Counterexample Guided Abstraction Refinement in Blast
|
|
|
- Kerry Ford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Counterexample Guided Abstraction Refinement in Blast Reading: Checking Memory Safety with Blast / Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 How would you analyze this? * means something we can t analyze (user input, random value) Line 10: the lock is held if and only if got_lock = 1 2 1
2 How would you analyze this? * means something we can t analyze (user input, random value) Line 5: the lock is held if and only if old = new 3 Motivation Dataflow analysis uses fixed abstraction e.g. zero/nonzero, locked/unlocked Model checking version of DFA similar PREfix shows need to eliminate infeasible paths E.g. lock/unlock on correlated branches Requires extending abstraction with branch predicates Unfortunately, PREfix sacrifices soundness Infeasible to cover all paths Although PREfix merges paths with similar analysis info, the information is too detailed to assure finitely many explored paths Can we get both soundness and the precision to eliminate infeasible paths? In general: of course not! That s undecideable. But in many situations we can solve it with abstraction refinement; it s just that this technique may not always terminate 4 2
3 CEGAR: Counterexample Guided Abstraction Refinement Program Abstract Using Predicates Abstract Program Model Checker No Error Property Holds New Predicates Error Found Generate New Predicates Infeasible Path Feasibility Checker Feasible Report Bug 5 CEGAR: Counterexample Guided Abstraction Refinement Begin with control flow graph abstraction Check reachability of error nodes Typically take cross product of dataflow abstraction and CFG, as in previous lecture However, can encode dataflow abstraction in CFG through error nodes assert(false) If error node is reachable, check if path is feasible Can use weakest preconditions; if you get false, the path is impossilbe For feasible paths, report an error For infeasible paths, figure out why e.g. correlation between lock and got_lock Add reason for infeasible paths to abstraction and try again! This time the analysis won t consider that path But it might consider other infeasible paths, so you may have to repeat the process multiple times 6 3
4 Control Flow Automaton One node for each location (before/after a statement) Edges Blocks of statements Assume clauses model if and loops some predicate must be true to take the edge 7 Control Flow Automaton Example 2 lock(); old=new; 4 [T] 3 [T] [new!= old] unlock(); new++; 5 [new = old] 6 unlock(); ret 8 4
5 Checking for Reachability Generate Abstract Reachability Tree Contains all reachable nodes Annotates each node with state Initially LOCK = 0 or LOCK = 1 Cross product of CFA and data flow abstraction Algorithm: depth-first search Generate nodes one by one If you come to a node that s already in the tree, stop This state has already been explored through a different control flow path If you come to an error node, stop The error is reachable 9 Depth First Search Example 10 5
6 Is the Error Real? Use weakest preconditions to find out the weakest precondition that leads to the error If the weakest precondition is false, there is no initial program condition that can lead to the error Therefore the error is spurious Blast uses a variant of weakest preconditions creates a new variable for each assignment before using weakest preconditions Instead of substituting on assignment, adds new constraint Helps isolate the reason for the spurious error more effectively 11 Is the Error Real? lock(); old = new; unlock(); new++; assume new==old error (lock==0) 12 6
7 Model Locking as Assignment lock = 1; old = new; lock = 0; new = new + 1; assume new==old error (lock==0) 13 Index the Variables lock1 = 1 old1 = new1; lock2 = 0 new2 = new1 + 1 assume new2==old1 error (lock2==0) 14 7
8 Generate Weakest Preconditions lock1 = 1 old1 = new1; lock2 = 0 new2 = new1 + 1 assume new2==old1 error (lock2==0) True lock1==1 old1==new1 True lock2==0 new2==new1+1 new2==old1 lock2==0 Contradictory! 15 Why is the Error Spurious? More precisely, what predicate could we track that would eliminate the spurious error message? Consider, for each node, the constraints generated before that node (c1) and after that node (c2) Find a condition I such that c1 => I I is true at the node I only contains variables mentioned in both c1 and c2 I mentions only variables in scope (not old or future copies) I c2 = false I is enough to show that the rest of the path is infeasible I is guaranteed to exist See Craig Interpolation True lock1==1 old1==new1 True lock2==0 new2==new1+1 new2==old1 lock2==0 Interpolant: old == new 16 8
9 Reanalyzing the Program Explore a subtree again Start where new predicates were discovered This time, track the new predicates If the conjunction of the predicates on a node is false, stop exploring this node is unreachable 17 Reanalysis Example Already Covered Unreachable 18 9
10 Analyzing the Right Hand Side 19 Generate Weakest Preconditions got_lock = 0; assume got_lock!= 0; error (lock==0) 20 10
11 Why is the Error Spurious? More precisely, what predicate could we track that would eliminate the spurious error message? Consider, for each node, the constraints generated before that node (c1) and after that node (c2) Find a condition I such that c1 => I I is true at the node I only contains variables mentioned in both c1 and c2 I mentions only variables in scope (not old or future copies) I c2 = false I is enough to show that the rest of the path is infeasible I is guaranteed to exist See Craig Interpolation True got_lock==0 True got_lock!=0 lock==0 21 Reanalysis Key: L = locked=1 Z = got_lock=
12 Blast Techniques, Graphically Explores reachable state, not all paths Stops when state already seen on another path Lazy Abstraction Uses predicates on demand Only applies predicate to relevant part of tree 23 Termination Not guaranteed The system could go on generating predicates forever Can guarantee termination The set of possible predicates is finite Finite height lattices in data flow analysis! Those predicates are enough to predict observable behavior of program E.g. the ordering of lock and unlock statements Predicates are restricted in practice E.g. likely can t handle arbitrary quantification as in ESC/Java Model checking is hard if properties depend on heap data, for example Can t prove arbitrary properties in this case In practice Terminate abstraction refinement after a time bound 24 12
13 Key Points of CEGAR To prove a property, may need to strengthen it Just like strengthening induction hypothesis CEGAR figures out strengthening automatically From analyzing why errors are spurious Blast uses lazy abstraction Only uses an abstraction in the parts of the program where it is needed Only builds the part of the abstract state that is reached Explored state space is much smaller than potential state space 25 Experimental Results 26 13
14 Blast in Practice Has scaled past 100,000 lines of code Realistically starts producing worse results after a few 10K lines Sound up to certain limitations Assumes safe use of C No aliases of different types; how realistic? No recursion, no function pointers Need models for library functions Has also been used to find memory safety errors, race conditions, generate test cases 27 14
CS 510/13. Predicate Abstraction
 CS 50/3 Predicate Abstraction Predicate Abstraction Extract a finite state model from an infinite state system Used to prove assertions or safety properties Successfully applied for verification of C programs
CS 50/3 Predicate Abstraction Predicate Abstraction Extract a finite state model from an infinite state system Used to prove assertions or safety properties Successfully applied for verification of C programs
Having a BLAST with SLAM
 Announcements Having a BLAST with SLAM Meetings -, CSCI 7, Fall 00 Moodle problems? Blog problems? Looked at the syllabus on the website? in program analysis Microsoft uses and distributes the Static Driver
Announcements Having a BLAST with SLAM Meetings -, CSCI 7, Fall 00 Moodle problems? Blog problems? Looked at the syllabus on the website? in program analysis Microsoft uses and distributes the Static Driver
Having a BLAST with SLAM
 Having a BLAST with SLAM Meeting, CSCI 555, Fall 20 Announcements Homework 0 due Sat Questions? Move Tue office hours to -5pm 2 Software Model Checking via Counterexample Guided Abstraction Refinement
Having a BLAST with SLAM Meeting, CSCI 555, Fall 20 Announcements Homework 0 due Sat Questions? Move Tue office hours to -5pm 2 Software Model Checking via Counterexample Guided Abstraction Refinement
Formal Systems Tutorial Hybrid System Modeling, Program Analysis
 Formal Systems Tutorial Hybrid System Modeling, Program Analysis Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 1. There are three taps in the system, namely Tap-1
Formal Systems Tutorial Hybrid System Modeling, Program Analysis Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 1. There are three taps in the system, namely Tap-1
Static Program Analysis
 Static Program Analysis Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University https://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ws-1617/spa/ Schedule of Lectures Jan 17/19: Interprocedural DFA
Static Program Analysis Thomas Noll Software Modeling and Verification Group RWTH Aachen University https://moves.rwth-aachen.de/teaching/ws-1617/spa/ Schedule of Lectures Jan 17/19: Interprocedural DFA
Software Model Checking with Abstraction Refinement
 Software Model Checking with Abstraction Refinement Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory MIT Armando Solar-Lezama With slides from Thomas Henzinger, Ranjit Jhala and Rupak Majumdar.
Software Model Checking with Abstraction Refinement Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory MIT Armando Solar-Lezama With slides from Thomas Henzinger, Ranjit Jhala and Rupak Majumdar.
Software Model Checking. Xiangyu Zhang
 Software Model Checking Xiangyu Zhang Symbolic Software Model Checking CS510 S o f t w a r e E n g i n e e r i n g Symbolic analysis explicitly explores individual paths, encodes and resolves path conditions
Software Model Checking Xiangyu Zhang Symbolic Software Model Checking CS510 S o f t w a r e E n g i n e e r i n g Symbolic analysis explicitly explores individual paths, encodes and resolves path conditions
Having a BLAST with SLAM
 Having a BLAST with SLAM # #2 Topic: Software Model Checking via Counter-Example Guided Abstraction Refinement There are easily two dozen SLAM/BLAST/MAGIC papers; I will skim. #3 SLAM Overview INPUT: Program
Having a BLAST with SLAM # #2 Topic: Software Model Checking via Counter-Example Guided Abstraction Refinement There are easily two dozen SLAM/BLAST/MAGIC papers; I will skim. #3 SLAM Overview INPUT: Program
Having a BLAST with SLAM
 Having a BLAST with SLAM # #2 Topic: Software Model Checking via Counter-Example Guided Abstraction Refinement There are easily two dozen SLAM/BLAST/MAGIC papers; I will skim. #3 SLAM Overview INPUT: Program
Having a BLAST with SLAM # #2 Topic: Software Model Checking via Counter-Example Guided Abstraction Refinement There are easily two dozen SLAM/BLAST/MAGIC papers; I will skim. #3 SLAM Overview INPUT: Program
On Reasoning about Finite Sets in Software Checking
 On Reasoning about Finite Sets in Software Model Checking Pavel Shved Institute for System Programming, RAS SYRCoSE 2 June 2010 Static Program Verification Static Verification checking programs against
On Reasoning about Finite Sets in Software Model Checking Pavel Shved Institute for System Programming, RAS SYRCoSE 2 June 2010 Static Program Verification Static Verification checking programs against
Scalable Program Verification by Lazy Abstraction
 Scalable Program Verification by Lazy Abstraction Ranjit Jhala U.C. Berkeley ars, July, 997 Lost contact due to real-time priority inversion bug ars, December, 999 Crashed due to uninitialized variable
Scalable Program Verification by Lazy Abstraction Ranjit Jhala U.C. Berkeley ars, July, 997 Lost contact due to real-time priority inversion bug ars, December, 999 Crashed due to uninitialized variable
Configurable Software Model Checking
 Configurable Software Model Checking CPAchecker Dirk Beyer Dirk Beyer 1 / 26 Software Verification C Program int main() { int a = foo(); int b = bar(a); } assert(a == b); Verification Tool TRUE i.e., specification
Configurable Software Model Checking CPAchecker Dirk Beyer Dirk Beyer 1 / 26 Software Verification C Program int main() { int a = foo(); int b = bar(a); } assert(a == b); Verification Tool TRUE i.e., specification
More on Verification and Model Checking
 More on Verification and Model Checking Wednesday Oct 07, 2015 Philipp Rümmer Uppsala University Philipp.Ruemmer@it.uu.se 1/60 Course fair! 2/60 Exam st October 21, 8:00 13:00 If you want to participate,
More on Verification and Model Checking Wednesday Oct 07, 2015 Philipp Rümmer Uppsala University Philipp.Ruemmer@it.uu.se 1/60 Course fair! 2/60 Exam st October 21, 8:00 13:00 If you want to participate,
Program Verification (6EC version only)
 Program Verification (6EC version only) Erik Poll Digital Security Radboud University Nijmegen Overview Program Verification using Verification Condition Generators JML a formal specification language
Program Verification (6EC version only) Erik Poll Digital Security Radboud University Nijmegen Overview Program Verification using Verification Condition Generators JML a formal specification language
An Eclipse Plug-in for Model Checking
 An Eclipse Plug-in for Model Checking Dirk Beyer, Thomas A. Henzinger, Ranjit Jhala Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley, USA Rupak Majumdar Computer Science
An Eclipse Plug-in for Model Checking Dirk Beyer, Thomas A. Henzinger, Ranjit Jhala Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley, USA Rupak Majumdar Computer Science
F-Soft: Software Verification Platform
 F-Soft: Software Verification Platform F. Ivančić, Z. Yang, M.K. Ganai, A. Gupta, I. Shlyakhter, and P. Ashar NEC Laboratories America, 4 Independence Way, Suite 200, Princeton, NJ 08540 fsoft@nec-labs.com
F-Soft: Software Verification Platform F. Ivančić, Z. Yang, M.K. Ganai, A. Gupta, I. Shlyakhter, and P. Ashar NEC Laboratories America, 4 Independence Way, Suite 200, Princeton, NJ 08540 fsoft@nec-labs.com
Introduction. Preliminaries. Original IC3. Tree-IC3. IC3 on Control Flow Automata. Conclusion
 .. Introduction Preliminaries Original IC3 Tree-IC3 IC3 on Control Flow Automata Conclusion 2 of 22 Lifting IC3 to Control Flow Automata Tim Lange tim.lange@cs.rwth-aachen.de Introduction Preliminaries
.. Introduction Preliminaries Original IC3 Tree-IC3 IC3 on Control Flow Automata Conclusion 2 of 22 Lifting IC3 to Control Flow Automata Tim Lange tim.lange@cs.rwth-aachen.de Introduction Preliminaries
Ufo: A Framework for Abstraction- and Interpolation-Based Software Verification
 Ufo: A Framework for Abstraction- and Interpolation-Based Software Verification Aws Albarghouthi 1, Yi Li 1, Arie Gurfinkel 2, and Marsha Chechik 1 1 Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto,
Ufo: A Framework for Abstraction- and Interpolation-Based Software Verification Aws Albarghouthi 1, Yi Li 1, Arie Gurfinkel 2, and Marsha Chechik 1 1 Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto,
Outline. Introduction SDV Motivation Model vs Real Implementation SLIC SDVRP SLAM-2 Comparisons Conclusions
 Outline Introduction SDV Motivation Model vs Real Implementation SIC SDVRP SAM-2 Comparisons Conclusions SDV Research Platform Academic release of SDV (Static Driver Verifier), based on the code that ships
Outline Introduction SDV Motivation Model vs Real Implementation SIC SDVRP SAM-2 Comparisons Conclusions SDV Research Platform Academic release of SDV (Static Driver Verifier), based on the code that ships
Abstraction Learning
 Abstraction Learning Joxan Jaffar National University of Singapore joxan@comp.nus.edu.sg Jorge Navas National University of Singapore navas@comp.nus.edu.sg Andrew E. Santosa National University of Singapore
Abstraction Learning Joxan Jaffar National University of Singapore joxan@comp.nus.edu.sg Jorge Navas National University of Singapore navas@comp.nus.edu.sg Andrew E. Santosa National University of Singapore
Hoare Logic: Proving Programs Correct
 Hoare Logic: Proving Programs Correct 17-654/17-765 Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich Reading: C.A.R. Hoare, An Axiomatic Basis for Computer Programming Some presentation ideas from a lecture
Hoare Logic: Proving Programs Correct 17-654/17-765 Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich Reading: C.A.R. Hoare, An Axiomatic Basis for Computer Programming Some presentation ideas from a lecture
Lecture Notes: Hoare Logic
 Lecture Notes: Hoare Logic 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich (jonathan.aldrich@cs.cmu.edu) Lecture 3 1 Hoare Logic The goal of Hoare logic is to provide a formal system for
Lecture Notes: Hoare Logic 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich (jonathan.aldrich@cs.cmu.edu) Lecture 3 1 Hoare Logic The goal of Hoare logic is to provide a formal system for
Finding and Fixing Bugs in Liquid Haskell. Anish Tondwalkar
 Finding and Fixing Bugs in Liquid Haskell Anish Tondwalkar Overview Motivation Liquid Haskell Fault Localization Fault Localization Evaluation Predicate Discovery Predicate Discovery Evaluation Conclusion
Finding and Fixing Bugs in Liquid Haskell Anish Tondwalkar Overview Motivation Liquid Haskell Fault Localization Fault Localization Evaluation Predicate Discovery Predicate Discovery Evaluation Conclusion
Verifying Multithreaded Software with Impact
 Verifying Multithreaded Software with Impact Björn Wachter, Daniel Kroening and Joël Ouaknine University of Oxford Intro Multi-threading C/C++ with POSIX/WIN 32 threads event processing, device drivers,
Verifying Multithreaded Software with Impact Björn Wachter, Daniel Kroening and Joël Ouaknine University of Oxford Intro Multi-threading C/C++ with POSIX/WIN 32 threads event processing, device drivers,
TRACER: A Symbolic Execution Tool for Verification
 TRACER: A Symbolic Execution Tool for Verification Joxan Jaffar, Vijayaraghavan Murali, Jorge A. Navas, and Andrew E. Santosa 3 National University of Singapore The University of Melbourne 3 University
TRACER: A Symbolic Execution Tool for Verification Joxan Jaffar, Vijayaraghavan Murali, Jorge A. Navas, and Andrew E. Santosa 3 National University of Singapore The University of Melbourne 3 University
Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics
 Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics Polyvios Pratikakis Computer Science Department, University of Crete Type Systems and Static Analysis Based on slides by George Necula Pratikakis (CSD) Axiomatic Semantics
Lectures 20, 21: Axiomatic Semantics Polyvios Pratikakis Computer Science Department, University of Crete Type Systems and Static Analysis Based on slides by George Necula Pratikakis (CSD) Axiomatic Semantics
The software model checker BLAST
 Int J Softw Tools Technol Transfer (2007) 9:505 525 DOI 10.1007/s10009-007-0044-z SPECIAL SECTION FASE 04/ 05 The software model checker BLAST Applications to software engineering Dirk Beyer Thomas A.
Int J Softw Tools Technol Transfer (2007) 9:505 525 DOI 10.1007/s10009-007-0044-z SPECIAL SECTION FASE 04/ 05 The software model checker BLAST Applications to software engineering Dirk Beyer Thomas A.
SYNERGY : A New Algorithm for Property Checking
 SYNERGY : A New Algorithm for Property Checking Bhargav S. Gulavani Thomas A. Henzinger Yamini Kannan Aditya V. Nori Sriram K. Rajamani bhargav@cse.iitb.ernet.in tah@epfl.ch yaminik@microsoft.com adityan@microsoft.com
SYNERGY : A New Algorithm for Property Checking Bhargav S. Gulavani Thomas A. Henzinger Yamini Kannan Aditya V. Nori Sriram K. Rajamani bhargav@cse.iitb.ernet.in tah@epfl.ch yaminik@microsoft.com adityan@microsoft.com
Sciduction: Combining Induction, Deduction and Structure for Verification and Synthesis
 Sciduction: Combining Induction, Deduction and Structure for Verification and Synthesis (abridged version of DAC slides) Sanjit A. Seshia Associate Professor EECS Department UC Berkeley Design Automation
Sciduction: Combining Induction, Deduction and Structure for Verification and Synthesis (abridged version of DAC slides) Sanjit A. Seshia Associate Professor EECS Department UC Berkeley Design Automation
Static Analysis Basics II
 Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Static Analysis Basics
Systems and Internet Infrastructure Security Network and Security Research Center Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pennsylvania State University, University Park PA Static Analysis Basics
Program Analysis and Constraint Programming
 Program Analysis and Constraint Programming Joxan Jaffar National University of Singapore CPAIOR MasterClass, 18-19 May 2015 1 / 41 Program Testing, Verification, Analysis (TVA)... VS... Satifiability/Optimization
Program Analysis and Constraint Programming Joxan Jaffar National University of Singapore CPAIOR MasterClass, 18-19 May 2015 1 / 41 Program Testing, Verification, Analysis (TVA)... VS... Satifiability/Optimization
Using Build-Integrated Static Checking to Preserve Correctness Invariants
 Using Build-Integrated Static Checking to Preserve Correctness Invariants Hao Chen University of California, Davis Jonathan Shapiro Johns Hopkins University Motivation A key problem in creating secure
Using Build-Integrated Static Checking to Preserve Correctness Invariants Hao Chen University of California, Davis Jonathan Shapiro Johns Hopkins University Motivation A key problem in creating secure
Overview. Verification with Functions and Pointers. IMP with assertions and assumptions. Proof rules for Assert and Assume. IMP+: IMP with functions
 Overview Verification with Functions and Pointers Işıl Dillig The IMP language considered so far does not have many features of realistics PLs Our goal today: Enrich IMP with two features, namely functions
Overview Verification with Functions and Pointers Işıl Dillig The IMP language considered so far does not have many features of realistics PLs Our goal today: Enrich IMP with two features, namely functions
Software Model Checking. From Programs to Kripke Structures
 Software Model Checking (in (in C or or Java) Java) Model Model Extraction 1: int x = 2; int y = 2; 2: while (y
Software Model Checking (in (in C or or Java) Java) Model Model Extraction 1: int x = 2; int y = 2; 2: while (y
Proofs from Tests. Nels E. Beckman, Aditya V. Nori, Sriram K. Rajamani, Robert J. Simmons, SaiDeep Tetali, Aditya V. Thakur
 1 Proofs from Tests Nels E. Beckman, Aditya V. Nori, Sriram K. Rajamani, Robert J. Simmons, SaiDeep Tetali, Aditya V. Thakur Abstract We present an algorithm DASH to check if a program P satisfies a safety
1 Proofs from Tests Nels E. Beckman, Aditya V. Nori, Sriram K. Rajamani, Robert J. Simmons, SaiDeep Tetali, Aditya V. Thakur Abstract We present an algorithm DASH to check if a program P satisfies a safety
No model may be available. Software Abstractions. Recap on Model Checking. Model Checking for SW Verif. More on the big picture. Abst -> MC -> Refine
 No model may be available Programmer Software Abstractions Tests Coverage Code Abhik Roychoudhury CS 5219 National University of Singapore Testing Debug Today s lecture Abstract model (Boolean pgm.) Desirable
No model may be available Programmer Software Abstractions Tests Coverage Code Abhik Roychoudhury CS 5219 National University of Singapore Testing Debug Today s lecture Abstract model (Boolean pgm.) Desirable
Double Header. Two Lectures. Flying Boxes. Some Key Players: Model Checking Software Model Checking SLAM and BLAST
 Model Checking #1 Double Header Two Lectures Model Checking Software Model Checking SLAM and BLAST Flying Boxes It is traditional to describe this stuff (especially SLAM and BLAST) with high-gloss animation
Model Checking #1 Double Header Two Lectures Model Checking Software Model Checking SLAM and BLAST Flying Boxes It is traditional to describe this stuff (especially SLAM and BLAST) with high-gloss animation
Algorithms for Software Model Checking: Predicate Abstraction vs. IMPACT
 Algorithms for Software Model Checking: Predicate Abstraction vs. IMPACT Dirk Beyer University of Passau, Germany Philipp Wendler University of Passau, Germany Abstract CEGAR, SMT solving, and Craig interpolation
Algorithms for Software Model Checking: Predicate Abstraction vs. IMPACT Dirk Beyer University of Passau, Germany Philipp Wendler University of Passau, Germany Abstract CEGAR, SMT solving, and Craig interpolation
Using Counterexample Analysis to Minimize the Number of Predicates for Predicate Abstraction
 Using Counterexample Analysis to Minimize the Number of Predicates for Predicate Abstraction Thanyapat Sakunkonchak, Satoshi Komatsu, and Masahiro Fujita VLSI Design and Education Center, The University
Using Counterexample Analysis to Minimize the Number of Predicates for Predicate Abstraction Thanyapat Sakunkonchak, Satoshi Komatsu, and Masahiro Fujita VLSI Design and Education Center, The University
Predicate Refinement Heuristics in Program Verification with CEGAR
 Predicate Refinement Heuristics in Program Verification with CEGAR Tachio Terauchi (JAIST) Part of this is joint work with Hiroshi Unno (U. Tsukuba) 1 Predicate Abstraction with CEGAR Iteratively generate
Predicate Refinement Heuristics in Program Verification with CEGAR Tachio Terauchi (JAIST) Part of this is joint work with Hiroshi Unno (U. Tsukuba) 1 Predicate Abstraction with CEGAR Iteratively generate
Unbounded Symbolic Execution for Program Verification
 Unbounded Symbolic Execution for Program Verification JOXAN JAFFAR 1, JORGE A. NAVAS 1, AND ANDREW E. SANTOSA 2 1 National University of Singapore 2 University of Sydney, Australia {joxan,navas}@comp.nus.edu.sg,
Unbounded Symbolic Execution for Program Verification JOXAN JAFFAR 1, JORGE A. NAVAS 1, AND ANDREW E. SANTOSA 2 1 National University of Singapore 2 University of Sydney, Australia {joxan,navas}@comp.nus.edu.sg,
Page # 20b -Advanced-DFA. Reading assignment. State Propagation. GEN and KILL sets. Data Flow Analysis
 b -Advanced-DFA Reading assignment J. L. Peterson, "Petri Nets," Computing Surveys, 9 (3), September 977, pp. 3-5. Sections -4 State Propagation For reference only M. Pezzè, R. N. Taylor and M. Young,
b -Advanced-DFA Reading assignment J. L. Peterson, "Petri Nets," Computing Surveys, 9 (3), September 977, pp. 3-5. Sections -4 State Propagation For reference only M. Pezzè, R. N. Taylor and M. Young,
Checking Program Properties with ESC/Java
 Checking Program Properties with ESC/Java 17-654/17-765 Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 ESC/Java A checker for Java programs Finds null pointers, array dereferences Checks Hoare logic
Checking Program Properties with ESC/Java 17-654/17-765 Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 ESC/Java A checker for Java programs Finds null pointers, array dereferences Checks Hoare logic
4/24/18. Overview. Program Static Analysis. Has anyone done static analysis? What is static analysis? Why static analysis?
 Overview Program Static Analysis Program static analysis Abstract interpretation Static analysis techniques 2 What is static analysis? The analysis to understand computer software without executing programs
Overview Program Static Analysis Program static analysis Abstract interpretation Static analysis techniques 2 What is static analysis? The analysis to understand computer software without executing programs
Predicate Abstraction and CEGAR for Higher Order Model Checking
 Predicate Abstraction and CEGAR for Higher Order Model Checking Naoki Kobayashi, Ryosuke Sato, and Hiroshi Unno Tohoku University (Presented at PLDI2011) 1 Our Goal Software model checker for functional
Predicate Abstraction and CEGAR for Higher Order Model Checking Naoki Kobayashi, Ryosuke Sato, and Hiroshi Unno Tohoku University (Presented at PLDI2011) 1 Our Goal Software model checker for functional
CS 4120 Lecture 31 Interprocedural analysis, fixed-point algorithms 9 November 2011 Lecturer: Andrew Myers
 CS 4120 Lecture 31 Interprocedural analysis, fixed-point algorithms 9 November 2011 Lecturer: Andrew Myers These notes are not yet complete. 1 Interprocedural analysis Some analyses are not sufficiently
CS 4120 Lecture 31 Interprocedural analysis, fixed-point algorithms 9 November 2011 Lecturer: Andrew Myers These notes are not yet complete. 1 Interprocedural analysis Some analyses are not sufficiently
Reducing Fair Stuttering Refinement of Transaction Systems
 Reducing Fair Stuttering Refinement of Transaction Systems Rob Sumners Advanced Micro Devices robert.sumners@amd.com November 16th, 2015 Rob Sumners (AMD) Transaction Progress Checking November 16th, 2015
Reducing Fair Stuttering Refinement of Transaction Systems Rob Sumners Advanced Micro Devices robert.sumners@amd.com November 16th, 2015 Rob Sumners (AMD) Transaction Progress Checking November 16th, 2015
Sliced Path Prefixes: An Effective Method to Enable Refinement Selection
 FORTE '15 Sliced Path Prefixes: An Effective Method to Enable Refinement Selection Dirk Beyer, Stefan Löwe, Philipp Wendler SoSy-Lab Software Systems We want Refinement Selection!!! Because straight-forward
FORTE '15 Sliced Path Prefixes: An Effective Method to Enable Refinement Selection Dirk Beyer, Stefan Löwe, Philipp Wendler SoSy-Lab Software Systems We want Refinement Selection!!! Because straight-forward
20b -Advanced-DFA. J. L. Peterson, "Petri Nets," Computing Surveys, 9 (3), September 1977, pp
 State Propagation Reading assignment J. L. Peterson, "Petri Nets," Computing Surveys, 9 (3), September 1977, pp. 223-252. Sections 1-4 For reference only M. Pezzè, R. N. Taylor and M. Young, Graph Models
State Propagation Reading assignment J. L. Peterson, "Petri Nets," Computing Surveys, 9 (3), September 1977, pp. 223-252. Sections 1-4 For reference only M. Pezzè, R. N. Taylor and M. Young, Graph Models
Towards a Software Model Checker for ML. Naoki Kobayashi Tohoku University
 Towards a Software Model Checker for ML Naoki Kobayashi Tohoku University Joint work with: Ryosuke Sato and Hiroshi Unno (Tohoku University) in collaboration with Luke Ong (Oxford), Naoshi Tabuchi and
Towards a Software Model Checker for ML Naoki Kobayashi Tohoku University Joint work with: Ryosuke Sato and Hiroshi Unno (Tohoku University) in collaboration with Luke Ong (Oxford), Naoshi Tabuchi and
VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification
 VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification Saurabh Srivastava 1,, Sumit Gulwani 2, and Jeffrey S. Foster 1 1 University of Maryland, College Park, {saurabhs,jfoster}@cs.umd.edu 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond,
VS 3 : SMT Solvers for Program Verification Saurabh Srivastava 1,, Sumit Gulwani 2, and Jeffrey S. Foster 1 1 University of Maryland, College Park, {saurabhs,jfoster}@cs.umd.edu 2 Microsoft Research, Redmond,
Introduction to Machine-Independent Optimizations - 4
 Introduction to Machine-Independent Optimizations - 4 Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012 NPTEL Course on Principles of Compiler Design Outline of
Introduction to Machine-Independent Optimizations - 4 Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012 NPTEL Course on Principles of Compiler Design Outline of
Formal Verification by Model Checking
 Formal Verication by Model Checking Jonathan Aldrich Carnegie Mellon University Based on slides developed by Natasha Sharygina 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artacts Spring 2006 1 CTL Model Checking
Formal Verication by Model Checking Jonathan Aldrich Carnegie Mellon University Based on slides developed by Natasha Sharygina 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artacts Spring 2006 1 CTL Model Checking
A survey of new trends in symbolic execution for software testing and analysis
 Int J Softw Tools Technol Transfer (2009) 11:339 353 DOI 10.1007/s10009-009-0118-1 REGULAR PAPER A survey of new trends in symbolic execution for software testing and analysis Corina S. Păsăreanu Willem
Int J Softw Tools Technol Transfer (2009) 11:339 353 DOI 10.1007/s10009-009-0118-1 REGULAR PAPER A survey of new trends in symbolic execution for software testing and analysis Corina S. Păsăreanu Willem
A Verifier for Temporal Properties
 A Verifier for Temporal Properties David Mandelin May 3, 2002 1 Background Before distributing a program, programmers would like to know for certain that it does what it is intended to do. The only way
A Verifier for Temporal Properties David Mandelin May 3, 2002 1 Background Before distributing a program, programmers would like to know for certain that it does what it is intended to do. The only way
1. true / false By a compiler we mean a program that translates to code that will run natively on some machine.
 1. true / false By a compiler we mean a program that translates to code that will run natively on some machine. 2. true / false ML can be compiled. 3. true / false FORTRAN can reasonably be considered
1. true / false By a compiler we mean a program that translates to code that will run natively on some machine. 2. true / false ML can be compiled. 3. true / false FORTRAN can reasonably be considered
Dataflow Analysis. Xiaokang Qiu Purdue University. October 17, 2018 ECE 468
 Dataflow Analysis Xiaokang Qiu Purdue University ECE 468 October 17, 2018 Program optimizations So far we have talked about different kinds of optimizations Peephole optimizations Local common sub-expression
Dataflow Analysis Xiaokang Qiu Purdue University ECE 468 October 17, 2018 Program optimizations So far we have talked about different kinds of optimizations Peephole optimizations Local common sub-expression
Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues
 Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Finding Bugs Last time Run-time reordering transformations Today Program Analysis for finding bugs, especially security bugs problem specification motivation approaches remaining issues CS553 Lecture Finding
Outline. Introduction. 2 Proof of Correctness. 3 Final Notes. Precondition P 1 : Inputs include
 Outline Computer Science 331 Correctness of Algorithms Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lectures #2-4 1 What is a? Applications 2 Recursive Algorithms 3 Final Notes Additional
Outline Computer Science 331 Correctness of Algorithms Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lectures #2-4 1 What is a? Applications 2 Recursive Algorithms 3 Final Notes Additional
Proofs from Tests. Sriram K. Rajamani. Nels E. Beckman. Aditya V. Nori. Robert J. Simmons.
 Proofs from Tests Nels E. Beckman Carnegie Mellon University nbeckman@cs.cmu.edu Aditya V. Nori Microsoft Research India adityan@microsoft.com Robert J. Simmons Carnegie Mellon University rjsimmon@cs.cmu.edu
Proofs from Tests Nels E. Beckman Carnegie Mellon University nbeckman@cs.cmu.edu Aditya V. Nori Microsoft Research India adityan@microsoft.com Robert J. Simmons Carnegie Mellon University rjsimmon@cs.cmu.edu
The Formal Semantics of Programming Languages An Introduction. Glynn Winskel. The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England
 The Formal Semantics of Programming Languages An Introduction Glynn Winskel The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Series foreword Preface xiii xv 1 Basic set theory 1 1.1 Logical notation
The Formal Semantics of Programming Languages An Introduction Glynn Winskel The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Series foreword Preface xiii xv 1 Basic set theory 1 1.1 Logical notation
Symbolic and Concolic Execution of Programs
 Symbolic and Concolic Execution of Programs Information Security, CS 526 Omar Chowdhury 10/7/2015 Information Security, CS 526 1 Reading for this lecture Symbolic execution and program testing - James
Symbolic and Concolic Execution of Programs Information Security, CS 526 Omar Chowdhury 10/7/2015 Information Security, CS 526 1 Reading for this lecture Symbolic execution and program testing - James
Hoare logic. A proof system for separation logic. Introduction. Separation logic
 Introduction Hoare logic Lecture 6: Examples in separation logic In the previous lecture, we saw how reasoning about pointers in Hoare logic was problematic, which motivated introducing separation logic.
Introduction Hoare logic Lecture 6: Examples in separation logic In the previous lecture, we saw how reasoning about pointers in Hoare logic was problematic, which motivated introducing separation logic.
Static Program Analysis CS701
 Static Program Analysis CS701 Thomas Reps [Based on notes taken by Aditya Venkataraman on Oct 6th, 2015] Abstract This lecture introduces the area of static program analysis. We introduce the topics to
Static Program Analysis CS701 Thomas Reps [Based on notes taken by Aditya Venkataraman on Oct 6th, 2015] Abstract This lecture introduces the area of static program analysis. We introduce the topics to
COS 320. Compiling Techniques
 Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
Topic 5: Types COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University Spring 2016 Lennart Beringer 1 Types: potential benefits (I) 2 For programmers: help to eliminate common programming mistakes, particularly
Abstractions from Proofs
 Abstractions from Proofs Thomas A. Henzinger Ranjit Jhala Rupak Majumdar EECS Department, University of California Berkeley, CA 94720-1770, U.S.A. {tah,jhala,rupak}@eecs.berkeley.edu Kenneth L. McMillan
Abstractions from Proofs Thomas A. Henzinger Ranjit Jhala Rupak Majumdar EECS Department, University of California Berkeley, CA 94720-1770, U.S.A. {tah,jhala,rupak}@eecs.berkeley.edu Kenneth L. McMillan
Reminder of the last lecture. Aliasing Issues: Call by reference, Pointer programs. Introducing Aliasing Issues. Home Work from previous lecture
 Reminder of the last lecture Aliasing Issues: Call by reference, Pointer programs Claude Marché Cours MPRI 2-36-1 Preuve de Programme 18 janvier 2017 Additional features of the specification language Abstract
Reminder of the last lecture Aliasing Issues: Call by reference, Pointer programs Claude Marché Cours MPRI 2-36-1 Preuve de Programme 18 janvier 2017 Additional features of the specification language Abstract
Handling Loops in Bounded Model Checking of C Programs via k-induction
 Software Tools for Technology Transfer manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Handling Loops in Bounded Model Checking of C Programs via k-induction Mikhail Y. R. Gadelha, Hussama I. Ismail, and
Software Tools for Technology Transfer manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Handling Loops in Bounded Model Checking of C Programs via k-induction Mikhail Y. R. Gadelha, Hussama I. Ismail, and
Static Analysis in Practice
 in Practice 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 Quick Poll Who is familiar and comfortable with design patterns? e.g. what is a Factory and why use it? 2 1 Outline: in Practice
in Practice 17-654/17-754: Analysis of Software Artifacts Jonathan Aldrich 1 Quick Poll Who is familiar and comfortable with design patterns? e.g. what is a Factory and why use it? 2 1 Outline: in Practice
Model Checking with Abstract State Matching
 Model Checking with Abstract State Matching Corina Păsăreanu QSS, NASA Ames Research Center Joint work with Saswat Anand (Georgia Institute of Technology) Radek Pelánek (Masaryk University) Willem Visser
Model Checking with Abstract State Matching Corina Păsăreanu QSS, NASA Ames Research Center Joint work with Saswat Anand (Georgia Institute of Technology) Radek Pelánek (Masaryk University) Willem Visser
Lecture Notes on Common Subexpression Elimination
 Lecture Notes on Common Subexpression Elimination 15-411: Compiler Design Frank Pfenning Lecture 18 October 29, 2015 1 Introduction Copy propagation allows us to have optimizations with this form: l :
Lecture Notes on Common Subexpression Elimination 15-411: Compiler Design Frank Pfenning Lecture 18 October 29, 2015 1 Introduction Copy propagation allows us to have optimizations with this form: l :
BDD-Based Software Model Checking with CPAchecker
 BDD-Based Software Model Checking with CPAchecker Dirk Beyer and Andreas Stahlbauer University of Passau, Germany Abstract. In symbolic software model checking, most approaches use predicates as symbolic
BDD-Based Software Model Checking with CPAchecker Dirk Beyer and Andreas Stahlbauer University of Passau, Germany Abstract. In symbolic software model checking, most approaches use predicates as symbolic
Duet: Static Analysis for Unbounded Parallelism
 Duet: Static Analysis for Unbounded Parallelism Azadeh Farzan and Zachary Kincaid University of Toronto Abstract. Duet is a static analysis tool for concurrent programs in which the number of executing
Duet: Static Analysis for Unbounded Parallelism Azadeh Farzan and Zachary Kincaid University of Toronto Abstract. Duet is a static analysis tool for concurrent programs in which the number of executing
Program Static Analysis. Overview
 Program Static Analysis Overview Program static analysis Abstract interpretation Data flow analysis Intra-procedural Inter-procedural 2 1 What is static analysis? The analysis to understand computer software
Program Static Analysis Overview Program static analysis Abstract interpretation Data flow analysis Intra-procedural Inter-procedural 2 1 What is static analysis? The analysis to understand computer software
Verifying Concurrent Programs
 Verifying Concurrent Programs Daniel Kroening 8 May 1 June 01 Outline Shared-Variable Concurrency Predicate Abstraction for Concurrent Programs Boolean Programs with Bounded Replication Boolean Programs
Verifying Concurrent Programs Daniel Kroening 8 May 1 June 01 Outline Shared-Variable Concurrency Predicate Abstraction for Concurrent Programs Boolean Programs with Bounded Replication Boolean Programs
Inductive Invariant Generation via Abductive Inference
 Inductive Invariant Generation via Abductive Inference Isil Dillig Department of Computer Science College of William & Mary idillig@cs.wm.edu Thomas Dillig Department of Computer Science College of William
Inductive Invariant Generation via Abductive Inference Isil Dillig Department of Computer Science College of William & Mary idillig@cs.wm.edu Thomas Dillig Department of Computer Science College of William
Static Program Checking
 Bounded Verification Jalloy Automated Software Analysis Group, Institute of Theoretical Informatics Jun.-prof. Mana Taghdiri June 5, 2014 KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National
Bounded Verification Jalloy Automated Software Analysis Group, Institute of Theoretical Informatics Jun.-prof. Mana Taghdiri June 5, 2014 KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National
On Reasoning About Finite Sets in Software Model Checking
 On Reasoning About Finite Sets in Software Model Checking Pavel Shved Institute for System Programming, RAS email: shved@ispras.ru Abstract A number of static checking techniques is based on constructing
On Reasoning About Finite Sets in Software Model Checking Pavel Shved Institute for System Programming, RAS email: shved@ispras.ru Abstract A number of static checking techniques is based on constructing
Lecture 6. Abstract Interpretation
 Lecture 6. Abstract Interpretation Wei Le 2014.10 Outline Motivation History What it is: an intuitive understanding An example Steps of abstract interpretation Galois connection Narrowing and Widening
Lecture 6. Abstract Interpretation Wei Le 2014.10 Outline Motivation History What it is: an intuitive understanding An example Steps of abstract interpretation Galois connection Narrowing and Widening
Static program checking and verification
 Chair of Software Engineering Software Engineering Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer March 2007 June 2007 Slides: Based on KSE06 With kind permission of Peter Müller Static program checking and verification Correctness
Chair of Software Engineering Software Engineering Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer March 2007 June 2007 Slides: Based on KSE06 With kind permission of Peter Müller Static program checking and verification Correctness
Program Verification. Aarti Gupta
 Program Verification Aarti Gupta 1 Agenda Famous bugs Common bugs Testing (from lecture 6) Reasoning about programs Techniques for program verification 2 Famous Bugs The first bug: A moth in a relay (1945)
Program Verification Aarti Gupta 1 Agenda Famous bugs Common bugs Testing (from lecture 6) Reasoning about programs Techniques for program verification 2 Famous Bugs The first bug: A moth in a relay (1945)
The Pointer Assertion Logic Engine
 The Pointer Assertion Logic Engine [PLDI 01] Anders Mφller Michael I. Schwartzbach Presented by K. Vikram Cornell University Introduction Pointer manipulation is hard Find bugs, optimize code General Approach
The Pointer Assertion Logic Engine [PLDI 01] Anders Mφller Michael I. Schwartzbach Presented by K. Vikram Cornell University Introduction Pointer manipulation is hard Find bugs, optimize code General Approach
Lecture Notes: Pointer Analysis
 Lecture Notes: Pointer Analysis 15-819O: Program Analysis Jonathan Aldrich jonathan.aldrich@cs.cmu.edu Lecture 9 1 Motivation for Pointer Analysis In programs with pointers, program analysis can become
Lecture Notes: Pointer Analysis 15-819O: Program Analysis Jonathan Aldrich jonathan.aldrich@cs.cmu.edu Lecture 9 1 Motivation for Pointer Analysis In programs with pointers, program analysis can become
Effectively-Propositional Modular Reasoning about Reachability in Linked Data Structures CAV 13, POPL 14 Shachar Itzhaky
 Effectively-Propositional Modular Reasoning about Reachability in Linked Data Structures CAV 13, POPL 14 Shachar Itzhaky Anindya Banerjee Neil Immerman Ori Lahav Aleks Nanevski Mooly Sagiv http://www.cs.tau.ac.il/~shachar/afwp.html
Effectively-Propositional Modular Reasoning about Reachability in Linked Data Structures CAV 13, POPL 14 Shachar Itzhaky Anindya Banerjee Neil Immerman Ori Lahav Aleks Nanevski Mooly Sagiv http://www.cs.tau.ac.il/~shachar/afwp.html
Simple Overflow. #include <stdio.h> int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff;
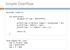 Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
Simple Overflow 1 #include int main(void){ unsigned int num = 0xffffffff; printf("num is %d bits long\n", sizeof(num) * 8); printf("num = 0x%x\n", num); printf("num + 1 = 0x%x\n", num + 1); }
PANDA: Simultaneous Predicate Abstraction and Concrete Execution
 PANDA: Simultaneous Predicate Abstraction and Concrete Execution Jakub Daniel and Pavel Parízek Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Department of Distributed and Dependable
PANDA: Simultaneous Predicate Abstraction and Concrete Execution Jakub Daniel and Pavel Parízek Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, Department of Distributed and Dependable
The ComFoRT Reasoning Framework
 Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 The ComFoRT Reasoning Framework Sagar Chaki James Ivers Natasha Sharygina Kurt Wallnau Predictable Assembly from Certifiable Components Enable the development of software systems
Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 The ComFoRT Reasoning Framework Sagar Chaki James Ivers Natasha Sharygina Kurt Wallnau Predictable Assembly from Certifiable Components Enable the development of software systems
Computer Sciences Department
 1 Reference Book: INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION, SECOND EDITION, by: MICHAEL SIPSER 3 D E C I D A B I L I T Y 4 Objectives 5 Objectives investigate the power of algorithms to solve problems.
1 Reference Book: INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION, SECOND EDITION, by: MICHAEL SIPSER 3 D E C I D A B I L I T Y 4 Objectives 5 Objectives investigate the power of algorithms to solve problems.
CSE 501 Midterm Exam: Sketch of Some Plausible Solutions Winter 1997
 1) [10 pts] On homework 1, I asked about dead assignment elimination and gave the following sample solution: 8. Give an algorithm for dead assignment elimination that exploits def/use chains to work faster
1) [10 pts] On homework 1, I asked about dead assignment elimination and gave the following sample solution: 8. Give an algorithm for dead assignment elimination that exploits def/use chains to work faster
Interprocedural Heap Analysis using Access Graphs and Value Contexts
 Interprocedural Heap Analysis using Access Graphs and Value Contexts Dissertation Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Technology by Rohan Padhye Roll No: 113050017
Interprocedural Heap Analysis using Access Graphs and Value Contexts Dissertation Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Technology by Rohan Padhye Roll No: 113050017
Unit Testing as Hypothesis Testing
 Unit Testing as Hypothesis Testing Jonathan Clark September 19, 2012 5 minutes You should test your code. Why? To find bugs. Even for seasoned programmers, bugs are an inevitable reality. Today, we ll
Unit Testing as Hypothesis Testing Jonathan Clark September 19, 2012 5 minutes You should test your code. Why? To find bugs. Even for seasoned programmers, bugs are an inevitable reality. Today, we ll
DPLL(Γ+T): a new style of reasoning for program checking
 DPLL(Γ+T ): a new style of reasoning for program checking Dipartimento di Informatica Università degli Studi di Verona Verona, Italy June, 2011 Motivation: reasoning for program checking Program checking
DPLL(Γ+T ): a new style of reasoning for program checking Dipartimento di Informatica Università degli Studi di Verona Verona, Italy June, 2011 Motivation: reasoning for program checking Program checking
Computer aided verification
 Computer aided verification lecture 10 Model-checking success stories Sławomir Lasota University of Warsaw 1 LITERATURE G. J. Holzman, Mars Code. Commun. ACM 57(2):64-73, 2014. D.L. Detlefs, C.H. Flood,
Computer aided verification lecture 10 Model-checking success stories Sławomir Lasota University of Warsaw 1 LITERATURE G. J. Holzman, Mars Code. Commun. ACM 57(2):64-73, 2014. D.L. Detlefs, C.H. Flood,
Week 3 Video 4. Automated Feature Generation Automated Feature Selection
 Week 3 Video 4 Automated Feature Generation Automated Feature Selection Automated Feature Generation The creation of new data features in an automated fashion from existing data features Multiplicative
Week 3 Video 4 Automated Feature Generation Automated Feature Selection Automated Feature Generation The creation of new data features in an automated fashion from existing data features Multiplicative
Crema. Research Briefing. Jacob Torrey & Mark Bridgman May 21, 2015
 Crema Research Briefing Jacob Torrey & Mark Bridgman May 21, 2015 The views, opinions, and/or findings contained in this presentation are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing
Crema Research Briefing Jacob Torrey & Mark Bridgman May 21, 2015 The views, opinions, and/or findings contained in this presentation are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing
Checking Memory Safety with Blast
 Checking Memory Safety with Blast Dirk Beyer 1 Thomas A. Henzinger 12 Ranjit Jhala 3 Rupak Majumdar 4 1 EPFL, Switzerland 2 University of California, Berkeley 3 University of California, San Diego 4 University
Checking Memory Safety with Blast Dirk Beyer 1 Thomas A. Henzinger 12 Ranjit Jhala 3 Rupak Majumdar 4 1 EPFL, Switzerland 2 University of California, Berkeley 3 University of California, San Diego 4 University
A Survey of Automated Techniques for Formal Software Verification
 TRANSACTIONS ON CAD 1 A Survey of Automated Techniques for Formal Software Verification Vijay D Silva Daniel Kroening Georg Weissenbacher Abstract The quality and the correctness of software is often the
TRANSACTIONS ON CAD 1 A Survey of Automated Techniques for Formal Software Verification Vijay D Silva Daniel Kroening Georg Weissenbacher Abstract The quality and the correctness of software is often the
Refinement Strategies for Inductive Learning Of Simple Prolog Programs
 Refinement Strategies for Inductive Learning Of Simple Prolog Programs Marc Kirschenbaum Mathematics & Computer Science Dept. John Carroll Univesity Cleveland, Ohio 44118 U.S.A. Leon S. Sterling Computer
Refinement Strategies for Inductive Learning Of Simple Prolog Programs Marc Kirschenbaum Mathematics & Computer Science Dept. John Carroll Univesity Cleveland, Ohio 44118 U.S.A. Leon S. Sterling Computer
Homework Assignment #1 Sample Solutions
 Homework Assignment # Sample Solutions Due Monday /, at the start of lecture. For the following control flow graph, for the purposes of a forward data flow analysis (such as available expressions), show
Homework Assignment # Sample Solutions Due Monday /, at the start of lecture. For the following control flow graph, for the purposes of a forward data flow analysis (such as available expressions), show
INF672 Protocol Safety and Verification. Karthik Bhargavan Xavier Rival Thomas Clausen
 INF672 Protocol Safety and Verication Karthik Bhargavan Xavier Rival Thomas Clausen 1 Course Outline Lecture 1 [Today, Sep 15] Introduction, Motivating Examples Lectures 2-4 [Sep 22,29, Oct 6] Network
INF672 Protocol Safety and Verication Karthik Bhargavan Xavier Rival Thomas Clausen 1 Course Outline Lecture 1 [Today, Sep 15] Introduction, Motivating Examples Lectures 2-4 [Sep 22,29, Oct 6] Network
