DFS Search on Undirected Graphs. Algorithm : Design & Analysis [13]
|
|
|
- Valentine Marsh
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DFS Search on Undirected Graphs Algorithm : Design & Analysis [13]
2 In the last class Directed Acyclic Graph Topological Order Critical Path Analysis Strongly Connected Component Strong Component and Condensation Leader of Strong Component The Algorihtm
3 DFS Search on Undirected Graph Undirected and Symmetric Digraph UDF Search Skeleton Biconnected Components Articulation Points and Biconnectedness Biconnected Component Algorithm Analysis of the Algorithm
4 What s the Different for Undirected The issue related to traversals for undirected graph is that one edge may be traversed for two times in opposite directions. For an undirected graph, the depth-first search provides an orientation for each of its edges; they are oriented in the direction in which they are first encountered.
5 Nontree edges in symmetric digraph Cross edge: not existing. Back edge: Back to the direct parent: second encounter Otherwise: first encounter Forward edge: always second encounter, and first time as back edge
6 Modifications to the DFS Skeleton All the second encounter are bypassed. So, the only substantial modification is for the possible back edges leading to an ancestor, but not direct parent. We need know the parent, that is, the direct ancestor, for the vertex to be processed.
7 DFS Skeleton for Undirected Graph int dfssweep(intlist[] adjvertices,int n, ) int ans; <Allocate color array and initialize to white> For each vertex v of G, in some order if (color[v]==white) int vans=dfs(adjvertices, color, v, -1, ); <Process vans> // Continue loop Recording the parent return ans;
8 DFS Skeleton for Undirected Graph int dfs(intlist[] adjvertices, int[] color, int v, int p, ) int w; IntList remadj; int ans; color[v]=gray; In In all all other cases, the the <Preorder processing of vertex v> edges are are the the second remadj=adjvertices[v]; encounter, so, ignored. while (remadj nil) w=first(remadj); if (color[w]==white) <Exploratory processing for tree edge vw> int wans=dfs(adjvertices, color, w, v ); < Backtrack processing for tree edge vw, using wans> else if (color[w]==gray && w p) <Checking for nontree edge vw> remadj=rest(remadj); <Postorder processing of vertex v, including final computation of ans> color[v]=black; return ans; encounter, so, ignored.
9 Complexity of Undirected DFS If each inserted statement for specialized application runs in constant time, the time cost is the same as for directed DFS, that is Θ(m+n). Extra space is in Θ(n) for array color, or activation frames of recursion.
10 Definition of Biconnected Components Biconnected component Biconnected graph Bicomponent: a maximal biconnected subgraph Articulation point v is an articulation point if it is in every path from w to x (w,x are vertices different from v) A connected graph is biconnected if and only if it has no articulation points.
11 Bicomponents G B I G B E I C Partitioning the set of edges, not of the vertices B E E C H F J H F F J A D A D
12 Bicomponent Algorithm: the Idea Ancestors of v w v v is is an an articulation point if if if no If and If v is only is the the if articulation no back edges linking any vertex point farthest away from in in the the w-rooted on on subtree the thebranch, and any then ancestor one bicomponent of of v. v. is is detected. Subtree rooted at w Back edge
13 Keeping the Track of Backing Tracking data For each vertex v, a local variable back is used to store the required information, as the value of discovertime of some vertex. Testing for bicomponent At backtracking from w to v, the condition implying a bicomponent is: wback discovertime(v) (where wback is the returned back value for w)
14 Updating the value of back v first discovered back=discovertime(v) Trying to explore, but only a by back v. edge vw from v encountered back=min(back, discovertime(w)) Backtracking from w to v Which means: the back value of v is the smallest discover time a back edge sees from any subtree of v. And, when this value is not larger than the discover time of v, we know that there is at least one subtree of v connected to other part of the graph back=min(back, wback)
15 Bicomponent: an Example second back edge encountered G B E I C 5/5 4/4 G B E I C 6/6 H 3/3 F J H 3/1 F J A D 1/1 2/2 first back edge encountered A 1/1 D 2/2
16 Bicomponent: an Example backtracking 5/4 4/4 G B E I C 6/4 third back edge encountered 8/8 5/4 G B 9/9 I C 4/4 E 6/4 H 3/1 F J H 3/1 F J A 1/1 2/2 D A 1/1 2/2 D
17 Bicomponent: an Example 8/5 backtracking 5/4 4/4 3/1 H G B E F 9/5 I C 6/4 J H 8/5 backtracking: gback=discovertime(b), so, first bicomponent 5/4 detected. 4/4 3/1 G B E F 9/5 I C 6/4 J A 1/1 2/2 D A 1/1 2/2 D
18 Bicomponent: an Example Backtracking from B to E: bback=discovertime(e), so, the second bicomponent is detect 8/5 5/4 4/4 G B E 9/5 I C 6/4 14/1 H 3/1 F J 16/2 Backtracking from E to F: eback>discovertime(f), so, the third bicomponent is detect A 1/1 D 2/2
19 Bicomponent Algorithm: Core int bicompdfs(v) color[v]=gray; time++; discovertime[v]=time; back=discovertime[v]; while (there is an untraversed edge vw) <push vw into edgestack> if (vw is a tree edge) wback=bicompdfs(w); if (wback discovertime[v]) Output a new bicomponent by popping edgestack down through vw ; back=min(back, wback); else if (vw is a back edge) back=min(discovertime[v], back); time++; finishtime[v]=time; color[v]=black; return back; Outline of core procedure
20 Correctness of Bicomponent Algorithm We have seen that: If v is the articulation point farthest away from the root on the branch, then one bicomponent is detected. So, we need only prove that: In a DFS tree, a vertex(not root) v is an articulation point if and only if (1)v is not a leaf; (2) some subtree of v has no back edge incident with a proper ancestor of v.
21 Characteristics of Articulation Point In a DFS tree, a vertex(not root) v is an articulation point if and only if (1)v is not a leaf; (2) some subtree of v has no back edge incident with a proper ancestor of v. Trivial By definition, v is on every path between some x,y(different from v). At least one of x,y is a proper descendent of v(otherwise, x root y not containing v). By contradiction, suppose that every subtree of v has a back edge to a proper ancestor of v, we can find a xy-path not containing v for all possible cases(only 2 cases)
22 Case 1 Case 1.2: another is an ancestor of v y v x Case 1.1: another is not an ancestor of v suppose that every subtree of v has a back edge to a proper ancestor of v, and, exactly one of x, y is a descendant of v. x y v
23 Case 2 suppose that every subtree of v has a back edge to a proper ancestor of v, and, both x, y are descendants of v. v y x
24 Home Assignments pp
Graph Traversals. Algorithm : Design & Analysis [11]
![Graph Traversals. Algorithm : Design & Analysis [11] Graph Traversals. Algorithm : Design & Analysis [11]](/thumbs/79/79366949.jpg) Graph Traversals Algorithm : Design & Analysis [11] In the last class Dynamic Equivalence Relation Implementing Dynamic Set by Union-Find Straight Union-Find Making Shorter Tree by Weighted Union Compressing
Graph Traversals Algorithm : Design & Analysis [11] In the last class Dynamic Equivalence Relation Implementing Dynamic Set by Union-Find Straight Union-Find Making Shorter Tree by Weighted Union Compressing
Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search
 Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search Analysis of Algorithms Week 8, Lecture 1 Prepared by John Reif, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor of Computer Science Duke University Graph Algorithms Using Depth
Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search Analysis of Algorithms Week 8, Lecture 1 Prepared by John Reif, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor of Computer Science Duke University Graph Algorithms Using Depth
Cut vertices, Cut Edges and Biconnected components. MTL776 Graph algorithms
 Cut vertices, Cut Edges and Biconnected components MTL776 Graph algorithms Articulation points, Bridges, Biconnected Components Let G = (V;E) be a connected, undirected graph. An articulation point of
Cut vertices, Cut Edges and Biconnected components MTL776 Graph algorithms Articulation points, Bridges, Biconnected Components Let G = (V;E) be a connected, undirected graph. An articulation point of
March 20/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Applications of BDF and DFS
 January 14, 2016 1 Deciding whether a graph is bipartite using BFS. 2 Finding connected components of a graph (both BFS and DFS) works. 3 Deciding whether a digraph is strongly connected. 4 Finding cut
January 14, 2016 1 Deciding whether a graph is bipartite using BFS. 2 Finding connected components of a graph (both BFS and DFS) works. 3 Deciding whether a digraph is strongly connected. 4 Finding cut
Lecture 3: Graphs and flows
 Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Graph Algorithms. Definition
 Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
Searching in Graphs (cut points)
 0 November, 0 Breath First Search (BFS) in Graphs In BFS algorithm we visit the verices level by level. The BFS algorithm creates a tree with root s. Once a node v is discovered by BFS algorithm we put
0 November, 0 Breath First Search (BFS) in Graphs In BFS algorithm we visit the verices level by level. The BFS algorithm creates a tree with root s. Once a node v is discovered by BFS algorithm we put
Graph. Vertex. edge. Directed Graph. Undirected Graph
 Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS
 Department of Computer Science University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS By Faculty of Science for Women( SCIW), University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@uobabylon.edu.iq
Department of Computer Science University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS By Faculty of Science for Women( SCIW), University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@uobabylon.edu.iq
Trees. Arash Rafiey. 20 October, 2015
 20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
MAL 376: Graph Algorithms I Semester Lecture 1: July 24
 MAL 376: Graph Algorithms I Semester 2014-2015 Lecture 1: July 24 Course Coordinator: Prof. B. S. Panda Scribes: Raghuvansh, Himanshu, Mohit, Abhishek Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to
MAL 376: Graph Algorithms I Semester 2014-2015 Lecture 1: July 24 Course Coordinator: Prof. B. S. Panda Scribes: Raghuvansh, Himanshu, Mohit, Abhishek Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to
Undirected Graphs. Hwansoo Han
 Undirected Graphs Hwansoo Han Definitions Undirected graph (simply graph) G = (V, E) V : set of vertexes (vertices, nodes, points) E : set of edges (lines) An edge is an unordered pair Edge (v, w) = (w,
Undirected Graphs Hwansoo Han Definitions Undirected graph (simply graph) G = (V, E) V : set of vertexes (vertices, nodes, points) E : set of edges (lines) An edge is an unordered pair Edge (v, w) = (w,
Trees : Part 1. Section 4.1. Theory and Terminology. A Tree? A Tree? Theory and Terminology. Theory and Terminology
 Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Lecture 2 - Graph Theory Fundamentals - Reachability and Exploration 1
 CME 305: Discrete Mathematics and Algorithms Instructor: Professor Aaron Sidford (sidford@stanford.edu) January 11, 2018 Lecture 2 - Graph Theory Fundamentals - Reachability and Exploration 1 In this lecture
CME 305: Discrete Mathematics and Algorithms Instructor: Professor Aaron Sidford (sidford@stanford.edu) January 11, 2018 Lecture 2 - Graph Theory Fundamentals - Reachability and Exploration 1 In this lecture
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12. Questions? Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first Search. (Introduce permutation and subset generation)
 MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
7.1 Introduction. A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w
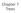 Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
Chapter 7 Trees 7.1 Introduction A (free) tree T is A simple graph such that for every pair of vertices v and w there is a unique path from v to w Tree Terminology Parent Ancestor Child Descendant Siblings
Brute Force: Selection Sort
 Brute Force: Intro Brute force means straightforward approach Usually based directly on problem s specs Force refers to computational power Usually not as efficient as elegant solutions Advantages: Applicable
Brute Force: Intro Brute force means straightforward approach Usually based directly on problem s specs Force refers to computational power Usually not as efficient as elegant solutions Advantages: Applicable
Section Summary. Introduction to Trees Rooted Trees Trees as Models Properties of Trees
 Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
Chapter 11 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications
( ) D. Θ ( ) ( ) Ο f ( n) ( ) Ω. C. T n C. Θ. B. n logn Ο
 CSE 0 Name Test Fall 0 Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The expected time for insertion sort for n keys is in which set? (All n! input permutations are equally
CSE 0 Name Test Fall 0 Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The expected time for insertion sort for n keys is in which set? (All n! input permutations are equally
Inf 2B: Graphs II - Applications of DFS
 Inf 2B: Graphs II - Applications of DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Reminder: Recursive DFS Algorithm dfs(g) 1. Initialise Boolean array visited by setting all entries
Inf 2B: Graphs II - Applications of DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Reminder: Recursive DFS Algorithm dfs(g) 1. Initialise Boolean array visited by setting all entries
Lecture 10: Strongly Connected Components, Biconnected Graphs
 15-750: Graduate Algorithms February 8, 2016 Lecture 10: Strongly Connected Components, Biconnected Graphs Lecturer: David Witmer Scribe: Zhong Zhou 1 DFS Continued We have introduced Depth-First Search
15-750: Graduate Algorithms February 8, 2016 Lecture 10: Strongly Connected Components, Biconnected Graphs Lecturer: David Witmer Scribe: Zhong Zhou 1 DFS Continued We have introduced Depth-First Search
Graph Algorithms. Textbook reading. Chapter 3 Chapter 4. CSci 3110 Graph Algorithms 1/41
 CSci 3110 Graph Algorithms 1/41 Graph Algorithms Textbook reading Chapter 3 Chapter 4 CSci 3110 Graph Algorithms 2/41 Overview Design principle: Learn the structure of a graph by systematic exploration
CSci 3110 Graph Algorithms 1/41 Graph Algorithms Textbook reading Chapter 3 Chapter 4 CSci 3110 Graph Algorithms 2/41 Overview Design principle: Learn the structure of a graph by systematic exploration
Trees Algorhyme by Radia Perlman
 Algorhyme by Radia Perlman I think that I shall never see A graph more lovely than a tree. A tree whose crucial property Is loop-free connectivity. A tree which must be sure to span. So packets can reach
Algorhyme by Radia Perlman I think that I shall never see A graph more lovely than a tree. A tree whose crucial property Is loop-free connectivity. A tree which must be sure to span. So packets can reach
Introduction to Computers and Programming. Concept Question
 Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Introduction to Computers and Programming Prof. I. K. Lundqvist Lecture 7 April 2 2004 Concept Question G1(V1,E1) A graph G(V, where E) is V1 a finite = {}, nonempty E1 = {} set of G2(V2,E2) vertices and
Undirected Graphs. DSA - lecture 6 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1
 Undirected Graphs Terminology. Free Trees. Representations. Minimum Spanning Trees (algorithms: Prim, Kruskal). Graph Traversals (dfs, bfs). Articulation points & Biconnected Components. Graph Matching
Undirected Graphs Terminology. Free Trees. Representations. Minimum Spanning Trees (algorithms: Prim, Kruskal). Graph Traversals (dfs, bfs). Articulation points & Biconnected Components. Graph Matching
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Algorithmic Aspects of Communication Networks
 Algorithmic Aspects of Communication Networks Chapter 5 Network Resilience Algorithmic Aspects of ComNets (WS 16/17): 05 Network Resilience 1 Introduction and Motivation Network resilience denotes the
Algorithmic Aspects of Communication Networks Chapter 5 Network Resilience Algorithmic Aspects of ComNets (WS 16/17): 05 Network Resilience 1 Introduction and Motivation Network resilience denotes the
12/5/17. trees. CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks. rooted trees. rooted trees
 trees CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications A tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks rooted trees Rooted trees. Given a tree T, choose
trees CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications A tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks rooted trees Rooted trees. Given a tree T, choose
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSE, Winter 8 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture : Graphs, DFS (Undirected, Directed), DAGs Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse-w8/ Graphs Internet topology Graphs Gene-gene interactions
CSE, Winter 8 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture : Graphs, DFS (Undirected, Directed), DAGs Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse-w8/ Graphs Internet topology Graphs Gene-gene interactions
Foundations of Discrete Mathematics
 Foundations of Discrete Mathematics Chapter 12 By Dr. Dalia M. Gil, Ph.D. Trees Tree are useful in computer science, where they are employed in a wide range of algorithms. They are used to construct efficient
Foundations of Discrete Mathematics Chapter 12 By Dr. Dalia M. Gil, Ph.D. Trees Tree are useful in computer science, where they are employed in a wide range of algorithms. They are used to construct efficient
Tree. A path is a connected sequence of edges. A tree topology is acyclic there is no loop.
 Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
Tree A tree consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges connecting pairs of nodes. A tree has the property that there is exactly one path (no more, no less) between any pair of nodes. A path is a connected
Graph Representations and Traversal
 COMPSCI 330: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 02/08/2017-02/20/2017 Graph Representations and Traversal Lecturer: Debmalya Panigrahi Scribe: Tianqi Song, Fred Zhang, Tianyu Wang 1 Overview This lecture
COMPSCI 330: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 02/08/2017-02/20/2017 Graph Representations and Traversal Lecturer: Debmalya Panigrahi Scribe: Tianqi Song, Fred Zhang, Tianyu Wang 1 Overview This lecture
CS/COE
 CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
Elementary Graph Algorithms CSE 6331
 Elementary Graph Algorithms CSE 6331 Reading Assignment: Chapter 22 1 Basic Depth-First Search Algorithm procedure Search(G = (V, E)) // Assume V = {1, 2,..., n} // // global array visited[1..n] // visited[1..n]
Elementary Graph Algorithms CSE 6331 Reading Assignment: Chapter 22 1 Basic Depth-First Search Algorithm procedure Search(G = (V, E)) // Assume V = {1, 2,..., n} // // global array visited[1..n] // visited[1..n]
Info 2950, Lecture 16
 Info 2950, Lecture 16 28 Mar 2017 Prob Set 5: due Fri night 31 Mar Breadth first search (BFS) and Depth First Search (DFS) Must have an ordering on the vertices of the graph. In most examples here, the
Info 2950, Lecture 16 28 Mar 2017 Prob Set 5: due Fri night 31 Mar Breadth first search (BFS) and Depth First Search (DFS) Must have an ordering on the vertices of the graph. In most examples here, the
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
BACKGROUND: A BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY
 BACKGROUND: A BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY General definitions; Representations; Graph Traversals; Topological sort; Graphs definitions & representations Graph theory is a fundamental tool in sparse
BACKGROUND: A BRIEF INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY General definitions; Representations; Graph Traversals; Topological sort; Graphs definitions & representations Graph theory is a fundamental tool in sparse
Chapter 3 Trees. Theorem A graph T is a tree if, and only if, every two distinct vertices of T are joined by a unique path.
 Chapter 3 Trees Section 3. Fundamental Properties of Trees Suppose your city is planning to construct a rapid rail system. They want to construct the most economical system possible that will meet the
Chapter 3 Trees Section 3. Fundamental Properties of Trees Suppose your city is planning to construct a rapid rail system. They want to construct the most economical system possible that will meet the
Trees and Graphs Shabsi Walfish NYU - Fundamental Algorithms Summer 2006
 Trees and Graphs Basic Definitions Tree: Any connected, acyclic graph G = (V,E) E = V -1 n-ary Tree: Tree s/t all vertices of degree n+1 A root has degree n Binary Search Tree: A binary tree such that
Trees and Graphs Basic Definitions Tree: Any connected, acyclic graph G = (V,E) E = V -1 n-ary Tree: Tree s/t all vertices of degree n+1 A root has degree n Binary Search Tree: A binary tree such that
Directed Graphs (II) Hwansoo Han
 Directed Graphs (II) Hwansoo Han Traversals of Directed Graphs To solve many problems dealing with digraphs, we need to visit vertexes and arcs in a systematic way Depth-first search (DFS) A generalization
Directed Graphs (II) Hwansoo Han Traversals of Directed Graphs To solve many problems dealing with digraphs, we need to visit vertexes and arcs in a systematic way Depth-first search (DFS) A generalization
Chapter Summary. Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees
 Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Introduction to Trees Section 11.1 Section Summary Introduction to Trees
Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Summary Introduction to Trees Applications of Trees Tree Traversal Spanning Trees Minimum Spanning Trees Introduction to Trees Section 11.1 Section Summary Introduction to Trees
UNIT III TREES. A tree is a non-linear data structure that is used to represents hierarchical relationships between individual data items.
 UNIT III TREES A tree is a non-linear data structure that is used to represents hierarchical relationships between individual data items. Tree: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that, there
UNIT III TREES A tree is a non-linear data structure that is used to represents hierarchical relationships between individual data items. Tree: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that, there
CMSC th Lecture: Graph Theory: Trees.
 CMSC 27100 26th Lecture: Graph Theory: Trees. Lecturer: Janos Simon December 2, 2018 1 Trees Definition 1. A tree is an acyclic connected graph. Trees have many nice properties. Theorem 2. The following
CMSC 27100 26th Lecture: Graph Theory: Trees. Lecturer: Janos Simon December 2, 2018 1 Trees Definition 1. A tree is an acyclic connected graph. Trees have many nice properties. Theorem 2. The following
CSC Intro to Intelligent Robotics, Spring Graphs
 CSC 445 - Intro to Intelligent Robotics, Spring 2018 Graphs Graphs Definition: A graph G = (V, E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge has either one or two
CSC 445 - Intro to Intelligent Robotics, Spring 2018 Graphs Graphs Definition: A graph G = (V, E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge has either one or two
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
CS 151. Binary Trees. Friday, October 5, 12
 CS 151 Binary Trees 1 Binary Tree Examples Without telling you what a binary tree is, here are some examples (that I will draw on the board): The dots/circles are called nodes, or vertices (singular: one
CS 151 Binary Trees 1 Binary Tree Examples Without telling you what a binary tree is, here are some examples (that I will draw on the board): The dots/circles are called nodes, or vertices (singular: one
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
CS 125 Section #6 Graph Traversal and Linear Programs 10/13/14
 CS 125 Section #6 Graph Traversal and Linear Programs 10/13/14 1 Depth first search 1.1 The Algorithm Besides breadth first search, which we saw in class in relation to Dijkstra s algorithm, there is one
CS 125 Section #6 Graph Traversal and Linear Programs 10/13/14 1 Depth first search 1.1 The Algorithm Besides breadth first search, which we saw in class in relation to Dijkstra s algorithm, there is one
Data Structure. IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017
 Data Structure IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017 Data Structure: In computer science, a data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in a computer s memory so that it can be used efficiently. Data
Data Structure IBPS SO (IT- Officer) Exam 2017 Data Structure: In computer science, a data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in a computer s memory so that it can be used efficiently. Data
Graph Biconnectivity
 HW5: Graph Biconnectivity Course: ENEE759K/CMSC751 Title: Graph Biconnectivity Date Assigned: April 21, 2012 Date Due: May 11, 2012, 11:59pm Contact: James Edwards jedward5@umd.edu 1 Assignment Goal Identify
HW5: Graph Biconnectivity Course: ENEE759K/CMSC751 Title: Graph Biconnectivity Date Assigned: April 21, 2012 Date Due: May 11, 2012, 11:59pm Contact: James Edwards jedward5@umd.edu 1 Assignment Goal Identify
Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 s of s s are abstract data types that are applicable
s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 s of s s are abstract data types that are applicable
Graph Representation
 Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graphs. CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
Graphs. Part I: Basic algorithms. Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College
 Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Undirected graphs Concepts: connectivity, connected components paths (undirected) cycles Basic problems, given undirected graph G: is G connected how many
Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Undirected graphs Concepts: connectivity, connected components paths (undirected) cycles Basic problems, given undirected graph G: is G connected how many
Algorithms and Data Structures
 Algorithms and Data Structures Graphs 3: Finding Connected Components Marius Kloft Content of this Lecture Finding Connected Components in Undirected Graphs Finding Strongly Connected Components in Directed
Algorithms and Data Structures Graphs 3: Finding Connected Components Marius Kloft Content of this Lecture Finding Connected Components in Undirected Graphs Finding Strongly Connected Components in Directed
Konigsberg Bridge Problem
 Graphs Konigsberg Bridge Problem c C d g A Kneiphof e D a B b f c A C d e g D a b f B Euler s Graph Degree of a vertex: the number of edges incident to it Euler showed that there is a walk starting at
Graphs Konigsberg Bridge Problem c C d g A Kneiphof e D a B b f c A C d e g D a b f B Euler s Graph Degree of a vertex: the number of edges incident to it Euler showed that there is a walk starting at
國立清華大學電機工程學系. Outline
 國立清華大學電機工程學系 EE Data Structure Chapter Graph (Part I) Outline The Graph Abstract Data Type Introduction Definitions Graph Representations Elementary Graph Operations Minimum Cost Spanning Trees ch.- River
國立清華大學電機工程學系 EE Data Structure Chapter Graph (Part I) Outline The Graph Abstract Data Type Introduction Definitions Graph Representations Elementary Graph Operations Minimum Cost Spanning Trees ch.- River
(Refer Slide Time: 05:25)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering IIT Delhi Lecture 30 Applications of DFS in Directed Graphs Today we are going to look at more applications
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering IIT Delhi Lecture 30 Applications of DFS in Directed Graphs Today we are going to look at more applications
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Graph Search. Adnan Aziz
 Graph Search Adnan Aziz Based on CLRS, Ch 22. Recall encountered graphs several weeks ago (CLRS B.4) restricted our attention to definitions, terminology, properties Now we ll see how to perform basic
Graph Search Adnan Aziz Based on CLRS, Ch 22. Recall encountered graphs several weeks ago (CLRS B.4) restricted our attention to definitions, terminology, properties Now we ll see how to perform basic
Graphs V={A,B,C,D,E} E={ (A,D),(A,E),(B,D), (B,E),(C,D),(C,E)}
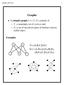 Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Chapter 20: Binary Trees
 Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Chapter 20: Binary Trees 20.1 Definition and Application of Binary Trees Definition and Application of Binary Trees Binary tree: a nonlinear linked list in which each node may point to 0, 1, or two other
Definition of Graphs and Trees. Representation of Trees.
 Definition of Graphs and Trees. Representation of Trees. Chapter 6 Definition of graphs (I) A directed graph or digraph is a pair G = (V,E) s.t.: V is a finite set called the set of vertices of G. E V
Definition of Graphs and Trees. Representation of Trees. Chapter 6 Definition of graphs (I) A directed graph or digraph is a pair G = (V,E) s.t.: V is a finite set called the set of vertices of G. E V
COS 423 Lecture14. Robert E. Tarjan 2011
 COS 423 Lecture14 Graph Search Robert E. Tarjan 2011 An undirected graph 4 connected components c a b g d e f h i j Vertex j is isolated: no incident edges Undirected graph search G= (V, E) V= vertex set,
COS 423 Lecture14 Graph Search Robert E. Tarjan 2011 An undirected graph 4 connected components c a b g d e f h i j Vertex j is isolated: no incident edges Undirected graph search G= (V, E) V= vertex set,
CS204 Discrete Mathematics. 11 Trees. 11 Trees
 11.1 Introduction to Trees Def. 1 A tree T = (V, E) is a connected undirected graph with no simple circuits. acyclic connected graph. forest a set of trees. A vertex of degree one is called leaf. Thm.
11.1 Introduction to Trees Def. 1 A tree T = (V, E) is a connected undirected graph with no simple circuits. acyclic connected graph. forest a set of trees. A vertex of degree one is called leaf. Thm.
Announcements. HW3 is graded. Average is 81%
 CSC263 Week 9 Announcements HW3 is graded. Average is 81% Announcements Problem Set 4 is due this Tuesday! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Recap The Graph ADT definition and data structures BFS gives us single-source
CSC263 Week 9 Announcements HW3 is graded. Average is 81% Announcements Problem Set 4 is due this Tuesday! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Recap The Graph ADT definition and data structures BFS gives us single-source
Friday, March 30. Last time we were talking about traversal of a rooted ordered tree, having defined preorder traversal. We will continue from there.
 Friday, March 30 Last time we were talking about traversal of a rooted ordered tree, having defined preorder traversal. We will continue from there. Postorder traversal (recursive definition) If T consists
Friday, March 30 Last time we were talking about traversal of a rooted ordered tree, having defined preorder traversal. We will continue from there. Postorder traversal (recursive definition) If T consists
CS 280 Problem Set 10 Solutions Due May 3, Part A
 CS 280 Problem Set 10 Due May 3, 2002 Part A (1) You are given a directed graph G with 1000 vertices. There is one weakly connected component of size 800 and several other weakly connected components of
CS 280 Problem Set 10 Due May 3, 2002 Part A (1) You are given a directed graph G with 1000 vertices. There is one weakly connected component of size 800 and several other weakly connected components of
logn D. Θ C. Θ n 2 ( ) ( ) f n B. nlogn Ο n2 n 2 D. Ο & % ( C. Θ # ( D. Θ n ( ) Ω f ( n)
 CSE 0 Test Your name as it appears on your UTA ID Card Fall 0 Multiple Choice:. Write the letter of your answer on the line ) to the LEFT of each problem.. CIRCLED ANSWERS DO NOT COUNT.. points each. The
CSE 0 Test Your name as it appears on your UTA ID Card Fall 0 Multiple Choice:. Write the letter of your answer on the line ) to the LEFT of each problem.. CIRCLED ANSWERS DO NOT COUNT.. points each. The
Section 5.5. Left subtree The left subtree of a vertex V on a binary tree is the graph formed by the left child L of V, the descendents
 Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
Section 5.5 Binary Tree A binary tree is a rooted tree in which each vertex has at most two children and each child is designated as being a left child or a right child. Thus, in a binary tree, each vertex
An Algorithm for Enumerating All Spanning Trees of a Directed Graph 1. S. Kapoor 2 and H. Ramesh 3
 Algorithmica (2000) 27: 120 130 DOI: 10.1007/s004530010008 Algorithmica 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. An Algorithm for Enumerating All Spanning Trees of a Directed Graph 1 S. Kapoor 2 and H. Ramesh
Algorithmica (2000) 27: 120 130 DOI: 10.1007/s004530010008 Algorithmica 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. An Algorithm for Enumerating All Spanning Trees of a Directed Graph 1 S. Kapoor 2 and H. Ramesh
Trees. CSE 373 Data Structures
 Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
Trees CSE 373 Data Structures Readings Reading Chapter 7 Trees 2 Why Do We Need Trees? Lists, Stacks, and Queues are linear relationships Information often contains hierarchical relationships File directories
n 2 C. Θ n ( ) Ο f ( n) B. n 2 Ω( n logn)
 CSE 0 Name Test Fall 0 Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to find the maximum of the n elements of an integer array is in: A.
CSE 0 Name Test Fall 0 Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to find the maximum of the n elements of an integer array is in: A.
Review: Graph Theory and Representation
 Review: Graph Theory and Representation Graph Algorithms Graphs and Theorems about Graphs Graph implementation Graph Algorithms Shortest paths Minimum spanning tree What can graphs model? Cost of wiring
Review: Graph Theory and Representation Graph Algorithms Graphs and Theorems about Graphs Graph implementation Graph Algorithms Shortest paths Minimum spanning tree What can graphs model? Cost of wiring
Chapter 5. Decrease-and-Conquer. Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
Graphs. A graph is a data structure consisting of nodes (or vertices) and edges. An edge is a connection between two nodes
 Graphs Graphs A graph is a data structure consisting of nodes (or vertices) and edges An edge is a connection between two nodes A D B E C Nodes: A, B, C, D, E Edges: (A, B), (A, D), (D, E), (E, C) Nodes
Graphs Graphs A graph is a data structure consisting of nodes (or vertices) and edges An edge is a connection between two nodes A D B E C Nodes: A, B, C, D, E Edges: (A, B), (A, D), (D, E), (E, C) Nodes
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms
 W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
Graph and Digraph Glossary
 1 of 15 31.1.2004 14:45 Graph and Digraph Glossary A B C D E F G H I-J K L M N O P-Q R S T U V W-Z Acyclic Graph A graph is acyclic if it contains no cycles. Adjacency Matrix A 0-1 square matrix whose
1 of 15 31.1.2004 14:45 Graph and Digraph Glossary A B C D E F G H I-J K L M N O P-Q R S T U V W-Z Acyclic Graph A graph is acyclic if it contains no cycles. Adjacency Matrix A 0-1 square matrix whose
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees
 Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
22.3 Depth First Search
 22.3 Depth First Search Depth-First Search(DFS) always visits a neighbour of the most recently visited vertex with an unvisited neighbour. This means the search moves forward when possible, and only backtracks
22.3 Depth First Search Depth-First Search(DFS) always visits a neighbour of the most recently visited vertex with an unvisited neighbour. This means the search moves forward when possible, and only backtracks
COL351: Analysis and Design of Algorithms (CSE, IITD, Semester-I ) Name: Entry number:
 Name: Entry number: There are 6 questions for a total of 75 points. 1. Consider functions f(n) = 10n2 n + 3 n and g(n) = n3 n. Answer the following: (a) ( 1 / 2 point) State true or false: f(n) is O(g(n)).
Name: Entry number: There are 6 questions for a total of 75 points. 1. Consider functions f(n) = 10n2 n + 3 n and g(n) = n3 n. Answer the following: (a) ( 1 / 2 point) State true or false: f(n) is O(g(n)).
Trees. Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT
 Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
Trees Truong Tuan Anh CSE-HCMUT Outline Basic concepts Trees Trees A tree consists of a finite set of elements, called nodes, and a finite set of directed lines, called branches, that connect the nodes
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 15. Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico
 CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 15 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 10-12-2010 1 Last Time Identifying BFS vs. DFS trees Can they be the same? Problems 3.6, 3.9, 3.2 details left as homework.
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 15 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 10-12-2010 1 Last Time Identifying BFS vs. DFS trees Can they be the same? Problems 3.6, 3.9, 3.2 details left as homework.
( ) ( ) C. " 1 n. ( ) $ f n. ( ) B. " log( n! ) ( ) and that you already know ( ) ( ) " % g( n) ( ) " #&
 CSE 0 Name Test Summer 008 Last 4 Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time for the following code is in which set? for (i=0; i
CSE 0 Name Test Summer 008 Last 4 Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time for the following code is in which set? for (i=0; i
Graph Algorithms. Imran Rashid. Jan 16, University of Washington
 Graph Algorithms Imran Rashid University of Washington Jan 16, 2008 1 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs & Topological Ordering 3 DFS 2 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs
Graph Algorithms Imran Rashid University of Washington Jan 16, 2008 1 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs & Topological Ordering 3 DFS 2 / 26 Lecture Outline 1 BFS Bipartite Graphs 2 DAGs
Representations of Graphs
 ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 04 Elementary Graph Algorithms (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) sscott@cse.unl.edu Introduction
Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 04 Elementary Graph Algorithms (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) sscott@cse.unl.edu Introduction
Graphs. Graph G = (V, E) Types of graphs E = O( V 2 ) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V)
 Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Computational Optimization ISE 407. Lecture 19. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 19 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 19 1 Search Algorithms Search algorithms are fundamental techniques applied to solve a wide range of optimization problems.
Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 19 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 19 1 Search Algorithms Search algorithms are fundamental techniques applied to solve a wide range of optimization problems.
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Graph Algorithms. Chapter 22. CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms 1
 Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Search means finding a path or traversal between a start node and one of a set of goal nodes. Search is a study of states and their transitions.
 UNIT 3 BASIC TRAVERSAL AND SEARCH TECHNIQUES Search means finding a path or traversal between a start node and one of a set of goal nodes. Search is a study of states and their transitions. Search involves
UNIT 3 BASIC TRAVERSAL AND SEARCH TECHNIQUES Search means finding a path or traversal between a start node and one of a set of goal nodes. Search is a study of states and their transitions. Search involves
15-451/651: Design & Analysis of Algorithms October 5, 2017 Lecture #11: Depth First Search and Strong Components last changed: October 17, 2017
 15-451/651: Design & Analysis of Algorithms October 5, 2017 Lecture #11: Depth First Search and Strong Components last changed: October 17, 2017 1 Introduction Depth first search is a very useful technique
15-451/651: Design & Analysis of Algorithms October 5, 2017 Lecture #11: Depth First Search and Strong Components last changed: October 17, 2017 1 Introduction Depth first search is a very useful technique
DARSHAN INST. OF ENGG. & TECH.
 (1) Explain with example how games can be formulated using graphs? Consider the following game. It is one of the many variants of Nim, also known as the Marienbad game. Initially there is a heap of matches
(1) Explain with example how games can be formulated using graphs? Consider the following game. It is one of the many variants of Nim, also known as the Marienbad game. Initially there is a heap of matches
Graphs: basic concepts and algorithms
 : basic concepts and algorithms Topics covered by this lecture: - Reminder Trees Trees (in-order,post-order,pre-order) s (BFS, DFS) Denitions: Reminder Directed graph (digraph): G = (V, E), V - vertex
: basic concepts and algorithms Topics covered by this lecture: - Reminder Trees Trees (in-order,post-order,pre-order) s (BFS, DFS) Denitions: Reminder Directed graph (digraph): G = (V, E), V - vertex
CISC 320 Introduction to Algorithms Fall Lecture 15 Depth First Search
 IS 320 Introduction to lgorithms all 2014 Lecture 15 epth irst Search 1 Traversing raphs Systematic search of every edge and vertex of graph (directed or undirected) fficiency: each edge is visited no
IS 320 Introduction to lgorithms all 2014 Lecture 15 epth irst Search 1 Traversing raphs Systematic search of every edge and vertex of graph (directed or undirected) fficiency: each edge is visited no
