Computer Security: Principles and Practice
|
|
|
- Antonia Robbins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer Security: Principles and Practice Chapter 5 Database Security First Edition by William Stallings and Lawrie Brown Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown
2 Database Security 2
3 Relational Databases constructed from tables of data each column holds a particular type of data each row contains a specific value these ideally has one column where all values are unique, forming an identifier/key for that row have multiple tables linked by identifiers use a query language to access data items meeting specified criteria 3
4 Relational Database Example 4
5 Relational Database Elements relation / table / file tuple / row / record attribute / column / field primary key uniquely identifies a row foreign key links one table to attributes in another view / virtual table 5
6 Relational Database Elements 6
7 Structured Query Language Structure Query Language (SQL) originally developed by IBM in the mid-1970s standardized language to define, manipulate, and query data in a relational database several similar versions of ANSI/ISO standard C REATE TABLE department ( Did INTE G E R PRIMAR Y KEY, Dname CHAR (30), Dacctno CHAR (6)) C R E ATE VIE W newtable (Dna m e, Ena me, Eid, Ephone) AS SELECT D.Dname E.Ename, E.Eid, E.Ephone FR O M Department D E mployee E W H E R E E.Did = D.Did C R E A T E TA BL E e mployee ( Ename CHAR (30), Did INTEG ER, SalaryCodeINTEGER, Eid INTE G E R PRIMAR Y KEY, Ephone CHAR (10), FOREIGN KEY (Did)REFERENCES department(did) ) 7
8 Database Access Control DBMS provide access control for database assume have authenticated user DBMS provides specific access rights to portions of the database e.g. create, insert, delete, update, read, write to entire database, tables, selected rows or columns possibly dependent on contents of a table entry can support a range of policies: centralized administration ownership-based administration decentralized administration 8
9 SQL Access Controls two commands: GRANT {privileges role }[ON table]to {user role PU BLIC } [IDENTIFIED BY password][with G RANT OPTION] e.g. GRANT SELECT ON ANY TABLE TO ricflair REVOKE {privileges role }[ON table] FRO M { user role PUBLIC } e.g. REVOKE SELECT ON ANY TABLE FROM ricflair typical access rights are: SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, REFERENCES 9
10 Cascading Authorizations 10
11 Role-Based Access Control role-based access control work well for DBMS eases admin burden, improves security categories of database users: application owner end user administrator DB RBAC must manage roles and their users cf. RBAC on Microsoft s SQL Server 11
12 Inference 12
13 Inference Example 13
14 Inference Countermeasures inference detection at database design alter database structure or access controls inference detection at query time by monitoring and altering or rejecting queries need some inference detection algorithm a difficult problem cf. employee-salary example 14
15 Statistical Databases provides data of a statistical nature e.g. counts, averages two types: pure statistical database ordinary database with statistical access some users have normal access, others statistical access control objective to allow statistical use without revealing individual entries security problem is one of inference 15
16 Statistical Database Security use a characteristic formula C a logical formula over the values of attributes e.g. (Sex=Male) AND ((Major=CS) O R (Major=EE)) query set X(C) of characteristic formula C, is the set of records matching C a statistical query is a query that produces a value calculated over a query set 16
17 Statistical Database Example 17
18 Protecting Against Inference 18
19 Tracker Attacks divide queries into parts C = C1.C2 count(c.d) = count(c1) - count (C1. ~C2) combination is called a tracker each part acceptable query size overlap is desired result 19
20 Other Query Restrictions query set overlap control limit overlap between new & previous queries has problems and overheads partitioning cluster records into exclusive groups only allow queries on entire groups query denial and information leakage denials can leak information to counter must track queries from user 20
21 Perturbation add noise to statistics generated from data will result in differences in statistics data perturbation techniques data swapping generate statistics from probability distribution output perturbation techniques random-sample query statistic adjustment must minimize loss of accuracy in results 21
22 Database Encryption databases typical a valuable info resource protected by multiple layers of security: firewalls, authentication, O/S access control systems, DB access control systems, and database encryption can encrypt entire database - very inflexible and inefficient individual fields - simple but inflexible records (rows) or columns (attributes) - best also need attribute indexes to help data retrieval varying trade-offs 22
23 Database Encryption 23
24 Summary introduced databases and DBMS relational databases database access control issues SQL, role-based inference statistical database security issues database encryption 24
CS419 Spring Computer Security. Vinod Ganapathy Lecture 15. Chapter 5: Database security
 CS419 Spring 2010 Computer Security Vinod Ganapathy Lecture 15 Chapter 5: Database security Database Security Relational Databases constructed from tables of data each column holds a particular type of
CS419 Spring 2010 Computer Security Vinod Ganapathy Lecture 15 Chapter 5: Database security Database Security Relational Databases constructed from tables of data each column holds a particular type of
Introduction To Security and Privacy Einführung in die IT-Sicherheit I
 Introduction To Security and Privacy Einführung in die IT-Sicherheit I Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Doğan Kesdoğan Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik kesdogan@fb5.uni-siegen.de http://www.uni-siegen.de/fb5/itsec/
Introduction To Security and Privacy Einführung in die IT-Sicherheit I Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Doğan Kesdoğan Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik kesdogan@fb5.uni-siegen.de http://www.uni-siegen.de/fb5/itsec/
Chapter 5: Database Security
 i Chapter 5: Comp Sci 3600 Outline i 1 2 i 3 4 5 Outline i 1 2 i 3 4 5 What is a i Structured collection of data stored for use by one or more applications Contains the relationships between data items
i Chapter 5: Comp Sci 3600 Outline i 1 2 i 3 4 5 Outline i 1 2 i 3 4 5 What is a i Structured collection of data stored for use by one or more applications Contains the relationships between data items
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018
 CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 12: Database Security Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Review of Access Control Types We previously studied four types
CSE 565 Computer Security Fall 2018 Lecture 12: Database Security Department of Computer Science and Engineering University at Buffalo 1 Review of Access Control Types We previously studied four types
ACS-3921/ Computer Security And Privacy. Chapter 5 Database and Data Centre Security
 ACS-3921/4921-001 Computer Security And Privacy Chapter 5 Database and Data Centre Security ACS-3921/4921-001 Slides Used In The Course A note on the use of these slides: These slides has been adopted
ACS-3921/4921-001 Computer Security And Privacy Chapter 5 Database and Data Centre Security ACS-3921/4921-001 Slides Used In The Course A note on the use of these slides: These slides has been adopted
COMPUTER NETWORK SECURITY
 COMPUTER NETWORK SECURITY Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (5 th Week) 5. Database and Cloud Security 5.Outline The Need for Database Security Database Management Systems Relational Databases SQL Injection
COMPUTER NETWORK SECURITY Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (5 th Week) 5. Database and Cloud Security 5.Outline The Need for Database Security Database Management Systems Relational Databases SQL Injection
University of Massachusetts Amherst Department of Computer Science Prof. Yanlei Diao
 University of Massachusetts Amherst Department of Computer Science Prof. Yanlei Diao CMPSCI 445 Midterm Practice Questions NAME: LOGIN: Write all of your answers directly on this paper. Be sure to clearly
University of Massachusetts Amherst Department of Computer Science Prof. Yanlei Diao CMPSCI 445 Midterm Practice Questions NAME: LOGIN: Write all of your answers directly on this paper. Be sure to clearly
The Relational Model. Outline. Why Study the Relational Model? Faloutsos SCS object-relational model
 The Relational Model CMU SCS 15-415 C. Faloutsos Lecture #3 R & G, Chap. 3 Outline Introduction Integrity constraints (IC) Enforcing IC Querying Relational Data ER to tables Intro to Views Destroying/altering
The Relational Model CMU SCS 15-415 C. Faloutsos Lecture #3 R & G, Chap. 3 Outline Introduction Integrity constraints (IC) Enforcing IC Querying Relational Data ER to tables Intro to Views Destroying/altering
Introduction to Data Management. Lecture #4 (E-R Relational Translation)
 Introduction to Data Management Lecture #4 (E-R Relational Translation) Instructor: Mike Carey mjcarey@ics.uci.edu Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Announcements v Today
Introduction to Data Management Lecture #4 (E-R Relational Translation) Instructor: Mike Carey mjcarey@ics.uci.edu Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Announcements v Today
COMP7640 Assignment 2
 COMP7640 Assignment 2 Due Date: 23:59, 14 November 2014 (Fri) Description Question 1 (20 marks) Consider the following relational schema. An employee can work in more than one department; the pct time
COMP7640 Assignment 2 Due Date: 23:59, 14 November 2014 (Fri) Description Question 1 (20 marks) Consider the following relational schema. An employee can work in more than one department; the pct time
Data Modelling and Databases. Exercise Session 7: Integrity Constraints
 Data Modelling and Databases Exercise Session 7: Integrity Constraints 1 Database Design Textual Description Complete Design ER Diagram Relational Schema Conceptual Modeling Logical Modeling Physical Modeling
Data Modelling and Databases Exercise Session 7: Integrity Constraints 1 Database Design Textual Description Complete Design ER Diagram Relational Schema Conceptual Modeling Logical Modeling Physical Modeling
LAB 3 Notes. Codd proposed the relational model in 70 Main advantage of Relational Model : Simple representation (relationstables(row,
 LAB 3 Notes The Relational Model Chapter 3 In the previous lab we discussed the Conceptual Database Design Phase and the ER Diagram. Today we will mainly discuss how to convert an ER model into the Relational
LAB 3 Notes The Relational Model Chapter 3 In the previous lab we discussed the Conceptual Database Design Phase and the ER Diagram. Today we will mainly discuss how to convert an ER model into the Relational
CSC 261/461 Database Systems Lecture 6. Fall 2017
 CSC 261/461 Database Systems Lecture 6 Fall 2017 Use of WITH The WITH clause allows a user to define a table that will only be used in a particular query (not available in all SQL implementations) Used
CSC 261/461 Database Systems Lecture 6 Fall 2017 Use of WITH The WITH clause allows a user to define a table that will only be used in a particular query (not available in all SQL implementations) Used
Chapter 4. Basic SQL. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Chapter 4 Basic SQL Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Chapter 4 Outline SQL Data Definition and Data Types Specifying Constraints in SQL Basic Retrieval Queries
Chapter 4 Basic SQL Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Chapter 4 Outline SQL Data Definition and Data Types Specifying Constraints in SQL Basic Retrieval Queries
The Relational Model. Chapter 3. Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall
 The Relational Model Chapter 3 Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall 2012 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model by industry. IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. It is simple,
The Relational Model Chapter 3 Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall 2012 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model by industry. IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. It is simple,
First lecture of this chapter is in slides (PPT file)
 First lecture of this chapter is in slides (PPT file) Review of referential integrity CREATE TABLE other_table ( b1 INTEGER, c1 INTEGER, PRIMARY KEY (b1, c1) ) CREATE TABLE t ( a integer PRIMARY KEY, b2
First lecture of this chapter is in slides (PPT file) Review of referential integrity CREATE TABLE other_table ( b1 INTEGER, c1 INTEGER, PRIMARY KEY (b1, c1) ) CREATE TABLE t ( a integer PRIMARY KEY, b2
Copyright 2016 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe
 CHAPTER 6 Basic SQL Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Outline SQL Data Definition and Data Types Specifying Constraints in SQL Basic Retrieval Queries in SQL INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE Statements in SQL Additional Features
CHAPTER 6 Basic SQL Slide 6-2 Chapter 6 Outline SQL Data Definition and Data Types Specifying Constraints in SQL Basic Retrieval Queries in SQL INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE Statements in SQL Additional Features
The Relational Model. Roadmap. Relational Database: Definitions. Why Study the Relational Model? Relational database: a set of relations
 The Relational Model CMU SCS 15-415/615 C. Faloutsos A. Pavlo Lecture #3 R & G, Chap. 3 Roadmap Introduction Integrity constraints (IC) Enforcing IC Querying Relational Data ER to tables Intro to Views
The Relational Model CMU SCS 15-415/615 C. Faloutsos A. Pavlo Lecture #3 R & G, Chap. 3 Roadmap Introduction Integrity constraints (IC) Enforcing IC Querying Relational Data ER to tables Intro to Views
QUERY OPTIMIZATION [CH 15]
![QUERY OPTIMIZATION [CH 15] QUERY OPTIMIZATION [CH 15]](/thumbs/79/79714738.jpg) Spring 2017 QUERY OPTIMIZATION [CH 15] 4/12/17 CS 564: Database Management Systems; (c) Jignesh M. Patel, 2013 1 Example SELECT distinct ename FROM Emp E, Dept D WHERE E.did = D.did and D.dname = Toy EMP
Spring 2017 QUERY OPTIMIZATION [CH 15] 4/12/17 CS 564: Database Management Systems; (c) Jignesh M. Patel, 2013 1 Example SELECT distinct ename FROM Emp E, Dept D WHERE E.did = D.did and D.dname = Toy EMP
Relational Databases BORROWED WITH MINOR ADAPTATION FROM PROF. CHRISTOS FALOUTSOS, CMU /615
 Relational Databases BORROWED WITH MINOR ADAPTATION FROM PROF. CHRISTOS FALOUTSOS, CMU 15-415/615 Roadmap 3 Introduction Integrity constraints (IC) Enforcing IC Querying Relational Data ER to tables Intro
Relational Databases BORROWED WITH MINOR ADAPTATION FROM PROF. CHRISTOS FALOUTSOS, CMU 15-415/615 Roadmap 3 Introduction Integrity constraints (IC) Enforcing IC Querying Relational Data ER to tables Intro
Comp 5311 Database Management Systems. 4b. Structured Query Language 3
 Comp 5311 Database Management Systems 4b. Structured Query Language 3 1 SQL as Data Definition Language Creates the Students relation. The type (domain) of each field is specified, and enforced by the
Comp 5311 Database Management Systems 4b. Structured Query Language 3 1 SQL as Data Definition Language Creates the Students relation. The type (domain) of each field is specified, and enforced by the
Chapter 4. Basic SQL. SQL Data Definition and Data Types. Basic SQL. SQL language SQL. Terminology: CREATE statement
 Chapter 4 Basic SQL Basic SQL SQL language Considered one of the major reasons for the commercial success of relational databases SQL Structured Query Language Statements for data definitions, queries,
Chapter 4 Basic SQL Basic SQL SQL language Considered one of the major reasons for the commercial success of relational databases SQL Structured Query Language Statements for data definitions, queries,
Sample Question Paper
 Sample Question Paper Marks : 70 Time:3 Hour Q.1) Attempt any FIVE of the following. a) List any four applications of DBMS. b) State the four database users. c) Define normalization. Enlist its type. d)
Sample Question Paper Marks : 70 Time:3 Hour Q.1) Attempt any FIVE of the following. a) List any four applications of DBMS. b) State the four database users. c) Define normalization. Enlist its type. d)
Using Relational Databases for Digital Research
 Using Relational Databases for Digital Research Definition (using a) relational database is a way of recording information in a structure that maximizes efficiency by separating information into different
Using Relational Databases for Digital Research Definition (using a) relational database is a way of recording information in a structure that maximizes efficiency by separating information into different
Question 1 (a) 10 marks
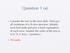 Question 1 (a) Consider the tree in the next slide. Find any/ all violations of a B+tree structure. Identify each bad node and give a brief explanation of each error. Assume the order of the tree is 4
Question 1 (a) Consider the tree in the next slide. Find any/ all violations of a B+tree structure. Identify each bad node and give a brief explanation of each error. Assume the order of the tree is 4
The Relational Model. Chapter 3. Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall
 The Relational Model Chapter 3 Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall 2014 1 Why the Relational Model? Most widely used model by industry. IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, MySQL, Postgres, Sqlite,
The Relational Model Chapter 3 Comp 521 Files and Databases Fall 2014 1 Why the Relational Model? Most widely used model by industry. IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, MySQL, Postgres, Sqlite,
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
 www..com Code No: N0321/R07 Set No. 1 1. a) What is a Superkey? With an example, describe the difference between a candidate key and the primary key for a given relation? b) With an example, briefly describe
www..com Code No: N0321/R07 Set No. 1 1. a) What is a Superkey? With an example, describe the difference between a candidate key and the primary key for a given relation? b) With an example, briefly describe
From ER to Relational Model. Book Chapter 3 (part 2 )
 From ER to Relational Model Book Chapter 3 (part 2 ) Logical DB Design: ER to Relational Translate Entity sets to tables: ssn name Employees lot CREATE TABLE Employees (ssn CHAR(11), name CHAR(20), lot
From ER to Relational Model Book Chapter 3 (part 2 ) Logical DB Design: ER to Relational Translate Entity sets to tables: ssn name Employees lot CREATE TABLE Employees (ssn CHAR(11), name CHAR(20), lot
The Relational Model. Chapter 3
 The Relational Model Chapter 3 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Systems: IBM DB2, Informix, Microsoft (Access and SQL Server), Oracle, Sybase, MySQL, etc. Legacy systems in older
The Relational Model Chapter 3 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Systems: IBM DB2, Informix, Microsoft (Access and SQL Server), Oracle, Sybase, MySQL, etc. Legacy systems in older
The Relational Model. Why Study the Relational Model? Relational Database: Definitions
 The Relational Model Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. Legacy systems in
The Relational Model Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc. Legacy systems in
CS W Introduction to Databases Spring Computer Science Department Columbia University
 CS W4111.001 Introduction to Databases Spring 2018 Computer Science Department Columbia University 1 in SQL 1. Key constraints (PRIMARY KEY and UNIQUE) 2. Referential integrity constraints (FOREIGN KEY
CS W4111.001 Introduction to Databases Spring 2018 Computer Science Department Columbia University 1 in SQL 1. Key constraints (PRIMARY KEY and UNIQUE) 2. Referential integrity constraints (FOREIGN KEY
Answers to the review questions can be found in the listed sections. What are the components of a workload description? (Section 20.1.
 685 20.13 REVIEW QUESTIONS Answers to the review questions can be found in the listed sections. What are the components of a workload description? (Section 20.1.1) What decisions need to be made during
685 20.13 REVIEW QUESTIONS Answers to the review questions can be found in the listed sections. What are the components of a workload description? (Section 20.1.1) What decisions need to be made during
Data Modeling. Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst. Slides Courtesy of R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke
 Data Modeling Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst Slides Courtesy of R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Outline v Conceptual Design: ER Model v Relational Model v Logical Design: from ER to Relational 2 Conceptual
Data Modeling Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst Slides Courtesy of R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Outline v Conceptual Design: ER Model v Relational Model v Logical Design: from ER to Relational 2 Conceptual
The Relational Model. Chapter 3. Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1
 The Relational Model Chapter 3 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc.
The Relational Model Chapter 3 Database Management Systems, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used model. Vendors: IBM, Informix, Microsoft, Oracle, Sybase, etc.
Database Applications (15-415)
 Database Applications (15-415) The Relational Model Lecture 3, January 18, 2015 Mohammad Hammoud Today Last Session: The entity relationship (ER) model Today s Session: ER model (Cont d): conceptual design
Database Applications (15-415) The Relational Model Lecture 3, January 18, 2015 Mohammad Hammoud Today Last Session: The entity relationship (ER) model Today s Session: ER model (Cont d): conceptual design
Database Management System Dr. S. Srinath Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No.
 Database Management System Dr. S. Srinath Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 13 Constraints & Triggers Hello and welcome to another session
Database Management System Dr. S. Srinath Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 13 Constraints & Triggers Hello and welcome to another session
DB Creation with SQL DDL
 DB Creation with SQL DDL Outline SQL Concepts Data Types Schema/Table/View Creation Transactions and Access Control Objectives of SQL Ideally, database language should allow user to: create the database
DB Creation with SQL DDL Outline SQL Concepts Data Types Schema/Table/View Creation Transactions and Access Control Objectives of SQL Ideally, database language should allow user to: create the database
Translating an ER Diagram to a Relational Schema
 Translating an ER Diagram to a Relational Schema CS386/586 Introduction to Database Systems, Lois Delcambre 1999-2009 Slide 1 Translate each entity set into a table, with keys. Entity set: represented
Translating an ER Diagram to a Relational Schema CS386/586 Introduction to Database Systems, Lois Delcambre 1999-2009 Slide 1 Translate each entity set into a table, with keys. Entity set: represented
After completing this unit, you should be able to: Define the terms
 Introduction Copyright IBM Corporation 2007 Course materials may not be reproduced in whole or in part without the prior written permission of IBM. 4.0.3 3.3.1 Unit Objectives After completing this unit,
Introduction Copyright IBM Corporation 2007 Course materials may not be reproduced in whole or in part without the prior written permission of IBM. 4.0.3 3.3.1 Unit Objectives After completing this unit,
The Relational Model (ii)
 ICS 321 Fall 2009 The Relational Model (ii) Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information and Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa 1 Internet Book Store Example Isbn title author qty price year
ICS 321 Fall 2009 The Relational Model (ii) Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information and Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa 1 Internet Book Store Example Isbn title author qty price year
The Relational Model
 The Relational Model What is the Relational Model Relations Domain Constraints SQL Integrity Constraints Translating an ER diagram to the Relational Model and SQL Views A relational database consists
The Relational Model What is the Relational Model Relations Domain Constraints SQL Integrity Constraints Translating an ER diagram to the Relational Model and SQL Views A relational database consists
Database Management Systems. Chapter 3 Part 2
 Database Management Systems Chapter 3 Part 2 The Relational Model Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Logical DB Design: ER to Relational Entity sets to tables: CREATE TABLE
Database Management Systems Chapter 3 Part 2 The Relational Model Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Logical DB Design: ER to Relational Entity sets to tables: CREATE TABLE
Which of the following is the best way to prevent most users from viewing AVG_SALARY data?
 Security 22. Which of the following is NOT a valid method of authentication that can be used by DB2 9? A. SERVER B. SERVER_ENCRYPT C. CLIENT D. DCS 23. In a client-server environment, which two of the
Security 22. Which of the following is NOT a valid method of authentication that can be used by DB2 9? A. SERVER B. SERVER_ENCRYPT C. CLIENT D. DCS 23. In a client-server environment, which two of the
The Relational Model 2. Week 3
 The Relational Model 2 Week 3 1 We have seen how to create a database schema, how do we create an actual database on our computers? professor(pid : string, name : string) course(pid : string, number :
The Relational Model 2 Week 3 1 We have seen how to create a database schema, how do we create an actual database on our computers? professor(pid : string, name : string) course(pid : string, number :
Access Control. Access control: ensures that all direct accesses to object are authorized a scheme for mapping users to allowed actions
 Access Control 1 Access Control Access control: ensures that all direct accesses to object are authorized a scheme for mapping users to allowed actions Protection objects: system resources for which protection
Access Control 1 Access Control Access control: ensures that all direct accesses to object are authorized a scheme for mapping users to allowed actions Protection objects: system resources for which protection
Slides by: Ms. Shree Jaswal
 Slides by: Ms. Shree Jaswal Overview of SQL, Data Definition Commands, Set operations, aggregate function, null values, Data Manipulation commands, Data Control commands, Views in SQL, Complex Retrieval
Slides by: Ms. Shree Jaswal Overview of SQL, Data Definition Commands, Set operations, aggregate function, null values, Data Manipulation commands, Data Control commands, Views in SQL, Complex Retrieval
EGCI 321: Database Systems. Dr. Tanasanee Phienthrakul
 1 EGCI 321: Database Systems Dr. Tanasanee Phienthrakul 2 Chapter 10 Data Definition Language (DDL) 3 Basic SQL SQL language Considered one of the major reasons for the commercial success of relational
1 EGCI 321: Database Systems Dr. Tanasanee Phienthrakul 2 Chapter 10 Data Definition Language (DDL) 3 Basic SQL SQL language Considered one of the major reasons for the commercial success of relational
192 Chapter 14. TotalCost=3 (1, , 000) = 6, 000
 192 Chapter 14 5. SORT-MERGE: With 52 buffer pages we have B> M so we can use the mergeon-the-fly refinement which costs 3 (M + N). TotalCost=3 (1, 000 + 1, 000) = 6, 000 HASH JOIN: Now both relations
192 Chapter 14 5. SORT-MERGE: With 52 buffer pages we have B> M so we can use the mergeon-the-fly refinement which costs 3 (M + N). TotalCost=3 (1, 000 + 1, 000) = 6, 000 HASH JOIN: Now both relations
The Relational Model Constraints and SQL DDL
 The Relational Model Constraints and SQL DDL Week 2-3 Weeks 2-3 MIE253-Consens 1 Schedule Week Date Lecture Topic 1 Jan 9 Introduction to Data Management 2 Jan 16 The Relational Model 3 Jan. 23 Constraints
The Relational Model Constraints and SQL DDL Week 2-3 Weeks 2-3 MIE253-Consens 1 Schedule Week Date Lecture Topic 1 Jan 9 Introduction to Data Management 2 Jan 16 The Relational Model 3 Jan. 23 Constraints
Physical Database Design and Tuning. Chapter 20
 Physical Database Design and Tuning Chapter 20 Introduction We will be talking at length about database design Conceptual Schema: info to capture, tables, columns, views, etc. Physical Schema: indexes,
Physical Database Design and Tuning Chapter 20 Introduction We will be talking at length about database design Conceptual Schema: info to capture, tables, columns, views, etc. Physical Schema: indexes,
The DBMS accepts requests for data from the application program and instructs the operating system to transfer the appropriate data.
 Managing Data Data storage tool must provide the following features: Data definition (data structuring) Data entry (to add new data) Data editing (to change existing data) Querying (a means of extracting
Managing Data Data storage tool must provide the following features: Data definition (data structuring) Data entry (to add new data) Data editing (to change existing data) Querying (a means of extracting
Oracle User Administration
 Oracle User Administration Creating user accounts User accounts consist of two components. These are: 1. User name - The name of the account. 2. Password - The password associated with the user account.
Oracle User Administration Creating user accounts User accounts consist of two components. These are: 1. User name - The name of the account. 2. Password - The password associated with the user account.
Database Systems ( 資料庫系統 )
 Database Systems ( 資料庫系統 ) 9.28.2011 Lecture #3 1 Course Administration Please download HW #1 from course homepage It is due 10/12/2011. This lecture: R&G Chapter 3 Next week reading: R&G Chapter 41~ 4.1
Database Systems ( 資料庫系統 ) 9.28.2011 Lecture #3 1 Course Administration Please download HW #1 from course homepage It is due 10/12/2011. This lecture: R&G Chapter 3 Next week reading: R&G Chapter 41~ 4.1
High-Level Database Models (ii)
 ICS 321 Spring 2011 High-Level Database Models (ii) Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information & Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa 1 Logical DB Design: ER to Relational Entity sets to
ICS 321 Spring 2011 High-Level Database Models (ii) Asst. Prof. Lipyeow Lim Information & Computer Science Department University of Hawaii at Manoa 1 Logical DB Design: ER to Relational Entity sets to
Essay Question: Explain 4 different means by which constrains are represented in the Conceptual Data Model (CDM).
 Question 1 Essay Question: Explain 4 different means by which constrains are represented in the Conceptual Data Model (CDM). By specifying participation conditions By specifying the degree of relationship
Question 1 Essay Question: Explain 4 different means by which constrains are represented in the Conceptual Data Model (CDM). By specifying participation conditions By specifying the degree of relationship
Database Laboratory Note (MS SQL Server 2000)
 Database Laboratory Note MS SQL Server 2000 Creating a New Database using QA query analyzer In MS-SQL server 2000 a database can be considered as a container to the objects in a database. A database has
Database Laboratory Note MS SQL Server 2000 Creating a New Database using QA query analyzer In MS-SQL server 2000 a database can be considered as a container to the objects in a database. A database has
D B M G. SQL language: basics. Managing tables. Creating a table Modifying table structure Deleting a table The data dictionary Data integrity
 SQL language: basics Creating a table Modifying table structure Deleting a table The data dictionary Data integrity 2013 Politecnico di Torino 1 Creating a table Creating a table (1/3) The following SQL
SQL language: basics Creating a table Modifying table structure Deleting a table The data dictionary Data integrity 2013 Politecnico di Torino 1 Creating a table Creating a table (1/3) The following SQL
CHAPTER 5 SECURITY ADVANCED DATABASE SYSTEMS. Assist. Prof. Dr. Volkan TUNALI
 CHAPTER 5 SECURITY ADVANCED DATABASE SYSTEMS Assist. Prof. Dr. Volkan TUNALI Topics 2 Introduction Discretionary Access Control Mandatory Access Control Statistical Databases Data Encryption SQL Facilities
CHAPTER 5 SECURITY ADVANCED DATABASE SYSTEMS Assist. Prof. Dr. Volkan TUNALI Topics 2 Introduction Discretionary Access Control Mandatory Access Control Statistical Databases Data Encryption SQL Facilities
Introduction to Data Management. Lecture #5 Relational Model (Cont.) & E-Rà Relational Mapping
 Introduction to Data Management Lecture #5 Relational Model (Cont.) & E-Rà Relational Mapping Instructor: Mike Carey mjcarey@ics.uci.edu Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1
Introduction to Data Management Lecture #5 Relational Model (Cont.) & E-Rà Relational Mapping Instructor: Mike Carey mjcarey@ics.uci.edu Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1
Access Control. Protects against accidental and malicious threats by
 Access Control 1 Access Control Access control: ensures that all direct accesses to object are authorized a scheme for mapping users to allowed actions Protection objects: system resources for which protection
Access Control 1 Access Control Access control: ensures that all direct accesses to object are authorized a scheme for mapping users to allowed actions Protection objects: system resources for which protection
Physical Database Design and Tuning. Review - Normal Forms. Review: Normal Forms. Introduction. Understanding the Workload. Creating an ISUD Chart
 Physical Database Design and Tuning R&G - Chapter 20 Although the whole of this life were said to be nothing but a dream and the physical world nothing but a phantasm, I should call this dream or phantasm
Physical Database Design and Tuning R&G - Chapter 20 Although the whole of this life were said to be nothing but a dream and the physical world nothing but a phantasm, I should call this dream or phantasm
Chapter 1 SQL and Data
 Chapter 1 SQL and Data What is SQL? Structured Query Language An industry-standard language used to access & manipulate data stored in a relational database E. F. Codd, 1970 s IBM 2 What is Oracle? A relational
Chapter 1 SQL and Data What is SQL? Structured Query Language An industry-standard language used to access & manipulate data stored in a relational database E. F. Codd, 1970 s IBM 2 What is Oracle? A relational
COSC 304 Introduction to Database Systems. Views and Security. Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan
 COSC 304 Introduction to Database Systems Views and Security Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Views A view is a named query that is defined in the database.
COSC 304 Introduction to Database Systems Views and Security Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Views A view is a named query that is defined in the database.
CS 356 Operating System Security. Fall 2013
 CS 356 Operating System Security Fall 2013 Review Chapter 1: Basic Concepts and Terminology Chapter 2: Basic Cryptographic Tools Chapter 3 User Authentication Chapter 4 Access Control Lists Chapter 5 Database
CS 356 Operating System Security Fall 2013 Review Chapter 1: Basic Concepts and Terminology Chapter 2: Basic Cryptographic Tools Chapter 3 User Authentication Chapter 4 Access Control Lists Chapter 5 Database
Solved MCQ on fundamental of DBMS. Set-1
 Solved MCQ on fundamental of DBMS Set-1 1) Which of the following is not a characteristic of a relational database model? A. Table B. Tree like structure C. Complex logical relationship D. Records 2) Field
Solved MCQ on fundamental of DBMS Set-1 1) Which of the following is not a characteristic of a relational database model? A. Table B. Tree like structure C. Complex logical relationship D. Records 2) Field
The Relational Model
 The Relational Model UVic C SC 370, Fall 2002 Daniel M. German Department of Computer Science University of Victoria 3 1 The Relational Model CSC 370 dmgerman@uvic.ca Overview How is data represented in
The Relational Model UVic C SC 370, Fall 2002 Daniel M. German Department of Computer Science University of Victoria 3 1 The Relational Model CSC 370 dmgerman@uvic.ca Overview How is data represented in
Outer Join, More on SQL Constraints
 Outer Join, More on SQL Constraints CS430/630 Lecture 10 Slides based on Database Management Systems 3 rd ed, Ramakrishnan and Gehrke Outer Joins Include in join result non-matching tuples Result tuple
Outer Join, More on SQL Constraints CS430/630 Lecture 10 Slides based on Database Management Systems 3 rd ed, Ramakrishnan and Gehrke Outer Joins Include in join result non-matching tuples Result tuple
Outline. Textbook Chapter 6. Note 1. CSIE30600/CSIEB0290 Database Systems Basic SQL 2
 Outline SQL Data Definition and Data Types Specifying Constraints in SQL Basic Retrieval Queries in SQL INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE Statements in SQL Additional Features of SQL Textbook Chapter 6 CSIE30600/CSIEB0290
Outline SQL Data Definition and Data Types Specifying Constraints in SQL Basic Retrieval Queries in SQL INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE Statements in SQL Additional Features of SQL Textbook Chapter 6 CSIE30600/CSIEB0290
Introduction to Database Systems. Motivation. Werner Nutt
 Introduction to Database Systems Motivation Werner Nutt 1 Databases Are Everywhere Database = a large (?) collection of related data Classically, a DB models a real-world organisation (e.g., enterprise,
Introduction to Database Systems Motivation Werner Nutt 1 Databases Are Everywhere Database = a large (?) collection of related data Classically, a DB models a real-world organisation (e.g., enterprise,
DATABASE SECURITY AND PRIVACY. Some slides were taken from Database Access Control Tutorial, Lars Olson, UIUC CS463, Computer Security
 DATABASE SECURITY AND PRIVACY Some slides were taken from 463.5.1 Database Access Control Tutorial, Lars Olson, UIUC CS463, Computer Security Database Security Protect Sensitive Data from Unauthorized
DATABASE SECURITY AND PRIVACY Some slides were taken from 463.5.1 Database Access Control Tutorial, Lars Olson, UIUC CS463, Computer Security Database Security Protect Sensitive Data from Unauthorized
ACS / Computer Security And Privacy. Fall 2018 Mid-Term Review
 ACS-3921-001/4921-001 Computer Security And Privacy Fall 2018 Mid-Term Review ACS-3921/4921-001 Slides Used In The Course A note on the use of these slides: These slides has been adopted and/or modified
ACS-3921-001/4921-001 Computer Security And Privacy Fall 2018 Mid-Term Review ACS-3921/4921-001 Slides Used In The Course A note on the use of these slides: These slides has been adopted and/or modified
CSIE30600 Database Systems Basic SQL 2. Outline
 Outline SQL Data Definition and Data Types Specifying Constraints in SQL Basic Retrieval Queries in SQL INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE Statements in SQL Additional Features of SQL CSIE30600 Database Systems
Outline SQL Data Definition and Data Types Specifying Constraints in SQL Basic Retrieval Queries in SQL INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE Statements in SQL Additional Features of SQL CSIE30600 Database Systems
Where Are We? Next Few Lectures. Integrity Constraints Motivation. Constraints in E/R Diagrams. Keys in E/R Diagrams
 Where Are We? Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lecture 15: Constraints We know quite a bit about using a DBMS Start with real-world problem, design ER diagram From ER diagram to relations -> conceptual
Where Are We? Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lecture 15: Constraints We know quite a bit about using a DBMS Start with real-world problem, design ER diagram From ER diagram to relations -> conceptual
Chapter 9: Database Security: An Introduction. Nguyen Thi Ai Thao
 Chapter 9: Database Security: An Introduction Nguyen Thi Ai Thao thaonguyen@cse.hcmut.edu.vn Spring- 2016 Outline Introduction to Database Security Issues Types of Security Threats to databases Database
Chapter 9: Database Security: An Introduction Nguyen Thi Ai Thao thaonguyen@cse.hcmut.edu.vn Spring- 2016 Outline Introduction to Database Security Issues Types of Security Threats to databases Database
Database Management System Dr. S. Srinath Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No.
 Database Management System Dr. S. Srinath Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 5 Structured Query Language Hello and greetings. In the ongoing
Database Management System Dr. S. Srinath Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture No. # 5 Structured Query Language Hello and greetings. In the ongoing
COGS 121 HCI Programming Studio. Week 03 - Tech Lecture
 COGS 121 HCI Programming Studio Week 03 - Tech Lecture Housekeeping Assignment #1 extended to Monday night 11:59pm Assignment #2 to be released on Tuesday during lecture Database Management Systems and
COGS 121 HCI Programming Studio Week 03 - Tech Lecture Housekeeping Assignment #1 extended to Monday night 11:59pm Assignment #2 to be released on Tuesday during lecture Database Management Systems and
Integrity constraints, relationships. CS634 Lecture 2
 Integrity constraints, relationships CS634 Lecture 2 Foreign Keys Defined in Sec. 3.2.2 without mentioning nulls. Nulls covered in Sec. 5.6 First example: nice not-null foreign key column: create table
Integrity constraints, relationships CS634 Lecture 2 Foreign Keys Defined in Sec. 3.2.2 without mentioning nulls. Nulls covered in Sec. 5.6 First example: nice not-null foreign key column: create table
Hash-Based Indexing 165
 Hash-Based Indexing 165 h 1 h 0 h 1 h 0 Next = 0 000 00 64 32 8 16 000 00 64 32 8 16 A 001 01 9 25 41 73 001 01 9 25 41 73 B 010 10 10 18 34 66 010 10 10 18 34 66 C Next = 3 011 11 11 19 D 011 11 11 19
Hash-Based Indexing 165 h 1 h 0 h 1 h 0 Next = 0 000 00 64 32 8 16 000 00 64 32 8 16 A 001 01 9 25 41 73 001 01 9 25 41 73 B 010 10 10 18 34 66 010 10 10 18 34 66 C Next = 3 011 11 11 19 D 011 11 11 19
Database Management Systems (COP 5725) Homework 3
 Database Management Systems (COP 5725) Homework 3 Instructor: Dr. Daisy Zhe Wang TAs: Yang Chen, Kun Li, Yang Peng yang, kli, ypeng@cise.uf l.edu November 26, 2013 Name: UFID: Email Address: Pledge(Must
Database Management Systems (COP 5725) Homework 3 Instructor: Dr. Daisy Zhe Wang TAs: Yang Chen, Kun Li, Yang Peng yang, kli, ypeng@cise.uf l.edu November 26, 2013 Name: UFID: Email Address: Pledge(Must
Introduction to Data Management. Lecture #4 (E-R à Relational Design)
 Introduction to Data Management Lecture #4 (E-R à Relational Design) Instructor: Mike Carey mjcarey@ics.uci.edu Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Announcements v Reminders:
Introduction to Data Management Lecture #4 (E-R à Relational Design) Instructor: Mike Carey mjcarey@ics.uci.edu Database Management Systems 3ed, R. Ramakrishnan and J. Gehrke 1 Announcements v Reminders:
Lecture 8. Database vs. Files SQL (I) Introduction to SQL database management systems (DBMS)
 Lecture 8 SQL (I) Money are kept by boxes buried in the ground in the backyard. Money are kept in the bank 1 Source: system analysis and design methods, by Jeffrey L Whitten et al., 2 McGraw-Hill/Irwin,
Lecture 8 SQL (I) Money are kept by boxes buried in the ground in the backyard. Money are kept in the bank 1 Source: system analysis and design methods, by Jeffrey L Whitten et al., 2 McGraw-Hill/Irwin,
SQL language. Jaroslav Porubän, Miroslav Biňas, Milan Nosáľ (c)
 SQL language Jaroslav Porubän, Miroslav Biňas, Milan Nosáľ (c) 2011-2016 SQL - Structured Query Language SQL is a computer language for communicating with DBSM Nonprocedural (declarative) language What
SQL language Jaroslav Porubän, Miroslav Biňas, Milan Nosáľ (c) 2011-2016 SQL - Structured Query Language SQL is a computer language for communicating with DBSM Nonprocedural (declarative) language What
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 14
 Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 14 Fifth Edition by William Stallings Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown Chapter 14 Key Management and Distribution No Singhalese, whether man or woman, would venture
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 14 Fifth Edition by William Stallings Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown Chapter 14 Key Management and Distribution No Singhalese, whether man or woman, would venture
Example 1 - Create Horizontal View. Example 2 - Create Vertical View. Views. Views
 Views Views RECALLS: View Dynamic result of one or more relational operations operating on the base relations to produce another relation. o Virtual relation that does not actually exist in the database
Views Views RECALLS: View Dynamic result of one or more relational operations operating on the base relations to produce another relation. o Virtual relation that does not actually exist in the database
Security Control Methods for Statistical Database
 Security Control Methods for Statistical Database Li Xiong CS573 Data Privacy and Security Statistical Database A statistical database is a database which provides statistics on subsets of records OLAP
Security Control Methods for Statistical Database Li Xiong CS573 Data Privacy and Security Statistical Database A statistical database is a database which provides statistics on subsets of records OLAP
Data about data is database Select correct option: True False Partially True None of the Above
 Within a table, each primary key value. is a minimal super key is always the first field in each table must be numeric must be unique Foreign Key is A field in a table that matches a key field in another
Within a table, each primary key value. is a minimal super key is always the first field in each table must be numeric must be unique Foreign Key is A field in a table that matches a key field in another
SQL Data Definition and Data Manipulation Languages (DDL and DML)
 .. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 365: Introduction to Database Systems Alexander Dekhtyar.. SQL Data Definition and Data Manipulation Languages (DDL and DML) Note: This handout instroduces both the ANSI SQL synatax
.. Cal Poly CPE/CSC 365: Introduction to Database Systems Alexander Dekhtyar.. SQL Data Definition and Data Manipulation Languages (DDL and DML) Note: This handout instroduces both the ANSI SQL synatax
Carnegie Mellon Univ. Dept. of Computer Science Database Applications. General Overview - rel. model. Overview - detailed - SQL
 Faloutsos 15-415 Carnegie Mellon Univ. Dept. of Computer Science 15-415 - Database Applications C. Faloutsos Lecture#7 (cont d): Rel. model - SQL part3 General Overview - rel. model Formal query languages
Faloutsos 15-415 Carnegie Mellon Univ. Dept. of Computer Science 15-415 - Database Applications C. Faloutsos Lecture#7 (cont d): Rel. model - SQL part3 General Overview - rel. model Formal query languages
SQL STRUCTURED QUERY LANGUAGE
 STRUCTURED QUERY LANGUAGE SQL Structured Query Language 4.1 Introduction Originally, SQL was called SEQUEL (for Structured English QUery Language) and implemented at IBM Research as the interface for an
STRUCTURED QUERY LANGUAGE SQL Structured Query Language 4.1 Introduction Originally, SQL was called SEQUEL (for Structured English QUery Language) and implemented at IBM Research as the interface for an
Database Security. Authentification: verifying the id of a user. Authorization: checking the access privileges
 Database Security Security Tasks Authentification: verifying the id of a user Authorization: checking the access privileges Auditing: looking for violations (in the past) 1 Data Security Dorothy Denning,
Database Security Security Tasks Authentification: verifying the id of a user Authorization: checking the access privileges Auditing: looking for violations (in the past) 1 Data Security Dorothy Denning,
CS698F Advanced Data Management. Instructor: Medha Atre. Aug 04, 2017 CS698F Adv Data Mgmt 1
 CS698F Advanced Data Management Instructor: Medha Atre Aug 04, 2017 CS698F Adv Data Mgmt 1 Recap Database Mgmt Sys Schema generation & normalization SQL query parsing, relational algebra File Sys, Indexes,
CS698F Advanced Data Management Instructor: Medha Atre Aug 04, 2017 CS698F Adv Data Mgmt 1 Recap Database Mgmt Sys Schema generation & normalization SQL query parsing, relational algebra File Sys, Indexes,
Cryptography and Network Security
 Cryptography and Network Security Third Edition by William Stallings Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown Chapter 14 Authentication Applications We cannot enter into alliance with neighbouring princes until
Cryptography and Network Security Third Edition by William Stallings Lecture slides by Lawrie Brown Chapter 14 Authentication Applications We cannot enter into alliance with neighbouring princes until
Objectives. After completing this lesson, you should be able to do the following:
 Objectives After completing this lesson, you should be able to do the following: Write SELECT statements to access data from more than one table using equality and nonequality joins View data that generally
Objectives After completing this lesson, you should be able to do the following: Write SELECT statements to access data from more than one table using equality and nonequality joins View data that generally
Database Management Systems,
 Database Management Systems Database Design (2) 1 Topics Data Base Design Logical Design (Review) Physical Design Entity Relationship (ER) Model to Relational Model Entity Relationship Attributes Normalization
Database Management Systems Database Design (2) 1 Topics Data Base Design Logical Design (Review) Physical Design Entity Relationship (ER) Model to Relational Model Entity Relationship Attributes Normalization
CSIT5300: Advanced Database Systems
 CSIT5300: Advanced Database Systems L11: Physical Database Design Dr. Kenneth LEUNG Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Hong Kong SAR, China
CSIT5300: Advanced Database Systems L11: Physical Database Design Dr. Kenneth LEUNG Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Hong Kong SAR, China
The Entity-Relationship Model
 The Entity-Relationship Model Chapter 2 Instructor: Vladimir Zadorozhny vladimir@sis.pitt.edu Information Science Program School of Information Sciences, University of Pittsburgh 1 Database: a Set of Relations
The Entity-Relationship Model Chapter 2 Instructor: Vladimir Zadorozhny vladimir@sis.pitt.edu Information Science Program School of Information Sciences, University of Pittsburgh 1 Database: a Set of Relations
Distributed KIDS Labs 1
 Distributed Databases @ KIDS Labs 1 Distributed Database System A distributed database system consists of loosely coupled sites that share no physical component Appears to user as a single system Database
Distributed Databases @ KIDS Labs 1 Distributed Database System A distributed database system consists of loosely coupled sites that share no physical component Appears to user as a single system Database
Relational Model. Topics. Relational Model. Why Study the Relational Model? Linda Wu (CMPT )
 Topics Relational Model Linda Wu Relational model SQL language Integrity constraints ER to relational Views (CMPT 354 2004-2) Chapter 3 CMPT 354 2004-2 2 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used
Topics Relational Model Linda Wu Relational model SQL language Integrity constraints ER to relational Views (CMPT 354 2004-2) Chapter 3 CMPT 354 2004-2 2 Why Study the Relational Model? Most widely used
Chapter # 7 Introduction to Structured Query Language (SQL) Part I
 Chapter # 7 Introduction to Structured Query Language (SQL) Part I Introduction to SQL SQL functions fit into two broad categories: Data definition language Data manipulation language Basic command set
Chapter # 7 Introduction to Structured Query Language (SQL) Part I Introduction to SQL SQL functions fit into two broad categories: Data definition language Data manipulation language Basic command set
Basic SQL. Basic SQL. Basic SQL
 Basic SQL Dr Fawaz Alarfaj Al Imam Mohammed Ibn Saud Islamic University ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Slides are adopted from: Elmasri & Navathe, Fundamentals of Database Systems MySQL Documentation Basic SQL Structured
Basic SQL Dr Fawaz Alarfaj Al Imam Mohammed Ibn Saud Islamic University ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Slides are adopted from: Elmasri & Navathe, Fundamentals of Database Systems MySQL Documentation Basic SQL Structured
