Process Modelling. Data flow Diagrams. Process Modelling Data Flow Diagrams. CSE Information Systems 1
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Willis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE104 - Information s 1 Process Modelling Data Flow Diagrams Process Modelling Process modelling aims to graphically represent the processes which capture, manipulate, store and distribute data. data flow diagrams function decomposition structured English decision tables and decision trees Data flow Diagrams Data flow diagrams model the flow of data into, through, and out of an information system: show the processes that change or transform data show the movement of data between processes represent a system as a network of processes which transform data flowing between them
2 Example DFD DFDs fit neatly onto a single page the user is not overwhelmed by a DFD invalid orders ORDERS CUSTOMERS shipping details WAREHOUSE order details books orders 1. RECEIVE ORDER customer name, customer address. SHIP BOOKS billing information CUSTOMERS customer name, customer address books INVOICES customer name, invoice details 3. COLLECT PAYMENTS invoices, statements CUSTOMERS payments, enquiries Data Flow Diagrams Data flow diagrams (or DFDs): a well-known process modelling technique easily understood a good communication tool model both manual and automated processes Components of a DFD 1. Process calculate price. Data flow loan application 3. Data store Products 4. External agent (Source/Sink) Suppliers
3 1. Process transforms incoming data flows into outgoing flows: the work performed on data which changes it data each process has a unique number and name calculate price 1. Process name each process using a verb and a noun phrase eg. calculate price check customer details accept supplier delivery the name of a process should describe what the process does avoid vague names where possible e.g. "process data". Data Flow a data flow represents data in motion, moving from one place in the system to another describes a "packet" of data or data that moves together: a data flow may consist of many individual, related pieces of data that move together to a common destination loan application
4 name each data flow using a noun or noun phrase eg. customer order the name of a data flow should describe the contents of the data "packet" the name should include as much information as possible about the data flow eg."customer payment" rather than just "payment" customer order validate customer order valid customer order invalid customer order 3. Data Store a data store represents a collection of data flows "at rest" each data store has a unique name the name should describe the contents of the data store a data store may represent many different types of physical locations of data a data store may be a temporary or a permanent repository of data The Data Store different notations
5 data flows to and from a data store can remain unlabelled if all attributes in the store are moving, i.e. if an entire data packet (or packets) is going into or out of the data store sales order check sales order Sales orders 3 produce weekly sales totals weekly sales totals 4. External Agent (Source/Sink) an external agent represents an entity with which the system communicates and which is outside the scope of the system eg. an outside organisation or individual, another department or another system, a person or group within the department supported by the system who interacts with the system an external agent is a source if it is an origin of data coming into the system an external agent is a sink if it is a destination of data leaving the system Suppliers 4. External Agent (Source/Sink) data flows connecting the external agents to the processes within the system represent the interface between the system and its environment external agents are outside the system and define its boundaries an external agent may be both a source and a sink what a sink does with data it receives from the system and how a source produces data which it inputs to the system are outside the boundary of the system and are not shown on the data flow diagram
6 Example DFD Sales Order sales order purchase order Suppliers goods returned goods unavailable notice Inventory supplier delivery Warehouse shipping slip checked supplier invoice Accounts Department Example Data Flow Diagram Customers sales order 1 check sales order Suppliers Sales orders produce purchase order purchase order Guidelines for Drawing DFDs each object on a data flow diagram must have a unique name each process must have at least one data flow coming in (input) and at least one data flow going out (output) the inputs to a process are different from the outputs of that process a process must be able to build its outputs using only the information in its input data flows plus any constant information
7 Guidelines for Drawing DFDs data flows are permitted: between processes from a data store to a process from a process to a data store from a source to a process from a process to a sink Guidelines for Drawing DFDs data flows are NOT permitted: between external agents between data stores from an external agent to a data store Identify six errors in this abstract DFD EE1 Data Store Data store 1 1 process EE Process1 EE3
8 Levelling Data Flow Diagrams Any "real" system is too large to represent as a single data flow diagram the solution is to decompose the system into a hierarchy of levels of processing the process model of the system then consists of a set of levelled data flow diagrams levelling of DFDs improves their readability and usefulness as a communication tool Levelling of DFDs Levelling creates a hierarchical decomposition of the processing within the system Context diagram Level 0 diagram Level 1 diagrams Level diagrams... Level n diagrams Levelling of DFDs Context diagram Level 0 diagram Level 1 diagrams Level diagrams
9 Context Diagram the highest level data flow diagram is the context diagram the context diagram shows the interaction of the system with its environment in terms of data flows the context diagram defines the boundary of the system (the scope of the system) only the data flows which leave the system and the data flows wh ich come from outside the system are shown Context Diagram the entire system is represented as a single process all external agents (sources and sinks) are shown no data stores are shown: they are inside the boundary of the sy stem EASY GO HOTEL Example Context Diagram Sales Order sales order purchase order Suppliers goods returned goods unavailable notice Inventory supplier delivery Warehouse shipping slip checked supplier invoice Accounts Department
10 Level Zero Diagram the level zero data flow diagram is the diagram at the level immediately below the context diagram it "expands" the single process on the context diagram to show the major, high-level processes (or functions) within the system Level Zero Diagram all external agents (sources and sinks) are included because the level zero diagram, like the context diagram, represents the entiresystem the number of each process ends in.0 which corresponds to the level of the diagram: e.g. 1.0,.0, 3.0 etc. often just 1,, 3 etc. are used Example Level Zero Diagram Order Entry out of stock notice sales order 1.0 Fill Sales Orders.0 Monitor Stock levels Stock file purchase order 3.0 Accept Deliveries Suppliers supplier delivery Warehouse shipping slip checked supplier invoice Accounts Department
11 Level 1 and lower level diagrams each Level 1 diagram and diagrams at lower levels (e.g. Level, Level 3) show only a part of the processing Level 1 processes are numbered 1.1, 1., 1.3, and.1,.,.3 etc that part is shown in more detail than on the Level zero diagram no external agents are shown on a Level 1 or lower diagrams, as the entire system is not being represented Level 1 diagrams a set of data flow diagrams is created at Level 1 there is one Level 1 diagram for each of the processes at Level zero each diagram decomposes a Level zero process into several processes Levelling DFDs 1 Context diagram 3 Level zero diagram Diagram 3 (level 1) Further diagrams or process descriptions. Diagram 3 (level 1)
12 Example Level zero diagram CUSTOMERS Customer details Product details qty holding customer invoice 1 Record and Invoice Sales INVENTORY holding order qty SALES ORDERS p.o. number delivered qty order qty Maintain Product Inventory SUPPLIERS order qty p.o. invoice delivery qty Example Level 1 diagram Customer details Product details qty 1.1 Check Customer Credit customer credit status 1.3 Record Sales Demand qty SALES ORDERS 1. INVENTORY Check Stock Available holding available qty 1.4 Create Sales Invoice INVOICES customer invoice Guidelines for Levelling DFDs numbering: when a process is decomposed, its diagram is given the same number as that process balancing of DFDs: all data flows entering and leaving a process must appear on the corresponding diagram which decomposes that process external agents: are only included on the two diagrams which represent the entire system, i.e. the context and level zero diagrams
13 Guidelines for Levelling DFDs balancing data flows: if data flows are decomposed at lower levels then the contents of the data flows across levels must be balanced out of stock notice 1 Fill Sales Orders sales order shipping slip customer shipping details 1.1 Check shipping details customer order items 1. Check stock available sales order = customer + customer order shipping details items Guidelines for Levelling DFDs The access to data stores across levels of diagrams must be consistent: the direction of accesses must match and all accesses on higher level diagrams must appear on corresponding lower level diagrams a data store is first shown on the highest level diagram where i t is accessed by more than one process it can then appear on all lower level diagrams where it is accessed Guidelines for Levelling DFDs partition processes to: form cohesive, related groups of activities minimise the data flows between them all parts of the system need not be decomposed to the same level
14 Guidelines for Levelling DFDs How many levels should be in a set of DFDs? each diagram usually has between 3 and 7 processes level the diagrams until bottom level or primitive processes are reached primitive processes cannot be further decomposed as a data flow diagram An example - Context Diagram Applicant Line Manager Address Applicant name Position Spec Position Acknowledgement Employment Successful Applicant Decision Position Payroll An example - Level zero diagram Applicant Position Address 1 Accept Application Acknowledgement Applicant name Ackn d Appn Position Spec Evaluate Applicants Decision Position Line Manager Applicant Unsuccessfuls file Evaluation results Successful Applicant Payroll
15 Level 1- Diagram 1 Address Applicant name Position 1.1 Verified Application Acknowledgement 1. Verify for Completeness Acknowledge Application Acknowledged Application Level 1 - Diagram Ackn d Appn Position Spec.1 Screen Applicants unqualified applicant Qualified applicant..3 Decision Reject Unsuitabl es Schedule Evaluation Decision Unsuccessfuls file Evaluation results Successful Applicant References WHITTEN, J.L., BENTLEY, L.D. and DITTMAN, K.C. (001) 5th ed., s Analysis and Design Methods, Irwin/McGraw-HilI, New York, NY. Chapters 8 HOFFER, J.A., GEORGE, J.F. and VALACICH (005) 4th ed., Modern s Analysis and Design, Benjamin/Cummings, Massachusetts. Chapter 7
Modelling as a Communication Tool: Introduction to Process Modelling. Modelling. Simplification in modelling. Representation in modelling
 CSE104 - Information Systems 1 Modelling as a Communication Tool: Introduction to Process Modelling The requirements specification document Must be communicated to key stakeholders Should contain: Functions
CSE104 - Information Systems 1 Modelling as a Communication Tool: Introduction to Process Modelling The requirements specification document Must be communicated to key stakeholders Should contain: Functions
information process modelling DFDs Process description
 Process modelling IMS9300 IS/IM FUNDAMENTALS information process modelling DFDs Process description processes are the action part of businesses process modelling graphically represents the processes which
Process modelling IMS9300 IS/IM FUNDAMENTALS information process modelling DFDs Process description processes are the action part of businesses process modelling graphically represents the processes which
Modelling: Review. Modelling Information Systems. Models in analysis and design. Process Modelling. Modelling perspectives
 Modelling: Review IMS100 Systems Analysis and Design Topic Review of Process Modelling Why do we do it? Communication and understanding Simplification all models are simplifications of the real world:
Modelling: Review IMS100 Systems Analysis and Design Topic Review of Process Modelling Why do we do it? Communication and understanding Simplification all models are simplifications of the real world:
CSE Information Systems 1
 CSE1204 - Information Systems 1 Detailed Process Definitions; The Data Dictionary Data Dictionary the data dictionary is a database or repository of information about objects identified during systems
CSE1204 - Information Systems 1 Detailed Process Definitions; The Data Dictionary Data Dictionary the data dictionary is a database or repository of information about objects identified during systems
System Analysis and Design. Data Flow Diagram. System Analysis and Design
 Data Flow Diagram 1 Data Flow diagram The dataflow diagram is a modeling tool that allows us to picture a system as a network of functional processes, connected to one another by pipelines and holding
Data Flow Diagram 1 Data Flow diagram The dataflow diagram is a modeling tool that allows us to picture a system as a network of functional processes, connected to one another by pipelines and holding
Lecture Notes. Structured Systems Analysis
 Lecture Notes Structured Systems Analysis Lecture 3 Structured Analysis & Data Flow Diagrams Written by Dr. Fred Grossman Copyright 1999 Fred Grossman All Rights Reserved Structured Systems Analysis Structured
Lecture Notes Structured Systems Analysis Lecture 3 Structured Analysis & Data Flow Diagrams Written by Dr. Fred Grossman Copyright 1999 Fred Grossman All Rights Reserved Structured Systems Analysis Structured
Process Modeling. Wei-Tsong Wang 1 IIM, NCKU
 Process Modeling Based on Chapter 9 of Whitten, Bentley, and Dittman: Systems Analysis and Design for the Global Enterprise (7th Ed). McGraw Hill. 2007 Wei-Tsong Wang 1 IIM, NCKU 2 Models: Logical and
Process Modeling Based on Chapter 9 of Whitten, Bentley, and Dittman: Systems Analysis and Design for the Global Enterprise (7th Ed). McGraw Hill. 2007 Wei-Tsong Wang 1 IIM, NCKU 2 Models: Logical and
Chapter 6 Structuring System Requirements: Process Modeling 6.1
 Chapter 6 Structuring System Requirements: Process Modeling 6.1 Learning Objectives Explain process modeling Discuss data-flow diagramming mechanics, definitions, and rules Discuss balancing data-flow
Chapter 6 Structuring System Requirements: Process Modeling 6.1 Learning Objectives Explain process modeling Discuss data-flow diagramming mechanics, definitions, and rules Discuss balancing data-flow
IMS1002/CSE1205 Lectures 1
 IMS1002/CSE1205 Systems Analysis and Design Lecture 2 & 3 Introduction to Data Modelling Entity Relationship Modelling Data Modelling Focus on the information aspects of the organisation In a database
IMS1002/CSE1205 Systems Analysis and Design Lecture 2 & 3 Introduction to Data Modelling Entity Relationship Modelling Data Modelling Focus on the information aspects of the organisation In a database
Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay. Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II)
 Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II) We will continue our discussion on process modeling. In the previous lecture
Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II) We will continue our discussion on process modeling. In the previous lecture
Detailed Data Modelling: Attribute Collection and Normalisation of Data
 Detailed Data Modelling IMS1002 /CSE1205 Systems Analysis and Design Detailed Data Modelling: Attribute Collection and Normalisation of Data The objective of detailed data modelling is to develop a detailed
Detailed Data Modelling IMS1002 /CSE1205 Systems Analysis and Design Detailed Data Modelling: Attribute Collection and Normalisation of Data The objective of detailed data modelling is to develop a detailed
DFD Symbols. Process. Data Store Data Store Data Store
 ? Context Diagram Level 1 Diagram Level 2 Diagram DFD Symbols External Entity Source/Sink User Data Flow Process Process Data Store Data Store Data Store Rule for naming a process: The Joe Test A process
? Context Diagram Level 1 Diagram Level 2 Diagram DFD Symbols External Entity Source/Sink User Data Flow Process Process Data Store Data Store Data Store Rule for naming a process: The Joe Test A process
We move from a general information system to a Computer Based Information System
 Introduction to Information Systems: In this section of the course we start to think of the computer as just being a component in a system which may contain one or many computers linked together. An Information
Introduction to Information Systems: In this section of the course we start to think of the computer as just being a component in a system which may contain one or many computers linked together. An Information
Detailed Data Modelling. Detailed Data Modelling. Detailed Data Modelling. Identifying Attributes. Attributes
 IMS1002 /CSE1205 Systems Analysis and Design Detailed Data Modelling The objective of detailed data modelling is to develop a detailed data structure that: Detailed Data Modelling: Attribute Collection
IMS1002 /CSE1205 Systems Analysis and Design Detailed Data Modelling The objective of detailed data modelling is to develop a detailed data structure that: Detailed Data Modelling: Attribute Collection
Data and Process Modeling
 Chapter 5 Data and Process Modeling 5 CHAPTER Data and Process Modeling Chapter 5 is the second of four chapters in the systems analysis phase of the SDLC. This chapter discusses data and process modeling
Chapter 5 Data and Process Modeling 5 CHAPTER Data and Process Modeling Chapter 5 is the second of four chapters in the systems analysis phase of the SDLC. This chapter discusses data and process modeling
17/03/2018. Meltem Özturan
 Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/samd 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Traditional Analysis Model Data flow diagrams Process description Data flow definiton Data store definition (Entity-Relationship
Meltem Özturan www.mis.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/samd 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Traditional Analysis Model Data flow diagrams Process description Data flow definiton Data store definition (Entity-Relationship
Chapter 9. Process Modeling. McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Process Modeling McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives Define systems modeling and differentiate logical and physical models. Define
Chapter 9 Process Modeling McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives Define systems modeling and differentiate logical and physical models. Define
Lab 16: Visio Introduction
 Lab 16: Visio Introduction () CONTENTS 1 Visio- Introduction to DFD Data Flow Diagraming... 2 1.1 In-Lab... 3 1.1.1 In-Lab Materials... 3 1.1.2 In-Lab Instructions... 3 2 Getting started: Let s decompose
Lab 16: Visio Introduction () CONTENTS 1 Visio- Introduction to DFD Data Flow Diagraming... 2 1.1 In-Lab... 3 1.1.1 In-Lab Materials... 3 1.1.2 In-Lab Instructions... 3 2 Getting started: Let s decompose
An Introduction to Business Process Modeling using Data Flow Diagrams
 An Introduction to Business Process Modeling using Data Flow Diagrams BSAD 141 Dave Novak BDIS: 2.2 (61-77) Lecture Overview Systems and Business processes Business process models Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs)
An Introduction to Business Process Modeling using Data Flow Diagrams BSAD 141 Dave Novak BDIS: 2.2 (61-77) Lecture Overview Systems and Business processes Business process models Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs)
(Murlidhar Group of Institutions,Bhavnagar Road, Rajkot) by:-assit. Prof. Vijay Vora (SOOADM) MCA-III
 Analysis Modeling What is Analysis Modeling? Analysis modeling uses a combination of text and diagrammatic forms to depict(represent) requirements for data, function, and behavior These text and diagrammatic
Analysis Modeling What is Analysis Modeling? Analysis modeling uses a combination of text and diagrammatic forms to depict(represent) requirements for data, function, and behavior These text and diagrammatic
STRUCTURED SYSTEMS ANALYSIS & DESIGN
 Lecture 5 STRUCTURED SYSTEMS ANALYSIS & DESIGN Objectives Explain SSADM Describe tools of SSADM 2 1 SSADM It is a data (logical) oriented approach to system analysis and design that focuses on nature and
Lecture 5 STRUCTURED SYSTEMS ANALYSIS & DESIGN Objectives Explain SSADM Describe tools of SSADM 2 1 SSADM It is a data (logical) oriented approach to system analysis and design that focuses on nature and
Data Flow Diagrams System Analysis ( (
 7 Data Flow Diagrams System Analysis (1932475( Kendall & Kendall 7-1 Data Flow Diagrams A top down approach to diagramming data movement, it moves from general to specific. Graphically characterize data
7 Data Flow Diagrams System Analysis (1932475( Kendall & Kendall 7-1 Data Flow Diagrams A top down approach to diagramming data movement, it moves from general to specific. Graphically characterize data
Requests Charges. Librarian. University affiliated patrons students, faculty, staff. Media Center Staff
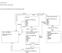 Catherine Rutan INFO 530-901 Dr. Valerie Yonker Circulation of Media Materials from University Media Center: Requests Charges Librarian Circulation Desk Attendant Inquires University ID # (Primary Key)
Catherine Rutan INFO 530-901 Dr. Valerie Yonker Circulation of Media Materials from University Media Center: Requests Charges Librarian Circulation Desk Attendant Inquires University ID # (Primary Key)
13/11/2017. Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515
 Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Data Flow Diagram (DFD) A graphical system model that shows all of the main requirements for an information
Meltem Özturan misprivate.boun.edu.tr/ozturan/mis515 2 1 Traditional Approach to Requirements Data Flow Diagram (DFD) A graphical system model that shows all of the main requirements for an information
Analysis and Design for Systems h. 9 th Edition
 Analysis and Design for Systems h 9 th Edition Chapter 5 Data and Process Analysis Chapter Objectives Describe data and process modeling dli concepts and tools, including data flow diagrams, a data dictionary,
Analysis and Design for Systems h 9 th Edition Chapter 5 Data and Process Analysis Chapter Objectives Describe data and process modeling dli concepts and tools, including data flow diagrams, a data dictionary,
Data. Entities. Accounting Information Systems. Chapter 4: Data Management
 Accounting Information Systems Chapter 4: Data Management Data Data may be defined broadly to include two interrelated components: Data Models that provide structure to data File Orientation Data-base
Accounting Information Systems Chapter 4: Data Management Data Data may be defined broadly to include two interrelated components: Data Models that provide structure to data File Orientation Data-base
System Analysis and Design
 System Analysis and Design M Umair www.m-umair.com System Description Techniques Graphical representation of any process is always better and more meaningful than its representation in words. System Analysis
System Analysis and Design M Umair www.m-umair.com System Description Techniques Graphical representation of any process is always better and more meaningful than its representation in words. System Analysis
Chapter 4: Data Management
 Accounting Information Systems: Essential Concepts and Applications Fourth Edition by Wilkinson, Cerullo, Raval, and Wong-On-Wing Chapter 4: Data Management Slides Authored by Somnath Bhattacharya, Ph.D.
Accounting Information Systems: Essential Concepts and Applications Fourth Edition by Wilkinson, Cerullo, Raval, and Wong-On-Wing Chapter 4: Data Management Slides Authored by Somnath Bhattacharya, Ph.D.
Requirements Engineering
 Requirements Engineering Semi-Formal Specification: Structural Functional Requirements Structured Analysis Data Flow Diagrams SADT IDEF0 1 Back to the past GO/AO OO SA (DT) DFD SADT IDEF (Back to the future)
Requirements Engineering Semi-Formal Specification: Structural Functional Requirements Structured Analysis Data Flow Diagrams SADT IDEF0 1 Back to the past GO/AO OO SA (DT) DFD SADT IDEF (Back to the future)
Data Import Guide DBA Software Inc.
 Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Data Import Instructions 5 3 Data Import - Customers 10 4 Data Import - Customer Contacts 16 5 Data Import - Delivery Addresses 19 6 Data Import - Suppliers
Contents 3 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 4 2 Data Import Instructions 5 3 Data Import - Customers 10 4 Data Import - Customer Contacts 16 5 Data Import - Delivery Addresses 19 6 Data Import - Suppliers
Introduction to Transaction Processing
 Modul ke: Introduction to Transaction Processing Fakultas Fakultas Ekonomi & Bisnis Iwan Setiadi, SE., M.Si Program Studi Akuntansi www.mercubuana.ac.id A Financial Transaction is... an economic event
Modul ke: Introduction to Transaction Processing Fakultas Fakultas Ekonomi & Bisnis Iwan Setiadi, SE., M.Si Program Studi Akuntansi www.mercubuana.ac.id A Financial Transaction is... an economic event
System Analysis & design
 Assiut University Faculty of Computers and Information System Analysis & design Year 2 Academic Year 2014/ 2015 Term (2) 5 A PICTURE IS WORTH A 1,000 WORDS A process model is a graphical way of representing
Assiut University Faculty of Computers and Information System Analysis & design Year 2 Academic Year 2014/ 2015 Term (2) 5 A PICTURE IS WORTH A 1,000 WORDS A process model is a graphical way of representing
For addition help including training and support please contact Scanco by or phone. Scanco Support -
 Scanco Mobility Module Contents Mobility Remote Setup... 2 Purchase Order EZ Import... 9 Sales Order EZ Import... 10 Bill of Materials EZ Import... 11 EZ Import Reject Maintenance... 12 Rejected Import
Scanco Mobility Module Contents Mobility Remote Setup... 2 Purchase Order EZ Import... 9 Sales Order EZ Import... 10 Bill of Materials EZ Import... 11 EZ Import Reject Maintenance... 12 Rejected Import
Invoice 13 Pro Outline
 Invoice 13 Pro Outline Invoice 13 Pro is a feature rich productivity tool for the small business or company from 1 to 30 users. It is notjust an Invoicing software. It is in fact an Invoicing, Accounts
Invoice 13 Pro Outline Invoice 13 Pro is a feature rich productivity tool for the small business or company from 1 to 30 users. It is notjust an Invoicing software. It is in fact an Invoicing, Accounts
An Automatic Tool for Checking Consistency between Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs)
 An Automatic Tool for Checking Consistency between Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) Rosziati Ibrahim, Siow Yen Yen Abstract System development life cycle (SDLC) is a process uses during the development of any
An Automatic Tool for Checking Consistency between Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) Rosziati Ibrahim, Siow Yen Yen Abstract System development life cycle (SDLC) is a process uses during the development of any
Lecture Objectives. Documentation What is it? User Documentation Purpose. User Documentation Report Format (an example) User Documentation Purpose
 Lecture Objectives IMS 2501 2 nd Year Studio Seminar 7 and Testing Semester 1, 2005 > What is it? > User, Report Format > Programming, Report Format > General Principles for Good Testing > What is testing?
Lecture Objectives IMS 2501 2 nd Year Studio Seminar 7 and Testing Semester 1, 2005 > What is it? > User, Report Format > Programming, Report Format > General Principles for Good Testing > What is testing?
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A process has a: 1) A) pronoun label B) noun phrase label C) verb phrase label D) adjective
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A process has a: 1) A) pronoun label B) noun phrase label C) verb phrase label D) adjective
Systems Development and Documentation Techniques. Lecture 2. (Chapter 3)
 Systems Development and Documentation Techniques Lecture 2 (Chapter 3) Introduction This chapter explains the most common systems documentation tools and techniques. 1 Data flow diagrams 2 Document flowcharts
Systems Development and Documentation Techniques Lecture 2 (Chapter 3) Introduction This chapter explains the most common systems documentation tools and techniques. 1 Data flow diagrams 2 Document flowcharts
1. Data flow diagrams (DFDs) are used to depict the flow and transformation of data
 SUMMARY OF MODULE 5 1. Data flow diagrams (DFDs) are used to depict the flow and transformation of data in an information processing system. 2. DFDs give an overview to an analyst specifying where data
SUMMARY OF MODULE 5 1. Data flow diagrams (DFDs) are used to depict the flow and transformation of data in an information processing system. 2. DFDs give an overview to an analyst specifying where data
COIT20248: Information Systems Analysis and Design Term 2, 2015 Assignment 2. Lecturer: Dr. Meena Jha Tutor: Aries Tao
 COIT20248: Information Systems Analysis and Design Term 2, 2015 Assignment 2 Lecturer: Dr. Meena Jha Tutor: Aries Tao Prepared by: AXXXX XXXX: S0XXXXXX AXXXX MXXXXX: BisXXXXX BaXXXX: S0XXXXX S02XXXX SXXXXX
COIT20248: Information Systems Analysis and Design Term 2, 2015 Assignment 2 Lecturer: Dr. Meena Jha Tutor: Aries Tao Prepared by: AXXXX XXXX: S0XXXXXX AXXXX MXXXXX: BisXXXXX BaXXXX: S0XXXXX S02XXXX SXXXXX
How do archivists identify and capture records?
 QUESTION How do archivists identify and capture records? AUTOMATED SYSTEMS MEETING THE CHALLENGE Critical Skill Set: Information System Analysis and Design Skills Being able to create conceptual models
QUESTION How do archivists identify and capture records? AUTOMATED SYSTEMS MEETING THE CHALLENGE Critical Skill Set: Information System Analysis and Design Skills Being able to create conceptual models
Information Technology Audit & Cyber Security
 Information Technology Audit & Cyber Security Structured Data Requirements Systems & Infrastructure Lifecycle Management with E-R LEARNING OBJECTIVES Explain the role of conceptual data modeling in the
Information Technology Audit & Cyber Security Structured Data Requirements Systems & Infrastructure Lifecycle Management with E-R LEARNING OBJECTIVES Explain the role of conceptual data modeling in the
Furniture Wizard Security Introduction
 Furniture Wizard Security Introduction In this section, we will introduce you to the new security features of Furniture Wizard. Furniture Wizard s security will allow you to set permissions for different
Furniture Wizard Security Introduction In this section, we will introduce you to the new security features of Furniture Wizard. Furniture Wizard s security will allow you to set permissions for different
Chapter No 13 Batch Management Information Systems. Management Information Systems. Compiled By: Muzammil Ahmad Khan and Kashif Shaikh
 Chapter 13 Compiled By: Muzammil Ahmad Khan Muhammad Kashif Shaikh HS-107 : Course Objectives: Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: Understand the role of Information
Chapter 13 Compiled By: Muzammil Ahmad Khan Muhammad Kashif Shaikh HS-107 : Course Objectives: Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: Understand the role of Information
Unit 6 - Software Design and Development LESSON 10 DESIGN TOOLS, INPUTS, OUTPUTS, STORYBOARDS
 Unit 6 - Software Design and Development LESSON 10 DESIGN TOOLS, INPUTS, OUTPUTS, STORYBOARDS Previously Key features of programming languages Software Development Lifecycle Using tools to demonstrate
Unit 6 - Software Design and Development LESSON 10 DESIGN TOOLS, INPUTS, OUTPUTS, STORYBOARDS Previously Key features of programming languages Software Development Lifecycle Using tools to demonstrate
Internet Web Site:
 1 Internet Web Site: www.reliableparts.com Click on Canadian Online Ordering To sign on: User ID = your account number -- Password = "Your assigned password" Note: A one time set up to change your browser
1 Internet Web Site: www.reliableparts.com Click on Canadian Online Ordering To sign on: User ID = your account number -- Password = "Your assigned password" Note: A one time set up to change your browser
CHAPTER 4 Data and Process Modeling (Phase 2: Systems Analysis)
 CHAPTER 4 Data and Process Modeling (Phase 2: Systems Analysis) Jakrapop Maisen DATA FLOW DIAGRAMS A data flow diagram (DFD) shows how data moves through an information system but does not show program
CHAPTER 4 Data and Process Modeling (Phase 2: Systems Analysis) Jakrapop Maisen DATA FLOW DIAGRAMS A data flow diagram (DFD) shows how data moves through an information system but does not show program
Input Design and Prototyping
 Types of Inputs Input Design and Prototyping Based on Chapter 16 of Whitten, Bentley, and Dittman: Systems Analysis and Design for the Global Enterprise (7th Ed). McGraw Hill. 2007 Inputs can be classified
Types of Inputs Input Design and Prototyping Based on Chapter 16 of Whitten, Bentley, and Dittman: Systems Analysis and Design for the Global Enterprise (7th Ed). McGraw Hill. 2007 Inputs can be classified
MRPEasy features. MRPEasy is a powerful yet simple manufacturing software especially built for effective manufacturing control.
 MRPEasy features MRPEasy is a powerful yet simple manufacturing software especially built for effective manufacturing control. The solution is an online service, extremely easy to use, effortless to maintain,
MRPEasy features MRPEasy is a powerful yet simple manufacturing software especially built for effective manufacturing control. The solution is an online service, extremely easy to use, effortless to maintain,
IS development: Quality Standards Documentation
 Lecture Objectives IS development: Quality Standards Documentation www.sims.monash.edu.au IMS9300 IS/IM FUNDAMENTALS At the completion of this topic, you should : understand the need for, and the role
Lecture Objectives IS development: Quality Standards Documentation www.sims.monash.edu.au IMS9300 IS/IM FUNDAMENTALS At the completion of this topic, you should : understand the need for, and the role
Cat ARCTIC CAT Dealer & Distributor Network
 Cat ARCTIC CAT Dealer & Distributor Network TUTORIAL Part 01 Content: Shop / Parts Ordering Service & Support Cat TUTORIAL Welcome to the Arctic Cat Europe Dealer online platform called Cat. This network
Cat ARCTIC CAT Dealer & Distributor Network TUTORIAL Part 01 Content: Shop / Parts Ordering Service & Support Cat TUTORIAL Welcome to the Arctic Cat Europe Dealer online platform called Cat. This network
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING. 2 Marks and 11 Marks for Unit - 3
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Subject Name: Subject Code: Staff name: Software Engineering CS T55 Dr K. Shantha Kumari 2 Marks and 11 Marks for Unit - 3 Software Design and Function Oriented
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Subject Name: Subject Code: Staff name: Software Engineering CS T55 Dr K. Shantha Kumari 2 Marks and 11 Marks for Unit - 3 Software Design and Function Oriented
Functional Modeling with Data Flow Diagrams
 Functional Modeling with Data Flow Diagrams Amasi Elbakush 5771668 Teaching Assistant : Daniel Alami Utrecht University 1 Introduction Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) are a visual representation of the flow
Functional Modeling with Data Flow Diagrams Amasi Elbakush 5771668 Teaching Assistant : Daniel Alami Utrecht University 1 Introduction Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) are a visual representation of the flow
Lorna Jane. Wholesale Website Guide
 Lorna Jane Wholesale Website Guide Wholesale Website Guide Contents New Look Features... 2 Header... 3 Footer... 4 Logging In... 5 Forgot Password... 6 Change Language... 6 Searching for Products... 7
Lorna Jane Wholesale Website Guide Wholesale Website Guide Contents New Look Features... 2 Header... 3 Footer... 4 Logging In... 5 Forgot Password... 6 Change Language... 6 Searching for Products... 7
IT Auditing, Hall, 3e
 IT Auditing, an economic event that affects the assets and equities of the firm, is reflected in its accounts, and is measured in monetary terms. similar types of transactions are grouped together into
IT Auditing, an economic event that affects the assets and equities of the firm, is reflected in its accounts, and is measured in monetary terms. similar types of transactions are grouped together into
Modern Systems Analysis and Design Seventh Edition
 Modern Systems Analysis and Design Seventh Edition Jeffrey A. Hoffer Joey F. George Joseph S. Valacich Structuring System Data Requirements Learning Objectives ü Concisely define each of the following
Modern Systems Analysis and Design Seventh Edition Jeffrey A. Hoffer Joey F. George Joseph S. Valacich Structuring System Data Requirements Learning Objectives ü Concisely define each of the following
Lecture 5 STRUCTURED ANALYSIS. PB007 So(ware Engineering I Faculty of Informa:cs, Masaryk University Fall Bühnová, Sochor, Ráček
 Lecture 5 STRUCTURED ANALYSIS PB007 So(ware Engineering I Faculty of Informa:cs, Masaryk University Fall 2015 1 Outline ² Yourdon Modern Structured Analysis (YMSA) Context diagram (CD) Data flow diagram
Lecture 5 STRUCTURED ANALYSIS PB007 So(ware Engineering I Faculty of Informa:cs, Masaryk University Fall 2015 1 Outline ² Yourdon Modern Structured Analysis (YMSA) Context diagram (CD) Data flow diagram
Chapter 13. Application Architecture and Modeling. McGraw-Hill/Irwin. Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 13 Application Architecture and Modeling McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 13-2 Define an information system s architecture in
Chapter 13 Application Architecture and Modeling McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 13-2 Define an information system s architecture in
Structured Modeling Methods. Lecture 15: Advantages and Disadvantages. University of Toronto Department of Computer Science.
 Lecture 15: Structured Modeling Methods Basics of Structured Analysis Notations used Modeling Process Variants SADT SASS SSADM SRD Advantages and Disadvantages 2001, Steve Easterbrook CSC444 Lec15 1 Definition
Lecture 15: Structured Modeling Methods Basics of Structured Analysis Notations used Modeling Process Variants SADT SASS SSADM SRD Advantages and Disadvantages 2001, Steve Easterbrook CSC444 Lec15 1 Definition
Lecture 8: Use Case -Driven Design. Where UML fits in
 Lecture 8: Use Case -Driven Design The Role of UML in the Software Process E.g. ICONIX Domain Models Use Cases 2008 Steve Easterbrook. This presentation is available free for non-commercial use with attribution
Lecture 8: Use Case -Driven Design The Role of UML in the Software Process E.g. ICONIX Domain Models Use Cases 2008 Steve Easterbrook. This presentation is available free for non-commercial use with attribution
On to Iteration 3, and Activity Diagrams CSSE 574: Session 6, Part 1
 On to Iteration 3, and Activity Diagrams CSSE 574: Session 6, Part 1 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu On to Iteration 3: NextGen POS Failover
On to Iteration 3, and Activity Diagrams CSSE 574: Session 6, Part 1 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu On to Iteration 3: NextGen POS Failover
Software Design. Software design is a blueprint or a plan for a computerbased solution for system
 Software Design Software Design Software design is a blueprint or a plan for a computerbased solution for system Software design deals with transforming the customer requirements, as described by the SRS
Software Design Software Design Software design is a blueprint or a plan for a computerbased solution for system Software design deals with transforming the customer requirements, as described by the SRS
Genesis Advantage. Version 7
 Welcome to Genesis Advantage version 7! We have packed many new features and enhancements into this release. Most of these features were suggested by our clients and we appreciate your input. We have included
Welcome to Genesis Advantage version 7! We have packed many new features and enhancements into this release. Most of these features were suggested by our clients and we appreciate your input. We have included
Request for Credit in Accounts Payable
 App Number: 010045 Request for Credit in Accounts Payable Last Updated 28 September 2016 Powered by: AppsForGreentree.com 2014 1 Table of Contents Features... 3 Detailed Features... 3 Important Notes...
App Number: 010045 Request for Credit in Accounts Payable Last Updated 28 September 2016 Powered by: AppsForGreentree.com 2014 1 Table of Contents Features... 3 Detailed Features... 3 Important Notes...
INFS 328 Systems Analysis and Design
 INFS 328 Systems Analysis and Design Session 13 Systems Analysis and Construction Tools Lecturer: Prof. Ellis Edwin Badu, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eebadu@ug.edu.gh College of Education
INFS 328 Systems Analysis and Design Session 13 Systems Analysis and Construction Tools Lecturer: Prof. Ellis Edwin Badu, Dept. of Information Studies Contact Information: eebadu@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Invoice Specification EDI 810
 Invoice Specification EDI 80 This document is solely for the use of Logicbroker, Inc. personnel and its intended client. No part of it may be circulated, Quoted, or reproduced for distribution outside
Invoice Specification EDI 80 This document is solely for the use of Logicbroker, Inc. personnel and its intended client. No part of it may be circulated, Quoted, or reproduced for distribution outside
RESOLV EDI CONTROL. User Guide Version 9.2 for HANA PRESENTED BY ACHIEVE IT SOLUTIONS
 RESOLV EDI CONTROL User Guide Version 9.2 for HANA PRESENTED BY ACHIEVE IT SOLUTIONS Copyright 2011-2016 by Achieve IT Solutions These materials are subject to change without notice. These materials are
RESOLV EDI CONTROL User Guide Version 9.2 for HANA PRESENTED BY ACHIEVE IT SOLUTIONS Copyright 2011-2016 by Achieve IT Solutions These materials are subject to change without notice. These materials are
Chapter 10. Object-Oriented Analysis and Modeling Using the UML. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 Chapter 10 Object-Oriented Analysis and Modeling Using the UML McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 10-2 Define object modeling and explain
Chapter 10 Object-Oriented Analysis and Modeling Using the UML McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 10-2 Define object modeling and explain
SIF8035. Events and System Requirements
 SIF8035 Lecture 4 DFD and PrM Events and System Requirements Events Occurrences at a specific time and place Trigger all system processing Requirement definition Determine relevant events External events
SIF8035 Lecture 4 DFD and PrM Events and System Requirements Events Occurrences at a specific time and place Trigger all system processing Requirement definition Determine relevant events External events
Ariba Manual INVOICING PO
 Ariba Manual INVOICING PO For Suppliers Date 6 september 2013 Document name Ariba Manual - Invoicing PO (SUPPLIER).docx Version Version 2.0 2013 N.V. Nederlandse Gasunie, Groningen Page 1 of 23 Contents
Ariba Manual INVOICING PO For Suppliers Date 6 september 2013 Document name Ariba Manual - Invoicing PO (SUPPLIER).docx Version Version 2.0 2013 N.V. Nederlandse Gasunie, Groningen Page 1 of 23 Contents
LAB-03 BPMN Resource Perspective and Events
 Lab for the course on Process and Service Modeling and Analysis LAB-03 BPMN Resource Perspective and Events Lecturer: Andrea MARRELLA Objectives of this lecture Recap: Pools, Swimlanes and Message Flows
Lab for the course on Process and Service Modeling and Analysis LAB-03 BPMN Resource Perspective and Events Lecturer: Andrea MARRELLA Objectives of this lecture Recap: Pools, Swimlanes and Message Flows
Full file at https://fratstock.eu INTRODUCTION TO TRANSACTION PROCESSING
 CHAPTER 2 2-1 OUTLINE OF CHAPTER 2 Learning Objectives An Overview of Transaction Processing Transaction Cycles The Expenditure Cycle The Conversion Cycle The Revenue Cycle Accounting Records Manual Systems
CHAPTER 2 2-1 OUTLINE OF CHAPTER 2 Learning Objectives An Overview of Transaction Processing Transaction Cycles The Expenditure Cycle The Conversion Cycle The Revenue Cycle Accounting Records Manual Systems
Bid Specification Process. Step 1. Obtain project specifications (minimum 7 weeks prior to anticipated project delivery date)
 Bid Specification Process Step 1. Obtain project specifications (minimum 7 weeks prior to anticipated project delivery date) If University Communications is designing the project, obtain the project s
Bid Specification Process Step 1. Obtain project specifications (minimum 7 weeks prior to anticipated project delivery date) If University Communications is designing the project, obtain the project s
Structured English Examples
 Logic Modeling Logic and timing are not represented on data flow diagrams or entity-relationship diagrams Processes contain logic - what happens under what conditions Logic is modeled per process Types
Logic Modeling Logic and timing are not represented on data flow diagrams or entity-relationship diagrams Processes contain logic - what happens under what conditions Logic is modeled per process Types
Abort: To stop a program execution immediately, usually in the event of an error that will prevent further execution.
 Commonly Used Terms Abort: To stop a program execution immediately, usually in the event of an error that will prevent further execution. Alphanumeric Code: A set of characters containing both letters
Commonly Used Terms Abort: To stop a program execution immediately, usually in the event of an error that will prevent further execution. Alphanumeric Code: A set of characters containing both letters
R.S. Pressman & Associates, Inc. For University Use Only
 Software Engineering: A Practitioner s Approach, 6/e Chapter 10 Architectural Design copyright 1996, 2001, 2005 R.S. Pressman & Associates, Inc. For University Use Only May be reproduced ONLY for student
Software Engineering: A Practitioner s Approach, 6/e Chapter 10 Architectural Design copyright 1996, 2001, 2005 R.S. Pressman & Associates, Inc. For University Use Only May be reproduced ONLY for student
Overview. What is system analysis and design? Tools and models Methodologies
 Overview What is system analysis and design? Tools and models Methodologies Information Systems What is a system? Why do systems fail? What is systems analysis and design? How do we do systems analysis?
Overview What is system analysis and design? Tools and models Methodologies Information Systems What is a system? Why do systems fail? What is systems analysis and design? How do we do systems analysis?
WebStore. Resellers. Brief User Guide. Invite. Self-Register. Log-In. Lost Password. Support. SIPHON 31 May Resellers must be invited to use
 Resellers WebStore Brief User Guide Invite Resellers must be invited to use the SIPHON WebStore. This is important as we need to approve your email address against your account. If you would like to register
Resellers WebStore Brief User Guide Invite Resellers must be invited to use the SIPHON WebStore. This is important as we need to approve your email address against your account. If you would like to register
SEM Dealer Management System Operation Manual
 SEM Dealer Management System Operation Manual 1 Content Chapter 1 System Introduction... 3 Chapter 2 System Installation... 4 Chapter 3 System Interface Introduction... 5 Chapter 4 System Operating Instruction...
SEM Dealer Management System Operation Manual 1 Content Chapter 1 System Introduction... 3 Chapter 2 System Installation... 4 Chapter 3 System Interface Introduction... 5 Chapter 4 System Operating Instruction...
A Framework for Converting Classical Design to Reusable Design
 A Framework for Converting Classical Design to Reusable Design Abdul Khader Jilani 1, Dr. Syed Abdul Sattar 2 1 Research Scholar, Rayalaseema University, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India 2 Dean, Royal Institute
A Framework for Converting Classical Design to Reusable Design Abdul Khader Jilani 1, Dr. Syed Abdul Sattar 2 1 Research Scholar, Rayalaseema University, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India 2 Dean, Royal Institute
TECSYS Streamline Enterprise System Page 1 of 7
 TECSYS Streamline Enterprise System Page 1 of 7 Section 1: Module: A/P Accounts Payable 1. 10.3.1 Enhancement to Interface to Scan and Store A/P Invoice Images Module: A/R Accounts Payable > A/P Invoicing..
TECSYS Streamline Enterprise System Page 1 of 7 Section 1: Module: A/P Accounts Payable 1. 10.3.1 Enhancement to Interface to Scan and Store A/P Invoice Images Module: A/R Accounts Payable > A/P Invoicing..
ABSTRACTION OF DATA FLOW DIAGRAM FOR A C PROGRAM
 International Journal of Operations System and Human Resource Management Vol. 2, Nos. 1-2, January-December 2012, pp. 69 77 International Science Press ABSTRACTION OF DATA FLOW DIAGRAM FOR A C PROGRAM
International Journal of Operations System and Human Resource Management Vol. 2, Nos. 1-2, January-December 2012, pp. 69 77 International Science Press ABSTRACTION OF DATA FLOW DIAGRAM FOR A C PROGRAM
Ch t 8 Chapter 8. System Models
 Ch t 8 Chapter 8. System Models Objectives To explain why the context t of a system should be modelled d as a part of requirements engineering process To describe behavioural modelling, data modelling
Ch t 8 Chapter 8. System Models Objectives To explain why the context t of a system should be modelled d as a part of requirements engineering process To describe behavioural modelling, data modelling
CS 4400 Introduction to Database Systems 2002 Spring Term Project (Section A)
 CS 4400 Introduction to Database Systems 2002 Spring Term Project (Section A) Last updated 1/15/2002, 9:30pm In this term project, you are asked to design a small database system, create and populate this
CS 4400 Introduction to Database Systems 2002 Spring Term Project (Section A) Last updated 1/15/2002, 9:30pm In this term project, you are asked to design a small database system, create and populate this
B2B User Guide: Getting started:
 B2B User Guide: Overview: Although this site is fairly intuitive this document covers the functions provided to Toyo dealers on this site. Not all functions may be provisioned for your particular user
B2B User Guide: Overview: Although this site is fairly intuitive this document covers the functions provided to Toyo dealers on this site. Not all functions may be provisioned for your particular user
Introduction to Informatics. Software Design: Flowcharts, Modular Design and Beyond
 MTAT.05.074 074 Introduction to Informatics Software Design: Flowcharts, Modular Design and Beyond Marlon Dumas marlon.dumas ät ut. ee Course Objectives To introduce the flowchart notation and one of its
MTAT.05.074 074 Introduction to Informatics Software Design: Flowcharts, Modular Design and Beyond Marlon Dumas marlon.dumas ät ut. ee Course Objectives To introduce the flowchart notation and one of its
Database Design: Conceptual Model and ER Diagramming
 Database Design: Conceptual Model and ER Diagramming Ray R. Larson University of California, Berkeley School of Information IS 257: Database Management 2015-09-03 - SLIDE 1 Announcements Accounts and MySQL
Database Design: Conceptual Model and ER Diagramming Ray R. Larson University of California, Berkeley School of Information IS 257: Database Management 2015-09-03 - SLIDE 1 Announcements Accounts and MySQL
CHAPTER 8B PURCHASE ORDER MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 8B PURCHASE ORDER MANAGEMENT Chapter 8B...1 Purchase Order Maintenance...2 Purchase Order Maintenance...3 Retrieving an Existing Purchase Order...5 Quick Search...6 Deleting an Existing Purchase
CHAPTER 8B PURCHASE ORDER MANAGEMENT Chapter 8B...1 Purchase Order Maintenance...2 Purchase Order Maintenance...3 Retrieving an Existing Purchase Order...5 Quick Search...6 Deleting an Existing Purchase
Lecture c, Process Mapping: Yourdon Notation for Data Flow Diagrams, covers Yourdon notation for data flow diagrams.
 WORKFLOW ANALYSIS Audio Transcript Component 10 Unit 3 Lecture C Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign Interpreting and Creating Process Diagrams Process Mapping Yourdon Notation
WORKFLOW ANALYSIS Audio Transcript Component 10 Unit 3 Lecture C Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis & Redesign Interpreting and Creating Process Diagrams Process Mapping Yourdon Notation
Version 5.7. Published: November 5th, Copyright 2018 Prologic. All rights reserved.
 Version 5.7 Published: November 5th, 2018 Copyright 2018 Prologic. All rights reserved. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Release Overview 3 2. Summary of Issues Fixed 3 2.1 Issues Fixed in v5.7 3 3. Known Issues 3
Version 5.7 Published: November 5th, 2018 Copyright 2018 Prologic. All rights reserved. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Release Overview 3 2. Summary of Issues Fixed 3 2.1 Issues Fixed in v5.7 3 3. Known Issues 3
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of
 Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
Purchase Order User Manual
 User Manual Copyright 2014 by Samco Software Inc. PROPRIETARY RIGHTS NOTICE: All rights reserved. No part of this material may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
User Manual Copyright 2014 by Samco Software Inc. PROPRIETARY RIGHTS NOTICE: All rights reserved. No part of this material may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
E2OPEN SUPPLIER TRAINING VERSION MARCH 15, 2018
 E2OPEN SUPPLIER TRAINING VERSION MARCH 15, 2018 Thank You for Participating Thank you for partnering with Bosch and agreeing to use the E2Open Web-based Supply Chain Management Portal. The new solution
E2OPEN SUPPLIER TRAINING VERSION MARCH 15, 2018 Thank You for Participating Thank you for partnering with Bosch and agreeing to use the E2Open Web-based Supply Chain Management Portal. The new solution
Unacknowledged/Late Delivery Web Tool
 Table of Contents Register:... 2 Log on to Web Site:... 2 Logoff Web Site:... 3 List PO s Page:... 4 To Acknowledge PO or Change PO date.... 5 To Mark a PO Shipped.... 6 To Change the Price.... 6 Send
Table of Contents Register:... 2 Log on to Web Site:... 2 Logoff Web Site:... 3 List PO s Page:... 4 To Acknowledge PO or Change PO date.... 5 To Mark a PO Shipped.... 6 To Change the Price.... 6 Send
FBL Weekly Sales Report
 FBL Weekly Sales Report Sales Report Method 1: From Order Tab 1. To check your sales on FBL, you can select the order tab 2 Sales Report Method 1: From Order Tab 1 1. Choose Shipped tab 2. Choose Fulfillment
FBL Weekly Sales Report Sales Report Method 1: From Order Tab 1. To check your sales on FBL, you can select the order tab 2 Sales Report Method 1: From Order Tab 1 1. Choose Shipped tab 2. Choose Fulfillment
Structured Analysis and Structured Design
 Structured Analysis and Structured Design - Introduction to SASD - Structured Analysis - Structured Design Ver. 1.5 Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr http://dslab.konkuk.ac.kr References Modern
Structured Analysis and Structured Design - Introduction to SASD - Structured Analysis - Structured Design Ver. 1.5 Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr http://dslab.konkuk.ac.kr References Modern
Lab # 1. Structuring System Requirements: Diagrams
 Lab # 1 Structuring System Requirements: Diagrams Objectives 1. Use Case diagrams 2. Class Objects (CO) diagrams 3. Context Data Flow Diagrams (Context DFDs) 4. Level-0 Data Flow Diagrams (Level-0 DFDs)
Lab # 1 Structuring System Requirements: Diagrams Objectives 1. Use Case diagrams 2. Class Objects (CO) diagrams 3. Context Data Flow Diagrams (Context DFDs) 4. Level-0 Data Flow Diagrams (Level-0 DFDs)
CYMA IV. Accounting for Windows. CYMA IV Getting Started Guide. Training Guide Series
 CYMA IV Accounting for Windows Training Guide Series CYMA IV Getting Started Guide November 2010 CYMA Systems, Inc. 2330 West University Drive, Suite 4 Tempe, AZ 85281 (800) 292-2962 Fax: (480) 303-2969
CYMA IV Accounting for Windows Training Guide Series CYMA IV Getting Started Guide November 2010 CYMA Systems, Inc. 2330 West University Drive, Suite 4 Tempe, AZ 85281 (800) 292-2962 Fax: (480) 303-2969
PUBLIC. How to Manage Batch Numbers. All Countries. Solutions from SAP. SAP Business One 2007 A and 2007 B. August English
 PUBLIC How to Manage Batch Numbers All Countries Solutions from SAP SAP Business One 2007 A and 2007 B August 2008 English Contents Purpose... 3 Defining General Settings... 4 Procedure... 4 Setting Authorizations...
PUBLIC How to Manage Batch Numbers All Countries Solutions from SAP SAP Business One 2007 A and 2007 B August 2008 English Contents Purpose... 3 Defining General Settings... 4 Procedure... 4 Setting Authorizations...
OBJECTIVES DEFINITIONS CHAPTER 1: THE DATABASE ENVIRONMENT AND DEVELOPMENT PROCESS. Figure 1-1a Data in context
 OBJECTIVES CHAPTER 1: THE DATABASE ENVIRONMENT AND DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Modern Database Management 11 th Edition Jeffrey A. Hoffer, V. Ramesh, Heikki Topi! Define terms! Name limitations of conventional
OBJECTIVES CHAPTER 1: THE DATABASE ENVIRONMENT AND DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Modern Database Management 11 th Edition Jeffrey A. Hoffer, V. Ramesh, Heikki Topi! Define terms! Name limitations of conventional
