CS 261: Data Structures. Skip Lists
|
|
|
- Charlene Collins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 261: Data Structures Skip Lists 1
2 Complexity Lists and Arrays OPERATIONS ORDINARY LISTS AND ARRAYS SORTED ARRAYS SORTED LISTS Add O(1) O(n) O(n) Remove O(n) O(n) O(n) Contains O(n) O(log n) O(n) 2
3 Sorted Linked Lists How to improve complexity of a sorted linked list? We could use two sorted linked lists, with pointers between them List
4 Two Sorted Linked Lists Constructed from the same elements Establish pointers between equal links down down down
5 Motivation Regular Trains vs. Express Trains down down down
6 Two Sorted Linked Lists : stores all elements : stores only a subset of elements down down down
7 How to Search for an Element? We start from the 1 st element of Stay on the "express line" as long as you can Then, take the "local line" down down down
8 How to Choose Elements for? Goal: Maximize fast access to all elements picks uniformly a subset of elements (e.g. every 2 nd, or rd, or 4 th element) down down down
9 How to Choose Elements for? But how exactly to uniformly sample elements for? down down down
10 The Goal: Minimize Complexity of Search down down down
11 What is Complexity of Search? num. of elements in L 1 + L 2 L 1 num. of elements in a segment of down down down
12 What is Complexity of Search? L 1 + L 2 L 1 down down down
13 What is Complexity of Search? minimize x + n x
14 What is Complexity of Search? minimum of the function d x + n x dx =0 14
15 What is Complexity of Search? d x + n x dx =1 n x 2 =0 ) x = p n 15
16 What is Complexity of Search? p n = = p n L 1 + L 2 L 1 = n down down down
17 What is Complexity of Search? 2 p n down down down
18 What is Complexity of Search? two sorted lists one sorted list down down down
19 How Many Lists Should We Form? If 2 lists have lower complexity, maybe lists will have even lower complexity down down down down down List
20 What is Complexity for Lists? down down down down down List
21 What is Complexity for Lists? down = x = x 2 down down down down List
22 What is Complexity for Lists? down down down down down List
23 What is Complexity for Lists? = p n down down down down down List
24 What is Complexity for Lists? lists 2 lists single list down down down down down List
25 What is Complexity for k Lists? for k linked lists: k kp n down down down down down List k
26 How Many Lists? minimize k kp n down down down down down List k
27 How Many Lists? minimize k kn 1 k = minimize k 2
28 How Many Lists? minimize k kn 1 k = minimize k log k + 1k log n 28
29 How Many Lists? d log k + 1 k log n dk =0 = 1 k 1 log n =0 k2 k = log n 29
30 Complexity for k=log n Lists? kn 1 k = (log n) n 1 log n down up down up down up down up down up List
31 n =2 log n n 1 log n =(2 log n ) 1 log n =2 (log n) n 1 log n = 2 log n
32 Complexity for log n Lists O(log n) down up down up down up down up down up List
33 Skip Lists Have It All Pugh 1989 Fast addition O(log n) Fast search O(log n) Fast removal O(log n) Disadvantage: - Slightly more complicated
34 Contains Skip List Makes a zig-zag motion top-to-bottom Complexity: O(log n), i.e., proportional to the number of linked lists 4
35 Contains Skip List 1. Start at topmost sentinel 2. Loop as follows 1. Slide right, get a link right before 2. If next element is OK, return true. If no down element, return false 4. Move down 5
36 Remove Skip List Makes a zig-zag motion top-to-bottom Only decrement the size at the bottom level Complexity: O(log n), i.e., proportional to the number of linked lists 6
37 Remove Skip List 1. Start at topmost sentinel 2. Loop as follows 1. Slide right, get a link right before 2. If next element is OK, remove it. If no down element, reduce size 4. Move down
38 How to construct a skip list when we do not know the number of elements in advance? 8
39 Add Skip List Add the element to the bottom list must increment size To move up to existing lists: Flip a coin, and if heads add the element up To add a new list at the top Flip a coin, and if heads make a new top list 9
40 Add Example Insert the following:
41 Add Example: Inserted : 9 14 Coin toss: T HT ( H = move up) down
42 Add Example: Inserted : Coin toss: T HT HHH T List down down down
43 Complexity of Add Proportional to the height, not to the number of nodes in the list O(log n) 4
44 Skip List Sorting Algorithm Problem: Sort an array A Step 1. Copy elements from A into a skip list Step 2. Copy elements from the skip list to A 44
45 Skip List Sorting Algorithm Complexity: Step 1. Copy elements from A into a skip list O(??) Step 2. Copy elements from the skip list to A O(??) 45
CS 350 : Data Structures Skip Lists
 CS 350 : Data Structures Skip Lists David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Skip List Introduction A data structure used for
CS 350 : Data Structures Skip Lists David Babcock (courtesy of James Moscola) Department of Physical Sciences York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Skip List Introduction A data structure used for
Skip Lists S 3 S 2 S 1. Skip Lists Goodrich, Tamassia
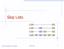 Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for a set S of distinct (key, element) items is a series of lists,,, S h such that Each list S i contains the special keys
Skip Lists S 3 15 15 23 10 15 23 36 Skip Lists 1 What is a Skip List A skip list for a set S of distinct (key, element) items is a series of lists,,, S h such that Each list S i contains the special keys
L10: Dictionary & Skip List
 Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India भ रत य व ज ञ न स स थ न ब गल र, भ रत Department of Computational and Data Sciences DS286 2016-09-14 L10: Dictionary & Skip List Yogesh Simmhan s i m m h a n
Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India भ रत य व ज ञ न स स थ न ब गल र, भ रत Department of Computational and Data Sciences DS286 2016-09-14 L10: Dictionary & Skip List Yogesh Simmhan s i m m h a n
Worksheet 28: Skip Lists
 Worksheet 28: Skip Lists In Preparation: Read Chapter 8 to learn more about the Bag data type. If you have not done so already, you should do Lessons 17 and 18 to learn more about the basic features of
Worksheet 28: Skip Lists In Preparation: Read Chapter 8 to learn more about the Bag data type. If you have not done so already, you should do Lessons 17 and 18 to learn more about the basic features of
Lecture 5. Treaps Find, insert, delete, split, and join in treaps Randomized search trees Randomized search tree time costs
 Lecture 5 Treaps Find, insert, delete, split, and join in treaps Randomized search trees Randomized search tree time costs Reading: Randomized Search Trees by Aragon & Seidel, Algorithmica 1996, http://sims.berkeley.edu/~aragon/pubs/rst96.pdf;
Lecture 5 Treaps Find, insert, delete, split, and join in treaps Randomized search trees Randomized search tree time costs Reading: Randomized Search Trees by Aragon & Seidel, Algorithmica 1996, http://sims.berkeley.edu/~aragon/pubs/rst96.pdf;
AVL Trees. (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 17
 AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
1 Probability Review. CS 124 Section #8 Hashing, Skip Lists 3/20/17. Expectation (weighted average): the expectation of a random quantity X is:
 CS 124 Section #8 Hashing, Skip Lists 3/20/17 1 Probability Review Expectation (weighted average): the expectation of a random quantity X is: x= x P (X = x) For each value x that X can take on, we look
CS 124 Section #8 Hashing, Skip Lists 3/20/17 1 Probability Review Expectation (weighted average): the expectation of a random quantity X is: x= x P (X = x) For each value x that X can take on, we look
R has a ordered clustering index file on its tuples: Read index file to get the location of the tuple with the next smallest value
 1 of 8 3/3/2018, 10:01 PM CS554, Homework 5 Question 1 (20 pts) Given: The content of a relation R is as follows: d d d d... d a a a a... a c c c c... c b b b b...b ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
1 of 8 3/3/2018, 10:01 PM CS554, Homework 5 Question 1 (20 pts) Given: The content of a relation R is as follows: d d d d... d a a a a... a c c c c... c b b b b...b ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
CS 106B Lecture 26: Esoteric Data Structures: Skip Lists and Bloom Filters
 CS 106B Lecture 26: Esoteric Data Structures: Skip Lists and Bloom Filters Monday, August 14, 2017 Programming Abstractions Summer 2017 Stanford University Computer Science Department Lecturer: Chris Gregg
CS 106B Lecture 26: Esoteric Data Structures: Skip Lists and Bloom Filters Monday, August 14, 2017 Programming Abstractions Summer 2017 Stanford University Computer Science Department Lecturer: Chris Gregg
CSE100. Advanced Data Structures. Lecture 8. (Based on Paul Kube course materials)
 CSE100 Advanced Data Structures Lecture 8 (Based on Paul Kube course materials) CSE 100 Treaps Find, insert, delete, split, and join in treaps Randomized search trees Randomized search tree time costs
CSE100 Advanced Data Structures Lecture 8 (Based on Paul Kube course materials) CSE 100 Treaps Find, insert, delete, split, and join in treaps Randomized search trees Randomized search tree time costs
Sorting. Data structures and Algorithms
 Sorting Data structures and Algorithms Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Goodrich, Tamassia and Mount (Wiley, 2004) Outline Bubble
Sorting Data structures and Algorithms Acknowledgement: These slides are adapted from slides provided with Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Goodrich, Tamassia and Mount (Wiley, 2004) Outline Bubble
Skip Lists in Julia. Drew Minnear. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. December 8, 2013
 in Julia Drew Minnear Massachusetts Institute of Technology December 8, 2013 Drew Minnear (MIT) in Julia December 8, 2013 1 / 14 What are? Introduction Randomized data structure invented by William Pugh
in Julia Drew Minnear Massachusetts Institute of Technology December 8, 2013 Drew Minnear (MIT) in Julia December 8, 2013 1 / 14 What are? Introduction Randomized data structure invented by William Pugh
Disk Accesses. CS 361, Lecture 25. B-Tree Properties. Outline
 Disk Accesses CS 361, Lecture 25 Jared Saia University of New Mexico Consider any search tree The number of disk accesses per search will dominate the run time Unless the entire tree is in memory, there
Disk Accesses CS 361, Lecture 25 Jared Saia University of New Mexico Consider any search tree The number of disk accesses per search will dominate the run time Unless the entire tree is in memory, there
Predictive Analysis: Evaluation and Experimentation. Heejun Kim
 Predictive Analysis: Evaluation and Experimentation Heejun Kim June 19, 2018 Evaluation and Experimentation Evaluation Metrics Cross-Validation Significance Tests Evaluation Predictive analysis: training
Predictive Analysis: Evaluation and Experimentation Heejun Kim June 19, 2018 Evaluation and Experimentation Evaluation Metrics Cross-Validation Significance Tests Evaluation Predictive analysis: training
Lecture 7. Random number generation More randomized data structures Skip lists: ideas and implementation Skip list time costs
 Lecture 7 Random number generation More randomized data structures Skip lists: ideas and implementation Skip list time costs Reading: Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees paper (Pugh);
Lecture 7 Random number generation More randomized data structures Skip lists: ideas and implementation Skip list time costs Reading: Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees paper (Pugh);
CS 561, Lecture 2 : Randomization in Data Structures. Jared Saia University of New Mexico
 CS 561, Lecture 2 : Randomization in Data Structures Jared Saia University of New Mexico Outline Hash Tables Bloom Filters Skip Lists 1 Dictionary ADT A dictionary ADT implements the following operations
CS 561, Lecture 2 : Randomization in Data Structures Jared Saia University of New Mexico Outline Hash Tables Bloom Filters Skip Lists 1 Dictionary ADT A dictionary ADT implements the following operations
Quick-Sort. Quick-sort is a randomized sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm:
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 2014 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9
Quick-Sort fi fi fi 7 9. Quick-Sort Goodrich, Tamassia
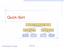 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 fi 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 fi 2 4 7 9 fi 7 9 2 fi 2 9 fi 9 Quick-Sort 1 Quick-Sort ( 10.2 text book) Quick-sort is a randomized sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm: x
Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 fi 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 fi 2 4 7 9 fi 7 9 2 fi 2 9 fi 9 Quick-Sort 1 Quick-Sort ( 10.2 text book) Quick-sort is a randomized sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm: x
lecture17: AVL Trees
 lecture17: Largely based on slides by Cinda Heeren CS 225 UIUC 9th July, 2013 Announcements mt2 tonight! mp5.1 extra credit due Friday (7/12) An interesting tree Can you make a BST that looks like a zig
lecture17: Largely based on slides by Cinda Heeren CS 225 UIUC 9th July, 2013 Announcements mt2 tonight! mp5.1 extra credit due Friday (7/12) An interesting tree Can you make a BST that looks like a zig
Red-Black, Splay and Huffman Trees
 Red-Black, Splay and Huffman Trees Kuan-Yu Chen ( 陳冠宇 ) 2018/10/22 @ TR-212, NTUST AVL Trees Review Self-balancing binary search tree Balance Factor Every node has a balance factor of 1, 0, or 1 2 Red-Black
Red-Black, Splay and Huffman Trees Kuan-Yu Chen ( 陳冠宇 ) 2018/10/22 @ TR-212, NTUST AVL Trees Review Self-balancing binary search tree Balance Factor Every node has a balance factor of 1, 0, or 1 2 Red-Black
Chapter 13 Control Structures
 Chapter 13 Control Structures Control Structures Conditional making a decision about which code to execute, based on evaluated expression if if-else switch Iteration executing code multiple times, ending
Chapter 13 Control Structures Control Structures Conditional making a decision about which code to execute, based on evaluated expression if if-else switch Iteration executing code multiple times, ending
Confidence Intervals. Dennis Sun Data 301
 Dennis Sun Data 301 Statistical Inference probability Population / Box Sample / Data statistics The goal of statistics is to infer the unknown population from the sample. We ve already seen one mode of
Dennis Sun Data 301 Statistical Inference probability Population / Box Sample / Data statistics The goal of statistics is to infer the unknown population from the sample. We ve already seen one mode of
Data Structure - Skip List etc. -
 Data Structure - Skip List etc. - Hanyang University Jong-Il Park SKIP LIST Introduction to Skip Lists An interesting generalization of linked lists for dictionary ADT. Keep the simplicity of linked lists
Data Structure - Skip List etc. - Hanyang University Jong-Il Park SKIP LIST Introduction to Skip Lists An interesting generalization of linked lists for dictionary ADT. Keep the simplicity of linked lists
Delaunay Triangulations
 Delaunay Triangulations (slides mostly by Glenn Eguchi) Motivation: Terrains Set of data points A R 2 Height ƒ(p) defined at each point p in A How can we most naturally approximate height of points not
Delaunay Triangulations (slides mostly by Glenn Eguchi) Motivation: Terrains Set of data points A R 2 Height ƒ(p) defined at each point p in A How can we most naturally approximate height of points not
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/25/2013 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS246: Mining Massive Datasets, http://cs246.stanford.edu 3 In many data mining
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/25/2013 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS246: Mining Massive Datasets, http://cs246.stanford.edu 3 In many data mining
CS 561, Lecture 2 : Hash Tables, Skip Lists, Bloom Filters, Count-Min sketch. Jared Saia University of New Mexico
 CS 561, Lecture 2 : Hash Tables, Skip Lists, Bloom Filters, Count-Min sketch Jared Saia University of New Mexico Outline Hash Tables Skip Lists Count-Min Sketch 1 Dictionary ADT A dictionary ADT implements
CS 561, Lecture 2 : Hash Tables, Skip Lists, Bloom Filters, Count-Min sketch Jared Saia University of New Mexico Outline Hash Tables Skip Lists Count-Min Sketch 1 Dictionary ADT A dictionary ADT implements
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 3/6/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS246: Mining Massive Datasets, http://cs246.stanford.edu 2 In many data mining
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 3/6/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS246: Mining Massive Datasets, http://cs246.stanford.edu 2 In many data mining
Balanced Search Trees. CS 3110 Fall 2010
 Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Computer Programming. Basic Control Flow - Loops. Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons
 Computer Programming Basic Control Flow - Loops Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons Objectives To learn about the three types of loops: while for do To avoid infinite
Computer Programming Basic Control Flow - Loops Adapted from C++ for Everyone and Big C++ by Cay Horstmann, John Wiley & Sons Objectives To learn about the three types of loops: while for do To avoid infinite
Announcements. Reading Material. Recap. Today 9/17/17. Storage (contd. from Lecture 6)
 CompSci 16 Intensive Computing Systems Lecture 7 Storage and Index Instructor: Sudeepa Roy Announcements HW1 deadline this week: Due on 09/21 (Thurs), 11: pm, no late days Project proposal deadline: Preliminary
CompSci 16 Intensive Computing Systems Lecture 7 Storage and Index Instructor: Sudeepa Roy Announcements HW1 deadline this week: Due on 09/21 (Thurs), 11: pm, no late days Project proposal deadline: Preliminary
Delaunay Triangulations. Presented by Glenn Eguchi Computational Geometry October 11, 2001
 Delaunay Triangulations Presented by Glenn Eguchi 6.838 Computational Geometry October 11, 2001 Motivation: Terrains Set of data points A R 2 Height ƒ(p) defined at each point p in A How can we most naturally
Delaunay Triangulations Presented by Glenn Eguchi 6.838 Computational Geometry October 11, 2001 Motivation: Terrains Set of data points A R 2 Height ƒ(p) defined at each point p in A How can we most naturally
Skip Lists: Motivation
 CSE 100: SKIP LISTS Announcements Please fill out the end of year survey and CAPEs https://wwwsurveymonkeycom/s/qfzpmt2 Please remove print statements to standard output when submitting your PA4 assignment
CSE 100: SKIP LISTS Announcements Please fill out the end of year survey and CAPEs https://wwwsurveymonkeycom/s/qfzpmt2 Please remove print statements to standard output when submitting your PA4 assignment
Hash Table. A hash function h maps keys of a given type into integers in a fixed interval [0,m-1]
![Hash Table. A hash function h maps keys of a given type into integers in a fixed interval [0,m-1] Hash Table. A hash function h maps keys of a given type into integers in a fixed interval [0,m-1]](/thumbs/82/85322795.jpg) Exercise # 8- Hash Tables Hash Tables Hash Function Uniform Hash Hash Table Direct Addressing A hash function h maps keys of a given type into integers in a fixed interval [0,m-1] 1 Pr h( key) i, where
Exercise # 8- Hash Tables Hash Tables Hash Function Uniform Hash Hash Table Direct Addressing A hash function h maps keys of a given type into integers in a fixed interval [0,m-1] 1 Pr h( key) i, where
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science. Final Examination
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science Final Examination CS 225 Data Structures and Software Principles Fall 2009 7-10p, Tuesday, December 15 Name: NetID: Lab Section
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science Final Examination CS 225 Data Structures and Software Principles Fall 2009 7-10p, Tuesday, December 15 Name: NetID: Lab Section
Graduate Algorithms CS F-12 Amortized Analysis
 Graduate Algorithms CS673-2016F-12 Amortized Analysis David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 12-0: Amortized Analysis Standard Stack Push(S,elem) Pop(S) How much time for
Graduate Algorithms CS673-2016F-12 Amortized Analysis David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 12-0: Amortized Analysis Standard Stack Push(S,elem) Pop(S) How much time for
Treaps. 1 Binary Search Trees (BSTs) CSE341T/CSE549T 11/05/2014. Lecture 19
 CSE34T/CSE549T /05/04 Lecture 9 Treaps Binary Search Trees (BSTs) Search trees are tree-based data structures that can be used to store and search for items that satisfy a total order. There are many types
CSE34T/CSE549T /05/04 Lecture 9 Treaps Binary Search Trees (BSTs) Search trees are tree-based data structures that can be used to store and search for items that satisfy a total order. There are many types
DIVIDE AND CONQUER ALGORITHMS ANALYSIS WITH RECURRENCE EQUATIONS
 CHAPTER 11 SORTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO AND
CHAPTER 11 SORTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO AND
Quick-Sort. Quick-Sort 1
 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 Quick-Sort 1 Outline and Reading Quick-sort ( 4.3) Algorithm Partition step Quick-sort tree Execution example Analysis of quick-sort (4.3.1) In-place
Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 Quick-Sort 1 Outline and Reading Quick-sort ( 4.3) Algorithm Partition step Quick-sort tree Execution example Analysis of quick-sort (4.3.1) In-place
Last time. Reasoning about programs. Coming up. Project Final Presentations. This Thursday, Nov 30: 4 th in-class exercise
 Last time Reasoning about programs Coming up This Thursday, Nov 30: 4 th in-class exercise sign up for group on moodle bring laptop to class Final projects: final project presentations: Tue Dec 12, in
Last time Reasoning about programs Coming up This Thursday, Nov 30: 4 th in-class exercise sign up for group on moodle bring laptop to class Final projects: final project presentations: Tue Dec 12, in
Reasoning about programs
 Reasoning about programs Last time Coming up This Thursday, Nov 30: 4 th in-class exercise sign up for group on moodle bring laptop to class Final projects: final project presentations: Tue Dec 12, in
Reasoning about programs Last time Coming up This Thursday, Nov 30: 4 th in-class exercise sign up for group on moodle bring laptop to class Final projects: final project presentations: Tue Dec 12, in
Microsoft Office Access 2007: Intermediate Course 01 Relational Databases
 Microsoft Office Access 2007: Intermediate Course 01 Relational Databases Slide 1 Relational Databases Course objectives Normalize tables Set relationships between tables Implement referential integrity
Microsoft Office Access 2007: Intermediate Course 01 Relational Databases Slide 1 Relational Databases Course objectives Normalize tables Set relationships between tables Implement referential integrity
Lecture 8 Index (B+-Tree and Hash)
 CompSci 516 Data Intensive Computing Systems Lecture 8 Index (B+-Tree and Hash) Instructor: Sudeepa Roy Duke CS, Fall 2017 CompSci 516: Database Systems 1 HW1 due tomorrow: Announcements Due on 09/21 (Thurs),
CompSci 516 Data Intensive Computing Systems Lecture 8 Index (B+-Tree and Hash) Instructor: Sudeepa Roy Duke CS, Fall 2017 CompSci 516: Database Systems 1 HW1 due tomorrow: Announcements Due on 09/21 (Thurs),
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I
 CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 02 / 15 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Questions? Comments? Loops to repeat code while loops for loops do while loops Today s Topics Logical operators Example
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 02 / 15 / 2016 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Questions? Comments? Loops to repeat code while loops for loops do while loops Today s Topics Logical operators Example
Chapter 10: Efficient Collections (skip lists, trees)
 Chapter 10: Efficient Collections (skip lists, trees) If you performed the analysis exercises in Chapter 9, you discovered that selecting a baglike container required a detailed understanding of the tasks
Chapter 10: Efficient Collections (skip lists, trees) If you performed the analysis exercises in Chapter 9, you discovered that selecting a baglike container required a detailed understanding of the tasks
Orthogonal range searching. Range Trees. Orthogonal range searching. 1D range searching. CS Spring 2009
 CS 5633 -- Spring 2009 Orthogonal range searching Range Trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with small changes by Carola Wenk CS 5633 Analysis of Algorithms 1 Input: n points in d dimensions
CS 5633 -- Spring 2009 Orthogonal range searching Range Trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with small changes by Carola Wenk CS 5633 Analysis of Algorithms 1 Input: n points in d dimensions
Ch04 Balanced Search Trees
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/24/2014 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS246: Mining Massive Datasets, http://cs246.stanford.edu 2 High dim. data
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/24/2014 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS246: Mining Massive Datasets, http://cs246.stanford.edu 2 High dim. data
Problem Solving through Programming In C Prof. Anupam Basu Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Problem Solving through Programming In C Prof. Anupam Basu Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 18 Switch Statement (Contd.) And Introduction to
Problem Solving through Programming In C Prof. Anupam Basu Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 18 Switch Statement (Contd.) And Introduction to
CSED233: Data Structures (2017F) Lecture10:Hash Tables, Maps, and Skip Lists
 (2017F) Lecture10:Hash Tables, Maps, and Skip Lists Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Maps A map models a searchable collection of key-value entries The main operations of a map are for searching,
(2017F) Lecture10:Hash Tables, Maps, and Skip Lists Daijin Kim CSE, POSTECH dkim@postech.ac.kr Maps A map models a searchable collection of key-value entries The main operations of a map are for searching,
Introduction. for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit times closer to O(log N) binary search tree
 Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees. Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler
 Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Multiway Seach Tree: a new type of search trees: for ordered d dictionary
Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Multiway Seach Tree: a new type of search trees: for ordered d dictionary
Binary Search Trees. Analysis of Algorithms
 Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015
 Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 2015 Goodrich and Tamassia
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 2015 Goodrich and Tamassia
COMP 430 Intro. to Database Systems. Indexing
 COMP 430 Intro. to Database Systems Indexing How does DB find records quickly? Various forms of indexing An index is automatically created for primary key. SQL gives us some control, so we should understand
COMP 430 Intro. to Database Systems Indexing How does DB find records quickly? Various forms of indexing An index is automatically created for primary key. SQL gives us some control, so we should understand
Hands-on Lab 1: LabVIEW NI-DAQ Basics 1
 Hands-on Lab 1: LabVIEW NI-DAQ Basics 1 This lab reviews LabVIEW concepts needed towards the course s final objective of position regulation using computer-controlled state feedback. Specific LabVIEW concepts
Hands-on Lab 1: LabVIEW NI-DAQ Basics 1 This lab reviews LabVIEW concepts needed towards the course s final objective of position regulation using computer-controlled state feedback. Specific LabVIEW concepts
Problem Set 5 Solutions
 Introduction to Algorithms November 4, 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Professors Erik D. Demaine and Charles E. Leiserson Handout 21 Problem Set 5 Solutions Problem 5-1. Skip
Introduction to Algorithms November 4, 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.046J/18.410J Professors Erik D. Demaine and Charles E. Leiserson Handout 21 Problem Set 5 Solutions Problem 5-1. Skip
Chapter 12. Path Planning. Beard & McLain, Small Unmanned Aircraft, Princeton University Press, 2012,
 Chapter 12 Path Planning Beard & McLain, Small Unmanned Aircraft, Princeton University Press, 212, Chapter 12: Slide 1 Control Architecture destination, obstacles map path planner waypoints status path
Chapter 12 Path Planning Beard & McLain, Small Unmanned Aircraft, Princeton University Press, 212, Chapter 12: Slide 1 Control Architecture destination, obstacles map path planner waypoints status path
CS 240 Fall Mike Lam, Professor. Priority Queues and Heaps
 CS 240 Fall 2015 Mike Lam, Professor Priority Queues and Heaps Priority Queues FIFO abstract data structure w/ priorities Always remove item with highest priority Store key (priority) with value Store
CS 240 Fall 2015 Mike Lam, Professor Priority Queues and Heaps Priority Queues FIFO abstract data structure w/ priorities Always remove item with highest priority Store key (priority) with value Store
Sorting Goodrich, Tamassia Sorting 1
 Sorting Put array A of n numbers in increasing order. A core algorithm with many applications. Simple algorithms are O(n 2 ). Optimal algorithms are O(n log n). We will see O(n) for restricted input in
Sorting Put array A of n numbers in increasing order. A core algorithm with many applications. Simple algorithms are O(n 2 ). Optimal algorithms are O(n log n). We will see O(n) for restricted input in
Adjust model for 3D Printing. Positioning - Orientate the part 13,0600,1489,1604(SP6)
 Adjust model for 3D Printing 13,0600,1489,1604(SP6) In this document, we will learn about. Position and Orientate a Body means that we move and rotate the body to fit our 3D printing considerations. Typical
Adjust model for 3D Printing 13,0600,1489,1604(SP6) In this document, we will learn about. Position and Orientate a Body means that we move and rotate the body to fit our 3D printing considerations. Typical
Binary Trees (and Big O notation)
 Binary Trees (and Big O notation) Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts (Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2 nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie, Absolute
Binary Trees (and Big O notation) Professor Hugh C. Lauer CS-2303, System Programming Concepts (Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2 nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie, Absolute
LSP 121. LSP 121 Math and Tech Literacy II. Topics. Loops. Loops. Loops
 LSP 121 Math and Tech Literacy II Greg Brewster DePaul University Topics The FOR loop Repeats a set of statements a fixed number of times The WHILE loop Repeats a set of statements until a condition is
LSP 121 Math and Tech Literacy II Greg Brewster DePaul University Topics The FOR loop Repeats a set of statements a fixed number of times The WHILE loop Repeats a set of statements until a condition is
University of Waterloo CS240 Winter 2018 Assignment 3
 University of Waterloo CS240 Winter 2018 Assignment 3 version: 2018-02-25 11:37 Due Date: Wednesday, Feb. 28th, at 5pm Please read the guidelines on submissions: http://www.student.cs.uwaterloo.ca/~cs240/
University of Waterloo CS240 Winter 2018 Assignment 3 version: 2018-02-25 11:37 Due Date: Wednesday, Feb. 28th, at 5pm Please read the guidelines on submissions: http://www.student.cs.uwaterloo.ca/~cs240/
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute. Week 02 Module 06 Lecture - 14 Merge Sort: Analysis
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Week 02 Module 06 Lecture - 14 Merge Sort: Analysis So, we have seen how to use a divide and conquer strategy, we
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Week 02 Module 06 Lecture - 14 Merge Sort: Analysis So, we have seen how to use a divide and conquer strategy, we
CSCI 104 Log Structured Merge Trees. Mark Redekopp
 1 CSCI 10 Log Structured Merge Trees Mark Redekopp Series Summation Review Let n = 1 + + + + k = σk i=0 n = k+1-1 i. What is n? What is log (1) + log () + log () + log (8)++ log ( k ) = 0 + 1 + + 3+ +
1 CSCI 10 Log Structured Merge Trees Mark Redekopp Series Summation Review Let n = 1 + + + + k = σk i=0 n = k+1-1 i. What is n? What is log (1) + log () + log () + log (8)++ log ( k ) = 0 + 1 + + 3+ +
Graph Theory and Optimization Approximation Algorithms
 Graph Theory and Optimization Approximation Algorithms Nicolas Nisse Université Côte d Azur, Inria, CNRS, I3S, France October 2018 Thank you to F. Giroire for some of the slides N. Nisse Graph Theory and
Graph Theory and Optimization Approximation Algorithms Nicolas Nisse Université Côte d Azur, Inria, CNRS, I3S, France October 2018 Thank you to F. Giroire for some of the slides N. Nisse Graph Theory and
CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 14 th Set of Notes
 1 CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 14 th Set of Notes Instructor: Philippos Mordohai Webpage: www.cs.stevens.edu/~mordohai E-mail: Philippos.Mordohai@stevens.edu Office: Lieb 215 Lecture Outline Triangulating
1 CS 532: 3D Computer Vision 14 th Set of Notes Instructor: Philippos Mordohai Webpage: www.cs.stevens.edu/~mordohai E-mail: Philippos.Mordohai@stevens.edu Office: Lieb 215 Lecture Outline Triangulating
CS 137 Part 8. Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Binary Search. November 20th, 2017
 CS 137 Part 8 Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Binary Search November 20th, 2017 This Week We re going to see two more complicated sorting algorithms that will be our first introduction to O(n log n) sorting algorithms.
CS 137 Part 8 Merge Sort, Quick Sort, Binary Search November 20th, 2017 This Week We re going to see two more complicated sorting algorithms that will be our first introduction to O(n log n) sorting algorithms.
Priority Queues and Binary Heaps
 Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland In this lecture, we will learn our first tree data structure called the binary heap which serves as an implementation of the priority queue. Priority Queue A priority
Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland In this lecture, we will learn our first tree data structure called the binary heap which serves as an implementation of the priority queue. Priority Queue A priority
Some Search Structures. Balanced Search Trees. Binary Search Trees. A Binary Search Tree. Review Binary Search Trees
 Some Search Structures Balanced Search Trees Lecture 8 CS Fall Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Some Search Structures Balanced Search Trees Lecture 8 CS Fall Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
COMP171. AVL-Trees (Part 1)
 COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
Chapter 4: Sorting. Spring 2014 Sorting Fun 1
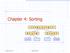 Chapter 4: Sorting 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 Spring 2014 Sorting Fun 1 What We ll Do! Quick Sort! Lower bound on runtimes for comparison based sort! Radix and Bucket sort Spring 2014
Chapter 4: Sorting 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 Spring 2014 Sorting Fun 1 What We ll Do! Quick Sort! Lower bound on runtimes for comparison based sort! Radix and Bucket sort Spring 2014
Splay tree, tree Marko Berezovský Radek Mařík PAL 2012
 Splay tree, --4 tree Marko erezovský Radek Mařík PL 0 p < Hi!?/ x+y x--y To read [] Weiss M.., Data Structures and lgorithm nalysis in ++, rd Ed., ddison Wesley, 4.5, pp.49-58. [] Daniel D. Sleator and
Splay tree, --4 tree Marko erezovský Radek Mařík PL 0 p < Hi!?/ x+y x--y To read [] Weiss M.., Data Structures and lgorithm nalysis in ++, rd Ed., ddison Wesley, 4.5, pp.49-58. [] Daniel D. Sleator and
Splay Trees. (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 27
 Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
Distributed Mutual Exclusion
 Distributed Mutual Exclusion Mutual Exclusion Well-understood in shared memory systems Requirements: at most one process in critical section (safety) if more than one requesting process, someone enters
Distributed Mutual Exclusion Mutual Exclusion Well-understood in shared memory systems Requirements: at most one process in critical section (safety) if more than one requesting process, someone enters
arxiv: v3 [math.co] 9 Jan 2015
![arxiv: v3 [math.co] 9 Jan 2015 arxiv: v3 [math.co] 9 Jan 2015](/thumbs/72/66800152.jpg) Subset-lex: did we miss an order? arxiv:1405.6503v3 [math.co] 9 Jan 2015 Jörg Arndt, Technische Hochschule Nürnberg January 12, 2015 Abstract We generalize a well-known algorithm for the
Subset-lex: did we miss an order? arxiv:1405.6503v3 [math.co] 9 Jan 2015 Jörg Arndt, Technische Hochschule Nürnberg January 12, 2015 Abstract We generalize a well-known algorithm for the
Direct Addressing Hash table: Collision resolution how handle collisions Hash Functions:
 Direct Addressing - key is index into array => O(1) lookup Hash table: -hash function maps key to index in table -if universe of keys > # table entries then hash functions collision are guaranteed => need
Direct Addressing - key is index into array => O(1) lookup Hash table: -hash function maps key to index in table -if universe of keys > # table entries then hash functions collision are guaranteed => need
DATA STRUCTURES/UNIT 3
 UNIT III SORTING AND SEARCHING 9 General Background Exchange sorts Selection and Tree Sorting Insertion Sorts Merge and Radix Sorts Basic Search Techniques Tree Searching General Search Trees- Hashing.
UNIT III SORTING AND SEARCHING 9 General Background Exchange sorts Selection and Tree Sorting Insertion Sorts Merge and Radix Sorts Basic Search Techniques Tree Searching General Search Trees- Hashing.
e-pg PATHSHALA- Computer Science Design and Analysis of Algorithms Module 10
 e-pg PATHSHALA- Computer Science Design and Analysis of Algorithms Module 10 Component-I (B) Description of Module Items Subject Name Computer Science Description of Module Paper Name Module Name/Title
e-pg PATHSHALA- Computer Science Design and Analysis of Algorithms Module 10 Component-I (B) Description of Module Items Subject Name Computer Science Description of Module Paper Name Module Name/Title
Lecture 7. SchemeList, finish up; Universal Hashing introduction
 Lecture 7. SchemeList, finish up; Universal Hashing introduction CS 16 February 24, 2010 1 / 15 foldleft #!/usr/bin/python def foldleft(func, slist, init): foldleft: ( * -> ) * ( SchemeList)
Lecture 7. SchemeList, finish up; Universal Hashing introduction CS 16 February 24, 2010 1 / 15 foldleft #!/usr/bin/python def foldleft(func, slist, init): foldleft: ( * -> ) * ( SchemeList)
Indexing: Overview & Hashing. CS 377: Database Systems
 Indexing: Overview & Hashing CS 377: Database Systems Recap: Data Storage Data items Records Memory DBMS Blocks blocks Files Different ways to organize files for better performance Disk Motivation for
Indexing: Overview & Hashing CS 377: Database Systems Recap: Data Storage Data items Records Memory DBMS Blocks blocks Files Different ways to organize files for better performance Disk Motivation for
Control Flow. COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science. Christopher Conway 3 June 2003
 Control Flow COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science Christopher Conway 3 June 2003 Overflow from Last Time: Why Types? Assembly code is typeless. You can take any 32 bits in memory, say this is an
Control Flow COMS W1007 Introduction to Computer Science Christopher Conway 3 June 2003 Overflow from Last Time: Why Types? Assembly code is typeless. You can take any 32 bits in memory, say this is an
Ensures that no such path is more than twice as long as any other, so that the tree is approximately balanced
 13 Red-Black Trees A red-black tree (RBT) is a BST with one extra bit of storage per node: color, either RED or BLACK Constraining the node colors on any path from the root to a leaf Ensures that no such
13 Red-Black Trees A red-black tree (RBT) is a BST with one extra bit of storage per node: color, either RED or BLACK Constraining the node colors on any path from the root to a leaf Ensures that no such
Searching, Sorting. Arizona State University 1
 Searching, Sorting CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 9 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State
Searching, Sorting CSE100 Principles of Programming with C++, Fall 2018 (based off Chapter 9 slides by Pearson) Ryan Dougherty Arizona State University http://www.public.asu.edu/~redoughe/ Arizona State
Line Arrangements. Applications
 Computational Geometry Chapter 9 Line Arrangements 1 Line Arrangements Applications On the Agenda 2 1 Complexity of a Line Arrangement Given a set L of n lines in the plane, their arrangement A(L) is the
Computational Geometry Chapter 9 Line Arrangements 1 Line Arrangements Applications On the Agenda 2 1 Complexity of a Line Arrangement Given a set L of n lines in the plane, their arrangement A(L) is the
*Starting Out with C++: From Control Structures through Objects, 7/E* by *Tony Gaddis* COMPUTER PROGRAMMING LECTURE 05 LOOPS IMRAN IHSAN
 PowerPoint Slides adapted from *Starting Out with C++: From Control Structures through Objects, 7/E* by *Tony Gaddis* Copyright 2012 Pearson Education Inc. COMPUTER PROGRAMMING LECTURE 05 LOOPS IMRAN IHSAN
PowerPoint Slides adapted from *Starting Out with C++: From Control Structures through Objects, 7/E* by *Tony Gaddis* Copyright 2012 Pearson Education Inc. COMPUTER PROGRAMMING LECTURE 05 LOOPS IMRAN IHSAN
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES. Chapter 11
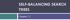 SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
Latest on Linear Sketches for Large Graphs: Lots of Problems, Little Space, and Loads of Handwaving. Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts
 Latest on Linear Sketches for Large Graphs: Lots of Problems, Little Space, and Loads of Handwaving Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Latest on Linear Sketches for Large Graphs: Lots of Problems,
Latest on Linear Sketches for Large Graphs: Lots of Problems, Little Space, and Loads of Handwaving Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Latest on Linear Sketches for Large Graphs: Lots of Problems,
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms
 CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 19: Comparison Sorting Algorithms Instructor: Lilian de Greef Quarter: Summer 2017 Today Intro to sorting Comparison sorting Insertion Sort Selection Sort
CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 19: Comparison Sorting Algorithms Instructor: Lilian de Greef Quarter: Summer 2017 Today Intro to sorting Comparison sorting Insertion Sort Selection Sort
CSC 261/461 Database Systems Lecture 17. Fall 2017
 CSC 261/461 Database Systems Lecture 17 Fall 2017 Announcement Quiz 6 Due: Tonight at 11:59 pm Project 1 Milepost 3 Due: Nov 10 Project 2 Part 2 (Optional) Due: Nov 15 The IO Model & External Sorting Today
CSC 261/461 Database Systems Lecture 17 Fall 2017 Announcement Quiz 6 Due: Tonight at 11:59 pm Project 1 Milepost 3 Due: Nov 10 Project 2 Part 2 (Optional) Due: Nov 15 The IO Model & External Sorting Today
Streaming algorithms for embedding and computing edit distance
 Streaming algorithms for embedding and computing edit distance in the low distance regime Diptarka Chakraborty joint work with Elazar Goldenberg and Michal Koucký 7 November, 2015 Outline 1 Introduction
Streaming algorithms for embedding and computing edit distance in the low distance regime Diptarka Chakraborty joint work with Elazar Goldenberg and Michal Koucký 7 November, 2015 Outline 1 Introduction
3. Priority Queues. ADT Stack : LIFO. ADT Queue : FIFO. ADT Priority Queue : pick the element with the lowest (or highest) priority.
 3. Priority Queues 3. Priority Queues ADT Stack : LIFO. ADT Queue : FIFO. ADT Priority Queue : pick the element with the lowest (or highest) priority. Malek Mouhoub, CS340 Winter 2007 1 3. Priority Queues
3. Priority Queues 3. Priority Queues ADT Stack : LIFO. ADT Queue : FIFO. ADT Priority Queue : pick the element with the lowest (or highest) priority. Malek Mouhoub, CS340 Winter 2007 1 3. Priority Queues
Chapter 22 Splay Trees
 Chapter 22 Splay Trees Introduction Splay trees support all the operations of binary trees. But they do not guarantee Ο(log N) worst-case performance. Instead, its bounds are amortized, meaning that although
Chapter 22 Splay Trees Introduction Splay trees support all the operations of binary trees. But they do not guarantee Ο(log N) worst-case performance. Instead, its bounds are amortized, meaning that although
BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015
 BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 7 due tonight at midnight -asking for regrades through assignment 5 and midterm must
BINARY SEARCH TREES cs2420 Introduction to Algorithms and Data Structures Spring 2015 1 administrivia 2 -assignment 7 due tonight at midnight -asking for regrades through assignment 5 and midterm must
5.1. Chapter 5: The Increment and Decrement Operators. The Increment and Decrement Operators. Looping. ++ is the increment operator.
 Chapter 5: Looping 5.1 The Increment and Decrement Operators Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright Publishing as Pearson 2009 Addison-Wesley Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
Chapter 5: Looping 5.1 The Increment and Decrement Operators Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright Publishing as Pearson 2009 Addison-Wesley Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
9/29/2016. Chapter 4 Trees. Introduction. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Approximation Algorithms
 Approximation Algorithms Frédéric Giroire FG Simplex 1/11 Motivation Goal: Find good solutions for difficult problems (NP-hard). Be able to quantify the goodness of the given solution. Presentation of
Approximation Algorithms Frédéric Giroire FG Simplex 1/11 Motivation Goal: Find good solutions for difficult problems (NP-hard). Be able to quantify the goodness of the given solution. Presentation of
! A data type for which: ! An ADT may be implemented using various. ! Examples:
 List ADT: Linked lists vs. Arrays CS 2308 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman Abstract Data Type! A data type for which: - only the properties of the data and the operations to be performed on the data are specific,
List ADT: Linked lists vs. Arrays CS 2308 Fall 2018 Jill Seaman Abstract Data Type! A data type for which: - only the properties of the data and the operations to be performed on the data are specific,
Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering. Lecture No. #43. Multidimensional Arrays
 Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering Lecture No. #43 Multidimensional Arrays In this video will look at multi-dimensional arrays. (Refer Slide Time: 00:03) In
Introduction to Programming in C Department of Computer Science and Engineering Lecture No. #43 Multidimensional Arrays In this video will look at multi-dimensional arrays. (Refer Slide Time: 00:03) In
1 ICS 161: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture notes for January 23, Bucket Sorting
 1 ICS 161: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture notes for January 23, 1996 2 Bucket Sorting We ve seen various algorithms for sorting in O(n log n) time and a lower bound showing that O(n log n) is
1 ICS 161: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture notes for January 23, 1996 2 Bucket Sorting We ve seen various algorithms for sorting in O(n log n) time and a lower bound showing that O(n log n) is
