Clinical Metadata Metadata management with a CDISC mindset
|
|
|
- Cassandra Smith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Paper SI02 Clinical Metadata Metadata management with a CDISC mindset Andrew Ndikom, Clinical Metadata, London, United Kingdom Liang Wang, Clinical Metadata, London, United Kingdom ABSTRACT Metadata is now an integral part of the clinical trial process. CDISC provides the framework for this metadata and Define.xml provides a way to share the final product. There is, however, no standard way to efficiently collect, manage and collaborate in the process of creating metadata. ClinicalMetadata.com provides an end-to-end metadata management solution, including CDASH, SDTM, ADaM and output metadata. It generates SAS code fragments and submission deliverables, automating repetitive programming tasks, accelerating and simplifying the development process. Clinical Metadata is built as a web-based single page application, using the latest technologies and practices, and is securely hosted in the Amazon Web Services cloud. Its visualisation tools present the user with a high-level metadata overview and allows them to drill down into individual metadata fragments. In-built standards management, traceability and impact analysis tools help users understand the relationships between each metadata element as well as encourage Agile and collaborative ways of working. KEYWORDS CDISC, SDTM, ADaM, Clinical Metadata, metadata repository, data standards, define.xml INTRODUCTION This paper begins with a short introduction into what metadata is, with a particular focus on metadata within clinical trials. It then provides a short explanation of why metadata and data standards have become an important part of the clinical trial process in recent years. It then moves on to look at the most widely adopted metadata solution and outlines the five key problems with this approach. Subsequently, the paper provides an overview of Clinical Metadata, an end-to-end metadata management solution. It briefly discusses the technology and software development principles which underpin its design, explaining how much of the inspiration for the tool came from observing how similar problems have been solved in other industries. Finally, the paper explores some of the tool s features, while demonstrating how it overcomes key problems with existing metadata management tools. WHAT I S METADATA Metadata is usually defined as data about data. This definition fails to convey its importance. More accurately, metadata could be defined as the information required to contextualize and understand a given data element. Within a clinical trial, metadata may exist at many levels. For example, dataset level metadata describes the properties of a dataset, for example: Dataset name Dataset label Dataset Class. Variable level metadata describes variable level properties and may consist of the following aspects: Variable name Variable label Variable format Variable type Controlled terminology Source variables Derivation In the following example we can see how data without metadata has little purpose or meaning.
2 DATA WITHOUT METADATA Consider a possible piece of clinical data: 192 Viewed in isolation it does not have utility or meaning, perhaps it is the result of some laboratory test, perhaps it is a patient s height measured in centimetres. If we attach the following metadata to it: Type: Numeric Length 8 Format: DATE9. NAME: BRTHDT Source: DM.BRTHDTC Derivation: Equal to DM.BRTHDTC converted to a numeric date. Label: Date of Birth (N) It becomes apparent that this number represents the date of birth of a patient, which in this case is the 11 th July WHY DO WE NEED ROBUST METADATA AND DATA STANDARDS IN CLINICAL TRIALS? Technological changes over the past 70 years have enabled the size, scope and complexity of clinical trials to increase. The pharmaceutical industry has moved from relatively simple paper-based trials collecting little information about a small patient population, to large complex trials where data is captured, transferred, transformed, stored and processed electronically. The number of sponsors, trials and analyses has also greatly increased, leading to the availability of ever-increasing quantities of data. Managing and using this data without industry wide standards was increasingly inefficient and time consuming for sponsors, those working in the drug development industry and regulatory authorities. In 2004 Lester Crawford, former Commissioner of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) stated: FDA reviewers spend too much valuable time simply reorganising large amounts of data submitted in varying formats. Having the data presented in a standard structure will improve FDA s ability to evaluate the data and help speed new discoveries to the public. 1 Since then there has been a move within the industry to adopt data standards and the collection, sharing, storage and presentation has become an increasingly important aspect of the clinical trial process. The Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) was formed in Its aim is: To develop and support global, platform-independent data standards that enable information system interoperability to improve medical research and related areas of healthcare. Its Foundational Standards provide the basis for supporting clinical and non-clinical research processes from end to end. CDISC standards have been accepted across the industry. What s more, the FDA 2 and other regulatory authorities now insist sponsors submit their data in a CDISC compliant format. CDISC details some of the benefits of adopting its standards as: Facilitated data sharing Complete traceability Improved data quality Streamlined processes. Over time the number of standards produced by CDISC has greatly increased, see for example, Winnpenny, G (2014) What s new in ADaM? 3. This increase offers opportunities for sponsors to standardize and improve their processes, however, understanding and conforming to these standards has presented challenges to sponsors.
3 CURRENT APPROACHES TO DATA STANDARDISATION AND METADATA MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS The adoption of data standardisation within the industry has been varied. Many sponsors have adopted a responsive rather than pro-active approach. Rather than using data standardisation to transform and improve the way they work, many sponsors have tried to retain their existing workflows and viewed each new metadata standard as a cumbersome add-on to their existing process. Sponsors have often built separate systems to manage each additional class of metadata as it has been introduced by CDISC. In trying to catch up, sponsors have sought the fastest, most readily available tool to deliver the desired solution. In many instances, the most readily accessible solution has been to use supplementary Excel spreadsheets and Word documents. As new classes of metadata have been introduced, this approach has led to a disjointed and complex web of spreadsheets to manage metadata at each stage of the process. Consider the following potential metadata and programming tracking system. It comprises 12 spreadsheets, a Word document and a PDF and is designed to manage an entire study s metadata, from raw data to reporting, including CDASH metadata, SDTM dataset metadata and annotated mock-ups. This fragmented solution presents many issues, including these five key problems: 1. Multiple spreadsheets are needed per study, leading to disconnected metadata silos. 2. It is difficult to understand the relationships between metadata elements. 3. Reading and writing information directly from the metadata is complicated. 4. It is complicated for multiple users to collaborate on same file, and for users working on one file to understand how their work impacts other users. 5. Assessment of CDISC compliance and standards management relies on additional tools outside of the system. In summary, CDISC lists some of the advantages of adopting its standards as: Facilitated data sharing Complete traceability Improved data quality Streamlined processes. Many implementations of CDISC however, have led to opaque metadata managements systems with in-built data redundancy and a lack of traceability. An alternative approach is required. Clinical Metadata provides this solution.
4 CLINICAL METADATA AN END-TO-END METADATA AND PROJECT MANAGEMENT SOLUTION Clinical Metadata is a complete metadata, data standards and project management solution. It uses the latest technologies and practices from the software industry and is built upon the CDISC core principles of traceability and transparency. Some of its key features include: 1. End-to-end metadata management within a trial. 2. Standards governance. 3. Metadata driven SAS code generation. 4. Evaluation of CDISC compliance. 5. Creation of submission deliverables. 6. Real-time assessment of study status. 7. Communication tools. 8. Metadata visualization. 9. Impact analysis 10. Metadata analysis. THE TECHNOLOGY As mentioned previously, technological developments in the financial services have been an inspiration for this new tool. During the past few years, as internet technologies have matured, the financial services industry has gradually moved from using desktop-based applications to web-based applications. This change is being reflected in other industries, including the pharmaceutical industry, where similar concerns have held back this transition in the past, such as: Information security and privacy System availability and network connectivity User authentication and authorization Data storage capacity. There are now effective solutions to these concerns. Companies making the transition from desktop applications to web applications benefit in terms of cost and efficiency, and individual users benefit from simpler workflows: Software does not require installation and can be accessed with a web browser, so there is less system maintenance overhead. The latest features are always immediately available and software upgrades are not necessary. Data can be accessed anywhere with an internet connection and does not rely on an individual PC. Data is stored securely in the cloud and back-ups are created automatically. Storage capacity is not limited by available hardware. Collaboration is improved as multiple users can access the same set of data concurrently. Clinical Metadata has been developed using an Agile methodology, with a focus on good User Experience (UX). It learns from software projects across many other industries. Features are continuously added and improved, those that add the most value to end users are prioritised, and regular deployments mean that they are quickly available. Automated testing means that problems are identified before going live and development time is reduced to a minimum. Clinical Metadata s focus is to deliver an application that is clean, simple and easy to use.
5 Data is secured through a variety of measures, including: PhUSE 2017 Traffic to the web application is secured using HTTPS. Users accessing the non-secure HTTP website are automatically redirected to HTTPS. Industry standard security practices are followed for login credential storage and session management. The database is secured, it is not visible to the outside world and access is restricted to within our network. Access to server configuration is secured using 2-factor authentication. The system has been built with the following technologies: C# and ASP.NET for the server side application logic SQL Server for data storage Angular and TypeScript for client side User Interface (UI) D3 for data visualisations AWS for hosting and infrastructure Git for source code version control.
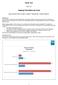
6 CLINICAL METADATA FEATURES Clinical Metadata can assist you in managing your metadata and data standards by overcoming the five key metadata and project management challenges identified earlier in the following ways. Through these five points we will outline some of the varied benefits of the tool. #1 NO MORE METADATA SILOS Traditional approaches to managing metadata can often result in disconnected metadata silos. Data exchange between these silos either does not happen, relies on human interventions or complicated bespoke programming. Clinical Metadata is designed to provide a truly end-to-end solution, as shown in the following image 1 : The system is designed around the principle that metadata should be defined once and used multiple times. Where possible, each metadata element is defined in terms of its predecessors, or imported from a higher level of the standards hierarchy. Built upon relational database principles, the individual properties of an element are inherited rather than duplicated, thus increasing efficiency, reducing the possibility of data entry errors and leading to greater traceability across the entire study metadata lifecycle. For example, in the disconnected metadata world, SDTM and ADaM metadata might be stored in separate spreadsheets. Metadata for a variable which exists in both SDTM and ADaM would need to be manually entered twice, once in each spreadsheet. This process is error-prone and inefficient. Within Clinical Metadata it is possible to: Define metadata once at the SDTM level. Use a point and click system to indicate that the ADaM variable is a direct copy of the SDTM variable. A permanent link is then established between these variables, meaning that any changes to the SDTM metadata for an element will automatically be reflected in the ADaM metadata. 1 * Functionality to be added quarter
7 #2 DIFFICULTY IN UNDERSTANDING THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN METADATA ELEMENTS Within the Excel based world, important metadata, for example variable names, is often embedded in human readable text fields which are not machine readable. Each metadata element generally exists in isolation, and there is no way to easily access the metadata of related elements. Within Clinical Metadata each element is connected to its related elements. Visualization tools help the user to understand these relationships. For example, consider a potential derivation for an ADaM variable. Name Label Derivation ONTRTFL On Treatment Record Flag Indication of whether concomitant medication was ongoing during treatment window. Set equal to "Y" if TRTSDT <= ASTDT <= TRTEDT + 28 or ASTDT <= trtsdt AND AENDT >=TRTSDT Otherwise ONTRTFL = "" A user familiar with CDISC could probably decipher this derivation, however users with limited CDISC knowledge or who are new to the industry would possibly be confused. They may have the following questions: Are the source variables TRTSDT, ASTDT, TRTEDT and AENDT taken from ADaM or SDTM? In which dataset is each of these variables? Where is the metadata of each of the source variables? How are the source variables created earlier in the process and how do they link back to the Case Report Form? Is the ONTRTFL variable used in any downstream processes, if so which? Clinical Metadata uses visualisations to ensure that users can easily understand the relationships between metadata elements and to provide end-to-end traceability. Clinical Metadata s visualisations are built using the latest web technologies. Its drill down functionality allows the user to switch between a high level visualisation, i.e. showing the relationships between datasets, and a lower level, i.e. showing the relationships between variables. Hover over functionality allows the user to see, not only the relationship between variables, but also the derivation rule used to map from one variable to another.
8 #3 MAKING PROGRAMMATIC USE OF METADATA Many sponsors moved towards CDISC from a situation where they relied on existing black box software capable of reading input data, performing complex derivations and outputting statistical reports. CDISC standards were often regarded as an undesirable adjunct to this streamlined process and little thought was given about the transformational possibilities of true end-to-end metadata management systems, for example that metadata could be used to create code. Clinical Metadata allows users to generate SAS code and submission deliverables directly from the tool including: Variable mappings Metadata correct zero observation dataset shells Define XML Annotated CRFs. Consider the example of mapping the variable COUNTRY to ACOUNTRY within the ADaM ADSL dataset. Previously users might have: 1. Manually created the COUNTRY codelist. 2. Manually created the ACOUNTRY codelist. 3. Manually created the metadata for the ADSL.COUNTRY variable. 4. Manually created the metadata for the ADSL.ACOUNTRY variable, as well as defined a pseudocode derivation rule. 5. Manually created the SAS code required to perform the mapping. Within Clinical Metadata the user: a. Imports the COUNTRY variable from SDTM.DM. b. Imports the ACOUNTRY variable from a project library. c. Creates the ACOUNTRY codelist. d. Uses a point and click system to define the mapping. The tool will then automatically build the SAS code needed to perform the derivation.
9 #4 FACILITATING COLLABORATION BETWEEN MULTIPLE USERS Currently, most approaches to managing metadata do not facilitate collaboration between users. Information is fragmented across multiple non-standardised documents. People working at one stage of the process have little awareness of how their deliverables impact their colleagues working at other stages. This type of approach may have been suitable when projects used waterfall project management methodologies, but as sponsors transition to Agile and modern ways of working, it is no longer appropriate. Clinical Metadata promotes collaboration between users by: 1. Ensuring that all users always access the latest version of the specifications. 2. Using in-built communication tools, meaning information is exchanged between users via the system, rather than being hidden in s. 3. Providing project management utilities so that users can clearly understand the status of each stage of the project. 4. Allowing the user to understand how metadata within the system has changed over time. For example, in existing systems users might share comments about a particular variable by . Anyone not in the chain would not be aware of the issues being discussed. Within Clinical Metadata comments are exchanged within the system, through a chat function, allowing everyone to see what is being discussed, by whom and when.
10 #5 MANAGING STANDARDS AND PROMOTING CDISC COMPLIANCE In previous disconnected metadata systems, metadata at different levels of the standards hierarchy often existed in separate files. Importing or promoting metadata between levels usually relied on manual copying and pasting information between spreadsheets. Within clinical trials it is often desirable to create standard program code which could be re-used across studies. In order to do this users needed to understand which metadata elements were the same across studies. However, disconnected metadata management systems did not facilitate this sort of comparison. Within Clinical Metadata, all metadata is held within one connected system built to facilitate the exchange and better understanding of metadata. Consider for example a typical data standards implementation. Previously, information held at each level of the hierarchy comprised a multitude of disconnected files. Even before attempting to understand the global metadata environment, considerable time and attention had to be devoted to rudimentary file management. For example consider the following data standards system for a sponsor, where we assume that at each analysis, study, project therapeutic area or corporate standard contains the files shown in the image on page 3. It is easy to see how the number of disparate files quickly becomes unmanageable.
11 Within Clinical Metadata all metadata is held within one system. Metadata can be imported down through the standards hierarchy, or promoted upwards for evaluation through a governance process, increasing both accuracy and efficiency and helping, for example, to avoid the common scenario where different names are given to variables of the same meaning across studies. CONCLUSION We have explained how, in recent years, metadata and data standards have become an important part of the clinical trial process. Inefficient metadata management solutions have, however, meant that sponsors failed to realise the transformative possibilities of data standards. The financial services industry has successfully transitioned from desktop based to web-based applications, and is now realising the benefits of this change in terms of cost, efficiency and simplification of workflows. A similar transition is required in the way sponsors manage their metadata. In a Business Case for CDISC Standards (2009) Rozwell et al 4, the authors set out a convincing argument for CDISC as well as detailing some impressive efficiency savings that can be obtained through adopting CDISC standards. Many sponsors have failed to fully realise these potential efficiencies because they have implemented metadata management processes that are based on outdated technologies, leading to systems that are fragmented, hard to maintain, and with large amounts of data redundancy. ClinicalMetadata.com is designed to overcome these problems. It leverages the latest technologies to deliver an integrated web-based, metadata management solution that enables the user to fully realise the benefits of CDISC and data standardisation.
12 REFERENCES 1 Handelsman D (2005) An Introduction to CDISC. Retrieved from: 2 The FDA (2016) Study Data Standards, what you need to know. Retrieved from: missions/ucm pdf 3 Winnpenny, G (2014) What s new in ADaM? Retrieved from: 4 Rozwell C, Kush R, Helton E, Newby F, Mason T, (2009) Business Case for CDISC Standards. Retrieved from: CONTACT INFORMATION Your comments and questions are valued and encouraged. Contact the authors at: Author Name: Andrew Ndikom Company: Clinical Metadata City: London andrew.ndikom@clinicalmetadata.com Web: Author Name: Liang Wang Company: Clinical Metadata City: London liang.wang@clinicalmetadata.com Web:
Clinical Metadata A complete metadata and project management solu6on. October 2017 Andrew Ndikom and Liang Wang
 A complete metadata and project management solu6on. October 2017 Andrew Ndikom and Liang Wang 1 Agenda How is metadata currently managed within the industry? Five key problems with current approaches.
A complete metadata and project management solu6on. October 2017 Andrew Ndikom and Liang Wang 1 Agenda How is metadata currently managed within the industry? Five key problems with current approaches.
Why organizations need MDR system to manage clinical metadata?
 PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper SS-17 Why organizations need MDR system to manage clinical metadata? Abhinav Jain, Ephicacy Consulting Group Inc. ABSTRACT In the last decade, CDISC standards undoubtedly have transformed
PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper SS-17 Why organizations need MDR system to manage clinical metadata? Abhinav Jain, Ephicacy Consulting Group Inc. ABSTRACT In the last decade, CDISC standards undoubtedly have transformed
PharmaSUG. companies. This paper. will cover how. processes, a fairly linear. before moving. be carried out. Lifecycle. established.
 PharmaSUG 2016 - Paper PO17 Standards Implementationn & Governance: Carrot or Stick? Julie Smiley, Akana, San Antonio, Texas Judith Goud, Akana, Bennekom, Netherlands ABSTRACT With the looming FDA mandate
PharmaSUG 2016 - Paper PO17 Standards Implementationn & Governance: Carrot or Stick? Julie Smiley, Akana, San Antonio, Texas Judith Goud, Akana, Bennekom, Netherlands ABSTRACT With the looming FDA mandate
CDASH Standards and EDC CRF Library. Guang-liang Wang September 18, Q3 DCDISC Meeting
 CDASH Standards and EDC CRF Library Guang-liang Wang September 18, 2014 2014 Q3 DCDISC Meeting 1 Disclaimer The content of this presentation does not represent the views of my employer or any of its affiliates.
CDASH Standards and EDC CRF Library Guang-liang Wang September 18, 2014 2014 Q3 DCDISC Meeting 1 Disclaimer The content of this presentation does not represent the views of my employer or any of its affiliates.
CDASH MODEL 1.0 AND CDASHIG 2.0. Kathleen Mellars Special Thanks to the CDASH Model and CDASHIG Teams
 CDASH MODEL 1.0 AND CDASHIG 2.0 Kathleen Mellars Special Thanks to the CDASH Model and CDASHIG Teams 1 What is CDASH? Clinical Data Acquisition Standards Harmonization (CDASH) Standards for the collection
CDASH MODEL 1.0 AND CDASHIG 2.0 Kathleen Mellars Special Thanks to the CDASH Model and CDASHIG Teams 1 What is CDASH? Clinical Data Acquisition Standards Harmonization (CDASH) Standards for the collection
Pharmaceuticals, Health Care, and Life Sciences. An Approach to CDISC SDTM Implementation for Clinical Trials Data
 An Approach to CDISC SDTM Implementation for Clinical Trials Data William T. Chen, Merck Research Laboratories, Rahway, NJ Margaret M. Coughlin, Merck Research Laboratories, Rahway, NJ ABSTRACT The Clinical
An Approach to CDISC SDTM Implementation for Clinical Trials Data William T. Chen, Merck Research Laboratories, Rahway, NJ Margaret M. Coughlin, Merck Research Laboratories, Rahway, NJ ABSTRACT The Clinical
How a Metadata Repository enables dynamism and automation in SDTM-like dataset generation
 Paper DH05 How a Metadata Repository enables dynamism and automation in SDTM-like dataset generation Judith Goud, Akana, Bennekom, The Netherlands Priya Shetty, Intelent, Princeton, USA ABSTRACT The traditional
Paper DH05 How a Metadata Repository enables dynamism and automation in SDTM-like dataset generation Judith Goud, Akana, Bennekom, The Netherlands Priya Shetty, Intelent, Princeton, USA ABSTRACT The traditional
Lex Jansen Octagon Research Solutions, Inc.
 Converting the define.xml to a Relational Database to enable Printing and Validation Lex Jansen Octagon Research Solutions, Inc. Leading the Electronic Transformation of Clinical R&D PhUSE 2009, Basel,
Converting the define.xml to a Relational Database to enable Printing and Validation Lex Jansen Octagon Research Solutions, Inc. Leading the Electronic Transformation of Clinical R&D PhUSE 2009, Basel,
Customizing SAS Data Integration Studio to Generate CDISC Compliant SDTM 3.1 Domains
 Paper AD17 Customizing SAS Data Integration Studio to Generate CDISC Compliant SDTM 3.1 Domains ABSTRACT Tatyana Kovtun, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Montville, NJ John Markle, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals,
Paper AD17 Customizing SAS Data Integration Studio to Generate CDISC Compliant SDTM 3.1 Domains ABSTRACT Tatyana Kovtun, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Montville, NJ John Markle, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals,
Harmonizing CDISC Data Standards across Companies: A Practical Overview with Examples
 PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper DS06 Harmonizing CDISC Data Standards across Companies: A Practical Overview with Examples Keith Shusterman, Chiltern; Prathima Surabhi, AstraZeneca; Binoy Varghese, Medimmune ABSTRACT
PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper DS06 Harmonizing CDISC Data Standards across Companies: A Practical Overview with Examples Keith Shusterman, Chiltern; Prathima Surabhi, AstraZeneca; Binoy Varghese, Medimmune ABSTRACT
Study Composer: a CRF design tool enabling the re-use of CDISC define.xml metadata
 Paper SD02 Study Composer: a CRF design tool enabling the re-use of CDISC define.xml metadata Dr. Philippe Verplancke, XClinical GmbH, Munich, Germany ABSTRACT define.xml is often created at the end of
Paper SD02 Study Composer: a CRF design tool enabling the re-use of CDISC define.xml metadata Dr. Philippe Verplancke, XClinical GmbH, Munich, Germany ABSTRACT define.xml is often created at the end of
Standards Driven Innovation
 Standards Driven Innovation PhUSE Annual Conference 2014 Frederik Malfait IMOS Consulting GmbH, Hoffmann-La Roche AG Managing Standards 2 Data Standards Value Proposition Standards are increasingly mandated
Standards Driven Innovation PhUSE Annual Conference 2014 Frederik Malfait IMOS Consulting GmbH, Hoffmann-La Roche AG Managing Standards 2 Data Standards Value Proposition Standards are increasingly mandated
PharmaSUG 2014 PO16. Category CDASH SDTM ADaM. Submission in standardized tabular form. Structure Flexible Rigid Flexible * No Yes Yes
 ABSTRACT PharmaSUG 2014 PO16 Automation of ADAM set Creation with a Retrospective, Prospective and Pragmatic Process Karin LaPann, MSIS, PRA International, USA Terek Peterson, MBA, PRA International, USA
ABSTRACT PharmaSUG 2014 PO16 Automation of ADAM set Creation with a Retrospective, Prospective and Pragmatic Process Karin LaPann, MSIS, PRA International, USA Terek Peterson, MBA, PRA International, USA
How to write ADaM specifications like a ninja.
 Poster PP06 How to write ADaM specifications like a ninja. Caroline Francis, Independent SAS & Standards Consultant, Torrevieja, Spain ABSTRACT To produce analysis datasets from CDISC Study Data Tabulation
Poster PP06 How to write ADaM specifications like a ninja. Caroline Francis, Independent SAS & Standards Consultant, Torrevieja, Spain ABSTRACT To produce analysis datasets from CDISC Study Data Tabulation
CDISC Standards End-to-End: Enabling QbD in Data Management Sam Hume
 CDISC Standards End-to-End: Enabling QbD in Data Management Sam Hume 1 Shared Health and Research Electronic Library (SHARE) A global electronic repository for developing, integrating
CDISC Standards End-to-End: Enabling QbD in Data Management Sam Hume 1 Shared Health and Research Electronic Library (SHARE) A global electronic repository for developing, integrating
The Submission Data File System Automating the Creation of CDISC SDTM and ADaM Datasets
 Paper AD-08 The Submission Data File System Automating the Creation of CDISC SDTM and ADaM Datasets Marcus Bloom, Amgen Inc, Thousand Oaks, CA David Edwards, Amgen Inc, Thousand Oaks, CA ABSTRACT From
Paper AD-08 The Submission Data File System Automating the Creation of CDISC SDTM and ADaM Datasets Marcus Bloom, Amgen Inc, Thousand Oaks, CA David Edwards, Amgen Inc, Thousand Oaks, CA ABSTRACT From
Implementing CDISC Using SAS. Full book available for purchase here.
 Implementing CDISC Using SAS. Full book available for purchase here. Contents About the Book... ix About the Authors... xv Chapter 1: Implementation Strategies... 1 The Case for Standards... 1 Which Models
Implementing CDISC Using SAS. Full book available for purchase here. Contents About the Book... ix About the Authors... xv Chapter 1: Implementation Strategies... 1 The Case for Standards... 1 Which Models
Improving Metadata Compliance and Assessing Quality Metrics with a Standards Library
 PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper SS-12 Improving Metadata Compliance and Assessing Quality Metrics with a Standards Library Veena Nataraj, Erica Davis, Shire ABSTRACT Establishing internal Data Standards helps companies
PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper SS-12 Improving Metadata Compliance and Assessing Quality Metrics with a Standards Library Veena Nataraj, Erica Davis, Shire ABSTRACT Establishing internal Data Standards helps companies
An Efficient Solution to Efficacy ADaM Design and Implementation
 PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper AD05 An Efficient Solution to Efficacy ADaM Design and Implementation Chengxin Li, Pfizer Consumer Healthcare, Madison, NJ, USA Zhongwei Zhou, Pfizer Consumer Healthcare, Madison,
PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper AD05 An Efficient Solution to Efficacy ADaM Design and Implementation Chengxin Li, Pfizer Consumer Healthcare, Madison, NJ, USA Zhongwei Zhou, Pfizer Consumer Healthcare, Madison,
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Retrospective vs. Prospective Data Standardization
 Cost-Benefit Analysis of Retrospective vs. Prospective Data Standardization Vicki Seyfert-Margolis, PhD Senior Advisor, Science Innovation and Policy Food and Drug Administration IOM Sharing Clinical Research
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Retrospective vs. Prospective Data Standardization Vicki Seyfert-Margolis, PhD Senior Advisor, Science Innovation and Policy Food and Drug Administration IOM Sharing Clinical Research
Edwin Ponraj Thangarajan, PRA Health Sciences, Chennai, India Giri Balasubramanian, PRA Health Sciences, Chennai, India
 Paper CD15 PhUSE 2016 How to handle different versions of SDTM & DEFINE generation in a Single Study? Edwin Ponraj Thangarajan, PRA Health Sciences, Chennai, India Giri Balasubramanian, PRA Health Sciences,
Paper CD15 PhUSE 2016 How to handle different versions of SDTM & DEFINE generation in a Single Study? Edwin Ponraj Thangarajan, PRA Health Sciences, Chennai, India Giri Balasubramanian, PRA Health Sciences,
CDISC Standards and the Semantic Web
 CDISC Standards and the Semantic Web Dave Iberson-Hurst 12 th October 2015 PhUSE Annual Conference, Vienna 1 Abstract With the arrival of the FDA guidance on electronic submissions, CDISC SHARE and the
CDISC Standards and the Semantic Web Dave Iberson-Hurst 12 th October 2015 PhUSE Annual Conference, Vienna 1 Abstract With the arrival of the FDA guidance on electronic submissions, CDISC SHARE and the
Introduction to ADaM and What s new in ADaM
 Introduction to ADaM and What s new in ADaM Italian CDISC UN Day - Milan 27 th October 2017 Silvia Faini Principal Statistical Programmer CROS NT - Verona ADaM Purpose Why are standards needed in analysis
Introduction to ADaM and What s new in ADaM Italian CDISC UN Day - Milan 27 th October 2017 Silvia Faini Principal Statistical Programmer CROS NT - Verona ADaM Purpose Why are standards needed in analysis
Traceability Look for the source of your analysis results
 Traceability Look for the source of your analysis results Herman Ament, Cromsource CDISC UG Milan 21 October 2016 Contents Introduction, history and CDISC Traceability Examples Conclusion 2 / 24 Introduction,
Traceability Look for the source of your analysis results Herman Ament, Cromsource CDISC UG Milan 21 October 2016 Contents Introduction, history and CDISC Traceability Examples Conclusion 2 / 24 Introduction,
SAS Clinical Data Integration 2.4
 SAS Clinical Data Integration 2.4 User s Guide SAS Documentation The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: SAS Institute Inc. 2013. SAS Clinical Data Integration 2.4: User's Guide.
SAS Clinical Data Integration 2.4 User s Guide SAS Documentation The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: SAS Institute Inc. 2013. SAS Clinical Data Integration 2.4: User's Guide.
The Benefits of Traceability Beyond Just From SDTM to ADaM in CDISC Standards Maggie Ci Jiang, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Great Valley, PA
 PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper DS23 The Benefits of Traceability Beyond Just From SDTM to ADaM in CDISC Standards Maggie Ci Jiang, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Great Valley, PA ABSTRACT Since FDA released the Analysis
PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper DS23 The Benefits of Traceability Beyond Just From SDTM to ADaM in CDISC Standards Maggie Ci Jiang, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Great Valley, PA ABSTRACT Since FDA released the Analysis
Taming Rave: How to control data collection standards?
 Paper DH08 Taming Rave: How to control data collection standards? Dimitri Kutsenko, Entimo AG, Berlin, Germany Table of Contents Introduction... 1 How to organize metadata... 2 How to structure metadata...
Paper DH08 Taming Rave: How to control data collection standards? Dimitri Kutsenko, Entimo AG, Berlin, Germany Table of Contents Introduction... 1 How to organize metadata... 2 How to structure metadata...
Automated Creation of Submission-Ready Artifacts Silas McKee, Accenture, Pennsylvania, USA Lourdes Devenney, Accenture, Pennsylvania, USA
 Paper DH06 Automated Creation of Submission-Ready Artifacts Silas McKee, Accenture, Pennsylvania, USA Lourdes Devenney, Accenture, Pennsylvania, USA ABSTRACT Despite significant progress towards the standardization
Paper DH06 Automated Creation of Submission-Ready Artifacts Silas McKee, Accenture, Pennsylvania, USA Lourdes Devenney, Accenture, Pennsylvania, USA ABSTRACT Despite significant progress towards the standardization
From Implementing CDISC Using SAS. Full book available for purchase here. About This Book... xi About The Authors... xvii Acknowledgments...
 From Implementing CDISC Using SAS. Full book available for purchase here. Contents About This Book... xi About The Authors... xvii Acknowledgments... xix Chapter 1: Implementation Strategies... 1 Why CDISC
From Implementing CDISC Using SAS. Full book available for purchase here. Contents About This Book... xi About The Authors... xvii Acknowledgments... xix Chapter 1: Implementation Strategies... 1 Why CDISC
How to handle different versions of SDTM & DEFINE generation in a Single Study?
 Paper CD15 How to handle different versions of SDTM & DEFINE generation in a Single Study? Edwin Ponraj Thangarajan, PRA Health Sciences, Chennai, India Giri Balasubramanian, PRA Health Sciences, Chennai,
Paper CD15 How to handle different versions of SDTM & DEFINE generation in a Single Study? Edwin Ponraj Thangarajan, PRA Health Sciences, Chennai, India Giri Balasubramanian, PRA Health Sciences, Chennai,
Paper DS07 PhUSE 2017 CDISC Transport Standards - A Glance. Giri Balasubramanian, PRA Health Sciences Edwin Ponraj Thangarajan, PRA Health Sciences
 Paper DS07 PhUSE 2017 CDISC Transport Standards - A Glance Giri Balasubramanian, PRA Health Sciences Edwin Ponraj Thangarajan, PRA Health Sciences Agenda Paper Abstract CDISC Standards Types Why Transport
Paper DS07 PhUSE 2017 CDISC Transport Standards - A Glance Giri Balasubramanian, PRA Health Sciences Edwin Ponraj Thangarajan, PRA Health Sciences Agenda Paper Abstract CDISC Standards Types Why Transport
SAS Clinical Data Integration 2.6
 SAS Clinical Data Integration 2.6 User s Guide SAS Documentation The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: SAS Institute Inc. 2015. SAS Clinical Data Integration 2.6: User's Guide.
SAS Clinical Data Integration 2.6 User s Guide SAS Documentation The correct bibliographic citation for this manual is as follows: SAS Institute Inc. 2015. SAS Clinical Data Integration 2.6: User's Guide.
Doctor's Prescription to Re-engineer Process of Pinnacle 21 Community Version Friendly ADaM Development
 PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper DS-15 Doctor's Prescription to Re-engineer Process of Pinnacle 21 Community Version Friendly ADaM Development Aakar Shah, Pfizer Inc; Tracy Sherman, Ephicacy Consulting Group, Inc.
PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper DS-15 Doctor's Prescription to Re-engineer Process of Pinnacle 21 Community Version Friendly ADaM Development Aakar Shah, Pfizer Inc; Tracy Sherman, Ephicacy Consulting Group, Inc.
Planning to Pool SDTM by Creating and Maintaining a Sponsor-Specific Controlled Terminology Database
 PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper DS13 Planning to Pool SDTM by Creating and Maintaining a Sponsor-Specific Controlled Terminology Database ABSTRACT Cori Kramer, Ragini Hari, Keith Shusterman, Chiltern When SDTM
PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper DS13 Planning to Pool SDTM by Creating and Maintaining a Sponsor-Specific Controlled Terminology Database ABSTRACT Cori Kramer, Ragini Hari, Keith Shusterman, Chiltern When SDTM
From ODM to SDTM: An End-to-End Approach Applied to Phase I Clinical Trials
 PhUSE 2014 Paper PP05 From ODM to SDTM: An End-to-End Approach Applied to Phase I Clinical Trials Alexandre Mathis, Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Allschwil, Switzerland
PhUSE 2014 Paper PP05 From ODM to SDTM: An End-to-End Approach Applied to Phase I Clinical Trials Alexandre Mathis, Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Allschwil, Switzerland
Streamline SDTM Development and QC
 Paper SI09 Streamline SDTM Development and QC Stephen Gormley, Amgen, United Kingdom ABSTRACT Amgen s Global Statistical Programming ( GSP ) function have one centralised team (The CDISC Consultancy and
Paper SI09 Streamline SDTM Development and QC Stephen Gormley, Amgen, United Kingdom ABSTRACT Amgen s Global Statistical Programming ( GSP ) function have one centralised team (The CDISC Consultancy and
PharmaSUG Paper PO22
 PharmaSUG 2015 - Paper PO22 Challenges in Developing ADSL with Baseline Data Hongyu Liu, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, Boston, MA Hang Pang, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, Boston, MA ABSTRACT
PharmaSUG 2015 - Paper PO22 Challenges in Developing ADSL with Baseline Data Hongyu Liu, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, Boston, MA Hang Pang, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, Boston, MA ABSTRACT
Data Governance Quick Start
 Service Offering Data Governance Quick Start Congratulations! You ve been named the Data Governance Leader Now What? Benefits Accelerate the initiation of your Data Governance program with an industry
Service Offering Data Governance Quick Start Congratulations! You ve been named the Data Governance Leader Now What? Benefits Accelerate the initiation of your Data Governance program with an industry
ADaM Compliance Starts with ADaM Specifications
 PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper DS16 ADaM Compliance Starts with ADaM Specifications Trevor Mankus, Kent Letourneau, PRA Health Sciences ABSTRACT As of December 17th, 2016, the FDA and PMDA require that all new
PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper DS16 ADaM Compliance Starts with ADaM Specifications Trevor Mankus, Kent Letourneau, PRA Health Sciences ABSTRACT As of December 17th, 2016, the FDA and PMDA require that all new
From SDTM to displays, through ADaM & Analyses Results Metadata, a flight on board METADATA Airlines
 From SDTM to displays, through ADaM & Analyses Results Metadata, a flight on board METADATA Airlines Omar SEFIANI - Stéphane BOUGET, Boehringer Ingelheim DH13, PhUSE Barcelona 2016, October, 12 th Outline
From SDTM to displays, through ADaM & Analyses Results Metadata, a flight on board METADATA Airlines Omar SEFIANI - Stéphane BOUGET, Boehringer Ingelheim DH13, PhUSE Barcelona 2016, October, 12 th Outline
Submission-Ready Define.xml Files Using SAS Clinical Data Integration Melissa R. Martinez, SAS Institute, Cary, NC USA
 PharmaSUG 2016 - Paper SS12 Submission-Ready Define.xml Files Using SAS Clinical Data Integration Melissa R. Martinez, SAS Institute, Cary, NC USA ABSTRACT SAS Clinical Data Integration simplifies the
PharmaSUG 2016 - Paper SS12 Submission-Ready Define.xml Files Using SAS Clinical Data Integration Melissa R. Martinez, SAS Institute, Cary, NC USA ABSTRACT SAS Clinical Data Integration simplifies the
The Wonderful World of Define.xml.. Practical Uses Today. Mark Wheeldon, CEO, Formedix DC User Group, Washington, 9 th December 2008
 The Wonderful World of Define.xml.. Practical Uses Today Mark Wheeldon, CEO, Formedix DC User Group, Washington, 9 th December 2008 Agenda Introduction to Formedix What is Define.xml? Features and Benefits
The Wonderful World of Define.xml.. Practical Uses Today Mark Wheeldon, CEO, Formedix DC User Group, Washington, 9 th December 2008 Agenda Introduction to Formedix What is Define.xml? Features and Benefits
Tips on Creating a Strategy for a CDISC Submission Rajkumar Sharma, Nektar Therapeutics, San Francisco, CA
 PharmaSUG 2015 - Paper IB09 Tips on Creating a Strategy for a CDISC Submission Rajkumar Sharma, Nektar Therapeutics, San Francisco, CA ABSTRACT A submission to FDA for an NDA (New Drug Application) or
PharmaSUG 2015 - Paper IB09 Tips on Creating a Strategy for a CDISC Submission Rajkumar Sharma, Nektar Therapeutics, San Francisco, CA ABSTRACT A submission to FDA for an NDA (New Drug Application) or
How to review a CRF - A statistical programmer perspective
 Paper DH07 How to review a CRF - A statistical programmer perspective Elsa Lozachmeur, Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland ABSTRACT The design of the Case Report Form (CRF) is critical for the capture
Paper DH07 How to review a CRF - A statistical programmer perspective Elsa Lozachmeur, Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland ABSTRACT The design of the Case Report Form (CRF) is critical for the capture
SAS Application to Automate a Comprehensive Review of DEFINE and All of its Components
 PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper AD19 SAS Application to Automate a Comprehensive Review of DEFINE and All of its Components Walter Hufford, Vincent Guo, and Mijun Hu, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation ABSTRACT
PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper AD19 SAS Application to Automate a Comprehensive Review of DEFINE and All of its Components Walter Hufford, Vincent Guo, and Mijun Hu, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation ABSTRACT
PhUSE US Connect 2019
 PhUSE US Connect 2019 Paper SI04 Creation of ADaM Define.xml v2.0 Using SAS Program and Pinnacle 21 Yan Lei, Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA, USA Yongjiang Xu, Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA,
PhUSE US Connect 2019 Paper SI04 Creation of ADaM Define.xml v2.0 Using SAS Program and Pinnacle 21 Yan Lei, Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA, USA Yongjiang Xu, Johnson & Johnson, Spring House, PA,
Harnessing the Web to Streamline Statistical Programming Processes
 Paper TT03 Harnessing the Web to Streamline Statistical Programming Processes Daniel Boisvert, Biogen, Cambridge MA, USA Pankaj Kumar, Biogen, Cambridge MA, USA Gordon Schantz, Biogen, Cambridge MA, USA
Paper TT03 Harnessing the Web to Streamline Statistical Programming Processes Daniel Boisvert, Biogen, Cambridge MA, USA Pankaj Kumar, Biogen, Cambridge MA, USA Gordon Schantz, Biogen, Cambridge MA, USA
Legacy to SDTM Conversion Workshop: Tools and Techniques
 Legacy to SDTM Conversion Workshop: Tools and Techniques Mike Todd President Nth Analytics Legacy Data Old studies never die Legacy studies are often required for submissions or pharmacovigilence. Often
Legacy to SDTM Conversion Workshop: Tools and Techniques Mike Todd President Nth Analytics Legacy Data Old studies never die Legacy studies are often required for submissions or pharmacovigilence. Often
R1 Test Case that tests this Requirement Comments Manage Users User Role Management
 2/19/2014 CDISC SHARE Requirements Page 1 of 23 Number Name Req ID Requirement Manage Users 2.1.1 User Role Manage Users 2.1.1 User Role Manage Users 2.1.1 User Role Manage Users 2.1.1 User Role Manage
2/19/2014 CDISC SHARE Requirements Page 1 of 23 Number Name Req ID Requirement Manage Users 2.1.1 User Role Manage Users 2.1.1 User Role Manage Users 2.1.1 User Role Manage Users 2.1.1 User Role Manage
PhUSE EU Connect Paper PP15. Stop Copying CDISC Standards. Craig Parry, SyneQuaNon, Diss, England
 Paper PP15 Abstract Stop Copying CDISC Standards Craig Parry, SyneQuaNon, Diss, England We repeatedly see repositories which require a large amount of front loading, a lot of duplicating of the Clinical
Paper PP15 Abstract Stop Copying CDISC Standards Craig Parry, SyneQuaNon, Diss, England We repeatedly see repositories which require a large amount of front loading, a lot of duplicating of the Clinical
What is the ADAM OTHER Class of Datasets, and When Should it be Used? John Troxell, Data Standards Consulting
 Accenture Accelerated R&D Services Rethink Reshape Restructure for better patient outcomes What is the ADAM OTHER Class of Datasets, and When Should it be Used? John Troxell, Data Standards Consulting
Accenture Accelerated R&D Services Rethink Reshape Restructure for better patient outcomes What is the ADAM OTHER Class of Datasets, and When Should it be Used? John Troxell, Data Standards Consulting
It s All About Getting the Source and Codelist Implementation Right for ADaM Define.xml v2.0
 PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper SS-15 It s All About Getting the Source and Codelist Implementation Right for ADaM Define.xml v2.0 ABSTRACT Supriya Davuluri, PPD, LLC, Morrisville, NC There are some obvious challenges
PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper SS-15 It s All About Getting the Source and Codelist Implementation Right for ADaM Define.xml v2.0 ABSTRACT Supriya Davuluri, PPD, LLC, Morrisville, NC There are some obvious challenges
Managing CDISC version changes: how & when to implement? Presented by Lauren Shinaberry, Project Manager Business & Decision Life Sciences
 1 Managing CDISC version changes: how & when to implement? Presented by Lauren Shinaberry, Project Manager Business & Decision Life Sciences 2 Content Standards Technical Standards SDTM v1.1 SDTM IG v3.1.1
1 Managing CDISC version changes: how & when to implement? Presented by Lauren Shinaberry, Project Manager Business & Decision Life Sciences 2 Content Standards Technical Standards SDTM v1.1 SDTM IG v3.1.1
SDD Unleashed - Extending the Capabilities of SAS Drug Development
 SDD Unleashed - Extending the Capabilities of SAS Drug Development Stephen Baker d-wise Technologies Raleigh, NC ABSTRACT SAS Drug Development is well known as a compliant, hosted repository for storing
SDD Unleashed - Extending the Capabilities of SAS Drug Development Stephen Baker d-wise Technologies Raleigh, NC ABSTRACT SAS Drug Development is well known as a compliant, hosted repository for storing
Taming the SHREW. SDTM Heuristic Research and Evaluation Workshop
 Taming the SHREW SDTM Heuristic Research and Evaluation Workshop September 13, 2013 Carlo Radovsky 2 Overview Introductions The Backstory CDISC IntraChange History of a Rule The Challenge Discuss Amongst
Taming the SHREW SDTM Heuristic Research and Evaluation Workshop September 13, 2013 Carlo Radovsky 2 Overview Introductions The Backstory CDISC IntraChange History of a Rule The Challenge Discuss Amongst
Material covered in the Dec 2014 FDA Binding Guidances
 Accenture Accelerated R&D Services Rethink Reshape Restructure for better patient outcomes Sandra Minjoe Senior ADaM Consultant Preparing ADaM and Related Files for Submission Presentation Focus Material
Accenture Accelerated R&D Services Rethink Reshape Restructure for better patient outcomes Sandra Minjoe Senior ADaM Consultant Preparing ADaM and Related Files for Submission Presentation Focus Material
Git with It and Version Control!
 Paper CT10 Git with It and Version Control! Carrie Dundas-Lucca, Zencos Consulting, LLC., Cary, NC, United States Ivan Gomez, Zencos Consulting, LLC., Cary, NC, United States ABSTRACT It is a long-standing
Paper CT10 Git with It and Version Control! Carrie Dundas-Lucca, Zencos Consulting, LLC., Cary, NC, United States Ivan Gomez, Zencos Consulting, LLC., Cary, NC, United States ABSTRACT It is a long-standing
Automate Analysis Results Metadata in the Define-XML v2.0. Hong Qi, Majdoub Haloui, Larry Wu, Gregory T Golm Merck & Co., Inc.
 Automate Analysis Results Metadata in the Define-XML v2.0 Hong Qi, Majdoub Haloui, Larry Wu, Gregory T Golm Merck & Co., Inc., USA 1 Topics Introduction Analysis Results Metadata (ARM) Version 1.0 o o
Automate Analysis Results Metadata in the Define-XML v2.0 Hong Qi, Majdoub Haloui, Larry Wu, Gregory T Golm Merck & Co., Inc., USA 1 Topics Introduction Analysis Results Metadata (ARM) Version 1.0 o o
Managing your metadata efficiently - a structured way to organise and frontload your analysis and submission data
 Paper TS06 Managing your metadata efficiently - a structured way to organise and frontload your analysis and submission data Kirsten Walther Langendorf, Novo Nordisk A/S, Copenhagen, Denmark Mikkel Traun,
Paper TS06 Managing your metadata efficiently - a structured way to organise and frontload your analysis and submission data Kirsten Walther Langendorf, Novo Nordisk A/S, Copenhagen, Denmark Mikkel Traun,
Best Practice for Explaining Validation Results in the Study Data Reviewer s Guide
 Paper DS06 Best Practice for Explaining Validation Results in the Study Data Reviewer s Guide Kristin Kelly, Pinnacle 21 LLC, Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA Michael Beers, Pinnacle 21 LLC, Plymouth Meeting,
Paper DS06 Best Practice for Explaining Validation Results in the Study Data Reviewer s Guide Kristin Kelly, Pinnacle 21 LLC, Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA Michael Beers, Pinnacle 21 LLC, Plymouth Meeting,
SDTM Implementation Guide Clear as Mud: Strategies for Developing Consistent Company Standards
 Paper CD02 SDTM Implementation Guide Clear as Mud: Strategies for Developing Consistent Company Standards Brian Mabe, UCB Biosciences, Raleigh, USA ABSTRACT Many pharmaceutical companies are now entrenched
Paper CD02 SDTM Implementation Guide Clear as Mud: Strategies for Developing Consistent Company Standards Brian Mabe, UCB Biosciences, Raleigh, USA ABSTRACT Many pharmaceutical companies are now entrenched
Paper FC02. SDTM, Plus or Minus. Barry R. Cohen, Octagon Research Solutions, Wayne, PA
 Paper FC02 SDTM, Plus or Minus Barry R. Cohen, Octagon Research Solutions, Wayne, PA ABSTRACT The CDISC Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM) has become the industry standard for the regulatory submission
Paper FC02 SDTM, Plus or Minus Barry R. Cohen, Octagon Research Solutions, Wayne, PA ABSTRACT The CDISC Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM) has become the industry standard for the regulatory submission
Sandra Minjoe, Accenture Life Sciences John Brega, PharmaStat. PharmaSUG Single Day Event San Francisco Bay Area
 Sandra Minjoe, Accenture Life Sciences John Brega, PharmaStat PharmaSUG Single Day Event San Francisco Bay Area 2015-02-10 What is the Computational Sciences Symposium? CSS originally formed to help FDA
Sandra Minjoe, Accenture Life Sciences John Brega, PharmaStat PharmaSUG Single Day Event San Francisco Bay Area 2015-02-10 What is the Computational Sciences Symposium? CSS originally formed to help FDA
CDISC SDTM and ADaM Real World Issues
 CDISC SDTM and ADaM Real World Issues Washington DC CDISC Data Standards User Group Meeting Sy Truong President MXI, Meta-Xceed, Inc. http://www.meta-x.com Agenda CDISC SDTM and ADaM Fundamentals CDISC
CDISC SDTM and ADaM Real World Issues Washington DC CDISC Data Standards User Group Meeting Sy Truong President MXI, Meta-Xceed, Inc. http://www.meta-x.com Agenda CDISC SDTM and ADaM Fundamentals CDISC
esubmission - Are you really Compliant?
 ABSTRACT PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper SS21 esubmission - Are you really Compliant? Majdoub Haloui, Merck & Co., Inc., Upper Gwynedd, PA, USA Suhas R. Sanjee, Merck & Co., Inc., Upper Gwynedd, PA, USA Pinnacle
ABSTRACT PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper SS21 esubmission - Are you really Compliant? Majdoub Haloui, Merck & Co., Inc., Upper Gwynedd, PA, USA Suhas R. Sanjee, Merck & Co., Inc., Upper Gwynedd, PA, USA Pinnacle
PhUSE Paper SD09. "Overnight" Conversion to SDTM Datasets Ready for SDTM Submission Niels Mathiesen, mathiesen & mathiesen, Basel, Switzerland
 Paper SD09 "Overnight" Conversion to SDTM Datasets Ready for SDTM Submission Niels Mathiesen, mathiesen & mathiesen, Basel, Switzerland ABSTRACT This demonstration shows how legacy data (in any format)
Paper SD09 "Overnight" Conversion to SDTM Datasets Ready for SDTM Submission Niels Mathiesen, mathiesen & mathiesen, Basel, Switzerland ABSTRACT This demonstration shows how legacy data (in any format)
Creating a Patient Profile using CDISC SDTM Marc Desgrousilliers, Clinovo, Sunnyvale, CA Romain Miralles, Clinovo, Sunnyvale, CA
 Creating a Patient Profile using CDISC SDTM Marc Desgrousilliers, Clinovo, Sunnyvale, CA Romain Miralles, Clinovo, Sunnyvale, CA ABSTRACT CDISC SDTM data is the standard format requested by the FDA for
Creating a Patient Profile using CDISC SDTM Marc Desgrousilliers, Clinovo, Sunnyvale, CA Romain Miralles, Clinovo, Sunnyvale, CA ABSTRACT CDISC SDTM data is the standard format requested by the FDA for
Out-of-the-box %definexml
 Out-of-the-box %definexml Just a Simple SAS Macro PhUSE / October 2016 / Katja Glaß Agenda Introduction Getting Started %DefineXML Collaborate Summary Page 2 DefineXML Katja Glaß 11. October 2016 Introduction
Out-of-the-box %definexml Just a Simple SAS Macro PhUSE / October 2016 / Katja Glaß Agenda Introduction Getting Started %DefineXML Collaborate Summary Page 2 DefineXML Katja Glaß 11. October 2016 Introduction
Define.xml 2.0: More Functional, More Challenging
 Define.xml 2.0: More Functional, More Challenging Bay Area CDISC Implementation Network 24 July 2013 John Brega, PharmaStat LLC Presentation Objectives 1. Introduce the new features in Define.xml 2.0 with
Define.xml 2.0: More Functional, More Challenging Bay Area CDISC Implementation Network 24 July 2013 John Brega, PharmaStat LLC Presentation Objectives 1. Introduce the new features in Define.xml 2.0 with
An Alternate Way to Create the Standard SDTM Domains
 PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper DS-12 ABSTRACT An Alternate Way to Create the Standard SDTM Domains Sunil Kumar Pusarla, Omeros Corporation Sponsors who initiate clinical trials after 2016-12-17 are required to
PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper DS-12 ABSTRACT An Alternate Way to Create the Standard SDTM Domains Sunil Kumar Pusarla, Omeros Corporation Sponsors who initiate clinical trials after 2016-12-17 are required to
SAS offers technology to facilitate working with CDISC standards : the metadata perspective.
 SAS offers technology to facilitate working with CDISC standards : the metadata perspective. Mark Lambrecht, PhD Principal Consultant, Life Sciences SAS Agenda SAS actively supports CDISC standards Tools
SAS offers technology to facilitate working with CDISC standards : the metadata perspective. Mark Lambrecht, PhD Principal Consultant, Life Sciences SAS Agenda SAS actively supports CDISC standards Tools
Beyond OpenCDISC: Using Define.xml Metadata to Ensure End-to-End Submission Integrity. John Brega Linda Collins PharmaStat LLC
 Beyond OpenCDISC: Using Define.xml Metadata to Ensure End-to-End Submission Integrity John Brega Linda Collins PharmaStat LLC Topics Part 1: A Standard with Many Uses Status of the Define.xml Standard
Beyond OpenCDISC: Using Define.xml Metadata to Ensure End-to-End Submission Integrity John Brega Linda Collins PharmaStat LLC Topics Part 1: A Standard with Many Uses Status of the Define.xml Standard
Dataset-XML - A New CDISC Standard
 Dataset-XML - A New CDISC Standard Lex Jansen Principal Software Developer @ SAS CDISC XML Technologies Team Single Day Event CDISC Tools and Optimization September 29, 2014, Cary, NC Agenda Dataset-XML
Dataset-XML - A New CDISC Standard Lex Jansen Principal Software Developer @ SAS CDISC XML Technologies Team Single Day Event CDISC Tools and Optimization September 29, 2014, Cary, NC Agenda Dataset-XML
Creating an ADaM Data Set for Correlation Analyses
 PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper DS-17 ABSTRACT Creating an ADaM Data Set for Correlation Analyses Chad Melson, Experis Clinical, Cincinnati, OH The purpose of a correlation analysis is to evaluate relationships
PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper DS-17 ABSTRACT Creating an ADaM Data Set for Correlation Analyses Chad Melson, Experis Clinical, Cincinnati, OH The purpose of a correlation analysis is to evaluate relationships
PharmaSUG Paper AD03
 PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper AD03 Three Issues and Corresponding Work-Around Solution for Generating Define.xml 2.0 Using Pinnacle 21 Enterprise Jeff Xia, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA Lugang (Larry) Xie,
PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper AD03 Three Issues and Corresponding Work-Around Solution for Generating Define.xml 2.0 Using Pinnacle 21 Enterprise Jeff Xia, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA Lugang (Larry) Xie,
Codelists Here, Versions There, Controlled Terminology Everywhere Shelley Dunn, Regulus Therapeutics, San Diego, California
 ABSTRACT PharmaSUG 2016 - Paper DS16 lists Here, Versions There, Controlled Terminology Everywhere Shelley Dunn, Regulus Therapeutics, San Diego, California Programming SDTM and ADaM data sets for a single
ABSTRACT PharmaSUG 2016 - Paper DS16 lists Here, Versions There, Controlled Terminology Everywhere Shelley Dunn, Regulus Therapeutics, San Diego, California Programming SDTM and ADaM data sets for a single
Optimization of the traceability when applying an ADaM Parallel Conversion Method
 Paper SI04 Optimization of the traceability when applying an ADaM Parallel Conversion Method DEBRUS Roxane, Business & Decision Life Sciences, Brussels, Belgium ABSTRACT One of the methods to create CDISC
Paper SI04 Optimization of the traceability when applying an ADaM Parallel Conversion Method DEBRUS Roxane, Business & Decision Life Sciences, Brussels, Belgium ABSTRACT One of the methods to create CDISC
ADaM for Medical Devices: Extending the Current ADaM Structures
 PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper MD-02 ADaM for Medical s: Extending the Current ADaM Structures Sandra Minjoe, PRA Health Sciences; Julia Yang, Medtronic PLC; Priya Gopal, TESARO, Inc. ABSTRACT The current ADaM
PharmaSUG 2018 - Paper MD-02 ADaM for Medical s: Extending the Current ADaM Structures Sandra Minjoe, PRA Health Sciences; Julia Yang, Medtronic PLC; Priya Gopal, TESARO, Inc. ABSTRACT The current ADaM
Helping The Define.xml User
 Paper TT01 Helping The Define.xml User Dave Iberson-Hurst, Assero Limited, Teignmouth, United Kingdom ABSTRACT The FDA often comment at industry gatherings on the quality of define.xml files received as
Paper TT01 Helping The Define.xml User Dave Iberson-Hurst, Assero Limited, Teignmouth, United Kingdom ABSTRACT The FDA often comment at industry gatherings on the quality of define.xml files received as
Study Data Reviewer s Guide Completion Guideline
 Study Data Reviewer s Guide Completion Guideline 22-Feb-2013 Revision History Date Version Summary 02-Nov-2012 0.1 Draft 20-Nov-2012 0.2 Added Finalization Instructions 10-Jan-2013 0.3 Updated based on
Study Data Reviewer s Guide Completion Guideline 22-Feb-2013 Revision History Date Version Summary 02-Nov-2012 0.1 Draft 20-Nov-2012 0.2 Added Finalization Instructions 10-Jan-2013 0.3 Updated based on
CDISC Public Webinar Standards Updates and Additions. 26 Feb 2015
 CDISC Public Webinar Standards Updates and Additions 26 Feb 2015 CDISC 2014 Agenda SHARE Research Concepts Julie Evans, CDISC Anthony Chow, CDISC Rene Dahlheimer, CDISC Sam Hume, CDISC CDISC Education
CDISC Public Webinar Standards Updates and Additions 26 Feb 2015 CDISC 2014 Agenda SHARE Research Concepts Julie Evans, CDISC Anthony Chow, CDISC Rene Dahlheimer, CDISC Sam Hume, CDISC CDISC Education
ADaM and traceability: Chiesi experience
 ADaM and traceability: Chiesi experience BIAS Seminar «Data handling and reporting in clinical trials with SAS» Glauco Cappellini 22-Feb-2013 Agenda Chiesi Model for Biometrics Regulatory Background ADaM:
ADaM and traceability: Chiesi experience BIAS Seminar «Data handling and reporting in clinical trials with SAS» Glauco Cappellini 22-Feb-2013 Agenda Chiesi Model for Biometrics Regulatory Background ADaM:
Reporting & Visualisation : D un Dun standard maison au format CDISC 02/02/2016 CDISC GUF 1
 Reporting & Visualisation : D un Dun standard maison au format CDISC Jérémy MAMBRINI Florence WAGER 02/02/2016 CDISC GUF 1 Contents CDISC Implementation ti at SERVIER Reporting & Visualisation using CDISC
Reporting & Visualisation : D un Dun standard maison au format CDISC Jérémy MAMBRINI Florence WAGER 02/02/2016 CDISC GUF 1 Contents CDISC Implementation ti at SERVIER Reporting & Visualisation using CDISC
Optimization of the traceability when applying an ADaM Parallel Conversion Method
 SI04 Optimization of the traceability when applying an ADaM Parallel Conversion Method Roxane Debrus ADaM Conversion Process Agenda %LIB_QC_contents_html %adam_sdtm_compa Conclusion ADaM Conversion Process
SI04 Optimization of the traceability when applying an ADaM Parallel Conversion Method Roxane Debrus ADaM Conversion Process Agenda %LIB_QC_contents_html %adam_sdtm_compa Conclusion ADaM Conversion Process
A Taste of SDTM in Real Time
 A Taste of SDTM in Real Time Changhong Shi, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ Beilei Xu, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ ABSTRACT The Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM) is a Clinical Data Interchange Standards
A Taste of SDTM in Real Time Changhong Shi, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ Beilei Xu, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ ABSTRACT The Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM) is a Clinical Data Interchange Standards
Lex Jansen Octagon Research Solutions, Inc.
 Converting the define.xml to a Relational Database to Enable Printing and Validation Lex Jansen Octagon Research Solutions, Inc. Leading the Electronic Transformation of Clinical R&D * PharmaSUG 2009,
Converting the define.xml to a Relational Database to Enable Printing and Validation Lex Jansen Octagon Research Solutions, Inc. Leading the Electronic Transformation of Clinical R&D * PharmaSUG 2009,
Implementing CDISC at Boehringer Ingelheim
 Paper CD03 Implementing CDISC at Boehringer Ingelheim Michael Knoessl, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ingelheim, Germany Peter Leister, IBM, Hamburg, Germany ABSTRACT The Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM), as
Paper CD03 Implementing CDISC at Boehringer Ingelheim Michael Knoessl, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ingelheim, Germany Peter Leister, IBM, Hamburg, Germany ABSTRACT The Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM), as
BUSINESS-BASED VALUE IN AN MDR
 MERCK METADATA REPOSITORY: BUSINESS-BASED VALUE IN AN MDR A. Brooke Hinkson Manori Turmel Karl Konrad PhUSE Connect Conference, Raleigh NC, 4-6 June 2018 2 Business Problems to Address Current information
MERCK METADATA REPOSITORY: BUSINESS-BASED VALUE IN AN MDR A. Brooke Hinkson Manori Turmel Karl Konrad PhUSE Connect Conference, Raleigh NC, 4-6 June 2018 2 Business Problems to Address Current information
DCDISC Users Group. Nate Freimark Omnicare Clinical Research Presented on
 DCDISC Users Group Nate Freimark Omnicare Clinical Research Presented on 2011-05-12 1 Disclaimer The opinions provided are solely those of the author and not those of the ADaM team or Omnicare Clinical
DCDISC Users Group Nate Freimark Omnicare Clinical Research Presented on 2011-05-12 1 Disclaimer The opinions provided are solely those of the author and not those of the ADaM team or Omnicare Clinical
Standardizing FDA Data to Improve Success in Pediatric Drug Development
 Paper RA01 Standardizing FDA Data to Improve Success in Pediatric Drug Development Case Study: Harmonizing Hypertensive Pediatric Data across Sponsors using SAS and the CDISC Model Julie Maddox, SAS Institute,
Paper RA01 Standardizing FDA Data to Improve Success in Pediatric Drug Development Case Study: Harmonizing Hypertensive Pediatric Data across Sponsors using SAS and the CDISC Model Julie Maddox, SAS Institute,
The development of standards management using EntimICE-AZ
 Paper PP19 The development of standards management using EntimICE-AZ Shyamprasad Perisetla, AstraZeneca, Cambridge, UK Per-Arne Stahl, AstraZeneca, Mölndal, Sweden INTRODUCTION Historically, using excel
Paper PP19 The development of standards management using EntimICE-AZ Shyamprasad Perisetla, AstraZeneca, Cambridge, UK Per-Arne Stahl, AstraZeneca, Mölndal, Sweden INTRODUCTION Historically, using excel
PTC Employs Its Own Arbortext Software to Improve Delivery of PTC University Learning Content Materials
 PTC Employs Its Own Arbortext Software to Improve Delivery of PTC University Learning Content Materials Produces Higher Quality Courseware, Faster Development Cycles for Global Training Content Produces
PTC Employs Its Own Arbortext Software to Improve Delivery of PTC University Learning Content Materials Produces Higher Quality Courseware, Faster Development Cycles for Global Training Content Produces
esource Initiative ISSUES RELATED TO NON-CRF DATA PRACTICES
 esource Initiative ISSUES RELATED TO NON-CRF DATA PRACTICES ISSUES RELATED TO NON-CRF DATA PRACTICES Introduction Non-Case Report Form (CRF) data are defined as data which include collection and transfer
esource Initiative ISSUES RELATED TO NON-CRF DATA PRACTICES ISSUES RELATED TO NON-CRF DATA PRACTICES Introduction Non-Case Report Form (CRF) data are defined as data which include collection and transfer
Dealing with changing versions of SDTM and Controlled Terminology (CT)
 CDISC UK Network Breakout session Notes 07/06/16 Afternoon Session 1: Dealing with changing versions of SDTM and Controlled Terminology (CT) How do people manage this? Is this managed via a sponsor Standards
CDISC UK Network Breakout session Notes 07/06/16 Afternoon Session 1: Dealing with changing versions of SDTM and Controlled Terminology (CT) How do people manage this? Is this managed via a sponsor Standards
Paper AD16 MDMAP An innovative application utilized in the management of clinical trial metadata
 Paper AD16 MDMAP An innovative application utilized in the management of clinical trial metadata Gregory Ridge and Neeru Bhardwaj The sanofi-aventis Group, Malvern, PA Abstract Since 1999, sanofi-aventis
Paper AD16 MDMAP An innovative application utilized in the management of clinical trial metadata Gregory Ridge and Neeru Bhardwaj The sanofi-aventis Group, Malvern, PA Abstract Since 1999, sanofi-aventis
The #1 Key to Removing the Chaos. in Modern Analytical Environments
 October/2018 Advanced Data Lineage: The #1 Key to Removing the Chaos in Modern Analytical Environments Claudia Imhoff, Ph.D. Sponsored By: Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Data Lineage Introduction...
October/2018 Advanced Data Lineage: The #1 Key to Removing the Chaos in Modern Analytical Environments Claudia Imhoff, Ph.D. Sponsored By: Table of Contents Executive Summary... 1 Data Lineage Introduction...
From raw data to submission: A metadata-driven, repository-based process of data conversion to CDISC models
 Paper CD08 From raw data to submission: A metadata-driven, repository-based process of data conversion to CDISC models Dimitri Kutsenko, Entimo AG, Berlin, Germany ABSTRACT The paper presents a visionary
Paper CD08 From raw data to submission: A metadata-driven, repository-based process of data conversion to CDISC models Dimitri Kutsenko, Entimo AG, Berlin, Germany ABSTRACT The paper presents a visionary
Aquila's Lunch And Learn CDISC The FDA Data Standard. Disclosure Note 1/17/2014. Host: Josh Boutwell, MBA, RAC CEO Aquila Solutions, LLC
 Aquila's Lunch And Learn CDISC The FDA Data Standard Host: Josh Boutwell, MBA, RAC CEO Aquila Solutions, LLC Disclosure Note This free training session will be placed on Aquila s website after the session
Aquila's Lunch And Learn CDISC The FDA Data Standard Host: Josh Boutwell, MBA, RAC CEO Aquila Solutions, LLC Disclosure Note This free training session will be placed on Aquila s website after the session
Data Science Services Dirk Engfer Page 1 of 5
 Page 1 of 5 Services SAS programming Conform to CDISC SDTM and ADaM within clinical trials. Create textual outputs (tables, listings) and graphical output. Establish SAS macros for repetitive tasks and
Page 1 of 5 Services SAS programming Conform to CDISC SDTM and ADaM within clinical trials. Create textual outputs (tables, listings) and graphical output. Establish SAS macros for repetitive tasks and
Use of Traceability Chains in Study Data and Metadata for Regulatory Electronic Submission
 PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper SS03 Use of Traceability Chains in Study Data and Metadata for Regulatory Electronic Submission ABSTRACT Tianshu Li, Celldex Therapeutics, Hampton, NJ Traceability is one of the
PharmaSUG 2017 - Paper SS03 Use of Traceability Chains in Study Data and Metadata for Regulatory Electronic Submission ABSTRACT Tianshu Li, Celldex Therapeutics, Hampton, NJ Traceability is one of the
