""""FGJTCFWP"KPUVKVWVG"QH"VGEJPQNQI["
|
|
|
- Derek Brown
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION 1.) Overview of power system operation: The electrical energy is the most convenient form of energy in comparison to all the other forms of energy. However the biggest drawback of it is that it cannot be stored in large amounts directly in the form of electrical energy. Of course it is possible to store it in small amounts in the form of rechargeable batteries. But no method for large scale storage of electrical energy has been devised so far. Therefore electrical energy has to be generated and supplied instantaneously. The operation of power system becomes very complex due to the following factors: 1. At every instant the total active power generated must equal the total active power demand plus losses. 2. The total active power demand varies from instant to instant, day to day and season to season. Power system has to meet this varying demand all the time. 3. Loads also require lagging reactive power. This must also be produced and supplied. 4. The voltage and frequency of the system must be maintained within limits as per the government regulations. 5. Energy must be generated in such a way that the overall cost is minimum. 6. Any part of the power system may suffer a forced outage at any time. The power system must be ready to meet such emergencies. 7. Because of those reasons which are beyond the control of power system engineers, the load may increase unexpectedly (beyond the forecast value) and this additional load must also be supplied. 2.) Structure of power system Introduction: The electrical power is the most convenient form of energy since it is available to the consumer at the very instant it is switched on. The other benefits of electrical energy are the ease with which it can be generated in bulk and transmitted efficiently and economically over long distances. An electrical power system is a complex network of several subsystems which transform other types of energy into electrical energy, transmit and distribute it for consumption at the consumer s terminals. The fig.1 shows the general structure of power system whereas the fig.2 shows the single line diagram of a typical power system.
2 Constituents of a Power System: The power system consists of three subsystems which have clearly demarcated functions. The coordinated working of all the three subsystems is absolutely essential as they are parts of the same system. The subsystems are:- i. The generation subsystem. ii. The transmission & distribution subsystem. iii. The load subsystem. iv. The protection & control subsystem. (a) Generation The generation subsystem maybe called GENCO, responsible for generating electric power as per the predicted load requirements. The generating subsystem consists of a group of generating stations, which converts some form of primary energy into electrical energy. The generating station (or power station) of a power system consists of prime mover, such as turbine driven by water, steam or combustion gases which is coupled to an electric generator. The prime mover rotates the generator which produces electrical energy. The 3 phase a.c. generator also called alternator is one of the essential components of power system. Another major component of a power system is the transformer. It transfers power with very high efficiency from one voltage level to another level. The power transferred from primary to secondary is same exactly except for losses in transformer. Step up transformers are used for transmission of power. At the receiving end step down transformers are used to reduce the voltage to suitable values for distribution or utilization. In a modern utility system, the power may undergo four or five transformations between generator and ultimate user. (b) Transmission and Distribution The transmission subsystem maybe called TRANSCO. The purpose of an overhead transmission network is to transfer electric energy from generating units at various locations to the distribution system which ultimately supplies the load. The transmission lines allow interconnect neighbouring power stations which not only allows economic dispatch of power between regions during emergencies. High voltage transmission lines are terminated in substations which are called H.V. substations or receiving substations or primary substations. The function of some substations is switching circuits in and out of service. Hence they are referred as switching substations. The portion of the transmission system that connects the H.V. substations through step down transformers to the distribution substations are called sub-transmission network. However there is no clear demarcation between transmission and sub-transmission voltage levels. The sub-transmission voltages typically range from 66 kv to 132 kv. Some heavy industrial consumers are connected to the sub-transmission system, for example, BHEL Haridwar is connected directly to a 132 kv substation. The distribution system is that part which connects the distribution substations to the consumer s service entrance equipment. The distribution subsystem maybe called DISCOM which is the actual link between system and the consumers. The primary distribution lines are usually in the range of 4 kv to 11 kv. Some small industrial consumers are served directly by the primary feeds. The secondary distribution network reduces the voltage for utilization by commercial and residential consumers. A distribution system is designed to supply continuous and reliable power supply at the consumer s terminal at minimum cost. A typical distribution system is shown in fig. 2
3 (c) Loads From the viewpoint of a power supplier any component which is consuming electrical energy is a load. The loads of a power system are divided into industrial, commercial and residential. Very large industrial loads maybe served from the transmission system. Large industrial loads are served directly from the sub-transmission network and small industrial loads are served from the primary feeder network. The commercial and residential loads are served from the secondary feeder network. (d) Protection & Control The protection and control subsystem consists of relays, switchgear and other control devices which protect the various subsystems against faults, overloads and ensures efficient, reliable, economic operation of power system. It is necessary to monitor the entire system in a control center to ensure reliable and economic operation. The modern control centres of today are well equipped with online computers performing the entire signal processing through the remote acquisition system. In India regional and national power grids are established to facilitate transfer of power within and across the regions with reliability, security and economy. The Indian Power Grid system is divided into five regional grids. 3.) Power system control centre: The power systems of today are essentially very huge in terms of energy generated, transmitted and utilized, number of customers and total investment. The installed capacity in USA exceeds 1000 GW with annual energy generated exceeding 5000 TWh. The installed capacity in India exceeds 140 GW with annual energy generated exceeding 700 TWh. The system is growing continuously with more generating plants, transmission lines and distribution lines being added every month. The power system feeds a very large number of domestic, commercial, industrial, agricultural, electric traction and other customers. The increase in unit sizes, growth of interconnections and the need to maintain the system in normal mode requires sophisticated control, instrumentation and protection. The multiplicity of monitoring instruments in the control room and their distance apart make the observation of more than a few ones almost impossible, especially during the intense activity of plant start up. The operators are called upon to visualize the implications of a variety of changing plant parameters and take critical decisions. These requirements led to the
4 development and application of more advanced solid-state modular instruments, computer based direct digital control and data processing systems. A modern power system control centre has the following functions to perform: - 1. Automatic generation control 2. Economic load dispatch 3. Automatic voltage control 4. On line load flow 5. On line short circuit 6. State estimation 7. Steady state security analysis 8. Security monitoring 9. Supervisory control 10. Automatic trouble analysis 11. Emergency control like load shedding, generator tripping 12. Automatic circuit restoration etc. The computer system involves dual configuration with external interfaces to monitor the data. The first one is a process computer linked by telechannels to various generating and sub stations for data acquisition. The second one is a larger one where major calculations are carried out and is linked to the process computer. For real time computer control of power systems, the following basic components are needed: 1. System wide instrumentation 2. High speed digital telemetry 3. Central processing unit 4. Memory and bulk storage 5. Interactive display 6. Software (operating and application) The real time computer is designed to perform data acquisition, storage and retrieval, data processing, interactive display and remote signaling and control. It consists of modems and interfaces, CPU, memory and bulk storage & input-output devices like display devices, card reader, printer etc. The fig.3 shows a functional block diagram of a real time computer. CORE MEMORY DISPLAY CPU MODEMS DATA FROM THE SYSTEM DISK / TAPE Fig. 3 functional block diagram of a real time computer The database consists of static data, dynamic data and software. The static data consists of the details of lines, transformers, generators etc. The dynamic data includes line flows, voltage
5 levels, breaker condition, generation and demand. The software includes operating software, application software and support software. The operating software is the system software for real time operating compiling routines, file management etc. The application software consists of programs written for power system operation and control, which were listed earlier. The support software consists of diagnostics, debugging, maintenance and testing programs. The computer control can take any of the following forms: i. Off line computer control ii. Computer assisted control iii. On line computer control For planning and operating computation, which are carried out at infrequent intervals, off line computer calculation suffice. The results are to be updated at regular time intervals. In the computer- assisted control scheme, necessary data is transmitted at regular intervals to the computer located in a central control station and its decisions are communicated to the human operator. For short time processes extending up to a few minutes, the system is under continuous control of direct acting devices. Under emergency conditions, the on line computer which processes the data continuously sends commands to the direct acting devices according to a pre planned strategy to prevent danger to the system. The type of computer control, the configuration and the peripherals used are ultimately decided by the cost that the utility industry is willing to invest. Level Decomposition in Power System with respect to power control centre The power systems are characterized by strong hierarchical structure order. Accordingly, control strategy can be devised to fit into the hierarchical structure advantageously as given in table 1 Level System Monitoring and Control First Level Generating stations and substations Local control centre Second Level Sub transmission and transmission networks Area load dispatch centre Third Level Transmission system State load dispatch centre Fourth Level Interconnected power systems Regional control centre or Top Level Local Control Centre A number of control functions can be performed locally at power generating stations and substations using local equipment and automatic devices. The following are some of the typical control applications of a local control centre: 1. Local monitoring and control. 2. Protection 3. Auto reclosures. 4. Voltage regulation. 5. Capacitor switching. 6. Feeder synchronization. 7. Load shedding in the event of necessity 8. Network restoration Area Load Dispatch Centre A group of generating stations and substations alongwith the associated network and loads may be considered as a unit for control under an area load dispatch centre. The area control centre receives information and processes if for appropriate control action.
6 State Load Dispatch Centre The minute to minute operation of the power system at the state level may be carried out by the state load dispatch centre. It may have the following functions: 1. System generation, load monitoring and control. 2. System wide state monitoring and control. 3. Circuit breaker state monitoring and control. 4. Load shedding and load restoration. 5. Supervisory control for lines and equipment states. 6. System alarm monitoring and corrective action 7. Planning and monitoring of system operations. Regional Load Dispatch Centre The regional load dispatch centre may be regarded as a coordinating and monitoring centre for state level dispatch centres with the following main objectives: 1. Integrated operation of state level dispatch centres. 2. Operation and maintenance schedules for the generating plant. 3. Operation and maintenance schedules for maximum capacity utilization. 4. Monitor and control inter state power transactions. 5. Monitor and control inter regional power transactions. Hierarchy of power system operation and control in India The total power system in India is not being operated in totally integrated manner. However attempts are being made to achieve full integration. The National Load Dispatch Centre headquartered at New Delhi is the coordinating agency. Then there are five regional load dispatch centres as follows: A. Northern Region load dispatch centre at New Delhi covering the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Uttarakhand and union territory of Chandigarh. B. Western Region load dispatch centre at Mumbai covering the states of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chattisgarh, Goa and union territories of Daman, Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli. C. Southern Region load dispatch centre at Bangalore covering the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and union territories of Pondicherry and Lakshadweep. D. Eastern Region load dispatch centre at Kolkata covering the states of West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, Sikkim, Jharkhand. E. North Easter Region load dispatch centre at Shillong covering the states of Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram. The third level of hierarchy consists of state load dispatch centres which are stationed in each state capital. Remote terminal units are installed at many points in each state. The fig.1 shows the hierarchy of power control centre in India.
7 National Load Dispatch Centre (New Delhi) Northern Region Load Dispatch Centre (New Delhi) Western Region Load Dispatch Centre (Mumbai) Southern Region Load Dispatch Centre (Bangalore) Eastern Region Load Dispatch Centre (Kolkata) North Eastern Region Load Dispatch Centre (Shillong) SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC SLDC RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU Fig.1 RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU RTU Hardware requirements for computer control of power system The main equipment is a computer with enough storage capability. Many years ago main frame computers were used for this purpose but now desktop computers also have huge storage capability and are sufficient for most power systems. In an energy control centre, computers area connected in ring formation. All computers have backup computers also. The main computer is used for online program execution. The other computers are for duties like data acquisition etc. The standby computers are used for emergency duty. Some CROs, printers are also there. The standby computer is kept updated so that there is no loss of data or control. The changeover from main computer to standby computer can be manual or automatic but mostly it is automatic. The communication channels go out from the station to remote terminal units. Computer based telemetry and data processing facilities are also provided. The modern trend is to use computers for relaying also. The advantages of using computers for relaying are logging capability and application expansion possibility. Accuracy, fast response and overall economy are the other advantages. The numerical relays sample the values of current, voltage etc. which are then converted to digital form using analog to digital converters and fed to the computer. Software for computer control of power system The computers used in power system control centre are equipped with requisite softwares for performing the following functions: 1. Online security monitoring and state estimation. 2. Data acquisition, supervisory control etc. 3. Real time monitoring and control 4. Operating systems.
8 SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System) A lot of data is required about the operating conditions of a power system when proper, efficient energy management needs to be carried out. A large number of operations have to be carried out at unattended locations from the operating centre. In many cases remote operation of a device situated at a remote location from a control centre needs to be carried out as the cost of providing a personal for the operation to be carried out the location maybe prohibitive. Not only that if the operation requires a personal to be send to the remote location for operation of the device then it will lead to a considerable delay. Such delays may result in long outage durations and poor reliability. SCADA systems have been developed to overcome such problems. The need to control remote operations and monitor them led to development of SCADA. The main functions of SCADA are as follows: Data Acquisition: To provide data, measurements and status information to operator Plotting: To plot different measurements in real time regime. Supervisory Control: To operate and control circuit breakers remotely. Alarms: To send alarm signals as regards undesirable operating conditions. Logging: To log al information, signals etc. Load Shedding: To provide automatic and manual load shedding in emergency conditions so as to maintain system synchronism and stability. Load Restoration: To restore loads after system returns to normal state. Automatic Generation Control: To control generation at the power plants. In addition to the above SCADA systems are many times used for additional tasks like security assessment, training, energy management etc. Need for SCADA The main reasons for adopting SCADA are as follows: 1. To reduce cost. 2. To reduce manpower 3. To reduce future capital requirements. 4. To improve level of service. 5. To avoid environmental accidents. 6. To comply with regulator requirements. 7. To attain and maintain competitive edge. 8. To replace existing ageing system. 9. To manage complex systems. Components of SCADA A SCADA has the following components 1. Sensors: These maybe digital or analog. They are basically control relays which interface with the power system. 2. Remote Terminal Units (RTUs): These are small computerized units deployed in field at specific sites and locations. RTUs are collection points for getting information and reports from sensors and for sending commands to relays. 3. Master Unit: They are basically large computer systems which serve as a central processor. 4. Communication Links 5. Software
9 Configurations of SCADA systems A SCADA system may have different configurations depending upon the system and its requirements. Each configuration consists of a master unit (M) and remote unit (R). The fig.2 (a) to fig.2 (d) shows the various configurations which are used in SCADA systems. M R R 3 R 4 M R R 2 M Fig.2 (a) One to One SCADA configuration R 5 R 1 Fig.2 (b) Star SCADA Configuration M R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 R 5 Fig.2 (c) Party line SCADA Configuration R 1 R 2 R 5 R 3 M R 4 R 7 R 6 R 8 R 9 Fig.2 (d) Network Configuration
10 Master Unit The fig.3 shows the layout of a typical SCADA system Operators console Modem RTU Printer Graphic Instrument Board MASTER UNIT COMPUTER Modem Modem Modem Modem Modem RTU RTU CRT System diagram RTU RTU Fig.3 layout of SCADA The master unit is the heart of SCADA system. All operations of different RTUs are made from the master unit and reported back by RTUs to the master unit. The master unit has a digital computer and ancillary equipment to permit communications between master unit and RTUs. One such equipment is a modem (modulator demodulator). The computer uses digital pulses. Modem converts these digital pulses to analog signal so that it can be transmitted to RTU. The messages from the master unit to RTUs are in the form of audio frequency and are sent by frequency shift techniques. Frequency shift signaling is pretty immune from noise. The other equipments include line printer, operator s console, CRT (or monitor), graphic instruments board etc. The printer enables the messages received from RTUs to be converted to hard copy. Sometimes a single line diagram of the power system controlled through SCADA also exists in the master station. Digital / Analog (D/A) converters are also provided in master unit so that informations like line currents, bus voltages, frequency, real and reactive power flows as received in digital form is converted to analog form and read by various indicating instruments. Some recording instruments are also provided so that visual representation of the conditions is displayed. Colour CRT screens enable different colours to indicated changes in voltage levels, position of circuit breakers (open or closed) etc. Some flashing indications and alarm signals are used to draw the attention of operator. For remote operations the operator at the master station follows select before operate procedure which is as follows: 1. The operator selects the RTU. 2. RTU acknowledges the selection. 3. Operator selects the device to be operated at that RTU. 4. RTU acknowledges that the device has been selected. 5. Operator performs the desired operation. 6. RTU performs the operation and sends a signal to master unit indicating that the desired operation has been performed. This signal maybe a message printed by printer or indication on CRT screen. Remote Terminal Units These units are located at selected locations in the power system. They are equipped with microcomputers and thus have logic and memory capabilities. Such
11 RTUs are also termed as intelligent remote terminal units. Sometimes these units can perform certain pre-programmed functions without any direction from the master unit but report all these actions to the master unit. They also have a modem to enable them to receive messages from master unit and also send compliance reports to the master unit. In addition they have relays to send trip signal to the circuit breakers and other disconnecting equipment. They are also provided with transducers to make different measurements. In situations where many operations take place in quick succession, the RTU is fitted with sequence of events recording facility. In this case the events separated by even a few milliseconds can be recorded in correct sequence e.g. in case of a fault both phase fault and ground fault relays may operate one after the other. The sequence of events is recorded in correct order so that the protection engineer can see whether the sequence of events was correct. In all such cases the RTU reports to the master unit and then the information is erased from its memory so that RTU can record next event. Communication Channels in SCADA The communication channels between the master unit and RTUs form an important part of SCADA. The communication links can be wire circuit, wireless (microwave) link or power line carrier channel. The important consideration in selecting a communicating channel is the signal to noise ration (SNR) and the bandwidth. Good SNR and high bandwidth enable errorless messages and high speed of signal transmission. Most of the time a telephone line with bandwidth of Hz is sufficient. Power line carrier system has been in use in power systems for pretty long time. Capacitors rated to withstand the transmission line voltage alongwith tuned circuits are used to couple a carrier to a power circuit. The capacitive reactance of the coupling capacitors is low at carrier frequency but high at power frequency. Thus carrier channel signals can be superimposed on power circuit. Wireless channel have high efficiency and reliability. Various Operational Stages of Power System Power systems are interconnected to improve reliability and quality of power supply to the consumer to reduce the spinning reserve requirements of individual systems and for similar other advantages. The operating state of a power system can be divided into following modes. 1. Normal mode 2. Alert mode 3. Emergency mode 4. Restorative mode 5. In Extremis mode The fig.4 shows the state transition diagram of a power system Restorative Mode Alert Mode Normal Mode In Extremis Mode Emergency Mode Fig.4 State Transition Diagram
12 In the normal mode of operation, the system has to maintain scheduled voltages, frequency and load flow profile maintaining the schedule tie line power flows. The most important aspect in any mode of operation is the matching between load demand and generation. The frequency deviation of the system is a direct measure of the mismatch between the total generation and combined load demand. It is only when the frequency is maintained at the rated value that the generation balances the load demand. 1. Normal Mode When the system is in normal state the generation matches the load and none of the equipments is overloaded. The system is secure in normal state and some amount of spinning reserve also exists. 2. Alert Mode In this mode of operation, the power system is synchronized but the security level is reduced below the specified limits. The generation and load are matching with none of the equipments getting overloaded. However no spinning reserve is available. In this mode, preventive control is provided to restore adequate generating margin, generation shifting, tie line rescheduling, and voltage reduction (if extremely necessary). 3. Emergency Mode In this mode of operation, the power system is synchronized as the generation matches the load but some equipment may be overloaded. In this mode, immediate control is provided to clear equipment overloads, fault clearing, fast valving dynamic braking, exciter control, load control, capacitor switching and all controls mentioned in Alert state. 4. Restorative Mode In this mode of operation, the power system may or may not be synchronized. The power engineers are taking necessary corrective actions so that the system is restored back to normal state. In this mode corrective measures like reestablishing viable system, generating units restarting and synchronization, load restoration, re-synchronization of different areas is done. In the restorative mode, control action is initiated but the load constraints are not completely satisfied. Under this condition, the system may be in a completely or partially shut down state. 5. In Extremis Mode In this mode of operation, the power system loses synchronism resulting in tripping of some generators, and overloading of equipments also occurs. Some parts of the country (or province) may also face black out if the system is in this mode of operation. Load shedding and all the controls mentioned in emergency state are to be taken. Power System Security The classification of the modes or states of operation of a power system helps in distinguishing the different types of controls to be applied to the system to make the system operate reliably. The objective of power system security is to keep the power system in normal mode of operation and prevent it from entering into either emergency or restorative mode. The system state is continuously assessed via data acquisition systems making use of telemetered data, redundant data and by predicting the missing or doubtful whenever a metering channel becomes erroneous or its accuracy is beyond the normal specified range. This job is referred to as security monitoring. During security assessment, a series of fast computations are made to examine the effect of various credible contingencies and those that are not so. If some of the assumed contingencies result in unsatisfactory performance from the point of view of security, a corrective strategy is called for, to determine the best corrective action either by special calculations within the computer or from results obtained from off line studies. Continuous monitoring for security and sending command signal for corrective action whenever necessary is referred to as security control. Steady state security maybe defined as the ability of the system to operate steady state wise within the specified limits of safety and supply
13 following a contingency in the time period, after which the fast acting control devices have restored the system balance but before the slow acting controls like transformer tappings, human decisions, etc. have responded. Steady state security analysis is performed to determine whether there will be a new steady state operating point at which the system will settle after the post fault oscillations have been damped out. The post contingency steady state solution will have to be checked for violation of operational constraints. If it violates the constraints, the contingency is declared to be insecure and necessary corrective action is to be initiated. For steady state security analysis the following contingencies maybe considered: 1. Loss of a generating unit. 2. Sudden loss of a load. 3. Sudden change in flow of power in a tie line. 4. Outage of a transmission line. 5. Outage of a transformer. 6. Outage of a shunt capacitor or reactor being used for compensation. The outage maybe a power outage or network outage. Fast and decoupled load flows are employed for security analysis of systems. The purpose of contingency analysis of a power system is to alert the operator about the possibility of occurring of vulnerable condition of the system on a real time basis as load and generation change. It determines the bus voltages that are excessively high or too low. It also calculates the power flows that are above the overload limits for generation and transmission lines. Precalculated results of the analysis are used to take corrective actions such as load shedding.
The various functions of an energy control center can be enumerated as under: 1. Load forecasting 6. Automatic generation control
 ENERGY CONTROL CENTERS To generated, Transmission and Distribution system, Number of customers and Total investment. Installed capacity in India exceeds 206 GW with annual energy generated energy exceeding
ENERGY CONTROL CENTERS To generated, Transmission and Distribution system, Number of customers and Total investment. Installed capacity in India exceeds 206 GW with annual energy generated energy exceeding
State-wise Gross State Domestic Product by Industry of Origin (at Prices) % Share to Total State GSDP at Constant Prices
 Andhra Pradesh Andaman & N. Islands Arunachal Pradesh Assam State-wise Gross State Domestic Product by of Origin (at 2004-05 25.07 24.28 22.27 23.34 22.00 21.09 19.84 18.61 18.99 19.04 20.58 20.04 18.31
Andhra Pradesh Andaman & N. Islands Arunachal Pradesh Assam State-wise Gross State Domestic Product by of Origin (at 2004-05 25.07 24.28 22.27 23.34 22.00 21.09 19.84 18.61 18.99 19.04 20.58 20.04 18.31
POWER SYSTEM SECURITY CONCEPTS
 POWER SYSTEM SECURITY CONCEPTS 1.1 INTRODUCTION The Power System needs to be operationally secure, i.e. with minimal probability of blackout and equipment damage. An important component of power system
POWER SYSTEM SECURITY CONCEPTS 1.1 INTRODUCTION The Power System needs to be operationally secure, i.e. with minimal probability of blackout and equipment damage. An important component of power system
Employer Registration
 Employer Registration Help File ESIC ONLINE REGISTRATION OF THE EMPLOYERS OVERVIEW: Registration of employers under ESI Act is fully online, without requirement of submission of any physical application
Employer Registration Help File ESIC ONLINE REGISTRATION OF THE EMPLOYERS OVERVIEW: Registration of employers under ESI Act is fully online, without requirement of submission of any physical application
Employer Registration Help File
 Employer Registration Help File ONLINE REGISTRATION OF THE EMPLOYERSOVERVIEW: Registration of employers under ESI Act is fully online, without requirement of submission of any physical application documents
Employer Registration Help File ONLINE REGISTRATION OF THE EMPLOYERSOVERVIEW: Registration of employers under ESI Act is fully online, without requirement of submission of any physical application documents
Real-time Power System Operation. Energy Management Systems. Introduction
 1 Real-time Power System Operation Energy Management Systems Introduction The time frame for Power Systems Operation varies from a few seconds to a week. To assist with the operation of the system, modern
1 Real-time Power System Operation Energy Management Systems Introduction The time frame for Power Systems Operation varies from a few seconds to a week. To assist with the operation of the system, modern
AUTOMATION OF POWER DISTRIBUTION USING SCADA
 1 2 ABSTRACT In every substation certain measurements, supervision, control, operation and protection functions are necessary. Traditionally these functions were performed manually by system operator from
1 2 ABSTRACT In every substation certain measurements, supervision, control, operation and protection functions are necessary. Traditionally these functions were performed manually by system operator from
Monthly changes in the General Indices and CFPIs are given below: Monthly changes (%) in All India CPI (General) and CFPI: Dec over Nov.
 Monthly changes in the General Indices and CFPIs are given below: Monthly changes in All India CPI (General) and CFPI: 20 over Nov. 20 Indices Rural Urban Combined Value % Change Nov. Value % Change Nov.
Monthly changes in the General Indices and CFPIs are given below: Monthly changes in All India CPI (General) and CFPI: 20 over Nov. 20 Indices Rural Urban Combined Value % Change Nov. Value % Change Nov.
Shabnam Rukhsar Electrical Engineering Department, Anjuman College of Engineering and Technology.India
 SCADA in Transmission Line Shabnam Rukhsar Electrical Engineering Department, Anjuman College of Engineering and Technology.India ABSTRACT: Transmission line equivalent circuit parameters are often 25%
SCADA in Transmission Line Shabnam Rukhsar Electrical Engineering Department, Anjuman College of Engineering and Technology.India ABSTRACT: Transmission line equivalent circuit parameters are often 25%
Handout on. Mobile Number Portability. For Sales Channels
 Handout on Mobile Number Portability For Sales Channels Contents 1. Introduction of MNP 2. Areas where MNP is permitted 3. Some terminologies related to MNP 4. Why a customer should join BSNL? 5. Porting
Handout on Mobile Number Portability For Sales Channels Contents 1. Introduction of MNP 2. Areas where MNP is permitted 3. Some terminologies related to MNP 4. Why a customer should join BSNL? 5. Porting
Small Generator Interconnection System Impact Study Report. Completed For Q0047
 Small Generator Interconnection Completed For Q0047 Proposed Interconnection PacifiCorp s Existing Goshen Rigby 69 kv Line March 7, 2005 1.0 Description of the Generation Facility Q0047 ( Interconnection
Small Generator Interconnection Completed For Q0047 Proposed Interconnection PacifiCorp s Existing Goshen Rigby 69 kv Line March 7, 2005 1.0 Description of the Generation Facility Q0047 ( Interconnection
Highlights of Telecom Subscription Data as on 28 th February, 2018
 For immediate release (Press Release No.48/2018) Information Note to the Press TELECOM REGULATORY AUTHORITY OF INDIA New Delhi, 24 th April, 2018 (www.trai.gov.in) 20 Glorious Years (1997-2017) Highlights
For immediate release (Press Release No.48/2018) Information Note to the Press TELECOM REGULATORY AUTHORITY OF INDIA New Delhi, 24 th April, 2018 (www.trai.gov.in) 20 Glorious Years (1997-2017) Highlights
Connectivity for NeGP. Presented By: Anil Kumar Balani Director Department of Information Technology
 Connectivity for NeGP Presented By: Anil Kumar Balani Director Department of Information Technology NeGP Connectivity Components SWAN (min 2 Mbps connectivity) Vertical Locations: 7500+ PoPs Horizontal
Connectivity for NeGP Presented By: Anil Kumar Balani Director Department of Information Technology NeGP Connectivity Components SWAN (min 2 Mbps connectivity) Vertical Locations: 7500+ PoPs Horizontal
Chapter 2 State Estimation and Visualization
 Chapter 2 State Estimation and Visualization One obvious application of GPS-synchronized measurements is the dynamic monitoring of the operating conditions of the system or the dynamic state estimation
Chapter 2 State Estimation and Visualization One obvious application of GPS-synchronized measurements is the dynamic monitoring of the operating conditions of the system or the dynamic state estimation
MoH&FW, Govt. of India, New Delhi
 National Medical College Network Health Education Content Delivery, Skill Enhancement and Healthcare Outreach Services Project MoH&FW, Govt. of India, New Delhi 1 VISION & Philosophy Health Education Content
National Medical College Network Health Education Content Delivery, Skill Enhancement and Healthcare Outreach Services Project MoH&FW, Govt. of India, New Delhi 1 VISION & Philosophy Health Education Content
Evolution of Control for the Power Grid
 Evolution of Control for the Power Grid Anjan Bose Washington State University Pullman, WA, USA PaiFest In Honor of Prof. M. A. Pai Urbana-Champaign, IL October 15, 2015 The Past (before 1960s) Hard
Evolution of Control for the Power Grid Anjan Bose Washington State University Pullman, WA, USA PaiFest In Honor of Prof. M. A. Pai Urbana-Champaign, IL October 15, 2015 The Past (before 1960s) Hard
HARDWARE OF SUPERVISORY CONTROL & DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEM
 Chapter 3 HARDWARE OF SUPERVISORY CONTROL & DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEM Dr. H.K. VERMA Distinguished Professor Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering School of Engineering and Technology SHARDA
Chapter 3 HARDWARE OF SUPERVISORY CONTROL & DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEM Dr. H.K. VERMA Distinguished Professor Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering School of Engineering and Technology SHARDA
9.Telecommunication. India s first 3G mobile services by the state owned MTNL (Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Limited)
 India s first 3G mobile services by the state owned MTNL (Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Limited) 299 300 9. TELECOMMUNICATION Concepts and Definitions Code-Division Multiple Access- refers to any of several
India s first 3G mobile services by the state owned MTNL (Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Limited) 299 300 9. TELECOMMUNICATION Concepts and Definitions Code-Division Multiple Access- refers to any of several
ELECTRICAL, INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL SYSTEMS
 ELECTRICAL, INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL SYSTEMS Presentation by: RANA NASIR ALI General Manager, Power Plants Projects, at PITCO November 02, 2017 ELECTRICAL PLANT CONCEPT The electrical equipment, depending
ELECTRICAL, INSTRUMENTATION & CONTROL SYSTEMS Presentation by: RANA NASIR ALI General Manager, Power Plants Projects, at PITCO November 02, 2017 ELECTRICAL PLANT CONCEPT The electrical equipment, depending
ELG4125: System Protection
 ELG4125: System Protection System Protection Any power system is prone to 'faults', (also called short-circuits), which occur mostly as a result of insulation failure and sometimes due to external causes.
ELG4125: System Protection System Protection Any power system is prone to 'faults', (also called short-circuits), which occur mostly as a result of insulation failure and sometimes due to external causes.
SCADA and Central Applications An introduction
 SCADA and Central Applications An introduction Course map Outline of the lecture Power System Operation - Centralised Control Applications SCADA - SCADA architecture & Components - SCADA system functions
SCADA and Central Applications An introduction Course map Outline of the lecture Power System Operation - Centralised Control Applications SCADA - SCADA architecture & Components - SCADA system functions
Power System Network Simulator (PSNsim)
 The PSNsim is hardware simulator that simulates all parts of power system from generation to utilization. The PSNsim is a scaled down model of the real power system that provides an experimental environment
The PSNsim is hardware simulator that simulates all parts of power system from generation to utilization. The PSNsim is a scaled down model of the real power system that provides an experimental environment
The modified file structure for the same is given in Annexure 1 of this circular for reference.
 NATIONAL COMMODIT & DERIVATIVES EXCHANGE LIMITED Circular to all trading and clearing Members of the Exchange Circular No : NCDEX/TECHNOLOG-018/2015/353 Date : November 09, 2015 Subject : CTCL Bulk Upload
NATIONAL COMMODIT & DERIVATIVES EXCHANGE LIMITED Circular to all trading and clearing Members of the Exchange Circular No : NCDEX/TECHNOLOG-018/2015/353 Date : November 09, 2015 Subject : CTCL Bulk Upload
NIRMAL XBRL GENERATOR
 NIRMAL XBRL GENERATOR USER GUIDE INDIAN COSTING TAXONOMY DEVELOPER INFORMATION DEVELOPED BY CONTACT CA. NIRMAL GHORAWAT 434, Ajanta Shopping Centre, Ring Road, Surat - 395 002 Gujarat Email: nirmal.ghorawat@icai.org
NIRMAL XBRL GENERATOR USER GUIDE INDIAN COSTING TAXONOMY DEVELOPER INFORMATION DEVELOPED BY CONTACT CA. NIRMAL GHORAWAT 434, Ajanta Shopping Centre, Ring Road, Surat - 395 002 Gujarat Email: nirmal.ghorawat@icai.org
IMPROVING POWER SYSTEM RELIABILITY USING MULTIFUNCTION PROTECTIVE RELAYS
 IMPROVING POWER SYSTEM RELIABILITY USING MULTIFUNCTION PROTECTIVE RELAYS Armando Guzmán Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. Pullman, WA 99163 A reliable power system maintains frequency and voltage
IMPROVING POWER SYSTEM RELIABILITY USING MULTIFUNCTION PROTECTIVE RELAYS Armando Guzmán Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. Pullman, WA 99163 A reliable power system maintains frequency and voltage
EMS-LECTURE 2: WORKING OF EMS
 EMS-LECTURE 2: WORKING OF EMS Introduction: Energy Management systems consists of several applications programs which are used by the operator in a control centre for effective decision making in the operation
EMS-LECTURE 2: WORKING OF EMS Introduction: Energy Management systems consists of several applications programs which are used by the operator in a control centre for effective decision making in the operation
SCADA Training - T&D Automation
 SCADA Training - T&D Automation Contact us Today for a FREE quotation to deliver this course at your company?s location. https://www.electricityforum.com/onsite-training-rfq This course covers all the
SCADA Training - T&D Automation Contact us Today for a FREE quotation to deliver this course at your company?s location. https://www.electricityforum.com/onsite-training-rfq This course covers all the
November 29, ECE 421 Session 28. Utility SCADA and Automation. Presented by: Chris Dyer
 ECE 421 Session 28 November 29, 2018 Utility SCADA and Automation Presented by: Chris Dyer Utility SCADA & Automation Chris Dyer, P.E. BSEE University of Idaho, 1997 SCADA & Automation Engineer POWER Engineers,
ECE 421 Session 28 November 29, 2018 Utility SCADA and Automation Presented by: Chris Dyer Utility SCADA & Automation Chris Dyer, P.E. BSEE University of Idaho, 1997 SCADA & Automation Engineer POWER Engineers,
Role of MoWR under NHP Avanish Kant, Sr. Hydrogeologist
 Role of MoWR under NHP Avanish Kant, Sr. Hydrogeologist 14 th September, 2015, New Delhi NHP Project Background Achievements of HP-I & HP-II:- establishment of hydro-meteorological equipment in the States
Role of MoWR under NHP Avanish Kant, Sr. Hydrogeologist 14 th September, 2015, New Delhi NHP Project Background Achievements of HP-I & HP-II:- establishment of hydro-meteorological equipment in the States
up of SPMU in States/UTs under NeGP A
 1/12/2015 Guidelines for Setting up of SPMU in States/UTs under NeGP A Department of Agriculture & Cooperation (DAC), Ministry of Agriculture, New Delhi Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Scope of Work of
1/12/2015 Guidelines for Setting up of SPMU in States/UTs under NeGP A Department of Agriculture & Cooperation (DAC), Ministry of Agriculture, New Delhi Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Scope of Work of
October 05, ECE 421 Session 12. Utility SCADA and Automation. Presented by: Chris Dyer
 ECE 421 Session 12 October 05, 2017 Utility SCADA and Automation Presented by: Chris Dyer Utility SCADA & Automation Chris Dyer, P.E. BSEE University of Idaho, 1997 SCADA & Automation Engineer POWER Engineers,
ECE 421 Session 12 October 05, 2017 Utility SCADA and Automation Presented by: Chris Dyer Utility SCADA & Automation Chris Dyer, P.E. BSEE University of Idaho, 1997 SCADA & Automation Engineer POWER Engineers,
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF COMMUNICATIONS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS
 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF COMMUNICATIONS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO.2496 TO BE ANSWERED ON 26 TH DECEMBER, 2018 2496. SHRI KAUSHALENDRA KUMAR: SHRIMATI NEELAM
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF COMMUNICATIONS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO.2496 TO BE ANSWERED ON 26 TH DECEMBER, 2018 2496. SHRI KAUSHALENDRA KUMAR: SHRIMATI NEELAM
Load Management of Industrial Facilities Electrical System Using Intelligent Supervision, Control and Monitoring Systems
 Load Management of Industrial Facilities Electrical Using Intelligent Supervision, and Monitoring s Selahattin Kucuk TÜPRAŞ İzmit Refinery selahattin.kucuk@tupras.com.tr Fahrettin Arslan Istanbul University
Load Management of Industrial Facilities Electrical Using Intelligent Supervision, and Monitoring s Selahattin Kucuk TÜPRAŞ İzmit Refinery selahattin.kucuk@tupras.com.tr Fahrettin Arslan Istanbul University
Address and Tel.No. of the Director, Legal Metrology GOI
 Address and Tel.No. of the Director, Legal Metrology GOI 1) Mr. B.N. Dixit, Director. Deptt. of Consumer Affairs, Room No.461-A, Krishi Bhawan, New Delhi - 110 001. Tel. No. 23389489 Fax No. 23385322 Controllers
Address and Tel.No. of the Director, Legal Metrology GOI 1) Mr. B.N. Dixit, Director. Deptt. of Consumer Affairs, Room No.461-A, Krishi Bhawan, New Delhi - 110 001. Tel. No. 23389489 Fax No. 23385322 Controllers
Approval...6. Current Revision...7. Introduction... 8 About PJM Manuals... 8 About This Manual... 8 Using This Manual...9
 PJM Manual 07: PJM Protection Standards Revision: 3 Effective Date: May 24, 2018 Prepared by System Planning Division Transmission Planning Department PJM 2018 Table of Contents Table of Contents Approval...6
PJM Manual 07: PJM Protection Standards Revision: 3 Effective Date: May 24, 2018 Prepared by System Planning Division Transmission Planning Department PJM 2018 Table of Contents Table of Contents Approval...6
IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO
 IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO PREPARED BY: System Management (WA) DOCUMENT REF: SO_OP_WA_3805 VERSION: 1.0 EFFECTIVE DATE: 13/10/2017 STATUS: FINAL Approved for distribution
IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO PREPARED BY: System Management (WA) DOCUMENT REF: SO_OP_WA_3805 VERSION: 1.0 EFFECTIVE DATE: 13/10/2017 STATUS: FINAL Approved for distribution
Synchronizing Systems
 Synchronizing Systems AGN Technology brings alternative solution to energy projects by using synchronizing systems. With combining more than one generator for your high KVA needs, this system provides
Synchronizing Systems AGN Technology brings alternative solution to energy projects by using synchronizing systems. With combining more than one generator for your high KVA needs, this system provides
Substation SCADA Monitoring
 Substation SCADA Monitoring Contact us Today for a FREE quotation to deliver this course at your company?s location. https://www.electricityforum.com/onsite-training-rfq Substations are a critical component
Substation SCADA Monitoring Contact us Today for a FREE quotation to deliver this course at your company?s location. https://www.electricityforum.com/onsite-training-rfq Substations are a critical component
Supplemental Information
 Retirement of NPCC Directory# 3 Supplemental Information On April 1, 2015, NPCC Directory# 3 was retired upon the effective date of PRC-005-2 Protection System Maintenance which is subject to a 12 year
Retirement of NPCC Directory# 3 Supplemental Information On April 1, 2015, NPCC Directory# 3 was retired upon the effective date of PRC-005-2 Protection System Maintenance which is subject to a 12 year
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI EE-2401 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT-III REACTIVE POWER VOLTAGE CONTROL
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621213 EE-2401 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT-III REACTIVE POWER VOLTAGE CONTROL TWO MARKS: 1. What are the sources of reactive power? How it is
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621213 EE-2401 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL UNIT-III REACTIVE POWER VOLTAGE CONTROL TWO MARKS: 1. What are the sources of reactive power? How it is
Power System Controls
 Power System Controls Control Schemes Ref: A. P. Meliopoulos, Power System Modeling, 1990-2006 Voltage Control The objective of this control loop is to regulate the voltage at the terminals of the generator.
Power System Controls Control Schemes Ref: A. P. Meliopoulos, Power System Modeling, 1990-2006 Voltage Control The objective of this control loop is to regulate the voltage at the terminals of the generator.
Smart Distribution Technology
 Smart Distribution Technology Presentation Agenda Alabama Power Company, A Southern Company Distribution Automation Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition (SCADA) Multiple Address System (MAS) communications
Smart Distribution Technology Presentation Agenda Alabama Power Company, A Southern Company Distribution Automation Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition (SCADA) Multiple Address System (MAS) communications
Flexible High-Speed Load Shedding Using a Crosspoint Switch
 Flexible High-Speed Load Shedding Using a Crosspoint Switch Will Allen and Tony Lee Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. Published in Wide-Area Protection and Control Systems: A Collection of Technical
Flexible High-Speed Load Shedding Using a Crosspoint Switch Will Allen and Tony Lee Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. Published in Wide-Area Protection and Control Systems: A Collection of Technical
AMR and SCADA in Outage Management System for MSEDCL Sangita B. Patil 1, Bapu K. Patil 2
 e-issn: 2349-9745 p-issn: 2393-8161 Scientific Journal Impact Factor (SJIF): 1.711 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com AMR and SCADA in Outage Management System
e-issn: 2349-9745 p-issn: 2393-8161 Scientific Journal Impact Factor (SJIF): 1.711 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com AMR and SCADA in Outage Management System
National e-governance Plan: State Data Centre (SDC) DVL Narayana Rao, Additional Director, DeitY
 National e-governance Plan: State Data Centre (SDC) DVL Narayana Rao, Additional Director, DeitY Vision of NeGP Make all Government services accessible to the COMMON MAN IN HIS LOCALITY, through Common
National e-governance Plan: State Data Centre (SDC) DVL Narayana Rao, Additional Director, DeitY Vision of NeGP Make all Government services accessible to the COMMON MAN IN HIS LOCALITY, through Common
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 10, 2015 ISSN (online):
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 10, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Comparison of Shunt Facts Devices for the Improvement of Transient Stability of Two Machine
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 10, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Comparison of Shunt Facts Devices for the Improvement of Transient Stability of Two Machine
SurvalentONE Distribution Management System
 SurvalentONE Distribution Management System Analyze & Optimize Critical Grid Functions for Advanced System Monitoring & Control SurvalentONE ADMS The SurvalentONE ADMS platform is a fully integrated SCADA,
SurvalentONE Distribution Management System Analyze & Optimize Critical Grid Functions for Advanced System Monitoring & Control SurvalentONE ADMS The SurvalentONE ADMS platform is a fully integrated SCADA,
Case Study: Implementation of 132kv Malegaon Sub-Station Using SCADA
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, PP 76-83 www.iosrjournals.org Case Study: Implementation of 132kv Malegaon Sub-Station Using SCADA
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, PP 76-83 www.iosrjournals.org Case Study: Implementation of 132kv Malegaon Sub-Station Using SCADA
IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO
 IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO PREPARED BY: System Management (WA) DOCUMENT REF: SO_OP_WA_3805 VERSION: 1.0 EFFECTIVE DATE: 13/10/2017 STATUS: DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION Approved
IMS INTERFACE MARKET PROCEDURE NETWORK OPERATORS AND AEMO PREPARED BY: System Management (WA) DOCUMENT REF: SO_OP_WA_3805 VERSION: 1.0 EFFECTIVE DATE: 13/10/2017 STATUS: DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION Approved
Design of Coal Mine Power Supply Monitoring System
 2nd International Conference on Electronics, Network and Computer Engineering (ICENCE 2016) Design of Coal Mine Power Supply Monitoring System Lei Shi 1, Guo Jin 2 and Jun Xu 3 1 2 Department of electronic
2nd International Conference on Electronics, Network and Computer Engineering (ICENCE 2016) Design of Coal Mine Power Supply Monitoring System Lei Shi 1, Guo Jin 2 and Jun Xu 3 1 2 Department of electronic
Digital Substation Overview of Technology, Industry
 Digital Substation Overview of Technology, Industry Trends and Standardization Efforts 4th International Scientific & Technical Conference Actual Trends in Development of Power System Protection and Automation
Digital Substation Overview of Technology, Industry Trends and Standardization Efforts 4th International Scientific & Technical Conference Actual Trends in Development of Power System Protection and Automation
Evolution of Control for the Power Grid
 Evolution of Control for the Power Grid Anjan Bose Washington State University Pullman, Washington, USA University of Seville Seville, Spain June 17, 2016 THE INTERCONNECTED GRID Economics Transfer electric
Evolution of Control for the Power Grid Anjan Bose Washington State University Pullman, Washington, USA University of Seville Seville, Spain June 17, 2016 THE INTERCONNECTED GRID Economics Transfer electric
Energy Efficiency Initiatives in Commercial Buildings. Bureau of Energy Efficiency Government of India
 Energy Efficiency Initiatives in Commercial Buildings Bureau of Energy Efficiency Government of India Overview of India s Commercial Building Sector Sector Wise Electricity Consumption Industri al, 45%
Energy Efficiency Initiatives in Commercial Buildings Bureau of Energy Efficiency Government of India Overview of India s Commercial Building Sector Sector Wise Electricity Consumption Industri al, 45%
Relion 630 series. Load-shedding controller PML630 High performing load-shedding solution for industrial and utility power networks
 Relion 630 series Load-shedding controller PML630 High performing load-shedding solution for industrial and utility power networks Integrated load-shedding and protection solution The PML630 is a freely-configurable
Relion 630 series Load-shedding controller PML630 High performing load-shedding solution for industrial and utility power networks Integrated load-shedding and protection solution The PML630 is a freely-configurable
Generation Interconnection Feasibility Study Report
 Project #169 Generation Interconnection Feasibility Study Report 7/2/2014 Regional Electric Transmission Planning TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary... 3 Generator and Interconnection Data... 5 Study
Project #169 Generation Interconnection Feasibility Study Report 7/2/2014 Regional Electric Transmission Planning TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary... 3 Generator and Interconnection Data... 5 Study
MODERN-PLANNING TOOLS CONNECTED WITH GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM IN UTILITY COMPANY
 MODERN-PLANNING TOOLS CONNECTED WITH GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM IN UTILITY COMPANY Vybiralik Frantisek STE - Stredoceska Energetika a.s. - Czech Republic fvybiralik@ste.cz Josef Tlusty Technical University
MODERN-PLANNING TOOLS CONNECTED WITH GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM IN UTILITY COMPANY Vybiralik Frantisek STE - Stredoceska Energetika a.s. - Czech Republic fvybiralik@ste.cz Josef Tlusty Technical University
SCADA Software. 3.1 SCADA communication architectures SCADA system
 3 SCADA Software 3.1 SCADA communication architectures 3.1.1 SCADA system A supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system means a system consisting of a number of remote terminal units (RTUs)
3 SCADA Software 3.1 SCADA communication architectures 3.1.1 SCADA system A supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system means a system consisting of a number of remote terminal units (RTUs)
Controllers Address, Phone No., Fax No. &
 Controllers Address, Phone No., Fax No. & Email S.No. Address, Phone No., Fax No., E-mail 1. Controller, Legal Metrology Department, Door.No: 48-8-12 & 12A, Boddupativari Street, Near ESI Hospital, Gunadala,
Controllers Address, Phone No., Fax No. & Email S.No. Address, Phone No., Fax No., E-mail 1. Controller, Legal Metrology Department, Door.No: 48-8-12 & 12A, Boddupativari Street, Near ESI Hospital, Gunadala,
POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL. CONTROL CENTRE OPERATION OF POWER SYSTEMS Syllabus : Topics to be studied
 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL CONTROL CENTRE OPERATION OF POWER SYSTEMS Syllabus : Introduction to SCADA, control centre, digital computer configuration, automatic generation control, area control
POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL CONTROL CENTRE OPERATION OF POWER SYSTEMS Syllabus : Introduction to SCADA, control centre, digital computer configuration, automatic generation control, area control
Road Map to Grid Modernization
 Road Map to Grid Modernization APIC, University of Alberta May 5 th, 2016 Presenter: Chris Chapelsky, MSc., P.Eng. Operations 1 Engineer About EPCOR Water & Power Transmission & Distribution in Edmonton
Road Map to Grid Modernization APIC, University of Alberta May 5 th, 2016 Presenter: Chris Chapelsky, MSc., P.Eng. Operations 1 Engineer About EPCOR Water & Power Transmission & Distribution in Edmonton
Highlights of Telecom Subscription Data as on 31 st October, 2018
 For immediate release (Press Release No. 01/2019) Information Note to the Press TELECOM REGULATORY AUTHORITY OF INDIA New Delhi, 2 nd January, 2019 (www.trai.gov.in) 20 Glorious Years (1997-2017) Highlights
For immediate release (Press Release No. 01/2019) Information Note to the Press TELECOM REGULATORY AUTHORITY OF INDIA New Delhi, 2 nd January, 2019 (www.trai.gov.in) 20 Glorious Years (1997-2017) Highlights
Chapter 2 Communication for Control in Heterogeneous Power Supply
 Chapter 2 Communication for Control in Heterogeneous Power Supply The need to modernize the power grid infrastructure, and governments commitment for a cleaner environment, is driving the move towards
Chapter 2 Communication for Control in Heterogeneous Power Supply The need to modernize the power grid infrastructure, and governments commitment for a cleaner environment, is driving the move towards
Mother and Child Tracking System. Achievements and Challenges
 Mother and Child Tracking System Achievements and Challenges 17 th November 2011 MCTS- A Path Breaking Initiative MCTS was launched in December 2009 A comprehensive system for improving delivery of health
Mother and Child Tracking System Achievements and Challenges 17 th November 2011 MCTS- A Path Breaking Initiative MCTS was launched in December 2009 A comprehensive system for improving delivery of health
3/2/ /2/ :05 AM EET 415/4 Power System Operation 1 3/2/ :05 AM EET 415 2
 Communication in Power System II 3/2/2009 11:05 AM EET 415/4 Power System Operation 1 Communication In Power System II CONTENTS SCADA Definition SCADA Evolution Basic SCADA System Architecture Typical
Communication in Power System II 3/2/2009 11:05 AM EET 415/4 Power System Operation 1 Communication In Power System II CONTENTS SCADA Definition SCADA Evolution Basic SCADA System Architecture Typical
HIGH LEVEL REQUIREMENTS OF FAST SIMULATION AND MODELLING SUITE OF TOOLS FOR FUTURE SELF-HEALING DISTRIBUTION POWER SYSTEM
 HIGH LEVEL REQUIREMENTS OF FAST SIMULATION AND MODELLING SUITE OF TOOLS FOR FUTURE SELF-HEALING DISTRIBUTION POWER SYSTEM A. Valenti* I Bel ** S. Lee *EDF **EPRI E2I ConEdison France USA USA arnaud.valenti@edf.fr
HIGH LEVEL REQUIREMENTS OF FAST SIMULATION AND MODELLING SUITE OF TOOLS FOR FUTURE SELF-HEALING DISTRIBUTION POWER SYSTEM A. Valenti* I Bel ** S. Lee *EDF **EPRI E2I ConEdison France USA USA arnaud.valenti@edf.fr
What is SCADA? What is Telemetry? What is Data Acquisition? Differences between SCADA and DCS? Components of SCADA. Field Instrumentation
 SCADA Primer This document discusses the basics of SCADA systems. It serves as introduction for those who are not familiar with it, and as a reviewer for those who are already knowledgeable about the SCADA
SCADA Primer This document discusses the basics of SCADA systems. It serves as introduction for those who are not familiar with it, and as a reviewer for those who are already knowledgeable about the SCADA
Designing a new IEC substation architecture
 Designing a new IEC 61850 substation architecture Gerrit Dogger Senior Product and Application Specialist Cooper Power Systems gerrit.dogger@cybectec.com Garry Tennese Station Integration Specialist Manitoba
Designing a new IEC 61850 substation architecture Gerrit Dogger Senior Product and Application Specialist Cooper Power Systems gerrit.dogger@cybectec.com Garry Tennese Station Integration Specialist Manitoba
JSONRecharge API Document
 JSONRecharge API Document URL : http://domainname/recharge/jsonrechargeapi.asmx Method Name : Recharge Url : http:// DomainName /ReCharge/JsonRechargeApi.asmx?op=Recharge Parameters: Source = (API) For
JSONRecharge API Document URL : http://domainname/recharge/jsonrechargeapi.asmx Method Name : Recharge Url : http:// DomainName /ReCharge/JsonRechargeApi.asmx?op=Recharge Parameters: Source = (API) For
INTERCONNECTION FACILITIES STUDY REPORT
 Interconnection Request No. TI-08-0312 INTERCONNECTION FACILITIES STUDY REPORT Prepared by Tri-State Generation and Transmission Association, Inc. 1 of 7 DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES AND LIMITATION OF LIABILITIES
Interconnection Request No. TI-08-0312 INTERCONNECTION FACILITIES STUDY REPORT Prepared by Tri-State Generation and Transmission Association, Inc. 1 of 7 DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTIES AND LIMITATION OF LIABILITIES
Meeting the Demands of Power Hungry China through a Real-time Data Driven Enterprise Platform
 Meeting the Demands of Power Hungry China through a Real-time Data Driven Enterprise Platform Place your company logo in this area. Then delete this text box FibrLINK Dr. Jun Zha EMS Users Conference San
Meeting the Demands of Power Hungry China through a Real-time Data Driven Enterprise Platform Place your company logo in this area. Then delete this text box FibrLINK Dr. Jun Zha EMS Users Conference San
Solutions for transmission network management
 EM SG SOLutions Solutions for transmission network management Energy Management Smart Grid Solutions Solutions for Transmission Network Management Overview Operator Training Simulator Blackout Prevention
EM SG SOLutions Solutions for transmission network management Energy Management Smart Grid Solutions Solutions for Transmission Network Management Overview Operator Training Simulator Blackout Prevention
Exercise 2. Single Bus Scheme EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE. The single bus scheme DISCUSSION
 Exercise 2 Single Bus Scheme EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with electric power substations using the single bus scheme with bus section circuit breakers.
Exercise 2 Single Bus Scheme EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with electric power substations using the single bus scheme with bus section circuit breakers.
Installation and Operation Back-UPS BR1000G-IN / BR1500G-IN
 Installation and Operation Back-UPS BR1000G-IN / BR1500G-IN Important Safety Information Read the instructions carefully to become familiar with the equipment before trying to install, operate, service
Installation and Operation Back-UPS BR1000G-IN / BR1500G-IN Important Safety Information Read the instructions carefully to become familiar with the equipment before trying to install, operate, service
Deploying Digital Substations: Experience with a Digital Substation Pilot in North America. Harsh Vardhan, R Ramlachan GE Grid Solutions, USA
 Deploying Digital Substations: Experience with a Digital Substation Pilot in North America Harsh Vardhan, R Ramlachan GE Grid Solutions, USA Wojciech Szela, Edward Gdowik PECO, USA SUMMARY Though IEC 61850
Deploying Digital Substations: Experience with a Digital Substation Pilot in North America Harsh Vardhan, R Ramlachan GE Grid Solutions, USA Wojciech Szela, Edward Gdowik PECO, USA SUMMARY Though IEC 61850
Interconnection Feasibility Study Report GIP-IR377-FEAS-R1
 Interconnection Feasibility Study Report GIP-IR377-FEAS-R1 Generator Interconnection Request 377 40 MW Wind Generating Facility Renfrew, NS Mar. 6, 2012 Control Centre Operations Nova Scotia Power Inc.
Interconnection Feasibility Study Report GIP-IR377-FEAS-R1 Generator Interconnection Request 377 40 MW Wind Generating Facility Renfrew, NS Mar. 6, 2012 Control Centre Operations Nova Scotia Power Inc.
Revised Generation Interconnection Impact Study Report. For. Queue Position 31 ( Interconnection Customer )
 Revised Generation Interconnection Impact Study Report For Queue Position 31 ( Interconnection Customer ) September 22, 2004 1 Generation Interconnection System Impact Study Report I. Revision of Original
Revised Generation Interconnection Impact Study Report For Queue Position 31 ( Interconnection Customer ) September 22, 2004 1 Generation Interconnection System Impact Study Report I. Revision of Original
SEL Real-Time Automation Controller (RTAC)
 SEL Real-Time Automation Controller (RTAC) Product Family Rugged, deterministic, and reliable automation controllers for any environment 1 ms deterministic processing intervals support critical protection
SEL Real-Time Automation Controller (RTAC) Product Family Rugged, deterministic, and reliable automation controllers for any environment 1 ms deterministic processing intervals support critical protection
Concept of Automation in Management of Electric Power Systems Richard Joseph, Nerey Mvungi
 Concept of Automation in Management of Electric Power Systems Richard Joseph, Nerey Mvungi Abstract An electric power system includes a generating, a transmission, a distribution, and consumers subsystems.
Concept of Automation in Management of Electric Power Systems Richard Joseph, Nerey Mvungi Abstract An electric power system includes a generating, a transmission, a distribution, and consumers subsystems.
OC IEEE IAS/PES Meeting February 21, 2013
 San Diego International Airport: Building For The Future, Through Underground Distribution Automation and SCADA OC IEEE IAS/PES Meeting February 21, 2013 1 Presenter: Randy Denton, PE Under Ground Utility
San Diego International Airport: Building For The Future, Through Underground Distribution Automation and SCADA OC IEEE IAS/PES Meeting February 21, 2013 1 Presenter: Randy Denton, PE Under Ground Utility
Auto-Check Circuit Breaker Interrupting Capabilities
 Auto-Check Circuit Breaker Interrupting Capabilities Thanh C. Nguyen and Sherman Chan ASPEN, Inc. Ron Bailey and Thanh Nguyen Dominion Virginia Power Paper published in IEEE Computer Applications in Power,
Auto-Check Circuit Breaker Interrupting Capabilities Thanh C. Nguyen and Sherman Chan ASPEN, Inc. Ron Bailey and Thanh Nguyen Dominion Virginia Power Paper published in IEEE Computer Applications in Power,
SCADA and Systems Monitoring
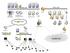 SCADA and Systems Monitoring SCADA stands for supervisory control and data acquisition system. There are locations, in most of the power systems, where operations, such as opening and closing circuit breakers,
SCADA and Systems Monitoring SCADA stands for supervisory control and data acquisition system. There are locations, in most of the power systems, where operations, such as opening and closing circuit breakers,
Secure energy supply Energy Automation for Infrastructure and Functional Buildings
 Secure energy supply Energy Automation for Infrastructure and Functional Buildings Power Transmission and Distribution Imagine the finals of the Soccer World Cup, with the score at 0:0 after overtime.
Secure energy supply Energy Automation for Infrastructure and Functional Buildings Power Transmission and Distribution Imagine the finals of the Soccer World Cup, with the score at 0:0 after overtime.
Digital Transformation of Power Delivery
 Digital Transformation of Power Delivery Keynote Speech Professor Saifur Rahman, PhD Virginia Tech, USA IEEMA Engineer Infinite Conference, Delhi NCR, India, 14 March 2018 Traditional Electricity Delivery
Digital Transformation of Power Delivery Keynote Speech Professor Saifur Rahman, PhD Virginia Tech, USA IEEMA Engineer Infinite Conference, Delhi NCR, India, 14 March 2018 Traditional Electricity Delivery
ABB static var compensator stabilizes Namibian grid voltage
 Power ABB static var compensator stabilizes Namibian grid voltage factor! Rolf Grünbaum, Mikael Halonen, Staffan Rudin The spectacular dune landscapes of Namibia are a key factor in the country s booming
Power ABB static var compensator stabilizes Namibian grid voltage factor! Rolf Grünbaum, Mikael Halonen, Staffan Rudin The spectacular dune landscapes of Namibia are a key factor in the country s booming
Indian Power Grid Developments
 Indian Power Grid Developments Rathin Basu Country President, Alstom Grid, March 25 th 2015 Evolution of Voltage level of Indian Grid kv Anticipated the evolution & Timely Investment in Indian Facilities
Indian Power Grid Developments Rathin Basu Country President, Alstom Grid, March 25 th 2015 Evolution of Voltage level of Indian Grid kv Anticipated the evolution & Timely Investment in Indian Facilities
Lessons Learned Implementing an IEC based Microgrid Power- Management System. K.A. GRAY, J.J. MRAZ* POWER Engineers, Inc.
 21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2015 Grid of the Future Symposium Lessons Learned Implementing an IEC 61850-based Microgrid Power- Management System K.A.
21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2015 Grid of the Future Symposium Lessons Learned Implementing an IEC 61850-based Microgrid Power- Management System K.A.
Generation Interconnection Impact Study Report. For. Interconnection Customer Q0022
 Generation Interconnection Impact Study Report For Interconnection Customer Q0022 Prepared by: PacifiCorp Date: 10/29/2003 Generation Interconnection System Impact Study Report Interconnection Customer
Generation Interconnection Impact Study Report For Interconnection Customer Q0022 Prepared by: PacifiCorp Date: 10/29/2003 Generation Interconnection System Impact Study Report Interconnection Customer
Power Transmission and Distribution. I m on guard here! SIMEAS R reports power system weaknesses quickly and accurately
 Power Transmission and Distribution I m on guard here! SIMEAS R reports power system weaknesses quickly and accurately SIMEAS R the watchdog in your power system Competition among Power Suppliers is increasing.
Power Transmission and Distribution I m on guard here! SIMEAS R reports power system weaknesses quickly and accurately SIMEAS R the watchdog in your power system Competition among Power Suppliers is increasing.
EMS / DMS. DISTRIBUTION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM- Functional Description
 EMS / DMS DISTRIBUTION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM- Content 1. INTRODUCTION... 4 2. MODES OF INTERACTION WITH THE SCADA SYSTEM... 5 2.1 Simulation Mode... 5 2.2 State Estimation Mode (See functional description
EMS / DMS DISTRIBUTION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM- Content 1. INTRODUCTION... 4 2. MODES OF INTERACTION WITH THE SCADA SYSTEM... 5 2.1 Simulation Mode... 5 2.2 State Estimation Mode (See functional description
INDUSTRIAL CONTROL SYSTEMS & COMPUTER PROCESS CONTROL
 1 INDUSTRIAL CONTROL SYSTEMS & COMPUTER PROCESS CONTROL INDUSTRIAL CONTROL - DEFINED The automatic regulation of unit operations and their associated equipment as well as the integration and coordination
1 INDUSTRIAL CONTROL SYSTEMS & COMPUTER PROCESS CONTROL INDUSTRIAL CONTROL - DEFINED The automatic regulation of unit operations and their associated equipment as well as the integration and coordination
CHAPTER 11 HOW TO ENHANCE THE RELIABILITY & POWER QUALITY OF ELECTRICITY SUPPLY
 CHAPTER 11 HOW TO ENHANCE THE RELIABILITY & POWER QUALITY OF ELECTRICITY SUPPLY CHAPTER 11 HOW TO ENHANCE THE RELIABILITY & POWER QUALITY OF ELECTRICITY SUPPLY 11.1 Introduction 1. HK Electric provides
CHAPTER 11 HOW TO ENHANCE THE RELIABILITY & POWER QUALITY OF ELECTRICITY SUPPLY CHAPTER 11 HOW TO ENHANCE THE RELIABILITY & POWER QUALITY OF ELECTRICITY SUPPLY 11.1 Introduction 1. HK Electric provides
SCADA Solutions for Water and Wastewater Treatment Plants
 SCADA Solutions for Water and Wastewater Treatment Plants Features Centralized control Increased reliability Improved management of treatment processes Reduced costs Preserved equipment investments Flexible
SCADA Solutions for Water and Wastewater Treatment Plants Features Centralized control Increased reliability Improved management of treatment processes Reduced costs Preserved equipment investments Flexible
DIMINISHING THE REQUIREMENT OF POWER USING PLC AND SCADA SYSTEMS IN POWER GRID SYSTEM
 DIMINISHING THE REQUIREMENT OF POWER USING PLC AND SCADA SYSTEMS IN POWER GRID SYSTEM Mr. T. Vignesh Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, Jay Shriram Group of Institutions, Tirupur, Tamilnadu, India
DIMINISHING THE REQUIREMENT OF POWER USING PLC AND SCADA SYSTEMS IN POWER GRID SYSTEM Mr. T. Vignesh Assistant Professor, Department of EEE, Jay Shriram Group of Institutions, Tirupur, Tamilnadu, India
Glencoe Light and Power
 Glencoe Light and Power REQUIREMENTS FOR GENERATION, TRANSMISSION, AND END-USER FACILITY INTERCONNECTIONS 1 Table of Contents Page I. INTRODUCTION...5 A. Authority... 5 B. Objectives...5 C. Interconnection
Glencoe Light and Power REQUIREMENTS FOR GENERATION, TRANSMISSION, AND END-USER FACILITY INTERCONNECTIONS 1 Table of Contents Page I. INTRODUCTION...5 A. Authority... 5 B. Objectives...5 C. Interconnection
Synchronous switching of distribution sub networks
 Synchronous switching of distribution sub networks Paul Stergiou ConEdison USA Manuel P Pimenta, - ConEdison USA Sergio A Rodriguez ConEdison USA Thomas Horan ConEdison USA Andre Smit- Siemens Industry
Synchronous switching of distribution sub networks Paul Stergiou ConEdison USA Manuel P Pimenta, - ConEdison USA Sergio A Rodriguez ConEdison USA Thomas Horan ConEdison USA Andre Smit- Siemens Industry
Specification Voltage Limiting Device
 Engineering Specification Electrical Networks L1-CHE-SPE-152 Specification Voltage Limiting Device Version: 1 Issued: 20 th April 2018 Owner: Chief Engineer Approved By: Andrew Russack Head of Engineering,
Engineering Specification Electrical Networks L1-CHE-SPE-152 Specification Voltage Limiting Device Version: 1 Issued: 20 th April 2018 Owner: Chief Engineer Approved By: Andrew Russack Head of Engineering,
Installation and Operation Back-UPS Pro 900
 Us er Documentation Installation and Operation Back-UPS Pro 900 Inventory bu001a User Documentation (2) Safety and General Information Inspect the package contents upon receipt. Notify the carrier and
Us er Documentation Installation and Operation Back-UPS Pro 900 Inventory bu001a User Documentation (2) Safety and General Information Inspect the package contents upon receipt. Notify the carrier and
Blackout 101. Dr. B. Don Russell Texas A&M University. Dr. Bruce Wollenberg University of Minnesota. Mr. John McDonald KEMA, Inc.
 Blackout 101 Dr. B. Don Russell Texas A&M University Dr. Bruce Wollenberg University of Minnesota Mr. John McDonald KEMA, Inc. Dr. Pete Sauer University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign An Electric Power
Blackout 101 Dr. B. Don Russell Texas A&M University Dr. Bruce Wollenberg University of Minnesota Mr. John McDonald KEMA, Inc. Dr. Pete Sauer University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign An Electric Power
GRAS Education and Training Services Pvt. Limited ( GRAS Academy ) In Partnership with National Skills Development Corporation (NSDC)
 GRAS Education and Training Services Pvt. Limited ( GRAS Academy ) In Partnership with National Skills Development Corporation (NSDC) Company Overview GRAS Academy ( GRAS ) is engaged in providing vocational
GRAS Education and Training Services Pvt. Limited ( GRAS Academy ) In Partnership with National Skills Development Corporation (NSDC) Company Overview GRAS Academy ( GRAS ) is engaged in providing vocational
UNITROL 5000 Excitation Systems for Medium and Large Synchronous Machines
 UNITROL 5000 Excitation Systems for Medium and Large Synchronous Machines Copyright 2000 Photodisc, Inc. 275 371 UNITROL 5000 System Overview The UNITROL 5000 is the most powerful product in the Switzerland
UNITROL 5000 Excitation Systems for Medium and Large Synchronous Machines Copyright 2000 Photodisc, Inc. 275 371 UNITROL 5000 System Overview The UNITROL 5000 is the most powerful product in the Switzerland
