2.71/2.710 Optics (Laser lecture) 12/12/01-1. Lasers
|
|
|
- Kenneth Golden
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 12/12/01-1 Lasers
2 Semi-classical view of atom excitations Energy e - Ze + Atom in ground state Energy Atom in excited state 12/12/01-2
3 Light generation Energy excited state equilibrium: most atoms in ground state ground state 12/12/01-3
4 Light generation Energy excited state A pump mechanism (e.g. thermal excitation or gas discharge) ejects some atoms to the excited state ground state 12/12/01-4
5 Light generation Energy excited state hν hν The excited atoms radiatively decay, emitting one photon each ground state 12/12/01-5
6 Light amplification: 3-level system Energy super-excited state excited state equilibrium: most atoms in ground state; note the existence of a third, super-excited state ground state 12/12/01-6
7 Light amplification: 3-level system Energy super-excited state excited state Utilizing the super-excited state as a short-lived pivot point, the pump creates a population inversion ground state 12/12/01-7
8 Light amplification: 3-level system Energy super-excited state excited state hν When a photon enters,... ground state 12/12/01-8
9 Light amplification: 3-level system Energy super-excited state excited state hν hν hν 12/12/01-9 When a photon enters, it knocks an electron from the inverted population down to the ground state, thus creating a new photon. This amplification process is called stimulated emission ground state
10 Light amplifier P in Gain medium (e.g. 3-level system w population inversion) P out =gp in 12/12/01-10
11 Light amplifier w positive feedback P in Gain medium (e.g. 3-level system w population inversion) P out =gp in When the gain exceeds the roundtrip losses, the system goes into oscillation + Σ + g 12/12/01-11
12 Laser initial photon Gain medium (e.g. 3-level system w population inversion) Light Amplification through Stimulated Emission of Radiation Partially reflecting mirror 12/12/01-12
13 Laser amplified once initial photon Gain medium (e.g. 3-level system w population inversion) Light Amplification through Stimulated Emission of Radiation Partially reflecting mirror 12/12/01-13
14 Laser amplified once initial photon reflected Gain medium (e.g. 3-level system w population inversion) Light Amplification through Stimulated Emission of Radiation Partially reflecting mirror 12/12/01-14
15 Laser amplified once initial photon reflected Gain medium (e.g. 3-level system w population inversion) amplified twice Light Amplification through Stimulated Emission of Radiation Partially reflecting mirror 12/12/01-15
16 Laser amplified once initial photon reflected Gain medium (e.g. 3-level system w population inversion) amplified twice output reflected Light Amplification through Stimulated Emission of Radiation Partially reflecting mirror 12/12/01-16
17 Laser amplified once initial photon reflected Gain medium (e.g. 3-level system w population inversion) amplified twice output amplified again etc. Light Amplification through Stimulated Emission of Radiation reflected Partially reflecting mirror 12/12/01-17
18 12/12/01-18 Overview of light sources Laser non-laser Thermal: polychromatic, spatially incoherent (e.g. light bulb) Gas discharge: monochromatic, spatially incoherent (e.g. Na lamp) Light emitting diodes (LEDs): monochromatic, spatially incoherent Continuous wave (or cw): strictly monochromatic, spatially coherent (e.g. HeNe, Ar +, laser diodes) Pulsed: quasi-monochromatic, spatially coherent (e.g. Q-switched, mode-locked) ~nsec pulse duration mono/poly-chromatic = single/multi color ~psec to few fsec
19 Monochromatic, spatially coherent light 1/ν nice, regular sinusoid λ λ, ν well defined stabilized HeNe laser good approximation most other cw lasers rough approximation pulsed lasers & nonlaser sources need more complicated description Incoherent: random, irregular waveform 12/12/01-19
Unit I Light and Optics
 Unit I Light and Optics Outline By the time you finish this, you should understand the following aspects of our experiment: 1) Why you produce a grating pattern when you cross two laser beams. 2) What
Unit I Light and Optics Outline By the time you finish this, you should understand the following aspects of our experiment: 1) Why you produce a grating pattern when you cross two laser beams. 2) What
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 23 Coherence Laser, Holography CUE Evaluation! This course is being evaluated because the course head has requested that the course be included in the CUE Guide. As you
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 23 Coherence Laser, Holography CUE Evaluation! This course is being evaluated because the course head has requested that the course be included in the CUE Guide. As you
Lecture 5 Chapter 1 & 2. Sources of light
 We are here Lecture 5 Chapter 1 & 2 Some history of technology How vision works What is light Wavelength and Frequency: c = f λ Scientific notation and metric units Electromagnetic spectrum Transmission
We are here Lecture 5 Chapter 1 & 2 Some history of technology How vision works What is light Wavelength and Frequency: c = f λ Scientific notation and metric units Electromagnetic spectrum Transmission
Phys 1020, Day 18: Questions? Cameras, Blmfld Reminders: Next Up: digital cameras finish Optics Note Final Project proposals next week!
 Lights. Action. Phys 1020, Day 18: Questions? Cameras, Blmfld 15.1 Reminders: Next Up: digital cameras finish Optics Note Final Project proposals next week! 1 What have we learned in this section: 1) Lasers
Lights. Action. Phys 1020, Day 18: Questions? Cameras, Blmfld 15.1 Reminders: Next Up: digital cameras finish Optics Note Final Project proposals next week! 1 What have we learned in this section: 1) Lasers
Sample Introduction Systems SOLID LASER ABLATION
 Sample Introduction Systems SOLID LASER ABLATION Laser ablation Benefits: spatial resolution of < 10 um little to no sample preparation required Drawbacks: transient signal reduced precision/accuracy relative
Sample Introduction Systems SOLID LASER ABLATION Laser ablation Benefits: spatial resolution of < 10 um little to no sample preparation required Drawbacks: transient signal reduced precision/accuracy relative
Sample Analysis Design
 Sample Analysis Design PART III Spectroscopic interferences Matrix effects Matrix Effects Physical physical effects from dissolved or undissolved solids present in solution Chemical Ionization suppression
Sample Analysis Design PART III Spectroscopic interferences Matrix effects Matrix Effects Physical physical effects from dissolved or undissolved solids present in solution Chemical Ionization suppression
Introduction of the Industry's Broadest Tunable Quantum Cascade Lasers. February Block Engineering 1
 Introduction of the Industry's Broadest Tunable Quantum Cascade Lasers February 2014 2014 Block Engineering 1 Widely-Tunable QCL Products LaserTune Mini-QCL Smallest widely-tunable QCL source Embedded
Introduction of the Industry's Broadest Tunable Quantum Cascade Lasers February 2014 2014 Block Engineering 1 Widely-Tunable QCL Products LaserTune Mini-QCL Smallest widely-tunable QCL source Embedded
RR July 2000 SS Dec 2001 Physics 342 Laboratory The Wave Nature of Light: Interference and Diffraction
 RR July 000 SS Dec 001 Physics 34 Laboratory The Wave Nature of Light: Interference and Diffraction Objectives: To demonstrate the wave nature of light, in particular diffraction and interference, using
RR July 000 SS Dec 001 Physics 34 Laboratory The Wave Nature of Light: Interference and Diffraction Objectives: To demonstrate the wave nature of light, in particular diffraction and interference, using
Wallace Hall Academy
 Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 2 - Waves Notes Name 1 Waves Revision You will remember the following equations related to Waves from National 5. d = vt f = n/t v = f T=1/f They form an integral
Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 2 - Waves Notes Name 1 Waves Revision You will remember the following equations related to Waves from National 5. d = vt f = n/t v = f T=1/f They form an integral
Polarization of Light
 From http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/optics/lightandcolor/polarization.html by Mortimer Abramowitz, Shannon Neaves and Michael Davidson and http://technology.niagarac.on.ca/courses/tech238g/lasers.html by
From http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/optics/lightandcolor/polarization.html by Mortimer Abramowitz, Shannon Neaves and Michael Davidson and http://technology.niagarac.on.ca/courses/tech238g/lasers.html by
Time-Resolved measurements by FEL spontaneous emission: A proposal for sub-picosecond pumps & probe structural and spectrometric investigations
 Time-Resolved measurements by FEL spontaneous emission: A proposal for sub-picosecond pumps & probe structural and spectrometric investigations V. Rossi Albertini, B. Paci & P. Perfetti Istituto di Struttura
Time-Resolved measurements by FEL spontaneous emission: A proposal for sub-picosecond pumps & probe structural and spectrometric investigations V. Rossi Albertini, B. Paci & P. Perfetti Istituto di Struttura
Spectroscopic equipment. Multispectral Imaging
 Spectroscopic equipment Multispectral Imaging Basic spectroscopic arrangement Source Sample Analyzer Detector Sun Lamps Lasers LEDs Synchrotron Plants Forests Tissue Cells Flames Chemical compounds etc.
Spectroscopic equipment Multispectral Imaging Basic spectroscopic arrangement Source Sample Analyzer Detector Sun Lamps Lasers LEDs Synchrotron Plants Forests Tissue Cells Flames Chemical compounds etc.
Mirror Example Consider a concave mirror radius -10 cm then = = Now consider a 1 cm candle s = 15 cm from the vertex Where is the image.
 Mirror Example Consider a concave mirror radius -10 cm then r 10 f = = = 5 cm 2 2 Now consider a 1 cm candle s = 15 cm from the vertex Where is the image 1 s 2 1 = = r s 1 1 2 + = = s s r 1 1 = 0.13333
Mirror Example Consider a concave mirror radius -10 cm then r 10 f = = = 5 cm 2 2 Now consider a 1 cm candle s = 15 cm from the vertex Where is the image 1 s 2 1 = = r s 1 1 2 + = = s s r 1 1 = 0.13333
1. Which diagram best represents the reflection of light from an irregular surface?
 waves 6-2-04 Name 02-JUN-04 1. Which diagram best represents the reflection of light from an irregular surface? 1. 1 3. 3 2. 2 4. 4 2. In a vacuum, a monochromatic beam of light as a frequency of 6.3 X
waves 6-2-04 Name 02-JUN-04 1. Which diagram best represents the reflection of light from an irregular surface? 1. 1 3. 3 2. 2 4. 4 2. In a vacuum, a monochromatic beam of light as a frequency of 6.3 X
Synchronization and pump-probe experiments
 Synchronization and pump-probe experiments by Stefan Düsterer Outline o Pump-probe probe infrastructure VUV + VUV VUV + optical o o Temporal overlap and jitter As example: the pump-probe probe chamber
Synchronization and pump-probe experiments by Stefan Düsterer Outline o Pump-probe probe infrastructure VUV + VUV VUV + optical o o Temporal overlap and jitter As example: the pump-probe probe chamber
Introduction: Experiment 1: Wave Properties of Light
 Natural Order Properties of Light Lab Introduction: In this lab we will explore the wave and particle nature of light. In the first experiment we will measure the diffraction pattern of light as it passes
Natural Order Properties of Light Lab Introduction: In this lab we will explore the wave and particle nature of light. In the first experiment we will measure the diffraction pattern of light as it passes
Mirror Example Consider a concave mirror radius r = -10 cm then. Now consider a 1 cm candle s = 15 cm from the vertex Where is the image.
 Mirror Example Consider a concave mirror radius r = -0 cm then r 0 f 5 cm 2 2 Now consider a cm candle s = 5 cm from the vertex Where is the image s 2 r s 2 s s r 0.3333 5 5 f s' 0.333 M ' s 7.5 Magnification
Mirror Example Consider a concave mirror radius r = -0 cm then r 0 f 5 cm 2 2 Now consider a cm candle s = 5 cm from the vertex Where is the image s 2 r s 2 s s r 0.3333 5 5 f s' 0.333 M ' s 7.5 Magnification
Attosecond Optics. Zenghu Chang Kansas State University University of Central Florida
 Attosecond Optics Zenghu Chang Kansas State University University of Central Florida CREOL Industrial Affiliates day, April 9, 2010 Why attosecond pulses? Zeptosecond (10-21 s) Attosecond (10-18 s) Femtosecond
Attosecond Optics Zenghu Chang Kansas State University University of Central Florida CREOL Industrial Affiliates day, April 9, 2010 Why attosecond pulses? Zeptosecond (10-21 s) Attosecond (10-18 s) Femtosecond
Physics 1230: Light and Color
 Physics 1230: Light and Color Chuck Rogers, Charles.Rogers@colorado.edu Ryan Henley, Valyria McFarland, Peter Siegfried physicscourses.colorado.edu/phys1230 Congratulations on completing Exam 1. Great
Physics 1230: Light and Color Chuck Rogers, Charles.Rogers@colorado.edu Ryan Henley, Valyria McFarland, Peter Siegfried physicscourses.colorado.edu/phys1230 Congratulations on completing Exam 1. Great
Basic Optics : Microlithography Topics Book pages
 Basic : Microlithography Topics Book pages171-183 1. Electromagnetic Radiation 2. Refractive Index and refraction 3. Optical Path length 4. Lens Basics 5. Geometrical References * Elements of Modern Optical
Basic : Microlithography Topics Book pages171-183 1. Electromagnetic Radiation 2. Refractive Index and refraction 3. Optical Path length 4. Lens Basics 5. Geometrical References * Elements of Modern Optical
Option G 1: Refraction
 Name: Date: Option G 1: Refraction 1. The table below relates to the electromagnetic spectrum. Complete the table by stating the name of the region of the spectrum and the name of a possible source of
Name: Date: Option G 1: Refraction 1. The table below relates to the electromagnetic spectrum. Complete the table by stating the name of the region of the spectrum and the name of a possible source of
LASer Cavity Analysis and Design
 The unique combination of simulation tools for LASer Cavity Analysis and Design During the last 15 years LASCAD has become industry-leading so ware for LASer Cavity Analysis and Design. The feedback from
The unique combination of simulation tools for LASer Cavity Analysis and Design During the last 15 years LASCAD has become industry-leading so ware for LASer Cavity Analysis and Design. The feedback from
2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes
 2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes Answer all four questions. All questions count equally. 3(a) A linearly polarized
2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes Answer all four questions. All questions count equally. 3(a) A linearly polarized
High-Power Femtosecond Lasers
 High-Power Femtosecond Lasers FEATURES 190 fs ps tunable pulse duration Up to 2 mj pulse energy Up to 20 W average power Single pulse 1 MHz tunable repetition rate Includes pulse picker for pulse-on-demand
High-Power Femtosecond Lasers FEATURES 190 fs ps tunable pulse duration Up to 2 mj pulse energy Up to 20 W average power Single pulse 1 MHz tunable repetition rate Includes pulse picker for pulse-on-demand
Figure 6.1 Determination of wavelength
 Figure 6.1 Determination of wavelength Figure 6.2 Particle size determination by LASER Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam 47 Wavelength of Laser and
Figure 6.1 Determination of wavelength Figure 6.2 Particle size determination by LASER Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam 47 Wavelength of Laser and
BRIGHTBOX-E1 LASER DIODE ENGINE
 0 BRIGHTBOX-E1 BRIGHTBOX-E1 LASER DIODE ENGINE 1 GENERAL INFORMATION 2017 OPI Photonics S.R.L. All rights reserved. OPI Photonics S.R.L. reserves the right to make changes to this document at any time
0 BRIGHTBOX-E1 BRIGHTBOX-E1 LASER DIODE ENGINE 1 GENERAL INFORMATION 2017 OPI Photonics S.R.L. All rights reserved. OPI Photonics S.R.L. reserves the right to make changes to this document at any time
( ) = First Bessel function, x = π Dθ
 Observational Astronomy Image formation Complex Pupil Function (CPF): (3.3.1) CPF = P( r,ϕ )e ( ) ikw r,ϕ P( r,ϕ ) = Transmittance of the aperture (unobscured P = 1, obscured P = 0 ) k = π λ = Wave number
Observational Astronomy Image formation Complex Pupil Function (CPF): (3.3.1) CPF = P( r,ϕ )e ( ) ikw r,ϕ P( r,ϕ ) = Transmittance of the aperture (unobscured P = 1, obscured P = 0 ) k = π λ = Wave number
Section 3 DEVELOPMENT IN SUBPICOSECOND RESEARCH
 Section 3 DEVELOPMENT IN SUBPICOSECOND RESEARCH 3.A A Simple Jitter-Free Picosecond Streak Camera The picosecond streak camera 4 3 p 4 4 is becoming a basic tool in the study of optical transients in the
Section 3 DEVELOPMENT IN SUBPICOSECOND RESEARCH 3.A A Simple Jitter-Free Picosecond Streak Camera The picosecond streak camera 4 3 p 4 4 is becoming a basic tool in the study of optical transients in the
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR)
 Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) http://code.google.com/creative/radiohead/ Types of aerial sensors passive active 1 Active sensors for mapping terrain Radar transmits microwaves in pulses determines
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) http://code.google.com/creative/radiohead/ Types of aerial sensors passive active 1 Active sensors for mapping terrain Radar transmits microwaves in pulses determines
OPTIX Module 3 Basic Interference of two Laser Beams
 OPTIX Module 3 Basic Interference of two Laser Beams Shelby Merrill, Michaela Kleinert 1 Objectives: In this module you will learn more about Helium-Neon lasers; the Michelson Interferometer; interference
OPTIX Module 3 Basic Interference of two Laser Beams Shelby Merrill, Michaela Kleinert 1 Objectives: In this module you will learn more about Helium-Neon lasers; the Michelson Interferometer; interference
Characteristics of Light
 Characteristics of Light The Nature of Light Light is electromagnetic energy that stimulates the photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye. This form of energy is our most important means of learning
Characteristics of Light The Nature of Light Light is electromagnetic energy that stimulates the photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye. This form of energy is our most important means of learning
600 mw Fiber Bragg Grating Stabilized 14xx nm Pump Modules with Ultra-Low Power Consumption. S35 Series
 600 mw Fiber Bragg Grating Stabilized 14xx nm Pump Modules with Ultra-Low Power Consumption S35 Series www.lumentum.com Data Sheet The Lumentum S35 series 14xx nm, Laser Diode pump is wavelength selected
600 mw Fiber Bragg Grating Stabilized 14xx nm Pump Modules with Ultra-Low Power Consumption S35 Series www.lumentum.com Data Sheet The Lumentum S35 series 14xx nm, Laser Diode pump is wavelength selected
ENY-C2005 Geoinformation in Environmental Modeling Lecture 4b: Laser scanning
 1 ENY-C2005 Geoinformation in Environmental Modeling Lecture 4b: Laser scanning Petri Rönnholm Aalto University 2 Learning objectives To recognize applications of laser scanning To understand principles
1 ENY-C2005 Geoinformation in Environmental Modeling Lecture 4b: Laser scanning Petri Rönnholm Aalto University 2 Learning objectives To recognize applications of laser scanning To understand principles
AUTOMOTIVE ENVIRONMENT SENSORS
 AUTOMOTIVE ENVIRONMENT SENSORS Lecture 3. LIDARs Dr. Szilárd Aradi BME KÖZLEKEDÉSMÉRNÖKI ÉS JÁRMŰMÉRNÖKI KAR 32708-2/2017/INTFIN SZÁMÚ EMMI ÁLTAL TÁMOGATOTT TANANYAG LIDAR intro Light Detection and Ranging
AUTOMOTIVE ENVIRONMENT SENSORS Lecture 3. LIDARs Dr. Szilárd Aradi BME KÖZLEKEDÉSMÉRNÖKI ÉS JÁRMŰMÉRNÖKI KAR 32708-2/2017/INTFIN SZÁMÚ EMMI ÁLTAL TÁMOGATOTT TANANYAG LIDAR intro Light Detection and Ranging
Last class. This class. Single molecule imaging Deconvolution. FLIM Confocal
 FLIM, Confocal Last class Single molecule imaging Deconvolution This class FLIM Confocal FLIM Fluorescence Lifetime IMaging FLIM Fluorescence lifetime imaging Easier and more accurate quantitation Much
FLIM, Confocal Last class Single molecule imaging Deconvolution This class FLIM Confocal FLIM Fluorescence Lifetime IMaging FLIM Fluorescence lifetime imaging Easier and more accurate quantitation Much
Laser readiness for all optical EUV FEL
 Laser readiness for all optical EUV FEL Akira Endo EUVA (Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography System Development Association) EUVL Source Workshop 19 October, 2006 Barcelona, Spain Acknowledgments This work
Laser readiness for all optical EUV FEL Akira Endo EUVA (Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography System Development Association) EUVL Source Workshop 19 October, 2006 Barcelona, Spain Acknowledgments This work
Introduction to Optical Networks
 Introduction to Optical Networks P. Michael Henderson mike@michael-henderson.us 1 Agenda The physics of light Laser and photodetector operation Characteristics of optical fiber Optical amplifiers SONET
Introduction to Optical Networks P. Michael Henderson mike@michael-henderson.us 1 Agenda The physics of light Laser and photodetector operation Characteristics of optical fiber Optical amplifiers SONET
Chapter 9. Coherence
 Chapter 9. Coherence Last Lecture Michelson Interferometer Variations of the Michelson Interferometer Fabry-Perot interferometer This Lecture Fourier analysis Temporal coherence and line width Partial
Chapter 9. Coherence Last Lecture Michelson Interferometer Variations of the Michelson Interferometer Fabry-Perot interferometer This Lecture Fourier analysis Temporal coherence and line width Partial
Leica s Pinpoint EDM Technology with Modified Signal Processing and Novel Optomechanical Features
 Leica s Pinpoint EDM Technology with Modified Signal Processing and Novel Optomechanical Features Fadi A Bayoud Ph.D. Geomatics Engineering Contents Leica s Total Stations and Telescope ATR PS Leica s
Leica s Pinpoint EDM Technology with Modified Signal Processing and Novel Optomechanical Features Fadi A Bayoud Ph.D. Geomatics Engineering Contents Leica s Total Stations and Telescope ATR PS Leica s
ULTRAFAST LASERS: TECHNOLOGIES AND GLOBAL MARKETS
 ULTRAFAST LASERS: TECHNOLOGIES AND GLOBAL MARKETS PHO017A February 2015 Sinha G. Project Analyst ISBN: 1-62296-036-X BCC Research 49 Walnut Park, Building 2 Wellesley, MA 02481 USA 866-285-7215 (toll-free
ULTRAFAST LASERS: TECHNOLOGIES AND GLOBAL MARKETS PHO017A February 2015 Sinha G. Project Analyst ISBN: 1-62296-036-X BCC Research 49 Walnut Park, Building 2 Wellesley, MA 02481 USA 866-285-7215 (toll-free
SPECIAL-PURPOSE DIODES. Dr. Paulraj M P, Associate Professor, Blok A, School of Mechatronic Engineering
 SPECIAL-PURPOSE DIODES 1 CONTENTS 3-1 zener diodes 3-2 zener diodes applications 3-3 varactor diodes 3-4 optical diodes 3-5 other types of diodes 3-6 trouble shooting 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the basic characteristics
SPECIAL-PURPOSE DIODES 1 CONTENTS 3-1 zener diodes 3-2 zener diodes applications 3-3 varactor diodes 3-4 optical diodes 3-5 other types of diodes 3-6 trouble shooting 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the basic characteristics
Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction. Notes
 Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction Notes What is light? Light is electromagnetic radiation Ultra-violet + visible + infra-red Behavior of Light Light behaves in 2 ways particles (photons)
Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction Notes What is light? Light is electromagnetic radiation Ultra-violet + visible + infra-red Behavior of Light Light behaves in 2 ways particles (photons)
Configuration of Light Sources
 UseCase.0012 (1.0) Configuration of Light Sources Keywords: LED, laser, harmonic fields, harmonic fields set, spectra, pulses, polarization Description This use case explains how light sources are configured
UseCase.0012 (1.0) Configuration of Light Sources Keywords: LED, laser, harmonic fields, harmonic fields set, spectra, pulses, polarization Description This use case explains how light sources are configured
6-1 LECTURE #6: OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS. Basic question: How do solids interact with light? The answers are linked to:
 LECTURE #6: OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Basic question: How do solids interact with light? The answers are linked to: Properties of light inside a solid Mechanisms behind light reflection, absorption
LECTURE #6: OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Basic question: How do solids interact with light? The answers are linked to: Properties of light inside a solid Mechanisms behind light reflection, absorption
Chapter 35 &36 Physical Optics
 Chapter 35 &36 Physical Optics Physical Optics Phase Difference & Coherence Thin Film Interference 2-Slit Interference Single Slit Interference Diffraction Patterns Diffraction Grating Diffraction & Resolution
Chapter 35 &36 Physical Optics Physical Optics Phase Difference & Coherence Thin Film Interference 2-Slit Interference Single Slit Interference Diffraction Patterns Diffraction Grating Diffraction & Resolution
Full-Colour, Computational Ghost Video. Miles Padgett Kelvin Chair of Natural Philosophy
 Full-Colour, Computational Ghost Video Miles Padgett Kelvin Chair of Natural Philosophy A Quantum Ghost Imager! Generate random photon pairs, illuminate both object and camera SPDC CCD Identical copies
Full-Colour, Computational Ghost Video Miles Padgett Kelvin Chair of Natural Philosophy A Quantum Ghost Imager! Generate random photon pairs, illuminate both object and camera SPDC CCD Identical copies
Lecture 6 Proper,es of laser beams *
 Lecture 6 Proper,es of laser beams * Min Yan Op,cs and Photonics, KTH 12/04/16 1 * Some figures and texts belong to: O. Svelto, Principles of Lasers, 5th Ed., Springer. Reading Principles of Lasers (5th
Lecture 6 Proper,es of laser beams * Min Yan Op,cs and Photonics, KTH 12/04/16 1 * Some figures and texts belong to: O. Svelto, Principles of Lasers, 5th Ed., Springer. Reading Principles of Lasers (5th
Diffraction and Interference
 Experiment #32 Diffraction and Interference Goals: Perform a quantitative investigation of two-slit interference Explore use of a photodiode to measure light intensity References 1. I. G. Main, Vibrations
Experiment #32 Diffraction and Interference Goals: Perform a quantitative investigation of two-slit interference Explore use of a photodiode to measure light intensity References 1. I. G. Main, Vibrations
 Introduction Introduction Introduction Introduction Introduction use damage for processing! Outline Outline Processing with fs pulses Role of focusing Low-energy processing Processing with fs pulses 10
Introduction Introduction Introduction Introduction Introduction use damage for processing! Outline Outline Processing with fs pulses Role of focusing Low-energy processing Processing with fs pulses 10
Huygens and Fermat s s principles (Textbook 4.4, 4.5) Application to reflection & refraction at an interface
 Huygens and Fermat s s principles (Textbook 4.4, 4.5) Application to reflection & refraction at an interface 1 Propagation of light: Sources E.g. point source a fundamental source Light is emitted in all
Huygens and Fermat s s principles (Textbook 4.4, 4.5) Application to reflection & refraction at an interface 1 Propagation of light: Sources E.g. point source a fundamental source Light is emitted in all
Formulas of possible interest
 Name: PHYS 3410/6750: Modern Optics Final Exam Thursday 15 December 2011 Prof. Bolton No books, calculators, notes, etc. Formulas of possible interest I = ɛ 0 c E 2 T = 1 2 ɛ 0cE 2 0 E γ = hν γ n = c/v
Name: PHYS 3410/6750: Modern Optics Final Exam Thursday 15 December 2011 Prof. Bolton No books, calculators, notes, etc. Formulas of possible interest I = ɛ 0 c E 2 T = 1 2 ɛ 0cE 2 0 E γ = hν γ n = c/v
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) Radiohead House of Cards
 Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) Radiohead House of Cards http://the-moni-blog.blogspot.com/2009/03/lidar-is-going-mainstream-mtv-baby.html h =? Laser Vision GPS + IMU θ H X a h Types of aerial sensors
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) Radiohead House of Cards http://the-moni-blog.blogspot.com/2009/03/lidar-is-going-mainstream-mtv-baby.html h =? Laser Vision GPS + IMU θ H X a h Types of aerial sensors
COHERENCE AND INTERFERENCE
 COHERENCE AND INTERFERENCE - An interference experiment makes use of coherent waves. The phase shift (Δφ tot ) between the two coherent waves that interfere at any point of screen (where one observes the
COHERENCE AND INTERFERENCE - An interference experiment makes use of coherent waves. The phase shift (Δφ tot ) between the two coherent waves that interfere at any point of screen (where one observes the
The role of light source in coherence scanning interferometry and optical coherence tomography
 The role of light source in coherence scanning interferometry and optical coherence tomography Dr Rong Su Research Fellow Advanced Manufacturing Research Group Manufacturing Metrology Team Precision manufacturing
The role of light source in coherence scanning interferometry and optical coherence tomography Dr Rong Su Research Fellow Advanced Manufacturing Research Group Manufacturing Metrology Team Precision manufacturing
Experimental Optics. Michelson Interferometer. Contact. Last edition:
 Experimental Optics Contact Last edition: Michelson Interferometer 1 Background... 3... 4... 5... 13... 13 4.2... 14... 15... 15... 17... 19... 21... 21... 22... 22... 23... 24... 24... 25 2 1 Background
Experimental Optics Contact Last edition: Michelson Interferometer 1 Background... 3... 4... 5... 13... 13 4.2... 14... 15... 15... 17... 19... 21... 21... 22... 22... 23... 24... 24... 25 2 1 Background
Calibration of the LIGO Interferometer Using the Recoil of Photons
 Calibration of the LIGO Interferometer Using the Recoil of Photons Justice Bruursema Mentor: Daniel Sigg Motivation The Photon Calibrator has been developed to provide a physically independent means of
Calibration of the LIGO Interferometer Using the Recoil of Photons Justice Bruursema Mentor: Daniel Sigg Motivation The Photon Calibrator has been developed to provide a physically independent means of
Beam Stabilizer Add-on Card
 Beam Stabilizer Add-on Card User s Manual September 19, 2011 Revision A 1 Introduction: Beam stabilizers are used to correct for dynamic laser beam pointing errors in optical systems. These pointing errors
Beam Stabilizer Add-on Card User s Manual September 19, 2011 Revision A 1 Introduction: Beam stabilizers are used to correct for dynamic laser beam pointing errors in optical systems. These pointing errors
Polarization. Components of Polarization: Malus Law. VS203B Lecture Notes Spring, Topic: Polarization
 VS03B Lecture Notes Spring, 013 011 Topic: Polarization Polarization Recall that I stated that we had to model light as a transverse wave so that we could use the model to explain polarization. The electric
VS03B Lecture Notes Spring, 013 011 Topic: Polarization Polarization Recall that I stated that we had to model light as a transverse wave so that we could use the model to explain polarization. The electric
LECTURE 37: Ray model of light and Snell's law
 Lectures Page 1 Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: LECTURE 37: Ray model of light and Snell's law Understand when the ray model of light is applicable. Be able to apply Snell's Law of Refraction to any system.
Lectures Page 1 Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: LECTURE 37: Ray model of light and Snell's law Understand when the ray model of light is applicable. Be able to apply Snell's Law of Refraction to any system.
Dielectric Optical-Controllable Magnifying Lens. by Nonlinear Negative Refraction
 Dielectric Optical-Controllable Magnifying Lens by Nonlinear Negative Refraction Jianjun Cao 1, Ce Shang 2, Yuanlin Zheng 1,Yaming Feng, Xianfeng Chen 1,3, Xiaogan Liang 4 and Wenjie Wan 1,2,3* 1 Key Laboratory
Dielectric Optical-Controllable Magnifying Lens by Nonlinear Negative Refraction Jianjun Cao 1, Ce Shang 2, Yuanlin Zheng 1,Yaming Feng, Xianfeng Chen 1,3, Xiaogan Liang 4 and Wenjie Wan 1,2,3* 1 Key Laboratory
Development of future spray imaging techniques using General Purpose GPU accelerated Monte Carlo simulation
 ICLASS 2012, 12 th Triennial International Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Heidelberg, Germany, September 2-6, 2012 Development of future spray imaging techniques using General Purpose
ICLASS 2012, 12 th Triennial International Conference on Liquid Atomization and Spray Systems, Heidelberg, Germany, September 2-6, 2012 Development of future spray imaging techniques using General Purpose
Optical Sectioning. Bo Huang. Pharmaceutical Chemistry
 Optical Sectioning Bo Huang Pharmaceutical Chemistry Approaches to 3D imaging Physical cutting Technical difficulty Highest resolution Highest sensitivity Optical sectioning Simple sample prep. No physical
Optical Sectioning Bo Huang Pharmaceutical Chemistry Approaches to 3D imaging Physical cutting Technical difficulty Highest resolution Highest sensitivity Optical sectioning Simple sample prep. No physical
Introduction to Inverse Problems
 Introduction to Inverse Problems What is an image? Attributes and Representations Forward vs Inverse Optical Imaging as Inverse Problem Incoherent and Coherent limits Dimensional mismatch: continuous vs
Introduction to Inverse Problems What is an image? Attributes and Representations Forward vs Inverse Optical Imaging as Inverse Problem Incoherent and Coherent limits Dimensional mismatch: continuous vs
Company Pioneer in Ytterbium ultrafast lasers High quality manufacturing Intense and active R&D Located in Bordeaux and Paris US offices in Boston and
 High power ultrafast lasers Eric Mottay High Brightness Laser sources Burgdorf, November 26, 2009 Company Pioneer in Ytterbium ultrafast lasers High quality manufacturing Intense and active R&D Located
High power ultrafast lasers Eric Mottay High Brightness Laser sources Burgdorf, November 26, 2009 Company Pioneer in Ytterbium ultrafast lasers High quality manufacturing Intense and active R&D Located
Lasers and Femtosecond Lasers
 1/26/2004 Lasers and Femtosecond Lasers As you learned in the lecture, a Ti:sapphire laser can operate either as a tunable, continuous-wave (CW) laser, or a pulsed, self-modelocked, laser. A slight alignment
1/26/2004 Lasers and Femtosecond Lasers As you learned in the lecture, a Ti:sapphire laser can operate either as a tunable, continuous-wave (CW) laser, or a pulsed, self-modelocked, laser. A slight alignment
Two slit interference - Prelab questions
 Two slit interference - Prelab questions 1. Show that the intensity distribution given in equation 3 leads to bright and dark fringes at y = mλd/a and y = (m + 1/2) λd/a respectively, where m is an integer.
Two slit interference - Prelab questions 1. Show that the intensity distribution given in equation 3 leads to bright and dark fringes at y = mλd/a and y = (m + 1/2) λd/a respectively, where m is an integer.
Lecture 05. First Example: A Real Lidar
 Lecture 05. First Example: A Real Lidar Brief review of lidar basics K Doppler lidar system architecture K lidar signal estimate from lidar equation Comparison of estimate to reality Summary Review of
Lecture 05. First Example: A Real Lidar Brief review of lidar basics K Doppler lidar system architecture K lidar signal estimate from lidar equation Comparison of estimate to reality Summary Review of
UNIT IV - Laser and advances in Metrology 2 MARKS
 UNIT IV - Laser and advances in Metrology 2 MARKS 81. What is interferometer? Interferometer is optical instruments used for measuring flatness and determining the lengths of slip gauges by direct reference
UNIT IV - Laser and advances in Metrology 2 MARKS 81. What is interferometer? Interferometer is optical instruments used for measuring flatness and determining the lengths of slip gauges by direct reference
Uncooled mini-dil 980nm Pump Laser Module. Applications
 LU96Z***-7* Uncooled mini-dil 980nm Pump Laser Module Features Up to 300mW kink-free power over full operating temperature range Operating temperature range from -5 C to +75 C Polarization maintaining
LU96Z***-7* Uncooled mini-dil 980nm Pump Laser Module Features Up to 300mW kink-free power over full operating temperature range Operating temperature range from -5 C to +75 C Polarization maintaining
LASCAD Tutorial No. 1: Modeling a laser cavity with end pumped rod
 LASCAD Tutorial No. 1: Modeling a laser cavity with end pumped rod Revised: January 15, 2009 Copyright 2006-2009 LAS-CAD GmbH Table of Contents 1 Starting LASCAD and Defining a Simple Laser Cavity...1
LASCAD Tutorial No. 1: Modeling a laser cavity with end pumped rod Revised: January 15, 2009 Copyright 2006-2009 LAS-CAD GmbH Table of Contents 1 Starting LASCAD and Defining a Simple Laser Cavity...1
Development of automated ultraviolet laser beam profiling system using fluorometric technique
 Development of automated ultraviolet laser beam profiling system using fluorometric technique BB Shrivastava*, NS Benerji, P Bhatnagar, HS Vora a and U Nundy Chemical and Excimer Laser Section a Laser
Development of automated ultraviolet laser beam profiling system using fluorometric technique BB Shrivastava*, NS Benerji, P Bhatnagar, HS Vora a and U Nundy Chemical and Excimer Laser Section a Laser
Models of Light The wave model: The ray model: The photon model:
 Models of Light The wave model: under many circumstances, light exhibits the same behavior as sound or water waves. The study of light as a wave is called wave optics. The ray model: The properties of
Models of Light The wave model: under many circumstances, light exhibits the same behavior as sound or water waves. The study of light as a wave is called wave optics. The ray model: The properties of
Optoelectronic packaging: from challenges to solutions
 Optoelectronic packaging: from challenges to solutions Seminar on Optical Packaging Alpnach Dorf Mai 16, 2012 Christian Bosshard CSEM Center Central Switzerland Challenges in optoelectronic packaging General
Optoelectronic packaging: from challenges to solutions Seminar on Optical Packaging Alpnach Dorf Mai 16, 2012 Christian Bosshard CSEM Center Central Switzerland Challenges in optoelectronic packaging General
Compact visible laser modules. QD laser, Inc.
 Compact visible laser modules and NIR DFBs with high speed modulation October, 2012 QD laser, Inc. DC0301-02 Contents About QD Laser, Inc. NIR DFB laser Introduction of semiconductor DFB laser Applications
Compact visible laser modules and NIR DFBs with high speed modulation October, 2012 QD laser, Inc. DC0301-02 Contents About QD Laser, Inc. NIR DFB laser Introduction of semiconductor DFB laser Applications
The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other.
 CH. 24 Wave Optics The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other. The waves need to have identical wavelengths. Can t be coherent without this.
CH. 24 Wave Optics The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other. The waves need to have identical wavelengths. Can t be coherent without this.
DEVELOPING AND 3D PROTOTYPING OF A CUSTOMIZED DEVICE FOR CNC LASER MICRO-MACHINING
 SCIENTIFIC PAPERS DEVELOPING AND 3D PROTOTYPING OF A CUSTOMIZED DEVICE FOR CNC LASER MICRO-MACHINING Mihaiela ILIESCU 1 ABSTRACT: There was the need of developing a device for CNC laser micro-machining
SCIENTIFIC PAPERS DEVELOPING AND 3D PROTOTYPING OF A CUSTOMIZED DEVICE FOR CNC LASER MICRO-MACHINING Mihaiela ILIESCU 1 ABSTRACT: There was the need of developing a device for CNC laser micro-machining
LASer Cavity Analysis and Design
 The unique combination of simulation tools for LASer Cavity Analysis and Design LASCAD is an industry-leading software package providing multiphysics analysis of the complicated interaction between thermal
The unique combination of simulation tools for LASer Cavity Analysis and Design LASCAD is an industry-leading software package providing multiphysics analysis of the complicated interaction between thermal
Detectors for Future Light Sources. Gerhard Grübel Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron (DESY) Notke-Str. 85, Hamburg
 Detectors for Future Light Sources Gerhard Grübel Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron (DESY) Notke-Str. 85, 22607 Hamburg Overview Radiation from X-Ray Free Electron lasers (XFEL, LCLS) Ultrafast detectors
Detectors for Future Light Sources Gerhard Grübel Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron (DESY) Notke-Str. 85, 22607 Hamburg Overview Radiation from X-Ray Free Electron lasers (XFEL, LCLS) Ultrafast detectors
StingRay and BioRay FEATURES
 StingRay and BioRay Coherent s high-performance laser in a compact module, measuring only 19 mm in diameter, is the StingRay and BioRay product families. Modular design using the industries premier laser
StingRay and BioRay Coherent s high-performance laser in a compact module, measuring only 19 mm in diameter, is the StingRay and BioRay product families. Modular design using the industries premier laser
This thesis is submitted as the fulfilment of the Requirement for the award of degree of. By research from
 D e v e lo p m e n t o f a L a s e r B a s e d I n s p e c t io n S y s t e m f o r S u r f a c e D e fe c t D e te c tio n By M o h a m m e d B e la l H o s s a in B h u ia n, B. S c. E n g. This thesis
D e v e lo p m e n t o f a L a s e r B a s e d I n s p e c t io n S y s t e m f o r S u r f a c e D e fe c t D e te c tio n By M o h a m m e d B e la l H o s s a in B h u ia n, B. S c. E n g. This thesis
Two Chemical Kinetics Models of a Laser
 Two Chemical Kinetics Models of a Laser Daniel Kerner, Ph.D. Civilized Software Inc. 12109 Heritage Park Circle Silver Spring, MD 20906 USA Tel: (301) 962-3711 Email: csi@civilized.com URL: http://www.civilized.com
Two Chemical Kinetics Models of a Laser Daniel Kerner, Ph.D. Civilized Software Inc. 12109 Heritage Park Circle Silver Spring, MD 20906 USA Tel: (301) 962-3711 Email: csi@civilized.com URL: http://www.civilized.com
Ron Ferril SBCC Physics 101 Chapter Jul27A Page 1 of 15. Chapter 10 Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction and Interference
 Ron Ferril SBCC Physics 101 Chapter 10 2017Jul27A Page 1 of 15 Chapter 10 Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction and Interference Overview When waves are incident at a boundary between media (such as water
Ron Ferril SBCC Physics 101 Chapter 10 2017Jul27A Page 1 of 15 Chapter 10 Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction and Interference Overview When waves are incident at a boundary between media (such as water
Physics 625 Femtosecond laser Project
 Physics 625 Femtosecond laser Project The purpose of this project is for each person to gain experience in designing part of a femtosecond laser system for pump-probe experiments. The system diagram is
Physics 625 Femtosecond laser Project The purpose of this project is for each person to gain experience in designing part of a femtosecond laser system for pump-probe experiments. The system diagram is
1 Laboratory #4: Division-of-Wavefront Interference
 1051-455-0073, Physical Optics 1 Laboratory #4: Division-of-Wavefront Interference 1.1 Theory Recent labs on optical imaging systems have used the concept of light as a ray in goemetrical optics to model
1051-455-0073, Physical Optics 1 Laboratory #4: Division-of-Wavefront Interference 1.1 Theory Recent labs on optical imaging systems have used the concept of light as a ray in goemetrical optics to model
Electrical Power Supply Matrix Systems
 Electrical Power Supply Matrix Systems A.Yu. Goncharov, PhD in Technical Sciences - AEPS-GROUP President Distributed electrical power supply systems consisting of a specified set of modules may be easily
Electrical Power Supply Matrix Systems A.Yu. Goncharov, PhD in Technical Sciences - AEPS-GROUP President Distributed electrical power supply systems consisting of a specified set of modules may be easily
3D TeraHertz Tomography
 3D TeraHertz Tomography B. Recur, 3 A. Younus, 1 S. Salort, 2 P. Mounaix, 1 B. Chassagne, 2 P. Desbarats, 3 1 LOMA, Université de Bordeaux / CNRS 2 ALPhANOV, Centre Technologique Optique et Lasers, Université
3D TeraHertz Tomography B. Recur, 3 A. Younus, 1 S. Salort, 2 P. Mounaix, 1 B. Chassagne, 2 P. Desbarats, 3 1 LOMA, Université de Bordeaux / CNRS 2 ALPhANOV, Centre Technologique Optique et Lasers, Université
Laser RangeFinders. Hamed Lotfizad Mehdi Modaresi Professor.. ...Dr. H.Tagirad
 Laser RangeFinders Hamed Lotfizad......791210122 Mehdi Modaresi.791210125 Professor.....Dr H.Tagirad The Invention of the Laser The Invention of the Laser Invented in 1958 by Charles Townes and Arthur
Laser RangeFinders Hamed Lotfizad......791210122 Mehdi Modaresi.791210125 Professor.....Dr H.Tagirad The Invention of the Laser The Invention of the Laser Invented in 1958 by Charles Townes and Arthur
waves_05 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
 waves_05 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 waves_05: MINDMAP SUMMARY - ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Electromagnetic waves, electromagnetic radiation, speed of light, electromagnetic spectrum, electric field, magnetic field,
waves_05 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 waves_05: MINDMAP SUMMARY - ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Electromagnetic waves, electromagnetic radiation, speed of light, electromagnetic spectrum, electric field, magnetic field,
Chapter 2: Wave Optics
 Chapter : Wave Optics P-1. We can write a plane wave with the z axis taken in the direction of the wave vector k as u(,) r t Acos tkzarg( A) As c /, T 1/ and k / we can rewrite the plane wave as t z u(,)
Chapter : Wave Optics P-1. We can write a plane wave with the z axis taken in the direction of the wave vector k as u(,) r t Acos tkzarg( A) As c /, T 1/ and k / we can rewrite the plane wave as t z u(,)
Optics Vac Work MT 2008
 Optics Vac Work MT 2008 1. Explain what is meant by the Fraunhofer condition for diffraction. [4] An aperture lies in the plane z = 0 and has amplitude transmission function T(y) independent of x. It is
Optics Vac Work MT 2008 1. Explain what is meant by the Fraunhofer condition for diffraction. [4] An aperture lies in the plane z = 0 and has amplitude transmission function T(y) independent of x. It is
Ray Optics. Lecture 23. Chapter 34. Physics II. Course website:
 Lecture 23 Chapter 34 Physics II Ray Optics Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 34: Section 34.1-3 Ray Optics Ray Optics Wave
Lecture 23 Chapter 34 Physics II Ray Optics Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 34: Section 34.1-3 Ray Optics Ray Optics Wave
1.Rayleigh and Mie scattering. 2.Phase functions. 4.Single and multiple scattering
 5 November 2014 Outline 1.Rayleigh and Mie scattering 2.Phase functions 3.Extinction 4.Single and multiple scattering Luca Lelli luca@iup.physik.uni-bremen.de Room U2080 Phone 0421.218.62097 Scattering
5 November 2014 Outline 1.Rayleigh and Mie scattering 2.Phase functions 3.Extinction 4.Single and multiple scattering Luca Lelli luca@iup.physik.uni-bremen.de Room U2080 Phone 0421.218.62097 Scattering
Pump laser requirements for next generation lasers.
 Dr. Lukas Krainer, CEO lukas.krainer@onefive.com Pump laser requirements for next generation lasers. Outline Company introduction Product portfolio Pump lasers field of use Pump lasers for high power cw
Dr. Lukas Krainer, CEO lukas.krainer@onefive.com Pump laser requirements for next generation lasers. Outline Company introduction Product portfolio Pump lasers field of use Pump lasers for high power cw
RoHS COMPLIANT 2002/95/EC
 Superlum Broadband Light Sources cblmd-series (2nd Generation) Compact Broadband Light Technical Product Specification Document Number SL.3328.00.000D3 June 2017 Revision 001 ATTENTION ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE
Superlum Broadband Light Sources cblmd-series (2nd Generation) Compact Broadband Light Technical Product Specification Document Number SL.3328.00.000D3 June 2017 Revision 001 ATTENTION ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE
1.1 The HeNe and Fourier Lab CCD Camera
 Chapter 1 CCD Camera Operation 1.1 The HeNe and Fourier Lab CCD Camera For several experiments in this course you will use the CCD cameras to capture images or movies. Make sure to copy all files to your
Chapter 1 CCD Camera Operation 1.1 The HeNe and Fourier Lab CCD Camera For several experiments in this course you will use the CCD cameras to capture images or movies. Make sure to copy all files to your
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Important announcements Homework #2 is assigned, due Feb. 11 Mid-term exam
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Important announcements Homework #2 is assigned, due Feb. 11 Mid-term exam
Second Year Optics 2017 Problem Set 1
 Second Year Optics 2017 Problem Set 1 Q1 (Revision of first year material): Two long slits of negligible width, separated by a distance d are illuminated by monochromatic light of wavelength λ from a point
Second Year Optics 2017 Problem Set 1 Q1 (Revision of first year material): Two long slits of negligible width, separated by a distance d are illuminated by monochromatic light of wavelength λ from a point
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
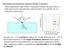 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
OptoSLT nano. Preserve vision in record time
 OptoSLT nano Preserve vision in record time OptoSLT nano THE FIRST 1ns SLT DEVICE ON THE MARKET Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) is an advanced, non-invasive, primary or secondary treatment for raised
OptoSLT nano Preserve vision in record time OptoSLT nano THE FIRST 1ns SLT DEVICE ON THE MARKET Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) is an advanced, non-invasive, primary or secondary treatment for raised
Part 7 Holography. Basic Hologram Setup
 Part 7 Holography Basic Holographic Technique Light Sources Recording Materials Holographic Non-Destructive Testing Real-Time Double-Exposure Time-Average 2000 - James C. Wyant Part 7 Page 1 of 28 Basic
Part 7 Holography Basic Holographic Technique Light Sources Recording Materials Holographic Non-Destructive Testing Real-Time Double-Exposure Time-Average 2000 - James C. Wyant Part 7 Page 1 of 28 Basic
