Babbage Analytical Machine
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Clark
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Von Neumann Machine
2 Babbage Analytical Machine The basis of modern computers is proposed by a professor of mathematics at Cambridge University named Charles Babbage ( ). He has invented a mechanical machine known as differential machine. This mechanical device can only add and subtract, designed to calculate the number of charts that are useful in piloting. This engine is the first ever computer that has four components: Store (memory) Contains 1000 words of 50 decimal digits which is used to hold variables and results Memory unit Receive operand from store, add, subtract, multiply or divide and will return the result to store Input punch cards Output output punch cards
3 Konrad Zuse German Engineering Student Create an automatic calculation machine which uses electromagnetic currents
4 John Atanasoff From College of Iowa States Create Atanasoff Machine Use binary arithmetic and capacitors to store memory But.. This machine is not working because of technology constraints
5 Howard Aiken Create computer for general use The extended of Babbage Machine Mark 1 Completed in Havard (1944) Use 72 words Input/Output punched on tape
6 ENIAC ENIAC is stand for Electronic Numerical Integrated And Computer The first ever electronic computer Used to understand the secret codes used by the German army but it was never completed Organization vacuum tube 1500 relay Weight 30 tan Power 140 KW 20 register each one capable of handling up to 10 digits decimal number 6000 multi position switch Many cables and sockets
7 Eckert & Arithmetic ENIAC
8 Motivation from ENIAC EDSAC The first electronic computer operating properly (1945) Build at University of Cambridge, UK by Maurice Wilkes JOHNIAC Rand Company ILLIAC University of Illinois MANIAC Built at Alanos Lab WEIZAC Built at Institute of Weizmann, Israel EDVAC unsuccessful
9 Von Neumann Machine John Von Neumann research of ENIAC machine ENIAC Built IAS another version of EDVAC Improvement made: Use the binary number system in parallel. Use the concept of stored programs Von Neumann bottleneck referred to: The separation between CPU and memory The limited throughput between CPU and memory compared to the amount of memory. In modern computers, throughput is much smaller that the rate at which CPU can work. This seriously limits the effective processing speed when CPU is required to perform minimal processing on large amount of data. The CPU is forced to wait for needed data to be transferred to or from memory. The bottleneck has become more of a problem whose severity increases with every newer generation of CPU.
10 Von Neumann Machine 5 important parts Memory Control Unit Arithmetic and Logic Unit Input Output
11 Bus System Direct connection of each component in a computer Began to be used on the PDP-8 machine Consist of parallel wires are covered with copper
12 Bus System Type of buses: System Bus Connect all the chips that form a computer system Local bus Special bus that connecting 2 components directly Example: connection between the microprocessor and co-processor Internal Bus Connecting components in one chip
13 Bus System System bus Register Internal Bus ALU Memory I/O Coprocessor Local bus
14 Bus Structure Although there are many different bus designs, on any bus the lines can be classified into three functional groups: data, address and control lines. Data lines: Provide a path for moving data among system modules. These lines, collectively are call data bus. The data bus may consist of , 128 or even more separate lines. The number of lines referred to as the width of the data bus.
15 Bus Structure Address Line: Used to designate the source or destination of the data on the data bus. Example: if the processor wishes to read a word of data from memory, it put the address of the desired word on the address lines. Clearly, the width of the address bus determines the maximum possible memory capacity of the system. Furthermore, the address lines are generally also used to address I/O ports.
16 Bus structure Control line: Used to control the access to and the used of the data and address line. Because the data and address line are shared by all components, there must be a means of controlling their use. Control signal transmit both command and timing information among system modules. Typical control line include: memory write, memory read, I/O write, I/O read, Transfer ACK, Bus request, bus grant, clock, reset, etc
17 Bus System Omnibus Connect all components use only one bus CPU Ingatan Konsol I/O
18 Bus Operation Master the device that gives instructions Slave the device that receive instructions Example: CPU directs disk controller to read data Master CPU Slave disk controller Disk controller directs the memory to receive a word from disk drive Master disk controller Slave memory
19 Bus Operations Bus Driver Used to strengthen the signal to be sent Bus Receiver Used to strengthen the received signal Transceiver Chip consisting bus driver and bus receiver
20 Bus System 3 important types of bus Data Bus Transfer data from one place to another Addressing Bus State memory address such as memory address, address of I/O peripherals Control Bus Carrying control signals such as signal for read or write
21 Bus System CPU MEMORY I/O Control Bus Address Bus Bus System Data Bus
22 Bus Synchronization Bus Synchronization: Bus driven by a crystal oscillator The crystal oscillator will produce a signal wave 5 to 50 MHz
23 Bus Arbitration Mechanism for determining which device to use the bus at the time 2 mechanism: Centralized requires hardware that will grant the bus to one of the requesting devices. This hardware can be part of the CPU or it can be a separate device on the motherboard. Distributed there isn t an arbiter, so the devices have to decide who goes next. This makes the devices more complicated, but saves the expense of having an arbiter. Arbitration: Device arbitration mechanism In CPU Chip Also in separated chip
24 Operation of Bus Arbitration The arbitration received a bus request Take over the bus and end the recognition yes Arbitration was a recognition in the bus line recognition Nearest device will check whether there is a bus request Send acknowledgment to the device next to his no
25 Operation of Bus Arbitration Arbitration Device 1 Device 2 Device 3 This arbitration mechanism is called daisy chain
26 Bus Arbitration Disadvantage of daisy chain The remote device low priority Other technique Each device is given priority repectively High priority device will make revisions before the other device For devices that have the same priority Used daisy chain
27 Distributed Bus Arbitration Does not need arbitration Use different bus requests 1 device 1 bus Each line has its own priorities High priority was given first review
28 Multi-programming and Input/Output Processor Execution of several programs in memory is done at the same time I/O Processor (IOP) Handle I/O device Modify the received data to a format adapted to the CPU data After IOP processing is complete, it will interrupt the CPU CPU stop doing his duties and perform operations duties for the IOP
29 Input Output Processor IOP for the IBM Machine known as channel 3 types of channel Multiplexor Connected to several devices that slow or medium speed. Selector Handle only one device with high-speed data transfer is done byte by byte Blocked-Multiplexor Provide facilities to handle multiple high-speed device transfer I/O performed by block.
30 Microcomputer Use a single bus Processor Main memory DMA-Direct Memory Access DMA controller IO Controller IO device
31 DMA Direct Memory Access Fully controlled by the CPU DMA request from the CPU to control bus If the CPU allows: It will take over the bus Do data transfer between the I/O and memory without the CPU DMA Controller Intel 8237A Interfaces to the 80x86 family of processors and to DRAM memory to provide a DMA capability.
32 DMA Direct Memory Access The DMA mechanism can be configured in a variety of ways. Some possible ways are; Single bus, detached DMA The DMA module, acting as surrogate processor, uses programmed I/O to exchange data between memory and an I/O module through DMA This configuration may inexpensive, is clearly inefficient. Single bus, integrated DMA-I/O The DMA may actually a part of an I/O module using an I/O bus. This reduces the number of I/O interfaces in the DMA module to one and provides for an easily expandable configuration. I/O Bus. The DMA module shares with the processor and memory is used by the DMA module only to exchange data with memory. The exchange of data between DMA and I/O modules takes place of the system bus. Turn to page 256 (Stalling, Eight Edition)
33 Other Bus EISA Extended Industry Standard Architecture To handle data size 32 bit VESA Video Electronics Standard Association Disk and monitor connected directly to the microprocessor SCSI Small Computer System Interface Connect the I/O device to a PC PCI Peripheral Control Interface
34 PCI Peripheral Control Interface Very popular with high bandwidth processor-independent bus. Deliver better system performance for high speed I/O subsystems. Designed to meet economically the I/O requirements of modern system. It requires very few chips to implement and supports other buses attached to the PCI Bus. Provides 2 type of busses 32 bit bus 64 bit bus Can support 1 processor or multiprocessor. The structure of PCI can be divided into the following functional groups: System pins. Address and data pins Interface control pins. Arbitration pins Error reporting pins.
Computer System architectures
 CSC 203 1.5 Computer System Architecture Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science University of Sri Jayewardenepura 1 Historical Developments 2 Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation-
CSC 203 1.5 Computer System Architecture Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science University of Sri Jayewardenepura 1 Historical Developments 2 Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation-
Computer Organization CS 206T
 Computer Organization CS 206T Topics Introduction Historical Background Structure & Function System Interconnection 2 1. Introduction Why study computer organization and architecture? Design better programs,
Computer Organization CS 206T Topics Introduction Historical Background Structure & Function System Interconnection 2 1. Introduction Why study computer organization and architecture? Design better programs,
Chapter 1 Basic Computer Organization
 Chapter 1 Basic Computer Organization Course Outcome (CO) CO1 Explain the basic principles of modern computer systems organization Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
Chapter 1 Basic Computer Organization Course Outcome (CO) CO1 Explain the basic principles of modern computer systems organization Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering
ENIAC - background. ENIAC - details. Structure of von Nuemann machine. von Neumann/Turing Computer Architecture
 168 420 Computer Architecture Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables
168 420 Computer Architecture Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables
Computers in Engineering COMP 208. A Brief History. Mechanical Calculators. A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker
 Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208
 Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computers in Engineering COMP 208 A Historic Perspective Michael A. Hawker Sept 4th, 2007 Computers in Engineering 1 A Brief History Abacus considered first mechanical computing device Used beads and rods
Computer Evolution. Budditha Hettige. Department of Computer Science
 Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science Computer Generation 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Computer Evolution. Computer Generation. The Zero Generation (3) Charles Babbage. First Generation- Time Line
 Computer Generation Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Computer Generation Computer Evolution Budditha Hettige Department of Computer Science 1. Zeroth generation- Mechanical Computers (1642-1940) 2. First generation - Vacuum Tubes (1940-1955) 3. Second Generation
Buses. Disks PCI RDRAM RDRAM LAN. Some slides adapted from lecture by David Culler. Pentium 4 Processor. Memory Controller Hub.
 es > 100 MB/sec Pentium 4 Processor L1 and L2 caches Some slides adapted from lecture by David Culler 3.2 GB/sec Display Memory Controller Hub RDRAM RDRAM Dual Ultra ATA/100 24 Mbit/sec Disks LAN I/O Controller
es > 100 MB/sec Pentium 4 Processor L1 and L2 caches Some slides adapted from lecture by David Culler 3.2 GB/sec Display Memory Controller Hub RDRAM RDRAM Dual Ultra ATA/100 24 Mbit/sec Disks LAN I/O Controller
Chapter 2. Perkembangan Komputer
 Chapter 2 Perkembangan Komputer 1 ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables for weapons Started 1943 Finished 1946
Chapter 2 Perkembangan Komputer 1 ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania Trajectory tables for weapons Started 1943 Finished 1946
Welcome to COS151! 1.1
 Welcome to COS151! Title: Introduction to Computer Science Course website: https://cs.up.ac.za/admin/courses/cos151 Find the study guide there Announcements Assignments (download & upload) Brief overview
Welcome to COS151! Title: Introduction to Computer Science Course website: https://cs.up.ac.za/admin/courses/cos151 Find the study guide there Announcements Assignments (download & upload) Brief overview
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Computer Architecture Hardware INFO 2603 Platform Technologies Week 1: 04-Sept-2018 Computer architecture refers to the overall design of the physical parts of a computer. It examines:
Computer Architecture Computer Architecture Hardware INFO 2603 Platform Technologies Week 1: 04-Sept-2018 Computer architecture refers to the overall design of the physical parts of a computer. It examines:
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition. Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance Analytical Engine ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 8 th Edition Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance Analytical Engine ENIAC - background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert
c) Byte Arrangement: The arrangement of bytes in a cell (word). There are two arrangements:
 1. Main Memory a) Memory is a component of the computer that saves instructions and data. i. Types of memory: ROM, RAM, Associate Memory and Cache Memory etc. (see point f) ii. Basic Unit: Bit which uses
1. Main Memory a) Memory is a component of the computer that saves instructions and data. i. Types of memory: ROM, RAM, Associate Memory and Cache Memory etc. (see point f) ii. Basic Unit: Bit which uses
Computer & Microprocessor Architecture HCA103
 Computer & Microprocessor Architecture HCA103 Computer Evolution and Performance UTM-RHH Slide Set 2 1 ENIAC - Background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania
Computer & Microprocessor Architecture HCA103 Computer Evolution and Performance UTM-RHH Slide Set 2 1 ENIAC - Background Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer Eckert and Mauchly University of Pennsylvania
STANDARD I/O INTERFACES
 STANDARD I/O INTERFACES The processor bus is the bus defied by the signals on the processor chip itself. Devices that require a very high-speed connection to the processor, such as the main memory, may
STANDARD I/O INTERFACES The processor bus is the bus defied by the signals on the processor chip itself. Devices that require a very high-speed connection to the processor, such as the main memory, may
Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was
 1 Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was used extensively and is still in use today, was not
1 Fundamentals of Digital Computers The mechanical computer age began with the advent of the abacus in 500 B.C by Babylonians. The abacus, which was used extensively and is still in use today, was not
Evolution of the Computer
 Evolution of the Computer Janaka Harambearachchi (Engineer/Systems Development) Zeroth Generation- Mechanical 1. Blaise Pascal -1642 Mechanical calculator only perform + - 2. Von Leibiniz -1672 Mechanical
Evolution of the Computer Janaka Harambearachchi (Engineer/Systems Development) Zeroth Generation- Mechanical 1. Blaise Pascal -1642 Mechanical calculator only perform + - 2. Von Leibiniz -1672 Mechanical
Corso di Biblioteche Digitali
 Corso di Biblioteche Digitali Vittore Casarosa casarosa@isti.cnr.it tel. 050-621 3115 cell. 348-397 2168 Skype vittore1201 Ricevimento dopo la lezione o per appuntamento Valutazione finale 70% esame orale
Corso di Biblioteche Digitali Vittore Casarosa casarosa@isti.cnr.it tel. 050-621 3115 cell. 348-397 2168 Skype vittore1201 Ricevimento dopo la lezione o per appuntamento Valutazione finale 70% esame orale
An Incomplete History of Computation
 An Incomplete History of Computation Charles Babbage 1791-1871 Lucasian Professor of Mathematics, Cambridge University, 1827-1839 First computer designer Ada Lovelace 1815-1852 First computer programmer
An Incomplete History of Computation Charles Babbage 1791-1871 Lucasian Professor of Mathematics, Cambridge University, 1827-1839 First computer designer Ada Lovelace 1815-1852 First computer programmer
Input/Output Problems. External Devices. Input/Output Module. I/O Steps. I/O Module Function Computer Architecture
 168 420 Computer Architecture Chapter 6 Input/Output Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In different formats All slower than CPU
168 420 Computer Architecture Chapter 6 Input/Output Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In different formats All slower than CPU
Chapter 3. Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection. Yonsei University
 Chapter 3 Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection Contents Computer Components Computer Function Interconnection Structures Bus Interconnection PCI 3-2 Program Concept Computer components
Chapter 3 Top Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection Contents Computer Components Computer Function Interconnection Structures Bus Interconnection PCI 3-2 Program Concept Computer components
RISC Architecture Ch 12
 RISC Ch 12 Some History Instruction Usage Characteristics Large Register Files Register Allocation Optimization RISC vs. CISC 1 General purpose computer Howard Aiken, Mark I, 1944 relays, 17m long, 2.4m
RISC Ch 12 Some History Instruction Usage Characteristics Large Register Files Register Allocation Optimization RISC vs. CISC 1 General purpose computer Howard Aiken, Mark I, 1944 relays, 17m long, 2.4m
Bus System. Bus Lines. Bus Systems. Chapter 8. Common connection between the CPU, the memory, and the peripheral devices.
 Bus System Chapter 8 CSc 314 T W Bennet Mississippi College 1 CSc 314 T W Bennet Mississippi College 3 Bus Systems Common connection between the CPU, the memory, and the peripheral devices. One device
Bus System Chapter 8 CSc 314 T W Bennet Mississippi College 1 CSc 314 T W Bennet Mississippi College 3 Bus Systems Common connection between the CPU, the memory, and the peripheral devices. One device
Overview of a computer
 Overview of a computer One marks 1. What is von Neumann concept also called as? Stored memory or stored program concept. 2. Who is the father of computer Charles Babbage 3. What is a computer? It is an
Overview of a computer One marks 1. What is von Neumann concept also called as? Stored memory or stored program concept. 2. Who is the father of computer Charles Babbage 3. What is a computer? It is an
Computer Systems Architecture
 Computer Systems Architecture Guoping Qiu School of Computer Science The University of Nottingham http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~qiu 1 The World of Computers Computers are everywhere Cell phones Game consoles
Computer Systems Architecture Guoping Qiu School of Computer Science The University of Nottingham http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~qiu 1 The World of Computers Computers are everywhere Cell phones Game consoles
The History of Computers
 The History of Computers First Generation Computers The first electronic computer was designed at Iowa State between 1939-1942 The Atanasoff-Berry Computer used the binary system (1 s and 0 s) Contained
The History of Computers First Generation Computers The first electronic computer was designed at Iowa State between 1939-1942 The Atanasoff-Berry Computer used the binary system (1 s and 0 s) Contained
Microprocessors I MICROCOMPUTERS AND MICROPROCESSORS
 Microprocessors I Outline of the Lecture Microcomputers and Microprocessors Evolution of Intel 80x86 Family Microprocessors Binary and Hexadecimal Number Systems MICROCOMPUTERS AND MICROPROCESSORS There
Microprocessors I Outline of the Lecture Microcomputers and Microprocessors Evolution of Intel 80x86 Family Microprocessors Binary and Hexadecimal Number Systems MICROCOMPUTERS AND MICROPROCESSORS There
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Context and Motivation To better understand a software system, it is mandatory understand two elements: - The computer as a basic building block for the application - The operating
Computer Architecture Context and Motivation To better understand a software system, it is mandatory understand two elements: - The computer as a basic building block for the application - The operating
Technology in Action
 Technology in Action Chapter 9 Behind the Scenes: A Closer Look at System Hardware 1 Binary Language Computers work in binary language. Consists of two numbers: 0 and 1 Everything a computer does is broken
Technology in Action Chapter 9 Behind the Scenes: A Closer Look at System Hardware 1 Binary Language Computers work in binary language. Consists of two numbers: 0 and 1 Everything a computer does is broken
6.823 Computer System Architecture
 6.823 Computer System Architecture http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 The emphasis in this course is on architectural mechanisms and not on quantitative performance evaluation. - Evolution of instruction
6.823 Computer System Architecture http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 The emphasis in this course is on architectural mechanisms and not on quantitative performance evaluation. - Evolution of instruction
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. 1 Part 2: Introduction to Computer Architecture Our goal: have a basic look at architecture of computer, its functions and structure, its history and
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. 1 Part 2: Introduction to Computer Architecture Our goal: have a basic look at architecture of computer, its functions and structure, its history and
Generic Model of I/O Module Interface to CPU and Memory Interface to one or more peripherals
 William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition Chapter 7 Input/Output Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 7 th Edition Chapter 7 Input/Output Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In
Computer Architecture CS 355 Busses & I/O System
 Computer Architecture CS 355 Busses & I/O System Text: Computer Organization & Design, Patterson & Hennessy Chapter 6.5-6.6 Objectives: During this class the student shall learn to: Describe the two basic
Computer Architecture CS 355 Busses & I/O System Text: Computer Organization & Design, Patterson & Hennessy Chapter 6.5-6.6 Objectives: During this class the student shall learn to: Describe the two basic
Figure 1-1. A multilevel machine.
 1 INTRODUCTION 1 Level n Level 3 Level 2 Level 1 Virtual machine Mn, with machine language Ln Virtual machine M3, with machine language L3 Virtual machine M2, with machine language L2 Virtual machine M1,
1 INTRODUCTION 1 Level n Level 3 Level 2 Level 1 Virtual machine Mn, with machine language Ln Virtual machine M3, with machine language L3 Virtual machine M2, with machine language L2 Virtual machine M1,
Chapter 1 : Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction A Microprocessor is a multipurpose programmable, clock driven, register based electronic device that reads binary instructions from a storage device called memory,
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction A Microprocessor is a multipurpose programmable, clock driven, register based electronic device that reads binary instructions from a storage device called memory,
Overview of Computer Organization. Chapter 1 S. Dandamudi
 Overview of Computer Organization Chapter 1 S. Dandamudi Outline Introduction Basic Terminology and Notation Views of computer systems User s view Programmer s view Advantages of high-level languages Why
Overview of Computer Organization Chapter 1 S. Dandamudi Outline Introduction Basic Terminology and Notation Views of computer systems User s view Programmer s view Advantages of high-level languages Why
6.823 Computer System Architecture. Course Information
 6.823 Computer System Architecture http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 6.823, L1-1 The emphasis in this course is on architectural mechanisms and not on quantitative performance evaluation. Lecturer: TA s:
6.823 Computer System Architecture http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 6.823, L1-1 The emphasis in this course is on architectural mechanisms and not on quantitative performance evaluation. Lecturer: TA s:
SYSTEM BUS AND MOCROPROCESSORS HISTORY
 SYSTEM BUS AND MOCROPROCESSORS HISTORY Dr. M. Hebaishy momara@su.edu.sa http://colleges.su.edu.sa/dawadmi/fos/pages/hebaishy.aspx Digital Logic Design Ch1-1 SYSTEM BUS The CPU sends various data values,
SYSTEM BUS AND MOCROPROCESSORS HISTORY Dr. M. Hebaishy momara@su.edu.sa http://colleges.su.edu.sa/dawadmi/fos/pages/hebaishy.aspx Digital Logic Design Ch1-1 SYSTEM BUS The CPU sends various data values,
Overview of Computer Organization. Outline
 Overview of Computer Organization Chapter 1 S. Dandamudi Outline Introduction Basic Terminology and Notation Views of computer systems User s view Programmer s view Advantages of high-level languages Why
Overview of Computer Organization Chapter 1 S. Dandamudi Outline Introduction Basic Terminology and Notation Views of computer systems User s view Programmer s view Advantages of high-level languages Why
Chapter Seven Morgan Kaufmann Publishers
 Chapter Seven Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be
Chapter Seven Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be
Computer Systems Organization
 The IAS (von Neumann) Machine Computer Systems Organization Input Output Equipment Stored Program concept Main memory storing programs and data ALU operating on binary data Control unit interpreting instructions
The IAS (von Neumann) Machine Computer Systems Organization Input Output Equipment Stored Program concept Main memory storing programs and data ALU operating on binary data Control unit interpreting instructions
EC 6504 Microprocessor and Microcontroller. Unit II System Bus Structure
 EC 6504 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Unit II 8086 System Bus Structure Syllabus: 8086 Signals Basic Configurations System bus timing System Design using 8086 IO Programming Introduction to multiprogramming
EC 6504 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Unit II 8086 System Bus Structure Syllabus: 8086 Signals Basic Configurations System bus timing System Design using 8086 IO Programming Introduction to multiprogramming
7/28/ Prentice-Hall, Inc Prentice-Hall, Inc Prentice-Hall, Inc Prentice-Hall, Inc Prentice-Hall, Inc.
 Technology in Action Technology in Action Chapter 9 Behind the Scenes: A Closer Look a System Hardware Chapter Topics Computer switches Binary number system Inside the CPU Cache memory Types of RAM Computer
Technology in Action Technology in Action Chapter 9 Behind the Scenes: A Closer Look a System Hardware Chapter Topics Computer switches Binary number system Inside the CPU Cache memory Types of RAM Computer
The Nios II Family of Configurable Soft-core Processors
 The Nios II Family of Configurable Soft-core Processors James Ball August 16, 2005 2005 Altera Corporation Agenda Nios II Introduction Configuring your CPU FPGA vs. ASIC CPU Design Instruction Set Architecture
The Nios II Family of Configurable Soft-core Processors James Ball August 16, 2005 2005 Altera Corporation Agenda Nios II Introduction Configuring your CPU FPGA vs. ASIC CPU Design Instruction Set Architecture
THE MICROCOMPUTER SYSTEM CHAPTER - 2
 THE MICROCOMPUTER SYSTEM CHAPTER - 2 20 2.1 GENERAL ASPECTS The first computer was developed using vacuum tubes. The computers thus developed were clumsy and dissipating more power. After the invention
THE MICROCOMPUTER SYSTEM CHAPTER - 2 20 2.1 GENERAL ASPECTS The first computer was developed using vacuum tubes. The computers thus developed were clumsy and dissipating more power. After the invention
Computer Science 146. Computer Architecture
 Computer Science 46 Computer Architecture Spring 24 Harvard University Instructor: Prof dbrooks@eecsharvardedu Lecture 22: More I/O Computer Science 46 Lecture Outline HW5 and Project Questions? Storage
Computer Science 46 Computer Architecture Spring 24 Harvard University Instructor: Prof dbrooks@eecsharvardedu Lecture 22: More I/O Computer Science 46 Lecture Outline HW5 and Project Questions? Storage
William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved.
 + William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved. 2 + Chapter 3 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection
+ William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 th Edition 2016 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All rights reserved. 2 + Chapter 3 A Top-Level View of Computer Function and Interconnection
CREATED BY M BILAL & Arslan Ahmad Shaad Visit:
 CREATED BY M BILAL & Arslan Ahmad Shaad Visit: www.techo786.wordpress.com Q1: Define microprocessor? Short Questions Chapter No 01 Fundamental Concepts Microprocessor is a program-controlled and semiconductor
CREATED BY M BILAL & Arslan Ahmad Shaad Visit: www.techo786.wordpress.com Q1: Define microprocessor? Short Questions Chapter No 01 Fundamental Concepts Microprocessor is a program-controlled and semiconductor
CHAPTER 1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 15 1.5 Historical Development 16 1.5.1 Generation
CHAPTER 1 Introduction 1.1 Overview 1 1.2 The Main Components of a Computer 3 1.3 An Example System: Wading through the Jargon 4 1.4 Standards Organizations 15 1.5 Historical Development 16 1.5.1 Generation
Computer Organization ECE514. Chapter 5 Input/Output (9hrs)
 Computer Organization ECE514 Chapter 5 Input/Output (9hrs) Learning Outcomes Course Outcome (CO) - CO2 Describe the architecture and organization of computer systems Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge
Computer Organization ECE514 Chapter 5 Input/Output (9hrs) Learning Outcomes Course Outcome (CO) - CO2 Describe the architecture and organization of computer systems Program Outcome (PO) PO1 Apply knowledge
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture
 Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
Chapter 2 Logic Gates and Introduction to Computer Architecture 2.1 Introduction The basic components of an Integrated Circuit (IC) is logic gates which made of transistors, in digital system there are
COMS 1003 Fall Introduction to Computer Programming in C. History & Computer Organization. September 15 th
 COMS 1003 Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Programming in C History & Computer Organization September 15 th What's Ahead Some computer history Introduction to major players in the development of hardware
COMS 1003 Fall 2005 Introduction to Computer Programming in C History & Computer Organization September 15 th What's Ahead Some computer history Introduction to major players in the development of hardware
INPUT-OUTPUT ORGANIZATION
 INPUT-OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Peripheral Devices: The Input / output organization of computer depends upon the size of computer and the peripherals connected to it. The I/O Subsystem of the computer, provides
INPUT-OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Peripheral Devices: The Input / output organization of computer depends upon the size of computer and the peripherals connected to it. The I/O Subsystem of the computer, provides
Organisasi Sistem Komputer
 LOGO Organisasi Sistem Komputer OSK 5 Input Output 1 1 PT. Elektronika FT UNY Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In different formats
LOGO Organisasi Sistem Komputer OSK 5 Input Output 1 1 PT. Elektronika FT UNY Input/Output Problems Wide variety of peripherals Delivering different amounts of data At different speeds In different formats
1: History, Generation & Classification. Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University
 1: History, Generation & Classification Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University History Computer originally (17 th century) meant someone who computes Only in the 20 th century it was associated
1: History, Generation & Classification Shobhanjana Kalita, Dept. of CSE, Tezpur University History Computer originally (17 th century) meant someone who computes Only in the 20 th century it was associated
Chapter One. Computers in Context
 Chapter One Computers in Context After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Characterize what a computer is and what it does Describe several ways computers play a critical role in modern life
Chapter One Computers in Context After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Characterize what a computer is and what it does Describe several ways computers play a critical role in modern life
Computer Architecture. Prologue. Topics Computer Architecture. Computer Organization. Organization vs. Architecture. History of Computers
 Computer Architecture Prologue 1 Topics Computer Architecture Computer Organization Organization vs. Architecture History of Computers Generations of Computers Moore s Law 2 Computer Architecture (1) Definition?
Computer Architecture Prologue 1 Topics Computer Architecture Computer Organization Organization vs. Architecture History of Computers Generations of Computers Moore s Law 2 Computer Architecture (1) Definition?
machine cycle, the CPU: (a) Fetches an instruction, (b) Decodes the instruction, (c) Executes the instruction, and (d) Stores the result.
 Central Processing Unit (CPU) A processor is also called the CPU, and it works hand in hand with other circuits known as main memory to carry out processing. The CPU is the "brain" of the computer; it
Central Processing Unit (CPU) A processor is also called the CPU, and it works hand in hand with other circuits known as main memory to carry out processing. The CPU is the "brain" of the computer; it
1. Define Peripherals. Explain I/O Bus and Interface Modules. Peripherals: Input-output device attached to the computer are also called peripherals.
 1. Define Peripherals. Explain I/O Bus and Interface Modules. Peripherals: Input-output device attached to the computer are also called peripherals. A typical communication link between the processor and
1. Define Peripherals. Explain I/O Bus and Interface Modules. Peripherals: Input-output device attached to the computer are also called peripherals. A typical communication link between the processor and
History of Electronic Computers
 1 / 28 History of Electronic Computers 1642 1945 Mechanical Era 1946 Electronic Age: divided into 4/5 generations 2 / 28 Key Developments/Relationships History Electromechanical Electronic George Stibitz
1 / 28 History of Electronic Computers 1642 1945 Mechanical Era 1946 Electronic Age: divided into 4/5 generations 2 / 28 Key Developments/Relationships History Electromechanical Electronic George Stibitz
Chronological History of the Pre-Computer Developments
 500 B. C. Abacus 1621 Slide Rule 1623 Schickard s Adding Machine (Germany) 1642 Pascal s Adding Machine (France) 1673 Leibniz Calculator (Germany) 1804 Jacquard Loom and Punch Cards 1822 Babbage s Difference
500 B. C. Abacus 1621 Slide Rule 1623 Schickard s Adding Machine (Germany) 1642 Pascal s Adding Machine (France) 1673 Leibniz Calculator (Germany) 1804 Jacquard Loom and Punch Cards 1822 Babbage s Difference
IO System. CP-226: Computer Architecture. Lecture 25 (24 April 2013) CADSL
 IO System Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
IO System Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
Top-Level View of Computer Organization
 Top-Level View of Computer Organization Bởi: Hoang Lan Nguyen Computer Component Contemporary computer designs are based on concepts developed by John von Neumann at the Institute for Advanced Studies
Top-Level View of Computer Organization Bởi: Hoang Lan Nguyen Computer Component Contemporary computer designs are based on concepts developed by John von Neumann at the Institute for Advanced Studies
5 Computer Organization
 5 Computer Organization 5.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: List the three subsystems of a computer. Describe the
5 Computer Organization 5.1 Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: List the three subsystems of a computer. Describe the
Introduction. Computer System Organization. Languages, Levels, Virtual Machines. A multilevel machine. Sarjana Magister Program
 Computer System Organization Sarjana Magister Program Introduction Tb. Maulana Kusuma Week 1 Session 1 Languages, Levels, Virtual Machines A multilevel machine 1 Contemporary Multilevel Machines A six-level
Computer System Organization Sarjana Magister Program Introduction Tb. Maulana Kusuma Week 1 Session 1 Languages, Levels, Virtual Machines A multilevel machine 1 Contemporary Multilevel Machines A six-level
Computer Architecture and Organization (CS-507)
 Computer Architecture and Organization (CS-507) Muhammad Zeeshan Haider Ali Lecturer ISP. Multan ali.zeeshan04@gmail.com https://zeeshanaliatisp.wordpress.com/ Lecture 4 Basic Computer Function, Instruction
Computer Architecture and Organization (CS-507) Muhammad Zeeshan Haider Ali Lecturer ISP. Multan ali.zeeshan04@gmail.com https://zeeshanaliatisp.wordpress.com/ Lecture 4 Basic Computer Function, Instruction
Part (01) Introduction to Computer
 Part (01) Introduction to Computer Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Summer 2014, Introduction to CS 1 TURING MODEL The idea of a universal computational device was first described by Alan
Part (01) Introduction to Computer Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee 1 Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Summer 2014, Introduction to CS 1 TURING MODEL The idea of a universal computational device was first described by Alan
Introduction. Chapter 1
 Introduction Chapter 1 The Digital Computer Machine to carry out instructions A program Instructions are simple Add numbers Check if a number is zero Copy data between memory locations Primitive instructions
Introduction Chapter 1 The Digital Computer Machine to carry out instructions A program Instructions are simple Add numbers Check if a number is zero Copy data between memory locations Primitive instructions
Bus Example: Pentium II
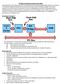 Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Conventional PCI, often shortened to PCI, is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer. PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Conventional PCI, often shortened to PCI, is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer. PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect
10 Input and output in von Neumann s Computer selected themes
 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE 10 Input and output in von Neumann s Computer selected themes RA - 3 2018, Škraba, Rozman, FRI 10. Input and output in von Neumann s computer I/O devices are used to convert information
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE 10 Input and output in von Neumann s Computer selected themes RA - 3 2018, Škraba, Rozman, FRI 10. Input and output in von Neumann s computer I/O devices are used to convert information
1. Internal Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor
 1. Internal Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor Control Unit Generates signals within up to carry out the instruction, which has been decoded. In reality causes certain connections between blocks of the
1. Internal Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor Control Unit Generates signals within up to carry out the instruction, which has been decoded. In reality causes certain connections between blocks of the
Overview of Computer Architecture & Organization. Co Attained : CO1 Hours required : 07 Self study : 10 hrs
 Overview of Computer Architecture & Organization Co Attained : CO1 Hours required : 07 Self study : 10 hrs Syllabus 1. Introduction of Computer Organization and Architecture. 2. Basic organization of computer
Overview of Computer Architecture & Organization Co Attained : CO1 Hours required : 07 Self study : 10 hrs Syllabus 1. Introduction of Computer Organization and Architecture. 2. Basic organization of computer
QUIZ Ch.6. The EAT for a two-level memory is given by:
 QUIZ Ch.6 The EAT for a two-level memory is given by: EAT = H Access C + (1-H) Access MM. Derive a similar formula for three-level memory: L1, L2 and RAM. Hint: Instead of H, we now have H 1 and H 2. Source:
QUIZ Ch.6 The EAT for a two-level memory is given by: EAT = H Access C + (1-H) Access MM. Derive a similar formula for three-level memory: L1, L2 and RAM. Hint: Instead of H, we now have H 1 and H 2. Source:
ECE 485/585 Microprocessor System Design
 Microprocessor System Design Lecture 15: Bus Fundamentals Zeshan Chishti Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept. Maseeh College of Engineering and Computer Science Source: Lecture based on materials
Microprocessor System Design Lecture 15: Bus Fundamentals Zeshan Chishti Electrical and Computer Engineering Dept. Maseeh College of Engineering and Computer Science Source: Lecture based on materials
INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION
 INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Accessing I/O Devices I/O interface Input/output mechanism Memory-mapped I/O Programmed I/O Interrupts Direct Memory Access Buses Synchronous Bus Asynchronous Bus I/O in CO and
INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Accessing I/O Devices I/O interface Input/output mechanism Memory-mapped I/O Programmed I/O Interrupts Direct Memory Access Buses Synchronous Bus Asynchronous Bus I/O in CO and
Downloaded from
 Learning Objectives : After learning the Unit the students will be able to: learn about the various inventions in computers understand the technological changes occurs in computer in terms of hardware
Learning Objectives : After learning the Unit the students will be able to: learn about the various inventions in computers understand the technological changes occurs in computer in terms of hardware
CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER OVERVIEW
 CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER OVERVIEW WHAT IS A COMPUTER? Def: A computer is an electronic device that can perform a variety of operations in accordance with set of instructions called program. DATA Data. Data in
CHAPTER 1 COMPUTER OVERVIEW WHAT IS A COMPUTER? Def: A computer is an electronic device that can perform a variety of operations in accordance with set of instructions called program. DATA Data. Data in
Computer Systems. Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction
 Computer Systems Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction 1 Automation & Computers Fundamental question of computer science: What can be automated? Computers automate processing of information Computer
Computer Systems Hardware, Software and Layers of Abstraction 1 Automation & Computers Fundamental question of computer science: What can be automated? Computers automate processing of information Computer
AVR Microcontrollers Architecture
 ก ก There are two fundamental architectures to access memory 1. Von Neumann Architecture 2. Harvard Architecture 2 1 Harvard Architecture The term originated from the Harvard Mark 1 relay-based computer,
ก ก There are two fundamental architectures to access memory 1. Von Neumann Architecture 2. Harvard Architecture 2 1 Harvard Architecture The term originated from the Harvard Mark 1 relay-based computer,
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 1 Technology in Action Technology in Focus: The History of the PC 2 The first personal computer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output Altair 8800 Bill Gates and Paul Allen created a compiler
1 Technology in Action Technology in Focus: The History of the PC 2 The first personal computer Sold as a kit Switches for input Lights for output Altair 8800 Bill Gates and Paul Allen created a compiler
EE108B Lecture 17 I/O Buses and Interfacing to CPU. Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University
 EE108B Lecture 17 I/O Buses and Interfacing to CPU Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements Remaining deliverables PA2.2. today HW4 on 3/13 Lab4 on 3/19
EE108B Lecture 17 I/O Buses and Interfacing to CPU Christos Kozyrakis Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee108b 1 Announcements Remaining deliverables PA2.2. today HW4 on 3/13 Lab4 on 3/19
Lecture 1: Intro to Computer Architecture. James C. Hoe Department of ECE Carnegie Mellon University
 18 447 Lecture 1: Intro to Computer Architecture James C. Hoe Department of ECE Carnegie Mellon University 18 447 S18 L01 S1, James C. Hoe, CMU/ECE/CALCM, 2018 18 447 S18 L01 S2, James C. Hoe, CMU/ECE/CALCM,
18 447 Lecture 1: Intro to Computer Architecture James C. Hoe Department of ECE Carnegie Mellon University 18 447 S18 L01 S1, James C. Hoe, CMU/ECE/CALCM, 2018 18 447 S18 L01 S2, James C. Hoe, CMU/ECE/CALCM,
QUESTION BANK UNIT-I. 4. With a neat diagram explain Von Neumann computer architecture
 UNIT-I 1. Write the basic functional units of computer? (Nov/Dec 2014) 2. What is a bus? What are the different buses in a CPU? 3. Define multiprogramming? 4.List the basic functional units of a computer?
UNIT-I 1. Write the basic functional units of computer? (Nov/Dec 2014) 2. What is a bus? What are the different buses in a CPU? 3. Define multiprogramming? 4.List the basic functional units of a computer?
Introduction To Computers. About the Course
 Introduction To Computers Chapter No 1 Introduction About the Course Course instructor Course policies Topics to be covered Course Website and Reference material Assignments and Projects ITC - Chapter
Introduction To Computers Chapter No 1 Introduction About the Course Course instructor Course policies Topics to be covered Course Website and Reference material Assignments and Projects ITC - Chapter
History of Computing. Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech
 History of Computing Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech Early Computational Devices (Chinese) Abacus 2700 2300 BC Used for performing arithmetic operations Early Computational Devices Napier s Bones, 1617
History of Computing Slides from NYU and Georgia Tech Early Computational Devices (Chinese) Abacus 2700 2300 BC Used for performing arithmetic operations Early Computational Devices Napier s Bones, 1617
Programmed I/O Interrupt-Driven I/O Direct Memory Access (DMA) I/O Processors. 10/12/2017 Input/Output Systems and Peripheral Devices (02-2)
 Programmed I/O Interrupt-Driven I/O Direct Memory Access (DMA) I/O Processors 1 Principle of Interrupt-Driven I/O Multiple-Interrupt Systems Priority Interrupt Systems Parallel Priority Interrupts Daisy-Chain
Programmed I/O Interrupt-Driven I/O Direct Memory Access (DMA) I/O Processors 1 Principle of Interrupt-Driven I/O Multiple-Interrupt Systems Priority Interrupt Systems Parallel Priority Interrupts Daisy-Chain
History of Modern Computing Lesson 1
 History of Modern Computing Lesson 1 www.soe.ucsc.edu/classes/cmpe080h/fall05 David Pease Computer Engineering Department Jack Baskin School of Engineering Lesson Outline Definition of a computer Types
History of Modern Computing Lesson 1 www.soe.ucsc.edu/classes/cmpe080h/fall05 David Pease Computer Engineering Department Jack Baskin School of Engineering Lesson Outline Definition of a computer Types
CS 101, Mock Computer Architecture
 CS 101, Mock Computer Architecture Computer organization and architecture refers to the actual hardware used to construct the computer, and the way that the hardware operates both physically and logically
CS 101, Mock Computer Architecture Computer organization and architecture refers to the actual hardware used to construct the computer, and the way that the hardware operates both physically and logically
Architecture of Computers and Parallel Systems Part 2: Communication with Devices
 Architecture of Computers and Parallel Systems Part 2: Communication with Devices Ing. Petr Olivka petr.olivka@vsb.cz Department of Computer Science FEI VSB-TUO Architecture of Computers and Parallel Systems
Architecture of Computers and Parallel Systems Part 2: Communication with Devices Ing. Petr Olivka petr.olivka@vsb.cz Department of Computer Science FEI VSB-TUO Architecture of Computers and Parallel Systems
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY,VIRUDHUNAGAR
 Year/sem: 02/04 Academic Year: 2014-2015 (even) UNIT II THE 8086 SYSTEM BUS STRUCTURE PART A 1. What are the three groups of signals in 8086? The 8086 signals are categorized in three groups. They are:
Year/sem: 02/04 Academic Year: 2014-2015 (even) UNIT II THE 8086 SYSTEM BUS STRUCTURE PART A 1. What are the three groups of signals in 8086? The 8086 signals are categorized in three groups. They are:
Chapter 8. A Typical collection of I/O devices. Interrupts. Processor. Cache. Memory I/O bus. I/O controller I/O I/O. Main memory.
 Chapter 8 1 A Typical collection of I/O devices Interrupts Cache I/O bus Main memory I/O controller I/O controller I/O controller Disk Disk Graphics output Network 2 1 Interfacing s and Peripherals I/O
Chapter 8 1 A Typical collection of I/O devices Interrupts Cache I/O bus Main memory I/O controller I/O controller I/O controller Disk Disk Graphics output Network 2 1 Interfacing s and Peripherals I/O
Computer Organization and Architecture William Stallings 8th Edition. Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance
 Computer Organization and Architecture William Stallings 8th Edition Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance BRIEF HISTORY OF COMPUTERS The First Generation: Vacuum Tubes ENIAC - background Electronic
Computer Organization and Architecture William Stallings 8th Edition Chapter 2 Computer Evolution and Performance BRIEF HISTORY OF COMPUTERS The First Generation: Vacuum Tubes ENIAC - background Electronic
MA Unit 4. Question Option A Option B Option C Option D
 Matoshri College of Engineering & Research Centre Nashik Department of Computer Engineering Class :- Second Year Computer Engineering Sem - 1 Subject :- MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTURE UNIT-IV 1 Accumulator
Matoshri College of Engineering & Research Centre Nashik Department of Computer Engineering Class :- Second Year Computer Engineering Sem - 1 Subject :- MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTURE UNIT-IV 1 Accumulator
Input/Output Introduction
 Input/Output 1 Introduction Motivation Performance metrics Processor interface issues Buses 2 Page 1 Motivation CPU Performance: 60% per year I/O system performance limited by mechanical delays (e.g.,
Input/Output 1 Introduction Motivation Performance metrics Processor interface issues Buses 2 Page 1 Motivation CPU Performance: 60% per year I/O system performance limited by mechanical delays (e.g.,
Introduction. Motivation Performance metrics Processor interface issues Buses
 Input/Output 1 Introduction Motivation Performance metrics Processor interface issues Buses 2 Motivation CPU Performance: 60% per year I/O system performance limited by mechanical delays (e.g., disk I/O)
Input/Output 1 Introduction Motivation Performance metrics Processor interface issues Buses 2 Motivation CPU Performance: 60% per year I/O system performance limited by mechanical delays (e.g., disk I/O)
Computer Organization
 Objectives 5.1 Chapter 5 Computer Organization Source: Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning 5.2 After studying this chapter, students should be able to: List the three subsystems of a computer.
Objectives 5.1 Chapter 5 Computer Organization Source: Foundations of Computer Science Cengage Learning 5.2 After studying this chapter, students should be able to: List the three subsystems of a computer.
Computer Organization
 Computer Organization KR Chowdhary Professor & Head Email: kr.chowdhary@gmail.com webpage: krchowdhary.com Department of Computer Science and Engineering MBM Engineering College, Jodhpur November 14, 2013
Computer Organization KR Chowdhary Professor & Head Email: kr.chowdhary@gmail.com webpage: krchowdhary.com Department of Computer Science and Engineering MBM Engineering College, Jodhpur November 14, 2013
5 Computer Organization
 5 Computer Organization 5.1 Foundations of Computer Science ã Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: q List the three subsystems of a computer. q Describe
5 Computer Organization 5.1 Foundations of Computer Science ã Cengage Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, the student should be able to: q List the three subsystems of a computer. q Describe
INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION
 INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Accessing I/O Devices I/O interface Input/output mechanism Memory-mapped I/O Programmed I/O Interrupts Direct Memory Access Buses Synchronous Bus Asynchronous Bus I/O in CO and
INPUT/OUTPUT ORGANIZATION Accessing I/O Devices I/O interface Input/output mechanism Memory-mapped I/O Programmed I/O Interrupts Direct Memory Access Buses Synchronous Bus Asynchronous Bus I/O in CO and
