(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
|
|
|
- Claude Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
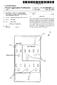
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 Mai (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 2, 2015 (54) WIRELESS CHARGING DEVICE, POWER (52) U.S. Cl. RECEIVING DEVICE, AND WIRELESS CPC... H02J 7/025 ( ); H02J 5/005 FLAT-PANEL CHARGING SYSTEM ( ); H02J 1700 ( ) USPC /108:307/104 (71) Applicant: SHENZHEN FEIFAN INDUSTRIAL CO.,LTD., Shenzhen, Guangdong (CN) (72) Inventor: Huabin Mai, Shenzhen (CN) (73) Assignee: Shenzhen Feifan Industrial Co., Ltd., Shenzhen (CN) (21) Appl. No.: 14/ (22) PCT Filed: Dec. 20, 2012 (86). PCT No.: PCT/CN2012/ S371 (c)(1), (2) Date: Oct. 23, 2014 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Apr. 24, 2012 (CN) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. H02. 7/02 ( ) H02) I 7/00 ( ) HO25/00 ( ) (57) ABSTRACT A wireless charging device, a power receiving device and a wireless flat-panel charging system have been disclosed. The wireless charging device includes a Support main body, at least two electrodes are arranged on the Surface of the Support main body, an insulation gap is arranged between the elec trodes, and each electrode is respectively connected to a charging power source. The power receiving device includes at least two conductive contacts, the Smallest edge distance of a single conductive contact is greater than the size of the insulation gap between the electrodes, and the Smallest dis tance between edges of adjacent conductive contacts is greater than the largest edge distance of a single electrode. The power receiving device is placed on the wireless charging device, the conductive contacts of the power receiving device contact the electrodes of the wireless charging device, and power is directly supplied for the conductive contacts by using the electrodes. Negative Switching Unit 132 Positive Switching ; Unit 131 Switching : Detection Unit 2 Detection -XXXXXXXXX-XXXXXXXX-XXXXXXXX-XXX-XXX Negative Dcticction Positive : Unit 121 Switching Switching - Detection ; Unit 131 Unit 132 Switching Detection Setting Module 141 Control Module 42 worw w:
2 Patent Application Publication Apr. 2, 2015 Sheet 1 of 7 US 201S/ A1, v y irrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrrr. ******************** ***************************** YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY sa& ******************* sasasasasasaasaaaaaaaaaaa Saaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa. Krssssssssssssssssss. z~~~~.~~~~.~~~~~.~~~~~); XXXXXXXXXXXXXX-XXXXX. Figure 1 Figure 2
3 Patent Application Publication Apr. 2, 2015 Sheet 2 of 7 US 201S/ A1 >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>} WWwww. aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx * *** * ** ** ** ** **} ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~); xxxxxxxxxxxx x^************************* Figure 3 -was--- Figure 4
4 Patent Application Publication Apr. 2, 2015 Sheet 3 of 7 US 201S/ A1 & --~~~~*~~~~); V*''''''''''''''''''''. Uo]] 0040CI OZI ][nojio VVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVVSSSVVVV. X s zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz # {** *** *** *** *** *** ***? zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz, Uo]] 0040CI zzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzz, aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
5 Patent Application Publication Apr. 2, 2015 Sheet 4 of 7 US 201S/ A1
6 Patent Application Publication Apr. 2, 2015 Sheet 5 of 7 US 201S/ A Figure 8
7 Patent Application Publication Apr. 2, 2015 Sheet 6 of 7 US 201S/ A1 Setting electrodes to a detection State w Detecting whether electrodes is in contact with a conductive contact of a power receiving device Determining association between all the electrodes in contact with the conductive contact and setting polarity of the electrodes respectively Connecting to a power Source corresponding to the polarity according to the polarity of the electrodes
8 Patent Application Publication Apr. 2, 2015 Sheet 7 of 7 US 201S/ A1 sis S. & Figure 11
9 US 2015/ A1 Apr. 2, 2015 WIRELESS CHARGING DEVICE, POWER RECEIVING DEVICE, AND WIRELESS FLAT-PANEL CHARGING SYSTEM TECHNICAL FIELD This disclosure relates to charging devices, and more particularly to wireless charging devices, power receiv ing devices and wireless flat-panel charging systems. BACKGROUND 0002 With developments in science and technology, more and more electric equipment are used in people's life. During their usage, the electric equipment or batteries thereof are powered by directly connecting to a power Source through a power plug. There will thus be increasing power plugs with the increasing electric equipment. This may bring about inconvenient operation to users In addition, different electric equipment usually employ different power plugs, and thus an adapter should be equipped for adapting different power plugs. Therefore, the user has to use many power adapters, which not only goes against energy conservation and environment protection but also results in huge wasting of resources Besides, when it is needed to charge a plurality of electric equipment at the same time, a plurality of power adapters are used simultaneously and power Strip(s) is/are additionally employed in this case. Moreover, connection lines of the power adapters easily twist with each other, thus causing inconvenience in the usage to the users. SUMMARY OF THIS DISCLOSURE The technical problem to be solved in this disclosure is to provide wireless charging devices with convenient operation and excellent universality Another technical problem to be solved in this dis closure is to provide power receiving devices that can be used on Such wireless charging devices Another technical problem to be solved in this dis closure is to provide wireless flat-panel charging systems with convenient operation and excellent universality According to one aspect, a wireless charging device is provided. The wireless charging device includes a Support main body. At least two electrodes are arranged on a Surface of the Support main body, and an insulation gap is arranged between the electrodes. Each of the electrodes is respectively connected to a charging power source. The electrodes have regular or irregular shape In the wireless charging device of this disclosure, the electrodes include a first electrode and a second electrode, where the second electrode surrounds a periphery of the first electrode In the wireless charging device of this disclosure, the insulation gap has an equal distance between the first electrode and the second electrode, and a limit flange is also disposed around a periphery of the second electrode In the wireless charging device of this disclosure, the Support main body is a flat-panel main body. The elec trodes include more than two electrodes, and the electrodes are arranged on the flat-panel main body with an equal or unequal spacing In the wireless charging device of this disclosure, the charging power source includes a power Supply circuit electrically connected with the electrodes. The power supply circuit is arranged on the Support main body or separated from the Support main body In the wireless charging device of this disclosure, the power Supply circuit includes a detection circuit, a Switch ing circuit, a control circuit and a power circuit, where the power circuit is connected with the detection circuit, the Switching circuit and the control circuit for Supplying power The detection circuit is electrically connected with each of the electrodes for detecting whether the electrodes are in contact with a conductive contact of a power receiving device The switching circuit is electrically connected with each of the electrodes for switching on or switching off the power supplied to the electrodes The control circuit is connected with the detection circuit and the switching circuit, wherein based on whether each of the electrodes is in contact with the conductive con tact detected by the detection circuit, the control circuit is operable to send out a control signal to the Switching circuit so that each of the electrodes is controlled to connect to or disconnect from the power circuit In the wireless charging device of this disclosure, the Switching circuit includes a positive Switching circuit and a negative Switching circuit which are simultaneously con nected with each of the electrodes The detection circuit includes a plurality of detec tion units, wherein each of the detection units is electrically connected with one of the electrodes correspondingly The positive switching circuit includes a plurality of positive Switching units, wherein each of the positive Switch ing units is electrically connected with one of the electrodes The negative switching circuit includes a plurality of negative Switching units, wherein each of the negative Switching units is electrically connected with one of the elec trodes The positive switching unit and the negative switch ing unit connected with the same electrode are controlled by the control circuit to be alternatively switched on or simulta neously switched off A power receiving device which can cooperate with any one of the above-described wireless charging device is also provided in this disclosure. The power receiving device includes at least two conductive contacts The smallest edge distance of a single conductive contact is larger than the size of the insulation gap between the electrodes of the wireless charging device, and the Small est distance between edges of adjacent conductive contacts is larger than a largest edge distance of a single electrode In the power receiving device of this disclosure, the power receiving device further includes a power module elec trically connected with the conductive contacts. The power module includes one or more of toy, game equipment, cell phone, battery, charger, handheld equipment, electric tool, power connector, electric cup, music player, camera, calcu lator, remote controller, video tape recorder, video player, fax machine, PDA beauty equipment, electric shaver, electric toothbrush, electric hair cutter, television, refrigerator In the power receiving device of this disclosure, the power receiving device also includes a housing, where the conductive contacts are disposed on the housing. The housing is also arranged with an interface modules electrically con nected with the conductive contacts.
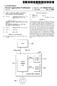
10 US 2015/ A1 Apr. 2, A wireless charging system is also provided in this disclosure. The wireless charging system includes any one of the above-described wireless charging devices and any one of the above-described power receiving devices. The power receiving device is placed on the wireless charging device, and two conductive contacts of the power receiving device are respectively in electrical contact with at least two electrodes of the wireless charging device, such that the power receiving device is powered by the wireless charging device When implementing this disclosure, the following advantageous effects can be achieved: the power receiving device is placed on the wireless charging device, while the conductive contacts of the power receiving device is in con tact with the electrodes of the wireless charging device, so that the conductive contact is directly powered by using the electrodes. In this way, the inconvenience of using the power plug in the prior art is avoided, thus achieving the advantages of convenient operation and excellent universality Moreover, the smallest edge distance of a single conductive contact is arranged to be larger than the size of the insulation gap between the electrodes of the wireless charging device, and the smallest distance between edges of adjacent conductive contacts is arranged to be larger than a largest edge distance of a single electrode. In this way, the power receiving device can be freely placed on the support main body of the wireless charging device, and the conductive contacts can electrically connect with the electrodes in any case, thus achieving more convenient operation Additionally, a plurality of power receiving devices can be simultaneously placed on the wireless charging device by arranging a plurality of electrodes. In this way, the plural ity of power receiving devices can be powered simulta neously, thereby avoiding the inconvenience of using a plu rality of power adapters in the prior art. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0030) Below this disclosure will be further described with reference to accompanying drawings and embodiments. In the figures: 0031 FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram for an embodiment of a wireless charging device in this disclosure; 0032 FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram illustrating round electrodes of a wireless charging device in this disclosure; 0033 FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram illustrating rectangle electrodes of a wireless charging device in this disclosure; 0034 FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram illustrating round electrodes in staggered arrangement of a wireless charging device in this disclosure; 0035 FIG. 5 is a schematic block diagram for a power supply circuit of a wireless charging device and a charging power source in this disclosure; 0036 FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram for an embodiment of a power receiving device in this disclosure; 0037 FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram illustrating one state in which a power receiving device is placed on a wireless charging device in this disclosure; 0038 FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram illustrating another state in which a power receiving device is placed on a wireless charging device in this disclosure; 0039 FIG.9 is a schematic diagram illustrating a working process of a power receiving device in this disclosure; 0040 FIG. 10 is a schematic diagram illustrating round electrodes in another embodiment of a wireless charging device in this disclosure; and 0041 FIG. 11 is a schematic diagram illustrating rectangle electrodes in another embodiment of a wireless charging device in this disclosure. DETAILED DESCRIPTION As shown in FIGS. 1-4, one embodiment for a wire less charging device 100 of this disclosure is represented. The wireless charging device 100 can be used for providing a power receiving device with a power supply platform so as to facilitate the usage of the power receiving device The wireless charging device 100 includes a support main body 110. A plurality of electrodes 111 are disposed on a surface of the support main body 110, and an insulation gap 112 is located between the electrodes 111 to respectively separate the plurality of electrodes 111. The electrodes 111 can each connect to a charging power source for being pow ered by accessing the power source As shown in figures, the support main body 110 in this embodiment is a flat-panel main body, of which the shape and the size can be adjusted as required The electrodes 111 which are square-shaped are arranged in matrix form with equal spacing on the Support main body 110. It can be understood that the electrodes 111 can be set to have any other shape as required, such as round shape (as shown in FIG. 2), rectangle shape (as shown in FIG. 3), prismatic shape, trapezoid shape, and irregular shape and SO O For facilitating the arrangement of the electrodes 111, the electrodes 111 are usually arranged to be regularly and equally spaced. In some circumstance in need of special design, those electrodes 111 can also be arranged irregularly or without equal spacing. As shown in FIG. 4, it is a schematic diagram illustrating the electrodes 111 in staggered arrange ment Further, the number of the electrodes 111 can be designed based on actual needs, as long as at least two elec trodes are included in the wireless charging device. In this embodiment, the support main body 110 is an insulated flat panel main body. The electrodes 111 are directly affixed on the surface of the support main body 110, and then the insu lation gap 112 is naturally formed between the electrodes 111. Some recesses and/or clamping elements can also be disposed on the support main body 110, where the electrodes 111 are embedded and fixed on the support main body 110. Besides, insulation paste can be filled between the electrodes 111 to prevent the short connection between the electrodes As shown in FIG. 5, the electrodes 111 of the wire less charging device 100 are connected to a charging power source. In this embodiment, the charging power source includes a power supply circuit electrically connected with the electrodes 111. The power supply circuit can be directly disposed within the support main body 110; alternatively, the power supply circuit can be disposed within an independent housing and then electrically connected with the electrodes 111 through wire, flat cable or contact The power supply circuit includes a detection circuit 120, a switching circuit 130, a control circuit 140 and a power circuit, where the power circuit is connected with the detec tion circuit 120, the switching circuit 130 and the control circuit 140 for supplying power Referring to FIGS.5 and 6, the detection circuit 120 is electrically connected with each electrode 111 for detecting whether the electrodes 111 are in contact with the conductive
11 US 2015/ A1 Apr. 2, 2015 contact(s) 151. The detection circuit 120 includes a plurality of detection units 121, where each of the detection units 121 is electrically connected with one electrode 111 correspond ingly. A micro voltage is loaded onto the electrodes 111 by the detection unit 121, so that each of the electrodes 111 is in a to-be-detected state and whether the electrode is in contact with the conductive contact 151 is detected. Furthermore, when there is the conductive contact 151 for contacting, trig ger signal is generated to the control circuit 140 for further determination and setting The switching circuit 130 is electrically connected with each electrode 111 for switching on or switching off the power supplied to the electrodes 111. In this embodiment, the Switching circuit 130 includes a positive Switching circuit and a negative Switching circuit which are simultaneously con nected with each electrode 111. The positive switching circuit or the negative Switching circuit is selected by the control circuit 140 to operate for connecting to the corresponding electrode In this embodiment, the positive switching circuit includes a plurality of positive switching units 131, where each of the positive switching units 131 is electrically con nected with one of the electrodes 111. The negative switching circuit includes a plurality of negative Switching units 132, where each of the negative switching units 132 is electrically connected with one of the electrodes 111. Each electrode 111 correspondingly connects with one positive Switching unit 131 and one negative switching unit 132 for freely setting the polarity of the electrode The control circuit 140 is connected with the detec tion circuit 120 and the switching circuit 130, wherein based on whether each of the electrodes 111 is in contact with the conductive contact 151 detected by the detection circuit 120, the control circuit 140 is operable to send out control signal to the switching circuit 130 so that each of the electrodes 111 is controlled to connect to or disconnect from the power circuit. In this embodiment, in order to set the polarity of the elec trodes 111, the positive switching unit 131 and the negative switching unit 132 connected with the same electrode 111 are controlled by the control circuit 140 to be alternatively switched on or simultaneously switched off As shown in FIG. 5, the control circuit 140 includes a detection setting module 141 and a control module 142. The detection setting module 141 is connected with the detection circuit 120. Based on the trigger signal inputted from the detection circuit 120, the detection setting module 141 is operable to take one of the electrodes 111 that is in contact with the conductive contact 151 as a reference while scanning the remaining electrodes 111, where the electrode(s) 111 in short connection with the electrode 111 as the reference isfare set as a same polarity and the electrode(s) 111 not in short connection with the electrode 111 as the reference isfare setas a different polarity The control module 142 is connected with the switching circuit 130 and the detection setting module 141, and it is operable to output an on-off control signal to the Switching circuit 130 according to a setting result of the detection setting module 141, so that the switching circuit 130 can control the disconnection or the polarity for connection of the corresponding electrode(s) Besides, it is needed to note that the polarity of the conductive contact in contact with the electrode (i.e., the polarity of an input port of the power module in connection with the conductive contact) can be detected by the detection unit of the corresponding power Supply circuit after the elec trode is in contact with the conductive contact of the power receiving device. When the polarity is detected to be a posi tive electrode, the corresponding positive Switching unit is controlled to be switched on so as to connect the electrode with a positive output end of the power circuit. On the other hand, when the polarity is detected to be a negative electrode, the corresponding negative Switching unit is controlled to be Switched on so as to connect the electrode with a negative output end of the power circuit. Alternatively, the power Sup ply circuit may also not detect the polarity of the conductive contact in contact with the electrode. Instead, the electrode is randomly allocated by the control circuit to connect with the positive output end or the negative output end of the power circuit, while the polarity of the electrode in contact with the conductive contact (i.e., the polarity of the output end of the power circuit in connection with this electrode) is detected within the power receiving device, and the two output ends of the power circuit are then correspondingly connected to two input ends of the power module Further, for the purpose of ensuring secure and stable operation of the wireless charging device 100, the wireless charging device 100 can also include a safety pro tection circuit, an over-current protection circuit and a power sensing circuit As shown in FIG. 6, it is a schematic diagram for an embodiment of the power receiving device 150 in this disclo Sure. This power receiving device can cooperate with the above-described wireless charging device 100. With refer ence to FIG. 7, the power receiving device 150 includes two conductive contacts 151, which can be in contact with the electrodes 111 of the wireless charging device 100 such that power is supplied to the power receiving device 150 through connecting to a power source. Aiming at convenient opera tion, more than two conductive contacts 151 can also be arranged as required, undoubtedly. 0059) Please referring to FIG.8, such two conductive con tacts 151 are needed to cooperate with the electrodes 111 of the wireless charging device 100. The smallest edge distance D of a single conductive contact 151 is larger than the size X of the insulation gap 112 between the electrodes 111, such that the whole conductive contact 151 is avoided to fall into the insulation gap 112, thereby ensuring that the conductive contact 151 always has electrical contact with the electrode(s) 111 when the power receiving device 150 is placed on the support main body Meanwhile, the smallest distance C between edges of adjacent conductive contacts 151 is larger than a largest edge distance L of a single electrode 111, thus ensuring the adjacent conductive contacts 151 are prevented from electri cally contacting with a same electrode 111. That is, the two adjacent conductive contacts 151 are ensured to have electri cal contact with two different electrodes 111. In this way, two electrodes 111 can be set as different polarities to form a power Supply loop The power receiving device 150 further includes a power module connected with the conductive contact 151. The power module includes one or more of toy, game equip ment, cellphone, battery, charger, handheld equipment, elec tric tool, power connector, electric cup, music player, camera, calculator, remote controller, video tape recorder, video player, fax machine, PDA beauty equipment, electric shaver, electric tooth brush, electric hair cutter, television, refrigera
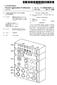
12 US 2015/ A1 Apr. 2, 2015 tor. The power module is directly powered by connecting to the power source through the conductive contacts In another implementation, the power receiving device 150 can include a housing. The conductive contacts 151 are disposed on a back surface or any other position of the housing. Meanwhile, an interface module electrically con nected with the conductive contact 151 is disposed within the housing. The housing is matched with the shape of some electronic equipment (Such as cell phone, PDA, tablet com puter etc.), and the interface module is matched with a charg ing interface of the electronic equipment. The housing is sleeved onto the periphery of the electronic equipment while the interface module is inserted into the charging interface of the electronic equipment. In this way, the power source can be accessed by the conductive contacts 151 and transmitted to the electronic equipment through the interface module, and thus the electronic equipment is powered A wireless charging system is consisted of the above-described wireless charging device 100 and power receiving device 150. During operation, the power receiving device 150 is directly placed on the wireless charging device 100, and two conductive contacts 151 of the power receiving device 150 respectively have electrical contacted with at least two electrodes 111 of the wireless charging device 100. In this way, the power receiving device 150 is powered by the wire less charging device As shown in FIG. 9, when using such wireless charging system for wireless charging operation, the elec trodes 111 of the wireless charging device 100 are first set to a detection state. In this embodiment, each detection unit 121 of the detection circuit 120 loads a micro voltage onto the electrodes 111 correspondingly connected with the detection unit, so as to make each electrode 111 be in a to-be-detected State Subsequently, whether the electrodes 111 are in contact with the conductive contact 151 of the power receiv ing device 150 is detected. When the electrode 111 is in contact with the conductive contact 151, its micro voltage may change, and the trigger signal is thus generated and sent to the control circuit 140. After receiving the trigger signal, the control circuit 140 can then determine whether the elec trode 111 is in contact with the conductive contact After that, association between all the electrodes 111 that are in contact with the conductive contact 151 is determined, and the polarity of the electrodes 111 is set respectively. In this embodiment, based on the trigger signal from the detection unit 121, the detection setting module 141 of the control circuit 140 takes one of the electrodes 111 that is in contact with the conductive contact 151 as the reference while Successively scanning the remaining electrodes 111, wherein the electrode(s) 111 in short connection with the electrode 111 as the reference is/are set as a same polarity and the electrode(s) 111 not in short connection with the electrode 111 as the reference is/are set as a different polarity. As shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, they illustrate several contact situations between the electrodes 111 and the conductive contacts 151. When two conductive contacts 151 are respectively in contact with two electrodes 111 as shown in FIG.7, the polarity of the two electrodes 111 can be simply set as one positive electrode and one negative electrode. As what is shown in FIG. 8, when the conductive contact 151 is simultaneously in contact with a plurality of electrodes 111, all these electrodes 111 are set to have the same polarity, and the a plurality of electrodes 111 simultaneously operate for power Supply It can be understood that when a plurality of power receiving devices 150 are placed on the wireless charging device 100 at the same time, those operations described above can also be performed to set the polarity, and the a plurality of power receiving devices 150 can be powered simultaneously According to the polarity set for the electrodes 111, the power source corresponding to the polarity is then con nected. In this embodiment, since each electrode 111 is con nected with the positive switching unit 131 of the positive Switching circuit and the negative Switching unit 132 of the negative Switching circuit, the control module 142 of the control circuit 140 sends corresponding control signal to the positive Switching unit 131 and the negative Switching unit 132 during the control process, and the positive Switching circuit or the negative Switching circuit correspondingly con nected with the electrode 111 is thus controlled to be switched on, such that a power Supply loop is achieved to connect the power receiving device 150 to the power source As shown in FIGS. 10 and 11, they are schematic diagrams for another embodiment of a wireless charging device 200 in this disclosure. Electrodes on a support main body of this wireless charging device 200 include a first electrode 211a and a second electrode 211b. The second electrode 211b surrounds the periphery of the first electrode 211a, and an insulation gap 212 is located between the first electrode 211a and the second electrode 211b. Insulation material can be filled into the insulation gap 212. Alterna tively, when the Support main body is made of insulation material, the insulation gap can be left empty In this embodiment, both the first electrode 211a and the second electrode 211b can adopt regular shapes such as round shape (FIG. 10) or square shape (FIG. 11). Any other shape Such as ellipse, prismatic shape, trapezoid shape, irregular shape can also be used As shown in figures, the insulation gap 212 has equal distance between the first electrode 211a and the sec ond electrode 211b, in which case it is convenient to place the power receiving device in a flexible way. As required, the distance of the insulation gap 212 can also be adjusted to be arranged unequally or irregularly, in which case the distance of the conductive contact of the power receiving device needs to be adjusted correspondingly Further, in order to prevent the power receiving device from exceeding the power Supply range by the elec trode of the wireless charging device 200, a limit flange 213 is also disposed around the periphery of the second electrode 211b so that the power receiving device can be placed within a range defined by the limit flange 213 to ensure the electrical contact between the conductive contact and the electrode Other structures and working principle in this embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment, therefore, which are not repeated here In addition, this disclosure is described through embodiments. However, this disclosure is not limited to those embodiments. The skilled in the art know that various modi fications can be made without departing from the scope of this disclosure (canceled) 11. A wireless charging device, comprising a Support main body; wherein at least two electrodes are arranged on a Sur face of the Support main body, and an insulation gap is arranged between the electrodes; each of the electrodes is respectively connected to a charging power source; the elec trodes have regular or irregular shape.
13 US 2015/ A1 Apr. 2, The wireless charging device of claim 11, wherein the electrodes comprise a first electrode and a second electrode, and the second electrode surrounds a periphery of the first electrode. 13. The wireless charging device of claim 12, wherein the insulation gap has an equal distance between the first elec trode and the second electrode, and a limit flange is also disposed around a periphery of the second electrode. 14. The wireless charging device of claim 11, wherein the Support main body is a flat-panel main body; said electrodes comprise more than two electrodes, and the electrodes are arranged on the flat-panel main body with an equal or unequal spacing. 15. The wireless charging device of claim 11, wherein the charging power source comprises a power Supply circuit elec trically connected with the electrodes; the power supply cir cuit is arranged on the Support main body or separated from the Support main body. 16. The wireless charging device of claim 15, wherein the power Supply circuit comprises a detection circuit, a Switch ing circuit, a control circuit and a power circuit; the power circuit is connected with the detection circuit, the Switching circuit and the control circuit for Supplying power, the detection circuit is electrically connected with each of the electrodes for detecting whether the electrodes are in contact with a conductive contact of a power receiving device; the switching circuit is electrically connected with each of the electrodes for switching on or switching off the power supplied to the electrodes; the control circuit is connected with the detection circuit and the switching circuit; wherein based on whether each of the electrodes is in contact with the conductive contact detected by the detection circuit, the control circuit is operable to send out a control signal to the Switching circuit so that each of the electrodes is con trolled to connect to or disconnect from the power cir cuit. 17. The wireless charging device of claim 16, wherein the Switching circuit comprises a positive Switching circuit and a negative Switching circuit which are simultaneously con nected with each of the electrodes; the detection circuit comprises a plurality of detection units, wherein each of the detection units is electrically connected with one of the electrodes; the positive Switching circuit comprises a plurality of posi tive switching units, wherein each of the positive switch ing units is electrically connected with one of the elec trodes; the negative Switching circuit comprises a plurality of negative Switching units, wherein each of the negative Switching units is electrically connected with one of the electrodes; the positive Switching unit and the negative Switching unit connected with the same electrode are controlled by the control circuit to be alternatively switched on or simul taneously switched off. 18. A power receiving device capable of cooperating with the wireless charging device of claims 11, wherein the power receiving device comprises at least two conductive contacts; wherein a smallest edge distance of a single conductive contact is larger than a size of the insulation gap between the electrodes of the wireless charging device, and a small est distance between edges of adjacent conductive con tacts is larger than a largest edge distance of a single electrode. 19. The power receiving device of claim 18, wherein the power receiving device also comprise a power module elec trically connected with the conductive contacts; the power module comprises one or more of toy, game equipment, cell phone, battery, charger, handheld equipment, electric tool, power connector, electric cup, music player, camera, calcu lator, remote controller, video tape recorder, video player, fax machine, PDA beauty equipment, electric shaver, electric toothbrush, electric hair cutter, television, refrigerator. 20. The power receiving device of claim 18, wherein the power receiving device also comprises a housing, and the conductive contacts are disposed on the housing; wherein the housing is also arranged with an interface module electrically connected with the conductive contacts. 21. A wireless charging system, comprising the wireless charging device of claim 11 and the power receiving device of claim 18; the power receiving device is placed on the wireless charging device, and two conductive contacts of the power receiving device are respectively in electrical contact with at least two electrodes of the wireless charging device. Such that the power receiving device is powered by the wireless charg ing device. 22. The wireless charging system of claim 21, wherein the electrodes comprise a first electrode and a second electrode, and the second electrode surrounds a periphery of the first electrode. 23. The wireless charging system of claim 22, wherein the insulation gap has equal distance between the first electrode and the second electrode, and a limit flange is also disposed around a periphery of the second electrode. 24. The wireless charging system of claim 21, wherein the Support main body is a flat-panel main body; said electrodes comprise more than two electrodes, and the electrodes are arranged on the flat-panel main body with an equal or unequal spacing. 25. The wireless charging system of claim 21, wherein the charging power source comprises a power Supply circuit elec trically connected with the electrodes; the power supply cir cuit is arranged on the Support main body or separated from the Support main body. 26. The wireless charging system of claim 25, wherein the power Supply circuit comprises a detection circuit, a Switch ing circuit, a control circuit and a power circuit; the power circuit is connected with the detection circuit, the Switching circuit and the control circuit for Supplying power, the detection circuit is electrically connected with each of the electrodes for detecting whether the electrodes are in contact with a conductive contact of a power receiving device; the switching circuit is electrically connected with each of the electrodes for switching on or switching off the power supplied to the electrodes; the control circuit is connected with the detection circuit and the switching circuit; wherein based on whether each of the electrodes is in contact with the conductive contact detected by the detection circuit, the control circuit is operable to send out a control signal to the Switching circuit so that each of the electrodes is con trolled to connect to or disconnect from the power cir cuit.
14 US 2015/ A1 Apr. 2, The wireless charging system of claim 26, wherein the Switching circuit comprises a positive Switching circuit and a negative Switching circuit which are simultaneously con nected with each of the electrodes; the detection circuit comprises a plurality of detection units, wherein each of the detection units is electrically connected with one of the electrodes; the positive Switching circuit comprises a plurality of posi tive switching units, wherein each of the positive switch ing units is electrically connected with one of the elec trodes; the negative Switching circuit comprises a plurality of negative Switching units, wherein each of the negative Switching units is electrically connected with one of the electrodes; the positive Switching unit and the negative Switching unit connected with the same electrode are controlled by the control circuit to be alternatively switched on or simul taneously switched off. 28. The wireless charging system of claim 21, wherein the power receiving device also comprise a power module elec trically connected with the conductive contacts; the power module comprises one or more of toy, game equipment, cell phone, battery, charger, handheld equipment, electric tool, power connector, electric cup, music player, camera, calcu lator, remote controller, video tape recorder, video player, fax machine, PDA beauty equipment, electric shaver, electric toothbrush, electric hair cutter, television, refrigerator. 29. The wireless charging system of claim 28, wherein the power receiving device also comprises a housing, and the conductive contacts are disposed on the housing; wherein the housing is also arranged with an interface module electrically connected with the conductive contacts. k k k k k
Gammalcode. Frame 1, Frame 2. drive signal. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Timing code.
 (19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 20160104.405A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0104405 A1 Fang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) DRIVE CIRCUIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(FSN JSO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,017,055 B1. H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006
 United States Patent USOO701.7055B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) HUB THAT CAN SUPPLY POWER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS ACTIVELY JP 20020945.45 A * 3/2002 : (75) Inventor:
United States Patent USOO701.7055B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: H0 (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2006 (54) HUB THAT CAN SUPPLY POWER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS ACTIVELY JP 20020945.45 A * 3/2002 : (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
(12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O104164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0104164 A1 YASUDA (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) CAMERA BODY (71) Applicant: PANASONIC CORPORATION, Osaka
(19) United States US 2015O104164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0104164 A1 YASUDA (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) CAMERA BODY (71) Applicant: PANASONIC CORPORATION, Osaka
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0234591 A1 Sanger et al. US 2016O234591 A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) MCROPHONE MODULE WITH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0234591 A1 Sanger et al. US 2016O234591 A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) MCROPHONE MODULE WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/ A1* 11/2004 Koda et al , 183
 (12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O128237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0128237 A1 SZEREMETA (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) SERVER WITH STORAGE DRIVE COOLING (52) U.S. Cl. SYSTEM
US 2016O128237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0128237 A1 SZEREMETA (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) SERVER WITH STORAGE DRIVE COOLING (52) U.S. Cl. SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.01.10403A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0110403 A1 Crutchfield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM FOR SHARED POWER SUPPLY IN COMPUTER
(19) United States US 2003.01.10403A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0110403 A1 Crutchfield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM FOR SHARED POWER SUPPLY IN COMPUTER
$26) 6, 2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun.
 (19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286639 A1 LASSMANN et al. US 20160286639A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MULT-FUNCTIONAL HIGH-CURRENT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286639 A1 LASSMANN et al. US 20160286639A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MULT-FUNCTIONAL HIGH-CURRENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004
 (19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Margalit et al. USOO6554621B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2003 (54) CABLE APPARATUS (75) Inventors: Yanki Margalit, Ramat Gan (IL); Dany Margalit, Ramat Gan
(12) United States Patent Margalit et al. USOO6554621B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2003 (54) CABLE APPARATUS (75) Inventors: Yanki Margalit, Ramat Gan (IL); Dany Margalit, Ramat Gan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OO63464A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0063464 A1 Akram et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) HIGH-SPEED DATA AND POWER SOURCE Publication Classification
US 2004OO63464A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0063464 A1 Akram et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) HIGH-SPEED DATA AND POWER SOURCE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0335343A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0335343 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN (52)
(19) United States US 2013 0335343A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0335343 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) DISPLAY DEVICE WITH INTEGRATED TOUCH SCREEN (52)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2. Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0128245A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0128245 A1 Inagaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) DISTANCE MEASUREMENT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010.0128245A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0128245 A1 Inagaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) DISTANCE MEASUREMENT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120162831A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0162831 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR (22) Filed: Dec. 26,
US 20120162831A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0162831 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR (22) Filed: Dec. 26,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109314A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109314 A1 Ku (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) HANDHELD CASE GRIPPER (76) Inventor: Man To Ku, Arcadia,
(19) United States US 2003.0109314A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109314 A1 Ku (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) HANDHELD CASE GRIPPER (76) Inventor: Man To Ku, Arcadia,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2. Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007
 United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
ED 302C A t 302B (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O141898A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/014 1898A1 Riphin (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CELL PHONE CHARGING SYSTEM Publication Classification
US 2016O141898A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/014 1898A1 Riphin (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CELL PHONE CHARGING SYSTEM Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2
 US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000
 US006058048A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54) FLASH MEMORY DEVICE USED ASA 56) References Cited BOOT-UP MEMORY IN A COMPUTER SYSTEM U.S. PATENT
US006058048A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54) FLASH MEMORY DEVICE USED ASA 56) References Cited BOOT-UP MEMORY IN A COMPUTER SYSTEM U.S. PATENT
United States Patent (19) Haines
 United States Patent (19) Haines 11 45 Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,697,107 Sep. 29, 1987 54) (75) (73) 21 22) (51) 52) (58) (56) FOUR-STATE I/O CONTROL CIRCUIT Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed:
United States Patent (19) Haines 11 45 Patent Number: Date of Patent: 4,697,107 Sep. 29, 1987 54) (75) (73) 21 22) (51) 52) (58) (56) FOUR-STATE I/O CONTROL CIRCUIT Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2
 US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080180 107A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0180107 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CABLE TESTER FOR STAGE LIGHTING ENVIRONMENT (75) Inventors: Robin
(19) United States US 20080180 107A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0180107 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CABLE TESTER FOR STAGE LIGHTING ENVIRONMENT (75) Inventors: Robin
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9426741B2 (12) United States Patent Wu et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 9.426,741 B2 Aug. 23, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) () (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING
USOO9426741B2 (12) United States Patent Wu et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: US 9.426,741 B2 Aug. 23, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) () (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) United States Patent
 US0088.12887B2 (12) United States Patent Liu et al. (54) ELECTRONIC DISPLAY DEVICE AUTOMATICALLY TURNS ON OR OFF ACCORDING TO WHETHER AUSERN FRONT OF THE DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Xu Liu, Shanghai (CN);
US0088.12887B2 (12) United States Patent Liu et al. (54) ELECTRONIC DISPLAY DEVICE AUTOMATICALLY TURNS ON OR OFF ACCORDING TO WHETHER AUSERN FRONT OF THE DISPLAY (75) Inventors: Xu Liu, Shanghai (CN);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 US 20170069991A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0069991 A1 HOmb0 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) ELECTRONIC APPARATUS H05K L/4 (2006.01) (71) Applicant:
US 20170069991A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0069991 A1 HOmb0 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) ELECTRONIC APPARATUS H05K L/4 (2006.01) (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140028097A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0028097 A1 Augur (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 30, 2014 (54) ELECTRICAL OUTLET ADAPTER WITH (52) U.S. Cl. AUTOMATIC
US 20140028097A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0028097 A1 Augur (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 30, 2014 (54) ELECTRICAL OUTLET ADAPTER WITH (52) U.S. Cl. AUTOMATIC
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,399,323 B1
 US0093.99323B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2016 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL PRINTING USPC... 425/470; 264/401, 497, 212, 308 STRUCTURE See application
US0093.99323B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2016 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL PRINTING USPC... 425/470; 264/401, 497, 212, 308 STRUCTURE See application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) United States Patent USOO7506087B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,506,087 B2 H0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR CONFIGURING A (56) References Cited PERPHERAL COMPONENT INTERCONNECT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O25O161A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0250161 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MONITORING SYSTEM FOR COLLECTION Publication Classification AND
(19) United States US 2010O25O161A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0250161 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MONITORING SYSTEM FOR COLLECTION Publication Classification AND
(12) United States Patent
 USOO853.8494B2 (12) United States Patent Hsu (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,538,494 B2 Sep. 17, 2013 (54) MOBILE PHONE AND METHOD FOR TRANSFERRING BATTERY POWER OF THE MOBILE PHONE (75) Inventor:
USOO853.8494B2 (12) United States Patent Hsu (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,538,494 B2 Sep. 17, 2013 (54) MOBILE PHONE AND METHOD FOR TRANSFERRING BATTERY POWER OF THE MOBILE PHONE (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. streaming media server
 (19) United States US 201401 15115A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0115115 A1 Kuang (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PLAYING Publication Classification STREAMING
(19) United States US 201401 15115A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0115115 A1 Kuang (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR PLAYING Publication Classification STREAMING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
SNN. United States Patent (19) Gibbs N YN N N R4 W44 CNACCS1. 11) 4,257,659 (45) Mar. 24, to insure proper polarization when a polarized plug is
 United States Patent (19) Gibbs 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR WITH SAFETY COVER MEANS 75) Inventor: Ronald D. Gibbs, Naperville, Ill. 73 Assignee: Belden Corporation, Geneva, Ill. 21 Appl. No.: 80,109 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Gibbs 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR WITH SAFETY COVER MEANS 75) Inventor: Ronald D. Gibbs, Naperville, Ill. 73 Assignee: Belden Corporation, Geneva, Ill. 21 Appl. No.: 80,109 22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 20130244475A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0244475A1 Sayadi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 19, 2013 (54) WALL OUTLET WITH RETRACTABLE USB (52) U.S. Cl.
US 20130244475A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0244475A1 Sayadi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 19, 2013 (54) WALL OUTLET WITH RETRACTABLE USB (52) U.S. Cl.
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
- NETWORK / SES A REMOTE
 (19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1
 USOO664275OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1 Egan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) SEQUENCING CIRCUIT FOR APPLYING A 5,886,561. A 3/1999 Eitan et al.... 327/408 HIGHEST
USOO664275OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,642,750 B1 Egan (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 2003 (54) SEQUENCING CIRCUIT FOR APPLYING A 5,886,561. A 3/1999 Eitan et al.... 327/408 HIGHEST
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO731.9457B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,319.457 B2 Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD OF SCROLLING WINDOW (56) References Cited SCREEN BY MEANS OF CONTROLLING
(12) United States Patent USOO731.9457B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,319.457 B2 Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD OF SCROLLING WINDOW (56) References Cited SCREEN BY MEANS OF CONTROLLING
United States Patent (19) Jones et al.
 United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2
 US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0231.630A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0231630 A1 Dannowski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) ADDRESS MAPPING IN VIRTUALIZED (52) U.S.
(19) United States US 2011 0231.630A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0231630 A1 Dannowski et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2011 (54) ADDRESS MAPPING IN VIRTUALIZED (52) U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,679,316 B2
 USOO7679.316B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,679,316 B2 Guthrie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2010 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 6,21 1,649 B1 4/2001 Matsuda... 320,115 CONTROLLING
USOO7679.316B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,679,316 B2 Guthrie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2010 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 6,21 1,649 B1 4/2001 Matsuda... 320,115 CONTROLLING
... (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. (19) United States. icopying unit d:
 (19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2003.01.01188A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0101188A1 Teng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR A NETWORK COPYING SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0156354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0156354 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2003 (54) DISK CLAMP OF HARD DISK DRIVE (75) Inventor: Do-Wan Kim,
(19) United States US 2003.0156354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0156354 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2003 (54) DISK CLAMP OF HARD DISK DRIVE (75) Inventor: Do-Wan Kim,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080 136777A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/013.6777 A1 Lu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2008 (54) SWEAT-FREE MOUSE DEVICE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080 136777A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/013.6777 A1 Lu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2008 (54) SWEAT-FREE MOUSE DEVICE Publication Classification
contact United States Patent (19) (11) 3,967,257 Hager (45) June 29, 1976 CURRENT MONITOR LOAD DEVICE 73) Assignee: Westinghouse Electric Corporation,
 United States Patent (19) Hager 54 CURRENT MNITR CIRCUITS (75) Inventor: Robert E. Hager, Pittsburgh, Pa. 73) Assignee: Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Pittsburgh, Pa. 22 Filed: Jan. 7, 1975 (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Hager 54 CURRENT MNITR CIRCUITS (75) Inventor: Robert E. Hager, Pittsburgh, Pa. 73) Assignee: Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Pittsburgh, Pa. 22 Filed: Jan. 7, 1975 (21) Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0186073 A1 Bryan et al. US 201701 86.073A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SHOPPING CART DISPLAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0186073 A1 Bryan et al. US 201701 86.073A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SHOPPING CART DISPLAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0231580 A1 Hsu US 20080231580A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) LCD DEVICE DRIVEN BY PRE-CHARGE PROCEDURE (76) Inventor:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0231580 A1 Hsu US 20080231580A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2008 (54) LCD DEVICE DRIVEN BY PRE-CHARGE PROCEDURE (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 200800 13292A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0013292 A1 SlikkerVeer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008 (54) ROLLABLE ELECTRONIC PANEL DEVICE (86). PCT
US 200800 13292A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0013292 A1 SlikkerVeer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008 (54) ROLLABLE ELECTRONIC PANEL DEVICE (86). PCT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Tan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2014
 USOO869727OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,697.270 B2 Tan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2014 (54) ENERGY STORAGE DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC... 429/99: 429/100; 429/120 (75) Inventors:
USOO869727OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,697.270 B2 Tan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2014 (54) ENERGY STORAGE DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl. USPC... 429/99: 429/100; 429/120 (75) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0019726A1 Park et al. US 2006OO19726A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LOCKINGAPPARATUS OF SWING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0019726A1 Park et al. US 2006OO19726A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LOCKINGAPPARATUS OF SWING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060041739A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0041739 A1 Iwakura et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2006 (54) MEMORY DUMP GENERATION WITH (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20060041739A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0041739 A1 Iwakura et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2006 (54) MEMORY DUMP GENERATION WITH (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0345775 A1 Chien US 20150345775A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 3, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) MULTIPLE SURFACE LED LIGHT Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0345775 A1 Chien US 20150345775A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 3, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) MULTIPLE SURFACE LED LIGHT Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004.0029581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0029581 A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE PHONE BEING SEPARATED INTO (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004.0029581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0029581 A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE PHONE BEING SEPARATED INTO (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140355048A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0355048A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF MOBILE Publication Classification
US 20140355048A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0355048A1 KANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. KM (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 US 200900.58834A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0058834 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR INPUTTING (30) Foreign Application
US 200900.58834A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0058834 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR INPUTTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. combiner box. A/D Data Processing AID 2OO 3O1 203.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0237058 A1 McClintock et al. US 20060237058A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) DIRECT CURRENT COMBINER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0237058 A1 McClintock et al. US 20060237058A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) DIRECT CURRENT COMBINER
