(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1 Cleghorn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 25, 2010 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING CONNECTIVITY BETWEEN TWO DIFFERENT NETWORKS USING DIFFERENT PROTOCOLS (75) Inventors: Monica Rose Cleghorn, Plano, TX (US); Kevin V. Nguyen, Allen, TX (US) Correspondence Address: RG & ASSOCATES 1103 TWINCREEKS, STE. 120 ALLEN, TX (US) (73) Assignee: (21) Appl. No.: 12/610,573 (22) Filed: Nov. 2, 2009 ACCUDATA TECHNOLOGIES, INC. Allen, TX (US) Related U.S. Application Data (63) Continuation of application No. 10/ , filed on Aug. 20, 2002, now Pat. No. 7,644,169, Continuation in-part of application No. 09/964,954, filed on Sep , now Pat. No. 7,373,335. Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. G06F 5/16 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /230; 709/232; 709/245 (57) ABSTRACT The present invention provides a system and method for providing message connectivity between a first network using a first protocol and a second network using a second protocol. If a message is received from the first network, the message is processed using one or more digital signal processors, a des tination in the second network is determined, the processed message is logged and translated into the second protocol, and the translated message is sent to the destination in the second network. If the message is received from the second network, the message is translated into the first protocol, a destination in the first network is determined, the translated message is logged and processed using one or more digital signal processors, and the processed message is sent to the destination in the first network. This method can be imple mented as a computer program embodied on a computer readable medium. 300 First Protocol Message Receive Message From First NetWork Process Message Using DigitalSignal Processors Determine Second NetWork Destination For Processed Message Log Processed Message Translate ProCeSSed Message into Second rotocol Send Translated MeSSade To Second NetWork Destination Second Protocol Message 304 O
2 Patent Application Publication Feb. 25, 2010 Sheet 1 of 6 US 2010/ A Financial 118 Bank 106 Server SS7 110 Server Server Financial Network 112 Fig.1 IP-STP Gateway Fig.2 Customer Equipment
3 Patent Application Publication Feb. 25, 2010 Sheet 2 of 6 US 2010/ A1 300 First Protocol Message 302 Receive Message From First NetWork 304 Process Message Using DigitalSignal Processors 306 Determine Second Network Destination For Processed Message Log Processed Message Translate PrOCeSSed Message into Second rotocol Send Translated MeSSace TO Second Network Destination 308 O Second Protocol Message Fig. 3A 350 Second Protocol Message 352 Receive Message From Second NetWork Translate Message into First Protocol Determine First NetWOrk Destination For Translated Message Log Translated Message PrOCeSS Translated Message Using Digital Signal Processors Send Processed Message To First Network Destination O First Protocol Message Fig.3B
4 Patent Application Publication Feb. 25, 2010 Sheet 3 of 6 US 2010/ A Client Module Server Module Routing Module One Or More NetWork Interface Modules Fig. 4A Fig. 4B Server Module Sends Out Time Out Response to Client Module Fig.6C 664
5 Patent Application Publication Feb. 25, 2010 Sheet 4 of 6 US 2010/ A1 5OO Start Osian ) 5 O 2 Client Connects to Server 5 O 4 Server Validates Client IP Ouery Sent from Client to Server IP Ouery Sent from Serve to Router 5 O 6 5 O 8 5 O Router Determines Destination SS7 Database and SS7 NetWork Server IP Query Sent from Router to SS7 Network Server 5 4 SS7 Network Server Translates IP Ouery into SS7 Query SS7 Ouery Sent from SS7 Network Server to Destination SS7 Database 5 SS7 Query Processed and SS7 Response Created SS7 Response Sent From Destination SS7 Database to SS7 Network Server SS7 Network Server Translates IP Ouery into IP Response IP Response Sent From SS7 Network Sever to ROuter Router Determines Client Destination for IP Response IP Response Sent From Router to Server O EP Response Sent From Server to Client 532 Client DiSCOnnects From Server (optional) End Fig.5 534
6 Patent Application Publication Feb. 25, 2010 Sheet 5 of 6 US 2010/ A User logs into Client Module 604 Client Module Connects to Server 606 Server Module Walidates User/Client Module 610 Deny Access to User Client Module 620 Return Error Message to Client MOdule Via Server Module Fig.6A Walidation Successful? 608 YES 612 User Submits Query to Server Module Via Client Module Query Sent from Sever Module to ROuter Module ROuter Module Determines Destination Database & NetWork interface DeStination Address & Network interface Found YES N
7 Patent Application Publication Feb. 25, 2010 Sheet 6 of 6 US 2010/ A1 622 Server Module Sends Query to Router Module -624 Sever Module Sets Timer for Query Server Module Stores Client Module Address and Query identification information Query Sent from Router Module to Network interface for Destination Address Network Interface Translates Ouery into Network Protocol Network Interface Logs Network Ouery Network Query Sent from NetWork interface to Destination Address Network Ouery Processed and Network Response Created Network Response Sent from Destination Address to Network Interface -640 Network interface Correlates Network Response with Network Ouery -642 Network interface Translates Network Response into Client Response -644 Client Response Sent from Network Interface to Router Module -646 Router Module Correlates Client Response with Query -648 Client Response Sent from Router Module to Server Module -650 Client Response Sent from Server Module to Client Module and QueryTimer Off Another Query? 652 YES NO -654 Use? LOGS Out of Client Module 656 C End ) Fig.6B
8 US 2010/ A1 Feb. 25, 2010 SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR PROVIDING CONNECTIVITY BETWEEN TWO DIFFERENT NETWORKS USING DIFFERENT PROTOCOLS CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION This application is a continuation of and claims priority to U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10/ which in turn is a continuation-in-part of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09/964,954 filed on Sep. 27, 2001, now issued Pat. No , the entire contents of each of which are incorpo rated by reference herein. TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION 0002 The present invention relates generally to the field of communications and, more particularly, to a system and method for providing connectivity between two different net works using different protocols. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Despite the fact that the government requires exist ing telecommunication service companies to allow competi tors to access their facilities and databases to the extent nec essary to provide competitive services, obtaining quick and reliable access to the information contained in these data bases has been difficult, if not impossible. For example, com petitive local exchange carriers ( CLEC) have not had an easy-to-use, near real-time or real-time system that can access an incumbent local exchange carrier's ( ILEC) database to determine whether a phone number will accept a collect call Similarly, the increased use of the Internet for pur chasing goods and services has increased the pressure to validate and check pending transactions before they are com pleted. For example, an Internet retailer would like to deter mine whether a potential customer's credit card or banking card is valid and whether the account has the creditor funds to pay for the proposed transaction In each of the cases described above, a database query will most likely have to cross network boundaries, Some of which may use proprietary or legacy protocols. As a result, the processing of these queries is difficult, slow and cumbersome. In addition, gateways located at these bound aries between different networks that use different protocols have traditionally used custom equipment that is both expen sive and difficult to integrate into an existing system. For example, Internet Protocol Signal Transfer Point ( IP-STP) communications capabilities in the telecommunications industry have been only possible via fixed traditional com munication links commonly referred to as 56K links, A-Links, D-Links or the like. Accordingly, there is a need for a system and method for providing connectivity between two different networks using different protocols that is inexpen sive, efficient and easy to install. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention provides a system and method for providing connectivity between two different networks using different protocols. The present invention can be easily installed on one or more off-the-shelf computers or servers. Moreover, the present invention can create, accept and track messages in the more commonly used protocols. Such as the Internet Protocol ( IP), and translate them into proprietary or legacy protocols in real or near-real time. In addition, the IP-STP provided by the present invention allows IP connec tivity to SS7 networks in a secure mode and allows program ming of specific applications. As a result, the present inven tion provides an efficient and inexpensive gateway to process messages between two different networks using different pro tocols The present invention provides a method for provid ing message connectivity between a first network using a first protocol and a second network using a second protocol. If a message is received from the first network, the message is processed using one or more digital signal processors, a des tination in the second network is determined, the processed message is logged and translated into the second protocol, and the translated message is sent to the destination in the second network. If the message is received from the second network, the message is translated into the first protocol, a destination in the first network is determined, the translated message is logged and processed using one or more digital signal processors, and the processed message is sent to the destination in the first network. This method can be imple mented as a computer program embodied on a computer readable medium In addition, the present invention provides a system for providing message connectivity between a first network using a first protocol and a second network using a second protocol. The system includes a computer, a first network interface communicably coupling the computer to the first network, a second network interface communicably coupling the computer to the second network, and a computer program resident on the computer. The computer program includes a code segment that whenever the message is received at the first network interface, processes the message using one or more digital signal processors, determines a destination in the second network for the processed message, logs the pro cessed message, translates the processed message into the second protocol and sends the translated message to the des tination in the second network via the second network inter face. The computer program also includes a code segment that whenever the message is received at the second network interface, translates the message into the first protocol, deter mines a destination in the first network for the translated message, logs the translated message, processes the trans lated message using one or more digital signal processors and sends the processed message to the destination in the first network via the first network interface Other features and advantages of the present inven tion shall be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art upon reference to the following detailed description taken in con junction with the accompanying drawings. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0010 For a better understanding of the invention, and to show by way of example how the same may be carried into effect, reference is now made to the detailed description of the invention along with the accompanying figures in which cor responding numerals in the different figures refer to corre sponding parts and in which: 0011 FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a networkinaccordance with one embodiment of the present invention; 0012 FIG. 2 illustrates the use of the present invention as a gateway between various networks:
9 US 2010/ A1 Feb. 25, FIGS. 3A and 3B are flowcharts depicting the method of providing connectivity between a first network and a second network in accordance with the present invention; 0014 FIGS. 4A and 4B are block diagrams of various implementations of the present invention; 0015 FIG. 5 is a flowchart of an IP to SS7 translation method in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention; and 0016 FIGS. 6A, 6B and 6C are schematic diagrams of a more detailed generic translation method in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION 0017 While the making and using of various embodi ments of the present invention are discussed in detail below, it should be appreciated that the present invention provides many applicable inventive concepts, which can be embodied in a wide variety of specific contexts. For example, in addition to telecommunications systems and the Internet, the present invention may be applicable to other forms of communica tions or general data processing. Other forms of communica tions may include communications between networks, com munications via satellite, or any form of communications not yet known to man as of the date of the present invention. The specific embodiments discussed herein are merely illustrative of specific ways to make and use the invention and do not limit the scope of the invention The present invention provides a system and method for providing connectivity between two different networks using different protocols. The present invention can be easily installed on one or more off-the-shelf computers or servers. Moreover, the present invention can create, accept and track messages in the more commonly used protocols. Such as the Internet Protocol ( IP), and translate them into proprietary or legacy protocols in real or near-real time. In addition, the Internet Protocol Signal Transfer Points ( IP-STP) provided by the present invention allows IP connectivity to SS7 net works in a secure mode and allows programming of specific applications. As a result, the present invention provides an efficient and inexpensive gateway to process messages between two different networks using different protocols Referring to FIG. 1, a block diagram of a network 100 in accordance with one embodiment of the present inven tion is shown. The network 100 includes one or more clients 102 communicably coupled to a server/router 104. The server/router 104 is communicably coupled to a Signaling System 7 (SS7) network 108 via SS7 server 106, one or more legacy networks 112 via legacy servers 110, and one or more financial networks 116 via bank server 114. One or more financial institutions 118 may also be communicably coupled to the server/router 104. The clients 102 are comput ers or other devices that Submit database queries for process ing via the server/router 104. The functions of the server/ router 104 can be split on separate computers or processing devices. The servers 106, 110 and 114 function as gateways between the network where the server/router 104 is resident and the networks 108, 112 and 116 where the databases are resident One or more databases, data storage devices, com puters or information sources responsive to database queries submitted by the clients 102 and financial institution 118 are resident within networks 108, 112 and 116. The database queries can be of any type known to those skilled in the art. For example, the database queries may be part of a call vali dation process, a call billing process, a bank card validation process, or a bank card settlement process. The devices ,106, 110, 114 and 118 can be communicably coupled via a local network, a wide area network, such as the Internet, satellite links, dedicated communication links, dial-up modems, or any other method of establishing a communica tion link between two devices. Communications between the various devices 102, 104,106, 110, 114 and 118 can be sent in the clear or encrypted Referring now to FIG. 2, the use of the present invention as a gateway 200 and 206 between various networks 202, 204 and 208 is shown. Gateway 200 provides connec tivity between a first network 202 (SS7 signaling network) and a second network 204 (Internet network). Likewise, gate way 206 provides connectivity between the second network 204 (Internet network) and a third network 208 (Customer Equipment). Note that the first, second and third networks can be of any type and are not limited to the examples shown in FIG. 2. Gateways 200 and 206 are IP-STP that provide con nectivity between an Internet network 204 and another net work 204 or 208. The STP is a telecommunication switch or router that processes signaling messages, such as SS7, and routes traffic through the signaling network. Traditional Sup pliers of prior art STP equipment are Tekelec, Alcatel and Nortel Unlike prior art STP equipment, gateway 200 and 206 of the present invention can be implemented using an off-the-shelf computer with the software described herein. The computer or server 200 and 206 will have a first network interface communicably coupling the computer 200 and 206 to the first network 202 or 208. Similarly, the computer or server 200 and 206 will have a second network interface communicably coupling the computer 200 and 206 to the second network 204. For example, gateway 200 and 206 can be a Pentium.RTM. 4 or higher class server with at least 1 GHZ processing speed and at least a 20 GB hard drive, such as those supplied by Dell, Gateway or Hewlett-Packard. Gate way 200 and 206 also include a digital signal processing ( DSP) board with SS7 communication capability as the interface to the SS7 network 204, such as those supplied by Natural Microsystems or Dialogic. Standard SS7-IP encod ing Software, also referred to as SigTran Software, which is available from Trillium or Convergent Software, Inc., is also installed on gateways 200 and 206. The remaining software is provided by Revenue Communications and is described herein. The DSP board, SigTran software and Revenue Com munications Software provide the processing described below in reference with FIGS 3A and 3B. (0023 Now referring to FIGS. 3A and 3B, flowcharts depicting the method of providing connectivity between a first network 202 or 208 (FIG. 2) and a second network 204 (FIG. 2) in accordance with the present invention are shown. Specifically, FIG. 3A depicts the translation or conversion of a message from the first network to the second network. A message in a first protocol 300 is received from the first network in block 302. The message 300 is processed using one or more digital signal processors in block 304 and a destination in the second network for the processed message is determined in block 306. The processed message is logged in block 308 and translated into the second protocol in block 310. Thereafter the translated message is sent to the destina tion in the second network in block 312. The translated mes sage is a message in the second protocol 314. The first pro tocol can be a signaling protocol. Such as SS7, or other
10 US 2010/ A1 Feb. 25, 2010 network protocol. Such as for legacy system. The second protocol can be an Internet protocol, such as TCP/IP Similarly, FIG.3B depicts the translation or conver sion of a message from the second network to the first net work. A message in the second protocol 350 is received from the second network in block 352. The message 350 is then translated into the first protocol in block 354 and a destination in the first network is determined in block 356. Thereafter, the translated message is logged in block 358 and processed using one or more digital signal processors in block 360. The processed message is then sent to the destination in the first network in block362. The processed message is a message in the first protocol 364. The first protocol can be a signaling protocol, such as SS7, or other network protocol, such as for a legacy system. The second protocol can be an Internet protocol, such as TCP/IP The messages described above can be requests or responses to a previous message or database queries. In addi tion, the process described above may also include the steps of validating the message, sending a time out response to the originator of the message whenevera response to the message has not been received within a specified time period, storing an address identifier for the originator of the message, storing a query identifier for the message, or decrypting or encrypting the message. The process can be part of a call validation process, call billing process, or bank card validation/settle ment process. As previously mentioned, these methods can be implemented as a computer program embodied on a com puter readable medium or as a combination of software and hardware Now referring to FIGS. 4A and 4B, block diagrams of various implementations of the present invention are shown. FIG. 4A shows an implementation of the present invention wherein the functionality of the client 102 (FIG.1), server/router 104 (FIG. 1) and server 106, 110 or 114 (FIG. 1) are combined on a single device 400. The device 400, which may be a computer, includes a client module 402, a server module 404, a routing module 406 and one or more network interface modules The client module 402 is a user application interface that allows the user to easily and seamlessly create a database query without having special knowledge of the system, net work or database that will process the database query. The client module 402 can be run in a demand mode where the user decides when to send a database query or in an automatic mode where a database query is automatically created and sent in response to one or more events. The client module 402 will also present the results of the database query in an easy to understand format The server module 404 is capable of dealing with many instances of the client module 402 wherever they reside. The server module 404 validates the client module 402 before any database queries are forwarded to the routing module 406. In addition, the server module 404 is responsible for receiving database queries from the client module 402 and sending responses to those queries to the appropriate client module The routing module 406 selects the network inter face 408 and the database to send the database query to and then sends the database query to the selected network inter face 408. When the routing module 406 receives a response to a database query, it determines which of the client modules 402 sent the database query and then sends the response to that client module The network interface module 408 translates the database query from a first protocol to a second protocol. The first protocol is used by the network where the database query originated and the second protocol is used by the network where the database resides. For example, the first protocol could be an IP or Internet capable protocol. Likewise, the second protocol could be a signaling protocol. Such as SS7, or a proprietary protocol used by the database owner. The net work interface module 408 then sends the translated database query to the selected database for processing. Thereafter, the network interface module 408 receives a response from the selected database and translates it from the second protocol to the first protocol. The translated response is then sent to the routing module FIG. 4B shows an implementation of the present invention wherein the functionality of the client 102 (FIG.1), server/router 104 (FIG. 1) and server 106, 110 or 114 (FIG. 1) are separated and placed on multiple devices 412, 414, 416 and 418. The client 412, which may be a computer, includes the client module. The server 414, which may be a computer, includes the server module. The router 416, which may be a computer, includes the routing module. The network server 418, which may be a computer, includes one or more of the network interface modules. The contrast between FIGS. 4A and 4B demonstrates the versatility of the present invention Referring now to FIGS. 4B and 5, a flowchart of an IP to SS7 translation method in accordance with one embodi ment of the present invention is shown in FIG. 5. The process starts in block 500. The client 412 connects to the server 414 in block 502 and the server 414 validates the client 412 in block 504. If the client 412 is successfully validated, an IP Query (a database query in an IP format the first protocol) is sent from the client 12 to the server 414 in block 506. The IP Query is then sent from the server 414 to the router 416 in block 508 where the router 416 determines the destination SS7 database and the SS7 network server 418 to which the IP Query should be sent in block 510. The IP Ouery is sent from the router 416 to the SS7 network server 418 in block 512 where the SS7 network server 418 translates the IP Ouery into a SS7 Query (a database query in a SS7 format the second protocol) in block 514. The SS7 Query is sent to the destina tion SS7 database for processing in block The destination SS7 database processes the SS7 Query and creates a SS7 Response in block518. Those skilled in the art will recognize that the actual processing of the SS7 Query may be accomplished with a database interface appli cation or other type of management software to control and handle queries to the database. The SS7 Response is then sent from the SS7 destination database to the SS7 network server 418 in block 520 where the SS7 network server 418 translates the SS7 Response (a database response in a SS7 format the second protocol) into an IP Response (a database response in an IP format the first protocol) in block 422. The IP Response is sent from the SS7 network server 418 to the router 416 in block 524 where the router 416 determines the client destination for the IP Response in block 526. The IP Response is then sent from the router 416 to the server 414 in block 528 and then from the server 414 to the client 412 in block 530. The client 412 can then either disconnect from the server 414 in block 532 or repeat the process previously described for new database queries. Once disconnected, the process ends in block 534. Those skilled in the art will rec ognize that the process described in FIG. 5 is not limited to the use of the IP and SS7 protocols.
11 US 2010/ A1 Feb. 25, ) Now referring to FIGS. 6A, 6B and 6C, schematic diagrams of a more detailed generic translation method in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention are shown. The process starts in block 600. The user logs into the client module in block 602 and the client module connects to the server module in block 604. The server module validates the user and/or client module in block 606. If the validation is not successful, as determined in decision block 608, the server module denies access to the user and/or client module in block 610 and the process loops back to allow the user and/or client module to try again in block 602 or ) If, however, the validation is successful, as deter mined in decision block 608, the user submits a query, which is formatted in a first protocol, to the server module via the client module in block 612. The query is then sent from the server module to the router module in block 614 where the router module determines the destination database and net work interface module in block 616. If the destination address (database) and network interface module are found, as deter mined in decision block 618, an error message is returned to the client module via the server module in block 620 and the process loops back to allow the user to Submit another query in block ) If, however, the destination address (database) and network interface module are found, as determined in deci sion block 618, the server module sends the query to the router module in block 622 and the server module sets a timer for the query in block 624. The server module also stores the client module address and query identification information in block 626 so that the response to the query can be sent to the correct client module. The query is then sent from the router module to the network interface module for the destination address (destination network server and database) in block 628. The network interface module translates the query into a network query (a database query formatted in the second protocol) in block 630. The network interface module then logs the network query in block 632 and sends the network query to the destination address (database) for processing in block The destination database processes the network query and creates a network response in block 636. Those skilled in the art will recognize that the actual processing of the network query may be accomplished with a database interface application or other type of management Software to control and handle queries to the database. The network response is then sent from the destination address (database) to the network interface module in block 638 where the net work interface module correlates the network response with the corresponding network query in block 640. The network interface module translates the network response (a database response in the second protocol format) into a client response (a database response in the first protocol format) in block 642. The client response is sent from the network interface module to the router module in block 644 where the router module correlates the client response with the query (determines the proper client module) in block 646. The client response is then sent from the router module to the server module in block 648 and then from the server module to the client module in block 650. The query timer is also turned offin block 650. If there are no other queries, as determined by decision block 652, the user logs out of the client module in block 654 and the process ends in block 656. If, however, there is another query, as determined in decision block 652, the process loops back to receive another query from the user in block After the query has been sent by the server module in block 622, the query timer monitors where a response to the query has been received. If the timer has not expired, as determined in decision block 662, the query timer continues to wait for a response. If, however, the timer has expired, as determined in decision block 662, the server module sends a time out response to the client module in block 664. As previously described, the client module, server module, router module and network interface module can be separated or combined in any configuration that fits the application of the present invention If encrypted messages are required, the steps of sending the translated database query to the selected database for processing and receiving a response to the database query from the selected database will be performed using the fol lowing steps. The translated database query is first encrypted. Thereafter, the encrypted database query is sent to the selected database for processing. With respect to the responses, the encrypted response to the encrypted database query is received from the selected database. Thereafter, the encrypted response is decrypted into a response. Any type of standard encryption/decryption method can be used. For example, the present invention can be used to find out infor mation about a specific telephone number. In such a case, the user uses the client module to create and Submit a query using the telephone number to the server module. The router then selects the proper database, which is usually a line informa tion database ( LIDB) located on an ILEC's signaling net work, to process the query. The response from the database can then be used to process a call related to the telephone number. Similarly, the user can Submit a calling card number, credit card number or bank card number The embodiments and examples set forth herein are presented to best explain the present invention and its practi cal application and to thereby enable those skilled in the art to make and utilize the invention. However, those skilled in the art will recognize that the foregoing description and examples have been presented for the purpose of illustration and example only. The description as set forth is not intended to be exhaustive or to limit the invention to the precise form dis closed. Many modifications and variations are possible in light of the above teaching without departing from the spirit and scope of the following claims. What is claimed is: 1. A method of providing message connectivity between a first network using a first protocol and a second network using a second protocol, the method comprising the steps of receiving a message from either the first network or the second network, the message related to information about a telephone number, the message sent using the telephone number; whenever the message is received from the first network, processing the message using one or more digital signal processors, translating the processed message into the second protocol and sending the translated message to a destination in the second network; and whenever the message is received from the second net work, translating the message into the first protocol, processing the translated message by a line information database using one or more digital signal processors, and sending the processed message to a destination in the first network, the processed message used to process a call related to the telephone number.
12 US 2010/ A1 Feb. 25, The method as recited in claim 1, further comprising at least one of the steps of: determining a destination in the second network for the processed message; logging the processed message; determining a destination in the first network for the trans lated message; and logging the translated message. 3. The method as recited in claim 1, further comprising the step of validating the message. 4. The method as recited in claim 1, wherein the message is at least one of a request, and a response to a previous mes Sage. 5. The method as recited in claim 1, further comprising the step of sending a time out response to the originator of the message whenever a response to the message has not been received within a specified time period. 6. The method as recited in claim 1, further comprising the step of storing an address identifier for the originator of the message. 7. The method as recited in claim 1, further comprising the step of storing a query identifier for the message. 8. The method as recited in claim 1, further comprising the step of decrypting the message. 9. The method as recited in claim 1, further comprising the step of encrypting the processed message. 10. The method as recited in claim 1, wherein the first protocol is a signaling protocol. 11. The method as recited in claim 10, wherein the signal ing protocol is a Signaling System 7 protocol. 12. The method as recited in claim 1, wherein the second protocol is an Internet protocol. 13. The method as recited in claim 12, wherein the signal ing protocol is a TCP/IP protocol. 14. The method as recited in claim 1, wherein the message is at least one of a database query; part of a call validation process; part of a call billing process; part of a bank card validation process; and part of a bank card settlement process. 15. A computer program embodied on a computer readable medium for providing message connectivity between a first network using a first protocol and a second network using a second protocol, the computer program comprising: a code segment for receiving a message from either the first network or the second network, the message related to information about a telephone number, the message sent using the telephone number; a code segment for whenever the message is received from the first network, processing the message using one or more digital signal processors, translating the processed message into the second protocol and sending the trans lated message to a destination in the second network; and a code segment for whenever the message is received from the second network, translating the message into the first protocol, processing the translated message by a line information database using one or more digital signal processors and sending the processed message to a des tination in the first network, the processed message used to process a call related to the telephone number. 16. A system for providing message connectivity between a first network using a first protocol and a second network using a second protocol, the system comprising: a computer; a first network interface communicably coupling the com puter to the first network; a second network interface communicably coupling the computer to the second net work; and a computer program resident on the computer comprising: a code segment for whenever the message is received at the first network interface, processing the message using one or more digital signal processors, translat ing the processed message into the second protocol and sending the translated message to a destination in the second network via the second network interface, and a code segment for whenever the message is received at the second network interface, translating the message into the first protocol, processing the translated mes sage by a line information database using one or more digital signal processors and sending the processed message to a destination in the first network via the first network interface, the processed message used to process a call related to a telephone number. 17. A method of providing connectivity between a first network using a first protocol and a second network using a second protocol, comprising: receiving a message from either the first network or the second network, the message related to information about a telephone number, the message sent using the telephone number; whenever the message is received from the first network, translating the processed message into the second pro tocol and sending the translated message to a destination in the second network; and whenever the message is received from the second net work, translating the message into the first protocol, processing the translated message by a line information database and sending the translated message to a desti nation in the first network. 18. A computer program embodied on a computer readable medium for providing connectivity between a first network using a first protocol and a second network using a second protocol, comprising: a code segment for receiving a message from either the first network or the second network, the message related to information about a telephone number, the message sent using the telephone number, a code segment for whenever the message is received from the first network, translating the processed message into the second protocol and sending the translated message to a destination in the second network; and a code segment for whenever the message is received from the second network, translating the message into the first protocol, processing the translated message by a line information database and sending the translated mes Sage to a destination in the first network, the translated message used to process a call related to the telephone number. 19. A system for providing connectivity between a first network using a first protocol and a second network using a second protocol, the system comprising:
13 US 2010/ A1 Feb. 25, computer; a first network interface communicably coupling the computer to the first network; a second network interface communicably coupling the computer to the second network; and a computer program resident on the computer comprising a code segment for: receiving a message from either the first network or the second network, the message related to information about a telephone number, the message sent using the telephone number; whenever the message is received from the first network, translating the processed message into the second pro tocol and sending the translated message to a destination in the second network; and whenever the message is received from the second net work, translating the message into the first protocol, processing the translated message by a line information database and sending the translated message to a desti nation in the first network, the translated message used to process a call related to the telephone number. ck
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120047545A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047545 A1 SELLERS et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 23, 2012 (54) TOPOGRAPHIC FRAUD DETECTION (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
US 2008.0020738A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0020738A1 H0 et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) MOBILE DEVICE SERVICE (22) Filed: Jul. 19, 2006 AUTHORIZATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120033670A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0033670 A1 Olakangil (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2012 (54) EGRESS PROCESSING OF INGRESS VLAN (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120033670A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0033670 A1 Olakangil (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2012 (54) EGRESS PROCESSING OF INGRESS VLAN (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(19) United States US 20070073878A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0073878A1 Issa (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 29, 2007 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR LOWERING (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/225
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(19) United States US 200601 01189A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0101189 A1 Chandrasekaran et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR HOT (52) U.S. Cl.... 711 f6 CLONING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010
 US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
US 20100057686A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0057686 A1 Breiner et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 4, 2010 - (54) DEEP WEB SEARCH Publication Classification (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(19) United States US 2003OO64711A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0064711 A1 Gilbert et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2003 (54) TELEPHONY CALL CONTROL USINGA PERSONAL DIGITAL
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) United States Patent Ramaswamy USOO6480717B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) TUNNELING OF NON-GSM SIGNALNG MESSAGES IN A GSM BASED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(19) United States US 2004O246971A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0246971 A1 Banerjee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) APPARATUS FOR ENABLING MULTI-TUPLE TCP SOCKETS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0192794A1 Ertemalp et al. US 2005O192794A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0192794A1 Ertemalp et al. US 2005O192794A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,933,486 Norby et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999
 USOO5933486A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Norby et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999 54) ENHANCED SERVICE CONTROL 5,390,242 2/1995 Bales et al.... 379/221 ARCHITECTURE OFA 5,539,884 7/1996
USOO5933486A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Norby et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999 54) ENHANCED SERVICE CONTROL 5,390,242 2/1995 Bales et al.... 379/221 ARCHITECTURE OFA 5,539,884 7/1996
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(19) United States US 2005O102233A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0102233 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ASSOCIATING MOBILE PHONE TO (52) U.S. Cl.... 705/44 VENDING MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(19) United States US 20110239111A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0239111A1 GROVER (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2011 (54) SPELL CHECKER INTERFACE (52) U.S. Cl.... 715/257; 715/764;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 2005O153733A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0153733 A1 Park et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 14, 2005 (54) CALL CONTROL METHOD FOR Publication Classification
Printer. Data input/ Printout unit. processor) Control unit. (Raster image RIP. Display unit. Image
 (19) United States US 20070057978A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0057978A1 Hagiwara (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2007 (54) PRINTER AND PRINTING METHOD (75) Inventor: Takahiro
(19) United States US 20070057978A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0057978A1 Hagiwara (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 15, 2007 (54) PRINTER AND PRINTING METHOD (75) Inventor: Takahiro
W15. Keung Wong, Hong Kong (HK) (21) Appl. No.: 09/875,350. (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong, Hong Kong (HK); Hoi (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
US 20020184150A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0184150 A1 Wong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) MOBILE BANKING SYSTEM (76) Inventors: Kam Fu Wong,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0162029 A1 Allen et al. US 2002O162029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 31, 2002 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0162029 A1 Allen et al. US 2002O162029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 31, 2002 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1
 USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
USOO6199058B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,199,058 B1 Wong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 6, 2001 (54) REPORT SERVER CACHING 5,168,444 12/1992 Cukor et al.... 705/1 5,625,818 4/1997
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,385,897 B1
 US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
US0083.85897 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Yadav-Ranjan (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2013 (54) GLOBAL TEXT MESSAGING SYSTEMAND (56) References Cited METHOD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004.00399.96A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0039996 A1 Flam (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2004 (54) BIDIRECTIONAL NETWORK LANGUAGE SUPPORT (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2004.00399.96A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0039996 A1 Flam (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 26, 2004 (54) BIDIRECTIONAL NETWORK LANGUAGE SUPPORT (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
$26) 6, 2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun.
 (19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, (54) E-CARD Publication Classification
 (19) United States US 2011 0010283A1 () Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010283 A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) E-CARD Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Eddie
(19) United States US 2011 0010283A1 () Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010283 A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) E-CARD Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Eddie
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(19) United States US 2017009 1001A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0091001 A1 PANDEY et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MANAGING (52) U.S. Cl. AND LINKING SOFTWARE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(19) United States US 20080244164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0244164 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2008 (54) STORAGE DEVICE EQUIPPED WITH NAND FLASH MEMORY AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O2.19234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0219234 A1 Forbes (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2010 (54) MOBILE TICKET AUTHENTICATION Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2010O2.19234A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0219234 A1 Forbes (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 2, 2010 (54) MOBILE TICKET AUTHENTICATION Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0222841 A1 Mirajkar et al. US 20090222841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 3, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) ACCELERATION OF RECEIVE DATA
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0222841 A1 Mirajkar et al. US 20090222841A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 3, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) ACCELERATION OF RECEIVE DATA
US 7.663,338 B2. Feb. 16, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Guthrie et al. used to receive a USB bus voltage from the USB interface and (51)
 USOO7663338B2 (12) United States Patent Guthrie et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.663,338 B2 Feb. 16, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND APPARATUS
USOO7663338B2 (12) United States Patent Guthrie et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.663,338 B2 Feb. 16, 2010 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD AND APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004OO32936A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0032936A1 Horel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 2004 (54) TRANSACTION PROCESSING (76) Inventors: Gerald Horel,
(19) United States US 2004OO32936A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0032936A1 Horel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 19, 2004 (54) TRANSACTION PROCESSING (76) Inventors: Gerald Horel,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/012 1932 A1 Joshi et al. US 201001 21932A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) DISTRIBUTED HEALTH CHECK FOR GLOBAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/012 1932 A1 Joshi et al. US 201001 21932A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) DISTRIBUTED HEALTH CHECK FOR GLOBAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,418,453 B1
 USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
USOO6418453B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Kraft et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 2002 (54) NETWORK REPOSITORY SERVICE FOR 6.295,529 B1 * 9/2001 Corston-Oliver et al.... 707/3 EFFICIENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
US 2016O156189A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0156189 A1 Ci (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2016 (54) CLOUD BASED ENERGY SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. H02J 3/32 (2013.01);
FL (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
l ll l l l l l US 20060040710A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0040710 A1 Ruetschi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF PROVIDING Publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020040308A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0040308A1 Hasegawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2002 (54) METHOD OF VALIDATING ENTRANCE TO (30) Foreign
(19) United States US 20020040308A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0040308A1 Hasegawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2002 (54) METHOD OF VALIDATING ENTRANCE TO (30) Foreign
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004.0156360A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0156360A1 Sexton et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 12, 2004 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PRIORITIZING DATA TRANSFERRED
(19) United States US 2004.0156360A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0156360A1 Sexton et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 12, 2004 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR PRIORITIZING DATA TRANSFERRED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060200516A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0200516 A1 Flaherty et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) DATA PROCESSING SYSTEMAND METHOD (30) Foreign
US 20060200516A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0200516 A1 Flaherty et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) DATA PROCESSING SYSTEMAND METHOD (30) Foreign
- NETWORK / SES A REMOTE
 (19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(19) United States US 2013 0179140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/017914.0 A1 Sharma (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FORVALIDATING (52) U.S. Cl. ANELECTRICAL NETWORK
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(19) United States US 20170041819A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0041819 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 9, 2017 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD OF HANDLING (52) U.S. Cl. WIRELESS LOCAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20120194446A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194446 A1 LIN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) ELECTRONIC DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152762 A1 Asano et al. US 2006O152762A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) IMAGE FORMING APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152762 A1 Asano et al. US 2006O152762A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) IMAGE FORMING APPARATUS
(73) Assignee: Nokia Networks Oy (FI) Wii: 12: 'We (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this * cited by examiner
 USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
USOO6246871B1 12) United States Patent 10) Patent No.: US 6,246,871 B1 9 9 Ala-Laurila (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 12, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR 5,941,946 8/1999 Baldwin et al.. PROVIDING ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. ? 200
 (19) United States US 20070288373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0288373 A1 Wilkes (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) TRANSACTION ALERT MESSAGES ASSOCATED WITH FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS
(19) United States US 20070288373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0288373 A1 Wilkes (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2007 (54) TRANSACTION ALERT MESSAGES ASSOCATED WITH FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 201600.48535A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0048535 A1 Shaw (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) INFORMATION SEARCHING METHOD (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant:
US 201600.48535A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0048535 A1 Shaw (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) INFORMATION SEARCHING METHOD (57) ABSTRACT (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. LOW et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 15, 2010
 US 20100178904A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0178904 A1 LOW et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 15, 2010 (54) MESSAGING SERVICE SUBSCRIPTION (30) Foreign Application
US 20100178904A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0178904 A1 LOW et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 15, 2010 (54) MESSAGING SERVICE SUBSCRIPTION (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,711,172 B1
 USOO6711 172B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,711,172 B1 Li (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 23, 2004 (54) NETWORK PACKET ROUTING 6,275,492 B1 * 8/2001 Zhang... 370/392 6,331,983 B1 * 12/2001
USOO6711 172B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,711,172 B1 Li (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 23, 2004 (54) NETWORK PACKET ROUTING 6,275,492 B1 * 8/2001 Zhang... 370/392 6,331,983 B1 * 12/2001
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000
 USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
USOO6125.108A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,125,108 Shafer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2000 54 METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ENHANCED 57 ABSTRACT CLIENT DENTIFICATION - A method and System
Selecting init r. Associating. Authenticating Unit Master Key. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1.
 (19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(19) United States US 20070153732A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0153732 A1 Yao (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 5, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR AWIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORK TERMINAL TO ACCESS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20020077080A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0077080A1 Greene (43) Pub. Date: (54) INSTANT MESSAGE USER LOCATION TRACKING SYSTEM (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,158,627 B1
 US007 158627 B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Lu (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR INHIBITING (56) References Cited SOFTSWITCH OVERLOAD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
US007 158627 B1 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Lu (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR INHIBITING (56) References Cited SOFTSWITCH OVERLOAD U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(19) United States US 2016037 1322A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0371322 A1 GUNTI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 22, 2016 (54) EFFICIENT MANAGEMENT OF LARGE (52) U.S. Cl. NUMBER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(19) United States US 20140282538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0282538A1 ConoVer et al. ( 43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) MINIMIZING SCSI
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
Xying. GoD-12 ACL 1-1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. (19) United States SUPPLIER POLICY DRIVER/-108 PLATFORM
 (19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(19) United States US 20090172797A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0172797 A1 Yao et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 2, 2009 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR SECURING APPLICATION PROGRAMINTERFACES
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7941.543B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941.543 B2 Moussallam et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MIGRATING 2002/0169781 A1* 11/2002 Poole et al....
USOO7941.543B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,941.543 B2 Moussallam et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR MIGRATING 2002/0169781 A1* 11/2002 Poole et al....
1a " " " ), Gigi Nii
 USOO8295862B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,295,862 B2 Suresh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM TO ENABLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 455/466 COMMUNICATION THROUGHSMS (58)
USOO8295862B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,295,862 B2 Suresh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM TO ENABLE (52) U.S. Cl.... 455/466 COMMUNICATION THROUGHSMS (58)
10-N 12. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0005459 A1 Pacey US 2013 0005459A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) (60) SOURCING OF ELECTRONICWAGERING GAMES
/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].
![/ client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. / client computer. \ single sign-on. application program server (AP) network. server (SS0) (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a].](/thumbs/90/103929709.jpg) US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
US007278155B2 (12) United States Patent Hsieh et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,278,155 B2 Oct. 2, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 22,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(19) United States US 20070022158A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0022158A1 Vasa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 25, 2007 (54) MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (52) U.S. Cl.... 709/204
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8, B2. Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013
 US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
US008554.937B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,554.937 B2 Cha et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2013 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR 6,259,701 B1* 7/2001 Shur et al.... 370/401 6,836,806 B1*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 200701 15488A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0115488 A1 Engelman et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 24, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMIS FOR MULTIPLE Publication
US 200701 15488A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0115488 A1 Engelman et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 24, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMIS FOR MULTIPLE Publication
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,377,725 B1
 USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
USOO6377725B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Stevens et al. 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 23, 2002 9 (54) OPTICAL WAVELENGTH DIVISION 5,907,551 A * 5/1999 Nishio et al. MULTIPLEXED INTERCONNECT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100091772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/009 1772 A1 CederVallet al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2010 (54) PROVIDING IPTV MULTICASTS (76) Inventors: Mats
(19) United States US 20100091772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/009 1772 A1 CederVallet al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2010 (54) PROVIDING IPTV MULTICASTS (76) Inventors: Mats
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1
 USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
USOO6467088B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,467,088 B1 alsafadi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2002 (54) RECONFIGURATION MANAGER FOR WO WO9015394 6/1990... GO6F/15/46 CONTROLLING
isits ar. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1 (19) United States y(n) second sub-filter feedback equalizer
 (19) United States US 20100027610A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0027610 A1 CHANG (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2010 (54) EQUALIZER AND EQUALIZATION METHOD (75) Inventor: Chiao-Chih
(19) United States US 20100027610A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0027610 A1 CHANG (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2010 (54) EQUALIZER AND EQUALIZATION METHOD (75) Inventor: Chiao-Chih
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 US 20090287845A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287845 A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) MEDIATOR WITH INTERLEAVED STATIC AND
US 20090287845A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287845 A1 Joshi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) MEDIATOR WITH INTERLEAVED STATIC AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147372A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR IMPLEMENTING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data MULTICAST
(19) United States US 20070147372A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) METHOD FOR IMPLEMENTING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data MULTICAST
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 HUI (43) Pub. Date: Mar.
 US 20150067353A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0067353 A1 HUI (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2015 (54) STORAGE MANAGEMENT DEVICE AND (52) US. Cl. STORAGE MANAGEMENT
US 20150067353A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0067353 A1 HUI (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2015 (54) STORAGE MANAGEMENT DEVICE AND (52) US. Cl. STORAGE MANAGEMENT
SCSI routing table (90) and a SCSI to Fibre Channel routing table (92). The system receives a cross bus transfer of data
 US00604.1381A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,041,381 Hoese (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2000 54 FIBRE CHANNEL TO SCSI ADDRESSING OTHER PUBLICATIONS METHOD AND SYSTEM Hoese, Geoffrey B.,
US00604.1381A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,041,381 Hoese (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 2000 54 FIBRE CHANNEL TO SCSI ADDRESSING OTHER PUBLICATIONS METHOD AND SYSTEM Hoese, Geoffrey B.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060O881 67A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0088167 A1 Bade et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR BACKUP AND RESTORE OF A CONTEXT
(19) United States US 20060O881 67A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0088167 A1 Bade et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR BACKUP AND RESTORE OF A CONTEXT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120162831A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0162831 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR (22) Filed: Dec. 26,
US 20120162831A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0162831 A1 Wang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) ESD PROTECTION CIRCUIT FOR (22) Filed: Dec. 26,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
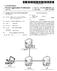 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,002,560 B2
 USOO700256OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,002,560 B2 Graham (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 21, 2006 (54) METHOD OF COMBINING DATA ENTRY OF 6,049,329 A * 4/2000 Zetts et al.... 345/179 HANDWRITTEN
USOO700256OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,002,560 B2 Graham (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 21, 2006 (54) METHOD OF COMBINING DATA ENTRY OF 6,049,329 A * 4/2000 Zetts et al.... 345/179 HANDWRITTEN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 (57) USPC /412. Initiate wireless Connection. Discover.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0378058 A1 Decuir et al. US 20140378058A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (51) (52) WIRELESS COMMUNICATION METHODS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O190769A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0190769 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SECURING REMOTEACCESS TO AREMOTE SYSTEM (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2005O190769A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0190769 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR SECURING REMOTEACCESS TO AREMOTE SYSTEM (76) Inventor:
