Chapter 14. Graphs Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1
|
|
|
- Alisha Long
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1
2 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset of a graph s vertices and a subset of its edges Adjacent vertices Two vertices that are joined by an edge 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-2
3 Terminology Figure 14-2 a) A campus map as a graph; b) a subgraph 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-3
4 Terminology A path between two vertices A sequence of edges that begins at one vertex and ends at another vertex May pass through the same vertex more than once A simple path A path that passes through a vertex only once A cycle A path that begins and ends at the same vertex A simple cycle A cycle that does not pass through a vertex more than once 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-4
5 Terminology A connected graph A graph that has a path between each pair of distinct vertices A disconnected graph A graph that has at least one pair of vertices without a path between them A complete graph A graph that has an edge between each pair of distinct vertices 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-5
6 Terminology Figure 14-3 Graphs that are a) connected; b) disconnected; and c) complete 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-6
7 Terminology Multigraph Not a graph Allows multiple edges between vertices Figure 14-4 a) A multigraph is not a graph; b) a self edge is not allowed in a graph 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-7
8 Terminology Weighted graph A graph whose edges have numeric labels Figure 14-5a a) A weighted graph 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-8
9 Terminology Undirected graph Edges do not indicate a direction Directed graph, or diagraph Each edge is a directed edge Figure 14-5b b) A directed graph 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-9
10 Terminology Directed graph Can have two edges between a pair of vertices, one in each direction Directed path A sequence of directed edges between two vertices Vertex y is adjacent to vertex x if There is a directed edge from x to y 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-10
11 Graphs As ADTs Graphs can be used as abstract data types Two options for defining graphs Vertices contain values Vertices do not contain values Operations of the ADT graph Create an empty graph Determine whether a graph is empty Determine the number of vertices in a graph Determine the number of edges in a graph 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-11
12 Graphs As ADTs Operations of the ADT graph (Continued) Determine whether an edge exists between two given vertices; for weighted graphs, return weight value Insert a vertex in a graph whose vertices have distinct search keys that differ from the new vertex s search key Insert an edge between two given vertices in a graph Delete a particular vertex from a graph and any edges between the vertex and other vertices Delete the edge between two given vertices in a graph Retrieve from a graph the vertex that contains a given search key 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-12
13 Implementing Graphs Most common implementations of a graph Adjacency matrix Adjacency list Adjacency matrix Adjacency matrix for a graph with n vertices numbered 0, 1,, n 1 An n by n array matrix such that matrix[i][j] is 1 (or true) if there is an edge from vertex i to vertex j 0 (or false) if there is no edge from vertex i to vertex j 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-13
14 Implementing Graphs Figure 14-6 a) A directed graph and b) its adjacency matrix 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-14
15 Implementing Graphs Adjacency matrix for a weighted graph with n vertices numbered 0, 1,, n 1 An n by n array matrix such that matrix[i][j] is The weight that labels the edge from vertex i to vertex j if there is an edge from i to j if there is no edge from vertex i to vertex j Figure 14-7 a) A weighted undirected graph and b) its adjacency matrix 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-15
16 Implementing Graphs Adjacency list An adjacency list for a graph with n vertices numbered 0, 1,, n 1 Consists of n linked lists The i th linked list has a node for vertex j if and only if the graph contains an edge from vertex i to vertex j This node can contain either» Vertex j s value, if any» An indication of vertex j s identity 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-16
17 Implementing Graphs Figure 14-8 a) A directed graph and b) its adjacency list 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-17
18 Implementing Graphs Adjacency list for an undirected graph Treats each edge as if it were two directed edges in opposite directions Figure 14-9 a) A weighted undirected graph and b) its adjacency list 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-18
19 Implementing Graphs Adjacency matrix compared with adjacency list Two common operations on graphs Determine whether there is an edge from vertex i to vertex j Find all vertices adjacent to a given vertex i Adjacency matrix Supports operation 1 more efficiently Adjacency list Supports operation 2 more efficiently Often requires less space than an adjacency matrix 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-19
20 Implementing a Graph Class Using the JCF ADT graph not part of JCF Can implement a graph using an adjacency list consisting of a vector of maps Implementation presented uses TreeSet class 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 5 B-20
21 Graph Traversals A graph-traversal algorithm Visits all the vertices that it can reach Visits all vertices of the graph if and only if the graph is connected A connected component The subset of vertices visited during a traversal that begins at a given vertex Can loop indefinitely if a graph contains a loop To prevent this, the algorithm must Mark each vertex during a visit, and Never visit a vertex more than once 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-21
22 Graph Traversals Figure Visitation order for a) a depth-first search; b) a breadth-first search 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-22
23 Depth-First Search Depth-first search (DFS) traversal Proceeds along a path from v as deeply into the graph as possible before backing up Does not completely specify the order in which it should visit the vertices adjacent to v A last visited, first explored strategy 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-23
24 Breadth-First Search Breadth-first search (BFS) traversal Visits every vertex adjacent to a vertex v that it can before visiting any other vertex A first visited, first explored strategy An iterative form uses a queue A recursive form is possible, but not simple 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-24
25 Implementing a BFS Iterator Class Using the JCF BFSIterator class uses the ListIterator class As a queue to keep track of the order the vertices should be processed BFSIterator constructor Initiates methods used to determine BFS order of vertices for the graph Graph is searched by processing vertices from each vertex s adjacency list In the order that they were pushed onto the queue 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-25
26 Applications of Graphs: Topological Sorting Topological order A list of vertices in a directed graph without cycles such that vertex x precedes vertex y if there is a directed edge from x to y in the graph There may be several topological orders in a given graph Topological sorting Arranging the vertices into a topological order 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-26
27 Topological Sorting Figure A directed graph without cycles Figure The graph in Figure arranged according to the topological orders a) a, g, d, b, e, c, f and b) a, b, g, d, e, f, c 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-27
28 Topological Sorting Simple algorithms for finding a topological order topsort1 Find a vertex that has no successor Remove from the graph that vertex and all edges that lead to it, and add the vertex to the beginning of a list of vertices Add each subsequent vertex that has no successor to the beginning of the list When the graph is empty, the list of vertices will be in topological order 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-28
29 Topological Sorting Simple algorithms for finding a topological order (Continued) topsort2 A modification of the iterative DFS algorithm Strategy Push all vertices that have no predecessor onto a stack Each time you pop a vertex from the stack, add it to the beginning of a list of vertices When the traversal ends, the list of vertices will be in topological order 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-29
30 Spanning Trees A tree An undirected connected graph without cycles A spanning tree of a connected undirected graph G A subgraph of G that contains all of G s vertices and enough of its edges to form a tree To obtain a spanning tree from a connected undirected graph with cycles Remove edges until there are no cycles 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-30
31 Spanning Trees You can determine whether a connected graph contains a cycle by counting its vertices and edges A connected undirected graph that has n vertices must have at least n 1 edges A connected undirected graph that has n vertices and exactly n 1 edges cannot contain a cycle A connected undirected graph that has n vertices and more than n 1 edges must contain at least one cycle 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-31
32 Spanning Trees Figure Connected graphs that each have four vertices and three edges 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-32
33 The DFS Spanning Tree To create a depth-first search (DFS) spanning tree Traverse the graph using a depth-first search and mark the edges that you follow After the traversal is complete, the graph s vertices and marked edges form the spanning tree 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-33
34 The BFS Spanning Tree To create a breath-first search (BFS) spanning tree Traverse the graph using a bread-first search and mark the edges that you follow When the traversal is complete, the graph s vertices and marked edges form the spanning tree 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-34
35 Minimum Spanning Trees Minimum spanning tree A spanning tree for which the sum of its edge weights is minimal Prim s algorithm Finds a minimal spanning tree that begins at any vertex Strategy Find the least-cost edge (v, u) from a visited vertex v to some unvisited vertex u Mark u as visited Add the vertex u and the edge (v, u) to the minimum spanning tree Repeat the above steps until there are no more unvisited vertices 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-35
36 Shortest Paths Shortest path between two vertices in a weighted graph The path that has the smallest sum of its edge weights Dijkstra s shortest-path algorithm Determines the shortest paths between a given origin and all other vertices Uses A set vertexset of selected vertices An array weight, where weight[v] is the weight of the shortest (cheapest) path from vertex 0 to vertex v that passes through vertices in vertexset 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-36
37 Circuits A circuit A special cycle that passes through every vertex (or edge) in a graph exactly once Euler circuit A circuit that begins at a vertex v, passes through every edge exactly once, and terminates at v Exists if and only if each vertex touches an even number of edges Figure a) Euler s bridge problem and b) its multigraph representation 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-37
38 Some Difficult Problems Three applications of graphs The traveling salesperson problem The three utilities problem The four-color problem A Hamilton circuit Begins at a vertex v, passes through every vertex exactly once, and terminates at v 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-38
39 Summary The two most common implementations of a graph are the adjacency matrix and the adjacency list Graph searching Depth-first search goes as deep into the graph as it can before backtracking Bread-first search visits all possible adjacent vertices before traversing further into the graph Topological sorting produces a linear order of the vertices in a directed graph without cycles 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-39
40 Summary Trees are connected undirected graphs without cycles A spanning tree of a connected undirected graph is a subgraph that contains all the graph s vertices and enough of its edges to form a tree A minimum spanning tree for a weighted undirected graph is a spanning tree whose edgeweight sum is minimal The shortest path between two vertices in a weighted directed graph is the path that has the smallest sum of its edge weights 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-40
41 Summary An Euler circuit in an undirected graph is a cycle that begins at vertex v, passes through every edge in the graph exactly once, and terminates at v A Hamilton circuit in an undirected graph is a cycle that begins at vertex v, passes through every vertex in the graph exactly once, and terminates at v 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 B-41
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value
 The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
Graphs. Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale Room - Faner 3131
 Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
Graphs Tessema M. Mengistu Department of Computer Science Southern Illinois University Carbondale tessema.mengistu@siu.edu Room - Faner 3131 1 Outline Introduction to Graphs Graph Traversals Finding a
UNIT 5 GRAPH. Application of Graph Structure in real world:- Graph Terminologies:
 UNIT 5 CSE 103 - Unit V- Graph GRAPH Graph is another important non-linear data structure. In tree Structure, there is a hierarchical relationship between, parent and children that is one-to-many relationship.
UNIT 5 CSE 103 - Unit V- Graph GRAPH Graph is another important non-linear data structure. In tree Structure, there is a hierarchical relationship between, parent and children that is one-to-many relationship.
Outline. Graphs. Divide and Conquer.
 GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
Understand graph terminology Implement graphs using
 raphs Understand graph terminology Implement graphs using djacency lists and djacency matrices Perform graph searches Depth first search Breadth first search Perform shortest-path algorithms Disjkstra
raphs Understand graph terminology Implement graphs using djacency lists and djacency matrices Perform graph searches Depth first search Breadth first search Perform shortest-path algorithms Disjkstra
Chapter 5. Decrease-and-Conquer. Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
UNIT Name the different ways of representing a graph? a.adjacencymatrix b. Adjacency list
 UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGIES Traversals of graphs are also called searches We can use either breadth-first
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGIES Traversals of graphs are also called searches We can use either breadth-first
Konigsberg Bridge Problem
 Graphs Konigsberg Bridge Problem c C d g A Kneiphof e D a B b f c A C d e g D a b f B Euler s Graph Degree of a vertex: the number of edges incident to it Euler showed that there is a walk starting at
Graphs Konigsberg Bridge Problem c C d g A Kneiphof e D a B b f c A C d e g D a b f B Euler s Graph Degree of a vertex: the number of edges incident to it Euler showed that there is a walk starting at
Basic Graph Definitions
 CMSC 341 Graphs Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices, V, and a finite set of edges, E. Each edge is a pair (v,w) where v, w V. V and E are sets, so each vertex
CMSC 341 Graphs Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices, V, and a finite set of edges, E. Each edge is a pair (v,w) where v, w V. V and E are sets, so each vertex
Homework Assignment #3 Graph
 CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal
 CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal Your Turn The array of vertices, which include dist, prev, and done fields (initialize dist to INFINITY and done to false ): V0: dist= prev= done= adj:
CSE 100 Minimum Spanning Trees Prim s and Kruskal Your Turn The array of vertices, which include dist, prev, and done fields (initialize dist to INFINITY and done to false ): V0: dist= prev= done= adj:
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms. Brute-Force Approach
 CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CSS 343 Data Structures, Algorithms, and Discrete Math II. Graphs II. Yusuf Pisan
 CSS 343 Data Structures, Algorithms, and Discrete Math II Graphs II Yusuf Pisan 2 3 Shortest Path: Dijkstra's Algorithm Shortest path from given vertex to all other vertices Initial weight is first row
CSS 343 Data Structures, Algorithms, and Discrete Math II Graphs II Yusuf Pisan 2 3 Shortest Path: Dijkstra's Algorithm Shortest path from given vertex to all other vertices Initial weight is first row
Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications
 Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications Topics: Introduction to Graph Theory Representing (undirected) graphs Basic graph algorithms 1 Consider the following: Traveling Salesman Problem
Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications Topics: Introduction to Graph Theory Representing (undirected) graphs Basic graph algorithms 1 Consider the following: Traveling Salesman Problem
Graph. Vertex. edge. Directed Graph. Undirected Graph
 Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Chapter 9. Greedy Technique. Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Greedy Technique Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Greedy Technique Constructs a solution to an optimization problem piece by piece through a sequence of choices that
Chapter 9 Greedy Technique Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Greedy Technique Constructs a solution to an optimization problem piece by piece through a sequence of choices that
CS200: Graphs. Rosen Ch , 9.6, Walls and Mirrors Ch. 14
 CS200: Graphs Rosen Ch. 9.1-9.4, 9.6, 10.4-10.5 Walls and Mirrors Ch. 14 Trees as Graphs Tree: an undirected connected graph that has no cycles. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Rooted Trees A rooted tree
CS200: Graphs Rosen Ch. 9.1-9.4, 9.6, 10.4-10.5 Walls and Mirrors Ch. 14 Trees as Graphs Tree: an undirected connected graph that has no cycles. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Rooted Trees A rooted tree
Graph Traversals. CS200 - Graphs 1
 Graph Traversals CS200 - Graphs 1 Tree traversal reminder A Pre order A B D G H C E F I B C In order G D H B A E C F I D E F Post order G H D B E I F C A G H I Level order A B C D E F G H I Connected Components
Graph Traversals CS200 - Graphs 1 Tree traversal reminder A Pre order A B D G H C E F I B C In order G D H B A E C F I D E F Post order G H D B E I F C A G H I Level order A B C D E F G H I Connected Components
Outline. Introduction. Representations of Graphs Graph Traversals. Applications. Definitions and Basic Terminologies
 Graph Chapter 9 Outline Introduction Definitions and Basic Terminologies Representations of Graphs Graph Traversals Breadth first traversal Depth first traversal Applications Single source shortest path
Graph Chapter 9 Outline Introduction Definitions and Basic Terminologies Representations of Graphs Graph Traversals Breadth first traversal Depth first traversal Applications Single source shortest path
Unweighted Graphs & Algorithms
 Unweighted Graphs & Algorithms Zachary Friggstad Programming Club Meeting References Chapter 4: Graph (Section 4.2) Chapter 22: Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Features: vertices/nodes/dots and edges/links/lines
Unweighted Graphs & Algorithms Zachary Friggstad Programming Club Meeting References Chapter 4: Graph (Section 4.2) Chapter 22: Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Features: vertices/nodes/dots and edges/links/lines
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007
 Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Undirected Graphs. Hwansoo Han
 Undirected Graphs Hwansoo Han Definitions Undirected graph (simply graph) G = (V, E) V : set of vertexes (vertices, nodes, points) E : set of edges (lines) An edge is an unordered pair Edge (v, w) = (w,
Undirected Graphs Hwansoo Han Definitions Undirected graph (simply graph) G = (V, E) V : set of vertexes (vertices, nodes, points) E : set of edges (lines) An edge is an unordered pair Edge (v, w) = (w,
Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs
 Next: Graph Algorithms Graphs Ch 22 Graph representations adjacency list adjacency matrix Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs Breadth-First Search Depth-First Search 11/30/17 CSE 3101 1 Graphs
Next: Graph Algorithms Graphs Ch 22 Graph representations adjacency list adjacency matrix Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs Breadth-First Search Depth-First Search 11/30/17 CSE 3101 1 Graphs
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
Graphs and Algorithms
 Graphs and Algorithms Graphs are a mathematical concept readily adapted into computer programming. Graphs are not just data structures, that is, they are not solutions to simple data storage problems.
Graphs and Algorithms Graphs are a mathematical concept readily adapted into computer programming. Graphs are not just data structures, that is, they are not solutions to simple data storage problems.
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12. Questions? Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first Search. (Introduce permutation and subset generation)
 MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS
 Further Mathematics 2017 Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS Chapter 9 Undirected Graphs and Networks Key knowledge the conventions, terminology, properties and types of graphs; edge, face, loop,
Further Mathematics 2017 Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS Chapter 9 Undirected Graphs and Networks Key knowledge the conventions, terminology, properties and types of graphs; edge, face, loop,
 CS6301 Programming and Data Structures II Unit -5 REPRESENTATION OF GRAPHS Graph and its representations Graph is a data structure that consists of following two components: 1. A finite set of vertices
CS6301 Programming and Data Structures II Unit -5 REPRESENTATION OF GRAPHS Graph and its representations Graph is a data structure that consists of following two components: 1. A finite set of vertices
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Introduction to Graphs. common/notes/ppt/
 Introduction to Graphs http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~pargas/courses/cs212/ common/notes/ppt/ Introduction Graphs are a generalization of trees Nodes or verticies Edges or arcs Two kinds of graphs irected
Introduction to Graphs http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~pargas/courses/cs212/ common/notes/ppt/ Introduction Graphs are a generalization of trees Nodes or verticies Edges or arcs Two kinds of graphs irected
11/22/2016. Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms. Introduction. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions
 Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II Anna University 2 & 16 Mark Questions & Answers Year / Semester: II / III
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II Anna University 2 & 16 Mark Questions & Answers Year / Semester: II / III
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Topics. Trees Vojislav Kecman. Which graphs are trees? Terminology. Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees CMSC 302
 Topics VCU, Department of Computer Science CMSC 302 Trees Vojislav Kecman Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees Binary Search Tree Decision Tree Tree Traversal Spanning Trees
Topics VCU, Department of Computer Science CMSC 302 Trees Vojislav Kecman Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees Binary Search Tree Decision Tree Tree Traversal Spanning Trees
Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs. CMSC 420: Lecture 3
 Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs CMSC 420: Lecture 3 Mini-Review Abstract Data Types: List Stack Queue Deque Dictionary Set Implementations: Linked Lists Circularly linked lists Doubly linked lists XOR
Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs CMSC 420: Lecture 3 Mini-Review Abstract Data Types: List Stack Queue Deque Dictionary Set Implementations: Linked Lists Circularly linked lists Doubly linked lists XOR
Theory of Computing. Lecture 10 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck
 Theory of Computing Lecture 10 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck Seven Bridges of Königsberg Can one take a walk that crosses each bridge exactly once? Seven Bridges of Königsberg Model as a graph Is there a path
Theory of Computing Lecture 10 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck Seven Bridges of Königsberg Can one take a walk that crosses each bridge exactly once? Seven Bridges of Königsberg Model as a graph Is there a path
Further Mathematics 2016 Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS Chapter 9 Undirected Graphs and Networks
 Further Mathematics 2016 Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS Chapter 9 Undirected Graphs and Networks Key knowledge the conventions, terminology, properties and types of graphs; edge, face, loop,
Further Mathematics 2016 Module 2: NETWORKS AND DECISION MATHEMATICS Chapter 9 Undirected Graphs and Networks Key knowledge the conventions, terminology, properties and types of graphs; edge, face, loop,
Trees. Arash Rafiey. 20 October, 2015
 20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
2. True or false: even though BFS and DFS have the same space complexity, they do not always have the same worst case asymptotic time complexity.
 1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
Week 9. CS 400 Programming III
 Week 9 p3b: final submission due before 10pm on Thursday, 3/28 p4: available soon x4: due before 10pm on Monday 4/1 x5: meet with x-team coach for design review 4/1-4/8 Module: Week 9 (and start on week
Week 9 p3b: final submission due before 10pm on Thursday, 3/28 p4: available soon x4: due before 10pm on Monday 4/1 x5: meet with x-team coach for design review 4/1-4/8 Module: Week 9 (and start on week
Part VI Graph algorithms. Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms Chapter 23 Minimum Spanning Trees Chapter 24 Single-source Shortest Paths
 Part VI Graph algorithms Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms Chapter 23 Minimum Spanning Trees Chapter 24 Single-source Shortest Paths 1 Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms Representations of graphs
Part VI Graph algorithms Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms Chapter 23 Minimum Spanning Trees Chapter 24 Single-source Shortest Paths 1 Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms Representations of graphs
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES. Chapter 11
 SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
SELF-BALANCING SEARCH TREES Chapter 11 Tree Balance and Rotation Section 11.1 Algorithm for Rotation BTNode root = left right = data = 10 BTNode = left right = data = 20 BTNode NULL = left right = NULL
Graph Theory. Many problems are mapped to graphs. Problems. traffic VLSI circuits social network communication networks web pages relationship
 Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
ECE4050 Data Structures and Algorithms. Lecture 8: Graphs
 ECE4050 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 8: Graphs 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) consists of a set of vertices V, and a set of edges E, such that each edge in E is a connection between a pair of vertices
ECE4050 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 8: Graphs 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) consists of a set of vertices V, and a set of edges E, such that each edge in E is a connection between a pair of vertices
Introduction to Computer Science and Programming for Astronomers
 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming for Astronomers Lecture 7. István Szapudi Institute for Astronomy University of Hawaii February 21, 2018 Outline 1 Reminder 2 Reminder We have seen that
Introduction to Computer Science and Programming for Astronomers Lecture 7. István Szapudi Institute for Astronomy University of Hawaii February 21, 2018 Outline 1 Reminder 2 Reminder We have seen that
Graphs. The ultimate data structure. graphs 1
 Graphs The ultimate data structure graphs 1 Definition of graph Non-linear data structure consisting of nodes & links between them (like trees in this sense) Unlike trees, graph nodes may be completely
Graphs The ultimate data structure graphs 1 Definition of graph Non-linear data structure consisting of nodes & links between them (like trees in this sense) Unlike trees, graph nodes may be completely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal
 Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Graph Algorithms. Chapter 22. CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms 1
 Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
CS/COE
 CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 dvanced ata Structures and lgorithms ssociate Professor r. Raed Ibraheem amed University of uman evelopment, College of Science and Technology Computer Science epartment 2015 2016 epartment of Computer
dvanced ata Structures and lgorithms ssociate Professor r. Raed Ibraheem amed University of uman evelopment, College of Science and Technology Computer Science epartment 2015 2016 epartment of Computer
Graph definitions. There are two kinds of graphs: directed graphs (sometimes called digraphs) and undirected graphs. An undirected graph
 Graphs Graph definitions There are two kinds of graphs: directed graphs (sometimes called digraphs) and undirected graphs start Birmingham 60 Rugby fill pan with water add salt to water take egg from fridge
Graphs Graph definitions There are two kinds of graphs: directed graphs (sometimes called digraphs) and undirected graphs start Birmingham 60 Rugby fill pan with water add salt to water take egg from fridge
CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman
 CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman Lecture 11: Graphs Graph Traversals: BFS Feb 16, 2018 What s Next What s Next Graph Algorithms: Graphs: Key Definitions, Properties, Representations Exploring
CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman Lecture 11: Graphs Graph Traversals: BFS Feb 16, 2018 What s Next What s Next Graph Algorithms: Graphs: Key Definitions, Properties, Representations Exploring
R10 SET - 1. Code No: R II B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May
 www.jwjobs.net R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May - 2012 (Com. to CSE, IT, ECC ) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 *******-****** 1. a) Which of the given options provides the
www.jwjobs.net R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May - 2012 (Com. to CSE, IT, ECC ) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 *******-****** 1. a) Which of the given options provides the
L10 Graphs. Alice E. Fischer. April Alice E. Fischer L10 Graphs... 1/37 April / 37
 L10 Graphs lice. Fischer pril 2016 lice. Fischer L10 Graphs... 1/37 pril 2016 1 / 37 Outline 1 Graphs efinition Graph pplications Graph Representations 2 Graph Implementation 3 Graph lgorithms Sorting
L10 Graphs lice. Fischer pril 2016 lice. Fischer L10 Graphs... 1/37 pril 2016 1 / 37 Outline 1 Graphs efinition Graph pplications Graph Representations 2 Graph Implementation 3 Graph lgorithms Sorting
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
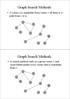 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 s of s s are abstract data types that are applicable
s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 s of s s are abstract data types that are applicable
Graphs. Data Structures 1 Graphs
 Graphs Graph Applications Definitions Graph Representations(adjacency matrix/list) Graph ADT Graph Traversals: BFS, DFS Shortest Path Algorithms Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms Data Structures Graphs
Graphs Graph Applications Definitions Graph Representations(adjacency matrix/list) Graph ADT Graph Traversals: BFS, DFS Shortest Path Algorithms Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms Data Structures Graphs
CS61BL. Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting
 CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms
 CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms
 W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
( ) ( ) C. " 1 n. ( ) $ f n. ( ) B. " log( n! ) ( ) and that you already know ( ) ( ) " % g( n) ( ) " #&
 CSE 0 Name Test Summer 008 Last 4 Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time for the following code is in which set? for (i=0; i
CSE 0 Name Test Summer 008 Last 4 Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time for the following code is in which set? for (i=0; i
// Source code example for "A Practical Introduction to Data Structures and // Algorithm Analysis" by Clifford A. Shaffer, Prentice Hall, 1998.
 // Source code example for "A Practical Introduction to Data Structures and // Algorithm Analysis" by Clifford A. Shaffer, Prentice Hall, 1998. // Copyright 1998 by Clifford A. Shaffer // graph.java interface
// Source code example for "A Practical Introduction to Data Structures and // Algorithm Analysis" by Clifford A. Shaffer, Prentice Hall, 1998. // Copyright 1998 by Clifford A. Shaffer // graph.java interface
Lecture 3: Graphs and flows
 Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms
 (Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs
 Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs Date and Time: May 10 2012 Thursday 11:50AM~1:50PM Location: Eng 120 Start with the Self-Test Exercises (pp.816) in Prichard. 1. Give the adjacency matrix
Worksheet for the Final Exam - Part I. Graphs Date and Time: May 10 2012 Thursday 11:50AM~1:50PM Location: Eng 120 Start with the Self-Test Exercises (pp.816) in Prichard. 1. Give the adjacency matrix
- Logic and Algorithms - Graph Algorithms
 Fundamentals of Computer Sience and Digital Communications - Logic and Algorithms - Graph Algorithms Johan Larsson Marco Loh 22..24 Overview What is a Graph? Representations of Graphs Breadth-first Search
Fundamentals of Computer Sience and Digital Communications - Logic and Algorithms - Graph Algorithms Johan Larsson Marco Loh 22..24 Overview What is a Graph? Representations of Graphs Breadth-first Search
GRAPHICAL ALGORITHMS. UNIT _II Lecture-12 Slides No. 3-7 Lecture Slides No Lecture Slides No
 GRAPHICAL ALGORITHMS UNIT _II Lecture-12 Slides No. 3-7 Lecture-13-16 Slides No. 8-26 Lecture-17-19 Slides No. 27-42 Topics Covered Graphs & Trees ( Some Basic Terminologies) Spanning Trees (BFS & DFS)
GRAPHICAL ALGORITHMS UNIT _II Lecture-12 Slides No. 3-7 Lecture-13-16 Slides No. 8-26 Lecture-17-19 Slides No. 27-42 Topics Covered Graphs & Trees ( Some Basic Terminologies) Spanning Trees (BFS & DFS)
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May/June DATA STRUCTURES (Com. to ECE, CSE, EIE, IT, ECC)
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May/June - 2016 PART A 1. a) Write a procedure for the Tower of Hanoi problem? b) What you mean by enqueue and dequeue operations in a queue? c)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May/June - 2016 PART A 1. a) Write a procedure for the Tower of Hanoi problem? b) What you mean by enqueue and dequeue operations in a queue? c)
LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD BACKGROUND All the objects stored in an array or linked list can be accessed sequentially
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD BACKGROUND All the objects stored in an array or linked list can be accessed sequentially
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 15/15 Hua Lu
 Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 15/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Minimum spanning trees Definitions Kruskal s algorithm Prim s algorithm
Algorithms and Data Structures (INF1) Lecture 15/15 Hua Lu Department of Computer Science Aalborg University Fall 2007 This Lecture Minimum spanning trees Definitions Kruskal s algorithm Prim s algorithm
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013
 GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
CSC Intro to Intelligent Robotics, Spring Graphs
 CSC 445 - Intro to Intelligent Robotics, Spring 2018 Graphs Graphs Definition: A graph G = (V, E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge has either one or two
CSC 445 - Intro to Intelligent Robotics, Spring 2018 Graphs Graphs Definition: A graph G = (V, E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge has either one or two
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014
 GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
10/31/18. About A6, Prelim 2. Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms. Facts about trees. Undirected trees
 //8 About A, Prelim Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture CS Fall 8 Prelim : Thursday, November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it (: or 7:) and what
//8 About A, Prelim Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture CS Fall 8 Prelim : Thursday, November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it (: or 7:) and what
Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms. Lecture 20 CS2110 Fall 2018
 1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 20 CS2110 Fall 2018 1 About A6, Prelim 2 Prelim 2: Thursday, 15 November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it
1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 20 CS2110 Fall 2018 1 About A6, Prelim 2 Prelim 2: Thursday, 15 November. Visit exams page of course website and read carefully to find out when you take it
Index. stack-based, 400 A* algorithm, 325
 Index Abstract transitive closure, 174-175, 217-221 Active vertex, 411 Acyclic graph. See Digraph; Directed acyclic graph (DAG) Acyclic network, 313-321, 334-335 maxflow, 427-429 Adjacency-lists representation,
Index Abstract transitive closure, 174-175, 217-221 Active vertex, 411 Acyclic graph. See Digraph; Directed acyclic graph (DAG) Acyclic network, 313-321, 334-335 maxflow, 427-429 Adjacency-lists representation,
DS UNIT 4. Matoshri College of Engineering and Research Center Nasik Department of Computer Engineering Discrete Structutre UNIT - IV
 Sr.No. Question Option A Option B Option C Option D 1 2 3 4 5 6 Class : S.E.Comp Which one of the following is the example of non linear data structure Let A be an adjacency matrix of a graph G. The ij
Sr.No. Question Option A Option B Option C Option D 1 2 3 4 5 6 Class : S.E.Comp Which one of the following is the example of non linear data structure Let A be an adjacency matrix of a graph G. The ij
CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms. Lecture 24 Fall 2017
 CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 24 Fall 2017 ANALYSIS OF DIJKSTRA S ALGORITHM CSC 172, Fall 2017 Implementation and analysis The initialization requires Q( V ) memory and run time We iterate
CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 24 Fall 2017 ANALYSIS OF DIJKSTRA S ALGORITHM CSC 172, Fall 2017 Implementation and analysis The initialization requires Q( V ) memory and run time We iterate
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT
 CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 20 TH TOPOLOGICAL SORT PROJECT 3 500 Internal Error problems Hopefully all resolved (or close to) P3P1 grades are up (but muted) Leave canvas comment Emails tomorrow End of quarter GRAPHS
Elementary Graph Algorithms. Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph:
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville. 3. Search (Part 1) CS 3030 Lecture Notes Yan Shi UW-Platteville
 Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville 3. Search (Part 1) CS 3030 Lecture Notes Yan Shi UW-Platteville Read: Textbook Chapter 3.7-3.9,3.12, 4. Problem Solving as
Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin - Platteville 3. Search (Part 1) CS 3030 Lecture Notes Yan Shi UW-Platteville Read: Textbook Chapter 3.7-3.9,3.12, 4. Problem Solving as
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1
 CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CSCE 350: Chin-Tser Huang. University of South Carolina
 CSCE 350: Data Structures and Algorithms Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Announcement Homework 2 will be returned on Thursday; solution will be available on class website
CSCE 350: Data Structures and Algorithms Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Announcement Homework 2 will be returned on Thursday; solution will be available on class website
Representations of Graphs
 ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
Graphs II: Trailblazing
 Graphs II: Trailblazing Paths In an undirected graph, a path of length n from u to v, where n is a positive integer, is a sequence of edges e 1,, e n of the graph such that f(e 1 )={x 0,x 1 }, f(e 2 )={x
Graphs II: Trailblazing Paths In an undirected graph, a path of length n from u to v, where n is a positive integer, is a sequence of edges e 1,, e n of the graph such that f(e 1 )={x 0,x 1 }, f(e 2 )={x
The Konigsberg Bridge Problem
 The Konigsberg Bridge Problem This is a classic mathematical problem. There were seven bridges across the river Pregel at Königsberg. Is it possible to take a walk in which each bridge is crossed exactly
The Konigsberg Bridge Problem This is a classic mathematical problem. There were seven bridges across the river Pregel at Königsberg. Is it possible to take a walk in which each bridge is crossed exactly
Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms. Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017
 1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017 1 We demo A8 Your space ship is on earth, and you hear a distress signal from a distance Planet X. Your job: 1. Rescue stage: Fly your ship
1 Spanning Trees, greedy algorithms Lecture 22 CS2110 Fall 2017 1 We demo A8 Your space ship is on earth, and you hear a distress signal from a distance Planet X. Your job: 1. Rescue stage: Fly your ship
Today s Outline. CSE 326: Data Structures. Topic #15: Cool Graphs n Pretty Pictures. A Great Mathematician. The Bridges of Königsberg
 CSE 326: Data Structures Topic #15: Cool Graphs n Pretty Pictures Ashish Sabharwal Autumn, 2003 Today s Outline Admin Project 3 in-progress checkin due tonight! Graph Algorithms Representation Applications
CSE 326: Data Structures Topic #15: Cool Graphs n Pretty Pictures Ashish Sabharwal Autumn, 2003 Today s Outline Admin Project 3 in-progress checkin due tonight! Graph Algorithms Representation Applications
Trees Algorhyme by Radia Perlman
 Algorhyme by Radia Perlman I think that I shall never see A graph more lovely than a tree. A tree whose crucial property Is loop-free connectivity. A tree which must be sure to span. So packets can reach
Algorhyme by Radia Perlman I think that I shall never see A graph more lovely than a tree. A tree whose crucial property Is loop-free connectivity. A tree which must be sure to span. So packets can reach
1. Graph and Representation
 Chapter Graphs Tree Root Direction: parent-child relationships No cycles Graph Vertices + Edges No tree restrictions Examples World Wide Web Maps. Graph and Representation A graph G: a pair (V, E) vertices
Chapter Graphs Tree Root Direction: parent-child relationships No cycles Graph Vertices + Edges No tree restrictions Examples World Wide Web Maps. Graph and Representation A graph G: a pair (V, E) vertices
Breadth First Search. Graph Traversal. CSE 2011 Winter Application examples. Two common graph traversal algorithms
 Breadth irst Search CSE Winter Graph raversal Application examples Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph ind all paths from s to the other vertices wo common graph traversal algorithms
Breadth irst Search CSE Winter Graph raversal Application examples Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph ind all paths from s to the other vertices wo common graph traversal algorithms
Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1
 AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
AND Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide 1 Chapter 14 Graph Theory Chapter 14 Section 3 - Slide WHAT YOU WILL LEARN Graphs, paths and circuits The Königsberg bridge problem Euler paths and Euler circuits Hamilton
Graphs. Pseudograph: multiple edges and loops allowed
 Graphs G = (V, E) V - set of vertices, E - set of edges Undirected graphs Simple graph: V - nonempty set of vertices, E - set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices (no multiple edges or loops) Multigraph:
Graphs G = (V, E) V - set of vertices, E - set of edges Undirected graphs Simple graph: V - nonempty set of vertices, E - set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices (no multiple edges or loops) Multigraph:
L22-23: Graph Algorithms
 Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India भ रत य व ज ञ न स स थ न ब गल र, भ रत Department of Computational and Data Sciences DS 0--0,0 L-: Graph Algorithms Yogesh Simmhan simmhan@cds.iisc.ac.in Slides
Indian Institute of Science Bangalore, India भ रत य व ज ञ न स स थ न ब गल र, भ रत Department of Computational and Data Sciences DS 0--0,0 L-: Graph Algorithms Yogesh Simmhan simmhan@cds.iisc.ac.in Slides
