Maneesh Tewari and H.S. Jamadagni Center for Electronics Design and Technology, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, 5612
A New Call Admission Control scheme for Real-time traffic in Wireless Networks Maneesh Tewari and H.S. Jamadagni Center for Electronics Design and Technology, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, 5612
SIMULATION FRAMEWORK MODELING
 CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION FRAMEWORK MODELING 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter starts with the design and development of the universal mobile communication system network and implementation of the TCP congestion
CHAPTER 5 SIMULATION FRAMEWORK MODELING 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter starts with the design and development of the universal mobile communication system network and implementation of the TCP congestion
QoS and Radio Resource Management in 3G and Beyond Systems. Oriol Sallent Kideok Cho
 QoS and Radio Resource Management in 3G and Beyond Systems Oriol Sallent Kideok Cho (kdcho@mmlab.snu.ac.kr) 2006. 10. 23 -2/30- Contents Radio Resource Management RRM in Beyond 3G Common RRM in a flexible
QoS and Radio Resource Management in 3G and Beyond Systems Oriol Sallent Kideok Cho (kdcho@mmlab.snu.ac.kr) 2006. 10. 23 -2/30- Contents Radio Resource Management RRM in Beyond 3G Common RRM in a flexible
Mobile Systems Challenges in Next Generation Networks
 International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking 15 Mobile Systems Challenges in Next Generation Networks Seyed Ali Alavian, Jahangir Dadkhah Chimeh Faculty of Applied Science of
International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking 15 Mobile Systems Challenges in Next Generation Networks Seyed Ali Alavian, Jahangir Dadkhah Chimeh Faculty of Applied Science of
Network Systems for Emerging WAN Applications
 Network Systems for Emerging WAN Applications Hitachi Review Vol. 48 (1999), No. 4 169 Akihiko Takase, D.Sc. OVERVIEW: This paper describes wide-area-network architecture from the viewpoints of networking
Network Systems for Emerging WAN Applications Hitachi Review Vol. 48 (1999), No. 4 169 Akihiko Takase, D.Sc. OVERVIEW: This paper describes wide-area-network architecture from the viewpoints of networking
Active Adaptation in QoS Architecture Model
 Active Adaptation in QoS Architecture Model Drago agar and Snjeana Rimac -Drlje Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Osijek Kneza Trpimira 2b, HR-31000 Osijek, CROATIA Abstract - A new complex
Active Adaptation in QoS Architecture Model Drago agar and Snjeana Rimac -Drlje Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Osijek Kneza Trpimira 2b, HR-31000 Osijek, CROATIA Abstract - A new complex
Channel Allocation and Performance Study for the Integrated GSM/GPRS System
 Channel Allocation and Performance Study for the Integrated GSM/GPRS System Huei-Wen Ferng and Yi-Chou Tsai Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science
Channel Allocation and Performance Study for the Integrated GSM/GPRS System Huei-Wen Ferng and Yi-Chou Tsai Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Taiwan University of Science
Part V. Appendices. Service M odelling: Principles and Applications Vilho Räisänen 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBN:
 Part V Appendices Service M odelling: Principles and Applications Vilho Räisänen 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBN: 0-470-01807-0 A 3GPP Bearer Concepts In the following text, we shall review 3GPP (Third
Part V Appendices Service M odelling: Principles and Applications Vilho Räisänen 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBN: 0-470-01807-0 A 3GPP Bearer Concepts In the following text, we shall review 3GPP (Third
WiMax-based Handovers in Next Generation Networks
 WiMax-based Handovers in Next Generation Networks Nadine Akkari Department of Computer Science Faculty of Computing and Information Technology King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia nakkari@kau.edu.sa
WiMax-based Handovers in Next Generation Networks Nadine Akkari Department of Computer Science Faculty of Computing and Information Technology King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia nakkari@kau.edu.sa
Telecommunication Services Engineering Lab
 Logistics Instructor Office: EV007-647, Tel: 1-514-8482424 ext 5846, Email: Glitho@ciiseconcordiaca URL: http://wwwececoncordiaca/~glitho/ Office hours: Tuesday: 3 pm 5 pm Time: Usually: Tuesday, 17h45-20h15
Logistics Instructor Office: EV007-647, Tel: 1-514-8482424 ext 5846, Email: Glitho@ciiseconcordiaca URL: http://wwwececoncordiaca/~glitho/ Office hours: Tuesday: 3 pm 5 pm Time: Usually: Tuesday, 17h45-20h15
Adaptive Resource Allocation Mechanisms for Support of Data Traffic over ATM Satellite Networks Introduction The Dynamic Flow Control Scheme
 Adaptive Resource Allocation Mechanisms for Support of Traffic over ATM Satellite Networks Tanja Lang and Nirmala Shenoy, Co-operative Research Centre for Satellite Systems, Institute for Telecommunications
Adaptive Resource Allocation Mechanisms for Support of Traffic over ATM Satellite Networks Tanja Lang and Nirmala Shenoy, Co-operative Research Centre for Satellite Systems, Institute for Telecommunications
A QoS aware Packet Scheduling Scheme for WiMAX
 A QoS aware Packet Scheduling Scheme for WiMAX Mahasweta Sarkar and Harpreet Sachdeva ABSTRACT WiMAX is one of the most promising broadband wireless technologies today. The WiMAX standard-802.16-is designed
A QoS aware Packet Scheduling Scheme for WiMAX Mahasweta Sarkar and Harpreet Sachdeva ABSTRACT WiMAX is one of the most promising broadband wireless technologies today. The WiMAX standard-802.16-is designed
Traffic and Congestion Control in ATM Networks Using Neuro-Fuzzy Approach
 Traffic and Congestion Control in ATM Networks Using Neuro-Fuzzy Approach Suriti Gupta College of Technology and Engineering Udaipur-313001 Vinod Kumar College of Technology and Engineering Udaipur-313001
Traffic and Congestion Control in ATM Networks Using Neuro-Fuzzy Approach Suriti Gupta College of Technology and Engineering Udaipur-313001 Vinod Kumar College of Technology and Engineering Udaipur-313001
Performance and Configuration of Link Adaptation Algorithms with Mobile Speed
 Performance and Configuration of Link Adaptation Algorithms with Mobile Speed Javier Gozalvez* and John Dunlop** *Now with the Signal Theory and Communications Division at the University Miguel Hernández
Performance and Configuration of Link Adaptation Algorithms with Mobile Speed Javier Gozalvez* and John Dunlop** *Now with the Signal Theory and Communications Division at the University Miguel Hernández
A Handover Optimisation Scheme in Cellular Networks
 A Handover Optimisation Scheme in Cellular Networks A.Gueroui and S.Boumerdassi Laboratoire PRiSM, Université de Versailles 45, Avenue des Etats-Unis 78035 Versailles France Laboratoire CEDRIC, CNAM 292,
A Handover Optimisation Scheme in Cellular Networks A.Gueroui and S.Boumerdassi Laboratoire PRiSM, Université de Versailles 45, Avenue des Etats-Unis 78035 Versailles France Laboratoire CEDRIC, CNAM 292,
On the Optimizing of LTE System Performance for SISO and MIMO Modes
 2015 Third International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation On the Optimizing of LTE System Performance for SISO and MIMO Modes Ali Abdulqader Bin Salem, Yung-Wey Chong, Sabri
2015 Third International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Modelling and Simulation On the Optimizing of LTE System Performance for SISO and MIMO Modes Ali Abdulqader Bin Salem, Yung-Wey Chong, Sabri
Telecommunication Services Engineering Lab
 Logistics Instructor Office: EV006-227, Tel: 1-514-8482424 ext 5846, Email: Glitho@ciiseconcordiaca URL: http://wwwececoncordiaca/~glitho/ Office hours: Friday: 3 pm 5 pm Time: Friday, 17h45-20h15 Room
Logistics Instructor Office: EV006-227, Tel: 1-514-8482424 ext 5846, Email: Glitho@ciiseconcordiaca URL: http://wwwececoncordiaca/~glitho/ Office hours: Friday: 3 pm 5 pm Time: Friday, 17h45-20h15 Room
Base Station Subsystem Key Performance Indicators in EGPRS
 Base Station Subsystem Key Performance Indicators in EGPRS Anders Arte Supervisor: Prof. Sven-Gustav Häggman Instructor: M.Sc. Leo Bhebhe Content Introduction Objectives and Methodology EGPRS EGPRS Fundamentals
Base Station Subsystem Key Performance Indicators in EGPRS Anders Arte Supervisor: Prof. Sven-Gustav Häggman Instructor: M.Sc. Leo Bhebhe Content Introduction Objectives and Methodology EGPRS EGPRS Fundamentals
Maximum Number of Users Which Can Be Served by TETRA Systems
 Maximum Number of Users Which Can Be Served by TETRA Systems Martin Steppler Aachen University of Technology Communication Networks Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernhard Walke Kopernikusstr. 16 D-52074 Aachen Germany
Maximum Number of Users Which Can Be Served by TETRA Systems Martin Steppler Aachen University of Technology Communication Networks Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernhard Walke Kopernikusstr. 16 D-52074 Aachen Germany
Radio Resource Management in GPRS with Quality of Service
 Radio Resource Management in GPRS with Quality of Service Josep Bada, Ferran Casadevall, Javier Jiménez and Eduardo Medrano Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), Dept. of Signal Theory and Communications,
Radio Resource Management in GPRS with Quality of Service Josep Bada, Ferran Casadevall, Javier Jiménez and Eduardo Medrano Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), Dept. of Signal Theory and Communications,
MPEG4 VIDEO OVER PACKET SWITCHED CONNECTION OF THE WCDMA AIR INTERFACE
 MPEG4 VIDEO OVER PACKET SWITCHED CONNECTION OF THE WCDMA AIR INTERFACE Jamil Y. Khan 1, Pratik Das 2 School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Newcastle, Callaghan, NSW 238,
MPEG4 VIDEO OVER PACKET SWITCHED CONNECTION OF THE WCDMA AIR INTERFACE Jamil Y. Khan 1, Pratik Das 2 School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Newcastle, Callaghan, NSW 238,
TCP CONGESTION CONTROL PROTOCOLS OVER UMTS WCDMA NETWORK
 International Journal of Computer Science Engineering and Information Technology Research (IJCSEITR) ISSN(P): 2249-6831; ISSN(E): 2249-7943 Vol. 4, Issue 5, Oct 2014, 83-90 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. TCP CONGESTION
International Journal of Computer Science Engineering and Information Technology Research (IJCSEITR) ISSN(P): 2249-6831; ISSN(E): 2249-7943 Vol. 4, Issue 5, Oct 2014, 83-90 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. TCP CONGESTION
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Emerging multimedia, high-speed data, and imaging applications are generating a demand for public networks to be able to multiplex and switch simultaneously a wide spectrum of data rates. These networks
Emerging multimedia, high-speed data, and imaging applications are generating a demand for public networks to be able to multiplex and switch simultaneously a wide spectrum of data rates. These networks
An Efficient Bandwidth Estimation Schemes used in Wireless Mesh Networks
 An Efficient Bandwidth Estimation Schemes used in Wireless Mesh Networks First Author A.Sandeep Kumar Narasaraopeta Engineering College, Andhra Pradesh, India. Second Author Dr S.N.Tirumala Rao (Ph.d)
An Efficient Bandwidth Estimation Schemes used in Wireless Mesh Networks First Author A.Sandeep Kumar Narasaraopeta Engineering College, Andhra Pradesh, India. Second Author Dr S.N.Tirumala Rao (Ph.d)
Maximum bitrate for uplink Maximum bitrate for downlink 20, 40, 72 kbps
 An Enhanced Quality Of Service Method for Guaranteed rate Services over Shared Channels in EGPRS Systems Daniel Fernández and Héctor Montes Nokia Networks, C/ Severo Ochoa, s/n Edif. de Inst. Universitarios,
An Enhanced Quality Of Service Method for Guaranteed rate Services over Shared Channels in EGPRS Systems Daniel Fernández and Héctor Montes Nokia Networks, C/ Severo Ochoa, s/n Edif. de Inst. Universitarios,
OVSF Code Tree Management for UMTS with Dynamic Resource Allocation and Class-Based QoS Provision
 OVSF Code Tree Management for UMTS with Dynamic Resource Allocation and Class-Based QoS Provision Huei-Wen Ferng, Jin-Hui Lin, Yuan-Cheng Lai, and Yung-Ching Chen Department of Computer Science and Information
OVSF Code Tree Management for UMTS with Dynamic Resource Allocation and Class-Based QoS Provision Huei-Wen Ferng, Jin-Hui Lin, Yuan-Cheng Lai, and Yung-Ching Chen Department of Computer Science and Information
Evaluating the GPRS Radio Interface for Different Quality of Service Profiles
 Evaluating the GPRS Radio Interface for Different Quality of Service Profiles Christoph Lindemann and Axel Thümmler University of Dortmund Department of Computer Science August-Schmidt-Str. 12 44227 Dortmund,
Evaluating the GPRS Radio Interface for Different Quality of Service Profiles Christoph Lindemann and Axel Thümmler University of Dortmund Department of Computer Science August-Schmidt-Str. 12 44227 Dortmund,
Dynamic Control and Optimization of Buffer Size for Short Message Transfer in GPRS/UMTS Networks *
 Dynamic Control and Optimization of for Short Message Transfer in GPRS/UMTS Networks * Michael M. Markou and Christos G. Panayiotou Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Cyprus Email:
Dynamic Control and Optimization of for Short Message Transfer in GPRS/UMTS Networks * Michael M. Markou and Christos G. Panayiotou Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Cyprus Email:
PROTOCOLS FOR HIGH-EFFICIENCY WIRELESS NETWORKS
 PROTOCOLS FOR HIGH-EFFICIENCY WIRELESS NETWORKS PROTOCOLS FOR HIGH-EFFICIENCY WIRELESS NETWORKS by Alessandro Andreadis Giovanni Giambene KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS NEW YORK, BOSTON, DORDRECHT, LONDON,
PROTOCOLS FOR HIGH-EFFICIENCY WIRELESS NETWORKS PROTOCOLS FOR HIGH-EFFICIENCY WIRELESS NETWORKS by Alessandro Andreadis Giovanni Giambene KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS NEW YORK, BOSTON, DORDRECHT, LONDON,
An Efficient Resource Allocation Protocol for Multimedia Wireless Networks
 International Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, Pages : 178-182 (213) Special Issue of ICACSE 213 - Held on 7-8 January, 213 in Lords Institute of Engineering
International Journal of Advanced Trends in Computer Science and Engineering, Vol.2, No.1, Pages : 178-182 (213) Special Issue of ICACSE 213 - Held on 7-8 January, 213 in Lords Institute of Engineering
Multichannel Outage-aware MAC Protocols for Wireless Networks
 Submitted - the 4th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA 29) Multichannel Outage-aware MAC Protocols for Wireless Networks Hyukjin Lee and Cheng-Chew Lim School of Electrical
Submitted - the 4th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA 29) Multichannel Outage-aware MAC Protocols for Wireless Networks Hyukjin Lee and Cheng-Chew Lim School of Electrical
Scheduling of real-time traffic in IEEE networks
 Scheduling of real-time traffic in IEEE 802.11 networks Afonso, José A. Neves, Joaquim E. Universidade do Minho, Departamento de Electrónica Industrial Campus de Azurém, 4800-058 Guimarães, ortugal jose.afonso@dei.uminho.pt
Scheduling of real-time traffic in IEEE 802.11 networks Afonso, José A. Neves, Joaquim E. Universidade do Minho, Departamento de Electrónica Industrial Campus de Azurém, 4800-058 Guimarães, ortugal jose.afonso@dei.uminho.pt
GPRS billing: getting ready for UMTS
 GPRS billing: getting ready for UMTS In his first article about UMTS, Lucas Baugé looks into the key challenges of GPRS billing. He seeks to show how solving these challenges will help operators succeed
GPRS billing: getting ready for UMTS In his first article about UMTS, Lucas Baugé looks into the key challenges of GPRS billing. He seeks to show how solving these challenges will help operators succeed
A Flow Label Based QoS Scheme for End-to-End Mobile Services
 A Flow Label Based QoS Scheme for End-to-End Mobile Services Tao Zheng, Lan Wang, Daqing Gu Orange Labs Beijing France Telecom Group Beijing, China e-mail: {tao.zheng; lan.wang; daqing.gu}@orange.com Abstract
A Flow Label Based QoS Scheme for End-to-End Mobile Services Tao Zheng, Lan Wang, Daqing Gu Orange Labs Beijing France Telecom Group Beijing, China e-mail: {tao.zheng; lan.wang; daqing.gu}@orange.com Abstract
Multimedia Document Communications over Wireless Network
 Multimedia Document Communications over Wireless Network 1 Convergence of Mobile Services Personal computer Access to any data Internet Telecommunications Mobile Technology Ubiquitous Portable processing
Multimedia Document Communications over Wireless Network 1 Convergence of Mobile Services Personal computer Access to any data Internet Telecommunications Mobile Technology Ubiquitous Portable processing
Performance Analysis of Integrated Voice and Data Systems Considering Different Service Distributions
 Performance Analysis of Integrated Voice and Data Systems Considering Different Service Distributions Eser Gemikonakli University of Kyrenia, Kyrenia, Mersin 10, Turkey Abstract In this study, the aim
Performance Analysis of Integrated Voice and Data Systems Considering Different Service Distributions Eser Gemikonakli University of Kyrenia, Kyrenia, Mersin 10, Turkey Abstract In this study, the aim
A Modified DRR-Based Non-real-time Service Scheduling Scheme in Wireless Metropolitan Networks
 A Modified DRR-Based Non-real-time Service Scheduling Scheme in Wireless Metropolitan Networks Han-Sheng Chuang 1, Liang-Teh Lee 1 and Chen-Feng Wu 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Tatung
A Modified DRR-Based Non-real-time Service Scheduling Scheme in Wireless Metropolitan Networks Han-Sheng Chuang 1, Liang-Teh Lee 1 and Chen-Feng Wu 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Tatung
Network simulation. Lecture 8
 Network simulation Lecture 8 Emulation vs. simulation Emulation: the functioning of a device or of a system is replicated as close to reality as possible Usually the emulated system can be replaced with
Network simulation Lecture 8 Emulation vs. simulation Emulation: the functioning of a device or of a system is replicated as close to reality as possible Usually the emulated system can be replaced with
A Fuzzy System for Adaptive Network Routing
 A Fuzzy System for Adaptive Network Routing A. Pasupuleti *, A.V. Mathew*, N. Shenoy** and S. A. Dianat* Rochester Institute of Technology Rochester, NY 14623, USA E-mail: axp1014@rit.edu Abstract In this
A Fuzzy System for Adaptive Network Routing A. Pasupuleti *, A.V. Mathew*, N. Shenoy** and S. A. Dianat* Rochester Institute of Technology Rochester, NY 14623, USA E-mail: axp1014@rit.edu Abstract In this
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction. Noman Muhammad, Davide Chiavelli, David Soldani and Man Li. 1.1 QoE value chain
 1 Introduction Noman Muhammad, Davide Chiavelli, David Soldani and Man Li Browsing through the literature, one may find many different definitions for quality of end-user experience (QoE) and quality of
1 Introduction Noman Muhammad, Davide Chiavelli, David Soldani and Man Li Browsing through the literature, one may find many different definitions for quality of end-user experience (QoE) and quality of
Mobility Management in Heterogeneous Mobile Communication Networks through an Always Best Connected Integrated Architecture
 Mobility Management in Heterogeneous Mobile Communication Networks through an Always Best Connected Integrated Architecture Dionysia Triantafyllopoulou *, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens
Mobility Management in Heterogeneous Mobile Communication Networks through an Always Best Connected Integrated Architecture Dionysia Triantafyllopoulou *, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens
CHAPTER 4 CALL ADMISSION CONTROL BASED ON BANDWIDTH ALLOCATION (CACBA)
 92 CHAPTER 4 CALL ADMISSION CONTROL BASED ON BANDWIDTH ALLOCATION (CACBA) 4.1 INTRODUCTION In our previous work, we have presented a cross-layer based routing protocol with a power saving technique (CBRP-PS)
92 CHAPTER 4 CALL ADMISSION CONTROL BASED ON BANDWIDTH ALLOCATION (CACBA) 4.1 INTRODUCTION In our previous work, we have presented a cross-layer based routing protocol with a power saving technique (CBRP-PS)
Prioritization scheme for QoS in IEEE e WLAN
 Prioritization scheme for QoS in IEEE 802.11e WLAN Yakubu Suleiman Baguda a, Norsheila Fisal b a,b Department of Telematics & Communication Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknologi
Prioritization scheme for QoS in IEEE 802.11e WLAN Yakubu Suleiman Baguda a, Norsheila Fisal b a,b Department of Telematics & Communication Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti Teknologi
2. Modelling of telecommunication systems (part 1)
 2. Modelling of telecommunication systems (part ) lect02.ppt S-38.45 - Introduction to Teletraffic Theory - Fall 999 2. Modelling of telecommunication systems (part ) Contents Telecommunication networks
2. Modelling of telecommunication systems (part ) lect02.ppt S-38.45 - Introduction to Teletraffic Theory - Fall 999 2. Modelling of telecommunication systems (part ) Contents Telecommunication networks
A Bandwidth Degradation Technique to Reduce Call Dropping Probability in Mobile Network Systems
 TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol. 16, No. 2, November 215, pp. 33 ~ 37 DOI: 1.11591/telkomnika.v16i2.8426 33 A Bandwidth Degradation Technique to Reduce Call Dropping Probability
TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol. 16, No. 2, November 215, pp. 33 ~ 37 DOI: 1.11591/telkomnika.v16i2.8426 33 A Bandwidth Degradation Technique to Reduce Call Dropping Probability
654 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 55, NO. 2, MARCH 2006
 654 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 55, NO. 2, MARCH 2006 Optimal Resource Allocation and Adaptive Call Admission Control for Voice/Data Integrated Cellular Networks Chi Wa Leong, Weihua
654 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 55, NO. 2, MARCH 2006 Optimal Resource Allocation and Adaptive Call Admission Control for Voice/Data Integrated Cellular Networks Chi Wa Leong, Weihua
Quality of Service Mechanism for MANET using Linux Semra Gulder, Mathieu Déziel
 Quality of Service Mechanism for MANET using Linux Semra Gulder, Mathieu Déziel Semra.gulder@crc.ca, mathieu.deziel@crc.ca Abstract: This paper describes a QoS mechanism suitable for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
Quality of Service Mechanism for MANET using Linux Semra Gulder, Mathieu Déziel Semra.gulder@crc.ca, mathieu.deziel@crc.ca Abstract: This paper describes a QoS mechanism suitable for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
Service Disciplines Performance for Best-Effort Policies in Packet-Switching Wireless Cellular Networks
 Service Disciplines Performance for Best-Effort Policies in Packet-Switching Wireless Cellular Networks Wessam Ajib and Philippe Godlewski cole Nationale Sup rieure des T 1 communications, Computer Sciences
Service Disciplines Performance for Best-Effort Policies in Packet-Switching Wireless Cellular Networks Wessam Ajib and Philippe Godlewski cole Nationale Sup rieure des T 1 communications, Computer Sciences
QoS based vertical handoff method between UMTS systems and wireless LAN networks
 QoS based vertical handoff method between UMTS systems and wireless LAN networks Sungkwan Jung and Dong-ho Cho Div. of EE, Dept. of EECS Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Daejeon, Rep.
QoS based vertical handoff method between UMTS systems and wireless LAN networks Sungkwan Jung and Dong-ho Cho Div. of EE, Dept. of EECS Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Daejeon, Rep.
ETSI TS V1.1.1 ( )
 TS 103 328 V1.1.1 (2015-12) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Railways Telecommunications (RT); GPRS/EGPRS requirements for ETCS 2 TS 103 328 V1.1.1 (2015-12) Reference DTS-RT-0031 Keywords GS-R, radio, railways
TS 103 328 V1.1.1 (2015-12) TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION Railways Telecommunications (RT); GPRS/EGPRS requirements for ETCS 2 TS 103 328 V1.1.1 (2015-12) Reference DTS-RT-0031 Keywords GS-R, radio, railways
PhD Thesis Defense Performance Improvements in Software-defined and Virtualized Wireless Networks
 PhD Thesis Defense Performance Improvements in Software-defined and Virtualized Wireless Networks Chengchao Liang Supervisor: Prof. F. Richard Yu Department of Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton
PhD Thesis Defense Performance Improvements in Software-defined and Virtualized Wireless Networks Chengchao Liang Supervisor: Prof. F. Richard Yu Department of Systems and Computer Engineering Carleton
Implementation of a WAP model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks
 Implementation of a model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks Henrik Fållby Outline Scoop of this thesis switched vs. circuit switched networks Data in GSM radio networks Wireless Application
Implementation of a model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks Henrik Fållby Outline Scoop of this thesis switched vs. circuit switched networks Data in GSM radio networks Wireless Application
INTRODUCTION TO GSM DATA SERVICES. ETI25111 Monday, April 3, 2017
 INTRODUCTION TO GSM DATA SERVICES ETI25111 Monday, April 3, 2017 BASIC GSM SERVICES 1. Teleservices (a) Voice full-rate (13kbs) (b) Voice Half-rate (6.5 kbps) (c) SMS (up to 160 characters) (d) MMS (e)
INTRODUCTION TO GSM DATA SERVICES ETI25111 Monday, April 3, 2017 BASIC GSM SERVICES 1. Teleservices (a) Voice full-rate (13kbs) (b) Voice Half-rate (6.5 kbps) (c) SMS (up to 160 characters) (d) MMS (e)
QoS in multiservice IP networks Vodafone-Italy s point of view
 QoS in multiservice IP networks Vodafone-Italy s point of view Alberto Bona and Livio Pogliano Catania February, 3 rd 2005 Page 1 Vodafone s footprint Page 2 QoS categories for wireless applications increasing
QoS in multiservice IP networks Vodafone-Italy s point of view Alberto Bona and Livio Pogliano Catania February, 3 rd 2005 Page 1 Vodafone s footprint Page 2 QoS categories for wireless applications increasing
The Effect of Code-Multiplexing on the High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) in a WCDMA Network
 The Effect of Code-Multiplexing on the High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) in a WCDMA Network Raymond Kwan, Peter H. J. Chong 2, Eeva Poutiainen, Mika Rinne Nokia Research Center, P.O. Box 47, FIN-45
The Effect of Code-Multiplexing on the High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) in a WCDMA Network Raymond Kwan, Peter H. J. Chong 2, Eeva Poutiainen, Mika Rinne Nokia Research Center, P.O. Box 47, FIN-45
A Call Admission Protocol for Wireless Cellular Multimedia Networks
 A Call Admission Protocol for Wireless Cellular Multimedia Networks Mokhtar A. Aboleaze Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering York University Toronto, ON. Canada aboelaze@cs.yorku.ca Fadi A. Aloul
A Call Admission Protocol for Wireless Cellular Multimedia Networks Mokhtar A. Aboleaze Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering York University Toronto, ON. Canada aboelaze@cs.yorku.ca Fadi A. Aloul
Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control
 Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control Qinqing Zhang, Hsuan-Jung Su Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies Holmdel, NJ 77 Abstract- The Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol in Universal Mobile Telecommunication
Performance of UMTS Radio Link Control Qinqing Zhang, Hsuan-Jung Su Bell Laboratories, Lucent Technologies Holmdel, NJ 77 Abstract- The Radio Link Control (RLC) protocol in Universal Mobile Telecommunication
VHDL framework for modeling fuzzy automata
 Doru Todinca Daniel Butoianu Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara SYNASC 2012 Outline Motivation 1 Motivation Why fuzzy automata? Why a framework for modeling FA? Why VHDL? 2 Fuzzy
Doru Todinca Daniel Butoianu Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara SYNASC 2012 Outline Motivation 1 Motivation Why fuzzy automata? Why a framework for modeling FA? Why VHDL? 2 Fuzzy
COST/FIT Seminar in Micronova, Otaniemi, Spectroscopy of the uplink Um interface of GPRS/GSM
 COST/FIT Seminar in Micronova, Otaniemi, 10.2.2004. 1 Spectroscopy of the uplink Um interface of GPRS/GSM Jorma Kilpi P.O.Box 1202, 02044 VTT, FINLAND Email: Jorma.Kilpi@vtt.fi 20th February 2004 COST/FIT
COST/FIT Seminar in Micronova, Otaniemi, 10.2.2004. 1 Spectroscopy of the uplink Um interface of GPRS/GSM Jorma Kilpi P.O.Box 1202, 02044 VTT, FINLAND Email: Jorma.Kilpi@vtt.fi 20th February 2004 COST/FIT
ADAPTIVE SLOT ALLOCATION AND BANDWIDTH SHARING FOR PRIORITIZED HANDOFF CALLS IN MOBILE NETWOKS
 ADAPTIVE SLOT ALLOCATION AND BANDWIDTH SHARING FOR PRIORITIZED HANDOFF CALLS IN MOBILE NETWOKS S.Malathy G.Sudhasadasivam K.Murugan S.Lokesh Research Scholar Professor, CSE Department Lecturer, IT Dept
ADAPTIVE SLOT ALLOCATION AND BANDWIDTH SHARING FOR PRIORITIZED HANDOFF CALLS IN MOBILE NETWOKS S.Malathy G.Sudhasadasivam K.Murugan S.Lokesh Research Scholar Professor, CSE Department Lecturer, IT Dept
Improved MAC protocol for urgent data transmission in wireless healthcare monitoring sensor networks
 , pp.282-286 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.116.57 Improved MAC protocol for urgent data transmission in wireless healthcare monitoring sensor networks Rae Hyeon Kim, Jeong Gon Kim 1 Department of
, pp.282-286 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.116.57 Improved MAC protocol for urgent data transmission in wireless healthcare monitoring sensor networks Rae Hyeon Kim, Jeong Gon Kim 1 Department of
Lecture 9. Quality of Service in ad hoc wireless networks
 Lecture 9 Quality of Service in ad hoc wireless networks Yevgeni Koucheryavy Department of Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology yk@cs.tut.fi Lectured by Jakub Jakubiak QoS statement
Lecture 9 Quality of Service in ad hoc wireless networks Yevgeni Koucheryavy Department of Communications Engineering Tampere University of Technology yk@cs.tut.fi Lectured by Jakub Jakubiak QoS statement
DEFINITION OF SUITABLE SIMULATION SCENARIOS FOR DYNAMIC INVESTIGATIONS IN CELLULAR NETWORKS WITH STEAM
 DEFINITION OF SUITABLE SIMULATION SCENARIOS FOR DYNAMIC INVESTIGATIONS IN CELLULAR NETWORKS WITH STEAM Holger Pampel Enrico Jugl Lucent Technologies Network Systems GmbH Thurn-und-Taxis Strasse 10 90411
DEFINITION OF SUITABLE SIMULATION SCENARIOS FOR DYNAMIC INVESTIGATIONS IN CELLULAR NETWORKS WITH STEAM Holger Pampel Enrico Jugl Lucent Technologies Network Systems GmbH Thurn-und-Taxis Strasse 10 90411
Implementation of a WAP model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks. Henrik Fållby
 Implementation of a WAP model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks Henrik Fållby Outline Scoop of this thesis Packet switched vs. circuit switched networks Packet Data in GSM radio networks
Implementation of a WAP model to evaluate Capacity in 3G radio access networks Henrik Fållby Outline Scoop of this thesis Packet switched vs. circuit switched networks Packet Data in GSM radio networks
Circuit switched network
 GPRS-Services Page 12 2. GPRS-Services GPRS integrates a vast sum of additional services in a GSM-network. For this it will be necessary to define a subscriber profile that corresponds with services the
GPRS-Services Page 12 2. GPRS-Services GPRS integrates a vast sum of additional services in a GSM-network. For this it will be necessary to define a subscriber profile that corresponds with services the
ETSI TR V9.0.0 ( ) Technical Report
 TR 122 986 V9.0.0 (2010-02) Technical Report Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Study on Service Specific Access Control (3GPP TR 22.986 version 9.0.0 Release 9) 1 TR 122 986 V9.0.0 (2010-02)
TR 122 986 V9.0.0 (2010-02) Technical Report Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Study on Service Specific Access Control (3GPP TR 22.986 version 9.0.0 Release 9) 1 TR 122 986 V9.0.0 (2010-02)
NGN: The Evolution of Wireless Networks
 NGN: The Evolution of Wireless Networks Research Brief Abstract: Operators of mobile phone networks are already working through the financial and technical challenges of their own next generation of networks.
NGN: The Evolution of Wireless Networks Research Brief Abstract: Operators of mobile phone networks are already working through the financial and technical challenges of their own next generation of networks.
A Survey on Signaling Load in Mobility Management
 ISSN: 2231-4946 Volume IV, Special Issue, December 2014 International Journal of Computer Applications in Engineering Sciences Special Issue on Advances in Computer and Communications www.caesjournals.org
ISSN: 2231-4946 Volume IV, Special Issue, December 2014 International Journal of Computer Applications in Engineering Sciences Special Issue on Advances in Computer and Communications www.caesjournals.org
Implementation of a Wake-up Radio Cross-Layer Protocol in OMNeT++ / MiXiM
 Implementation of a Wake-up Radio Cross-Layer Protocol in OMNeT++ / MiXiM Jean Lebreton and Nour Murad University of La Reunion, LE2P 40 Avenue de Soweto, 97410 Saint-Pierre Email: jean.lebreton@univ-reunion.fr
Implementation of a Wake-up Radio Cross-Layer Protocol in OMNeT++ / MiXiM Jean Lebreton and Nour Murad University of La Reunion, LE2P 40 Avenue de Soweto, 97410 Saint-Pierre Email: jean.lebreton@univ-reunion.fr
Can Multiple Subchannels Improve the Delay Performance of RTS/CTS-based MAC Schemes?
 Can Multiple Subchannels Improve the Delay Performance of RTS/CTS-based MAC Schemes? By: Jing Deng, Yunghsiang S. Han, and Sanjeev R. Kulkarni. J. Deng, Y. S. Han, and S. R. Kulkarni, "Can Multiple Subchannels
Can Multiple Subchannels Improve the Delay Performance of RTS/CTS-based MAC Schemes? By: Jing Deng, Yunghsiang S. Han, and Sanjeev R. Kulkarni. J. Deng, Y. S. Han, and S. R. Kulkarni, "Can Multiple Subchannels
Configuring Advanced Radio Settings on the WAP371
 Article ID: 5069 Configuring Advanced Radio Settings on the WAP371 Objective Radio settings are used to configure the wireless radio antenna and its properties on the wireless access point (WAP) device
Article ID: 5069 Configuring Advanced Radio Settings on the WAP371 Objective Radio settings are used to configure the wireless radio antenna and its properties on the wireless access point (WAP) device
An Architecture for Broadband Virtual Networks Under Customer Control
 An Architecture for Broadband Virtual Networks Under Customer Control Mun Choon Chan, Hisaya Hadama* and Rolf Stadler Center for Telecommunications Research Columbia University, New York, N. Y, USA {mcchan,
An Architecture for Broadband Virtual Networks Under Customer Control Mun Choon Chan, Hisaya Hadama* and Rolf Stadler Center for Telecommunications Research Columbia University, New York, N. Y, USA {mcchan,
Distributed Queue Dual Bus
 Distributed Queue Dual Bus IEEE 802.3 to 802.5 protocols are only suited for small LANs. They cannot be used for very large but non-wide area networks. IEEE 802.6 DQDB is designed for MANs It can cover
Distributed Queue Dual Bus IEEE 802.3 to 802.5 protocols are only suited for small LANs. They cannot be used for very large but non-wide area networks. IEEE 802.6 DQDB is designed for MANs It can cover
In-Band Flow Establishment for End-to-End QoS in RDRN. Saravanan Radhakrishnan
 In-Band Flow Establishment for End-to-End QoS in RDRN Saravanan Radhakrishnan Organization Introduction Motivation QoS architecture Flow Establishment Protocol QoS Layer Experiments and Results Conclusion
In-Band Flow Establishment for End-to-End QoS in RDRN Saravanan Radhakrishnan Organization Introduction Motivation QoS architecture Flow Establishment Protocol QoS Layer Experiments and Results Conclusion
Due to the many benefits provided by both the third-generation (3G) mobile networks and the IEEE wireless local area networks (WLANs), it is
 Performance of UMTS/WLAN Integration at Hot-Spot Locations Using OPNET Marwan Abu-Amara, Ashraf Mahmoud, Tarek Sheltami, Adel Al-Shahrani, Khalid Al-Otaibi, S.M.Rehman, and Taha Anwar {marwan, ashraf,
Performance of UMTS/WLAN Integration at Hot-Spot Locations Using OPNET Marwan Abu-Amara, Ashraf Mahmoud, Tarek Sheltami, Adel Al-Shahrani, Khalid Al-Otaibi, S.M.Rehman, and Taha Anwar {marwan, ashraf,
CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS
 28 CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS Introduction Measurement-based scheme, that constantly monitors the network, will incorporate the current network state in the
28 CHAPTER 3 EFFECTIVE ADMISSION CONTROL MECHANISM IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS Introduction Measurement-based scheme, that constantly monitors the network, will incorporate the current network state in the
Converged Networks. Objectives. References
 Converged Networks Professor Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Discuss what is meant by convergence in the context of current telecommunications terminology Provide a network architecture
Converged Networks Professor Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Discuss what is meant by convergence in the context of current telecommunications terminology Provide a network architecture
GPRS and UMTS T
 GPRS and UMTS T-110.2100 Global Packet Radio Service GPRS uses the time slots not used for circuit switched services Data rate depends on the availability of free time slots GPRS uses the multislot technique,
GPRS and UMTS T-110.2100 Global Packet Radio Service GPRS uses the time slots not used for circuit switched services Data rate depends on the availability of free time slots GPRS uses the multislot technique,
Cross Layer QoS Provisioning in Home Networks
 Cross Layer QoS Provisioning in Home Networks Jiayuan Wang, Lukasz Brewka, Sarah Ruepp, Lars Dittmann Technical University of Denmark E-mail: jwan@fotonik.dtu.dk Abstract This paper introduces an innovative
Cross Layer QoS Provisioning in Home Networks Jiayuan Wang, Lukasz Brewka, Sarah Ruepp, Lars Dittmann Technical University of Denmark E-mail: jwan@fotonik.dtu.dk Abstract This paper introduces an innovative
Optimizing WiMAX: A Dynamic Strategy for Reallocation of Underutilized Downlink Sub-Frame to Uplink in TDD Mode
 Int. J. Communications, Network and System Sciences, 2009, 2, 888-894 doi:10.4236/ijcns.2009.29103 Published Online December 2009 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcns/). Optimizing WiMAX: A Dynamic Strategy
Int. J. Communications, Network and System Sciences, 2009, 2, 888-894 doi:10.4236/ijcns.2009.29103 Published Online December 2009 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcns/). Optimizing WiMAX: A Dynamic Strategy
Random Early Detection (RED) gateways. Sally Floyd CS 268: Computer Networks
 Random Early Detection (RED) gateways Sally Floyd CS 268: Computer Networks floyd@eelblgov March 20, 1995 1 The Environment Feedback-based transport protocols (eg, TCP) Problems with current Drop-Tail
Random Early Detection (RED) gateways Sally Floyd CS 268: Computer Networks floyd@eelblgov March 20, 1995 1 The Environment Feedback-based transport protocols (eg, TCP) Problems with current Drop-Tail
Vertical Handover in Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks A Survey
 Vertical Handover in Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks A Survey U. Kumaran Department of computer Applications Noorul Islam Center for Higher Education, Kumaracoil,Tamilnadu, India. Abstract- Vehicular Ad-hoc
Vertical Handover in Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks A Survey U. Kumaran Department of computer Applications Noorul Islam Center for Higher Education, Kumaracoil,Tamilnadu, India. Abstract- Vehicular Ad-hoc
ETSI TS V1.1.1 ( )
 TS 102 250-1 V1.1.1 (2003-10) Technical Specification Speech Processing, Transmission and Quality Aspects (STQ); QoS aspects for popular services in GSM and 3G networks; Part 1: Identification of Quality
TS 102 250-1 V1.1.1 (2003-10) Technical Specification Speech Processing, Transmission and Quality Aspects (STQ); QoS aspects for popular services in GSM and 3G networks; Part 1: Identification of Quality
Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (JECET)
 Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (JECET) JECET I A E M E Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (JECET)ISSN ISSN 2347-4181 (Print) ISSN 2347-419X
Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (JECET) JECET I A E M E Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (JECET)ISSN ISSN 2347-4181 (Print) ISSN 2347-419X
WIRELESS/MOBILE networking is one of the strongest
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 53, NO. 3, MAY 2004 835 An Integrated Adaptive Bandwidth-Management Framework for QoS-Sensitive Multimedia Cellular Networks Sungwook Kim and Pramod K. Varshney,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 53, NO. 3, MAY 2004 835 An Integrated Adaptive Bandwidth-Management Framework for QoS-Sensitive Multimedia Cellular Networks Sungwook Kim and Pramod K. Varshney,
Impact of Service and Mobility Modelling on Network Dimensioning Shyamalie Thilakawardana and Rahim Tafazolli
 Impact of Service and Mobility Modelling on Network Dimensioning Shyamalie hilakawardana and Rahim afazolli Centre for Communications Systems Research,University of Surrey, Guildford, UK e-mail: S.hilakawardana@eim.surrey.ac.uk
Impact of Service and Mobility Modelling on Network Dimensioning Shyamalie hilakawardana and Rahim afazolli Centre for Communications Systems Research,University of Surrey, Guildford, UK e-mail: S.hilakawardana@eim.surrey.ac.uk
Doctoral Written Exam in Networking, Fall 2008
 Doctoral Written Exam in Networking, Fall 2008 December 5, 2008 Answer all parts of all questions. There are four multi-part questions, each of equal weight. Turn in your answers by Thursday, December
Doctoral Written Exam in Networking, Fall 2008 December 5, 2008 Answer all parts of all questions. There are four multi-part questions, each of equal weight. Turn in your answers by Thursday, December
Chapter 10: Wireless Networking. School of information science and Engineering, SDU
 Chapter 10: Wireless Networking School of information science and Engineering, SDU 10.1 Introduction to Wireless Networks Requirement to the networks: Provides ubiquitous personal communications; Accommodate
Chapter 10: Wireless Networking School of information science and Engineering, SDU 10.1 Introduction to Wireless Networks Requirement to the networks: Provides ubiquitous personal communications; Accommodate
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction. Harri Holma and Antti Toskala. 1.1 WCDMA technology and deployment status
 1 Introduction Harri Holma and Antti Toskala 1.1 WCDMA technology and deployment status The first Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) networks were
1 Introduction Harri Holma and Antti Toskala 1.1 WCDMA technology and deployment status The first Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) networks were
Configuring QoS on the GGSN
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure Quality of Service (QoS) functions to differentiate traffic flow through the GGSN. For a complete description of the GGSN commands in this chapter, refer
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure Quality of Service (QoS) functions to differentiate traffic flow through the GGSN. For a complete description of the GGSN commands in this chapter, refer
Pre-processor for MAC-layer Scheduler to Efficiently Manage Buffer in Modern Wireless Networks
 Pre-processor for MAC-layer Scheduler to Efficiently Manage Buffer in Modern Wireless Networks Ankit Bhamri, Navid Nikaein, Florian Kaltenberger, Jyri Hämäläinen, Raymond Knopp Eurecom, France (email :
Pre-processor for MAC-layer Scheduler to Efficiently Manage Buffer in Modern Wireless Networks Ankit Bhamri, Navid Nikaein, Florian Kaltenberger, Jyri Hämäläinen, Raymond Knopp Eurecom, France (email :
Comparison of the Quality of Service (QoS) on the IEEE e and the g Wireless LANs
 ENSC 427: COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Comparison of the Quality of Service (QoS) on the IEEE 802.11e and the 802.11g Wireless LANs Spring 2010 Final Report Group 5 Yalda Hakki (yha17@sfu.ca) Rosy Johal (rja2@sfu.ca)
ENSC 427: COMMUNICATION NETWORKS Comparison of the Quality of Service (QoS) on the IEEE 802.11e and the 802.11g Wireless LANs Spring 2010 Final Report Group 5 Yalda Hakki (yha17@sfu.ca) Rosy Johal (rja2@sfu.ca)
Quality of Service in the Internet
 Quality of Service in the Internet Problem today: IP is packet switched, therefore no guarantees on a transmission is given (throughput, transmission delay, ): the Internet transmits data Best Effort But:
Quality of Service in the Internet Problem today: IP is packet switched, therefore no guarantees on a transmission is given (throughput, transmission delay, ): the Internet transmits data Best Effort But:
Neuro-fuzzy admission control in mobile communications systems
 University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2005 Neuro-fuzzy admission control in mobile communications systems
University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2005 Neuro-fuzzy admission control in mobile communications systems
UMTS FTP Performance Enhancement Using Admission Control Algorithm
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 10, Issue 2, Ver.1 (Mar - Apr.2015), PP 13-19 www.iosrjournals.org UMTS FTP Performance
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 10, Issue 2, Ver.1 (Mar - Apr.2015), PP 13-19 www.iosrjournals.org UMTS FTP Performance
FAIR DELAY OPTIMIZATION-BASED RESOURCE ALLOCATION ALGORITHM FOR VIDEO TRAFFIC OVER WIRELESS MULTIMEDIA SYSTEM
 FAIR DELAY OPTIMIZATION-BASED RESOURCE ALLOCATION ALGORITHM FOR VIDEO TRAFFIC OVER WIRELESS MULTIMEDIA SYSTEM 1 M. R. M. Rizk, Senior Member, IEEE, 2 M. I. Dessouky, 3 Sami A. El-Dolil, and 4 Mohammed
FAIR DELAY OPTIMIZATION-BASED RESOURCE ALLOCATION ALGORITHM FOR VIDEO TRAFFIC OVER WIRELESS MULTIMEDIA SYSTEM 1 M. R. M. Rizk, Senior Member, IEEE, 2 M. I. Dessouky, 3 Sami A. El-Dolil, and 4 Mohammed
