Major Themes. Trees. Types of Graphs. Which of the following are trees? G 3 G 1 G 2 G 4. Dr Papalaskari 1
|
|
|
- Scarlett Hawkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Major Themes Trees Villanova University Trees Binary trees Binary search trees Spanning trees Minimum spanning trees Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 2 Types of Graphs graph mulhgraph digraph: directed graph/mulhgraph weighted graphs/digraphs Special graphs Cycle C x Wheel W x Hypercube Q x Complete graph K x A Complete BiparHte K x,y Connected graph Tree: a connected graph with no cycles Forest: a graph with no cycles Review Which of the following are trees? G 1 G 3 G 2 G 4 Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 4 Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 5 Dr Papalaskari 1
2 Tree: a connected graph with no cycles A tree with n verhces has n - 1 edges A connected graph with n verhces and n - 1 edges is a tree. Every tree with at least 2 verhces has 2 or more leaves A leaf is a vertex of degree 1. Rooted Tree A rooted tree has a dishnguished vertex called the root Rooted trees are usually drawn with the root at the top and all other verhces connected by edges growing downward Each edge in a rooted tree connects a parent vertex with a child vertex below it. Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 6 Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 7 Binary Tree A rooted tree Each vertex has at most 2 children: le. and right child. the k th level (or rank) of a binary tree is the collechon of verhces at distance k from the root In a complete binary tree every vertex has exactly two children, except for the leaves in the bo\om level. More about binary trees: How many leaves in a complete binary tree with n levels? If a binary tree has 6 levels and 50 verhces, is it possible for it to be: a binary tree? a complete binary tree? Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 9 Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 10 Dr Papalaskari 2
3 Binary Search Trees A binary search tree has a datum associated with each node such that in the ordering of the data set, the datum occurs earlier than any of the data downward and to the right and occurs later than any of the data downward and to the le^. Exercise Place baa at the root and draw the binary search tree for aaa, ab, baa, baba Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 12 Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 13 A Spanning Trees Depth-first/Breadth-first Search Trees 5 5 Spanning Tree: A subgraph that is a tree and contains all the verhces of a given graph. Every connected graph has at least 1 spanning tree. Every weighted connected graph has a minimum spanning tree Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 14 Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari Dr Papalaskari 3
4 Kruskal s Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm Order the edges of G, by increasing weight G starts out as the graph with all the verhces of G and none of the edges Keep adding edges to G, at each iterahon adding the lowest weighted edge that does not introduce a cycle Stop when the graph becomes connected. G is now the minimum spanning tree. Prim s Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm G starts out as the graph with just one vertex of graph G and no edges. Select the lowest weighted edge that connects a vertex in G to any of the remaining verhces of G; add edge and vertex to G and repeat unhl all the verhces of G are added to G G is now the minimum spanning tree. Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 16 Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 17 Kruskal s Algorithm Prim s Algorithm Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 18 Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 19 Dr Papalaskari 4
5 Fake coin puzzle You have eight gold coins and a balance scale. One of the coins is a fake and weighs less (gold is HEAVY). How can you determine which coin is fake with the least number of weighings? Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 22 Dr Papalaskari 5
Trees. CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University
 Trees CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Major Themes Trees Spanning trees Binary trees Binary search trees ApplicaAons But first: Review Graphs Villanova CSC 1300 - Dr Papalaskari 2 Review
Trees CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Major Themes Trees Spanning trees Binary trees Binary search trees ApplicaAons But first: Review Graphs Villanova CSC 1300 - Dr Papalaskari 2 Review
Foundations of Discrete Mathematics
 Foundations of Discrete Mathematics Chapter 12 By Dr. Dalia M. Gil, Ph.D. Trees Tree are useful in computer science, where they are employed in a wide range of algorithms. They are used to construct efficient
Foundations of Discrete Mathematics Chapter 12 By Dr. Dalia M. Gil, Ph.D. Trees Tree are useful in computer science, where they are employed in a wide range of algorithms. They are used to construct efficient
CSE 21 Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
 CSE 21 Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Unit 4: Basic Concepts in Graph Theory Section 3: Trees 1 Review : Decision Tree (DT-Section 1) Root of the decision tree on the left: 1 Leaves of the
CSE 21 Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Unit 4: Basic Concepts in Graph Theory Section 3: Trees 1 Review : Decision Tree (DT-Section 1) Root of the decision tree on the left: 1 Leaves of the
License. Discrete Mathematics. Tree. Topics. Definition tree: connected graph with no cycle. examples. c T. Uyar, A. Yayımlı, E.
 License c 2001-2016 T. Uyar, A. Yayımlı, E. Harmancı Discrete Mathematics Trees H. Turgut Uyar Ayşegül Gençata Yayımlı Emre Harmancı 2001-2016 You are free to: Share copy and redistribute the material
License c 2001-2016 T. Uyar, A. Yayımlı, E. Harmancı Discrete Mathematics Trees H. Turgut Uyar Ayşegül Gençata Yayımlı Emre Harmancı 2001-2016 You are free to: Share copy and redistribute the material
Warm Up. Use Kruskal s algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree and it s weight.
 Warm Up Use Kruskal s algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree and it s weight. Edge Weight (1,4) 1 (6,7) 1 (1,2) 2 (3,4) 2 (2,4) 3 (1,3) 4 (4,7) 4 (3,6) 5 (5,7) 6 1 Section 5.6 Binary Trees, Expression
Warm Up Use Kruskal s algorithm to find the minimum spanning tree and it s weight. Edge Weight (1,4) 1 (6,7) 1 (1,2) 2 (3,4) 2 (2,4) 3 (1,3) 4 (4,7) 4 (3,6) 5 (5,7) 6 1 Section 5.6 Binary Trees, Expression
Chapter 4 Trees. Theorem A graph G has a spanning tree if and only if G is connected.
 Chapter 4 Trees 4-1 Trees and Spanning Trees Trees, T: A simple, cycle-free, loop-free graph satisfies: If v and w are vertices in T, there is a unique simple path from v to w. Eg. Trees. Spanning trees:
Chapter 4 Trees 4-1 Trees and Spanning Trees Trees, T: A simple, cycle-free, loop-free graph satisfies: If v and w are vertices in T, there is a unique simple path from v to w. Eg. Trees. Spanning trees:
Graph Planarity. CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University
 Graph Planarity CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Major Themes Planar and non-planar graphs The graphs K 5 and K 3,3 Dividing the plane into regions Euler s formula Villanova CSC 1300 -
Graph Planarity CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Major Themes Planar and non-planar graphs The graphs K 5 and K 3,3 Dividing the plane into regions Euler s formula Villanova CSC 1300 -
Trees Algorhyme by Radia Perlman
 Algorhyme by Radia Perlman I think that I shall never see A graph more lovely than a tree. A tree whose crucial property Is loop-free connectivity. A tree which must be sure to span. So packets can reach
Algorhyme by Radia Perlman I think that I shall never see A graph more lovely than a tree. A tree whose crucial property Is loop-free connectivity. A tree which must be sure to span. So packets can reach
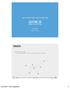
7.1 Introduction. A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w
 Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
Topics. Trees Vojislav Kecman. Which graphs are trees? Terminology. Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees CMSC 302
 Topics VCU, Department of Computer Science CMSC 302 Trees Vojislav Kecman Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees Binary Search Tree Decision Tree Tree Traversal Spanning Trees
Topics VCU, Department of Computer Science CMSC 302 Trees Vojislav Kecman Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees Binary Search Tree Decision Tree Tree Traversal Spanning Trees
CS204 Discrete Mathematics. 11 Trees. 11 Trees
 11.1 Introduction to Trees Def. 1 A tree T = (V, E) is a connected undirected graph with no simple circuits. acyclic connected graph. forest a set of trees. A vertex of degree one is called leaf. Thm.
11.1 Introduction to Trees Def. 1 A tree T = (V, E) is a connected undirected graph with no simple circuits. acyclic connected graph. forest a set of trees. A vertex of degree one is called leaf. Thm.
Graph and Digraph Glossary
 1 of 15 31.1.2004 14:45 Graph and Digraph Glossary A B C D E F G H I-J K L M N O P-Q R S T U V W-Z Acyclic Graph A graph is acyclic if it contains no cycles. Adjacency Matrix A 0-1 square matrix whose
1 of 15 31.1.2004 14:45 Graph and Digraph Glossary A B C D E F G H I-J K L M N O P-Q R S T U V W-Z Acyclic Graph A graph is acyclic if it contains no cycles. Adjacency Matrix A 0-1 square matrix whose
Graph Traversals. CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University. Villanova CSC Dr Papalaskari 1
 Graph Traversals CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Villanova CSC 1300 - Dr Papalaskari 1 Graph traversals: Euler circuit/path Major Themes Every edge exactly once Hamilton circuit/path
Graph Traversals CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Villanova CSC 1300 - Dr Papalaskari 1 Graph traversals: Euler circuit/path Major Themes Every edge exactly once Hamilton circuit/path
COP 4531 Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms
 COP 4531 Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 8 Data Structures for Disjoint Sets Thanks to the text authors who contributed to these slides Data Structures for Disjoint Sets Also
COP 4531 Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 8 Data Structures for Disjoint Sets Thanks to the text authors who contributed to these slides Data Structures for Disjoint Sets Also
An undirected graph is a tree if and only of there is a unique simple path between any 2 of its vertices.
 Trees Trees form the most widely used subclasses of graphs. In CS, we make extensive use of trees. Trees are useful in organizing and relating data in databases, file systems and other applications. Formal
Trees Trees form the most widely used subclasses of graphs. In CS, we make extensive use of trees. Trees are useful in organizing and relating data in databases, file systems and other applications. Formal
Undirected Graphs. Hwansoo Han
 Undirected Graphs Hwansoo Han Definitions Undirected graph (simply graph) G = (V, E) V : set of vertexes (vertices, nodes, points) E : set of edges (lines) An edge is an unordered pair Edge (v, w) = (w,
Undirected Graphs Hwansoo Han Definitions Undirected graph (simply graph) G = (V, E) V : set of vertexes (vertices, nodes, points) E : set of edges (lines) An edge is an unordered pair Edge (v, w) = (w,
March 20/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
managing an evolving set of connected components implementing a Union-Find data structure implementing Kruskal s algorithm
 Spanning Trees 1 Spanning Trees the minimum spanning tree problem three greedy algorithms analysis of the algorithms 2 The Union-Find Data Structure managing an evolving set of connected components implementing
Spanning Trees 1 Spanning Trees the minimum spanning tree problem three greedy algorithms analysis of the algorithms 2 The Union-Find Data Structure managing an evolving set of connected components implementing
Chapter 10: Trees. A tree is a connected simple undirected graph with no simple circuits.
 Chapter 10: Trees A tree is a connected simple undirected graph with no simple circuits. Properties: o There is a unique simple path between any 2 of its vertices. o No loops. o No multiple edges. Example
Chapter 10: Trees A tree is a connected simple undirected graph with no simple circuits. Properties: o There is a unique simple path between any 2 of its vertices. o No loops. o No multiple edges. Example
Section Summary. Introduction to Trees Rooted Trees Trees as Models Properties of Trees
 Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
Uses for Trees About Trees Binary Trees. Trees. Seth Long. January 31, 2010
 Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
Minimum Spanning Trees My T. UF
 Introduction to Algorithms Minimum Spanning Trees @ UF Problem Find a low cost network connecting a set of locations Any pair of locations are connected There is no cycle Some applications: Communication
Introduction to Algorithms Minimum Spanning Trees @ UF Problem Find a low cost network connecting a set of locations Any pair of locations are connected There is no cycle Some applications: Communication
CSE 373 MAY 10 TH SPANNING TREES AND UNION FIND
 CSE 373 MAY 0 TH SPANNING TREES AND UNION FIND COURSE LOGISTICS HW4 due tonight, if you want feedback by the weekend COURSE LOGISTICS HW4 due tonight, if you want feedback by the weekend HW5 out tomorrow
CSE 373 MAY 0 TH SPANNING TREES AND UNION FIND COURSE LOGISTICS HW4 due tonight, if you want feedback by the weekend COURSE LOGISTICS HW4 due tonight, if you want feedback by the weekend HW5 out tomorrow
Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A tree is A) any graph that is connected and every
Practice Exam #3, Math 100, Professor Wilson MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A tree is A) any graph that is connected and every
A graph is a set of objects (called vertices or nodes) and edges between pairs of nodes.
 Section 1.4: raphs and Trees graph is a set of objects (called vertices or nodes) and edges between pairs of nodes. Eq Co Ve Br S Pe Bo Pa U Ch Vertices = {Ve,, S,, Br, Co, Eq, Pe, Bo,Pa, Ch,, U} Edges
Section 1.4: raphs and Trees graph is a set of objects (called vertices or nodes) and edges between pairs of nodes. Eq Co Ve Br S Pe Bo Pa U Ch Vertices = {Ve,, S,, Br, Co, Eq, Pe, Bo,Pa, Ch,, U} Edges
Trees Rooted Trees Spanning trees and Shortest Paths. 12. Graphs and Trees 2. Aaron Tan November 2017
 12. Graphs and Trees 2 Aaron Tan 6 10 November 2017 1 10.5 Trees 2 Definition Definition Definition: Tree A graph is said to be circuit-free if, and only if, it has no circuits. A graph is called a tree
12. Graphs and Trees 2 Aaron Tan 6 10 November 2017 1 10.5 Trees 2 Definition Definition Definition: Tree A graph is said to be circuit-free if, and only if, it has no circuits. A graph is called a tree
Chapter Summary. Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees
 Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Introduction to Trees Section 11.1 Section Summary Introduction to Trees
Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Introduction to Trees Section 11.1 Section Summary Introduction to Trees
Problem Set 2 Solutions
 Problem Set 2 Solutions Graph Theory 2016 EPFL Frank de Zeeuw & Claudiu Valculescu 1. Prove that the following statements about a graph G are equivalent. - G is a tree; - G is minimally connected (it is
Problem Set 2 Solutions Graph Theory 2016 EPFL Frank de Zeeuw & Claudiu Valculescu 1. Prove that the following statements about a graph G are equivalent. - G is a tree; - G is minimally connected (it is
CSCI-401 Examlet #5. Name: Class: Date: True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false.
 Name: Class: Date: CSCI-401 Examlet #5 True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The root node of the standard binary tree can be drawn anywhere in the tree diagram. 2.
Name: Class: Date: CSCI-401 Examlet #5 True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The root node of the standard binary tree can be drawn anywhere in the tree diagram. 2.
Major Themes. Graph Traversals. Euler s SoluWon to The Bridges of Königsberg. The Bridges of Königsberg Puzzle. Dr Papalaskari 1
 Major Themes raph Traversals CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Villanova CSC 1300 - Dr Papalaskari 1 raph traversals: Euler circuit/path Every edge exactly once amilton circuit/path Every
Major Themes raph Traversals CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Villanova CSC 1300 - Dr Papalaskari 1 raph traversals: Euler circuit/path Every edge exactly once amilton circuit/path Every
LECTURE 26 PRIM S ALGORITHM
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 26 IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGY Suppose we take a vertex Given a single vertex v 1, it forms a minimum spanning tree on one
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 26 IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGY Suppose we take a vertex Given a single vertex v 1, it forms a minimum spanning tree on one
Topic 18 Binary Trees "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb
 Topic 18 "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A tree is an abstract data type one entry point, the root Each node is either a leaf
Topic 18 "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A tree is an abstract data type one entry point, the root Each node is either a leaf
BMI/STAT 768: Lecture 06 Trees in Graphs
 BMI/STAT 768: Lecture 06 Trees in Graphs Moo K. Chung mkchung@wisc.edu February 11, 2018 Parts of this lecture is based on [3, 5]. Many objects and data can be represented as networks. Unfortunately networks
BMI/STAT 768: Lecture 06 Trees in Graphs Moo K. Chung mkchung@wisc.edu February 11, 2018 Parts of this lecture is based on [3, 5]. Many objects and data can be represented as networks. Unfortunately networks
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spanning Trees Overview Problem A town has a set of houses and a set of roads. A road connects and only houses. A road connecting houses u and v has a repair cost w(u, v). Goal: Repair enough (and
Minimum Spanning Trees Overview Problem A town has a set of houses and a set of roads. A road connects and only houses. A road connecting houses u and v has a repair cost w(u, v). Goal: Repair enough (and
Self-Balancing Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Week 12: Minimum Spanning trees and Shortest Paths
 Agenda: Week 12: Minimum Spanning trees and Shortest Paths Kruskal s Algorithm Single-source shortest paths Dijkstra s algorithm for non-negatively weighted case Reading: Textbook : 61-7, 80-87, 9-601
Agenda: Week 12: Minimum Spanning trees and Shortest Paths Kruskal s Algorithm Single-source shortest paths Dijkstra s algorithm for non-negatively weighted case Reading: Textbook : 61-7, 80-87, 9-601
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2008S-19 B-Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 19-0: Indexing Operations: Add an element Remove an element Find an element,
Data Structures and Algorithms CS245-2008S-19 B-Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 19-0: Indexing Operations: Add an element Remove an element Find an element,
Course Review for Finals. Cpt S 223 Fall 2008
 Course Review for Finals Cpt S 223 Fall 2008 1 Course Overview Introduction to advanced data structures Algorithmic asymptotic analysis Programming data structures Program design based on performance i.e.,
Course Review for Finals Cpt S 223 Fall 2008 1 Course Overview Introduction to advanced data structures Algorithmic asymptotic analysis Programming data structures Program design based on performance i.e.,
Partha Sarathi Manal
 MA 515: Introduction to Algorithms & MA5 : Design and Analysis of Algorithms [-0-0-6] Lecture 20 & 21 http://www.iitg.ernet.in/psm/indexing_ma5/y09/index.html Partha Sarathi Manal psm@iitg.ernet.in Dept.
MA 515: Introduction to Algorithms & MA5 : Design and Analysis of Algorithms [-0-0-6] Lecture 20 & 21 http://www.iitg.ernet.in/psm/indexing_ma5/y09/index.html Partha Sarathi Manal psm@iitg.ernet.in Dept.
Hamilton paths & circuits. Gray codes. Hamilton Circuits. Planar Graphs. Hamilton circuits. 10 Nov 2015
 Hamilton paths & circuits Def. A path in a multigraph is a Hamilton path if it visits each vertex exactly once. Def. A circuit that is a Hamilton path is called a Hamilton circuit. Hamilton circuits Constructing
Hamilton paths & circuits Def. A path in a multigraph is a Hamilton path if it visits each vertex exactly once. Def. A circuit that is a Hamilton path is called a Hamilton circuit. Hamilton circuits Constructing
MAT 7003 : Mathematical Foundations. (for Software Engineering) J Paul Gibson, A207.
 MAT 7003 : Mathematical Foundations (for Software Engineering) J Paul Gibson, A207 paul.gibson@it-sudparis.eu http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/ Graphs and Trees http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/l2-graphsandtrees.pdf
MAT 7003 : Mathematical Foundations (for Software Engineering) J Paul Gibson, A207 paul.gibson@it-sudparis.eu http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/ Graphs and Trees http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/l2-graphsandtrees.pdf
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Minimum Spanning Tree Kostas Alexis The Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm A telecommunication company wants to connect all the blocks in a new neighborhood. However,
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Minimum Spanning Tree Kostas Alexis The Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm A telecommunication company wants to connect all the blocks in a new neighborhood. However,
Graphs and Network Flows ISE 411. Lecture 7. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Graphs and Network Flows ISE 411 Lecture 7 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 411 Lecture 7 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Chapter 20 References AMO Chapter 13 CLRS Chapter 23 ISE 411 Lecture 7 2 Minimum
Graphs and Network Flows ISE 411 Lecture 7 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 411 Lecture 7 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Chapter 20 References AMO Chapter 13 CLRS Chapter 23 ISE 411 Lecture 7 2 Minimum
Recitation 9. Prelim Review
 Recitation 9 Prelim Review 1 Heaps 2 Review: Binary heap min heap 1 2 99 4 3 PriorityQueue Maintains max or min of collection (no duplicates) Follows heap order invariant at every level Always balanced!
Recitation 9 Prelim Review 1 Heaps 2 Review: Binary heap min heap 1 2 99 4 3 PriorityQueue Maintains max or min of collection (no duplicates) Follows heap order invariant at every level Always balanced!
Section 5.5. Left subtree The left subtree of a vertex V on a binary tree is the graph formed by the left child L of V, the descendents
 Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
Definitions A A tree is an abstract t data type. Topic 17. "A tree may grow a. its leaves will return to its roots." Properties of Trees
 Topic 17 Introduction ti to Trees "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A A tree is an abstract t data t d internal type nodes one
Topic 17 Introduction ti to Trees "A tree may grow a thousand feet tall, but its leaves will return to its roots." -Chinese Proverb Definitions A A tree is an abstract t data t d internal type nodes one
Advanced algorithms. topological ordering, minimum spanning tree, Union-Find problem. Jiří Vyskočil, Radek Mařík 2012
 topological ordering, minimum spanning tree, Union-Find problem Jiří Vyskočil, Radek Mařík 2012 Subgraph subgraph A graph H is a subgraph of a graph G, if the following two inclusions are satisfied: 2
topological ordering, minimum spanning tree, Union-Find problem Jiří Vyskočil, Radek Mařík 2012 Subgraph subgraph A graph H is a subgraph of a graph G, if the following two inclusions are satisfied: 2
In this lecture, we ll look at applications of duality to three problems:
 Lecture 7 Duality Applications (Part II) In this lecture, we ll look at applications of duality to three problems: 1. Finding maximum spanning trees (MST). We know that Kruskal s algorithm finds this,
Lecture 7 Duality Applications (Part II) In this lecture, we ll look at applications of duality to three problems: 1. Finding maximum spanning trees (MST). We know that Kruskal s algorithm finds this,
Elementary Graph Algorithms: Summary. Algorithms. CmSc250 Intro to Algorithms
 Elementary Graph Algorithms: Summary CmSc250 Intro to Algorithms Definition: A graph is a collection (nonempty set) of vertices and edges A path from vertex x to vertex y : a list of vertices in which
Elementary Graph Algorithms: Summary CmSc250 Intro to Algorithms Definition: A graph is a collection (nonempty set) of vertices and edges A path from vertex x to vertex y : a list of vertices in which
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
CHAPTER 11 Trees. 294 Chapter 11 Trees. f) This is a tree since it is connected and has no simple circuits.
 294 Chapter 11 Trees SECTION 11.1 Introduction to Trees CHAPTER 11 Trees 2. a) This is a tree since it is connected and has no simple circuits. b) This is a tree since it is connected and has no simple
294 Chapter 11 Trees SECTION 11.1 Introduction to Trees CHAPTER 11 Trees 2. a) This is a tree since it is connected and has no simple circuits. b) This is a tree since it is connected and has no simple
Minimum spanning trees
 Carlos Moreno cmoreno @ uwaterloo.ca EI-3 https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~cmoreno/ece5 Standard reminder to set phones to silent/vibrate mode, please! During today's lesson: Introduce the notion of spanning
Carlos Moreno cmoreno @ uwaterloo.ca EI-3 https://ece.uwaterloo.ca/~cmoreno/ece5 Standard reminder to set phones to silent/vibrate mode, please! During today's lesson: Introduce the notion of spanning
Weighted Graphs and Greedy Algorithms
 COMP 182 Algorithmic Thinking Weighted Graphs and Greedy Algorithms Luay Nakhleh Computer Science Rice University Reading Material Chapter 10, Section 6 Chapter 11, Sections 4, 5 Weighted Graphs In many
COMP 182 Algorithmic Thinking Weighted Graphs and Greedy Algorithms Luay Nakhleh Computer Science Rice University Reading Material Chapter 10, Section 6 Chapter 11, Sections 4, 5 Weighted Graphs In many
Trees : Part 1. Section 4.1. Theory and Terminology. A Tree? A Tree? Theory and Terminology. Theory and Terminology
 Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Spanning Trees. Lecture 20 CS2110 Spring 2015
 1 Spanning Trees Lecture 0 CS110 Spring 01 1 Undirected trees An undirected graph is a tree if there is exactly one simple path between any pair of vertices Root of tree? It doesn t matter choose any vertex
1 Spanning Trees Lecture 0 CS110 Spring 01 1 Undirected trees An undirected graph is a tree if there is exactly one simple path between any pair of vertices Root of tree? It doesn t matter choose any vertex
CSC 505, Fall 2000: Week 7. In which our discussion of Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms and their data Structures is brought to a happy Conclusion.
 CSC 505, Fall 2000: Week 7 In which our discussion of Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms and their data Structures is brought to a happy Conclusion. Page 1 of 18 Prim s algorithm without data structures
CSC 505, Fall 2000: Week 7 In which our discussion of Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms and their data Structures is brought to a happy Conclusion. Page 1 of 18 Prim s algorithm without data structures
18 Spanning Tree Algorithms
 November 14, 2017 18 Spanning Tree Algorithms William T. Trotter trotter@math.gatech.edu A Networking Problem Problem The vertices represent 8 regional data centers which need to be connected with high-speed
November 14, 2017 18 Spanning Tree Algorithms William T. Trotter trotter@math.gatech.edu A Networking Problem Problem The vertices represent 8 regional data centers which need to be connected with high-speed
EE 368. Weeks 5 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 5 (Notes) 1 Chapter 5: Trees Skip pages 273-281, Section 5.6 - If A is the root of a tree and B is the root of a subtree of that tree, then A is B s parent (or father or mother) and B is A
EE 368 Weeks 5 (Notes) 1 Chapter 5: Trees Skip pages 273-281, Section 5.6 - If A is the root of a tree and B is the root of a subtree of that tree, then A is B s parent (or father or mother) and B is A
Elements of Graph Theory
 Elements of Graph Theory Quick review of Chapters 9.1 9.5, 9.7 (studied in Mt1348/2008) = all basic concepts must be known New topics we will mostly skip shortest paths (Chapter 9.6), as that was covered
Elements of Graph Theory Quick review of Chapters 9.1 9.5, 9.7 (studied in Mt1348/2008) = all basic concepts must be known New topics we will mostly skip shortest paths (Chapter 9.6), as that was covered
Lecture 13. Reading: Weiss, Ch. 9, Ch 8 CSE 100, UCSD: LEC 13. Page 1 of 29
 Lecture 13 Connectedness in graphs Spanning trees in graphs Finding a minimal spanning tree Time costs of graph problems and NP-completeness Finding a minimal spanning tree: Prim s and Kruskal s algorithms
Lecture 13 Connectedness in graphs Spanning trees in graphs Finding a minimal spanning tree Time costs of graph problems and NP-completeness Finding a minimal spanning tree: Prim s and Kruskal s algorithms
CSC 373: Algorithm Design and Analysis Lecture 4
 CSC 373: Algorithm Design and Analysis Lecture 4 Allan Borodin January 14, 2013 1 / 16 Lecture 4: Outline (for this lecture and next lecture) Some concluding comments on optimality of EST Greedy Interval
CSC 373: Algorithm Design and Analysis Lecture 4 Allan Borodin January 14, 2013 1 / 16 Lecture 4: Outline (for this lecture and next lecture) Some concluding comments on optimality of EST Greedy Interval
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Exercises & Solutions Chapters -4: Search methods. Search Tree. Draw the complete search tree (starting from S and ending at G) of the graph below. The numbers beside the nodes
Artificial Intelligence Exercises & Solutions Chapters -4: Search methods. Search Tree. Draw the complete search tree (starting from S and ending at G) of the graph below. The numbers beside the nodes
CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 26. Graphs. CS 441 Discrete mathematics for CS. Final exam
 CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 26 Graphs Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Final exam Saturday, April 26, 2014 at 10:00-11:50am The same classroom as lectures The exam
CS 441 Discrete Mathematics for CS Lecture 26 Graphs Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Final exam Saturday, April 26, 2014 at 10:00-11:50am The same classroom as lectures The exam
Greedy Algorithms. Mohan Kumar CSE5311 Fall The Greedy Principle
 Greedy lgorithms Mohan Kumar CSE@UT CSE53 Fall 5 8/3/5 CSE 53 Fall 5 The Greedy Principle The problem: We are required to find a feasible solution that either maximizes or minimizes a given objective solution.
Greedy lgorithms Mohan Kumar CSE@UT CSE53 Fall 5 8/3/5 CSE 53 Fall 5 The Greedy Principle The problem: We are required to find a feasible solution that either maximizes or minimizes a given objective solution.
Algorithm Design (8) Graph Algorithms 1/2
 Graph Algorithm Design (8) Graph Algorithms / Graph:, : A finite set of vertices (or nodes) : A finite set of edges (or arcs or branches) each of which connect two vertices Takashi Chikayama School of
Graph Algorithm Design (8) Graph Algorithms / Graph:, : A finite set of vertices (or nodes) : A finite set of edges (or arcs or branches) each of which connect two vertices Takashi Chikayama School of
Graphs Definitions. Gunnar Gotshalks. GraphDefinitions 1
 Graphs Definitions GraphDefinitions 1 Examples of Graphs Street maps» Vertices are the intersections» Edges are the streets Power line network» Vertices are the houses & power stations» Edges are the power
Graphs Definitions GraphDefinitions 1 Examples of Graphs Street maps» Vertices are the intersections» Edges are the streets Power line network» Vertices are the houses & power stations» Edges are the power
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Lesson 3: trees and visits Luciano Bononi http://www.cs.unibo.it/~bononi/ (slide credits: these slides are a revised version of slides created by Dr. Gabriele D Angelo) International
Lesson 3: trees and visits Luciano Bononi http://www.cs.unibo.it/~bononi/ (slide credits: these slides are a revised version of slides created by Dr. Gabriele D Angelo) International
Spanning Tree. Lecture19: Graph III. Minimum Spanning Tree (MSP)
 Spanning Tree (015) Lecture1: Graph III ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr efinition and property Subgraph that contains all vertices of the original graph and is a tree Often, a graph has many different
Spanning Tree (015) Lecture1: Graph III ohyung Han S, POSTH bhhan@postech.ac.kr efinition and property Subgraph that contains all vertices of the original graph and is a tree Often, a graph has many different
Data Structure. IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017
 Data Structure IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017 Data Structure: In computer science, a data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in a computer s memory so that it can be used efficiently. Data
Data Structure IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017 Data Structure: In computer science, a data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in a computer s memory so that it can be used efficiently. Data
Minimal Spanning Tree
 Minimal Spanning Tree P. Sreenivasulu Reddy and Abduselam Mahamed Derdar Department of mathematics, Samara University Semera, Afar Regional State, Ethiopia. Post Box No.131 Abstract: In this paper authors
Minimal Spanning Tree P. Sreenivasulu Reddy and Abduselam Mahamed Derdar Department of mathematics, Samara University Semera, Afar Regional State, Ethiopia. Post Box No.131 Abstract: In this paper authors
Trees. Eric McCreath
 Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Introduction to Computers and Programming. Concept Question
 Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Week 9 Student Responsibilities. Mat Example: Minimal Spanning Tree. 3.3 Spanning Trees. Prim s Minimal Spanning Tree.
 Week 9 Student Responsibilities Reading: hapter 3.3 3. (Tucker),..5 (Rosen) Mat 3770 Spring 01 Homework Due date Tucker Rosen 3/1 3..3 3/1 DS & S Worksheets 3/6 3.3.,.5 3/8 Heapify worksheet ttendance
Week 9 Student Responsibilities Reading: hapter 3.3 3. (Tucker),..5 (Rosen) Mat 3770 Spring 01 Homework Due date Tucker Rosen 3/1 3..3 3/1 DS & S Worksheets 3/6 3.3.,.5 3/8 Heapify worksheet ttendance
Computational Optimization ISE 407. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture- 9: B- Trees
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture- 9: B- Trees Dr. Chung- Wen Albert Tsao atsao@svuca.edu www.408codingschool.com/cs502_algorithm 1/12/16 Slide Source: http://www.slideshare.net/anujmodi555/b-trees-in-data-structure
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture- 9: B- Trees Dr. Chung- Wen Albert Tsao atsao@svuca.edu www.408codingschool.com/cs502_algorithm 1/12/16 Slide Source: http://www.slideshare.net/anujmodi555/b-trees-in-data-structure
1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1
![1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1](/thumbs/80/82301067.jpg) Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. O(logn) 2. O(n) 3. O(nlogn) 4. O(n 2 ) 5. O(2 n ) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution
Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. O(logn) 2. O(n) 3. O(nlogn) 4. O(n 2 ) 5. O(2 n ) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution
CSC148 Week 6. Larry Zhang
 CSC148 Week 6 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 coverage: trees (topic of today and Wednesday) are not covered Assignment 1 slides posted on the course website. 2 Data Structures 3 Data Structures A data
CSC148 Week 6 Larry Zhang 1 Announcements Test 1 coverage: trees (topic of today and Wednesday) are not covered Assignment 1 slides posted on the course website. 2 Data Structures 3 Data Structures A data
Solutions to Exercises 9
 Discrete Mathematics Lent 2009 MA210 Solutions to Exercises 9 (1) There are 5 cities. The cost of building a road directly between i and j is the entry a i,j in the matrix below. An indefinite entry indicates
Discrete Mathematics Lent 2009 MA210 Solutions to Exercises 9 (1) There are 5 cities. The cost of building a road directly between i and j is the entry a i,j in the matrix below. An indefinite entry indicates
6. Finding Efficient Compressions; Huffman and Hu-Tucker Algorithms
 6. Finding Efficient Compressions; Huffman and Hu-Tucker Algorithms We now address the question: How do we find a code that uses the frequency information about k length patterns efficiently, to shorten
6. Finding Efficient Compressions; Huffman and Hu-Tucker Algorithms We now address the question: How do we find a code that uses the frequency information about k length patterns efficiently, to shorten
CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal
 CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal Your Turn The array of vertices, which include dist, prev, and done fields (initialize dist to INFINITY and done to false ): V0: dist= prev= done= adj:
CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal Your Turn The array of vertices, which include dist, prev, and done fields (initialize dist to INFINITY and done to false ): V0: dist= prev= done= adj:
Friday, March 30. Last time we were talking about traversal of a rooted ordered tree, having defined preorder traversal. We will continue from there.
 Friday, March 30 Last time we were talking about traversal of a rooted ordered tree, having defined preorder traversal. We will continue from there. Postorder traversal (recursive definition) If T consists
Friday, March 30 Last time we were talking about traversal of a rooted ordered tree, having defined preorder traversal. We will continue from there. Postorder traversal (recursive definition) If T consists
Lecture Summary CSC 263H. August 5, 2016
 Lecture Summary CSC 263H August 5, 2016 This document is a very brief overview of what we did in each lecture, it is by no means a replacement for attending lecture or doing the readings. 1. Week 1 2.
Lecture Summary CSC 263H August 5, 2016 This document is a very brief overview of what we did in each lecture, it is by no means a replacement for attending lecture or doing the readings. 1. Week 1 2.
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
11/22/2016. Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms. Introduction. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions
 Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
1. Why Study Trees? Trees and Graphs. 2. Binary Trees. CITS2200 Data Structures and Algorithms. Wood... Topic 10. Trees are ubiquitous. Examples...
 . Why Study Trees? CITS00 Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 0 Trees and Graphs Trees and Graphs Binary trees definitions: size, height, levels, skinny, complete Trees, forests and orchards Wood... Examples...
. Why Study Trees? CITS00 Data Structures and Algorithms Topic 0 Trees and Graphs Trees and Graphs Binary trees definitions: size, height, levels, skinny, complete Trees, forests and orchards Wood... Examples...
looking ahead to see the optimum
 ! Make choice based on immediate rewards rather than looking ahead to see the optimum! In many cases this is effective as the look ahead variation can require exponential time as the number of possible
! Make choice based on immediate rewards rather than looking ahead to see the optimum! In many cases this is effective as the look ahead variation can require exponential time as the number of possible
Chapter 3 Trees. Theorem A graph T is a tree if, and only if, every two distinct vertices of T are joined by a unique path.
 Chapter 3 Trees Section 3. Fundamental Properties of Trees Suppose your city is planning to construct a rapid rail system. They want to construct the most economical system possible that will meet the
Chapter 3 Trees Section 3. Fundamental Properties of Trees Suppose your city is planning to construct a rapid rail system. They want to construct the most economical system possible that will meet the
CSE 100: B+ TREE, 2-3 TREE, NP- COMPLETNESS
 CSE 100: B+ TREE, 2-3 TREE, NP- COMPLETNESS Analyzing find in B-trees Since the B-tree is perfectly height-balanced, the worst case time cost for find is O(logN) Best case: If every internal node is completely
CSE 100: B+ TREE, 2-3 TREE, NP- COMPLETNESS Analyzing find in B-trees Since the B-tree is perfectly height-balanced, the worst case time cost for find is O(logN) Best case: If every internal node is completely
4 Basics of Trees. Petr Hliněný, FI MU Brno 1 FI: MA010: Trees and Forests
 4 Basics of Trees Trees, actually acyclic connected simple graphs, are among the simplest graph classes. Despite their simplicity, they still have rich structure and many useful application, such as in
4 Basics of Trees Trees, actually acyclic connected simple graphs, are among the simplest graph classes. Despite their simplicity, they still have rich structure and many useful application, such as in
CSC Intro to Intelligent Robotics, Spring Graphs
 CSC 445 - Intro to Intelligent Robotics, Spring 2018 Graphs Graphs Definition: A graph G = (V, E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge has either one or two
CSC 445 - Intro to Intelligent Robotics, Spring 2018 Graphs Graphs Definition: A graph G = (V, E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge has either one or two
Lower Bound on Comparison-based Sorting
 Lower Bound on Comparison-based Sorting Different sorting algorithms may have different time complexity, how to know whether the running time of an algorithm is best possible? We know of several sorting
Lower Bound on Comparison-based Sorting Different sorting algorithms may have different time complexity, how to know whether the running time of an algorithm is best possible? We know of several sorting
Undirected Graphs. DSA - lecture 6 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1
 Undirected Graphs Terminology. Free Trees. Representations. Minimum Spanning Trees (algorithms: Prim, Kruskal). Graph Traversals (dfs, bfs). Articulation points & Biconnected Components. Graph Matching
Undirected Graphs Terminology. Free Trees. Representations. Minimum Spanning Trees (algorithms: Prim, Kruskal). Graph Traversals (dfs, bfs). Articulation points & Biconnected Components. Graph Matching
COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam. Part 1: multiple choice (1 mark each, total 30 marks, circle the correct answer)
 COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam Thursday, April 13 th, 2006 This is a closed book and closed notes exam. There are total 3 parts. Please answer the questions in the provided space and use back
COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam Thursday, April 13 th, 2006 This is a closed book and closed notes exam. There are total 3 parts. Please answer the questions in the provided space and use back
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
Chapter 9. Greedy Technique. Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Greedy Technique Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Greedy Technique Constructs a solution to an optimization problem piece by piece through a sequence of choices that
Chapter 9 Greedy Technique Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Greedy Technique Constructs a solution to an optimization problem piece by piece through a sequence of choices that
CSE100 Practice Final Exam Section C Fall 2015: Dec 10 th, Problem Topic Points Possible Points Earned Grader
 CSE100 Practice Final Exam Section C Fall 2015: Dec 10 th, 2015 Problem Topic Points Possible Points Earned Grader 1 The Basics 40 2 Application and Comparison 20 3 Run Time Analysis 20 4 C++ and Programming
CSE100 Practice Final Exam Section C Fall 2015: Dec 10 th, 2015 Problem Topic Points Possible Points Earned Grader 1 The Basics 40 2 Application and Comparison 20 3 Run Time Analysis 20 4 C++ and Programming
Major Themes. Graph Coloring. Vertex Colorings. Dr Papalaskari 1
 Major Themes Graph Coloring CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Vertex coloring ChromaFc number χ(g) Map coloring Greedy coloring algorithm ApplicaFons Villanova CSC 1300 - Dr Papalaskari
Major Themes Graph Coloring CSC 1300 Discrete Structures Villanova University Vertex coloring ChromaFc number χ(g) Map coloring Greedy coloring algorithm ApplicaFons Villanova CSC 1300 - Dr Papalaskari
Multi-way Search Trees. (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 25
 Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
