Algorithm Design and Analysis
|
|
|
- Joshua Owen Roberts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne
2 Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected. True or false? G has at least n-1 edges. Suppose that an undirected graph G has exactly n-1 edges (and no self-loops) True or false? G is connected. What if G has n-1 edges and no cycles? 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne
3 Paths and Connectivity Def. A path in an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a sequence P of nodes v 1, v 2,, v k-1, v k with the property that each consecutive pair v i, v i+1 is joined by an edge in E. Def. A path is simple if all nodes are distinct. Def. An undirected graph is connected if for every pair of nodes u and v, there is a path between u and v. 3
4 Cycles Def. A cycle is a path v 1, v 2,, v k-1, v k in which v 1 = v k, k > 2, and the first k-1 nodes are all distinct. cycle C =
5 Trees Def. An undirected graph is a tree if it is connected and does not contain a cycle. Theorem. Let G be an undirected graph on n nodes. Any two of the following statements imply the third. G is connected. G does not contain a cycle. G has n-1 edges. 5
6 Rooted Trees Rooted tree. Given a tree T, choose a root node r and orient each edge away from r. Importance. Models hierarchical structure. root r parent of v v child of v a tree the same tree, rooted at 1 6
7 Phylogeny Trees Phylogeny trees. Describe evolutionary history of species. 7
8 Exploring a graph Classic problem: Given vertices s,t V, is there a path from s to t? Idea: explore all vertices reachable from s Two basic techniques: Breadth-first search (BFS) Explore children in order of distance to start node Depth-first search (DFS) How to convert these descriptions to precise algorithms? Recursively explore vertex s children before exploring siblings 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne
9 Breadth First Search BFS intuition. Explore outward from s in all possible directions, adding nodes one "layer" at a time. BFS algorithm. L 0 = { s }. L 1 = all neighbors of L 0. s L 1 L 2 L n-1 L 2 = all nodes that do not belong to L 0 or L 1, and that have an edge to a node in L 1. L i+1 = all nodes that do not belong to an earlier layer, and that have an edge to a node in L i. Theorem. For each i, L i consists of all nodes at distance exactly i from s. There is a path from s to t iff t appears in some layer. 9
10 Breadth First Search Property. Let T be a BFS tree of G = (V, E), and let (x, y) be an edge of G. Then the level of x and y differ by at most 1. L 0 L 1 L 2 L 3 10
11 Connected Component Connected component. Find all nodes reachable from s. Connected component containing node 1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }. 11
12 Flood Fill Flood fill. Given lime green pixel in an image, change color of entire blob of neighboring lime pixels to blue. Node: pixel. Edge: two neighboring lime pixels. Blob: connected component of lime pixels. recolor lime green blob to blue 12
13 Flood Fill Flood fill. Given lime green pixel in an image, change color of entire blob of neighboring lime pixels to blue. Node: pixel. Edge: two neighboring lime pixels. Blob: connected component of lime pixels. recolor lime green blob to blue 13
14 Connected Component Connected component. Find all nodes reachable from s. s R u v it's safe to add v Theorem. Upon termination, R is the connected component containing s. BFS = explore in order of distance from s. DFS = explore in a different way. 14
15 Implementing Traversals Generic traversal algorithm 1. R = {s} 2. While there is an edge (u,v) where u R and v R, Add v to R To implement this, need to choose Graph representation Data structures to track Vertices already explored Edge to be followed next These choices affect the order of traversal 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne
16 Adjacency-matrix representation The adjacency matrix of a graph G = (V, E), where V = {1, 2,, n}, is the matrix A[1.. n, 1.. n] given by A[i, j] = A if (i, j) E, 0 if (i, j) E Storage: ϴ(V 2 ) Good for dense graphs Lookup: O(1) time List all neighbors: O( V ) 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne
17 Adjacency list representation An adjacency list of a vertex v V is the list Adj[v] of vertices adjacent to v Adj[1] = {2, 3} Adj[2] = {3} Adj[3] = {} Adj[4] = {3} For undirected graphs, Adj[v] = degree(v). For digraphs, Adj[v] = out-degree(v). How many entries in lists? 2 E Total ϴ(V + E) storage good for sparse graphs. Typical notation: n = V = # vertices m = E = # edges 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne
18 BFS with adjacency list rep. Discovered[1.. n]: array of bits (explored or not) initialized to all zeros Queue Q initialized to empty Tree T initialized to empty 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne
19 BFS pseudocode BFS(s): 1. Set Discovered[s]=1 2. Add s to Q 3. While (Q not empty) a) Dequeue (u) b) For each edge (u,v) adjacent to u a) IF Discovered[v]= false then a) Set Discovered[v] =true b) Add edge (u,v) to tree T c) Add v to Q 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne
20 Theorem: BFS takes O(m+n) time BFS(s): 1. Set Discovered[s]=1 2. Add s to Q 3. While (Q not empty) a) Dequeue (u) b) For each edge (u,v) adjacent to u a) IF Discovered[v]= false then a) Set Discovered[v] =true b) Add edge (u,v) to tree T c) Add v to Q O(1) time, run once overall. O(1) time, run once per vertex O(1) time per execution, run at most twice per edge Total: O(m+n) time (linear in input size) 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne
21 Notes If s is the roof of BFS tree For every vertex u, path in BFS tree from s to u is a shortest path in G depth in BFS tree = distance from u to s Proof of BFS correctness: see KT, Chapter 3. 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
Chapter 3. Graphs CLRS Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Graphs CLRS 12-13 Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V
Chapter 3 Graphs CLRS 12-13 Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V
Algorithms: Lecture 10. Chalmers University of Technology
 Algorithms: Lecture 10 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Topics Basic Definitions Path, Cycle, Tree, Connectivity, etc. Graph Traversal Depth First Search Breadth First Search Testing Bipartatiness
Algorithms: Lecture 10 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Topics Basic Definitions Path, Cycle, Tree, Connectivity, etc. Graph Traversal Depth First Search Breadth First Search Testing Bipartatiness
Undirected Graphs. V = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 } E = { 1-2, 1-3, 2-3, 2-4, 2-5, 3-5, 3-7, 3-8, 4-5, 5-6 } n = 8 m = 11
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications. Chapter 3. Graphs. Undirected Graphs. Some Graph Applications
 Chapter 3 31 Basic Definitions and Applications Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley All rights reserved 1 Undirected Graphs Some Graph Applications Undirected graph G = (V,
Chapter 3 31 Basic Definitions and Applications Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley All rights reserved 1 Undirected Graphs Some Graph Applications Undirected graph G = (V,
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications
 Chapter 3 Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E
Chapter 3 Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 7 Greedy Graph Algorithms Topological sort Shortest paths Adam Smith The (Algorithm) Design Process 1. Work out the answer for some examples. Look for a general principle
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 7 Greedy Graph Algorithms Topological sort Shortest paths Adam Smith The (Algorithm) Design Process 1. Work out the answer for some examples. Look for a general principle
COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms
 COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms Topic 14. Graph Algorithms 11/7/2016 1 Elementary Graph Algorithms How to represent a graph? Adjacency lists Adjacency matrix How to search a graph? Breadth-first
COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms Topic 14. Graph Algorithms 11/7/2016 1 Elementary Graph Algorithms How to represent a graph? Adjacency lists Adjacency matrix How to search a graph? Breadth-first
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Linear Time: O(n) CS 580: Algorithm Design and Analysis 2.4 A Survey of Common Running Times Merge. Combine two sorted lists A = a 1,a 2,,a n with B = b 1,b 2,,b n into sorted whole. Jeremiah Blocki Purdue
Linear Time: O(n) CS 580: Algorithm Design and Analysis 2.4 A Survey of Common Running Times Merge. Combine two sorted lists A = a 1,a 2,,a n with B = b 1,b 2,,b n into sorted whole. Jeremiah Blocki Purdue
12/5/17. trees. CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks. rooted trees. rooted trees
 trees CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications A tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks rooted trees Rooted trees. Given a tree T, choose
trees CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications A tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks rooted trees Rooted trees. Given a tree T, choose
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity. 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications. Goals. Chapter 3. Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 3 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Graphs Reading: 3.1-3.6 Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
Chapter 3 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Graphs Reading: 3.1-3.6 Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. graphs zybooks chapter 10
 CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman
 CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman Lecture 11: Graphs Graph Traversals: BFS Feb 16, 2018 What s Next What s Next Graph Algorithms: Graphs: Key Definitions, Properties, Representations Exploring
CS4800: Algorithms & Data Jonathan Ullman Lecture 11: Graphs Graph Traversals: BFS Feb 16, 2018 What s Next What s Next Graph Algorithms: Graphs: Key Definitions, Properties, Representations Exploring
Lecture 3: Graphs and flows
 Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search
 Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search Analysis of Algorithms Week 8, Lecture 1 Prepared by John Reif, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor of Computer Science Duke University Graph Algorithms Using Depth
Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search Analysis of Algorithms Week 8, Lecture 1 Prepared by John Reif, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor of Computer Science Duke University Graph Algorithms Using Depth
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M.
 Lecture 9 Graphs Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M. Wootters (2017) 1 Graphs A graph is a set of vertices
Lecture 9 Graphs Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M. Wootters (2017) 1 Graphs A graph is a set of vertices
Chapter 3. Graphs. Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E
Chapter 3 Graphs Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E
CS781 Lecture 2 January 13, Graph Traversals, Search, and Ordering
 CS781 Lecture 2 January 13, 2010 Graph Traversals, Search, and Ordering Review of Lecture 1 Notions of Algorithm Scalability Worst-Case and Average-Case Analysis Asymptotic Growth Rates: Big-Oh Prototypical
CS781 Lecture 2 January 13, 2010 Graph Traversals, Search, and Ordering Review of Lecture 1 Notions of Algorithm Scalability Worst-Case and Average-Case Analysis Asymptotic Growth Rates: Big-Oh Prototypical
Graph Algorithms. Chapter 22. CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms 1
 Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007
 Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Graphs & Digraphs Tuesday, November 06, 2007 10:34 PM 16.1 Directed Graphs (digraphs) like a tree but w/ no root node & no guarantee of paths between nodes consists of: nodes/vertices - a set of elements
Elementary Graph Algorithms. Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph:
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Graphs. Graph G = (V, E) Types of graphs E = O( V 2 ) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V)
 Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Jana Kosecka. Red-Black Trees Graph Algorithms. Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides
 Jana Kosecka Red-Black Trees Graph Algorithms Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides Binary Search Trees (BSTs) are an important data structure for dynamic sets In addition to satellite
Jana Kosecka Red-Black Trees Graph Algorithms Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides Binary Search Trees (BSTs) are an important data structure for dynamic sets In addition to satellite
This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science.
 Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices» E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs» Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.)» Directed: (u, v)
Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices» E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs» Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.)» Directed: (u, v)
Review: Graph Theory and Representation
 Review: Graph Theory and Representation Graph Algorithms Graphs and Theorems about Graphs Graph implementation Graph Algorithms Shortest paths Minimum spanning tree What can graphs model? Cost of wiring
Review: Graph Theory and Representation Graph Algorithms Graphs and Theorems about Graphs Graph implementation Graph Algorithms Shortest paths Minimum spanning tree What can graphs model? Cost of wiring
3. GRAPHS. Lecture slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley Copyright 2013 Kevin Wayne. Last updated on Sep 8, :19 AM
 3. GRAPHS basic definitions and applications graph connectivity and graph traversal testing bipartiteness connectivity in directed graphs DAGs and topological ordering Lecture slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright
3. GRAPHS basic definitions and applications graph connectivity and graph traversal testing bipartiteness connectivity in directed graphs DAGs and topological ordering Lecture slides by Kevin Wayne Copyright
Trees. Arash Rafiey. 20 October, 2015
 20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
Searching in Graphs (cut points)
 0 November, 0 Breath First Search (BFS) in Graphs In BFS algorithm we visit the verices level by level. The BFS algorithm creates a tree with root s. Once a node v is discovered by BFS algorithm we put
0 November, 0 Breath First Search (BFS) in Graphs In BFS algorithm we visit the verices level by level. The BFS algorithm creates a tree with root s. Once a node v is discovered by BFS algorithm we put
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Graphs Applications of DFS Topological sort Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova S. Raskhodnikova; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, A. Smith,
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Graphs Applications of DFS Topological sort Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova S. Raskhodnikova; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, A. Smith,
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms CSE 5311 Lecture 18 Graph Algorithm Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Graphs Graph G = (V,
Design and Analysis of Algorithms CSE 5311 Lecture 18 Graph Algorithm Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Graphs Graph G = (V,
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 13. Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico
 CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 13 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 10-5-2010 1 Last Time Spanning Trees BFS DFS Testing Bipartiteness 2 Today Inside BFS Running Time Implementation Degrees
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 13 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 10-5-2010 1 Last Time Spanning Trees BFS DFS Testing Bipartiteness 2 Today Inside BFS Running Time Implementation Degrees
CS/COE
 CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms
 (Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
Introduction to Algorithms
 Introduction to Algorithms, Lecture 1 /1/200 Introduction to Algorithms.04J/1.401J LECTURE 11 Graphs, MST, Greedy, Prim Graph representation Minimum spanning trees Greedy algorithms hallmarks. Greedy choice
Introduction to Algorithms, Lecture 1 /1/200 Introduction to Algorithms.04J/1.401J LECTURE 11 Graphs, MST, Greedy, Prim Graph representation Minimum spanning trees Greedy algorithms hallmarks. Greedy choice
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications
 Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Graph Algorithms: Chapters Part 1: Introductory graph concepts
 UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Algorithms Dr. Haim Levkowitz Fall, 2007 Graph Algorithms: Chapters 22-25 Part 1: Introductory graph concepts 1 91.404 Graph Review Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum
UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Algorithms Dr. Haim Levkowitz Fall, 2007 Graph Algorithms: Chapters 22-25 Part 1: Introductory graph concepts 1 91.404 Graph Review Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
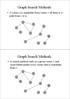 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
DFS & STRONGLY CONNECTED COMPONENTS
 DFS & STRONGLY CONNECTED COMPONENTS CS 4407 Search Tree Breadth-First Search (BFS) Depth-First Search (DFS) Depth-First Search (DFS) u d[u]: when u is discovered f[u]: when searching adj of u is finished
DFS & STRONGLY CONNECTED COMPONENTS CS 4407 Search Tree Breadth-First Search (BFS) Depth-First Search (DFS) Depth-First Search (DFS) u d[u]: when u is discovered f[u]: when searching adj of u is finished
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees
 Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms
 CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
Introduction to Algorithms
 Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J LECTURE 16 Greedy Algorithms (and Graphs) Graph representation Minimum spanning trees Optimal substructure Greedy choice Prim s greedy MST algorithm Prof. Charles
Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J LECTURE 16 Greedy Algorithms (and Graphs) Graph representation Minimum spanning trees Optimal substructure Greedy choice Prim s greedy MST algorithm Prof. Charles
Homework Assignment #3 Graph
 CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
Shortest Path Routing Communications networks as graphs Graph terminology Breadth-first search in a graph Properties of breadth-first search
 Shortest Path Routing Communications networks as graphs Graph terminology Breadth-first search in a graph Properties of breadth-first search 6.082 Fall 2006 Shortest Path Routing, Slide 1 Routing in an
Shortest Path Routing Communications networks as graphs Graph terminology Breadth-first search in a graph Properties of breadth-first search 6.082 Fall 2006 Shortest Path Routing, Slide 1 Routing in an
Introduction to Algorithms
 Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J LECTURE 13 Graph algorithms Graph representation Minimum spanning trees Greedy algorithms Optimal substructure Greedy choice Prim s greedy MST algorithm Prof.
Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J LECTURE 13 Graph algorithms Graph representation Minimum spanning trees Greedy algorithms Optimal substructure Greedy choice Prim s greedy MST algorithm Prof.
22.3 Depth First Search
 22.3 Depth First Search Depth-First Search(DFS) always visits a neighbour of the most recently visited vertex with an unvisited neighbour. This means the search moves forward when possible, and only backtracks
22.3 Depth First Search Depth-First Search(DFS) always visits a neighbour of the most recently visited vertex with an unvisited neighbour. This means the search moves forward when possible, and only backtracks
Trees : Part 1. Section 4.1. Theory and Terminology. A Tree? A Tree? Theory and Terminology. Theory and Terminology
 Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal
 Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Undirected Graphs. DSA - lecture 6 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1
 Undirected Graphs Terminology. Free Trees. Representations. Minimum Spanning Trees (algorithms: Prim, Kruskal). Graph Traversals (dfs, bfs). Articulation points & Biconnected Components. Graph Matching
Undirected Graphs Terminology. Free Trees. Representations. Minimum Spanning Trees (algorithms: Prim, Kruskal). Graph Traversals (dfs, bfs). Articulation points & Biconnected Components. Graph Matching
Representations of Graphs
 ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
Depth-First Search Depth-first search (DFS) is another way to traverse the graph.
 Depth-First Search Depth-first search (DFS) is another way to traverse the graph. Motivating example: In a video game, you are searching for a path from a point in a maze to the exit. The maze can be modeled
Depth-First Search Depth-first search (DFS) is another way to traverse the graph. Motivating example: In a video game, you are searching for a path from a point in a maze to the exit. The maze can be modeled
Graph Representation
 Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]
![Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch] Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]](/thumbs/81/84350835.jpg) Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
Graphs. Part I: Basic algorithms. Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College
 Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Undirected graphs Concepts: connectivity, connected components paths (undirected) cycles Basic problems, given undirected graph G: is G connected how many
Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Undirected graphs Concepts: connectivity, connected components paths (undirected) cycles Basic problems, given undirected graph G: is G connected how many
Graph Algorithms. Definition
 Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
TIE Graph algorithms
 TIE-20106 239 11 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
TIE-20106 239 11 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
Announcements Problem Set 4 is out!
 CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
CSC263 Week 8 Announcements Problem Set 4 is out! Due Tuesday (Nov 17) Other Announcements Drop date Nov 8 Final exam schedule is posted CSC263 exam Dec 11, 2-5pm This week s outline Graphs BFS Graph A
CSC263 Week 8. Larry Zhang.
 CSC263 Week 8 Larry Zhang http://goo.gl/forms/s9yie3597b Announcements (strike related) Lectures go as normal Tutorial this week everyone go to BA32 (T8, F2, F2, F3) Problem sets / Assignments are submitted
CSC263 Week 8 Larry Zhang http://goo.gl/forms/s9yie3597b Announcements (strike related) Lectures go as normal Tutorial this week everyone go to BA32 (T8, F2, F2, F3) Problem sets / Assignments are submitted
Breadth First Search. cse2011 section 13.3 of textbook
 Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
Lecture 10 Graph algorithms: testing graph properties
 Lecture 10 Graph algorithms: testing graph properties COMP 523: Advanced Algorithmic Techniques Lecturer: Dariusz Kowalski Lecture 10: Testing Graph Properties 1 Overview Previous lectures: Representation
Lecture 10 Graph algorithms: testing graph properties COMP 523: Advanced Algorithmic Techniques Lecturer: Dariusz Kowalski Lecture 10: Testing Graph Properties 1 Overview Previous lectures: Representation
Goals! CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity!
 Goals! CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity! Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology! Representation: input, internal! Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search! Three Algorithms:!!Connected
Goals! CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity! Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology! Representation: input, internal! Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search! Three Algorithms:!!Connected
Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs
 Next: Graph Algorithms Graphs Ch 22 Graph representations adjacency list adjacency matrix Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs Breadth-First Search Depth-First Search 11/30/17 CSE 3101 1 Graphs
Next: Graph Algorithms Graphs Ch 22 Graph representations adjacency list adjacency matrix Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs Breadth-First Search Depth-First Search 11/30/17 CSE 3101 1 Graphs
implementing the breadth-first search algorithm implementing the depth-first search algorithm
 Graph Traversals 1 Graph Traversals representing graphs adjacency matrices and adjacency lists 2 Implementing the Breadth-First and Depth-First Search Algorithms implementing the breadth-first search algorithm
Graph Traversals 1 Graph Traversals representing graphs adjacency matrices and adjacency lists 2 Implementing the Breadth-First and Depth-First Search Algorithms implementing the breadth-first search algorithm
GRAPHS (Undirected) Graph: Set of objects with pairwise connections. Why study graph algorithms?
 GRAPHS (Undirected) Graph: Set of objects with pairwise connections. Why study graph algorithms? Interesting and broadly useful abstraction. Challenging branch of computer science and discrete math. Hundreds
GRAPHS (Undirected) Graph: Set of objects with pairwise connections. Why study graph algorithms? Interesting and broadly useful abstraction. Challenging branch of computer science and discrete math. Hundreds
Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms Pierre Flener Lars-enrik Eriksson (version of 2013-02-10) Different kinds of graphs List Tree A B C A B C Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) D A B C D E Directed Graph (Digraph)
Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms Pierre Flener Lars-enrik Eriksson (version of 2013-02-10) Different kinds of graphs List Tree A B C A B C Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) D A B C D E Directed Graph (Digraph)
COP 4531 Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms
 COP Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms Overview of Graphs Breadth irst Search, and Depth irst Search hanks to several people who contributed to these slides including Piyush Kumar and
COP Complexity & Analysis of Data Structures & Algorithms Overview of Graphs Breadth irst Search, and Depth irst Search hanks to several people who contributed to these slides including Piyush Kumar and
Graph. Vertex. edge. Directed Graph. Undirected Graph
 Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms
 W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
W4231: Analysis of Algorithms 10/21/1999 Definitions for graphs Breadth First Search and Depth First Search Topological Sort. Graphs AgraphG is given by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. Normally
CS473-Algorithms I. Lecture 13-A. Graphs. Cevdet Aykanat - Bilkent University Computer Engineering Department
 CS473-Algorithms I Lecture 3-A Graphs Graphs A directed graph (or digraph) G is a pair (V, E), where V is a finite set, and E is a binary relation on V The set V: Vertex set of G The set E: Edge set of
CS473-Algorithms I Lecture 3-A Graphs Graphs A directed graph (or digraph) G is a pair (V, E), where V is a finite set, and E is a binary relation on V The set V: Vertex set of G The set E: Edge set of
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Graphs (review) Definition. A directed graph (digraph) G = (V, E) is an ordered pair consisting of a set V of vertices
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Graphs (review) Definition. A directed graph (digraph) G = (V, E) is an ordered pair consisting of a set V of vertices
CS 161 Lecture 11 BFS, Dijkstra s algorithm Jessica Su (some parts copied from CLRS) 1 Review
 1 Review 1 Something I did not emphasize enough last time is that during the execution of depth-firstsearch, we construct depth-first-search trees. One graph may have multiple depth-firstsearch trees,
1 Review 1 Something I did not emphasize enough last time is that during the execution of depth-firstsearch, we construct depth-first-search trees. One graph may have multiple depth-firstsearch trees,
Chapter 22. Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Graph Algorithms - Spring 2011 Set 7. Lecturer: Huilan Chang Reference: (1) Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest, and Stein, Introduction to Algorithms, 2nd Edition, The MIT Press. (2) Lecture notes from C. Y. Chen
Graph Algorithms - Spring 2011 Set 7. Lecturer: Huilan Chang Reference: (1) Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest, and Stein, Introduction to Algorithms, 2nd Edition, The MIT Press. (2) Lecture notes from C. Y. Chen
Figure 1: A directed graph.
 1 Graphs A graph is a data structure that expresses relationships between objects. The objects are called nodes and the relationships are called edges. For example, social networks can be represented as
1 Graphs A graph is a data structure that expresses relationships between objects. The objects are called nodes and the relationships are called edges. For example, social networks can be represented as
Broadcast: Befo re 1
 Broadcast: Before 1 After 2 Spanning Tree ffl assume fixed spanning tree ffl asynchronous model 3 Processor State parent terminated children 4 Broadcast: Step One parent terminated children 5 Broadcast:Step
Broadcast: Before 1 After 2 Spanning Tree ffl assume fixed spanning tree ffl asynchronous model 3 Processor State parent terminated children 4 Broadcast: Step One parent terminated children 5 Broadcast:Step
TIE Graph algorithms
 TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014
 GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
Plan. CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms. Recall. Adjacency List Representation. DFS Descriptions. BFS Description
 Plan CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Akshay Krishnamurthy and Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Review: Breadth First Search Depth First Search Traversal Implementation and Running Time
Plan CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Akshay Krishnamurthy and Andrew McGregor University of Massachusetts Review: Breadth First Search Depth First Search Traversal Implementation and Running Time
Algorithms and Theory of Computation. Lecture 3: Graph Algorithms
 Algorithms and Theory of Computation Lecture 3: Graph Algorithms Xiaohui Bei MAS 714 August 20, 2018 Nanyang Technological University MAS 714 August 20, 2018 1 / 18 Connectivity In a undirected graph G
Algorithms and Theory of Computation Lecture 3: Graph Algorithms Xiaohui Bei MAS 714 August 20, 2018 Nanyang Technological University MAS 714 August 20, 2018 1 / 18 Connectivity In a undirected graph G
Data Structures and Algorithms. Chapter 7. Graphs
 1 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 7 Werner Nutt 2 Acknowledgments The course follows the book Introduction to Algorithms, by Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest and Stein, MIT Press [CLRST]. Many examples
1 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 7 Werner Nutt 2 Acknowledgments The course follows the book Introduction to Algorithms, by Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest and Stein, MIT Press [CLRST]. Many examples
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
Objec&ves. Wrap up: Implemen&ng BFS and DFS Graph Applica&on: Bipar&te Graphs. Get out your BFS implementa&on handouts. Feb 2, 2018 CSCI211 - Sprenkle
 Objec&ves Wrap up: Implemen&ng BFS and DFS Graph Applica&on: Bipar&te Graphs Get out your BFS implementa&on handouts Feb 2, 2018 CSCI211 - Sprenkle 1 Review What are two ways to find a connected component?
Objec&ves Wrap up: Implemen&ng BFS and DFS Graph Applica&on: Bipar&te Graphs Get out your BFS implementa&on handouts Feb 2, 2018 CSCI211 - Sprenkle 1 Review What are two ways to find a connected component?
Chapter 3. Graphs. 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications
 Chapter 3 Graphs Our focus in this book is on problems with a discrete flavor. Just as continuous mathematics is concerned with certain basic structures such as real numbers, vectors, and matrices, discrete
Chapter 3 Graphs Our focus in this book is on problems with a discrete flavor. Just as continuous mathematics is concerned with certain basic structures such as real numbers, vectors, and matrices, discrete
Fundamental Algorithms
 Fundamental Algorithms Chapter 8: Graphs Jan Křetínský Winter 2017/18 Chapter 8: Graphs, Winter 2017/18 1 Graphs Definition (Graph) A graph G = (V, E) consists of a set V of vertices (nodes) and a set
Fundamental Algorithms Chapter 8: Graphs Jan Křetínský Winter 2017/18 Chapter 8: Graphs, Winter 2017/18 1 Graphs Definition (Graph) A graph G = (V, E) consists of a set V of vertices (nodes) and a set
CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 5: Graphs an Introduction
 CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 5: Graphs an Introduction Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork 1 Outline Motivation Importance of graphs for algorithm design applications
CS 4407 Algorithms Lecture 5: Graphs an Introduction Prof. Gregory Provan Department of Computer Science University College Cork 1 Outline Motivation Importance of graphs for algorithm design applications
COL351: Analysis and Design of Algorithms (CSE, IITD, Semester-I ) Name: Entry number:
 Name: Entry number: There are 6 questions for a total of 75 points. 1. Consider functions f(n) = 10n2 n + 3 n and g(n) = n3 n. Answer the following: (a) ( 1 / 2 point) State true or false: f(n) is O(g(n)).
Name: Entry number: There are 6 questions for a total of 75 points. 1. Consider functions f(n) = 10n2 n + 3 n and g(n) = n3 n. Answer the following: (a) ( 1 / 2 point) State true or false: f(n) is O(g(n)).
Graphs. CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
CSE 101. Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 6: BFS and Dijkstra s
 CSE 101 Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones mej016@eng.ucsd.edu Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 6: BFS and Dijkstra s BREADTH FIRST SEARCH (BFS) Given a graph G and a starting vertex s, BFS computes
CSE 101 Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones mej016@eng.ucsd.edu Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 6: BFS and Dijkstra s BREADTH FIRST SEARCH (BFS) Given a graph G and a starting vertex s, BFS computes
Applications of BDF and DFS
 January 14, 2016 1 Deciding whether a graph is bipartite using BFS. 2 Finding connected components of a graph (both BFS and DFS) works. 3 Deciding whether a digraph is strongly connected. 4 Finding cut
January 14, 2016 1 Deciding whether a graph is bipartite using BFS. 2 Finding connected components of a graph (both BFS and DFS) works. 3 Deciding whether a digraph is strongly connected. 4 Finding cut
Graphs. Graphs. Representation of Graphs. CSE 680 Prof. Roger Crawfis. Two standard ways. Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices
 Introduction to Algorithms Graph Algorithms CSE 680 Prof. Roger Crawfis Partially from io.uwinnipeg.ca/~ychen2 Graphs Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices» E = set of edges (V V) V) Types of graphs» Undirected:
Introduction to Algorithms Graph Algorithms CSE 680 Prof. Roger Crawfis Partially from io.uwinnipeg.ca/~ychen2 Graphs Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices» E = set of edges (V V) V) Types of graphs» Undirected:
22.1 Representations of graphs
 22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
1. Graph and Representation
 Chapter Graphs Tree Root Direction: parent-child relationships No cycles Graph Vertices + Edges No tree restrictions Examples World Wide Web Maps. Graph and Representation A graph G: a pair (V, E) vertices
Chapter Graphs Tree Root Direction: parent-child relationships No cycles Graph Vertices + Edges No tree restrictions Examples World Wide Web Maps. Graph and Representation A graph G: a pair (V, E) vertices
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
Graphs and Graph Algorithms. Slides by Larry Ruzzo
 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Larry Ruzzo Goals Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology Representation: input, internal Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search Three Algorithms: Connected
Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Larry Ruzzo Goals Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology Representation: input, internal Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search Three Algorithms: Connected
