a (12) United States Patent CONTROL CONTROLS US 6,356,500 B1 POWER 102 Mar. 12, 2002 (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 22 e a 110 SA10 SA9
|
|
|
- Kelley Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
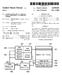
1 (12) United States Patent Cloud et al. USOO63565OOB1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,356,500 B1 Mar. 12, 2002 (54) REDUCED POWER DRAM DEVICE AND METHOD (75) Inventors: Eugene H. Cloud, Boise, ID (US); Kie Y. Ahn, Chappaqua, NY (US); Leonard Forbes; Paul A. Farrar, both of Corvallis, OR (US); Kevin G. Donohoe, Boise, ID (US); Alan R. Reinberg, Westport, CT (US); David J. Mcelroy, Livingston, TX (US); Luan C. Tran, Meridian, ID (US); Joseph Geusic, Berkeley Heights, NJ (US) (73) Assignee: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID (US) (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. (21) Appl. No.: 09/643,945 (22) Filed: Aug. 23, 2000 (51) Int. Cl.... G11C 7700 (52) U.S. Cl /226; 365/230.01; 365/240 (58) Field of Search /226, 229, 365/230.01, 236, 240 (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 5,493,574. A * 2/1996 McKinley /40.1 5,825,691 A * 10/1998 McClure / ,184,067 B1 * 2/2001 Casper /123 * cited by examiner Primary Examiner David Nelms Assistant Examiner Thong Le (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Dickstein Shapiro Morin & Oshinsky LLP (57) ABSTRACT A memory device and method employing a Scheme for reduced power consumption is disclosed. By dividing a memory array Sector into memory Sub arrays, the memory device can provide power to memory Sub arrays that need to be powered up or, in the alternative, powered down. This reduces the power consumption and heat generation asso ciated with high Speed and high capacity memory devices. 39 Claims, 9 Drawing Sheets MEMORY CONTROLLER POWER 102 SUPPLY CONTROLS DRAM CONTROL 132 POWER DISTRIBUTION TERMINAL 22 e a 110 a SA9 SA10 SA11 SA12 SA13 SA14 SA15 SA16 118
2 U.S. Patent Mar. 12, 2002 Sheet 1 of 9 US 6,356,500 B1 100 POWER SUPPLY DRAM oram confrol POWER DISTRIBUTION TERMINAL CONTROLS LOGIC ADDRESS É s 110 SA13 SA14 SA15 SA FIG. 1
3 U.S. Patent Mar. 12, 2002 Sheet 2 of 9 US 6,356,500 B1 SIVS WIWS 8I ÅRIOWAHWN \{FITTORILNOO zd on
4 U.S. Patent Mar. 12, Sheet 3 of 9 US 6,356,500 B1 300 EXTERNAL MEMORY CONTROLLER SENDS (i) A MEMORY COMMAND AND (ii) RANGE OF ADDRESSES THAT ARENOTCURRENTLYNEEDED TO EXECUTE THAT COMMAND. 302 ADDRESS REGISTER RECEIVESRANGE OF ADDRESSES AND PASSES THEMTO INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC. 304 INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC RECEIVES THE MEMORY COMMAND FROM THE EXTERNAL MEMORY CONTROLLER AND RANGE OF ADDRESSES FROM THE ADDRESS REGISTER 306 INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC MAPSRANGE OF ADDRESSESTO INTERNAL MEMORY SUBARRAYS. MULTI-TASKING N. INTERNALDRAM CONTROL LOGIC CHECKS IF ANY OTHER MEMORY OPERATIONS ARE USING ADDRESSES CONTAINED IN THE INTERNAL MEMORY SUB-ARRAYS CONTINUING UNNEEDED ADDRESSES. 308 INTERNALDRAM CONTROL LOGIC DIRECTS POWER DISTRIBUTION BUS TO POWER DOWN THE INTERNAL MEMORY SUBARRAYS WHICHARE NOT NEEDED. 310 INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC DISCONTINUES REFRESH COMMAND TO POWERED DOWN MEMORY SUBARRAYS. FIG. 3a
5 U.S. Patent Mar. 12, 2002 Sheet 4 of 9 US 6,356,500 B1 88A0OA88A00A Q9. "OIH
6 U.S. Patent Mar. 12, 2002 Sheet 5 of 9 US 6,356,500 B1 400 INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC SETS ALL SUBARRAYS TO APOWERED DOWN STATE. 402 SYSTEM SENDSA MEMORY COMMAND TO THE EXTERNAL MEMORY CONTROLLER. EXTERNAL MEMORY CONTROLLER SENDS (i) MEMORY COMMAND(i) 404 RANGE OF ADDRESSES THAT ARE NEEDED BY THE MEMORY COMMAND TOEXECUTE THE MEMORY COMMAND. 406 ADDRESS REGISTER RECEIVES RANGE OF ADDRESSES AND PASSES THEM TO INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC, 408 INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC RECEIVES THE MEMORY COMMAND FROM THE EXTERNAL MEMORY CONTROLLER AND RANGE OF ADDRESSES FROM THE ADDRESS REGISTER. 410 INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC MAPS RANGE OF ADDRESSESTO INTERNAL MEMORY SUBARRAYS. INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC INTERNALDRAM CONTROL 412 DIRECTS POWER DISTRIBUTION BUS LOGICBEGINS SENDING TO POWER UPTHE INTERNAL REFRESH COMMAND TO MEMORY SUBARRAYS WHICHARE POWERED UP MEMORY NEEDED. SUBARRAYS. FIG. 4
7 U.S. Patent Mar. 12, Sheet 6 of 9 US 6,356,500 B1 EXTERNAL MEMORY CONTROLLER 500 SENDSA MEMORY COMMAND AND (ii)range OF ADDRESSES THAT ARE NEEDED TOEXECUTE THE MEMORY COMMAND. ADDRESS REGISTER RECEIVESRANGE OF ADDRESSES AND PASSES THEMTO INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC. INTERNALDRAMCONTROLLOGIC RECEIVES THE MEMORY COMMAND FROM THE EXTERNAL MEMORY CONTROLLER AND RANGE OF ADDRESSES FROM THE ADDRESS REGISTER. INTERNALDRAM CONTROLLOGIC MAPSRANGE OF ADDRESSESTO INTERNAL MEMORY SUBARRAYS. INTERNALDRAM CONTROL LOGIC UPDATES THE "WARIABLE 510 PERSISTENCE"TABLE, INTERNALDRAM CONTROL INTERNALDRAM CONTROL LOGIC LOGICWRITES DATAIN DIRECTSPOWER DISTRIBUTION BUS THE SUBARRAYS WHICH 512 TO POWER DOWN THE INTERNAL HAVE REACHED POWER DOWN MEMORY SUBARRAYS WHICH HAVE STATEACCORDING TO THE REACHED POWER DOWN STATE "WARIABLE PERSISTENCE" ACCORDING TO THE "WARIABLE TABLE TO ANON-VOLATILE PERSISTENCE"TABLE. STORAGE DEVICE. 514 INTERNALDRAMCONTROLLOGIC DISCONTINUES REFRESH COMMAND TO POWERED DOWN SUBARRAYS. FIG. 5a
8 U.S. Patent Mar. 12, Sheet 7 of 9 US 6,356,500 B1 SUB ARRAY COUNTER INPUT OUTPUT O e FIG. 5b
9 U.S. Patent Mar. 12, Sheet 8 of 9 US 6,356,500 B1 600 I/O 602 CPU ( ) DEVICE I/O 610 DEVICE 606 CD ROM DRIVE 620 FIG. 6
10 U.S. Patent Mar. 12, Sheet 9 of 9 US 6,356,500 B1 s O
11 1 REDUCED POWER DRAM DEVICE AND METHOD BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION I. Field of the Invention The present invention relates generally to dynamic ran dom access memory (DRAM). More specifically, the present invention relates to an improved memory device, which permits increased memory size with reduced power require ments. II. Description of the Related Art Improved manufacturing techniques are constantly being developed to increase the memory capacity of DRAM. These techniques have increased the possible number of transistors and other components on a single Silicon chip. However, with increased capacity, the need for reduced power requirements Still exists. This is most readily apparent in mobile devices which utilize memory, e.g., laptop computers, cellular telephones, etc. New DRAM device bus architectures have also increased the speed of DRAM access. However, this increased speed results in greater power consumption and heat generation, which may cause overheating problems. For example, a Rambus DRAM SIMM (single in-line memory module) typically contains a heat Sink as an effort to address the overheating problem. Therefore, a DRAM architecture that reduces power consumption would also help alleviate over heating associated with these new faster DRAM devices. Accordingly, there is a need for a memory device having increased memory size, yet reduced power consumption. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention provides a device and method that permits the use of modern techniques to increase DRAM memory size while reducing power consumption. The present invention utilizes the internal memory Sub array partitioning of a DRAM device and provides the capability of independently powering down each internal memory Sub array thereby reducing power consumption when memory Sub arrays are not being used for a period of time. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The foregoing and other advantages and features of the invention will become more apparent from the detailed description of preferred embodiments of the invention which are provided below with reference to the accompanying drawings in which: FIG. 1 is a diagram of a DRAM device employing memory Sub arrays in accordance with the present invention; FIG. 2 is a diagram of a DRAM device employing memory Sub arrays which uses an external memory control ler in accordance with the present invention; FIG.3(a) is a flow chart of a method for reducing power consumption of the DRAM device of FIG. 2 by powering down unneeded addresses; FIG.3(b) illustrates a cross sectional view of the substrate upon which the DRAM device resides; FIG. 4 is a flow chart of a method for reducing power consumption of the DRAM device of FIG. 2 by activating needed addresses; FIG. 5(a) is a flow chart of a method for reducing power consumption of the DRAM device of FIG. 2 by using a variable persistence technique; FIG. 5(b) is an illustration of a table used to employ the variable persistence technique of FIG. 5(a); US 6,356,500 B1 1O FIG. 6 is an illustration of a processor-based system employing the reduced power consumption device and method of the present invention; and FIG. 7 is an illustration of a memory module employing the reduced power consumption device and method of the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Referring now to the drawings, where like reference numerals designate like elements, there is shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 a relevant portion of a memory device 100 for providing and Storing data for data driven devices, e.g., computers, cellular telephones, etc. Memory device 100 includes a power Supply 102, an internal DRAM control logic 104, address register 106, power distribution terminal 108 and a plurality of memory array sectors 110. Each memory array Sector 110 contains of a plurality of memory Sub arrays 118. Memory device 100 may command the memory array sectors 110 itself, as in FIG. 1, or receive memory commands and corresponding memory addresses from an external memory controller 112, as depicted in FIG. 2. FIG.3(a) illustrates in a first exemplary embodiment of the operation of the memory devices 100 shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 with particular reference to the external memory controller embodiment in FIG. 2. The external memory controller 112 sends a memory command at step 300 to internal DRAM control logic 104 via data control bus 114. A memory command can be a WRITE, READ, etc. Simul taneously with Sending the memory command, the external memory controller 112 also sends a range of unneeded addresses for the memory command over address bus 116 to the address register 106 at step 300. The address register 106 Simply provides an interface for address information. The address register 106 passes the range of unneeded addresses at step 302 to internal DRAM control logic 104 in the form of data which identifies the range of addresses which require power for execution of the memory command. Given the range of unneeded addresses at Step 302, the remaining memory Sub arrays 118 are those which are needed for the memory command. The internal DRAM control logic 104 receives and maps (translates) the data indicating the address range(s) of the needed addresses at operational steps 304 and 306. The internal DRAM control logic 104 maps the needed addresses to memory Sub arrays 118 which contain the needed addresses. That is, those Sub arrays 118 which are needed for the memory operation are identified. The internal DRAM control logic 104, having translated which addresses in the range of addresses correspond to needed memory Sub arrays 118 at step 306, sends control signals, via control signal bus 130, to the power distribution terminal 108 at step 308. The control signals instruct the power distribution terminal 108 to power down all sub arrays 118 not desig nated as needed by the memory command. For purpose of this disclosure, power, which is distributed by the power distribution terminal 108, includes both a source positive voltage (Vcc) and a negative voltage (Vbb). Both Vcc and Vbb are partitioned for each memory Sub array 118. It is necessary to partition Vcc and Vbb to isolate each memory Sub array 118 on the n-rail and p-rail of the substrate on which the memory device 100 resides, respectively. FIG. 3(b) shows a cross sectional view of a substrate upon which the memory device 100 resides including Vcc terminals 380, 384 and Vbb terminals 382,386. When power distribution terminal 108 powers down a memory sub-array 118, both a Vcc terminal and a Vbb terminal, for the corresponding memory sub-array 118, are grounded (0 volts).
12 3 This is one way in which power consumption is reduced. In addition, the internal DRAM control logic 104 discon tinues sending a REFRESH command, which is normally sent via REFRESH bus 132, to the unneeded memory Sub arrays 118, that is, the memory Sub arrays 118 which are not designated as needed for the memory operation at Step 310. In this way overall memory System power consumption is reduced. For Simplicity of explanation, it has been assumed that the memory device 100 is operating in a single tasking envi ronment. In a multi-tasking environment the internal DRAM control logic 104 would check if any other memory com mands are using the unneeded memory Sub arrays 118 before powering them down. The internal DRAM control logic 104 could complete such a task with a simple truth table which is updated on each clock cycle indicating if a memory Sub array 118 is being used by a memory command initiated in a previous clock cycle. In another operational embodiment, depicted in FIG.4, all memory sub arrays 118 are initially powered off as a default condition by the internal DRAM control logic 104 at step 400. At this step the power distribution terminal 108 is instructed, through a control Signal Sent via control Signal bus 130, to cease Supplying power to all memory Sub arrays 118. In addition, as a consequence of all memory Sub arrays 118 not being supplied power, the internal DRAM control logic 104 does not send the REFRESH command, which is normally sent via REFRESH bus 132, to any memory Sub arrays 118. When a memory function is needed, the external memory controller 112 Sends a memory command, which effectuates the desired memory function, on data control bus 114 at step 404. Simultaneously with sending the memory command, the external memory controller 112 also sends a range of addresses needed for the memory command over address bus 116 to the address register 106 at step 404. The address register 106 Simply provides an interface for address information. The address register 106 receives and passes the range of needed addresses to internal DRAM control logic 104 at step 406 in the form of data which identifies the range of addresses which require power for execution of the memory command. After receiving the memory command and data identifying the range of needed addresses in Step 408, the internal DRAM control logic 104 maps (translates) the address range of the needed addresses to memory Sub arrays 118 which contain the needed addresses in step 410. That is, those Sub arrays 118 which are needed for the memory operation are identified. The internal DRAM con trol logic 104, having translated which addresses in the range of addresses correspond to needed memory Sub arrays 118, sends control signals to the power distribution terminal 108 at step 412. The control signals instruct the power distribution terminal 108 to power up the memory Sub arrays 118 needed for the memory command at step 412. In addition, the internal DRAM control logic 104 begins send ing the REFRESH command only for the needed memory Sub arrays 118 at step 414. FIG. 5(a) illustrates yet another exemplary embodiment of operation which employs a variable persistence' tech nique. When a memory function is needed the external memory controller 112 Sends a memory command, which effectuates the desired memory function, on data control bus 114 at step 500. Simultaneously with sending the memory command, the external memory controller 112 also sends a range of addresses needed for the memory command over address bus 116 to the address register 106 at step 500. The address register 106 Simply provides an interface for address information. The address register 106 receives and passes US 6,356,500 B the range of needed addresses to internal DRAM control logic 104 at step 502 in the form of data which identifies the range of addresses which require power for execution of the memory command. After receiving the memory command and data identifying the range of needed addresses in Step 504, the internal DRAM control logic 104 maps (translates) the address range of the needed addresses to memory Sub arrays 118 which contain the needed addresses in step 506. That is, those Sub arrays 118 which are needed for the memory operation are identified. The internal DRAM con trol logic 104, having translated which addresses in the range of addresses correspond to needed memory Sub arrays 118, under this variable persistence' technique, updates a variable persistence table at step 508. The variable per sistence table, shown in FIG. 5(b), is maintained by the internal DRAM control logic 104. The table includes a counter for each memory Sub array 118, which corresponds to a memory address range, indicating the number of memory clock cycles which have passed since each memory Sub array 118 was last accessed, e.g. to perform a READ, WRITE operation, etc. When the counter for a memory sub array 118 reaches a predetermined memory clock cycle number, e.g., 1000, then the memory Sub array 118 in question will be powered down Since it is not being used at step 512. The predetermined number can be, for example, the number of clock cycles equivalent to one minute, where one could fairly assume a memory Sub array 118 is not going to be used in the immediate future if it has been idle for one minute. Prior to instructing the power distribution terminal 108 to power down those memory Sub arrays 118 which have exceeded the allowable time on the counter and dis continuing the REFRESH function at steps 512 and 514, the internal DRAM control logic 104 will cause the data from those memory Sub arrays 118 to be written back to a non-volatile Storage device, e.g. hard drive at Step 510. In the alternative, the internal DRAM control logic 104 can power those memory sub array 118 to less than full power and maintain its REFRESH function. While the later technique does not conserve as much power as the previous technique, it allows for a quicker response time as data may not need to be written and then re-retrieved from a non-volatile Storage device, which is typically slower then a volatile memory device such as memory device 100. FIG. 6 illustrates a processor system 600, including memory device 612 constructed in accordance with the present invention as described above with reference to FIGS The processor system 600 may be a computer system, a process control System or any other System employing a processor and associated memory devices. The processor System includes a central processing unit (CPU) 602, e.g., microprocessor, that communicates with input/output devices 608, 610, floppy drive 604, memory device 614 and CD ROM drive 606 over a bus 620. The CPU 602 and memory device 612 may be provided on a single integrated circuit chip. FIG. 7 shows a memory module 700 having memory chips with semiconductor memory devices con Structed in accordance with the present invention as described above with reference to FIGS Memory module 700 is a SIMM (single in line memory module) having nine memory chips (ICs) aligned on one side of a printed circuit board substrate. Memory chips employ the reduced power consumption Structure and method of the present invention. It is to be understood that the above description is intended to be illustrative and not restrictive of the inven tion. Many variations to the above-described device and
13 S method including Substitution of equivalent StepS and struc tures will be readily apparent to those having ordinary skill in the art. Accordingly, the present invention is not to be considered as limited by the Specifics of the particular devices and methods, which have been described and illustrated, but is only limited by the Scope of the appended claims. What is claimed as new and desired to be protected by Letters Patent of the United States is: 1. A memory device comprising: a plurality of memory Sub arrays, a power distribution terminal coupled to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays, Said power distribution terminal Selectively providing power to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays, and internal memory control logic coupled to Said power distribution terminal, Said internal memory control logic receiving a memory command and data which identifies a range of addresses required for Said memory command and identifying which ones of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays contain Said addresses within Said range, Said internal memory control logic causing Said power distribution terminal to Supply power only to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays containing Said addresses in Said range. 2. The device of claim 1, wherein Said data contains a range of addresses which are not needed to execute said memory command. 3. The device of claim 1, wherein Said data contains a range of addresses which are needed to execute Said memory command. 4. The device of claims 1, 2 or 3, wherein said internal memory control logic includes a table which comprises a plurality of counters respectively corresponding to said plurality of memory Sub arrays, each of Said plurality of counters indicating a period of time which has elapsed since each corresponding memory Sub array was last accessed, Said internal memory control logic updating Said counters in accordance with Said data, Said internal memory control logic instructing Said power distribution terminal to cease power to a particular memory Sub array where said counter corresponding to Said particular memory Sub array reaches a predetermined value. 5. The device of claim 1 further comprising an external memory controller for Sending Said memory command to Said internal memory control logic. 6. The device of claim 5 further comprising an address register for receiving Said range of addresses from Said external memory controller and Sending Said data which identifies Said range of addresses required for said memory command to Said internal memory control logic. 7. The device of claim 3 further comprising a refresh command bus, wherein Said internal memory control logic Sends a refresh command over Said refresh command bus to Said power distribution terminal for Said plurality of memory Sub arrays containing Said range of addresses. 8. The device of claim 2 further comprising a refresh command bus, wherein Said internal memory control logic disables the transmission of a refresh command over Said refresh command bus to said power distribution terminal for Said plurality of memory Sub arrays containing Said range of addresses. 9. A memory module comprising: at least one memory chip, Said at least one memory chip comprising: a plurality of memory Sub arrays, a power distribution terminal coupled to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays, Said power distribution ter US 6,356,500 B minal Selectively providing power to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays, and internal memory control logic coupled to Said power distribution terminal, Said internal memory control logic receiving a memory command and data which identifies a range of addresses required for Said memory command and identifying which ones of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays contain Said addresses within Said range, Said internal memory control logic causing Said power distribution termi nal to Supply power only to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays containing Said addresses in Said range. 10. The module of claim 9, wherein said data contains a range of addresses which are not needed to execute Said memory command. 11. The module of claim 9, wherein said data contains a range of addresses which are needed to execute Said memory command. 12. The module of claims 9, 10 or 11, wherein said internal memory control logic includes a table which com prises a plurality of counters respectively corresponding to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays, each of Said plurality of counters indicating a period of time which has elapsed since each corresponding memory Sub array was last accessed, Said internal memory control logic updating Said counters in accordance with Said data, Said internal memory control logic instructing Said power distribution terminal to cease power to a particular memory Sub array where Said counter corresponding to Said particular memory Sub array reaches a predetermined value. 13. The module of claim 9 further comprising an external memory controller for Sending Said memory command to Said internal memory control logic. 14. The module of claim 13 further comprising an address register for receiving Said range of addresses from Said external memory controller and Sending Said data which identifies said range of addresses required for Said memory command to Said internal memory control logic. 15. The module of claim 11 further comprising a refresh command bus, wherein Said internal memory control logic Sends a refresh command over Said refresh command bus to Said power distribution terminal for Said plurality of memory Sub arrays containing Said range of addresses. 16. The module of claim 10 further comprising a refresh command bus, wherein Said internal memory control logic disables the transmission of a refresh command over Said refresh command bus to said power distribution terminal for Said plurality of memory Sub arrays containing Said range of addresses. 17. A processor System comprising: a processor, and a memory device coupled to Said processor, Said memory device comprising: a plurality of memory Sub arrays, a power distribution terminal coupled to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays, Said power distribution ter minal Selectively providing power to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays, and internal memory control logic coupled to Said power distribution terminal, Said internal memory control logic receiving a memory command and data which identifies a range of addresses required for Said memory command and identifying which ones of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays contain Said addresses within Said range, Said internal memory control logic causing Said power distribution termi nal to Supply power only to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays containing Said addresses in Said range.
14 7 18. The system of claim 17, wherein said data contains a range of addresses which are not needed to execute said memory command. 19. The system of claim 17, wherein said data contains a range of addresses which are needed to execute Said memory command. 20. The system of claims 17, 18 or 19, wherein said internal memory control logic includes a table which com prises a plurality of counters respectively corresponding to Said plurality of memory Sub arrays, each of Said plurality of counters indicating a period of time which has elapsed since each corresponding memory Sub array was last accessed, Said internal memory control logic updating Said counters in accordance with Said data, Said internal memory control logic instructing Said power distribution terminal to cease power to a particular memory Sub array where said counter corresponding to Said particular memory Sub array reaches a predetermined value. 21. The system of claim 17 further comprising an external memory controller for Sending Said memory command to Said internal memory control logic. 22. The System of claim 21 further comprising an address register for receiving Said range of addresses from Said external memory controller and Sending Said data which identifies Said range of addresses required for said memory command to Said internal memory control logic. 23. The system of claim 19 further comprising a refresh command bus, wherein Said internal memory control logic Sends a refresh command over Said refresh command bus to Said power distribution terminal for Said plurality of memory Sub arrays containing Said range of addresses. 24. The system of claim 18 further comprising a refresh command bus, wherein Said internal memory control logic disables the transmission of a refresh command over Said refresh command bus to said power distribution terminal for Said plurality of memory Sub arrays containing Said range of addresses. 25. A method of operating a memory device, Said method comprising: receiving a memory command and data which identifies a range of addresses required for said memory command within a memory device; identifying which of a plurality of memory Sub arrays contains Said addresses within Said range; and Supplying power to Said identified memory Sub arrays which contains Said addresses within Said range. 26. The method of claim 25 further comprising receiving a range of addresses not needed to execute Said memory command and using Said range of addresses not needed to US 6,356,500 B define Said data which identifies a range of addresses required for Said memory command. 27. The method of claim 26 further comprising powering down ones of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays which are not needed for Said memory command. 28. The method of claim 26 further comprising disabling the transmission of a refresh command for ones of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays which are not needed for Said memory command. 29. The method of claim 25 further comprising powering down all of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays as an initial Step. 30. The method of claim 25 further comprising disabling the transmission of a refresh command to all of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays as an initial Step. 31. The method of claims 25, 29 or 30 further comprising receiving a range of addresses needed to execute Said memory command and using Said range of addresses needed to define Said data which identifies a range of addresses required for Said memory command. 32. The method of claim 29 further comprising Supplying power to ones of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays which are needed for Said memory command. 33. The method of claim 30 further comprising enabling the transmission of a refresh command for ones of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays which are needed for Said memory command. 34. The method of claim 25 further comprising resetting a plurality of counters in a table, wherein Said plurality of counters indicate a period of time which has elapsed since a respective one of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays was last accessed. 35. The method of claim 34 further comprising incre menting Said plurality of counters when a respective one of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays has been accessed. 36. The method of claim 34 further comprising powering down ones of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays which Said plurality of counters indicates has not been accessed for a predetermined period of time. 37. The method of claim 34 further comprising reducing the power provided to ones of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays which Said plurality of counters indicates have been not been accessed for a predetermined time period. 38. The method of claim 36 or 37, wherein said prede termined time period is one minute. 39. The method of claim 36 further comprising writing the data contained in ones of Said plurality of memory Sub arrays to be powered down to a non-volatile Storage device prior to powering down.
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000
 US006058048A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54) FLASH MEMORY DEVICE USED ASA 56) References Cited BOOT-UP MEMORY IN A COMPUTER SYSTEM U.S. PATENT
US006058048A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54) FLASH MEMORY DEVICE USED ASA 56) References Cited BOOT-UP MEMORY IN A COMPUTER SYSTEM U.S. PATENT
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2. Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007
 United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1
 USOO664275OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1 Egan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) SEQUENCING CIRCUIT FOR APPLYING A 5,886,561. A 3/1999 Eitan et al.... 327/408 HIGHEST
USOO664275OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1 Egan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) SEQUENCING CIRCUIT FOR APPLYING A 5,886,561. A 3/1999 Eitan et al.... 327/408 HIGHEST
260k] 2801K].éGND MROUT I.12
![260k] 2801K].éGND MROUT I.12 260k] 2801K].éGND MROUT I.12](/thumbs/94/118236695.jpg) United States Patent [19] Nesheiwat et al. US00589 2777A [11] Patent Number: 5,892,777 [45] Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 [54] APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR OBSERVING THE MODE OF A MEMORY DEVICE [75] Inventors:
United States Patent [19] Nesheiwat et al. US00589 2777A [11] Patent Number: 5,892,777 [45] Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 [54] APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR OBSERVING THE MODE OF A MEMORY DEVICE [75] Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Haines
 United States Patent (19) Haines 11 45 Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,697,107 Sep. 29, 1987 54) (75) (73) 21 22) (51) 52) (58) (56) FOUR-STATE I/O CONTROL CIRCUIT Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed:
United States Patent (19) Haines 11 45 Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,697,107 Sep. 29, 1987 54) (75) (73) 21 22) (51) 52) (58) (56) FOUR-STATE I/O CONTROL CIRCUIT Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1. Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2. Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,103,736 B2. Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006
 United States Patent US007103736B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006 (54) SYSTEM FOR REPAIR OF ROM 5.325,504 A * 6/1994 Tipley et al.... T11/128 PROGRAMMING ERRORS ORDEFECTS
United States Patent US007103736B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Sachs (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 5, 2006 (54) SYSTEM FOR REPAIR OF ROM 5.325,504 A * 6/1994 Tipley et al.... T11/128 PROGRAMMING ERRORS ORDEFECTS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
(12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
(12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,879,518 B1. Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005
 United States Patent US006879518B1 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005 (54) EMBEDDED MEMORY WITH SECURITY 6,076,149 A * 6/2000 Usami et a1...... 711/163 ROW LOCK PROTECTION 6,088,262
United States Patent US006879518B1 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005 (54) EMBEDDED MEMORY WITH SECURITY 6,076,149 A * 6/2000 Usami et a1...... 711/163 ROW LOCK PROTECTION 6,088,262
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Buckland et al. USOO6467022B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (62) (51) (52) (58) EXTENDING ADAPTER MEMORY WITH SOLID STATE DISKS
(12) United States Patent Buckland et al. USOO6467022B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (62) (51) (52) (58) EXTENDING ADAPTER MEMORY WITH SOLID STATE DISKS
Is more than one finger placed on touchpad surface?
 USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004
 (19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,017,055 B1. H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006
 United States Patent USOO701.7055B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) HUB THAT CAN SUPPLY POWER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS ACTIVELY JP 20020945.45 A * 3/2002 : (75) Inventor:
United States Patent USOO701.7055B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) HUB THAT CAN SUPPLY POWER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS ACTIVELY JP 20020945.45 A * 3/2002 : (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
US 7.663,338 B2. Feb. 16, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Guthrie et al. used to receive a USB bus voltage from the USB interface and (51)
 USOO7663338B2 (12) United States Patent Guthrie et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.663,338 B2 Feb. 16, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND APPARATUS
USOO7663338B2 (12) United States Patent Guthrie et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.663,338 B2 Feb. 16, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2
 US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
Gammalcode. Frame 1, Frame 2. drive signal. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Timing code.
 (19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120162831A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0162831 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR (22) Filed: Dec. 26,
US 20120162831A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0162831 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR (22) Filed: Dec. 26,
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2. Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008
 United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,008,921 Brusky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 1999
 US006008.921A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,008,921 Brusky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 1999 54 METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR 56) References Cited CONVERTING REMOTE CONTROL SIGNALS
US006008.921A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,008,921 Brusky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 1999 54 METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR 56) References Cited CONVERTING REMOTE CONTROL SIGNALS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1
 USOO6199163B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1 Dumas et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 9 (54) HARD DISK PASSWORD LOCK 5,231,662 * 7/1993 van Rumpt et al.... 380/9 5,283,828
USOO6199163B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,163 B1 Dumas et al. 45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 9 (54) HARD DISK PASSWORD LOCK 5,231,662 * 7/1993 van Rumpt et al.... 380/9 5,283,828
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2
 US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,845,158 B2
 USOO684.5158B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,845,158 B2 KOester et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2005 (54) RETRACTABLE-REMOVABLE HEADPHONE 5,136,446 A 8/1992 Yamamoto et al. MODULE
USOO684.5158B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,845,158 B2 KOester et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2005 (54) RETRACTABLE-REMOVABLE HEADPHONE 5,136,446 A 8/1992 Yamamoto et al. MODULE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,536,920 B2 Shen
 l 1 L L IL L. I 1 L _ I L L L L US008536920B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,536,920 B2 Shen (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 2013 (54) CLOCK CIRCUIT WITH DELAY FUNCTIONS AND RELATED METHOD
l 1 L L IL L. I 1 L _ I L L L L US008536920B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,536,920 B2 Shen (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 2013 (54) CLOCK CIRCUIT WITH DELAY FUNCTIONS AND RELATED METHOD
wo W /1997 * cited by examiner
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
( 57 ) ABSTRACT G11C 11 / 4078
 COMMUNICATE WITH US009741421B1 THAT AT THE ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 10 ) Patent No.: US 9, 741, 421 B1 Hedden ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Aug. 22, 2017 ( 54 ) REFRESH ( 71 ) Applicant : Micron Technology,
COMMUNICATE WITH US009741421B1 THAT AT THE ( 12 ) United States Patent ( 10 ) Patent No.: US 9, 741, 421 B1 Hedden ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Aug. 22, 2017 ( 54 ) REFRESH ( 71 ) Applicant : Micron Technology,
United States Patent 19 Norris
 United States Patent 19 Norris 54 75 73 21 22 63 51 52 58 56 DYNAMIC PROCESSOR PERFORMANCE AND POWER MANAGEMENT INA COMPUTER SYSTEM Inventor: David Norris, Portland, Oreg. Assignee: Intel Corporation,
United States Patent 19 Norris 54 75 73 21 22 63 51 52 58 56 DYNAMIC PROCESSOR PERFORMANCE AND POWER MANAGEMENT INA COMPUTER SYSTEM Inventor: David Norris, Portland, Oreg. Assignee: Intel Corporation,
(12) United States Patent
 US007110229B2 (12) United States Patent Yang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY PANELUSING THE SAME (76) Inventors: Sheng-Chieh Yang, No. 120, Jhenfu St.,
US007110229B2 (12) United States Patent Yang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY PANELUSING THE SAME (76) Inventors: Sheng-Chieh Yang, No. 120, Jhenfu St.,
58 Field of Search /341,123, NEE"E", "E.
 USOO597.7975A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Mugura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1999 54) ARRAY OF DISPLAYED GRAPHIC IMAGES 5,233,333 8/1993 Borsuk... 345/127 FOR ENABLING SELECTION
USOO597.7975A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Mugura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1999 54) ARRAY OF DISPLAYED GRAPHIC IMAGES 5,233,333 8/1993 Borsuk... 345/127 FOR ENABLING SELECTION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,418,141 B1 Votava (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002
 US006418141B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,418,141 B1 Votava (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) MULTI-CAST ENABLED WEB SERVER 6,011,782 A * 1/2000 DeSimone et al...... 370/260 6,038,601
US006418141B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,418,141 B1 Votava (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) MULTI-CAST ENABLED WEB SERVER 6,011,782 A * 1/2000 DeSimone et al...... 370/260 6,038,601
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7941.543B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941.543 B2 Moussallam et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MIGRATING 2002/0169781 A1* 11/2002 Poole et al....
USOO7941.543B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941.543 B2 Moussallam et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MIGRATING 2002/0169781 A1* 11/2002 Poole et al....
(12) United States Patent
 US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
US007107617B2 (12) United States Patent Hursey et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 12, 2006 (54) MALWARE SCANNING OF COMPRESSED COMPUTER S (75) Inventors: Nell John Hursey, Hertfordshire
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,158,627 B1
 US007 158627 B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Lu (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR INHIBITING (56) References Cited SOFTSWITCH OVERLOAD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
US007 158627 B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Lu (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR INHIBITING (56) References Cited SOFTSWITCH OVERLOAD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2
 USOO773905OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2 Tatro (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 15, 2010 (54) SOFTWARE-BASED QUALITY CONTROL (56) References Cited ANALYSIS OF WELL LOG DATA U.S.
USOO773905OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,739,050 B2 Tatro (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 15, 2010 (54) SOFTWARE-BASED QUALITY CONTROL (56) References Cited ANALYSIS OF WELL LOG DATA U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2
 US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
US008131217B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.131,217 B2 Srinivasa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2012 (54) IDENTIFICATION OF MAKE AND MODEL 2004/0266347 A1* 12/2004 Palin et al....
10-N 12. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O1981 75A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198175 A1 Badawi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS HIGH (22) Filed:
US 2006O1981 75A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198175 A1 Badawi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS HIGH (22) Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
336w 330 FPGA / 330 MW} Compgnenf _/14 / 38 US 7,774,801 B1. Aug. 10, 2010 (56) (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: (12) United States Patent Fitkin
 US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
US007774801B1 (12) United States Patent Fitkin (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) CORBA FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAY/DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,237,112 B1
 USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
USOO62371.12B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yo0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 22, 2001 (54) SCSI DEVICE AVAILABLE FOR BREAKDOWN PREDICTION AND 5,966,510 * 10/1999 Carbonneau et al.... 714/44
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,446,174 B1 Dow (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002
 US006446174B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,446,174 B1 Dow (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) COMPUTER SYSTEM WITH DRAM BUS 5,969,728 A 10/1999 Dye et al...... 345/515 6,003,121 A
US006446174B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 6,446,174 B1 Dow (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 3, 2002 (54) COMPUTER SYSTEM WITH DRAM BUS 5,969,728 A 10/1999 Dye et al...... 345/515 6,003,121 A
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
edram Macro MUX SR (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1 1" (RH) Read-Buffer" JO s (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2002O174291A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0174291 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2002 (54) HIGH SPEED EMBEDDED DRAM WITH SRAM-LIKE INTERFACE
(19) United States US 2002O174291A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0174291 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2002 (54) HIGH SPEED EMBEDDED DRAM WITH SRAM-LIKE INTERFACE
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,094,695 KOrnher (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 25, 2000
 US0094695A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: KOrnher () Date of Patent: Jul., 2000 54). STORAGE BUFFER THAT DYNAMICALLY 5,6,691 10/1995 Snell... 7/30 ADJUSTS BOUNDARY BETWEEN TWO 5,581,736 12/1996
US0094695A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: KOrnher () Date of Patent: Jul., 2000 54). STORAGE BUFFER THAT DYNAMICALLY 5,6,691 10/1995 Snell... 7/30 ADJUSTS BOUNDARY BETWEEN TWO 5,581,736 12/1996
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1
 USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7.263,017 B2. VOShe (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 28, 2007
 United States Patent USOO7263017B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7.263,017 B2 VOShe (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 28, 2007 (54) AC SENSING FOR A RESISTIVE MEMORY 5,881,007 A 3/1999 Jeong et al. 6,226,222 B1 5,
United States Patent USOO7263017B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7.263,017 B2 VOShe (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 28, 2007 (54) AC SENSING FOR A RESISTIVE MEMORY 5,881,007 A 3/1999 Jeong et al. 6,226,222 B1 5,
/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].
![/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. / client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].](/thumbs/90/103929709.jpg) US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
(51) Int. Cl... G11C 16/06
 US005920509A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,920,509 Hirano et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) NONVOLATILE SEMICONDUCTOR 5,576,991 11/1996 Rady et al.... 365/185.24 MEMORY DEVICE
US005920509A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,920,509 Hirano et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) NONVOLATILE SEMICONDUCTOR 5,576,991 11/1996 Rady et al.... 365/185.24 MEMORY DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 USOO853.8494B2 (12) United States Patent Hsu (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,538,494 B2 Sep. 17, 2013 (54) MOBILE PHONE AND METHOD FOR TRANSFERRING BATTERY POWER OF THE MOBILE PHONE (75) Inventor:
USOO853.8494B2 (12) United States Patent Hsu (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,538,494 B2 Sep. 17, 2013 (54) MOBILE PHONE AND METHOD FOR TRANSFERRING BATTERY POWER OF THE MOBILE PHONE (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
... (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. icopying unit d:
 (19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,649,849 B2
 USOO6649849B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,649,849 B2 Bass et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) HANDHELD MAILING SYSTEM 5,710.706 A * 1/1998 Marklet al.... 177/25.15 6,153,835
USOO6649849B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,649,849 B2 Bass et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) HANDHELD MAILING SYSTEM 5,710.706 A * 1/1998 Marklet al.... 177/25.15 6,153,835
(12) United States Patent
 USOO966.6254B1 (12) United States Patent WOO () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,666.254 B1 May 30, 2017 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY APPARATUS HAVING OPEN BIT LINE STRUCTURE IN WHICH A SENSE AMPLIFER
USOO966.6254B1 (12) United States Patent WOO () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,666.254 B1 May 30, 2017 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY APPARATUS HAVING OPEN BIT LINE STRUCTURE IN WHICH A SENSE AMPLIFER
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Sanchez et al. USOO6477666B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,477,666 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 5, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC FAULT INJECTION INTO A JAVA VIRTUAL MACHINE (JVM) (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Sanchez et al. USOO6477666B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,477,666 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 5, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC FAULT INJECTION INTO A JAVA VIRTUAL MACHINE (JVM) (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
( 12 ) United States Patent
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Daddis, Jr. et al. ( 54 ) ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONING UNIT TESTING ( 71 ) Applicant : Carrier Corporation, Farmington, CT ( US ) HAO WALA NAMAN UTAMA UNATAKA MA NA MALO MATTER
( 12 ) United States Patent Daddis, Jr. et al. ( 54 ) ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONING UNIT TESTING ( 71 ) Applicant : Carrier Corporation, Farmington, CT ( US ) HAO WALA NAMAN UTAMA UNATAKA MA NA MALO MATTER
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,385,897 B1
 US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7366822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,366,822 B2 KWalk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE (56) References Cited CAPABLE OF READING AND WRITING
(12) United States Patent USOO7366822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,366,822 B2 KWalk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE (56) References Cited CAPABLE OF READING AND WRITING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,650,589 B2
 USOO6650589B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,650,589 B2 Clark (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) LOW VOLTAGE OPERATION OF STATIC 6,205,078 B1 * 3/2001 Merritt... 365/226 RANDOMACCESS
USOO6650589B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,650,589 B2 Clark (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 18, 2003 (54) LOW VOLTAGE OPERATION OF STATIC 6,205,078 B1 * 3/2001 Merritt... 365/226 RANDOMACCESS
United States Patent (19) Pinard et al.
 United States Patent (19) Pinard et al. US005454032A 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 1995 54 METHOD OF ESTABLISHING COMMUNICATION LINK TO ONE OF MULTIPLE DEVICES ASSOCIATED WITH SINGLETELEPHONE
United States Patent (19) Pinard et al. US005454032A 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 1995 54 METHOD OF ESTABLISHING COMMUNICATION LINK TO ONE OF MULTIPLE DEVICES ASSOCIATED WITH SINGLETELEPHONE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(FSN JSO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,055,373 McElroy et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2000
 US006055373A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,055,373 McElroy et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2000 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM INCLUDING A 5,291,614 3/1994 Baker et al.... 395/800 DIGITAL SIGNAL
US006055373A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,055,373 McElroy et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2000 54) COMPUTER SYSTEM INCLUDING A 5,291,614 3/1994 Baker et al.... 395/800 DIGITAL SIGNAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,818,742 B2
 USOO8818742B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 8,818,742 B2 Ansari (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2014 (54) SYSTEMS, METHODS, AND APPARATUS FOR 5,736,877 * 4/1998 Tihanyi... 327/77 DETECTING
USOO8818742B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 8,818,742 B2 Ansari (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2014 (54) SYSTEMS, METHODS, AND APPARATUS FOR 5,736,877 * 4/1998 Tihanyi... 327/77 DETECTING
IIII 42 Y. United States Patent 19 RO et al. 46 G 40 N& 75) Inventors: Jong-Wong Ro; Yeong-Ju Kim, both
 United States Patent 19 RO et al. 54 OPTICAL COUPLING DEVICE WITH BALL LENS AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME 75) Inventors: Jong-Wong Ro; Yeong-Ju Kim, both of Gumi, Keon-Joon Ahn, Daegukwangyeok,
United States Patent 19 RO et al. 54 OPTICAL COUPLING DEVICE WITH BALL LENS AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME 75) Inventors: Jong-Wong Ro; Yeong-Ju Kim, both of Gumi, Keon-Joon Ahn, Daegukwangyeok,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) 11 USOO5944769A Patent Number: 5,944,769 Musk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 31, 1999 54 INTERACTIVE NETWORK DIRECTORY 5,543,789 8/1996 Behr et al.... 340/995 SERVICE WITH INTEGRATED
United States Patent (19) 11 USOO5944769A Patent Number: 5,944,769 Musk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 31, 1999 54 INTERACTIVE NETWORK DIRECTORY 5,543,789 8/1996 Behr et al.... 340/995 SERVICE WITH INTEGRATED
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Margalit et al. USOO6554621B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2003 (54) CABLE APPARATUS (75) Inventors: Yanki Margalit, Ramat Gan (IL); Dany Margalit, Ramat Gan
(12) United States Patent Margalit et al. USOO6554621B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2003 (54) CABLE APPARATUS (75) Inventors: Yanki Margalit, Ramat Gan (IL); Dany Margalit, Ramat Gan
isits ar. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1 (19) United States y(n) second sub-filter feedback equalizer
 (19) United States US 20100027610A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0027610 A1 CHANG (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2010 (54) EQUALIZER AND EQUALIZATION METHOD (75) Inventor: Chiao-Chih
(19) United States US 20100027610A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0027610 A1 CHANG (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2010 (54) EQUALIZER AND EQUALIZATION METHOD (75) Inventor: Chiao-Chih
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO6941277B2 (10) Patent No.: Imag0 (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 6, 2005 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PROVIDING (56) References Cited ONLINE INFORMATION FOR NETWORKED DEVICES U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0222841 A1 Mirajkar et al. US 20090222841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 3, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) ACCELERATION OF RECEIVE DATA
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0222841 A1 Mirajkar et al. US 20090222841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 3, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) ACCELERATION OF RECEIVE DATA
OSPATCHER. United States Patent (19) Anschuetz et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,305,455 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 1994
 United States Patent (19) Anschuetz et al. USOO5305455A 11 Patent Number: 5,305,455 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 1994 54 75 (73) 21 22 (51) (52) 58 PER THREAD EXCEPTION MANAGEMENT FOR MULTTASKING MULTITHREADED
United States Patent (19) Anschuetz et al. USOO5305455A 11 Patent Number: 5,305,455 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 1994 54 75 (73) 21 22 (51) (52) 58 PER THREAD EXCEPTION MANAGEMENT FOR MULTTASKING MULTITHREADED
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9729447B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,729.447 B2 *Aug. 8, 2017 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52)
USOO9729447B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,729.447 B2 *Aug. 8, 2017 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52)
United States Patent (19) Jones et al.
 United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
