Computer Systems Architecture I. CSE 560M Lecture 18 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James
|
|
|
- Patricia Skinner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 18 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James
2 Plan for Today Announcements No class meeting on Monday, meet in project groups Project demos < 2 weeks, Nov 23 rd Questions Review of project logistics Today s discussion: Main and Virtual Memory 2
3 Project Logistics Five major deadlines Project Demo Nov 23 Report due Dec 7 Project Timeline 3
4 CPU-DRAM gap * CPU (registers) Speed: 0.25 ns C a c h e Improve performance Memory bus 1 ns Memory (DRAM) 100 ns I/O bus I/O devices 5 ms 4 * 2003 Elsevier Science (USA). All rights reserved.
5 Main Memory Recall that on a cache miss, need to access memory. This process has three components Send the address Get the contents of the memory location Transfer contents Parameters for dynamic random access memory (DRAM) Access time: time between the read is requested and the desired word arrives Cycle time: minimum time between requests to memory cycle time > access time to allow address lines to stabilize and to write back data (i.e., reads are destructive) In 2002, cycle times were 80 ns (compared to 250ns in 1980) 5
6 DRAM Bits stored in single transistors Reads are destructive Transistors leak (i.e. Dynamic) so must be refreshed Address lines split into row and column addresses. A read consists of RAS row access strobe CAS column access strobe Access time is typically RAS + CAS, but periodic refreshing can stall requests 6
7 DRAM Structure 7
8 DRAM and SRAM Both are a memory organization using transistors S stands for static Traditionally uses 6 Ts/bit (some use 4 or less) No refresh No need to write after read Main memory uses DRAM; on-chip caches use SRAM; onboard caches have been built with both DRAM semiconductor fabs use specific processes to create chips Different layers, fewer layers Different physical properties 8
9 Improving Main Memory Sending address Can t really be improved Bandwidth Can use split-transaction bus to allow overlap Make memory wider Send one address, return more than one word Wider main memory increases memory increment size Complicates error correcting codes when writing one word in a multi-word memory 9
10 Interleaving Memory is organized in banks Bank i stores all words at address j mod I Requests to different banks can occur in consecutive clock cycles All banks can read a word in parallel Number of banks should match L2 block size Bus does not need to be wider Writes to individual banks for different addresses can proceed without waiting for the preceding write to finish Problem: number of banks limited by increasing chip capacity With 1M*1 bit chips, it takes 64*8=512 chips to get 64MB (easy to put 16 banks of 32 chips) With 64M*1 bit chips, it takes only 8 chips (only one bank) 10
11 Memory Width Illustration 11
12 Page-mode, Synchronous and Double Data Rate DRAMs Fast page mode: Add a row buffer to DRAM Keep most recently accessed row (i.e. page) open as a buffer Hit: read out of buffer, skip RAS Miss: cost of miss + RAS + CAS Synchronous: Add a clock Traditional DRAMs were asynchronous; adding a clock eliminates sync overhead at each request Also adds a width register to control number of words to be returned DDR: Transfer data on the rising and falling edge of clock Doubles data rate All three add a small amount of logic to exploit internal DRAM bandwidth (small cost, large improvement) 12
13 Virtual Memory Purpose: give program(mer) illusion of full-sized, unshared main memory Hardware assists for address translation and memory protection Largely invisible to programmer Prior to virtual memory Overlays Relocation registers Paging Segmentation Paging systems predate caches But same questions arise (mapping, replacement and write policies) An enormous difference: miss penalty 13
14 Paged Virtual Memory Illustrated 14
15 Two Extremes in the Memory Hierarchy Parameter L1 Cache Paging System Block (page) size bytes 4K-8K bytes Miss (fault) time cycles ( ns) Millions (3-20 ms) Miss (fault) rate 1-10% % Memory size 4K-64K bytes Gigabytes 15
16 Other Extreme Differences Mapping: Restricted (L1) vs. general (Paging) Hardware assist for virtual address translation (TLB) Miss handler Hardware only for caches Software only for paging system (context switch) Hardware/Software for TLB Replacement algorithm Not important for caches Critical for paging systems Write policy Always write back for paging systems 16
17 Paging and Segmentation Paging: fixed block sizes Easy to map, translate, replace, transfer to/from disk Does not correspond to semantic objects, hence internal fragmentation Segmentation: variable block sizes Requires two addresses per word: segment and offset Difficult to translate (need to check segment length), place and replace (external fragmentation), transfer to/from disk Allocation can be problematic (need contiguous memory) Corresponds to semantic objects Segmentation with paging (segment holds N pages) Good for large objects Helps allocation problem 17
18 Page Table Illustration 18
19 Page Tables Page tables contain page table entries (PTEs): Physical page number, as well as valid, protection, dirty, and use bits virtual page number is often known implicitly based on the address, but can be stored explicitly as below Hardware register points to the page table of the running process Page table structures Traditional structure needs one entry per virtual page 32-bit addresses, 4KB pages gives 2 20 =1M entries Assuming 4 bytes per entry, size is 4MB Some systems have inverted page tables Goal: reduce size of page table One entry for each physical page Hash the virtual page number to form table index Size now due to physical page count, rather than virtual 512MB main memory needs a 1MB table, assuming an additional 4 bytes per entry to store the virtual address In all modern systems, page table entries are cached in a translation lookaside buffer (TLB) 19
20 TLBs Cache for page table entries (PTEs) Usually fully associative TLB miss handled by hardware or by software TLB miss cycles, means you don t need to context switch Addressed in parallel with access to cache TLB is smaller than page table, admits faster access Can be on the processor s critical path For a given TLB size (number of entries) Larger page size implies larger effective capacity (ie, each TLB entry translates more addresses) Modern O.S.s have a page size parameter 20
21 Virtually Indexed, Physically Tagged Caches Does the cache use virtual or physical addresses? Why not all physical? Need to translate every time: serialize hierarchy Why not all virtual? Protection (page level protection is checked at translation time?) Context switches (each switch changes the meaning of virtual addresses) Can add PID to cache address tag Aliasing (OS and apps can use synonyms to refer to same locations) I/O uses physical addresses Idea: use page offset, which is the same for virtual and physical addresses, to index a small cache TLB entry (virtual page number) and Cache tag entry (portion of the page offset) are indexed in parallel Tags are physical addresses Limits the size of direct-mapped cache to a page! 21
22 Caches and Address Translation 22
23 I/O and Caches (a first look at cache coherence) Alternatives I/O data passes through the cache on its way from/to memory No coherency problem but contention for cache access I/O interacts directly with main memory Coherency problem 23
24 I/O Consistency Illustrated 24
25 I/O Consistency - Software Approach On Output: If write through cache, no problem If write back cache, purge the cache via O.S. interaction On Input: Both WT and WB: use a non-cacheable buffer space After input is completed, flush the cache of blocks mapping to these addresses and make the buffer cacheable. 25
26 I/O Consistency - Hardware Approach Subset of the shared-bus multiprocessor cache coherence protocol Cache controller snoops on the bus On output, if there is a match in tags: if WT nothing to do, else if WB send the cache entry instead On input, if there is a match in tags: store in both the cache and main memory (or invalidate the cache entry) 26
27 Assignment Project demos in < 2 weeks Readings For Monday No class meeting, meet in project groups 27
Reducing Hit Times. Critical Influence on cycle-time or CPI. small is always faster and can be put on chip
 Reducing Hit Times Critical Influence on cycle-time or CPI Keep L1 small and simple small is always faster and can be put on chip interesting compromise is to keep the tags on chip and the block data off
Reducing Hit Times Critical Influence on cycle-time or CPI Keep L1 small and simple small is always faster and can be put on chip interesting compromise is to keep the tags on chip and the block data off
Translation Buffers (TLB s)
 Translation Buffers (TLB s) To perform virtual to physical address translation we need to look-up a page table Since page table is in memory, need to access memory Much too time consuming; 20 cycles or
Translation Buffers (TLB s) To perform virtual to physical address translation we need to look-up a page table Since page table is in memory, need to access memory Much too time consuming; 20 cycles or
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design (Part 3) Introduction Caches Main Memory (Section 2.2) Virtual Memory (Section 2.4, Appendix B.4, B.
 Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design (Part 3) Introduction Caches Main Memory (Section 2.2) Virtual Memory (Section 2.4, Appendix B.4, B.5) Memory Technologies Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) Optimized
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design (Part 3) Introduction Caches Main Memory (Section 2.2) Virtual Memory (Section 2.4, Appendix B.4, B.5) Memory Technologies Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) Optimized
CS252 S05. Main memory management. Memory hardware. The scale of things. Memory hardware (cont.) Bottleneck
 Main memory management CMSC 411 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 16 Memory Hierarchy 3 (Main Memory & Memory) Questions: How big should main memory be? How to handle reads and writes? How to find
Main memory management CMSC 411 Computer Systems Architecture Lecture 16 Memory Hierarchy 3 (Main Memory & Memory) Questions: How big should main memory be? How to handle reads and writes? How to find
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal locality Items accessed recently are likely to
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal locality Items accessed recently are likely to
Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design. In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST
 Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST Why cache? Microprocessor performance increment: 55% per year Memory performance increment: 7% per year Principles of locality Spatial
Chapter 5 Memory Hierarchy Design In-Cheol Park Dept. of EE, KAIST Why cache? Microprocessor performance increment: 55% per year Memory performance increment: 7% per year Principles of locality Spatial
Virtual Memory Review. Page faults. Paging system summary (so far)
 Lecture 22 (Wed 11/19/2008) Virtual Memory Review Lab #4 Software Simulation Due Fri Nov 21 at 5pm HW #3 Cache Simulator & code optimization Due Mon Nov 24 at 5pm More Virtual Memory 1 2 Paging system
Lecture 22 (Wed 11/19/2008) Virtual Memory Review Lab #4 Software Simulation Due Fri Nov 21 at 5pm HW #3 Cache Simulator & code optimization Due Mon Nov 24 at 5pm More Virtual Memory 1 2 Paging system
Chapter Seven. Memories: Review. Exploiting Memory Hierarchy CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY
 Chapter Seven CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY 1 Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored
Chapter Seven CACHE MEMORY AND VIRTUAL MEMORY 1 Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored
Memory latency: Affects cache miss penalty. Measured by:
 Main Memory Main memory generally utilizes Dynamic RAM (DRAM), which use a single transistor to store a bit, but require a periodic data refresh by reading every row. Static RAM may be used for main memory
Main Memory Main memory generally utilizes Dynamic RAM (DRAM), which use a single transistor to store a bit, but require a periodic data refresh by reading every row. Static RAM may be used for main memory
Memory latency: Affects cache miss penalty. Measured by:
 Main Memory Main memory generally utilizes Dynamic RAM (DRAM), which use a single transistor to store a bit, but require a periodic data refresh by reading every row. Static RAM may be used for main memory
Main Memory Main memory generally utilizes Dynamic RAM (DRAM), which use a single transistor to store a bit, but require a periodic data refresh by reading every row. Static RAM may be used for main memory
CPS 104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 20: Virtual Memory
 CPS 104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 20: Virtual Nov. 10, 1999 Dietolf (Dee) Ramm http://www.cs.duke.edu/~dr/cps104.html CPS 104 Lecture 20.1 Outline of Today s Lecture O Virtual. 6 Paged
CPS 104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 20: Virtual Nov. 10, 1999 Dietolf (Dee) Ramm http://www.cs.duke.edu/~dr/cps104.html CPS 104 Lecture 20.1 Outline of Today s Lecture O Virtual. 6 Paged
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface. 5 th. Edition. Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address
Lecture 11. Virtual Memory Review: Memory Hierarchy
 Lecture 11 Virtual Memory Review: Memory Hierarchy 1 Administration Homework 4 -Due 12/21 HW 4 Use your favorite language to write a cache simulator. Input: address trace, cache size, block size, associativity
Lecture 11 Virtual Memory Review: Memory Hierarchy 1 Administration Homework 4 -Due 12/21 HW 4 Use your favorite language to write a cache simulator. Input: address trace, cache size, block size, associativity
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Memory System
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
Computer Science 146. Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Spring 2004 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture 18: Virtual Memory Lecture Outline Review of Main Memory Virtual Memory Simple Interleaving Cycle
Computer Architecture Spring 2004 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture 18: Virtual Memory Lecture Outline Review of Main Memory Virtual Memory Simple Interleaving Cycle
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Memory Organization Part II
 ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Organization Part II Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn,
ELEC 5200/6200 Computer Architecture and Design Spring 2017 Lecture 7: Organization Part II Ujjwal Guin, Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn,
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 16: Virtual Memory. Robert Wagner
 CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 16: Virtual Memory Robert Wagner cps 104 VM.1 RW Fall 2000 Outline of Today s Lecture Virtual Memory. Paged virtual memory. Virtual to Physical translation:
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 16: Virtual Memory Robert Wagner cps 104 VM.1 RW Fall 2000 Outline of Today s Lecture Virtual Memory. Paged virtual memory. Virtual to Physical translation:
The levels of a memory hierarchy. Main. Memory. 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms
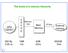 The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
HY225 Lecture 12: DRAM and Virtual Memory
 HY225 Lecture 12: DRAM and irtual Memory Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos University of Crete and FORTH-ICS May 16, 2011 Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos Lecture 12: DRAM and irtual Memory 1 / 36 DRAM Fundamentals Random-access
HY225 Lecture 12: DRAM and irtual Memory Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos University of Crete and FORTH-ICS May 16, 2011 Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos Lecture 12: DRAM and irtual Memory 1 / 36 DRAM Fundamentals Random-access
EN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Memory System
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Topic 6: Memory System Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University Spring
Memory Technology. Chapter 5. Principle of Locality. Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy 1
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy 5 th Edition Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy 5 th Edition Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic
Main Memory. EECC551 - Shaaban. Memory latency: Affects cache miss penalty. Measured by:
 Main Memory Main memory generally utilizes Dynamic RAM (DRAM), which use a single transistor to store a bit, but require a periodic data refresh by reading every row (~every 8 msec). Static RAM may be
Main Memory Main memory generally utilizes Dynamic RAM (DRAM), which use a single transistor to store a bit, but require a periodic data refresh by reading every row (~every 8 msec). Static RAM may be
Mainstream Computer System Components
 Mainstream Computer System Components Double Date Rate (DDR) SDRAM One channel = 8 bytes = 64 bits wide Current DDR3 SDRAM Example: PC3-2800 (DDR3-600) 200 MHz (internal base chip clock) 8-way interleaved
Mainstream Computer System Components Double Date Rate (DDR) SDRAM One channel = 8 bytes = 64 bits wide Current DDR3 SDRAM Example: PC3-2800 (DDR3-600) 200 MHz (internal base chip clock) 8-way interleaved
CPU issues address (and data for write) Memory returns data (or acknowledgment for write)
 The Main Memory Unit CPU and memory unit interface Address Data Control CPU Memory CPU issues address (and data for write) Memory returns data (or acknowledgment for write) Memories: Design Objectives
The Main Memory Unit CPU and memory unit interface Address Data Control CPU Memory CPU issues address (and data for write) Memory returns data (or acknowledgment for write) Memories: Design Objectives
Virtual to physical address translation
 Virtual to physical address translation Virtual memory with paging Page table per process Page table entry includes present bit frame number modify bit flags for protection and sharing. Page tables can
Virtual to physical address translation Virtual memory with paging Page table per process Page table entry includes present bit frame number modify bit flags for protection and sharing. Page tables can
Main Memory (Fig. 7.13) Main Memory
 Main Memory (Fig. 7.13) CPU CPU CPU Cache Multiplexor Cache Cache Bus Bus Bus Memory Memory bank 0 Memory bank 1 Memory bank 2 Memory bank 3 Memory b. Wide memory organization c. Interleaved memory organization
Main Memory (Fig. 7.13) CPU CPU CPU Cache Multiplexor Cache Cache Bus Bus Bus Memory Memory bank 0 Memory bank 1 Memory bank 2 Memory bank 3 Memory b. Wide memory organization c. Interleaved memory organization
Copyright 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Background. Memory Hierarchies. Register File. Background. Forecast Memory (B5) Motivation for memory hierarchy Cache ECC Virtual memory.
 Memory Hierarchies Forecast Memory (B5) Motivation for memory hierarchy Cache ECC Virtual memory Mem Element Background Size Speed Price Register small 1-5ns high?? SRAM medium 5-25ns $100-250 DRAM large
Memory Hierarchies Forecast Memory (B5) Motivation for memory hierarchy Cache ECC Virtual memory Mem Element Background Size Speed Price Register small 1-5ns high?? SRAM medium 5-25ns $100-250 DRAM large
Chapter 5B. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5B Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy One Transistor Dynamic RAM 1-T DRAM Cell word access transistor V REF TiN top electrode (V REF ) Ta 2 O 5 dielectric bit Storage capacitor (FET gate,
Chapter 5B Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy One Transistor Dynamic RAM 1-T DRAM Cell word access transistor V REF TiN top electrode (V REF ) Ta 2 O 5 dielectric bit Storage capacitor (FET gate,
MEMORY HIERARCHY BASICS. B649 Parallel Architectures and Programming
 MEMORY HIERARCHY BASICS B649 Parallel Architectures and Programming BASICS Why Do We Need Caches? 3 Overview 4 Terminology cache virtual memory memory stall cycles direct mapped valid bit block address
MEMORY HIERARCHY BASICS B649 Parallel Architectures and Programming BASICS Why Do We Need Caches? 3 Overview 4 Terminology cache virtual memory memory stall cycles direct mapped valid bit block address
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Copyright 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology
Computer Architecture. A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition. Chapter 2. Memory Hierarchy Design. Copyright 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more expensive per
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more expensive per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1)
 Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory
 Virtual memory Main Memory Disk I P D L1 L2 M Goals Physical address space Virtual address space 1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory 2. Make provisions for
Virtual memory Main Memory Disk I P D L1 L2 M Goals Physical address space Virtual address space 1. Creates the illusion of an address space much larger than the physical memory 2. Make provisions for
Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science. TDT4255 Memory hierarchies
 TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition. Chapter 2. Memory Hierarchy Design. Copyright 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more
LECTURE 5: MEMORY HIERARCHY DESIGN
 LECTURE 5: MEMORY HIERARCHY DESIGN Abridged version of Hennessy & Patterson (2012):Ch.2 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more expensive
LECTURE 5: MEMORY HIERARCHY DESIGN Abridged version of Hennessy & Patterson (2012):Ch.2 Introduction Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more expensive
The University of Adelaide, School of Computer Science 13 September 2018
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Sixth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more expensive per
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Sixth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Programmers want unlimited amounts of memory with low latency Fast memory technology is more expensive per
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1
 CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
CSE 431 Computer Architecture Fall 2008 Chapter 5A: Exploiting the Memory Hierarchy, Part 1 Mary Jane Irwin ( www.cse.psu.edu/~mji ) [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, 4 th Edition, Patterson
Adapted from David Patterson s slides on graduate computer architecture
 Mei Yang Adapted from David Patterson s slides on graduate computer architecture Introduction Ten Advanced Optimizations of Cache Performance Memory Technology and Optimizations Virtual Memory and Virtual
Mei Yang Adapted from David Patterson s slides on graduate computer architecture Introduction Ten Advanced Optimizations of Cache Performance Memory Technology and Optimizations Virtual Memory and Virtual
CSEE W4824 Computer Architecture Fall 2012
 CSEE W4824 Computer Architecture Fall 2012 Lecture 8 Memory Hierarchy Design: Memory Technologies and the Basics of Caches Luca Carloni Department of Computer Science Columbia University in the City of
CSEE W4824 Computer Architecture Fall 2012 Lecture 8 Memory Hierarchy Design: Memory Technologies and the Basics of Caches Luca Carloni Department of Computer Science Columbia University in the City of
The Memory Hierarchy. Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2)
 The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
Memory. Lecture 22 CS301
 Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Memory Lecture 22 CS301 Administrative Daily Review of today s lecture w Due tomorrow (11/13) at 8am HW #8 due today at 5pm Program #2 due Friday, 11/16 at 11:59pm Test #2 Wednesday Pipelined Machine Fetch
Memory systems. Memory technology. Memory technology Memory hierarchy Virtual memory
 Memory systems Memory technology Memory hierarchy Virtual memory Memory technology DRAM Dynamic Random Access Memory bits are represented by an electric charge in a small capacitor charge leaks away, need
Memory systems Memory technology Memory hierarchy Virtual memory Memory technology DRAM Dynamic Random Access Memory bits are represented by an electric charge in a small capacitor charge leaks away, need
Computer Architecture Computer Science & Engineering. Chapter 5. Memory Hierachy BK TP.HCM
 Computer Architecture Computer Science & Engineering Chapter 5 Memory Hierachy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic
Computer Architecture Computer Science & Engineering Chapter 5 Memory Hierachy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic
Chapter Seven Morgan Kaufmann Publishers
 Chapter Seven Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be
Chapter Seven Memories: Review SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors) DRAM: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be
ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB
 ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 3 submission deadline: Nov.
ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 3 submission deadline: Nov.
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Memory Hierarchies. Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev. Fall Lecture 10, October 8, CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology
 Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Memory Hierarchies Instructor: Dmitri A. Gusev Fall 2007 CS 502: Computers and Communications Technology Lecture 10, October 8, 2007 Memories SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast
Chapter 5 (Part II) Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy. Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs
 Chapter 5 (Part II) Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Virtual Machines Host computer emulates guest operating system and machine resources Improved isolation of multiple
Chapter 5 (Part II) Baback Izadi Division of Engineering Programs bai@engr.newpaltz.edu Virtual Machines Host computer emulates guest operating system and machine resources Improved isolation of multiple
Lecture: DRAM Main Memory. Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3)
 Lecture: DRAM Main Memory Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3) 1 TLB and Cache Is the cache indexed with virtual or physical address? To index with a physical address, we
Lecture: DRAM Main Memory Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3) 1 TLB and Cache Is the cache indexed with virtual or physical address? To index with a physical address, we
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address
Virtual Memory. Patterson & Hennessey Chapter 5 ELEC 5200/6200 1
 Virtual Memory Patterson & Hennessey Chapter 5 ELEC 5200/6200 1 Virtual Memory Use main memory as a cache for secondary (disk) storage Managed jointly by CPU hardware and the operating system (OS) Programs
Virtual Memory Patterson & Hennessey Chapter 5 ELEC 5200/6200 1 Virtual Memory Use main memory as a cache for secondary (disk) storage Managed jointly by CPU hardware and the operating system (OS) Programs
Lecture 20: Memory Hierarchy Main Memory and Enhancing its Performance. Grinch-Like Stuff
 Lecture 20: ory Hierarchy Main ory and Enhancing its Performance Professor Alvin R. Lebeck Computer Science 220 Fall 1999 HW #4 Due November 12 Projects Finish reading Chapter 5 Grinch-Like Stuff CPS 220
Lecture 20: ory Hierarchy Main ory and Enhancing its Performance Professor Alvin R. Lebeck Computer Science 220 Fall 1999 HW #4 Due November 12 Projects Finish reading Chapter 5 Grinch-Like Stuff CPS 220
Virtual Memory: Mechanisms. CS439: Principles of Computer Systems February 28, 2018
 Virtual Memory: Mechanisms CS439: Principles of Computer Systems February 28, 2018 Last Time Physical addresses in physical memory Virtual/logical addresses in process address space Relocation Algorithms
Virtual Memory: Mechanisms CS439: Principles of Computer Systems February 28, 2018 Last Time Physical addresses in physical memory Virtual/logical addresses in process address space Relocation Algorithms
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY
 LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
Chapter Seven. SRAM: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRAM (4 to 6 transistors)
 Chapter Seven emories: Review SRA: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRA (4 to transistors) DRA: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be refreshed)
Chapter Seven emories: Review SRA: value is stored on a pair of inverting gates very fast but takes up more space than DRA (4 to transistors) DRA: value is stored as a charge on capacitor (must be refreshed)
Lecture 21: Virtual Memory. Spring 2018 Jason Tang
 Lecture 21: Virtual Memory Spring 2018 Jason Tang 1 Topics Virtual addressing Page tables Translation lookaside buffer 2 Computer Organization Computer Processor Memory Devices Control Datapath Input Output
Lecture 21: Virtual Memory Spring 2018 Jason Tang 1 Topics Virtual addressing Page tables Translation lookaside buffer 2 Computer Organization Computer Processor Memory Devices Control Datapath Input Output
Introduction to cache memories
 Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Introduction to cache memories Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Summary Summary Main goal Spatial and temporal
Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Introduction to cache memories Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Summary Summary Main goal Spatial and temporal
Handout 4 Memory Hierarchy
 Handout 4 Memory Hierarchy Outline Memory hierarchy Locality Cache design Virtual address spaces Page table layout TLB design options (MMU Sub-system) Conclusion 2012/11/7 2 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced
Handout 4 Memory Hierarchy Outline Memory hierarchy Locality Cache design Virtual address spaces Page table layout TLB design options (MMU Sub-system) Conclusion 2012/11/7 2 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced
EI338: Computer Systems and Engineering (Computer Architecture & Operating Systems)
 EI338: Computer Systems and Engineering (Computer Architecture & Operating Systems) Chentao Wu 吴晨涛 Associate Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University SEIEE Building
EI338: Computer Systems and Engineering (Computer Architecture & Operating Systems) Chentao Wu 吴晨涛 Associate Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University SEIEE Building
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache optimization Virtual memory Case study AMD Opteron Summary 2 Memory hierarchy 3 Cache
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache optimization Virtual memory Case study AMD Opteron Summary 2 Memory hierarchy 3 Cache
CSE Memory Hierarchy Design Ch. 5 (Hennessy and Patterson)
 CSE 4201 Memory Hierarchy Design Ch. 5 (Hennessy and Patterson) Memory Hierarchy We need huge amount of cheap and fast memory Memory is either fast or cheap; never both. Do as politicians do: fake it Give
CSE 4201 Memory Hierarchy Design Ch. 5 (Hennessy and Patterson) Memory Hierarchy We need huge amount of cheap and fast memory Memory is either fast or cheap; never both. Do as politicians do: fake it Give
COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory
 1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University Credits: Slides adapted from presentations
1 COEN-4730 Computer Architecture Lecture 3 Review of Caches and Virtual Memory Cristinel Ababei Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Marquette University Credits: Slides adapted from presentations
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (III)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (III) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014 Memory Technology Performance metrics Latency problems handled through caches Bandwidth main concern for main memory
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (III) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2014 Memory Technology Performance metrics Latency problems handled through caches Bandwidth main concern for main memory
ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB
 ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 4 submission deadline: Mar.
ADDRESS TRANSLATION AND TLB Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 4 submission deadline: Mar.
Advanced Memory Organizations
 CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
CSE 3421: Introduction to Computer Architecture Advanced Memory Organizations Study: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 (only parts) Gojko Babić 03-29-2018 1 Growth in Performance of DRAM & CPU Huge mismatch between CPU
Mainstream Computer System Components CPU Core 2 GHz GHz 4-way Superscaler (RISC or RISC-core (x86): Dynamic scheduling, Hardware speculation
 Mainstream Computer System Components CPU Core 2 GHz - 3.0 GHz 4-way Superscaler (RISC or RISC-core (x86): Dynamic scheduling, Hardware speculation One core or multi-core (2-4) per chip Multiple FP, integer
Mainstream Computer System Components CPU Core 2 GHz - 3.0 GHz 4-way Superscaler (RISC or RISC-core (x86): Dynamic scheduling, Hardware speculation One core or multi-core (2-4) per chip Multiple FP, integer
Computer Organization and Structure. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Virtual Memory Virtual memory first used to relive programmers from the burden of managing overlays.
 CSE420 Virtual Memory Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) Virtual Memory Virtual memory first used to relive programmers from the burden
CSE420 Virtual Memory Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) Virtual Memory Virtual memory first used to relive programmers from the burden
Lecture 18: Memory Hierarchy Main Memory and Enhancing its Performance Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Spring 1996
 Lecture 18: Memory Hierarchy Main Memory and Enhancing its Performance Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Spring 1996 RHK.S96 1 Review: Reducing Miss Penalty Summary Five techniques Read priority
Lecture 18: Memory Hierarchy Main Memory and Enhancing its Performance Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Spring 1996 RHK.S96 1 Review: Reducing Miss Penalty Summary Five techniques Read priority
Adapted from instructor s supplementary material from Computer. Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK]
![Adapted from instructor s supplementary material from Computer. Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK] Adapted from instructor s supplementary material from Computer. Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK]](/thumbs/80/82108809.jpg) Lecture 17 Adapted from instructor s supplementary material from Computer Organization and Design, 4th Edition, Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK] SRAM / / Flash / RRAM / HDD SRAM / / Flash / RRAM/ HDD SRAM
Lecture 17 Adapted from instructor s supplementary material from Computer Organization and Design, 4th Edition, Patterson & Hennessy, 2008, MK] SRAM / / Flash / RRAM / HDD SRAM / / Flash / RRAM/ HDD SRAM
Lecture: DRAM Main Memory. Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3)
 Lecture: DRAM Main Memory Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3) 1 TLB and Cache 2 Virtually Indexed Caches 24-bit virtual address, 4KB page size 12 bits offset and 12 bits
Lecture: DRAM Main Memory Topics: virtual memory wrap-up, DRAM intro and basics (Section 2.3) 1 TLB and Cache 2 Virtually Indexed Caches 24-bit virtual address, 4KB page size 12 bits offset and 12 bits
Memory Technologies. Technology Trends
 . 5 Technologies Random access technologies Random good access time same for all locations DRAM Dynamic Random Access High density, low power, cheap, but slow Dynamic need to be refreshed regularly SRAM
. 5 Technologies Random access technologies Random good access time same for all locations DRAM Dynamic Random Access High density, low power, cheap, but slow Dynamic need to be refreshed regularly SRAM
Memory: Page Table Structure. CSSE 332 Operating Systems Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology
 Memory: Page Table Structure CSSE 332 Operating Systems Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology General address transla+on CPU virtual address data cache MMU Physical address Global memory Memory management
Memory: Page Table Structure CSSE 332 Operating Systems Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology General address transla+on CPU virtual address data cache MMU Physical address Global memory Memory management
INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO. Architectures for Embedded Computing
 UNIVERSIDADE TÉCNICA DE LISBOA INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO Departamento de Engenharia Informática Architectures for Embedded Computing MEIC-A, MEIC-T, MERC Lecture Slides Version 3.0 - English Lecture 17
UNIVERSIDADE TÉCNICA DE LISBOA INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO Departamento de Engenharia Informática Architectures for Embedded Computing MEIC-A, MEIC-T, MERC Lecture Slides Version 3.0 - English Lecture 17
CS650 Computer Architecture. Lecture 9 Memory Hierarchy - Main Memory
 CS65 Computer Architecture Lecture 9 Memory Hierarchy - Main Memory Andrew Sohn Computer Science Department New Jersey Institute of Technology Lecture 9: Main Memory 9-/ /6/ A. Sohn Memory Cycle Time 5
CS65 Computer Architecture Lecture 9 Memory Hierarchy - Main Memory Andrew Sohn Computer Science Department New Jersey Institute of Technology Lecture 9: Main Memory 9-/ /6/ A. Sohn Memory Cycle Time 5
Paging! 2/22! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica CS162 UCB Fall 2012! " (0xE0)" " " " (0x70)" " (0x50)"
 CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 22, 2011! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Segmentation! Paging! Recap Segmentation
CS162 Operating Systems and Systems Programming Lecture 10 Caches and TLBs" February 22, 2011! Anthony D. Joseph and Ion Stoica! http//inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs162! Segmentation! Paging! Recap Segmentation
Processes and Virtual Memory Concepts
 Processes and Virtual Memory Concepts Brad Karp UCL Computer Science CS 37 8 th February 28 (lecture notes derived from material from Phil Gibbons, Dave O Hallaron, and Randy Bryant) Today Processes Virtual
Processes and Virtual Memory Concepts Brad Karp UCL Computer Science CS 37 8 th February 28 (lecture notes derived from material from Phil Gibbons, Dave O Hallaron, and Randy Bryant) Today Processes Virtual
Virtual Memory. Reading. Sections 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8, 5.10 (2) Lecture notes from MKP and S. Yalamanchili
 Virtual Memory Lecture notes from MKP and S. Yalamanchili Sections 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8, 5.10 Reading (2) 1 The Memory Hierarchy ALU registers Cache Memory Memory Memory Managed by the compiler Memory Managed
Virtual Memory Lecture notes from MKP and S. Yalamanchili Sections 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8, 5.10 Reading (2) 1 The Memory Hierarchy ALU registers Cache Memory Memory Memory Managed by the compiler Memory Managed
Computer System Components
 Computer System Components CPU Core 1 GHz - 3.2 GHz 4-way Superscaler RISC or RISC-core (x86): Deep Instruction Pipelines Dynamic scheduling Multiple FP, integer FUs Dynamic branch prediction Hardware
Computer System Components CPU Core 1 GHz - 3.2 GHz 4-way Superscaler RISC or RISC-core (x86): Deep Instruction Pipelines Dynamic scheduling Multiple FP, integer FUs Dynamic branch prediction Hardware
Virtual Memory. Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. April 12, 2018 L16-1
 Virtual Memory Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L16-1 Reminder: Operating Systems Goals of OS: Protection and privacy: Processes cannot access each other s data Abstraction:
Virtual Memory Daniel Sanchez Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab M.I.T. L16-1 Reminder: Operating Systems Goals of OS: Protection and privacy: Processes cannot access each other s data Abstraction:
Mainstream Computer System Components
 Mainstream Computer System Components Double Date Rate (DDR) SDRAM One channel = 8 bytes = 64 bits wide Current DDR3 SDRAM Example: PC3-12800 (DDR3-1600) 200 MHz (internal base chip clock) 8-way interleaved
Mainstream Computer System Components Double Date Rate (DDR) SDRAM One channel = 8 bytes = 64 bits wide Current DDR3 SDRAM Example: PC3-12800 (DDR3-1600) 200 MHz (internal base chip clock) 8-way interleaved
Virtual Memory. Virtual Memory
 Virtual Memory Virtual Memory Main memory is cache for secondary storage Secondary storage (disk) holds the complete virtual address space Only a portion of the virtual address space lives in the physical
Virtual Memory Virtual Memory Main memory is cache for secondary storage Secondary storage (disk) holds the complete virtual address space Only a portion of the virtual address space lives in the physical
Views of Memory. Real machines have limited amounts of memory. Programmer doesn t want to be bothered. 640KB? A few GB? (This laptop = 2GB)
 CS6290 Memory Views of Memory Real machines have limited amounts of memory 640KB? A few GB? (This laptop = 2GB) Programmer doesn t want to be bothered Do you think, oh, this computer only has 128MB so
CS6290 Memory Views of Memory Real machines have limited amounts of memory 640KB? A few GB? (This laptop = 2GB) Programmer doesn t want to be bothered Do you think, oh, this computer only has 128MB so
Chapter 5A. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
Chapter 5A Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) Fast, expensive Dynamic RAM (DRAM) In between Magnetic disk Slow, inexpensive Ideal memory Access time of SRAM
This Unit: Main Memory. Virtual Memory. Virtual Memory. Other Uses of Virtual Memory
 This Unit: Virtual Application OS Compiler Firmware I/O Digital Circuits Gates & Transistors hierarchy review DRAM technology A few more transistors Organization: two level addressing Building a memory
This Unit: Virtual Application OS Compiler Firmware I/O Digital Circuits Gates & Transistors hierarchy review DRAM technology A few more transistors Organization: two level addressing Building a memory
Memory Technology. Caches 1. Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Magnetic disk. Ideal memory. 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB
 Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Computer Architecture. Memory Hierarchy. Lynn Choi Korea University
 Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy Lynn Choi Korea University Memory Hierarchy Motivated by Principles of Locality Speed vs. Size vs. Cost tradeoff Locality principle Temporal Locality: reference to
Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy Lynn Choi Korea University Memory Hierarchy Motivated by Principles of Locality Speed vs. Size vs. Cost tradeoff Locality principle Temporal Locality: reference to
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CSE 351. Virtual Memory
 CSE 351 Virtual Memory Virtual Memory Very powerful layer of indirection on top of physical memory addressing We never actually use physical addresses when writing programs Every address, pointer, etc
CSE 351 Virtual Memory Virtual Memory Very powerful layer of indirection on top of physical memory addressing We never actually use physical addresses when writing programs Every address, pointer, etc
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Types of cache misses Compulsory Misses: first access to a block cannot be in the cache (cold start misses) Capacity
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Types of cache misses Compulsory Misses: first access to a block cannot be in the cache (cold start misses) Capacity
Lecture 18: DRAM Technologies
 Lecture 18: DRAM Technologies Last Time: Cache and Virtual Memory Review Today DRAM organization or, why is DRAM so slow??? Lecture 18 1 Main Memory = DRAM Lecture 18 2 Basic DRAM Architecture Lecture
Lecture 18: DRAM Technologies Last Time: Cache and Virtual Memory Review Today DRAM organization or, why is DRAM so slow??? Lecture 18 1 Main Memory = DRAM Lecture 18 2 Basic DRAM Architecture Lecture
Chapter 7 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy. Memory Hierarchy. Locality. Memories: Review
 Memories: Review Chapter 7 Large and Fast: Exploiting Hierarchy DRAM (Dynamic Random Access ): value is stored as a charge on capacitor that must be periodically refreshed, which is why it is called dynamic
Memories: Review Chapter 7 Large and Fast: Exploiting Hierarchy DRAM (Dynamic Random Access ): value is stored as a charge on capacitor that must be periodically refreshed, which is why it is called dynamic
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 16 - Cache and virtual memory review
 CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 6 - Cache and virtual memory review Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 6 - Cache and virtual memory review Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David
Virtual Memory. Motivation:
 Virtual Memory Motivation:! Each process would like to see its own, full, address space! Clearly impossible to provide full physical memory for all processes! Processes may define a large address space
Virtual Memory Motivation:! Each process would like to see its own, full, address space! Clearly impossible to provide full physical memory for all processes! Processes may define a large address space
Spring 2016 :: CSE 502 Computer Architecture. Caches. Nima Honarmand
 Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
k -bit address bus n-bit data bus Control lines ( R W, MFC, etc.)
 THE MEMORY SYSTEM SOME BASIC CONCEPTS Maximum size of the Main Memory byte-addressable CPU-Main Memory Connection, Processor MAR MDR k -bit address bus n-bit data bus Memory Up to 2 k addressable locations
THE MEMORY SYSTEM SOME BASIC CONCEPTS Maximum size of the Main Memory byte-addressable CPU-Main Memory Connection, Processor MAR MDR k -bit address bus n-bit data bus Memory Up to 2 k addressable locations
