(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
|
|
|
- Chester Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 MICHAEL et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) PERSONAL SOUND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAY Related U.S. Application Data OF SOUND PRESSURE LEVEL OR OTHER ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITION (60) Pyigal application No. 61/020,189, filed on Jan. (75) Inventors: NICHOLAS R. MICHAEL, San Publication Classification Francisco, CA (US); Ephram (51) Int. Cl. Cohen, San Francisco, CA (US); H04R 29/00 ( ) Caslav V. Pavlovic, Palo Alto, CA H04B I/38 ( ) (US); Meena Ramani, Mountain (52) U.S. Cl /58; 455/566 View, CA (US) (57) ABSTRACT Correspondence Address: A cell phone providing a display of Sound pressure level or other environmental condition is described. An ear-level HAYNES BEFFEL & WOLFELD LLP PO BOX 366 module, which includes a microphone or other sensor, and processing resources for analyzing the input from the micro HALF MOON BAY, CA (US) phone to provide a measure of an environmental condition, Such as sound pressure level, at the ear, and deliver it to a cell (73) Assignee: SOUND ID, Palo Alto, CA (US) phone or other hand held device for display in a manner readable by the user. The companion cell phone provides display and Supporting processing resources, presenting a (21) Appl. No.: 12/350,823 graphical meter view. Alternatively, the audio data or other measurement is produced using a microphone on the cell (22) Filed: Jan. 8, 2009 phone.
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 4 US 2009/ A1 22 OTHER AUDIO SOURCES A 4 f MOBILE PHONE NETWORK 1O ill -1 WIRELESS S. AUDIO LINK S. w LINKED COMPANION MIC WIRELESS CONFIG. LINK -20 Å 19 FIG. 1
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 4 US 2009/ A JOSS3OOJ) 99 ) JosueSduel
4
5 Patent Application Publication Sheet 4 of 4 US 2009/ A FIG. 4
6 PERSONAL SOUND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAY OF SOUND PRESSURE LEVEL OR OTHER ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITION CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION 0001 Benefit is claimed of U.S. Provisional Application No. 61/020, 189, filed 10 Jan. 2008, entitled PERSONAL SOUND SYSTEM FOR DISPLAY OF SOUND PRES SURE LEVEL OR OTHER ENVIRONMENTAL CONDI TION. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Field of the Invention The present invention relates to personalized sound systems, including a cell phone, or a combination of an ear level device adapted to be worn on the ear and provide audio processing and a cellphone or other handheld device, and use of Such systems for Sound pressure level measurement and display, or measurement and display of other environmental conditions Description of Related Art 0005 Mobile phones are widely used devices with signifi cant processing power. Modern phones also include usable displays, making them Suitable platforms for a wide variety of applications One area in which the processing power of mobile phones can be utilized is the adaptation of the audio output to an individual's hearing profile. For example, U.S. Pat. No. 6,944,474 B2, by Rader et al., describes a mobile phone with audio processing functionality that can be adapted to the hearing profile of the user, addressing many of the problems of the use of mobile phones by hearing impaired persons, including the idea of sensing background noise and applying the information to dynamically adjusting processing of sound in the mobile phone. See also, International Publication No. WO 01/24576 A1, entitled PRODUCING AND STORING HEARINGPROFILES AND CUSTOMIZED AUDIODATA BASED (sic), by Pluvinage et al., which describes a variety of applications of hearing profile data With improved wireless technologies, such as Blue tooth R technology, techniques have been developed to couple hearing aids using wireless networks to other devices, for the purpose of programming the hearing aid and for cou pling the hearing aid with Sources of Sound other than the ambient environment. In copending U.S. patent application Ser. No. 11/569,499; filed 21 Nov. 2006; entitled PER SONAL SOUND SYSTEM INCLUDING MULTI-MODE EAR-LEVEL MODULE WITH PRIORITY LOGIC, which is incorporated by reference as if fully set forth herein, an ear-level module is described with processing resources usable for adaptation of the audio at the ear-level module according to a user's hearing profile, and for a variety of functions that take advantage of the processor on the ear-level module and of communication with a mobile phone It is often useful to measure an environmental char acteristic in a listening environment so that persons in that environment can take action to avoid harm to their hearing or make other adjustments to respond to conditions in the envi ronment. It is desirable to provide systems that make this information more available to consumers without requiring the use of specialized equipment. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION A mobile phone is described that includes resources for displaying a Sound pressure level measurement, or a mea Surement of another characteristic of the immediate environ ment. The data used for the measurement is detected either at an ear-level module such as a hearing aid or a headset, or at the mobile phone A personal sound system is described that includes an ear-level module, which includes a microphone or other sensor, and processing resources for analyzing the input from the microphone or other sensor to provide a measure of an environmental condition, Such as Sound pressure level or temperature, at the ear, and deliver it to a cell phone or other hand held device for display in a manner readable by the user In an alternative, the microphone, or other sensor, and processing resources used for Sound pressure level mea Surement and display, or measurement and display of other environmental conditions, are provided on the mobile phone The microphone data from the ear-level module or from a sensor on the mobile phone is processed according to technology provided herein, to obtain Sound pressure level of the immediate environment in decibels, for example, as used in standard Sound meters. A frequency weighting may or may not be applied to the data. A standard A-weighting defined in industry standards relating to the measurement of per ceived loudness may be used The ear-level module includes a radio for transmit ting and receiving communication signals encoding audio data, an audio transducer, one or more microphones, a user input and control circuitry. In embodiments of the technol ogy, the ear-level module is configured with hearing aid func tionality for processing audio received on one or more of the microphones according to a hearing profile of the user, and playing the processed sound back on the audio transducer. The control circuitry includes logic for communication using the radio with a plurality of Sources of audio data in memory storing a set of variables for processing the audio data. Logic on the ear-level module is operable in a plurality of signal processing modes in addition to, or combined with, the mode described above for delivering measurement data to a com panion hand held phone Other aspects and advantages of the present inven tion can be seen on review of the drawings, the detailed description and the claims, which follow. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0015 FIG. 1 illustrates a wireless audio network including a multimode ear-level module and a plurality of other audio Sources, along with a wireless configuration network includ ing a sound pressure level display on the mobile phone FIG. 2 is a system block diagram of data processing resources in the multimode ear module including sensors and computing resources of measuring an environmental condi tion FIG. 3 is a simplified block diagram of a mobile phone, representative of personal communication devices according to the present invention, including computing resources for displaying measurement of an environmental condition.
7 0018 FIG. 4 is a drawing of a mobile phone including a graphical Sound pressure level display. DETAILED DESCRIPTION A detailed description of embodiments of the present invention is provided with reference to the FIGS FIG. 1 illustrates a wireless network which extends the capabilities of an ear module 10, adapted to be worn at ear level, and operating in multiple modes including a mode in which data indicating a measurement of an environmental condition at the ear-level module is transmitted to a compan ion device, such as a mobile phone 11. The ear module 10 can include a hearing aid mode having hearing aid functionality. The network facilitates techniques for providing personalized Sound from a plurality of audio Sources such as mobile phones 11, other audio sources 22 Such as televisions and radios, and with a linked companion microphone 12. In addition, a wire less network provides communication channels for configur ing the ear module 10 and other audio Sources ("companion modules ) in the network using a configuration host 13, which comprises a program executed on a computer that includes an interface to the wireless network. In one embodi ment described herein, the wireless audio links 14, 15, 21 between the ear module 10 and the linked companion micro phone 12, between the ear module 10 and the companion mobile phone 11 (See, FIG. 37), and between the ear module 10 and other companion audio Sources 22, respectively, are implemented according to Bluetooth R compliant synchro nous connection-oriented SCO channel protocol (See, for example, Specification of the Bluetooth System, Version 2.0, 4 Nov. 2004). Wireless link 16 couples the mobile phone 11 to a network service provider for the mobile phone service. The wireless configuration links 17, 18, 19, 20 between the con figuration host 13 and the ear module 10, the mobile phone 11, the linked companion microphone 12, and the other audio Sources 22 are implemented using a control channel. Such as a modified version of the Bluetooth R compliant serial port profile SPP protocol or a combination of the control channel and SCO channels. (See, for example, BLUETOOTHSPECI FICATION, SERIAL PORT PROFILE, Version 1.1, Part K:5, 22 Feb. 2001). Of course, a wide variety of other wireless communication technologies may be applied in alternative embodiments. The mobile phone 11 includes a display and a program that displays a measurement such as Sound pressure level based on data delivered by the ear-level module, or in an alternative, based on data provided by a microphone or other sensor on the mobile phone itself. The mobile phone 11 also provides mobile phone functions including call setup, call answering and other basic telephone call management tasks in communication with a service provider on a wireless tele phone network Companion modules, such as the companion micro phone 12 consist of Small components, such as a battery operated module designed to be worn on a lapel, that house thin data processing platforms, and therefore do not have the rich user interface needed to support configuration of private network communications to pair with the ear module. For example, thin platforms in this context do not include a keyboard or touch pad practically suitable for the entry of personal identification numbers or other authentication fac tors, network addresses, and so on. Thus, to establisha private connection pairing with the ear module, the radio is utilized in place of the user interface In embodiments described herein, each of the audio Sources in communication with the ear module 10 may oper ate with a different subset of the set of variables stored on the ear module for audio processing, where each different Subset is optimized for the particular audio source, and for the hear ing profile of the user. The set of variables on the ear module 10 is stored in nonvolatile memory on the ear module, and includes for example, indicators for selecting data processing algorithms to be applied and parameters used by data pro cessing algorithms The ear-level module is implemented with a micro phone that is separate from the microphone on a companion mobile phone, and is preferably designed with a frequency response much broader than the typical telephone micro phone. For example, the microphone and associated electron ics on the ear module may handle frequencies up to 20 KHZ or So, compared with the typical cellular phone designed to handle frequencies up to about 4 KHZ. Also, the earpiece microphone and electronics are designed to handle higher Sound levels, which are not processed in typical cell phones. The companion cellphone provides a display and Supporting processing resources, presenting a graphical meter view that the user may easily read, based on the data retrieved from the ear-level module Using the microphone on the ear-level module, a measure of Sound pressure is made, and processed to produce a Sound pressure level measurement. A-weighting filters can be used. Other standard frequency weightings may be used, including B, C, and D weightings. Also, no weighting filters or non-standard weighting filters may be used An A-weighting process will produce results in units of dba, which is a common measurement that approxi mates the response of the human ear to sound levels. The basic calculation performed using data processing resources on the ear-level module in embodiments that conserve radio band width, includes computation of the Root Mean Square (RMS) value of sound pressure data from a microphone. This RMS value is divided by a standard reference level, averaged over a given time interval, expressed in decibels is the Sound pres sure level. The time interval may be 1 second, 10 seconds, 1 minute and so on, depending on the processing resources available, the time response of the measurement desired and SO. O In alternative systems, the environmental data sensed can be temperature, sensed using a temperature sensor on the ear-level module exposed to the environment, or body temperature sensed using a temperature sensor arranged to detect temperature within the ear canal, for example FIG. 2 is a system diagram for microelectronic and audio transducer components of a representative embodiment of the ear module 10. The system includes a data processing module 50 and a radio module 51. The data processing mod ule includes a digital signal processor 52 (hence the reference to DSP in some of the Figures) coupled to nonvolatile memory 54. A digital-to-analog converter 56 converts digital output from the digital signal processor 52 into analog signals for supply to speaker 58 at the tip of the interior lobe of the ear module. A first analog-to-digital converter 60 and a second analog-to-digital converter 62 are coupled to the omnidirec tional microphone 64 and a directional microphone 66, respectively, on the exterior lobe of the ear module. The analog-to-digital converters 60, 62.Supply digital inputs to the digital signal processor 52. The embodiment shown also includes a temperature sensor 80, coupled via an analog-to
8 digital converter 81 to the DSP processor 52 for use in a mode delivering temperature measurements to the companion mobile phone The nonvolatile memory 54 stores computer pro grams that provide logic for processing the data from the microphone in digital form to provide a dba measurement or other measurement data to the companion cellphone, and for controlling the ear module as described in more detail below. Alternatively, the Sound pressure measurement may be done using analog circuitry, the output of which is converted to digital form for processing and transmission to the compan ion phone. In addition, the nonvolatile memory 54 stores a data structure for a set of variables used by the computer programs for audio processing, where each mode of operation of the ear module may have one or more separate Subsets of the set of variables, referred to as presets herein The radio module 51 is coupled to the digital signal processor 52 by a data/audio bus 70 and a control bus 71. The radio module 51 includes, in this example, a Bluetooth R. radio/baseband/control processor 72. The processor 72 is coupled to an antenna 74 and to nonvolatile memory 76. The nonvolatile memory 76 stores computer programs for oper ating a radio 72 and control parameters as known in the art. The processor module 51 also controls the man-machine interface 48 for the ear module 10, including accepting input data from the buttons and providing output data to the status light, according to well-known techniques The nonvolatile memory 76 is adapted to store at least first and second link parameters for establishing radio communication links with companion devices, in a respective data structure referred to as pre-pairing slots in nonvolatile memory. In the illustrated embodiment the first and second link parameters comprise authentication factors, such as Bluetooth R. PIN codes, needed for pairing with companion devices. The first link parameter is preferably stored on the device as manufactured, and known to the user. Thus, it can be used for establishing radio communication with phones and the configuration host or other platforms that provide user input resources to input the PIN code. The second link param eter also comprises an authentication factor. Such as a Blue tooth R. PIN code, and is not pre-stored in the embodiment described herein. Rather the second link parameter is com puted by the configuration host in the field, for private pairing of a companion module with the ear module. In one preferred embodiment, the second link parameter is unique to the pair ing, and not known to the user. In this way, the ear module is able to recognize authenticated companion modules within a network which attempt communication with the ear module, without requiring the user to enter the known first link param eter at the companion module. Embodiments of the technol ogy Support a plurality of unique pairing link parameters in addition to the second link parameter, for connection to a plurality of variant sources of audio data using the radio In addition, the processing resources in the ear mod ule include resources for establishing a configuration channel with a configuration host for retrieving the second link param eter, for establishing a first audio channel with the first link parameter, and for establishing a second audio channel with the second link parameter, in order to Support a variety of audio Sources Also, the configuration channel and audio channels comprise a plurality of connection protocols in the embodi ment described herein. The channels include a control chan nel protocol, such as a modified SPP as mentioned above, and an audio streaming channel protocol. Such as an SCO com pliant channel. The data processing resources Support role Switching on the configuration and audio channels between the control and audio streaming protocols In an embodiment of the ear module, the data pro cessing resources include logic Supporting an extended API for the Bluetooth RSPP profile. The extended API can include a Sound Meter Mode (or similar mode for other environmen tal measurement data), in which the measurement data is transmitted to the companion mobile phone. Also, the extended API can include other extensions used as the control channel protocol for the configuration host and for the com panion modules, including the following commands: 0034 Echo echoes the sent string back to the sender Pre-Pairing slot read reads one of the pre-pair ing slots Pre-Pairing Slot Set sets one of the pre-pairing slots PSKEY set generic state set. Used for changing Bluetooth R address amongst other things PSKEY Read generic state read command. Has access to Software version etc Battery Read read battery voltage (in milli volts) Report more on turn on special report mode where certain things are reported to the computer with out prompting MMI Control-control Man Machine Interface remotely LED control set and clear LED's remotely PWR Off for the LM, turn the LM off DSP send send data to the DSP command port DSP read read data from the DSP command port Volume Set set the volume of the EP VolumeRead read the current volume of the EP. (0.048 Preset Set set the current program of the EP Set Max Preset set the maximum preset that the device will allow via the MMI Pairing off exit pairing mode Mem Status read the memory pool status Sound Meter Mode In the illustrated embodiment, the data/audio bus 70 transfers pulse code modulated audio signals between the radio module 51 and the processor module 50. The control bus 71 in the illustrated embodiment comprises a serial bus for connecting universal asynchronous receive/transmit UART ports on the radio module 51 and on a processor module 50 for passing control signals. 0054) A power control bus 75 couples the radio module 51 and the processor module 50 to power management circuitry 77. The power management circuitry 77 provides power to the microelectronic components on the ear module in both the processor module 50 and the radio module 51 using a rechargeable battery 78. A battery charger 79 is coupled to the battery 78 and the power management circuitry 77 for recharging the rechargeable battery The microelectronics and transducers shown in FIG. 2 are adapted to fit within the ear module The ear module operates in a plurality of modes, including in the illustrated example, a hearing aid mode for listening to conversation or ambient audio, a phone mode Supporting a telephone call, and a companion microphone mode for playing audio picked up by the companion micro
9 phone which may be worn for example on the lapel of a friend. The signal flow in the device changes depending on which mode is currently in use. A hearing aid mode does not involve a wireless audio connection. The audio signals origi nate on the ear module itself. The phone mode and companion microphone mode involve audio data transfer using the radio. In the phone mode, audio data is both sent and received through a communication channel between the radio and the phone. In the companion microphone mode, the ear module receives a unidirectional audio data stream from the compan ion microphone The measurement data is provided to the companion mobile phone90 in the phone mode, which provides agraphic meter display 91 readable by the user. Also, the ear-level module can be adapted to provide the measurement data on a periodic basis to the companion mobile phone in the hearing aid mode or in the companion microphone mode, or when a control signal is received indicating that the data is to be transmitted. The control signal can originate from the com panion mobile phone 90, in response to user input selecting the meter display mode on the phone, or it can originate from the ear-level module in response to a threshold loudness in the environment or other environmental trigger The control circuitry is adapted to change modes in response to commands exchanged by the radio, and in response to user input, according to priority logic. For example, the system can change from the hearing aid mode to the phone mode and back to the hearing aid mode, the system can change from the hearing aid mode to the companion microphone mode and back to the hearing aid mode. For example, if the system is operating in hearing aid mode, a command from the radio which initiates the companion microphone may be received by the system, signaling a change to the companion microphone mode. In this case, the system loads audio processing variables (including preset parameters and configuration indicators) that are associated with the companion microphone mode. Then, the pulse code modulated data from the radio is received in the processor and up-sampled for use by the audio processing system and deliv ery of audio to the user. At this point, the system is operating in a companion microphone mode. To change out of the companion microphone mode, the system may receive a hear ing aid mode command via the serial interface from the radio. In this case, the processor loads audio processing variables associated with the hearing aid mode. At this point, the system is again operating in the hearing aid mode If the system is operating in the hearing aid mode and receives a phone mode command from the control bus via the radio, it loads audio processing variables associated with the phone mode. Then, the processor starts processing the pulse code modulated data with an up-sampling algorithm for delivery to the audio processing algorithms selected for the phone mode and providing audio to the microphone. The processor also starts processing microphone data with a down-sampling algorithm for delivery to the radio and trans mission to the phone. At this point, the system is operating in the phone mode. When the system receives a hearing aid mode command, it then loads the hearing aid audio process ing variables and returns to hearing aid mode FIG. 3 is a simplified diagram of a mobile phone 200, representative of personal communication devices according to the present invention which provides resources for mobile phone functions including call setup, call answer ing and other basic telephone call management tasks in com munication with a service provider on a wireless telephone network. The mobile phone 200 includes an antenna 201 and a radio including a radio frequency RF receiver/transmitter 202, by which the phone 200 is coupled to a wireless com munication medium, according to one or more of a variety of protocols. In examples described herein, the RF receiver/ transmitter 202 can include one or more radios to Support multiprotocol/multiband communications for communica tion with the wireless service provider of the mobile phone network, as well as the establishment of wireless local radio links using a protocol like Bluetooth R. The receiver/trans mitter 202 is coupled to baseband and digital signal processor DSP processing section 203, in which the audio signals are processed and call signals are managed. A codec 204, includ ing analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters, is coupled to the processing section203. A microphone 205 and a speaker 206 are coupled to the codec Read-only program memory 207 stores instruc tions, parameters and other data for execution by the process ing section 203. In addition, a read/write memory 208 stores instructions, parameters and other data for use by the process ing section 203. There may be multiple types of read/write memory on the phone 200, such as nonvolatile read/write memory 208 (flash memory or EEPROM for example) and volatile read/write memory 209 (DRAM or SRAM for example), as shown in FIG. 2. Other embodiments include removable memory modules in which instructions, param eters and other data for use by the processing section 203 are stored An input/output controller 210 is coupled to a dis play 211, to user input devices 212, Such as a numerical keypad, a function keypad, and a Volume control Switch, and to an accessory port (orports) 213. The accessory port orports 213 are used for other types of input/output devices, such as binaural and monaural headphones, connections to process ing devices such as PDAs, or personal computers, alternative communication channels such as an infrared port or Universal Serial Bus USB port, a portable storage device port, and other things. The controller 210 is coupled to the processing section 203. User input concerning call set up and management, and concerning use of the hearing profile, user preference and environmental noise factors is received via the input devices 212 and optionally via accessories. User interaction is enhanced, and the user is prompted to interact, using the display 211 and optionally other accessories. Input may also be received via the microphone 205 supported by voice rec ognition programs, and user interaction and prompting may utilize the speaker 206 for various purposes In the illustrated embodiment, memory 208 stores a program for computing a sound pressure level value, and for displaying the computed value on the display 211. The Sound pressure level value is computed as described above, using the microphone 205 on the mobile phone 200. Alternatively, the memory 208 stores a program for communication with a companion ear-level module, as described above, in which the sound pressure level value is received from the ear-level module and displayed on the mobile phone FIG. 4 shows a mobile phone 300 including a graphic display 301, showing A-weighted Sound pressure level in dba, as measured by sensor and processing resources either on a companion ear-level module or on the mobile phone 300. The display includes a color bar, which has a length corresponding to the measured sound pressure level. and which is color coded to indicate level. The three-color bar
10 is a meter that shows the Sound level. If the sound was quiet, only the first color (e.g. green) section 303 would show. As the Sound gets louder, the bar increases in size and adds the different colors, such as a second color (e.g. orange) section 304 and a third color (e.g. red) section 305. So the bar length changes continuously with the Sound level. Also, the display includes a numerical value 306 indicating the actual current measurement result, in an enlarged size for ease of reading. Similar graphic can be applied to display environmental tem perature, body temperature, and other environmental mea SurementS While the present invention is disclosed by refer ence to the preferred embodiments and examples detailed above, it is to be understood that these examples are intended in an illustrative rather than in a limiting sense. It is contem plated that modifications and combinations will readily occur to those skilled in the art, which modifications and combina tions will be within the spirit of the invention and the scope of the following claims. What is claimed is: 1. A device comprising: an ear-level module including an audio transducer, one or more microphones, a user input, a radio and control circuitry which transmits and receives communication signals encoding audio data using the radio to and from a companion module; wherein the control circuitry includes logic for producing a measurement of a characteristic of sound detected by the one or more microphones, and uses the radio to transmit data indicating the measurement to the companion mod ule. 2. The device of claim 1, wherein said measurement is Sound pressure level. 3. The device of claim 1, wherein said measurement is an A-weighted Sound pressure level. 4. The device of claim 1, wherein said measurement is an indication of loudness near the ear-level module. 5. A device comprising: an ear-level module including an audio transducer, one or more microphones, a user input, a radio and control circuitry which transmits and receives communication signals encoding audio data using the radio to and from a companion mobile phone; wherein the control circuitry includes logic for producing a measurement of an environmental condition near the ear-level module, and uses the radio to transmit data indicating the measurement to the companion mobile phone or other hand held device. 6. The device of claim 5, wherein said measurement is temperature. 7. A mobile phone, comprising a display; resources providing mobile phone functions, including an audio transducer, a microphone, a user input, a radio and control circuitry; and wherein the control circuitry includes processing resources for displaying a measurement on the display of a char acteristic of Sound, where the measurement is produced from one of sound detected by the microphone and data indicating the measurement received via a radio link from a companion module. 8. The phone of claim 7, wherein said measurement is Sound pressure level. 9. The phone of claim 7, wherein said measurement is an A-weighted Sound pressure level. 10. The phone of claim 7, wherein said measurement is an indication of loudness near the ear-level module. 11. The phone of claim 7, including a radio transmitter and receiver adapted for communication with an ear-level mod ule, and the control circuitry includes resources for receiving the data indicating the measurement from the ear-level mod ule. 12. A mobile phone, comprising a display; resources providing mobile phone functions, including an audio transducer, a microphone, a user input, a radio and control circuitry; and wherein the control circuitry includes processing resources for displaying a measurement on the display of a char acteristic of an environmental condition near the mobile phone, where the measurement is one of made based on data sensed at the mobile phone and data indicating the measurement received via a radio link from a companion module. 13. The phone of claim 12, wherein said measurement is temperature. 14. The phone of claim 12, including a radio transmitter and receiver adapted for communication with an ear-level module, and the control circuitry includes resources for receiving the data indicating the measurement from the ear level module. 15. A method for operating a personal sound system including an ear-level module including a radio including a transmitter and a receiver adapted to transmit and receive communication signals which encode audio signals, an audio transducer, and control circuitry for establishing a communi cation link using the radio, and a companion module includ ing a display, a radio including a transmitter and a receiver adapted to transmit communication signals on the communi cation link encoding audio signals, a microphone and control circuitry, the method comprising: measuring an environmental condition using a sensor on the ear-level module: establishing a radio communication link between the ear level module and the companion module, and delivering data resulting from the measurement to the companion module using the radio communication link; and displaying results of the measurements on the companion module. 16. The method of claim 15, wherein said measurement is Sound pressure level. 17. The method of claim 15, wherein said measurement is an A-weighted Sound pressure level. 18. The method of claim 15, wherein said measurement is an indication of loudness near the ear-level module. 19. The method of claim 15, wherein said measurement is temperature. 20. A method for operating a personal sound system including an ear-level module including a radio including a transmitter and a receiver adapted to transmit and receive communication signals which encode audio signals, an audio transducer, a microphone and control circuitry for establish ing a communication link using the radio, and a companion mobile phone including a display, a radio including a trans mitter and a receiver adapted to transmit communication sig nals on the communication link encoding audio signals, a
11 microphone and control circuitry for performing mobile phone functions, the method comprising: measuring sound pressure level of the microphone on the ear-level module: establishing a radio communication link between the ear level module and the companion mobile phone, and delivering data resulting from the measurement to the companion mobile phone using the radio communica tion link; and displaying results of the measurement on the companion mobile phone.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2006.0062400A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chia-Chun (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2006 (54) BLUETOOTH HEADSET DEVICE CAPABLE OF PROCESSING BOTH AUDIO AND DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
US 2001 0021659A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021659 A1 Okamura (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR CONNECTING (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 (57) USPC /412. Initiate wireless Connection. Discover.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O141898A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/014 1898A1 Riphin (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CELL PHONE CHARGING SYSTEM Publication Classification
US 2016O141898A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/014 1898A1 Riphin (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CELL PHONE CHARGING SYSTEM Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O181241A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0181241 A1 Veselic (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 17, 2006 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl.... 320/107
US 2006O181241A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0181241 A1 Veselic (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 17, 2006 (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl.... 320/107
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0049262A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0049262 A1 Lehtonen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) HANDS-FREE FUNCTION (76) Inventor: Arto Lehtonen, Tampere
(19) United States US 2001.0049262A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0049262 A1 Lehtonen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) HANDS-FREE FUNCTION (76) Inventor: Arto Lehtonen, Tampere
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 US 20140327628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0327628A1 Tijssen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 6, 2014 (54) PHYSICAL OBJECT DETECTION AND Publication Classification
US 20140327628A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0327628A1 Tijssen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 6, 2014 (54) PHYSICAL OBJECT DETECTION AND Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0234591 A1 Sanger et al. US 2016O234591 A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) MCROPHONE MODULE WITH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0234591 A1 Sanger et al. US 2016O234591 A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) MCROPHONE MODULE WITH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O132582A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0132582 A1 Mooney (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE EXTENSION USING WIRELESS PICONET (76) Inventor: Philip D.
(19) United States US 2002O132582A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0132582 A1 Mooney (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE EXTENSION USING WIRELESS PICONET (76) Inventor: Philip D.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OO63464A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0063464 A1 Akram et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) HIGH-SPEED DATA AND POWER SOURCE Publication Classification
US 2004OO63464A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0063464 A1 Akram et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2004 (54) HIGH-SPEED DATA AND POWER SOURCE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
MEMORY 14. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States. ucontroller MEMORY 16 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
 (19) United States US 20050097499A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0097499 A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2005 (54) IN-CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION ARCHITECTURE WITH NON-VOLATLE
(19) United States US 20050097499A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0097499 A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2005 (54) IN-CIRCUIT CONFIGURATION ARCHITECTURE WITH NON-VOLATLE
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000
 USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
ED 302C A t 302B (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O132798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0132798 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2008 (54) WIRELESS HEADSETS AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(19) United States US 2008O132798A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0132798 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 5, 2008 (54) WIRELESS HEADSETS AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(19) United States US 20170 126039A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0126039 A1 NGUYEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) BATTERY CHARGER WITH USB TYPE-C (52) U.S. Cl. ADAPTER CPC... H02J
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0019726A1 Park et al. US 2006OO19726A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LOCKINGAPPARATUS OF SWING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0019726A1 Park et al. US 2006OO19726A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LOCKINGAPPARATUS OF SWING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,818,742 B2
 USOO8818742B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 8,818,742 B2 Ansari (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2014 (54) SYSTEMS, METHODS, AND APPARATUS FOR 5,736,877 * 4/1998 Tihanyi... 327/77 DETECTING
USOO8818742B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 8,818,742 B2 Ansari (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2014 (54) SYSTEMS, METHODS, AND APPARATUS FOR 5,736,877 * 4/1998 Tihanyi... 327/77 DETECTING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080070528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0070528A1 Joyner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) MID-CALL FEATURES (76) Inventors: Tom Joyner, Chicago,
(19) United States US 20080070528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0070528A1 Joyner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) MID-CALL FEATURES (76) Inventors: Tom Joyner, Chicago,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2. Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008
 United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
United States Patent USOO7330395 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,330,395 B2 Ichijo (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 12, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 2002fOO67835 A1 6/2002 Vatter... 381.58 AUTOMATICALLY CALIBRATING
10-N 12. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(19) United States US 20080114930A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0114930 A1 Sanvido et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DISK DRIVE WITH CACHE HAVING VOLATLE AND NONVOLATILE MEMORY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(19) United States US 2015O199665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0199665 A1 Chu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 16, 2015 (54) METHOD OF PAYMENT FORWIRELESS (52) U.S. Cl. CHARGING SERVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004.0029581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0029581 A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE PHONE BEING SEPARATED INTO (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2004.0029581A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0029581 A1 Lu (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE PHONE BEING SEPARATED INTO (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,282,154 B1
 USOO62821.54B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Webb (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2001 (54) PORTABLE HANDS-FREE DIGITAL VOICE 5,265,075 11/1993 Bergeron et al.... 369/25 RECORDING AND TRANSCRIPTION
USOO62821.54B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Webb (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2001 (54) PORTABLE HANDS-FREE DIGITAL VOICE 5,265,075 11/1993 Bergeron et al.... 369/25 RECORDING AND TRANSCRIPTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O118664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0118664 A1 Ishibashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMMUNICATION SETUP METHOD AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE (75) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2002O118664A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0118664 A1 Ishibashi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) COMMUNICATION SETUP METHOD AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,856,601 B1. Bell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005
 USOO68566O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bell et al. () Date of Patent: Feb., 2005 (54) SHARED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (56) References Cited RESOURCES FOR COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES U.S.
USOO68566O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bell et al. () Date of Patent: Feb., 2005 (54) SHARED DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (56) References Cited RESOURCES FOR COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES U.S.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,845,158 B2
 USOO684.5158B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,845,158 B2 KOester et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2005 (54) RETRACTABLE-REMOVABLE HEADPHONE 5,136,446 A 8/1992 Yamamoto et al. MODULE
USOO684.5158B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,845,158 B2 KOester et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2005 (54) RETRACTABLE-REMOVABLE HEADPHONE 5,136,446 A 8/1992 Yamamoto et al. MODULE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070116246A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0116246A1 Walker et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 24, 2007 (54) CATEGORIZATION OF TELEPHONE CALLS Publication Classification
US 20070116246A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0116246A1 Walker et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 24, 2007 (54) CATEGORIZATION OF TELEPHONE CALLS Publication Classification
Xying. GoD-12 ACL 1-1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States SUPPLIER POLICY DRIVER/-108 PLATFORM
 (19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. combiner box. A/D Data Processing AID 2OO 3O1 203.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0237058 A1 McClintock et al. US 20060237058A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) DIRECT CURRENT COMBINER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0237058 A1 McClintock et al. US 20060237058A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) DIRECT CURRENT COMBINER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/013524.0 A1 Miller US 2013 O135240A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 30, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) APPARATUS FOR REMOTELY CONTROLLING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/013524.0 A1 Miller US 2013 O135240A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 30, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) APPARATUS FOR REMOTELY CONTROLLING
Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/ A1* 11/2004 Koda et al , 183
 (12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
INSTANTTEXT REPLY SAVED MESSAGES NEW MESSAGE SETTINGS. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0238474 A1 Ballas et al. US 20070238474A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 11, 2007 (54) INSTANT TEXT REPLY FOR MOBILE TELEPHONY DEVICES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0238474 A1 Ballas et al. US 20070238474A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 11, 2007 (54) INSTANT TEXT REPLY FOR MOBILE TELEPHONY DEVICES
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2
 US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(19) United States US 2016028627OA1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0286270 A1 YUEN (43) Pub. Date: (54) KIND OF INTERACTIVE SHARING H4N2L/214 (2006.01) PLATFORMINTEGRATING TV
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1. Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001
 USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
USOO620834OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,340 B1 Amin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE 5,317,687 5/1994 Torres... 395/159 INCLUDING A DROP-DOWN
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
(12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
S.C. OSC, PCMCIA (Personal Computer Memory Card International
 USOO5890O16A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: TSO (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 30, 1999 54 HYBRID COMPUTER ADD IN DEVICE FOR 5,500,517 3/1996 Cagliostro... 235/486 SELECTIVELY COUPLING TO PERSONAL
USOO5890O16A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: TSO (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 30, 1999 54 HYBRID COMPUTER ADD IN DEVICE FOR 5,500,517 3/1996 Cagliostro... 235/486 SELECTIVELY COUPLING TO PERSONAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060098613A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0098613 A1 Kish et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMPROVED DATA THROUGHPUT IN COMMUNICATIONS
(19) United States US 20060098613A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0098613 A1 Kish et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMPROVED DATA THROUGHPUT IN COMMUNICATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0345775 A1 Chien US 20150345775A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 3, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) MULTIPLE SURFACE LED LIGHT Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0345775 A1 Chien US 20150345775A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 3, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) MULTIPLE SURFACE LED LIGHT Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140376386A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0376386 A1 Koshy (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM FOR INTERCONNECTING (52) U.S. Cl. DEVICES FOR CREATING AUTOMATION
(19) United States US 20140376386A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0376386 A1 Koshy (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM FOR INTERCONNECTING (52) U.S. Cl. DEVICES FOR CREATING AUTOMATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
(19) United States US 2010.0017439A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0017439 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIMEDIA DATA STREAMING SYSTEM Publication Classification AND
FL (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.01.10403A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0110403 A1 Crutchfield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM FOR SHARED POWER SUPPLY IN COMPUTER
(19) United States US 2003.01.10403A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0110403 A1 Crutchfield et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM FOR SHARED POWER SUPPLY IN COMPUTER
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007809394B1 () Patent No.: Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 20 (54) TRANSMIT POWER CONTROL INA (56) References Cited WIRELESS SYSTEM U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent US007809394B1 () Patent No.: Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 20 (54) TRANSMIT POWER CONTROL INA (56) References Cited WIRELESS SYSTEM U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,679,316 B2
 USOO7679.316B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,679,316 B2 Guthrie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2010 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 6,21 1,649 B1 4/2001 Matsuda... 320,115 CONTROLLING
USOO7679.316B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,679,316 B2 Guthrie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2010 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 6,21 1,649 B1 4/2001 Matsuda... 320,115 CONTROLLING
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2. McDOWell et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2006
 United States Patent US007039435B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,039.435 B2 McDOWell et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2006 (54) PROXIMITY REGULATION SYSTEM FOR 6, 195,562 B1* 2/2001 Pirhonen et al.... 455,553.1
United States Patent US007039435B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,039.435 B2 McDOWell et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2006 (54) PROXIMITY REGULATION SYSTEM FOR 6, 195,562 B1* 2/2001 Pirhonen et al.... 455,553.1
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2
 US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,641,111 B2
 USOO7641111B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,641,111 B2 Adams et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 2010 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 7.350,701 B2 * 4/2008 Miyashita... 235,382 CONTACTLESS
USOO7641111B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,641,111 B2 Adams et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 2010 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 7.350,701 B2 * 4/2008 Miyashita... 235,382 CONTACTLESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(19) United States US 2002009 1840A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0091840 A1 Pulier et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 11, 2002 (54) REAL-TIME OPTIMIZATION OF STREAMING MEDIA FROM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
US 7.663,338 B2. Feb. 16, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Guthrie et al. used to receive a USB bus voltage from the USB interface and (51)
 USOO7663338B2 (12) United States Patent Guthrie et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.663,338 B2 Feb. 16, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND APPARATUS
USOO7663338B2 (12) United States Patent Guthrie et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.663,338 B2 Feb. 16, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND APPARATUS
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000
 US006058048A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54) FLASH MEMORY DEVICE USED ASA 56) References Cited BOOT-UP MEMORY IN A COMPUTER SYSTEM U.S. PATENT
US006058048A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,058,048 KWOn (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54) FLASH MEMORY DEVICE USED ASA 56) References Cited BOOT-UP MEMORY IN A COMPUTER SYSTEM U.S. PATENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O25O161A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0250161 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MONITORING SYSTEM FOR COLLECTION Publication Classification AND
(19) United States US 2010O25O161A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0250161 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MONITORING SYSTEM FOR COLLECTION Publication Classification AND
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,385,897 B1
 US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
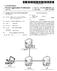 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 US 20090287845A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287845 A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) MEDIATOR WITH INTERLEAVED STATIC AND
US 20090287845A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287845 A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) MEDIATOR WITH INTERLEAVED STATIC AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Frequency. Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 (19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
Is more than one finger placed on touchpad surface?
 USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
USOO776O189B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Cheston et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) TOUCHPAD DIAGONAL SCROLLING 6,043,809 A 3/2000 Holehan 6,707.449 B2 3/2004 Hinckley et al.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014O146982A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0146982 A1 Pelosi (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND ACCESSORIES (52) U.S. Cl. WITH
(19) United States US 2014O146982A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0146982 A1 Pelosi (43) Pub. Date: May 29, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND ACCESSORIES (52) U.S. Cl. WITH
(12) (10) Patent N0.: US 6,879,518 B1. Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005
 United States Patent US006879518B1 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005 (54) EMBEDDED MEMORY WITH SECURITY 6,076,149 A * 6/2000 Usami et a1...... 711/163 ROW LOCK PROTECTION 6,088,262
United States Patent US006879518B1 (12) (10) Patent N0.: Curry (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 12, 2005 (54) EMBEDDED MEMORY WITH SECURITY 6,076,149 A * 6/2000 Usami et a1...... 711/163 ROW LOCK PROTECTION 6,088,262
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,847,351 B2
 USOO6847351B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Noguera (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 25, 2005 (54) TILT-BASED POINTING FOR HAND-HELD 5,602,566 2/1997 Motosyuku et al.... 345/123 DEVICES 5,638,092
USOO6847351B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Noguera (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 25, 2005 (54) TILT-BASED POINTING FOR HAND-HELD 5,602,566 2/1997 Motosyuku et al.... 345/123 DEVICES 5,638,092
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
e-a) (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 (19) United States CAPSUE CAPSULE 2 6 Q A) A) ()
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0252365A1 Lin US 20090252365A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 8, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MCROPHONES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0252365A1 Lin US 20090252365A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 8, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MCROPHONES
