CSE 2331/5331. Topic 9: Basic Graph Alg. Representations Basic traversal algorithms Topological sort CSE 2331/5331
|
|
|
- Giles Cobb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topic 9: Basic Graph Alg. Representations Basic traversal algorithms Topological sort
2 What Is A Graph Graph G = (V, E) V: set of nodes E: set of edges a b c Example: d e f V ={ a, b, c, d, e, f } E ={(a, b), (a, d), (a, e), (b, c), (b, d), (b, e), (c, e), (e,f)}
3 Un-directed graph EE VV 2 Directed graph EE VV 2 a b c d e f
4 Un-directed graphs
5 Vertex Degree deg(v) = degree of v = # edges incident on v a b c d e f Lemma: vvii VV(GG) deg vv ii = 2 EE
6 Some Special Graphs Complete graph Path Cycle Planar graph Tree
7 Representations of Graphs Adjacency lists Each vertex u has a list, recording its neighbors i.e., all v s such that (u, v) E An array of V lists V[i].degree = size of adj list for node vv ii V[i].AdjList = adjacency list for node vv ii
8 Adjacency Lists For vertex v V, its adjacency list has size: deg(v) decide whether (v, u) E or not in time Θ (deg(v)) Size of data structure (space complexity): Θ( V + E ) = Θ (V+E)
9 Adjacency Matrix VV VV matrix AA AA ii, jj = 1 if vv ii, vv jj is an edge Otherwise, AA ii, jj = 0
10 Adjacency Matrix Size of data structure: Θ ( V V) Time to determine if (v, u) E : Θ(1) Though larger, it is simpler compared to adjacency list.
11 Sample Graph Algorithm Input: Graph G represented by adjacency lists Running time: Θ(V + E)
12 Connectivity A path in a graph is a sequence of vertices uu 1, uu 2,, uu kk such that there is an edge uu ii, uu ii+1 between any two adjacent vertices in the sequence Two vertices uu, ww VV GG are connected if there is a path in G from u to w. We also say that w is reachable from u. A graph G is connected if every pair of nodes uu, ww VV GG are connected.
13 Connectivity Checking How to check if the graph is connected? One approach: Graph traversal BFS: breadth-first search DFS: depth-first search
14 BFS: Breadth-first search Input: Given graph G = (V, E), and a source node s V Output: Will visit all nodes in V reachable from s For each vv VV, output a value vv. dd vv. dd = distance (smallest # of edges) from s to v. vv. dd = if v is not reachable from s.
15 Intuition Starting from source node s, Spread a wavefront to visit other nodes First visit all nodes one edge away from s Then all nodes two edges away from s Need a data-structure to store nodes to be explored.
16 Intuition cont. A node can be: un-discovered discovered, but not explored explored (finished) vv. dd : is set when node v is first discovered. Need a data structure to store discovered but unexplored nodes FIFO! Queue
17 Pseudo-code Use adjacency list representation Time complexity: Θ(V+E)
18 Correctness of Algorithm A node not reachable from s will not be visited A node reachable from s will be visited vv. dd computed is correct: Intuitively, if all nodes k distance away from s are in level k, and no other nodes are in level k, Then all nodes (k+1)-distance away from s must be in level (k+1). Rigorous proof by induction
19 BFS tree A node vv is the parent of uu if uu was first discovered when exploring vv A BFS tree TT Root: source node ss Nodes in level kk of TT are distance kk away from ss
20 Connectivity-Checking Time complexity: Θ(V+E)
21 Summary for BFS Starting from source node s, visits remaining nodes of graph from small distance to large distance This is one way to traverse an input graph With some special property where nodes are visited in non-decreasing distance to the source node s. Return distance between s to any reachable node in time Θ ( V + E )
22 DFS: Depth-First Search Another graph traversal algorithm BFS: Go as broad as possible in the algorithm DFS: Go as deep as possible in the algorithm
23 Example Perform DFS starting from vv 1 What if we add edge vv 1, vv 8
24 DFS Time complexity Θ(V+E)
25 Depth First Search Tree If v is discovered when exploring u Set vv. pppppppppppp = uu The collection of edges vv. pppppppppppp, vv form a tree, called Depth-first search tree.
26 DFS with DFS Tree
27 Example Perform DFS starting from vv 1
28 Another Connectivity Test
29 Traverse Entire Graph
30 Remarks DFS(G, k) Another way to compute all nodes reachable to the node vv kk Same time complexity as BFS There are nice properties of DFS and DFS tree that we are not reviewing in this class.
31 Directed Graphs
32 Un-directed graph EE VV 2 Directed graph Each edge uu, vv is directed from u to v EE VV 2 a b c d e f
33 Vertex Degree indeg(v) = # edges of the form uu, vv outdeg(v) = # edges of the form vv, uu a b c d e f Lemma: vvii VV(GG) indeg vv ii = EE Lemma: vvii VV(GG) outdeg vv ii = EE
34 Representations of Graphs Adjacency lists Each vertex u has a list, recording its neighbors i.e., all v s such that (u, v) E An array of V lists V[i].degree = size of adj list for node vv ii V[i].AdjList = adjacency list for node vv ii
35 Adjacency Lists For vertex v V, its adjacency list has size: outdeg(v) decide whether (v, u) E or not in time O(outdeg(v)) Size of data structure (space complexity): Θ(V+E)
36 Adjacency Matrix VV VV matrix AA AA ii, jj = 1 if vv ii, vv jj is an edge Otherwise, AA ii, jj = 0
37 Adjacency Matrix Size of data structure: Θ ( V V) Time to determine if (v, u) E : O(1) Though larger, it is simpler compared to adjacency list.
38 Sample Graph Algorithm Input: Directed graph G represented by adjacency list Running time: O(V + E)
39 Connectivity A path in a graph is a sequence of vertices uu 1, uu 2,, uu kk such that there is an edge uu ii, uu ii+1 between any two adjacent vertices in the sequence Given two vertices uu, ww VV GG, we say that w is reachable from u if there is a path in G from u to w. Note: w is reachable from u DOES NOT necessarily mean that u is reachable from w.
40 Reachability Test How many (or which) vertices are reachable from a source node, say vv 1?
41 BFS and DFS The algorithms for BFS and DFS remain the same Each edge is now understood as a directed edge BFS(V,E, s) : visits all nodes reachable from s in non-decreasing order
42 BFS Starting from source node s, Spread a wavefront to visit other nodes First visit all nodes one edge away from s Then all nodes two edges away from s
43 Pseudo-code Use adjacency list representation Time complexity: Θ(V+E)
44 Number of Reachable Nodes Compute # nodes reachable from vv kk Time complexity: Θ(V+E)
45 DFS: Depth-First Search Similarly, DFS remains the same Each edge is now a directed edge If we start with all nodes unvisited, Then DFS(G, kk) visits all nodes reachable to node vv kk BFS from previous NumReachable() procedure can be replaced with DFS.
46 More Example Is vv 1 reachable from vv 12? Is vv 12 reachable from vv 1?
47 DFS(G, k); DFS above can be replaced with BFS
48 Topological Sort
49 Directed Acyclic Graph A directed cycle is a sequence uu 1, uu 2,, uu kk, uu 1 such that there is a directed edge between any two consecutive nodes. DAG: directed acyclic graph Is a directed graph with no directed cycles.
50 Topological Sort A topological sort of a DAG G = (V, E) A linear ordering A of all vertices from V If edge (u,v) E => A[u] < A[v] undershorts pants socks shoes watch belt shirt tie jacket
51 Another Example Why requires DAG? Is the sorting order unique?
52 A topological sorted order of graph G exists if and only if G is a directed acyclic graph (DAG).
53 Question How to topologically sort a given DAG? Intuition: Which node can be the first node in the topological sort order? A node with in-degree 0! After we remove this, the process can be repeated.
54 Example undershorts pants socks shoes watch belt shirt tie jacket
55
56 Topological Sort Simplified Implementation
57 Time complexity Θ(V+E) Correctness: What if the algorithm terminates before we finish visiting all nodes? Procedure TopologicalSort(G) outputs a sorted list of all nodes if and only if the input graph G is a DAG If G is not DAG, the algorithm outputs only a partial list of vertices.
58 Remarks Other topological sort algorithm by using properties of DFS
59 Last Analyzing graph algorithms Adjacency list representation or Adjacency matrix representation CSE 2331 / 5331
60 Edge-weighted un-directed graph G = (V, E) and edge weight function ww: EE RR E.g, road network, where each node is a city, and each edge is a road, and weight is the length of this road. a 1 d 3 5 b e 4 c f CSE 2331 / 5331
61 Example 1 Assume G is represented by adjacency list Q is priority-queue implemented by min-heap CSE 2331 / 5331
62 Example 2 Assume G is represented by adjacency matrix What if move line 10 to above line 8? What if move line 10 to above line 9? CSE 2331 / 5331
Graph Representation
 Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Basic Graph Algorithms (CLRS B.4-B.5, )
 Basic Graph Algorithms (CLRS B.-B.,.-.) Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices V and a finite set of edges E. Directed graphs: E is a set of ordered pairs of vertices
Basic Graph Algorithms (CLRS B.-B.,.-.) Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices V and a finite set of edges E. Directed graphs: E is a set of ordered pairs of vertices
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms CSE 5311 Lecture 18 Graph Algorithm Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Graphs Graph G = (V,
Design and Analysis of Algorithms CSE 5311 Lecture 18 Graph Algorithm Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Graphs Graph G = (V,
Review: Graph Theory and Representation
 Review: Graph Theory and Representation Graph Algorithms Graphs and Theorems about Graphs Graph implementation Graph Algorithms Shortest paths Minimum spanning tree What can graphs model? Cost of wiring
Review: Graph Theory and Representation Graph Algorithms Graphs and Theorems about Graphs Graph implementation Graph Algorithms Shortest paths Minimum spanning tree What can graphs model? Cost of wiring
Data Structures and Algorithms. Chapter 7. Graphs
 1 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 7 Werner Nutt 2 Acknowledgments The course follows the book Introduction to Algorithms, by Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest and Stein, MIT Press [CLRST]. Many examples
1 Data Structures and Algorithms Chapter 7 Werner Nutt 2 Acknowledgments The course follows the book Introduction to Algorithms, by Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest and Stein, MIT Press [CLRST]. Many examples
Trees. Arash Rafiey. 20 October, 2015
 20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms. Lecture 24 Fall 2017
 CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 24 Fall 2017 ANALYSIS OF DIJKSTRA S ALGORITHM CSC 172, Fall 2017 Implementation and analysis The initialization requires Q( V ) memory and run time We iterate
CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 24 Fall 2017 ANALYSIS OF DIJKSTRA S ALGORITHM CSC 172, Fall 2017 Implementation and analysis The initialization requires Q( V ) memory and run time We iterate
CISC 320 Introduction to Algorithms Fall Lecture 15 Depth First Search
 IS 320 Introduction to lgorithms all 2014 Lecture 15 epth irst Search 1 Traversing raphs Systematic search of every edge and vertex of graph (directed or undirected) fficiency: each edge is visited no
IS 320 Introduction to lgorithms all 2014 Lecture 15 epth irst Search 1 Traversing raphs Systematic search of every edge and vertex of graph (directed or undirected) fficiency: each edge is visited no
Data Structures and Algorithms. Werner Nutt
 Data Structures and Algorithms Werner Nutt nutt@inf.unibz.it http://www.inf.unibz/it/~nutt Part 9 Academic Year 2011-2012 1 Acknowledgements & Copyright Notice These slides are built on top of slides developed
Data Structures and Algorithms Werner Nutt nutt@inf.unibz.it http://www.inf.unibz/it/~nutt Part 9 Academic Year 2011-2012 1 Acknowledgements & Copyright Notice These slides are built on top of slides developed
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees
 Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
Lecture 10. Elementary Graph Algorithm Minimum Spanning Trees T. H. Cormen, C. E. Leiserson and R. L. Rivest Introduction to Algorithms, 3rd Edition, MIT Press, 2009 Sungkyunkwan University Hyunseung Choo
Graphs. CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
22.3 Depth First Search
 22.3 Depth First Search Depth-First Search(DFS) always visits a neighbour of the most recently visited vertex with an unvisited neighbour. This means the search moves forward when possible, and only backtracks
22.3 Depth First Search Depth-First Search(DFS) always visits a neighbour of the most recently visited vertex with an unvisited neighbour. This means the search moves forward when possible, and only backtracks
Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices» E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs» Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.)» Directed: (u, v)
Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E)» V = set of vertices» E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs» Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.)» Directed: (u, v)
Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms Graph Representations Graph G = (V,E) Directed Undirected Adjacency Lists Adjacency Matrix Graph Representations Adjacency List: Undirected Memory: Adjacency: Graph
Chapter 22 Elementary Graph Algorithms Graph Representations Graph G = (V,E) Directed Undirected Adjacency Lists Adjacency Matrix Graph Representations Adjacency List: Undirected Memory: Adjacency: Graph
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort
 Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (V G ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (V G ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in
Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs
 Next: Graph Algorithms Graphs Ch 22 Graph representations adjacency list adjacency matrix Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs Breadth-First Search Depth-First Search 11/30/17 CSE 3101 1 Graphs
Next: Graph Algorithms Graphs Ch 22 Graph representations adjacency list adjacency matrix Minimum Spanning Trees Ch 23 Traversing graphs Breadth-First Search Depth-First Search 11/30/17 CSE 3101 1 Graphs
Graphs. Graph G = (V, E) Types of graphs E = O( V 2 ) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V)
 Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC5835, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC5835, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 7 Greedy Graph Algorithms Topological sort Shortest paths Adam Smith The (Algorithm) Design Process 1. Work out the answer for some examples. Look for a general principle
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 7 Greedy Graph Algorithms Topological sort Shortest paths Adam Smith The (Algorithm) Design Process 1. Work out the answer for some examples. Look for a general principle
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal
 Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms Pierre Flener Lars-enrik Eriksson (version of 2013-02-10) Different kinds of graphs List Tree A B C A B C Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) D A B C D E Directed Graph (Digraph)
Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms Pierre Flener Lars-enrik Eriksson (version of 2013-02-10) Different kinds of graphs List Tree A B C A B C Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) D A B C D E Directed Graph (Digraph)
COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms
 COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms Topic 14. Graph Algorithms 11/7/2016 1 Elementary Graph Algorithms How to represent a graph? Adjacency lists Adjacency matrix How to search a graph? Breadth-first
COT 6405 Introduction to Theory of Algorithms Topic 14. Graph Algorithms 11/7/2016 1 Elementary Graph Algorithms How to represent a graph? Adjacency lists Adjacency matrix How to search a graph? Breadth-first
Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]
![Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch] Graph Algorithms. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]](/thumbs/81/84350835.jpg) Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
Graph Algorithms Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Directed Graphs Let V be a finite set and E a binary relation on V, that is, E VxV. Then the pair G=(V,E) is called a directed graph.
Unit #9: Graphs. CPSC 221: Algorithms and Data Structures. Will Evans 2012W1
 Unit #9: Graphs CPSC 1: Algorithms and Data Structures Will Evans 01W1 Unit Outline Topological Sort: Getting to Know Graphs with a Sort Graph ADT and Graph Representations Graph Terminology More Graph
Unit #9: Graphs CPSC 1: Algorithms and Data Structures Will Evans 01W1 Unit Outline Topological Sort: Getting to Know Graphs with a Sort Graph ADT and Graph Representations Graph Terminology More Graph
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity. 3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications. Goals. Chapter 3. Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 3 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Graphs Reading: 3.1-3.6 Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
Chapter 3 CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity Graphs Reading: 3.1-3.6 Winter 2012 Graphs and Graph Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
Graph Algorithms: Chapters Part 1: Introductory graph concepts
 UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Algorithms Dr. Haim Levkowitz Fall, 2007 Graph Algorithms: Chapters 22-25 Part 1: Introductory graph concepts 1 91.404 Graph Review Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum
UMass Lowell Computer Science 91.503 Algorithms Dr. Haim Levkowitz Fall, 2007 Graph Algorithms: Chapters 22-25 Part 1: Introductory graph concepts 1 91.404 Graph Review Elementary Graph Algorithms Minimum
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS Topological Sort
 Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS Topological Sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (VG ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in G,
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS Topological Sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (VG ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in G,
Info 2950, Lecture 16
 Info 2950, Lecture 16 28 Mar 2017 Prob Set 5: due Fri night 31 Mar Breadth first search (BFS) and Depth First Search (DFS) Must have an ordering on the vertices of the graph. In most examples here, the
Info 2950, Lecture 16 28 Mar 2017 Prob Set 5: due Fri night 31 Mar Breadth first search (BFS) and Depth First Search (DFS) Must have an ordering on the vertices of the graph. In most examples here, the
Undirected Graphs. V = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 } E = { 1-2, 1-3, 2-3, 2-4, 2-5, 3-5, 3-7, 3-8, 4-5, 5-6 } n = 8 m = 11
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Representations of Graphs
 ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS -- CS-5321 Presentation -- I am Nishit Kapadia Representations of Graphs There are two standard ways: A collection of adjacency lists - they provide a compact way to represent
Graph representation
 Graph Algorithms 1 Graph representation Given graph G = (V, E). May be either directed or undirected. Two common ways to represent for algorithms: 1. Adjacency lists. 2. Adjacency matrix. When expressing
Graph Algorithms 1 Graph representation Given graph G = (V, E). May be either directed or undirected. Two common ways to represent for algorithms: 1. Adjacency lists. 2. Adjacency matrix. When expressing
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected.
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Exploring graphs Adam Smith 9/5/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Puzzles Suppose an undirected graph G is connected.
Breadth First Search. Graph Traversal. CSE 2011 Winter Application examples. Two common graph traversal algorithms
 Breadth irst Search CSE Winter Graph raversal Application examples Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph ind all paths from s to the other vertices wo common graph traversal algorithms
Breadth irst Search CSE Winter Graph raversal Application examples Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph ind all paths from s to the other vertices wo common graph traversal algorithms
Graph Theory. Many problems are mapped to graphs. Problems. traffic VLSI circuits social network communication networks web pages relationship
 Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Graph Algorithms. Definition
 Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Graph. Vertex. edge. Directed Graph. Undirected Graph
 Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
CS 270 Algorithms. Oliver Kullmann. Breadth-first search. Analysing BFS. Depth-first. search. Analysing DFS. Dags and topological sorting.
 Week 5 General remarks and 2 We consider the simplest graph- algorithm, breadth-first (). We apply to compute shortest paths. Then we consider the second main graph- algorithm, depth-first (). And we consider
Week 5 General remarks and 2 We consider the simplest graph- algorithm, breadth-first (). We apply to compute shortest paths. Then we consider the second main graph- algorithm, depth-first (). And we consider
Goals! CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity!
 Goals! CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity! Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology! Representation: input, internal! Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search! Three Algorithms:!!Connected
Goals! CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity! Graphs: defns, examples, utility, terminology! Representation: input, internal! Traversal: Breadth- & Depth-first search! Three Algorithms:!!Connected
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms CS 5311 Lecture 19 Topological Sort Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and ngineering CS5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Topological Sort Want
Design and Analysis of Algorithms CS 5311 Lecture 19 Topological Sort Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and ngineering CS5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Topological Sort Want
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 3 Data Structures Graphs Traversals Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova L3.1 Measuring Running Time Focus on scalability: parameterize the running time
Data Structures. Elementary Graph Algorithms BFS, DFS & Topological Sort
 Data Structures Elementary Graph Algorithms BFS, DFS & Topological Sort 1 Graphs A graph, G = (V, E), consists of two sets: V is a finite non-empty set of vertices. E is a set of pairs of vertices, called
Data Structures Elementary Graph Algorithms BFS, DFS & Topological Sort 1 Graphs A graph, G = (V, E), consists of two sets: V is a finite non-empty set of vertices. E is a set of pairs of vertices, called
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 4 Graphs Definitions Traversals Adam Smith 9/8/10 Exercise How can you simulate an array with two unbounded stacks and a small amount of memory? (Hint: think of a
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12. Questions? Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first Search. (Introduce permutation and subset generation)
 MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
Graph Algorithms. Chapter 22. CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms 1
 Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Representations Breadth-First Search Depth-First Search Topological Sort Strongly Connected Components CS 5633 Analysis of Algorithms Chapter 22: Slide 1 Graph Representations
Elementary Graph Algorithms Representations Breadth-First Search Depth-First Search Topological Sort Strongly Connected Components CS 5633 Analysis of Algorithms Chapter 22: Slide 1 Graph Representations
Chapter 22. Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Graph Algorithms - Spring 2011 Set 7. Lecturer: Huilan Chang Reference: (1) Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest, and Stein, Introduction to Algorithms, 2nd Edition, The MIT Press. (2) Lecture notes from C. Y. Chen
Graph Algorithms - Spring 2011 Set 7. Lecturer: Huilan Chang Reference: (1) Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest, and Stein, Introduction to Algorithms, 2nd Edition, The MIT Press. (2) Lecture notes from C. Y. Chen
Lecture 3: Graphs and flows
 Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications
 Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications Topics: Introduction to Graph Theory Representing (undirected) graphs Basic graph algorithms 1 Consider the following: Traveling Salesman Problem
Module 11: Additional Topics Graph Theory and Applications Topics: Introduction to Graph Theory Representing (undirected) graphs Basic graph algorithms 1 Consider the following: Traveling Salesman Problem
Week 5. 1 Analysing BFS. 2 Depth-first search. 3 Analysing DFS. 4 Dags and topological sorting. 5 Detecting cycles. CS 270 Algorithms.
 1 2 Week 5 3 4 5 General remarks We finish, by analysing it. Then we consider the second main graph- algorithm, depth-first (). And we consider one application of, of graphs. Reading from CLRS for week
1 2 Week 5 3 4 5 General remarks We finish, by analysing it. Then we consider the second main graph- algorithm, depth-first (). And we consider one application of, of graphs. Reading from CLRS for week
2. True or false: even though BFS and DFS have the same space complexity, they do not always have the same worst case asymptotic time complexity.
 1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
Unit 2: Algorithmic Graph Theory
 Unit 2: Algorithmic Graph Theory Course contents: Introduction to graph theory Basic graph algorithms Reading Chapter 3 Reference: Cormen, Leiserson, and Rivest, Introduction to Algorithms, 2 nd Ed., McGraw
Unit 2: Algorithmic Graph Theory Course contents: Introduction to graph theory Basic graph algorithms Reading Chapter 3 Reference: Cormen, Leiserson, and Rivest, Introduction to Algorithms, 2 nd Ed., McGraw
Graph Representations and Traversal
 COMPSCI 330: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 02/08/2017-02/20/2017 Graph Representations and Traversal Lecturer: Debmalya Panigrahi Scribe: Tianqi Song, Fred Zhang, Tianyu Wang 1 Overview This lecture
COMPSCI 330: Design and Analysis of Algorithms 02/08/2017-02/20/2017 Graph Representations and Traversal Lecturer: Debmalya Panigrahi Scribe: Tianqi Song, Fred Zhang, Tianyu Wang 1 Overview This lecture
CS583 Lecture 09. Jana Kosecka. Graph Algorithms Topological Sort Strongly Connected Component Minimum Spanning Tree
 CS3 Lecture 0 Jana Kosecka Graph Algorithms Topological Sort Strongly Connected Component Minimum Spanning Tree Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke, Kleinberg-Tardos slides Graph Algs.
CS3 Lecture 0 Jana Kosecka Graph Algorithms Topological Sort Strongly Connected Component Minimum Spanning Tree Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke, Kleinberg-Tardos slides Graph Algs.
CS 270 Algorithms. Oliver Kullmann. Analysing BFS. Depth-first search. Analysing DFS. Dags and topological sorting.
 General remarks Week 5 2 We finish, by analysing it. Then we consider the second main graph- algorithm, depth-first (). And we consider one application of, of graphs. Reading from CLRS for week 5 Chapter
General remarks Week 5 2 We finish, by analysing it. Then we consider the second main graph- algorithm, depth-first (). And we consider one application of, of graphs. Reading from CLRS for week 5 Chapter
3.1 Basic Definitions and Applications
 Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Graphs hapter hapter Graphs. Basic efinitions and Applications Graph. G = (V, ) n V = nodes. n = edges between pairs of nodes. n aptures pairwise relationship between objects: Undirected graph represents
Content. 1 Algorithms. 2 Assignment and Knapsack problem 3 Bin Packing. 4 Scheduling
 Content 1 Algorithms 2 Assignment and Knapsack problem 3 Bin Packing 4 Scheduling 5 Graph algorithms 5.1 Definitions 5.2 Depth First Search (DFS) and Breadth First Search (BFS) 5.3 Topological Sorting
Content 1 Algorithms 2 Assignment and Knapsack problem 3 Bin Packing 4 Scheduling 5 Graph algorithms 5.1 Definitions 5.2 Depth First Search (DFS) and Breadth First Search (BFS) 5.3 Topological Sorting
12/5/17. trees. CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks. rooted trees. rooted trees
 trees CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications A tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks rooted trees Rooted trees. Given a tree T, choose
trees CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications A tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles. Trees Chapter 11 in zybooks rooted trees Rooted trees. Given a tree T, choose
Lecture 5: Graphs & their Representation
 Lecture 5: Graphs & their Representation Why Do We Need Graphs Graph Algorithms: Many problems can be formulated as problems on graphs and can be solved with graph algorithms. To learn those graph algorithms,
Lecture 5: Graphs & their Representation Why Do We Need Graphs Graph Algorithms: Many problems can be formulated as problems on graphs and can be solved with graph algorithms. To learn those graph algorithms,
CHAPTER 23: ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS Representations of graphs
 CHAPTER 23: ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS This chapter presents methods for representing a graph and for searching a graph. Searching a graph means systematically following the edges of the graph so as to
CHAPTER 23: ELEMENTARY GRAPH ALGORITHMS This chapter presents methods for representing a graph and for searching a graph. Searching a graph means systematically following the edges of the graph so as to
Elementary Graph Algorithms. Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph:
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Graph Theory. ICT Theory Excerpt from various sources by Robert Pergl
 Graph Theory ICT Theory Excerpt from various sources by Robert Pergl What can graphs model? Cost of wiring electronic components together. Shortest route between two cities. Finding the shortest distance
Graph Theory ICT Theory Excerpt from various sources by Robert Pergl What can graphs model? Cost of wiring electronic components together. Shortest route between two cities. Finding the shortest distance
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
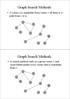 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Solutions to relevant spring 2000 exam problems
 Problem 2, exam Here s Prim s algorithm, modified slightly to use C syntax. MSTPrim (G, w, r): Q = V[G]; for (each u Q) { key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; π[r] = 0; while (Q not empty) { u = ExtractMin (Q); for
Problem 2, exam Here s Prim s algorithm, modified slightly to use C syntax. MSTPrim (G, w, r): Q = V[G]; for (each u Q) { key[u] = ; key[r] = 0; π[r] = 0; while (Q not empty) { u = ExtractMin (Q); for
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II Anna University 2 & 16 Mark Questions & Answers Year / Semester: II / III
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI Department of Computer Science and Engineering CS6301 PROGRAMMING DATA STRUCTURES II Anna University 2 & 16 Mark Questions & Answers Year / Semester: II / III
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013
 GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
GRAPHS Lecture 19 CS2110 Spring 2013 Announcements 2 Prelim 2: Two and a half weeks from now Tuesday, April16, 7:30-9pm, Statler Exam conflicts? We need to hear about them and can arrange a makeup It would
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Graphs Applications of DFS Topological sort Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova S. Raskhodnikova; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, A. Smith,
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 5 Graphs Applications of DFS Topological sort Strongly connected components Sofya Raskhodnikova S. Raskhodnikova; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, A. Smith,
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 s of s s are abstract data types that are applicable
s of s Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Lecture 03 (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) 1 / 29 s of s s are abstract data types that are applicable
TIE Graph algorithms
 TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
Chapter 22: Elementary Graph Algorithms. Definitions:
 Chapter 22: Elementary Graph Algorithms. Definitions: 1. G = (V, E), where V is a set of points and E is a set of edges connecting point-pairs from V. 2. We use V synonymously with V and E with E when
Chapter 22: Elementary Graph Algorithms. Definitions: 1. G = (V, E), where V is a set of points and E is a set of edges connecting point-pairs from V. 2. We use V synonymously with V and E with E when
CSE 101. Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 5: SCC/BFS
 CSE 101 Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones mej016@eng.ucsd.edu Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 5: SCC/BFS DECOMPOSITION There is a linear time algorithm that decomposes a directed graph into its
CSE 101 Algorithm Design and Analysis Miles Jones mej016@eng.ucsd.edu Office 4208 CSE Building Lecture 5: SCC/BFS DECOMPOSITION There is a linear time algorithm that decomposes a directed graph into its
Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search
 Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search Analysis of Algorithms Week 8, Lecture 1 Prepared by John Reif, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor of Computer Science Duke University Graph Algorithms Using Depth
Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search Analysis of Algorithms Week 8, Lecture 1 Prepared by John Reif, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor of Computer Science Duke University Graph Algorithms Using Depth
Algorithms: Lecture 10. Chalmers University of Technology
 Algorithms: Lecture 10 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Topics Basic Definitions Path, Cycle, Tree, Connectivity, etc. Graph Traversal Depth First Search Breadth First Search Testing Bipartatiness
Algorithms: Lecture 10 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Topics Basic Definitions Path, Cycle, Tree, Connectivity, etc. Graph Traversal Depth First Search Breadth First Search Testing Bipartatiness
Graph Algorithms. Textbook reading. Chapter 3 Chapter 4. CSci 3110 Graph Algorithms 1/41
 CSci 3110 Graph Algorithms 1/41 Graph Algorithms Textbook reading Chapter 3 Chapter 4 CSci 3110 Graph Algorithms 2/41 Overview Design principle: Learn the structure of a graph by systematic exploration
CSci 3110 Graph Algorithms 1/41 Graph Algorithms Textbook reading Chapter 3 Chapter 4 CSci 3110 Graph Algorithms 2/41 Overview Design principle: Learn the structure of a graph by systematic exploration
Jana Kosecka. Red-Black Trees Graph Algorithms. Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides
 Jana Kosecka Red-Black Trees Graph Algorithms Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides Binary Search Trees (BSTs) are an important data structure for dynamic sets In addition to satellite
Jana Kosecka Red-Black Trees Graph Algorithms Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides Binary Search Trees (BSTs) are an important data structure for dynamic sets In addition to satellite
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CSE, Winter 8 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture : Graphs, DFS (Undirected, Directed), DAGs Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse-w8/ Graphs Internet topology Graphs Gene-gene interactions
CSE, Winter 8 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture : Graphs, DFS (Undirected, Directed), DAGs Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse-w8/ Graphs Internet topology Graphs Gene-gene interactions
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications. graphs zybooks chapter 10
 CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
CS 220: Discrete Structures and their Applications graphs zybooks chapter 10 directed graphs A collection of vertices and directed edges What can this represent? undirected graphs A collection of vertices
CS 341: Algorithms. Douglas R. Stinson. David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo. February 26, 2019
 CS 341: Algorithms Douglas R. Stinson David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo February 26, 2019 D.R. Stinson (SCS) CS 341 February 26, 2019 1 / 296 1 Course Information 2 Introduction
CS 341: Algorithms Douglas R. Stinson David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science University of Waterloo February 26, 2019 D.R. Stinson (SCS) CS 341 February 26, 2019 1 / 296 1 Course Information 2 Introduction
CS 161 Lecture 11 BFS, Dijkstra s algorithm Jessica Su (some parts copied from CLRS) 1 Review
 1 Review 1 Something I did not emphasize enough last time is that during the execution of depth-firstsearch, we construct depth-first-search trees. One graph may have multiple depth-firstsearch trees,
1 Review 1 Something I did not emphasize enough last time is that during the execution of depth-firstsearch, we construct depth-first-search trees. One graph may have multiple depth-firstsearch trees,
Outline. Graphs. Divide and Conquer.
 GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
CSE 421 DFS / Topological Ordering
 CSE 421 DFS / Topological Ordering Shayan Oveis Gharan 1 Depth First Search Follow the first path you find as far as you can go; back up to last unexplored edge when you reach a dead end, then go as far
CSE 421 DFS / Topological Ordering Shayan Oveis Gharan 1 Depth First Search Follow the first path you find as far as you can go; back up to last unexplored edge when you reach a dead end, then go as far
Unweighted directed graphs
 Unweighted directed graphs Announcements Midterm & gradescope - will get an email today to register (username name is your email) - tests should appear next Tuesday (nothing there now) Graph A directed
Unweighted directed graphs Announcements Midterm & gradescope - will get an email today to register (username name is your email) - tests should appear next Tuesday (nothing there now) Graph A directed
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014
 GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
GRAPHS Lecture 17 CS2110 Spring 2014 These are not Graphs 2...not the kind we mean, anyway These are Graphs 3 K 5 K 3,3 = Applications of Graphs 4 Communication networks The internet is a huge graph Routing
Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 04 Elementary Graph Algorithms (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) sscott@cse.unl.edu Introduction
Computer Science & Engineering 423/823 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 04 Elementary Graph Algorithms (Chapter 22) Stephen Scott (Adapted from Vinodchandran N. Variyam) sscott@cse.unl.edu Introduction
Chapter 5. Decrease-and-Conquer. Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
Strongly Connected Components
 Strongly Connected Components Let G = (V, E) be a directed graph Write if there is a path from to in G Write if and is an equivalence relation: implies and implies s equivalence classes are called the
Strongly Connected Components Let G = (V, E) be a directed graph Write if there is a path from to in G Write if and is an equivalence relation: implies and implies s equivalence classes are called the
CSE 417: Algorithms and Computational Complexity
 CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity More Graph Algorithms Autumn 00 Paul Beame Given: a directed acyclic graph (DAG) G=(V,E) Output: numbering of the vertices of G with distinct numbers from
CSE : Algorithms and Computational Complexity More Graph Algorithms Autumn 00 Paul Beame Given: a directed acyclic graph (DAG) G=(V,E) Output: numbering of the vertices of G with distinct numbers from
Brute Force: Selection Sort
 Brute Force: Intro Brute force means straightforward approach Usually based directly on problem s specs Force refers to computational power Usually not as efficient as elegant solutions Advantages: Applicable
Brute Force: Intro Brute force means straightforward approach Usually based directly on problem s specs Force refers to computational power Usually not as efficient as elegant solutions Advantages: Applicable
Figure 1: A directed graph.
 1 Graphs A graph is a data structure that expresses relationships between objects. The objects are called nodes and the relationships are called edges. For example, social networks can be represented as
1 Graphs A graph is a data structure that expresses relationships between objects. The objects are called nodes and the relationships are called edges. For example, social networks can be represented as
Algorithm Analysis Graph algorithm. Chung-Ang University, Jaesung Lee
 Algorithm Analysis Graph algorithm Chung-Ang University, Jaesung Lee Basic definitions Graph = (, ) where is a set of vertices and is a set of edges Directed graph = where consists of ordered pairs
Algorithm Analysis Graph algorithm Chung-Ang University, Jaesung Lee Basic definitions Graph = (, ) where is a set of vertices and is a set of edges Directed graph = where consists of ordered pairs
CS/COE
 CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
Graphs. Part I: Basic algorithms. Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College
 Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Undirected graphs Concepts: connectivity, connected components paths (undirected) cycles Basic problems, given undirected graph G: is G connected how many
Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Undirected graphs Concepts: connectivity, connected components paths (undirected) cycles Basic problems, given undirected graph G: is G connected how many
22.1 Representations of graphs
 22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
1 Start with each vertex being its own component. 2 Merge two components into one by choosing the light edge
 Taking Stock IE170: in Systems Engineering: Lecture 19 Jeff Linderoth Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Lehigh University March 16, 2007 Last Time Minimum This Time More Strongly Connected
Taking Stock IE170: in Systems Engineering: Lecture 19 Jeff Linderoth Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Lehigh University March 16, 2007 Last Time Minimum This Time More Strongly Connected
Breadth First Search. cse2011 section 13.3 of textbook
 Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
