IS 258 PC Maintenance
|
|
|
- Lewis Jackson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IS 258 PC Maintenance Lecture 1: Hardware Basics Instructor: Henry Kalisti 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering
2 Objectives To Understand: PC Functions and Components: Tools and Equipment Maintenance Toolkit 2
3 Introduction to Computer A device made up of electronic and electro mechanical components. A computer is an electronic device that accepts information and instructions from a user, manipulates the information according to the instructions, displays the information in some way, and stores the information for retrieval later 3
4 Introduction to Computer A computer system elements: Hardware The physical portion of the computer including processors, Memory, input/output Software Set of instructions used to manipulate the hardware, refers to the non tangible parts of the computer and it includes the system software and application software and People (Users) 4
5 Introduction to Computer The design and construction of the hardware of a particular computer is referred to as its architecture or configuration A number of computer architecture exists which includes Von Neumann, AMD, SPARC. The technical details about each component are called specifications, this includes processor speed, memory size, screen size, type of operating systems installed etc. 5
6 What is PC A compact computer that uses a microprocessor and is designed for individual use, as by a person in an office or at home or school, for such applications as word processing, data management, financial analysis, or computer games. 6
7 The System Case/Computer Case Store your components Computer Case Designs: Desktop or Tower ATX form:- It can accommodate ATX motherboards 7
8 The Motherboard Sometime known as Main Board or System Board It is a main circuit board which connects all the device on a microcomputer There are several factors used to choose a motherboard (Homework) Components contained into motherboard: Processor slot, Processor voltage regulators, Motherboard chipset, Level 2 cache, Memory SIMM or DIMM sockets, Bus slots, ROM BIOS, Clock / CMOS battery, Super I/O chips 8
9 The Motherboard Chipset Controls the system and its capabilities. Hub of all data transfer. Some of the items it dictates: Memory controller, Real-time clock, Keyboard and mouse controller, Secondary cache controller, PCI bridge, EIDE controller Form Factors Physical size and dimensions of the motherboard. It determines general layout, size and feature placement on a motherboard. Baby AT, ATX, Proprietary 9
10 Types of Motherboard 1: XT Motherboards XT Stands for extended Technology. These are all old model motherboard. In this motherboards, we find old model processor socket LIF (Low Insertion Force) sockets, ram slots DIMMs and ISA (Industry Standards Architecture) slots, 12pin Power Connector. Eg: Pentium-I, Pentium-MMX, Pentium -II and Pentium-II Processors. 10
11 Types of Motherboard 2: AT Motherboards AT stands for Advanced Technology. Have PGA (Pin Grid Array) Socket, SD Ram slots, 20pin power connector PCI slots and ISA slots. Eg: Pentium-III Processors 11
12 Types of Motherboard 3: Baby AT Motherboards: Baby AT Motherboards have the combination of XT and AT. They have both slot type processor sockets and PGA processor sockets, SD Ram slots and DDR Ram slots, PCI slots and ISA slots, 12 Pin power connector and 20Pin power connector and Ports. Eg: Pentium-III and Pentium-IV 12
13 Types of Motherboard 4: ATX Motherboards: ATX stands for Advanced Technology extended. Latest motherboards are called as ATX motherboards. Designed by ATX form factor. In this motherboards, we find MPGA Processor Sockets, DDR Ram slots, PCI slots, AGP slots, Primary and secondary IDE interfaces, SATA connectors, 20pin and 24 pin ATX power connector and Ports. Eg: Pentium-IV, Dual Core, Core 2 Duo, Quad Core, i3, i5 and i7 Processors. 13
14 The Motherboard Onboard devices - Video/Audio/LAN Lower cost. Lesser Flexibility. Upgradability Bus speeds supported. Number of expansion slots. Number and Types of IO ports available. 14
15 The Motherboard 15
16 CPU/MCP Its main component of motherboard It Controls all the inner functions of the system. Some key concepts Clock Speed: The number of pulses per second that sets the tempo for the processor. Cache: A small but fast memory area. There are levels of cache Bus (FSB and BSB): Collection of wires connecting different devices. Pipeline : Implementation technique where multiple instructions are overlapped 16
17 CPU/MCP 32/64 bit processors: The amount of data a processor can process in a clock cycle. Clock speed and overclocking: BUS SPEED x MULTIPLIER = CPU SPEED (Clock) CPU chips are intel 8088,8086,80286,80386,80486 Pentium I-IV, Celeron, Athlon, Duron, Cyrix C3, Itanium (64 bit), Opteron (64 bit) 17
18 CPU/MCP 32/64 bit processors: The amount of data a processor can process in a clock cycle. Clock speed and overclocking: BUS SPEED x MULTIPLIER = CPU SPEED (Clock) CPU chips are intel 8088,8086,80286,80386,80486 Pentium I-IV, Celeron, Athlon, Duron, Cyrix C3, Itanium (64 bit), Opteron (64 bit) Coprocessor Coprocessor is a special purpose microprocessor, which is used to speed up main processor job by taking over some of the main processors work. Most common type of coprocessor is a math coprocessor. Coprocessor chips are used to help the main processor in carrying out its various functions. A math coprocessor helps main processor in performing mathematical calculations 18
19 CPU/MCP 19
20 Memory Computer stores program and data that help the program in carrying out its operations. Types of Memory: RAM Memory and ROM Memory RAM Memory Read/Write type of memory It used by the processor to keep program, data and intermediate results during program executions. It is VOLATILE type of memory Physically installed into motherboard: DIP (dual In-line Pin) memory chips were used on initial motherboards. Later SIMM (single inline memory modules) became common. Currently DIMM (dual inline memory modules) are most common memory module. 20
21 Memory ROM Memory ROM or Read Only Memory It cannot be written Advantage of ROM!!? (Homework) A motherboard contains one or more of these ROM chips. The memory capacity of a ROM varies from one type of system to another. 64 KiloByte (KB) was normally sufficient for a XT system, whereas as AT system requires 256KB of ROM. 21
22 Memory 22
23 I/O Expansion Slot Expansion slot The expansion slots are long thin connectors on the motherboard, near the backside of the computer. They are connected to the motherboards through data, address and control lines/buses on these slots. Expansion cards can connect to these expansion slots such as display card, hard drive controller, sound card, network card, modem card etc. on these slots via Data address and Control Bus on the motherboard 23
24 I/O Expansion Slot Depending on the width and the technology, the expansion slot bus can be divided into the following categories: 8 bit ISA, 16 bit ISA, MCA, EISA, VESA local bus or VL bus, PCI local Bus 24
25 Bus Its an electronic path on which signals are sent from one part of the computer to another. Categorizes according to the number of BINARY DIGITS (bits) that they can transfer at a time. 8 bit wide is called an 8 bit bus. Bus referred as bandwidth. The bandwidth of a bus is the measure of data that can fit in the bus at a given time. Data Bus: Is a set of wires or tracks on the motherboard Data bus is used to transfer data from one part of the computer to another part. Address Bus: is a set of wires or tracks on the motherboard Printed Circuit Board(PCB) which is used to specify address of a memory location 25
26 I/O Ports and Cables A Port is the physical connector used to connect an external device to the system; they are usually found in the back of the system. PC system I/O ports: Serial ports, Parallel ports, PS/2 ports, USB, SCSI, Network, Audio, Video and FireWire ports 26
27 I/O Ports and Cables Serial ports and Cables Serial port serializes data Send data one bit at a time Slower than Parallel ports. Advantage: it needs only one wire to transmit the 8 bits Disadvantage: is that it takes longer to transmit the data Cables are small and low in cost Serial ports, also called communication (COM) ports, are bidirectional. Some systems provide (2) serial ports, a 25-pin and a 9-pin. A 25-pin port only needs 9 pins so in the interest of size most manufacturers only provide 9-pin connectors. Serial ports are male and D-Shell male connectors 27
28 I/O Ports and Cables Serial device (e.g. printers and modem) needs serial Maximum length of 50 feet (15.2 m). Mouse, Modems, PDAs, Digital Cameras etc use Serial port. 28
29 I/O Ports and Cables Parallel ports and cables Its a 25-pin D-Shell female connector Bits transmitted in parallel It faster compare to serial port. Devices that connect to a parallel port are limited by the distance. Parallel devices uses parallel cables to connects to parallel ports A parallel cable has a maximum length of 15 feet (4.5 m). Parallel ports can be used to connect computer peripherals: Printers, Scanners, CD burners, External hard drives, Iomega Zip removable drives, Network, adapters, Tape backup drives 29
30 I/O Ports and Cables PS/2 ports Used to interface keyboards, mouse and pointing devices. The PS/2 port is a six-pin mini-din female connector. Frees the serial port for other devices 30
31 I/O Ports and Cables USB ports and Cables It provides single, standardized, easy-to-use way to connect up to 127 devices to a computer USB 1.1 allowed transmission rates of up to 12 Mbps in full-speed mode and 1.5 Mbps in low-speed mode. USB 2.0 allows transmission speeds up to 480 Mbps. USB devices: Printers, Scanners, Mice, Joysticks, Flight yokes, Digital cameras, Webcams, Scientific data acquisition devices, Modems, Speakers, Telephones, Video phones, Storage devices such as Zip drives, Network connections Universal Serial Bus connectors are on the back. Its Hot pluggable, Plug-andplay. Most OSs supports USB and installation of the device drivers is quick and easy The USB standard uses A and B connectors; A connectors head upstream toward the computer and B connectors head downstream and connect to individual devices. 31
32 I/O Ports and Cables SCSI Ports and Cables A SCSI port can transmit data at rates in excess of 320 Mbps and can support up to 15 devices. If a single SCSI device is connected to a SCSI port, the cable can be up to 80 feet (24.4 m) in length. If multiple SCSI devices are connected to a SCSI port, the cable can be up to 40 (12.2 m) feet in length. A SCSI port on a computer can be one of three different types:db-25 female connector, High-density 50-pin female connector and High-density 68-pin female connector 32
33 I/O Ports and Cables Network Ports and Cables Its also called an RJ-45 port It connects a computer to a network. The RJ45 connector vs. RJ11 connector The connection speed depends on the type of network port. Standard Ethernet can transmit up to 10 Mbps, Fast Ethernet can transmit up to 100 Mbps, and Gigabit Ethernet can transmit up to 1000 Mbps. The maximum length of network cable is 328 feet (100 m). 33
34 I/O Ports and Cables Audio Ports An audio port connects audio devices to the computer. The following audio ports are commonly used - Line In connects to an external source, such as a stereo system. - Microphone In connects to a microphone. - Line Out connects to speakers or headphones. - Auxiliary In is an additional line in. - Gameport/MIDI connects to a joystick or MIDI -interfaced device. 34
35 I/O Ports and Cables Video Ports and Connectros A video port connects a monitor cable to a computer. Several video port and connector types exist: 1. Video Graphics Array (VGA) has a three-row 15-pin D-Shell female connector and provides analog output to a monitor. 2. Digital Visual Interface (DVI) has a 24-pin female connector or a 29-pin female 3. High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) has a 19-pin connector and provides digital video and digital audio signals. 4. S-Video has a four-pin connector and provides analog video signals. 5. Component/RGB has three shielded cables (red, green, and blue) with RCA jacks and provides analog video signals. 35
36 PC Functions and Components I/O Ports and Cables The video ports and video card 36
37 I/O Ports and Cables FireWire Ports and Cables FireWire is a high-speed, hot-swappable interface that connects peripheral devices to a computer. A single FireWire port in a computer can support up to 63 devices. Some devices can also be powered through the FireWire port FireWire uses the IEEE 1394 standard and is also known as i.link. The IEEE 1394a standard supports data rates up to 400 Mbps and cable lengths up to 15 feet (4.5 m). This standard uses a six-pin connector or a four-pin connector. The IEEE 1394b standard supports data rates in excess of 800 Mbps and uses a nine-pin connector. 37
38 I/O Ports and Cables The IEEE 1394a standard supports data rates up to 400 Mbps and cable lengths up to 15 feet (4.5 m). This standard uses a six-pin connector or a fourpin connector. The IEEE 1394b standard supports data rates in excess of 800 Mbps and uses a nine-pin connector. 38
39 I/O Ports and Cables 39
40 Homework With the aid of diagrams explain in details the following computer architecture Von Neumann, AMD and SPARC 40
41 Interface Cards A.K.A. Adapter Cards Advantage: increase a computer s functionality by adding controllers for specific devices or by replacing malfunctioning ports
42 Interface Cards Adapter cards are used to expand and customize the computer s capability: NIC connects a computer to a network using a network cable. Wireless NIC connects a computer to a network using radio frequencies. Sound adapter provides audio capability. Video adapter provides graphic capability. Modem adapter connects a computer to the Internet using a phone line. SCSI adapter connects SCSI devices, such as hard drives or tape drives to a computer.
43 Interface Cards RAID adapter connects multiple hard drives to a computer to provide redundancy and to improve performance. USB port connects a computer to peripheral devices. Parallel port connects a computer to peripheral devices. Serial port connects a computer to peripheral devices
44 Interface Cards The type of adapter card connector must match the expansion slot. The different types of expansion slots are as follows: Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is an 8-bit or 16-bit expansion slot. Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA) is a 32-bit expansion slot. Microchannel Architecture (MCA) is an IBM-proprietary 32- bit expansion slot. Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a 32-bit or 64-bit expansion slot. Advanced Graphics Port (AGP) is a 32-bit expansion slot. 44 PCI-Express is a serial bus expansion slot. PCI-Express is backward-compatible with PCI slots. PCI-Express has x1, x4, x8, and x16 slots. 44
45 Video Card A modern graphics card is a circuit board with memory and a dedicated processor. Converts digital information into the pixels to display it on the monitor. Different range of cards: 3D Acceleration and Video Memory. It is a Expensive component 45
46 Sound Card Converts digital data (bits) into analog sound wave and vice-versa. It has Digital Signal Processor, RAM, ADC and DAC. It has jacks for speaker, microphone, line in, line out and joysticks 46
47 Network Interface Card Connects PC to LAN (Local Area Network). Ethernet, Token Ring. Speeds: 10Mbps, 100Mbps and 1000Mbps Onboard or Add-on Card 47
48 Storage Devices Referred as Removable device Reads/Writes information to magnetic or optical storage media. Store data permanently or to retrieve information from a media disk. For portability, some storage drives can connect to the computer using a USB port, a FireWire port, or a SCSI port. The common types of storage drives: Floppy drive, Hard drive, Optical drive, Flash drive and Network drive 48
49 Storage devices Floppy disk Uses removable 3.5-inch floppy disks. Storage Capacity: 720 KB or 1.44 MB of data. The floppy drive can be used to boot the computer if it contains a bootable floppy disk. The floppy drive is slowly being replaced by cheaper, faster, and larger-capacity storage such as writable CDs, DVDs, and flash drive media
50 Storage devices Hard drives It is a magnetic storage device Stores data permanently Configurations: C: drive and contains OS and Applications Boot Sequence: First drive Storage capacity measured in billions of bytes, or gigabytes (GB). Speed measured in revolutions per minute (rpm). Multiple hard drives can be added to increase 50 storage capacity. 50
51 Storage devices Optical devices It use lasers to read data on the optical media. Optical drives types: Compact disc (CD) and Digital versatile disc (DVD) Prerecorded (read-only), Recordable (write once), or Re-recordable (read and write multiple times). CDs Storage Capacity: max. 700 MB. DVDs Storage Capacity: 8.5 GB Optical Media types: CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD- ROM, DVD-RAM, DVD+/-R and DVD+/
52 Storage devices Flash Drives A flash drive, also known as a thumb drive Connects to USB Port A flash drive uses a special type of memory that requires no power to maintain the data. These drives can be accessed by the operating system in the same way other types of drives are accessed. The storage capacity of a flash drive varies from a couple of megabytes to 16 gigabytes. Network Drives A network drive is a connection to a remote 52 computer s storage for access to files, directories, and applications. 52
53 Types of Drive Interfaces Hard drives and optical drives are manufactured with different interfaces that are used to connect the drive to the computer. When you install a storage drive in a computer, the connection interface on the drive must be the same as the controller on the motherboard
54 Types of Drive Interfaces Some common drive interfaces are as follows: Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE), also called Advanced Technology Attachment (ATA), is an early drive controller interface that connects computers and hard-disk drives. An IDE interface uses a 40-pin connector. Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics (EIDE), also called ATA-2, is an updated version of the IDE drive controller interface. EIDE supports hard drives larger than 512 MB, enables Direct Memory Access (DMA) for speed, and uses the AT Attachment Packet Interface (ATAPI) to accommodate optical drives and 54 tape drives on the EIDE bus. An EIDE interface uses a 40-pin connector. 54
55 Types of Drive Interfaces Parallel ATA (PATA) refers to the parallel version of the ATA drive controller interface. Serial ATA (SATA) refers to the serial version of the ATA drive controller interface. A SATA interface uses a seven-pin connector. Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) is a drive controller interface that can connect up to 15 drives. SCSI can connect both internal and external drives. A SCSI interface uses a 50-pin, 68-pin, or 80-pin connector
56 Internal cables Drives require both a power cable and a data cable. A power supply has a SATA power Connector for SATA drives, a Molex power connector for PATA drives, and a Berg four-pin connector for floppy drives. The buttons and the LED lights on the front of the case connect to the motherboard with the front panel cables. Some examples of internal PC cables: 56 56
57 Internal cables Data cables connect drives to the drive controller, which is located on an adapter card or the motherboard. Some common types of data cables are as follows: Floppy disk drive (FDD) data cable has up to two 34- pin drive connectors and one 34-pin connector for the drive controller. PATA (IDE) data cable has 40 conductors, up to two 40-pin connectors for drives, and one 40-pin connector for the drive controller. PATA (EIDE) data cable has 80 conductors, up to two 40-pin connectors 57 for drives, and one 40-pin connector for the drive controller. 57
58 Internal cables SATA data cable has seven conductors, one keyed connector for the drive, and one keyed connector the drive controller. 26 IT Essentials: PC Hardware and Software Companion Guide SCSI data cable: Three types of SCSI data cables exist: A narrow SCSI data cable has 50 conductors, up to seven 50-pin connectors for drives, and one 50-pin connector for the drive controller, also called the host adapter. A wide SCSI data cable has 68 conductors, up to pin connectors for drives, and one 68-pin connector for the host adapter. An Alt-4 SCSI data cable has 80 conductors, up to pin connectors for drives, and one 80-pin connector for the host adapter. 58
59 Power Supply Unit (PSU) Supplies power to every single part in the PC. Convert the Alternating Current power (230 V AC) into Direct Current power (3.3 V, 5 V and 12 V DC) The power supply also ensures that the system does not run unless the power supplied is sufficient to operate the system properly. The power supply completes internal checks and tests before allowing the system to start. If the tests are successful, the power supply sends a special signal to the motherboard called Power_Good. If this signal is not present continuously, the computer does not run. Therefore, when the AC voltage dips and 59 the power supply becomes stressed or overheated, the Power_Good signal goes down and forces a system reset or complete shutdown. 59
60 Connectors keyed connectors. Designed to be inserted in only one direction. Each part of the connector has a colored wire with a different voltage running through it Different power supply form factors provide different power output connections, depending on system requirements. AT form factors have been slowly phased out by ATX form factor power supplies because of the different case sizes and advanced features. ATXv12 was created to add power support for the motherboard by adding another four-pin power connector. 60
61 Connectors Connectors are used to connect specific components and various locations on the motherboard: A Molex connector is a keyed connector used to connect to an optical drive or hard drive. A Berg connector is a keyed connector used to connect to a floppy drive. A Berg connector is smaller than a Molex connector. A 20-pin or 24-pin slotted connector is used to connect to the motherboard. The 24 pin slotted connector has two rows of 12 pins each, and the 20- pin slotted connector has two rows of 10 pins each. A four-pin-to-eight-pin auxiliary power connector has two rows of two to four pins and supplies power 61 to all areas of the motherboard. The four-pin-toeight-pin auxiliary power connector is the same shape as the main power connector, but smaller. 61
62 The Display Subsystem AKA Output devices Eg. Monitors and Projects Types of Monitor: Cathode Ray Tube (CRT), LCD and DLP 62
63 The Display Subsystem Difference between monitor types: technology used to create an image CRT: Cathode ray tube monitors are the most common monitor type. Red, green, and blue electron beams move back and forth across the phosphorous-coated screen. The phosphor glows when struck by the electron beam. Areas not struck by the electron beam do not glow. The combination of glowing and non glowing areas is what creates the image on the screen. 63 Most televisions also use this technology. 63
64 The Display Subsystem LCD: Liquid crystal display is commonly used in laptops and some projectors. It consists of two polarizing filters with a liquid crystal solution between them. An electronic current aligns the crystals so that light can either pass through or not pass through. The effect of light passing through in certain areas and not in others is what creates the image. LCD comes in two forms active matrix and passive matrix. Active matrix is sometimes called thin film transistor (TFT). TFT allows each pixel to be controlled, which creates very sharp color images. Passive matrix is less expensive than active matrix but does not provide the same level of 64 image control. LCD Monitors are becoming the most common type of computer monitor. 64
65 The Display Subsystem DLP: Digital light processing is another technology that is used in projectors. DLP projectors use a spinning color wheel with a microprocessor-controlled array of mirrors called a digital micromirror device (DMD). Each mirror corresponds to a specific pixel. Each mirror reflects light toward or away from the projector optics. This creates a monochromatic image of up to 1024 shades of gray between white and black. The color wheel then adds the color data to complete the projected color image. 65
66 The Display Subsystem Display Resolutions Display Standard Linear Pixels (HXV) Aspect Ratio CGA :10 EGA :6 VGA :3 WVGA :9 SVGA :3 XGA :
67 The Display Subsystem Higher-resolution settings produce better image quality. Several factors are involved in monitor resolution: Pixels: The term pixel is an abbreviation of picture element. Pixels are the tiny dots that comprise a screen. Each pixel consists of red, green, and blue. Dot pitch: Dot pitch is the distance between pixels on the screen. A lower dot pitch number produces a better image. Refresh rate: The refresh rate is how often per second the image is rebuilt. A higher refresh rate produces a better image and reduces the level of flicker. Interlaced/non interlaced: Interlaced monitors create the image by scanning the screen two times. The first scan covers the odd lines, top to bottom, and the second scan 67 covers the even lines. Non interlaced monitors create the image by scanning the screen one line at a time from top to bottom. Most CRT monitors today are non interlaced. 67
68 The Display Subsystem Horizontal Vertical Colors (HVC): The number of pixels in a line is the horizontal resolution. The number of lines in a screen is the vertical resolution. The number of Colors that can be reproduced is the color resolution. Aspect ratio: Aspect ratio is the horizontal-to-vertical measurement of the monitor s viewing area. For example, a 4:3 aspect ratio applies to a viewing area that is 16 inches wide by 12 inches high. A 4:3 aspect ratio also applies to a viewing area that is 24 inches wide by 18 inches high. A viewing area that is 22 inches wide by 12 inches high has an aspect ratio of 11:6. Monitors have controls for adjusting the image quality. Some common monitor settings: Brightness is the image s intensity. Contrast is the ratio of light to dark. Position is the 68vertical and horizontal location of the image on the screen. Reset returns the monitor settings to the factory defaults. 68
69 Modem Modem (Modulator and Demodulator) Send data over a phone The sending modem converts digital data into analog data Modems are available in Different capacities modems. 300 bps s through 1983 or so 1200 bps - Gained popularity in 1984 and bps 9600 bps - First appeared in late 1990 and early kilobits per second (Kbps) 28.8 Kbps and 33.6 Kbps 56 Kbps - Became the standard in ADSL, with theoretical maximum of up to 8 megabits per second (Mbps) - Gained popularity in
70 InternalModem 70
71 Modem Internal Modem Resides on the expansion board on the slot of the motherboard. Does not require separate power adapter. Cheaper than external modem. Has natural protection inside PC cabinet. 71
72 Modem External Modem Resides on a self-contained box outside the PC. Requires external power adapter. Connected to PC s serial port via the cable. Easy to install and troubleshoot such as resetting the modem. Expensive than internal modems. 72
73 ExternalModem 73
About the Presentations
 About the Presentations The presentations cover the objectives found in the opening of each chapter. All chapter objectives are listed in the beginning of each presentation. You may customize the presentations
About the Presentations The presentations cover the objectives found in the opening of each chapter. All chapter objectives are listed in the beginning of each presentation. You may customize the presentations
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware
 : Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 1 Introducing Hardware Objectives Learn that a computer requires both hardware and software to work Learn about the many different hardware components
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Personal Computer
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Personal Computer IT Essentials: PC Hardware and Software v4.0 1 Chapter 1 Objectives 1.1 Explain the IT industry certification 1.2 Describe a computer system 1.3 Identify
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Personal Computer IT Essentials: PC Hardware and Software v4.0 1 Chapter 1 Objectives 1.1 Explain the IT industry certification 1.2 Describe a computer system 1.3 Identify
This course is focused on the following two industry standard certifications:
 1.0 Introduction Information technology (IT) is the design, development, implementation, support, and management of computer hardware and software applications. An IT professional is knowledgeable about
1.0 Introduction Information technology (IT) is the design, development, implementation, support, and management of computer hardware and software applications. An IT professional is knowledgeable about
Components of a personal computer
 Components of a personal computer Computer systems ranging from a controller in a microwave oven to a large supercomputer contain components providing five functions. A typical personal computer has hard,
Components of a personal computer Computer systems ranging from a controller in a microwave oven to a large supercomputer contain components providing five functions. A typical personal computer has hard,
FUNCTIONS OF COMPONENTS OF A PERSONAL COMPUTER
 FUNCTIONS OF COMPONENTS OF A PERSONAL COMPUTER Components of a personal computer - Summary Computer Case aluminium casing to store all components. Motherboard Central Processor Unit (CPU) Power supply
FUNCTIONS OF COMPONENTS OF A PERSONAL COMPUTER Components of a personal computer - Summary Computer Case aluminium casing to store all components. Motherboard Central Processor Unit (CPU) Power supply
IT ESSENTIALS V. 4.1 Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PERSONAL COMPUTER
 IT ESSENTIALS V. 4.1 Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PERSONAL COMPUTER 1.0 Introduction 1. What is information technology? The design, development, implementation, support, and management of computer hardware
IT ESSENTIALS V. 4.1 Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PERSONAL COMPUTER 1.0 Introduction 1. What is information technology? The design, development, implementation, support, and management of computer hardware
Chapter 0: IT Essentials Introduction Chapter 1: Introduction to the Personal Computer
 Name Date Chapter 0: IT Essentials Introduction Chapter 1: Introduction to the Personal Computer After completion of this chapter, students should be able to: Explain IT industry certifications and technician
Name Date Chapter 0: IT Essentials Introduction Chapter 1: Introduction to the Personal Computer After completion of this chapter, students should be able to: Explain IT industry certifications and technician
Buses, Video, and Upgrades
 Unit 9 Buses, Video, and Upgrades Copyright 2005 Heathkit Company, Inc. All rights reserved. CPU Parallel Port Memory Keyboard Controller Video Adapter The Data Bus System Controller 2 CPU Memory Keyboard
Unit 9 Buses, Video, and Upgrades Copyright 2005 Heathkit Company, Inc. All rights reserved. CPU Parallel Port Memory Keyboard Controller Video Adapter The Data Bus System Controller 2 CPU Memory Keyboard
Displayport, as shown, has 20 pins and can be used for audio, video, or both audio and video transmission.
 EXTERNAL PORTS AND CABLES A video port connects a monitor to a computer using a cable. Video ports and monitor cables transfer analog signals, digital signals, or both. Computers are digital devices that
EXTERNAL PORTS AND CABLES A video port connects a monitor to a computer using a cable. Video ports and monitor cables transfer analog signals, digital signals, or both. Computers are digital devices that
Introduction to the Personal Computer
 Introduction to the Personal Computer 2.1 Describe a computer system A computer system consists of hardware and software components. Hardware is the physical equipment such as the case, storage drives,
Introduction to the Personal Computer 2.1 Describe a computer system A computer system consists of hardware and software components. Hardware is the physical equipment such as the case, storage drives,
Computers Are Your Future
 Computers Are Your Future 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Inside the System Unit 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Slide 2 What You Will Learn... Understand how computers represent
Computers Are Your Future 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 6 Inside the System Unit 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Slide 2 What You Will Learn... Understand how computers represent
Introduction To Computer Hardware. Hafijur Rahman
 Introduction To Computer Hardware Lecture 2 Hafijur Rahman What is a Computer? A computer is an electronic device, which can input, process, and output data. input processing output A computer is a machine
Introduction To Computer Hardware Lecture 2 Hafijur Rahman What is a Computer? A computer is an electronic device, which can input, process, and output data. input processing output A computer is a machine
Computer Overview. A computer item you can physically see or touch. A computer program that tells computer hardware how to operate.
 Hardware Computer Overview A computer item you can physically see or touch. Software A computer program that tells computer hardware how to operate. Information Technology (IT) The broad subject related
Hardware Computer Overview A computer item you can physically see or touch. Software A computer program that tells computer hardware how to operate. Information Technology (IT) The broad subject related
computer case. Various form factors exist for motherboards, as shown in this chart.
 INTERNAL COMPONENTS The motherboard is the main printed circuit board and contains the buses, or electrical pathways, found in a computer. These buses allow data to travel between the various components
INTERNAL COMPONENTS The motherboard is the main printed circuit board and contains the buses, or electrical pathways, found in a computer. These buses allow data to travel between the various components
Personal computer hardware From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (Redirected from Computer hardware)
 Personal computer hardware From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (Redirected from Computer hardware) Personal computer hardware are component devices which are typically installed into or peripheral to
Personal computer hardware From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (Redirected from Computer hardware) Personal computer hardware are component devices which are typically installed into or peripheral to
Computers Are Your Future
 Computers Are Your Future Twelfth Edition Chapter 2: Inside the System Unit Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 Inside the Computer System Copyright 2012 Pearson Education,
Computers Are Your Future Twelfth Edition Chapter 2: Inside the System Unit Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1 Inside the Computer System Copyright 2012 Pearson Education,
Notes - Computer Hardware Basics
 The Computer A computer is made up of many parts: Notes - Computer Hardware Basics 1. Input/Output (I/O) devices These allow you to send information to the computer or get information from the computer.
The Computer A computer is made up of many parts: Notes - Computer Hardware Basics 1. Input/Output (I/O) devices These allow you to send information to the computer or get information from the computer.
Intentionally Blank 0
 Intentionally Blank 0 Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1 Understanding Your Computer: Computers are Data Processing Devices Perform four major functions Input:
Intentionally Blank 0 Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1 Understanding Your Computer: Computers are Data Processing Devices Perform four major functions Input:
IT Essentials v5.0: Introduction to the Personal Computer Online Study Questions Chapter 1
 Name: Per.: IT Essentials v5.0: Introduction to the Personal Computer Online Study Questions Chapter 1 Curr Question Answer 1.0.1 1. How large were the first computers? The OS 2. What makes up a computer?
Name: Per.: IT Essentials v5.0: Introduction to the Personal Computer Online Study Questions Chapter 1 Curr Question Answer 1.0.1 1. How large were the first computers? The OS 2. What makes up a computer?
What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? 1-1
 What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did the computer become known as the stored-program computer? Do they all have the same
What is the typical configuration of a computer sold today? 1-1 Computer Hardware Components In this chapter: How did the computer become known as the stored-program computer? Do they all have the same
Inside the Computer System
 Inside the Computer System What s on the Motherboard? What s on the Motherboard? What s on the Motherboard? Parallel processing o Method where more than one processor performs at the same time faster processing
Inside the Computer System What s on the Motherboard? What s on the Motherboard? What s on the Motherboard? Parallel processing o Method where more than one processor performs at the same time faster processing
Assembling Computers Summer Academy Presented by the Petters Research Institute (PRI) in cooperation with the Belize Defense Force
 Assembling Computers 2007 Summer Academy Presented by the Petters Research Institute (PRI) in cooperation with the Belize Defense Force Andrew Schretter Paola Zamora What Will You Learn? What is a computer?
Assembling Computers 2007 Summer Academy Presented by the Petters Research Institute (PRI) in cooperation with the Belize Defense Force Andrew Schretter Paola Zamora What Will You Learn? What is a computer?
Computer Hardware. Created Spring 1996 Revised Fall 2005
 Computer Hardware Created Spring 1996 Revised Fall 2005 1 Computer An electronic device that has the ability to accept data, internally store and execute a program of instructions, perform mathematical,
Computer Hardware Created Spring 1996 Revised Fall 2005 1 Computer An electronic device that has the ability to accept data, internally store and execute a program of instructions, perform mathematical,
The Components of the System Unit
 The Components of the System Unit The System Unit What is the system unit? Case that contains electronic components of the computer used to process data Sometimes called the chassis system unit system
The Components of the System Unit The System Unit What is the system unit? Case that contains electronic components of the computer used to process data Sometimes called the chassis system unit system
Module 1. Introduction. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 1 Introduction Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 3 Embedded Systems Components Part I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Structural Layout with Example Instructional Objectives After going through
Module 1 Introduction Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 3 Embedded Systems Components Part I Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Structural Layout with Example Instructional Objectives After going through
Identify Components of the. Motherboard
 Identify Components of the Chipset Motherboard Collection of chips that work together to provide the switching circuitry needed to move data throughout the computer 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
Identify Components of the Chipset Motherboard Collection of chips that work together to provide the switching circuitry needed to move data throughout the computer 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
Buses, Video, and Upgrades
 Unit 9 Buses, Video, and Upgrades Copyright 2005 Heathkit Company, Inc. All rights reserved. CPU Parallel Port Memory Keyboard Controller Video Adapter The Data Bus System Controller 2 CPU Memory Keyboard
Unit 9 Buses, Video, and Upgrades Copyright 2005 Heathkit Company, Inc. All rights reserved. CPU Parallel Port Memory Keyboard Controller Video Adapter The Data Bus System Controller 2 CPU Memory Keyboard
Inside Your PC. Introduction to Computer Science. Polly Huang NTU EE
 Introduction to Computer Science Polly Huang NTU EE http://homepage.ntu.edu.tw/~pollyhuang pollyhuang@ntu.edu.tw Polly Huang, NTU EE Hardware 1 Inside Your PC Polly Huang, NTU EE Hardware 2 Today s Computer
Introduction to Computer Science Polly Huang NTU EE http://homepage.ntu.edu.tw/~pollyhuang pollyhuang@ntu.edu.tw Polly Huang, NTU EE Hardware 1 Inside Your PC Polly Huang, NTU EE Hardware 2 Today s Computer
I/O, Input Ports and Devices
 I/O, Input Ports and Devices Daren Russ All Rights Reserved No part of this material or any of its contents may be reproduced, copied, modified or adapted, without the prior written consent of the author,
I/O, Input Ports and Devices Daren Russ All Rights Reserved No part of this material or any of its contents may be reproduced, copied, modified or adapted, without the prior written consent of the author,
By Dr. Samaher Hussein Ali
 Department of Information Networks The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES ON Evolving Technology of Laptops By Dr. Samaher Hussein Ali College of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@itnet.uobabylon.edu.iq
Department of Information Networks The University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES ON Evolving Technology of Laptops By Dr. Samaher Hussein Ali College of Information Technology, University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@itnet.uobabylon.edu.iq
Buying a PC? Consider the following Before Buying A New Computer or Laptop:
 Buying a PC? Computer technology is changing so fast it is sometimes very hard for the average consumer to keep up. New products and systems are coming out at such a pace even some the salesmen are probably
Buying a PC? Computer technology is changing so fast it is sometimes very hard for the average consumer to keep up. New products and systems are coming out at such a pace even some the salesmen are probably
PARTS OF THE COMPUTER. 2nd ESO IES CAP DE LLEVANT
 PARTS OF THE COMPUTER 2nd ESO IES CAP DE LLEVANT 1. COMPUTING OR INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY The branch of engineering science that studies (with the aid of computers)the procedure of calculating and information
PARTS OF THE COMPUTER 2nd ESO IES CAP DE LLEVANT 1. COMPUTING OR INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY The branch of engineering science that studies (with the aid of computers)the procedure of calculating and information
HP TouchSmart Desktop PC Product Specifications
 HP TouchSmart 520-1049 Desktop PC Product Specifications Product release information Product number QX342AA Country/region sold in Canada Display 58.42 cm (23 inch) LCD panel display with touchscreen Resolution:
HP TouchSmart 520-1049 Desktop PC Product Specifications Product release information Product number QX342AA Country/region sold in Canada Display 58.42 cm (23 inch) LCD panel display with touchscreen Resolution:
Technical Specifications: Dell OptiPlex GX150 System
 Technical Specifications: Dell OptiPlex GX150 System Processor Microprocessor type Internal cache Intel Pentium III or Celeron microprocessor 32-kilobyte (KB) first-level (16-KB data cache; 16-KB instruction
Technical Specifications: Dell OptiPlex GX150 System Processor Microprocessor type Internal cache Intel Pentium III or Celeron microprocessor 32-kilobyte (KB) first-level (16-KB data cache; 16-KB instruction
Contents: Computer definition Computer literacy Computer components Computer categories Computer usage. Tablet PC
 bas design Prepared by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti Putra Malaysia Serdang Contents: Computer
bas design Prepared by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti Putra Malaysia Serdang Contents: Computer
Full file at
 Exam Name Full file at https://fratstock.eu MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) is data that has been organized or presented in a meaningful
Exam Name Full file at https://fratstock.eu MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) is data that has been organized or presented in a meaningful
Certifications Available After Taking this Course
 Certifications Available After Taking this Course Your Path to Success ITE v6.0 1 Certification Value The More The Better Technical certifications are worth more than degrees in this field The number of
Certifications Available After Taking this Course Your Path to Success ITE v6.0 1 Certification Value The More The Better Technical certifications are worth more than degrees in this field The number of
1.- Search for information about the difference between BITS, BYTES and other units of measure for digital information.
 Hardware Activities: 1.- Search for information about the difference between BITS, BYTES and other units of measure for digital information. a) A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and digital
Hardware Activities: 1.- Search for information about the difference between BITS, BYTES and other units of measure for digital information. a) A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and digital
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 1 Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 2 Chapter Topics Functions of a computer Data versus information Bits and bytes Input devices Output devices Processing Storage
1 Technology in Action Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 2 Chapter Topics Functions of a computer Data versus information Bits and bytes Input devices Output devices Processing Storage
HARDWARE AND OPERATING SYSTEMS
 HARDWARE AND OPERATING SYSTEMS UNIT 2. IES MIGUEL ESPINOSA - MURCIA 3º ESO HARDWARE AND OPERATING SYSTEMS COMPUTERS LANGUAGE AND FUNCTION Binary System ASCII code Units of information Computer functions
HARDWARE AND OPERATING SYSTEMS UNIT 2. IES MIGUEL ESPINOSA - MURCIA 3º ESO HARDWARE AND OPERATING SYSTEMS COMPUTERS LANGUAGE AND FUNCTION Binary System ASCII code Units of information Computer functions
4) Apple's OS X and Microsoft Windows are examples of software. A) utility B) application C) operating system D) communication
 Technology in Action Complete, 13e (Evans et al.) Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1) Computers use language consisting of 0s and 1s. A) symbol B) binary C) byte D) system 2) In
Technology in Action Complete, 13e (Evans et al.) Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1) Computers use language consisting of 0s and 1s. A) symbol B) binary C) byte D) system 2) In
CMSC 1513 Lecture 1.2
 Key Point: A computer is an electronic device that stores and processes data. Hardware Software Hardware comprises the visible, physical elements of the computer. Software provides the invisible instructions
Key Point: A computer is an electronic device that stores and processes data. Hardware Software Hardware comprises the visible, physical elements of the computer. Software provides the invisible instructions
Sahalsoftware college. Welcome To understanding Basic Computer Concept
 Welcome To understanding Basic Computer Concept 1 Chapter1: Understanding Computer Concepts What is a computer? A computer is a machine that takes in data, processes if following a set of instructions
Welcome To understanding Basic Computer Concept 1 Chapter1: Understanding Computer Concepts What is a computer? A computer is a machine that takes in data, processes if following a set of instructions
Show how to connect three Full Adders to implement a 3-bit ripple-carry adder
 Show how to connect three Full Adders to implement a 3-bit ripple-carry adder 1 Reg. A Reg. B Reg. Sum 2 Chapter 5 Computing Components Yet another layer of abstraction! Components Circuits Gates Transistors
Show how to connect three Full Adders to implement a 3-bit ripple-carry adder 1 Reg. A Reg. B Reg. Sum 2 Chapter 5 Computing Components Yet another layer of abstraction! Components Circuits Gates Transistors
Question. Announcement. Computer Hardware. Definition of a Computer. Essential Parts. The Box (CPU) input/output device that processes information
 Question Announcement What are the three essential components of a modern computer? Be general or specific Definition of a Computer A computer is an device that receives information (input), processes
Question Announcement What are the three essential components of a modern computer? Be general or specific Definition of a Computer A computer is an device that receives information (input), processes
Introduction To Computer Hardware
 Introduction To Computer Hardware In this section of notes you will learn what are the basic parts of a computer and how they work. High Level View Of A Computer Buses Connect the different parts of the
Introduction To Computer Hardware In this section of notes you will learn what are the basic parts of a computer and how they work. High Level View Of A Computer Buses Connect the different parts of the
CS1101: Lecture 21. Organization: Input/Output. Lecture Outline. Buses. A simple personal computer. Buses
 CS1101: Lecture 21 Computer Systems Organization: Input/Output Dr. Barry O Sullivan b.osullivan@cs.ucc.ie Buses Lecture Outline A simple personal computer Direct Memory Access Interrupts Bus Arbiter &
CS1101: Lecture 21 Computer Systems Organization: Input/Output Dr. Barry O Sullivan b.osullivan@cs.ucc.ie Buses Lecture Outline A simple personal computer Direct Memory Access Interrupts Bus Arbiter &
COMPUTER HARDWARE & NETWORK TROUBLESHOOTING
 COMPUTER HARDWARE & NETWORK TROUBLESHOOTING UNIT 1 1. What is processor? (NOV 2013) 2. Define system clock? (NOV 2013) 3. What are the two types of hardware interrupts (NOV 2010) 4. List the type of switching
COMPUTER HARDWARE & NETWORK TROUBLESHOOTING UNIT 1 1. What is processor? (NOV 2013) 2. Define system clock? (NOV 2013) 3. What are the two types of hardware interrupts (NOV 2010) 4. List the type of switching
Motherboard Components of a Desktop Computer
 Motherboard Components of a Desktop Computer The motherboard is the main component inside the case. It is a large rectangular board with integrated circuitry that connects the rest of the parts of the
Motherboard Components of a Desktop Computer The motherboard is the main component inside the case. It is a large rectangular board with integrated circuitry that connects the rest of the parts of the
Motherboard Central Processing Unit (CPU) Random access memory (RAM)
 Cool Careers in Cyber Security Missing Computer Parts Delivery: Can be used as a table demo (hands-on) activity or during a presentation session. Large display table recommended. Pre-cut and laminate the
Cool Careers in Cyber Security Missing Computer Parts Delivery: Can be used as a table demo (hands-on) activity or during a presentation session. Large display table recommended. Pre-cut and laminate the
Chapter One. Introduction to Computer System
 Principles of Programming-I / 131101 Prepared by: Dr. Bahjat Qazzaz -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Chapter One Introduction to Computer System
Principles of Programming-I / 131101 Prepared by: Dr. Bahjat Qazzaz -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Chapter One Introduction to Computer System
Introduction. Computer System Organization. Languages, Levels, Virtual Machines. A multilevel machine. Sarjana Magister Program
 Computer System Organization Sarjana Magister Program Introduction Tb. Maulana Kusuma Week 1 Session 1 Languages, Levels, Virtual Machines A multilevel machine 1 Contemporary Multilevel Machines A six-level
Computer System Organization Sarjana Magister Program Introduction Tb. Maulana Kusuma Week 1 Session 1 Languages, Levels, Virtual Machines A multilevel machine 1 Contemporary Multilevel Machines A six-level
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS When we talk about computers, we really are talking about a Computer System. Computer System: It is a combination of Hardware and Software. This combination allows a computer
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS When we talk about computers, we really are talking about a Computer System. Computer System: It is a combination of Hardware and Software. This combination allows a computer
Information Communications Technology (CE-ICT) 6 th Class
 Information Communications Technology (CE-ICT) 6 th Class Lecture 2: Computer Concepts (Part A) Lecturer: Objectives Hardware Concepts Types of Computer Components of a Computer System Computer Performance
Information Communications Technology (CE-ICT) 6 th Class Lecture 2: Computer Concepts (Part A) Lecturer: Objectives Hardware Concepts Types of Computer Components of a Computer System Computer Performance
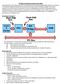
Chapter No. 1. Motherboard & its Components
 Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components What is Motherboard? The main circuit board of a microcomputer. The motherboard contains the connectors for attaching additional boards. It contains the CPU,
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components What is Motherboard? The main circuit board of a microcomputer. The motherboard contains the connectors for attaching additional boards. It contains the CPU,
Discovering Computers 2012
 Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Edited by : Asma AlOsaimi The System Unit Memory The inside of the system unit on a desktop personal computer includes: Drive bay(s)
Discovering Computers 2012 Your Interactive Guide to the Digital World Edited by : Asma AlOsaimi The System Unit Memory The inside of the system unit on a desktop personal computer includes: Drive bay(s)
Computer Systems. Communication (networks, radio links) Meatware (people, users don t forget them)
 Computers are useful machines, but they are generally useless by themselves. Computers are usually part of a system a computer system includes: Hardware (machines) Software (programs, applications) Communication
Computers are useful machines, but they are generally useless by themselves. Computers are usually part of a system a computer system includes: Hardware (machines) Software (programs, applications) Communication
True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Bubble A for True and B for False
 1A Name _ Midterm Review Part 1 Lesson 1 and 2 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Bubble A for True and B for False 1. A computer is an electronic device that receives data (input),
1A Name _ Midterm Review Part 1 Lesson 1 and 2 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Bubble A for True and B for False 1. A computer is an electronic device that receives data (input),
True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Bubble A for True and B for False
 1 Name Midterm Review Part 1 Lesson 1 and 2 "B" True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Bubble A for True and B for False 1. Eight bits are equal to one byte. 2. A computer is an electronic
1 Name Midterm Review Part 1 Lesson 1 and 2 "B" True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Bubble A for True and B for False 1. Eight bits are equal to one byte. 2. A computer is an electronic
FC0-U21 CompTIA Strata IT Fundamentals
 FC0-U21 CompTIA Strata IT Fundamentals Version 13.8 QUESTION NO: 1 Which of the following is NOT a parallel port mode? A. EPP/ECP B. ECP C. EPS D. EPP QUESTION NO: 2 Which of the following expansion buses
FC0-U21 CompTIA Strata IT Fundamentals Version 13.8 QUESTION NO: 1 Which of the following is NOT a parallel port mode? A. EPP/ECP B. ECP C. EPS D. EPP QUESTION NO: 2 Which of the following expansion buses
Motherboard Specifications, A8AE-LE (AmberineM)
 1 of 7 6/28/2009 11:14 PM» Return to original page Motherboard Specifications, A8AE-LE (AmberineM) Motherboard specifications table Motherboard layout and photos Clearing the CMOS settings Clearing the
1 of 7 6/28/2009 11:14 PM» Return to original page Motherboard Specifications, A8AE-LE (AmberineM) Motherboard specifications table Motherboard layout and photos Clearing the CMOS settings Clearing the
LabSim Mapping Matrix
 LabSim Mapping Matrix A+ Guide to Hardware Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting Fourth Edition (220-601) Mapping: Chapters to LabSims Chapter Page Number LabSim Chapter 1 Pages 2-3 Pages 3-6 Pages
LabSim Mapping Matrix A+ Guide to Hardware Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting Fourth Edition (220-601) Mapping: Chapters to LabSims Chapter Page Number LabSim Chapter 1 Pages 2-3 Pages 3-6 Pages
Downloaded from various sources on the NET
 Overview Computers. Hardware components of a Computer. Purpose and functions of computer operating systems. Evolution of computer operating systems. Operating systems available today. Downloaded from various
Overview Computers. Hardware components of a Computer. Purpose and functions of computer operating systems. Evolution of computer operating systems. Operating systems available today. Downloaded from various
Q1. Describe C.P.U and its subunits with the help of diagram?
 Q1. Describe C.P.U and its subunits with the help of diagram? Ans. C.P.U (CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT) Book page # 27 The C.P.U is the brain of computer.it controls and supervises all the units. Processing
Q1. Describe C.P.U and its subunits with the help of diagram? Ans. C.P.U (CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT) Book page # 27 The C.P.U is the brain of computer.it controls and supervises all the units. Processing
Computer Hardware. In this lesson we will learn about Computer Hardware, so that we have a better understanding of what a computer is.
 In this lesson we will learn about, so that we have a better understanding of what a computer is. USB Port Ports and Connectors USB Cable and Connector Universal Serial Bus (USB) is by far the most common
In this lesson we will learn about, so that we have a better understanding of what a computer is. USB Port Ports and Connectors USB Cable and Connector Universal Serial Bus (USB) is by far the most common
QUESTIONS ABOUT COMPUTERS
 1. What is a computer? QUESTIONS ABOUT COMPUTERS A computer is a machine that processes information, in other words, it receives and stores data, performs calculations with this data and presents the results
1. What is a computer? QUESTIONS ABOUT COMPUTERS A computer is a machine that processes information, in other words, it receives and stores data, performs calculations with this data and presents the results
TECHNOLOGY IN ACTION. Chapter 2. Alan Evans * Kendall Martin * Mary Anne Poatsy. Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts
 TECHNOLOGY IN ACTION Alan Evans * Kendall Martin * Mary Anne Poatsy Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices Output
TECHNOLOGY IN ACTION Alan Evans * Kendall Martin * Mary Anne Poatsy Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts Understanding Digital Components Understanding Your Computer Input Devices Output
Parts are adapted from Windows 98 by Mark Twain Media, Inc. A Computer System has Hardware and Software
 Parts are adapted from Windows 98 by Mark Twain Media, Inc. A Computer System has Hardware and Software All the parts--monitor, printer, hard drive, etc.-- cables, cabinets, and programs that make a computer
Parts are adapted from Windows 98 by Mark Twain Media, Inc. A Computer System has Hardware and Software All the parts--monitor, printer, hard drive, etc.-- cables, cabinets, and programs that make a computer
PowerPoint Presentation to Accompany. Chapter 4. Hardware. Copyright 2014 Pearson Educa=on, Inc. Publishing as Pren=ce Hall
 PowerPoint Presentation to Accompany Chapter 4 Hardware Objectives 1. Explain the function of the CPU. 2. Identify the parts of a system unit and motherboard. 3. Compare different types of storage devices.
PowerPoint Presentation to Accompany Chapter 4 Hardware Objectives 1. Explain the function of the CPU. 2. Identify the parts of a system unit and motherboard. 3. Compare different types of storage devices.
Defining Computers. Defining Computers. Understanding Essential Computer Concepts
 Understanding Essential Computer Concepts Defining Computers A high-speed idiot must be told exactly what to do by humans and programs step-by-step instructions An electronic device that accepts input,
Understanding Essential Computer Concepts Defining Computers A high-speed idiot must be told exactly what to do by humans and programs step-by-step instructions An electronic device that accepts input,
Providing Fundamental ICT Skills for Syrian Refugees PFISR
 Yarmouk University Providing Fundamental ICT Skills for Syrian Refugees (PFISR) Providing Fundamental ICT Skills for Syrian Refugees PFISR Dr. Amin Jarrah Amin.jarrah@yu.edu.jo Objectives Covered 1.1 Given
Yarmouk University Providing Fundamental ICT Skills for Syrian Refugees (PFISR) Providing Fundamental ICT Skills for Syrian Refugees PFISR Dr. Amin Jarrah Amin.jarrah@yu.edu.jo Objectives Covered 1.1 Given
Part 1 of 3 -Understand the hardware components of computer systems
 Part 1 of 3 -Understand the hardware components of computer systems The main circuit board, the motherboard provides the base to which a number of other hardware devices are connected. Devices that connect
Part 1 of 3 -Understand the hardware components of computer systems The main circuit board, the motherboard provides the base to which a number of other hardware devices are connected. Devices that connect
Introduction to a Typical PC. Freedom High School
 Introduction to a Typical PC Freedom High School A Day in the Life of a Student A Day in the Life of a Student Wake up using a digital alarm clock Utilize handheld-vibrating electric toothbrush Check email,
Introduction to a Typical PC Freedom High School A Day in the Life of a Student A Day in the Life of a Student Wake up using a digital alarm clock Utilize handheld-vibrating electric toothbrush Check email,
Memory Study Material
 Computer memory refers to the devices that are used to store data or programs on a temporary or permanent basis for use in a computer. Any data or instruction entered into the memory of a computer is considered
Computer memory refers to the devices that are used to store data or programs on a temporary or permanent basis for use in a computer. Any data or instruction entered into the memory of a computer is considered
What step should a technician perform first when servicing computer equipment?
 - 1 IT EssClass Test 2 1 What is the unit used to measure CPU speed? Bits. Bytes. Hertz. Voltage. 2 What is the purpose of a heat sink on a processor? To cool the processor. To ground the processor. To
- 1 IT EssClass Test 2 1 What is the unit used to measure CPU speed? Bits. Bytes. Hertz. Voltage. 2 What is the purpose of a heat sink on a processor? To cool the processor. To ground the processor. To
TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. PREFACE KEY FEATURES PERFORMANCE LIST BLOCK DIAGRAM...
 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. PREFACE... 1-1 1.2. KEY FEATURES... 1-1 1.3. PERFORMANCE LIST... 1-3 1.4. BLOCK DIAGRAM... 1-4 1.5. INTRODUCE THE PCI - BUS... 1-5 1.6. FEATURES...
Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. PREFACE... 1-1 1.2. KEY FEATURES... 1-1 1.3. PERFORMANCE LIST... 1-3 1.4. BLOCK DIAGRAM... 1-4 1.5. INTRODUCE THE PCI - BUS... 1-5 1.6. FEATURES...
Computer Basics PC-100
 Computer Basics PC-100 Course Group Overview PC-100 Computer Basics PC-101 Intro to Operating Systems and Window s Basics PC-102 Computer Programs and File Management PC-103 Computer Security PC-104 The
Computer Basics PC-100 Course Group Overview PC-100 Computer Basics PC-101 Intro to Operating Systems and Window s Basics PC-102 Computer Programs and File Management PC-103 Computer Security PC-104 The
Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software
 Page 1 Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software In this section of notes you will learn about the basic parts of a computer and how they work. Page 2 What Is Hardware? A computer is made up of
Page 1 Introduction To Computers: Hardware and Software In this section of notes you will learn about the basic parts of a computer and how they work. Page 2 What Is Hardware? A computer is made up of
Bus Example: Pentium II
 Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Conventional PCI, often shortened to PCI, is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer. PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Conventional PCI, often shortened to PCI, is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer. PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect
Chapter 9: Other Peripherals
 Chapter 9: Other Peripherals Complete CompTIA A+ Guide to PCs, 6e To identify the components of the video subsystem The various display types including laptop displays Basic display terminology To install
Chapter 9: Other Peripherals Complete CompTIA A+ Guide to PCs, 6e To identify the components of the video subsystem The various display types including laptop displays Basic display terminology To install
ROYAL INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION & MANAGEMENT
 ROYAL INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION & MANAGEMENT Computer Hardware Course Contents : A+ Operating System Technologies: Introduction to Computers Types of Software & languages Introduction to Operating System
ROYAL INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION & MANAGEMENT Computer Hardware Course Contents : A+ Operating System Technologies: Introduction to Computers Types of Software & languages Introduction to Operating System
Chapter 4 The Components of the System Unit
 Chapter 4 The Components of the System Unit Chapter 4 Objectives Differentiate among various styles of of system units Differentiate among the the various types of of memory Identify chips, adapter cards,
Chapter 4 The Components of the System Unit Chapter 4 Objectives Differentiate among various styles of of system units Differentiate among the the various types of of memory Identify chips, adapter cards,
Master List of Key Topics
 Master List of Key Topics Table 1-3 Key Topics for Chapter 1 List The components and subsystems real computers contain Table 1-2 The six-step CompTIA A+ troubleshooting theory 14 Figure 1-8 An antistatic
Master List of Key Topics Table 1-3 Key Topics for Chapter 1 List The components and subsystems real computers contain Table 1-2 The six-step CompTIA A+ troubleshooting theory 14 Figure 1-8 An antistatic
EVGA assumes you have purchased all necessary parts needed to allow for proper system functionality.
 Before You Begin Parts NOT in the Kit This kit contains all the hardware necessary to install and connect your new EVGA e-7050/610i GPU motherboard with integrated GeForce graphics processing. However,
Before You Begin Parts NOT in the Kit This kit contains all the hardware necessary to install and connect your new EVGA e-7050/610i GPU motherboard with integrated GeForce graphics processing. However,
Chapter 3: Computer Assembly
 Chapter 3: Computer Assembly IT Essentials v6.0 ITE v6.0 1 Chapter 3 - Sections & Objectives 3.1 Assemble the Computer Build a Computer. 3.2 Boot the Computer Explain how to verify BIOS and UEFI settings.
Chapter 3: Computer Assembly IT Essentials v6.0 ITE v6.0 1 Chapter 3 - Sections & Objectives 3.1 Assemble the Computer Build a Computer. 3.2 Boot the Computer Explain how to verify BIOS and UEFI settings.
Chapter 2 Motherboards and Processors
 A+ Certification Guide Chapter 2 Motherboards and Processors Chapter 2 Objectives Students should be able to explain: Motherboards and Their Components: Form factors, integrated ports and interfaces, memory
A+ Certification Guide Chapter 2 Motherboards and Processors Chapter 2 Objectives Students should be able to explain: Motherboards and Their Components: Form factors, integrated ports and interfaces, memory
INFORMATION SYSTEM PARTS AND COMPUTER TYPES
 INFORMATION SYSTEM PARTS AND COMPUTER TYPES PARTS OF INFORMATION SYSTEM People are end users who use computers to make themselves more productive. Hardware refers to the physical components of your computer
INFORMATION SYSTEM PARTS AND COMPUTER TYPES PARTS OF INFORMATION SYSTEM People are end users who use computers to make themselves more productive. Hardware refers to the physical components of your computer
Introduction To Computers: Hardware
 Introduction To Computers: Hardware In this section of notes you will learn about the basic parts of a computer and how they work. What Is Hardware? A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware consists
Introduction To Computers: Hardware In this section of notes you will learn about the basic parts of a computer and how they work. What Is Hardware? A computer is made up of hardware. Hardware consists
MSc-IT 1st Semester Fall 2016, Course Instructor M. Imran khalil 1
 Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips, adapter cards, and other components of a motherboard
Objectives Overview Differentiate among various styles of system units on desktop computers, notebook computers, and mobile devices Identify chips, adapter cards, and other components of a motherboard
Computers Are Your Future Prentice-Hall, Inc.
 Computers Are Your Future 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 7 Input/Output and Storage 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 What You Will Learn About ü The purpose of special keys and
Computers Are Your Future 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 7 Input/Output and Storage 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 What You Will Learn About ü The purpose of special keys and
Specifications for the Gateway 400SD4 Notebook
 Specifications for the Gateway 400SD4 Notebook Specifications are subject to change without notice or obligation. Processor and Core Logic Processor options One Intel Celeron CPU -OR- One Intel Pentium
Specifications for the Gateway 400SD4 Notebook Specifications are subject to change without notice or obligation. Processor and Core Logic Processor options One Intel Celeron CPU -OR- One Intel Pentium
Removable Storage and Computer Interfaces
 Removable Storage and Computer Interfaces JICA Computer Science Course in 2009 H. Miyata Contents Preface Computer Interfaces IDE(ATAPI) SCSI USB etc. Storage Devices and Media CD, DVD MO Flash memory
Removable Storage and Computer Interfaces JICA Computer Science Course in 2009 H. Miyata Contents Preface Computer Interfaces IDE(ATAPI) SCSI USB etc. Storage Devices and Media CD, DVD MO Flash memory
Computers Are Your Future
 Computers Are Your Future 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 7 Input/Output and Storage 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 Input Input is any data entered into the computer s memory
Computers Are Your Future 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Computers Are Your Future Chapter 7 Input/Output and Storage 2006 Prentice-Hall, Inc Slide 2 Input Input is any data entered into the computer s memory
PC BIOS Settings: (22 Jan 2004) These settings will be required for either O.S. Installation or to improve the PC performance.
 PC BIOS Settings: (22 Jan 2004) These settings will be required for either O.S. Installation or to improve the PC performance. S.No. Standard Hard Disks Operation Reason 1. CMOS SETUP Keep Type setting
PC BIOS Settings: (22 Jan 2004) These settings will be required for either O.S. Installation or to improve the PC performance. S.No. Standard Hard Disks Operation Reason 1. CMOS SETUP Keep Type setting
ZOTAC ZBOX User s Manual
 ZOTAC ZBOX User s Manual No part of this manual, including the products and software described in it, may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language
ZOTAC ZBOX User s Manual No part of this manual, including the products and software described in it, may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language
Introduction to Computer Graphics (CS602) Lecture No 03 Graphics Systems
 Introduction to Computer Graphics (CS602) Lecture No 03 Graphics Systems 3.1 Raster-Scan Systems Interactive raster graphics systems typically employ several processing units. In addition to the CPU, a
Introduction to Computer Graphics (CS602) Lecture No 03 Graphics Systems 3.1 Raster-Scan Systems Interactive raster graphics systems typically employ several processing units. In addition to the CPU, a
A+ Guide to Managing & Maintaining Your PC, 8th Edition. Chapter 4 Part II All About Motherboards
 Chapter 4 Part II All About Motherboards Part 2 Buses and Expansion Slots Bus System of pathways used for communication Carried by bus: Power, control signals, memory addresses, data Data and instructions
Chapter 4 Part II All About Motherboards Part 2 Buses and Expansion Slots Bus System of pathways used for communication Carried by bus: Power, control signals, memory addresses, data Data and instructions
IT Infrastructure: Hardware LEARNING GOALS. The Core Computer Components. September 16, 2015
 IT Infrastructure: Hardware September 16, 2015 LEARNING GOALS Identify the major components of modern PCs Explain the role of the components of a computer system; Explain input devices and how they operate.
IT Infrastructure: Hardware September 16, 2015 LEARNING GOALS Identify the major components of modern PCs Explain the role of the components of a computer system; Explain input devices and how they operate.
Chapter 6 Cubix SP1 Blade Server
 Chapter 6 Cubix SP1 Blade Server Introduction Cubix designed the SP1 Blade Server to fit inside a BladePoint or BladeStation enclosure. The Blade Server features the Intel Pentium 4 processor, the Intel
Chapter 6 Cubix SP1 Blade Server Introduction Cubix designed the SP1 Blade Server to fit inside a BladePoint or BladeStation enclosure. The Blade Server features the Intel Pentium 4 processor, the Intel
