Efficient Secured Model For Communication In Dynamic Multicast Groups
|
|
|
- Derick Jackson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): , ISSN (p): Vol. 05, Issue 06 (June. 2015), V1 PP Efficient Secured Model For Communication In Dynamic Multicast Groups Prof. Shilpa Harnale Asst. Professor, Dept. of CSE BKIT, Bhalki Abstract: Many network applications are based on a group communications model where one party sends messages to a large number of authorized recipients and/or receives messages from multiple senders. In this paper we propose a series of novel approaches for achieving scalable security in IP multicast, providing privacy and authentication on a group-wide basis. They can be employed to efficiently secure multi-party applications where members of highly dynamic groups of arbitrary size may participate. The main idea is to have group members actively participate to the security of the multicast group, therefore reducing the communication and computation load on the source. Since the group security is distributed among the group members, A communication model is proposed for dynamic multicast groups which is secure and authenticated. In this scheme a group is established and the text messages are transmitted between the users of the group. I. INTRODUCTION IP multicast is used to distribute data to a group of receivers efficiently. A Datagram addressed to the multicast group, identified by a Class D IP address, will be delivered to all group members. Efficiency can be achieved because datagram s need to be transmitted once and they traverse any link between two nodes only once, saving the cost of sender as well as network Bandwidth. The main problem in secure multicast is access control for making sure that only legitimate members of multicast group have access to the group Communication. The security algorithms applicable to unicasting (one to one) environment cannot be applied in multicast groups. The commonly used technique in secure multicast is to maintain a group key that is known to all users in the multicast group, but is unknown to others outside the group. Each time a member either joins or leaves the group, the group key has to be refreshed. The members of the group should be able to compute the new group key efficiently, guaranteeing forward and backward secrecy simultaneously. In a dynamic secure multicast, the group key need to be refreshed very frequently. Once a communication group is formed, the members in a group can send/receive messages from other members of same/different groups. II. RELATED WORK Existing protocols for secure multicasting are limited to distribute session keys in static and/or small groups. For dealing with the group key distribution in a large group with frequent membership changes, some good explorations have been done: Spanning Tree [BD96] proposes the distribution of the key along a spanning tree generated between the members. It relies on trust in all members to forward the data without modification and does not handle group membership changes securely and efficiently. Cliques The approach proposed in [STW97] is to improve the capability of a system to distribute session keys in dynamic groups, but the solution does not scale well to large groups, since the group manager has to perform O(n) exponentiations for each group membership change and messages get prohibitively large. Iolus In Iolus[Mit97], a large group is decomposed into a number of subgroups, thus reducing the number of members affected by a key change due to membership changes. It relies on relay nodes performing admission control and packet rekeying. This not only requires full trust into these relays, but also increases the transmission delay, and does not handle relay failures gracefully. Multicast Trees Very recently we came across two schemes for multicast key distribution that are remarkably similar to our own tree-based approach. One is by D. Wallner, E. Harder, and R. Agee, from the National 55 P a g e
2 Security Agency, currently only available as an expired Internet draft. The other scheme, by C. Wong, M. Gouda, and S. Lam, from the University of Texas, is scheduled to appear in SIGCOMM 98. III. SECURE MULTICASTING In the solutions presented here, changes to the group s membership are possible with minimal involvement of dedicated nodes and group members, limiting number and size of messages and computing resources needed. The approaches cope with several properties inherent to multicast and broadcast environments: An unreliable (and in the case of IP also unordered) transmission channel and the transmissions may be one-way, with no or only a minimal return channel, to reflect the nature of broadcast environments likely users of secure multicasting. While third party entities such as routers or intermediate systems are entrusted with forwarding secured data, they are not allowed to gain access to actual keying material or plaintext payload. As seen earlier, it is important to have a system which even with large groups and frequent joins or leaves neither is susceptible to implosion nor enables users to understand what was transmitted at times they were not part of the group, either before they joined or after they left or were expulsed. Additionally, any third party recording ongoing transmission and later capturing the secrets held by a participant must not be able to understand its recordings. This is known as perfect forward secrecy [Dif90]. To completely achieve this, the unicast connections also need to be set up using ephemeral secrets. Figure 1: Secure multicasting components in a single sender, multiple recipients scenario The basic architecture as shown in the figure the simplest scenario, forming the basis of the descriptions: A single sender and any number of participants (multiple sender and other scenarios will be explained below). Fundamental and common functions are explained here, while individual extensions and modifications will be pursued later. Generally, the components can be separated into two groups: (1) A group of data related components, covering components very similar to those of current insecure multicast or broadcast communication architecture. It consists of the sender, recipients, and one or more Data Multicast Groups. (2) A group of control (or key management) related components, which includes all components involved in the key agreement and key exchange process. 56 P a g e
3 Figure 2: Group collaboration scenario Often, there is more than one sender, and senders and receivers cannot be distinguished. Also, any receiver is free to send data encrypted or authenticated using the current TEK, and in a group collaboration environment every member of the group holds both roles at the same time, resulting in a situation as shown in Figure 2. This is a transformation of Figure 1 where sender and recipient were integrated, and the Group Manager has been isolated. All of the schemes also work in that scenario, and the distributed key management scheme even is very well suited for it. If senders and receivers are treated equally, they will be referred to using the term participant. Should a unique, unmistakable identification of the sender be required, as opposed to the identification as an admitted group member, it is necessary for the sender to asymmetrically authenticate each data packet. For many applications, immediate recognition of outsiders injecting traffic is crucial, but it is acceptable to detect sender impersonation by already admitted group members within a certain pre-defined time limit after the fact has occurred. For these applications, it is possible to have the messages authenticated symmetrically (using a MAC) and amortize the costly asymmetric operation over several packets. To achieve this, the sender retains MAC values of all packets sent. In regular time intervals, it distributes the collected list of MAC values together with a single asymmetric signature over these MACs to the recipients. Thus, the authenticity of all the data packets sent out can be verified by the recipients with a single asymmetric operation, even if they did not get all of the original packets1. This procedure also can be used by the group manager to uniquely authenticate the source of keying material to the group members. IV. PROPOSED ARCHITECTURE A. Basic Operations on the Group To transmit the Traffic Encryption Key (TEK) secretly, a number of Key Encryption Keys (KEKs) are used to encrypt the control traffic containing the TEK. To distinguish the keys, each key consists of a reference tuple containing a unique ID, a version, a revision, and the keying material proper. The key to be used to decrypt a message (or part of it) is always referred to by an (ID, version, revision) tuple. The usage of independent version and revision fields allows zero-message joining and is explained below in the leave and joins descriptions, respectively. The abovementioned components and keys will be involved in different activities: Group Creation The Group Manager is configured with group and access control information. Additionally, the group parameters are published using a directory service. Single Join The new participant s Key Manager sends its request to the Group Manager, which checks whether this participant is allowed to join. If yes, the GroupManager assigns a unique ID to him, and selects a series of KEKs which will be transmitted to the newcomer. The selection of KEKs will be discussed separately for each key management scheme. The Group Manager now increases the revision of all keys (TEK and KEKs) to be 57 P a g e
4 transmitted to the participant by passing the keying material through a one-way function (e.g. a cryptographically secure hash), then sends the keys out to the new participant. It also informs the sender(s) to update their revision and TEK. The other participants will notice the revision change from the key reference tuple in ordinary data packets, and also pass their TEK through the one-way function. Since the function is not reversible, the newcomer has no way to determine the key that was used beforehand. Single Leave There are three ways to leave a group, namely Silent Leave, Voluntary Leave and Forced Leave. Only the third kind is of interest here as the first two do not require any action from the group manager. If the Admission Control feels a need to forcibly exclude a participant, a leave message is to be sent out. Also, participants may ask the Admission Control to exclude a member. It is up to the admission policy how to deal with such requests. To exclude a member, all keys known to it need to be replaced with entirely new keying material. To make all remaining participants aware of this change, the key s version number is increased. The Group Manager sends out a message with new keying material which can be decrypted by all the remaining participants Key Managers, but not the member which just left. Multiple Join, Multiple Leave, Group Merge, Group Split These functions have a number of dependencies on the chosen scheme, and enhance usability of the presented architectures. Due to space constraints, see [CWSP98] for a description. Group Destruction The Group Manager notifies all remaining participants of the destruction, closes all network connections, destroys all keying material and frees all memory. As soon as all parties have thrown away their keying material, perfect forward secrecy covering all traffic against third party opponents is guaranteed. B. Centralized, Tree-Based Key management Tightest control over the individual participants can be achieved by this centralized approach, which is thus suitable for applications with high security demands. It is very easy to implement and maintain, and poses very little load on the network and the receivers. All keying material is managed centrally by the Group Manager, where all joining participants have to register. All keying material is managed centrally by the Group Manager, where all joining participants have to register. To store the keying material, any tree of arbitrary degree2 can be used. The participants are represented by leaves therein. For simplicity of the explanation assume that the tree is a fully balanced, complete binary tree. C. Algorithm The basic idea of our scheme is the usage of an identity tree, where each ode in the tree has an identity. A node in the identity tree is also associated with a key generation key (KGK) which is used for generating a parent key. The root nodes KGK is used as the group key. Each SGC (Sub Group Controller) constructs an identity tree and gives it to the KGCs (Key Generation Centre). Given a nodes Ni user id, KGC generates the keys for the nodes by ECC algorithm. The generated key is then encrypted using KGK of the user through DES algorithm and encrypted key is transmitted to the user. The user decrypts the key using its KGK, which provides security to the key and saves it in its key ring. Whenever a new user joins the group a new node is added to the group tree with user 58 P a g e
5 name as its identity and GC/SGC requests KGC to refresh the group key and also to generate KGK for the new user. Whenever a user requests to leave the group the GC/SGC removes the node corresponding to user from group tree and KGC is request to re-key. Whenever a user wants to send a message to group it generates the message as a text file, it is encrypted using the RSA algorithm and encrypted text file is sent to the SGC/GCI of the subgroup to which it belongs through TCP/IP connection. SGC/GCI of sub tree to which sender belongs establishes a TCP/IP connection with SGC/GCI of sub tree to which receiver belongs and sends the text containing the encrypted message through socket API. The SGC/CGI of receiver establishes a TCP/IP connection with receiver and transmits the text file to it. The encrypted text file is decrypted and is added to the mailbox of user. The user can sign in and view its messages. For a user to sign-in a secret code is generated by GC and provided to the user when it joins the group. V. CONCLUSION The mechanism is secured by using RSA algorithm for message encryption or decryption, authenticated as each message contains the identity of the user. The KGC supports large and dynamic multicast groups. Maintaining the users in form of a tree makes this scheme scalable and efficient. REFERENCES [1] Liming Wang and Chuan Kun Wu, Efficient Key Agreement for Dynamic and Large Multicast Groups, International Journal of Network Security, Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Vol.3, No.1, PP.8 17, July 2006 [2] P.S.L.M. Barreto, H Y Kim and Scott Efficient algorithms for pairingbased cryptosystems in CRYPTO 2002, LNCS [3] D Bonch and M Franklin, Identity-based encryption fron weil pairing, in CRYPTO 2001, LNCS [4] R Canetti, J Garay, G Itkis, K Micciancio, M Naor and B Pinkas, Multicast security: a taxanomy and some efficient constuctions, in INFOCOM [5] R Canetti, S Halevi and J Katz, A forward secure public key encryption scheme, in Eurocrypt 2003, LNCS [6] I Chang, R Engel, D Pendarakis and D Saha, Key management for secure Internet multicast using Boolean function minimization techniques, in INFOCOM P a g e
EFFECTIVE KEY GENERATION FOR MULTIMEDIA AND WEB APPLICATION
 EFFECTIVE KEY GENERATION FOR MULTIMEDIA AND WEB APPLICATION Mr. Sagar Sharad Bhuite Department of Computer Science and Engg, College of Engg. Pandharpur Solapur University, Solapur, India Prof. Yoginath
EFFECTIVE KEY GENERATION FOR MULTIMEDIA AND WEB APPLICATION Mr. Sagar Sharad Bhuite Department of Computer Science and Engg, College of Engg. Pandharpur Solapur University, Solapur, India Prof. Yoginath
The VersaKey Framework: Versatile Group Key Management. Author(s): Waldvogel, Marcel; Caronni, Germano; Sun, Dan; Weiler, Nathalie; Plattner, Bernhard
 Research Collection Working Paper The VersaKey Framework: Versatile Group Key Management Author(s): Waldvogel, Marcel; Caronni, Germano; Sun, Dan; Weiler, Nathalie; Plattner, Bernhard Publication Date:
Research Collection Working Paper The VersaKey Framework: Versatile Group Key Management Author(s): Waldvogel, Marcel; Caronni, Germano; Sun, Dan; Weiler, Nathalie; Plattner, Bernhard Publication Date:
The VersaKey Framework: Versatile Group Key Management
 IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 17, NO. 8, AUGUST 1999 1 The VersaKey Framework: Versatile Group Key Management Marcel Waldvogel, Germano Caronni, Member, IEEE, Dan Sun, Student
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 17, NO. 8, AUGUST 1999 1 The VersaKey Framework: Versatile Group Key Management Marcel Waldvogel, Germano Caronni, Member, IEEE, Dan Sun, Student
Secure Group Key Management Scheme for Multicast Networks
 International Journal of Network Security, Vol.11, No.1, PP.33 38, July 21 33 Secure Group Key Management Scheme for Multicast Networks R. Srinivasan, V. Vaidehi, R. Rajaraman, S. Kanagaraj, R. Chidambaram
International Journal of Network Security, Vol.11, No.1, PP.33 38, July 21 33 Secure Group Key Management Scheme for Multicast Networks R. Srinivasan, V. Vaidehi, R. Rajaraman, S. Kanagaraj, R. Chidambaram
Iolus: A Framework for Scalable Secure Multicasting
 Iolus: A Framework for Scalable Secure Multicasting Vladica Stanisic Multicast Efficient means of distributing data to a group of participants Supports one to many and many to many service Needs to transmit
Iolus: A Framework for Scalable Secure Multicasting Vladica Stanisic Multicast Efficient means of distributing data to a group of participants Supports one to many and many to many service Needs to transmit
Cluster Based Group Key Management in Mobile Ad hoc Networks
 42 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.9 No.4, April 2009 Cluster Based Group Key Management in Mobile Ad hoc Networks Renuka A. and K.C.Shet, Dept. of Computer Science
42 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.9 No.4, April 2009 Cluster Based Group Key Management in Mobile Ad hoc Networks Renuka A. and K.C.Shet, Dept. of Computer Science
FDLKH: Fully Decentralized Key Management Scheme on Logical Key Hierarchy
 FDLKH: Fully Decentralized Key Management Scheme on Logical Key Hierarchy Daisuke Inoue and Masahiro Kuroda National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, 3-4, Hikarino-oka, Yokosuka,
FDLKH: Fully Decentralized Key Management Scheme on Logical Key Hierarchy Daisuke Inoue and Masahiro Kuroda National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, 3-4, Hikarino-oka, Yokosuka,
Mykil: A Highly Scalable Key Distribution Protocol for Large Group Multicast
 Mykil: A Highly Scalable Key Distribution Protocol for Large Group Multicast Jyh-How Huang and Shivakant Mishra Department of Computer Science University of Colorado, Campus Box 0430 Boulder, CO 80309-0430,
Mykil: A Highly Scalable Key Distribution Protocol for Large Group Multicast Jyh-How Huang and Shivakant Mishra Department of Computer Science University of Colorado, Campus Box 0430 Boulder, CO 80309-0430,
Dynamic Group Key Distribution Using MDS Codes
 Dynamic Group Key Distribution Using MDS Codes Lihao Xu Department of Computer Science Washington University St. Louis, MO 63130 lihao@cs.wustl.edu Abstract Efficient key distribution is an important problem
Dynamic Group Key Distribution Using MDS Codes Lihao Xu Department of Computer Science Washington University St. Louis, MO 63130 lihao@cs.wustl.edu Abstract Efficient key distribution is an important problem
Scalable Secure Group Communication over IP Multicast. Authors:Suman Banerjee, Bobby Bhattacharjee. Speaker: Kun Sun
 Scalable Secure Group Communication over IP Multicast Authors:Suman Banerjee, Bobby Bhattacharjee Speaker: Kun Sun Contents Introduction Related Work Secure multicast using clustering Spatial Clustering
Scalable Secure Group Communication over IP Multicast Authors:Suman Banerjee, Bobby Bhattacharjee Speaker: Kun Sun Contents Introduction Related Work Secure multicast using clustering Spatial Clustering
AN OPTIMAL AND COST EFFECTIVE KEY MANAGEMENT SCHEME FOR SECURE MULTICAST COMMUNICATION
 AN OPTIMAL AND COST EFFECTIVE KEY MANAGEMENT SCHEME FOR SECURE MULTICAST COMMUNICATION SRIDHAR J K 1, SENTHIL KUMAR R 2, ARUN KUMAR S 3 1,2 Student, School Of Computing, SASTRA University, Thanjavur, India.
AN OPTIMAL AND COST EFFECTIVE KEY MANAGEMENT SCHEME FOR SECURE MULTICAST COMMUNICATION SRIDHAR J K 1, SENTHIL KUMAR R 2, ARUN KUMAR S 3 1,2 Student, School Of Computing, SASTRA University, Thanjavur, India.
Efficient Group Key Management Schemes for Multicast Dynamic Communication Systems. Muhammad Yasir Malik
 Efficient Group Key Management Schemes for Multicast Dynamic Communication Systems Muhammad Yasir Malik 2012 Abstract Key management in multicast dynamic groups, where users can leave or join at their
Efficient Group Key Management Schemes for Multicast Dynamic Communication Systems Muhammad Yasir Malik 2012 Abstract Key management in multicast dynamic groups, where users can leave or join at their
Network Security: Broadcast and Multicast. Tuomas Aura T Network security Aalto University, Nov-Dec 2010
 Network Security: Broadcast and Multicast Tuomas Aura T-110.5240 Network security Aalto University, Nov-Dec 2010 Outline 1. Broadcast and multicast 2. Receiver access control (i.e. data confidentiality)
Network Security: Broadcast and Multicast Tuomas Aura T-110.5240 Network security Aalto University, Nov-Dec 2010 Outline 1. Broadcast and multicast 2. Receiver access control (i.e. data confidentiality)
Balanced Batch LKH: New Proposal, Implementation and Performance Evaluation.
 Balanced Batch LKH: New Proposal, Implementation and Performance Evaluation. Josep Pegueroles, Francisco Rico-Novella Departamento de Ingeniería Telemática. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya. Jordi
Balanced Batch LKH: New Proposal, Implementation and Performance Evaluation. Josep Pegueroles, Francisco Rico-Novella Departamento de Ingeniería Telemática. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya. Jordi
Network Security: Broadcast and Multicast. Tuomas Aura T Network security Aalto University, Nov-Dec 2011
 Network Security: Broadcast and Multicast Tuomas Aura T-110.5241 Network security Aalto University, Nov-Dec 2011 Outline 1. Broadcast and multicast 2. Receiver access control (i.e. data confidentiality)
Network Security: Broadcast and Multicast Tuomas Aura T-110.5241 Network security Aalto University, Nov-Dec 2011 Outline 1. Broadcast and multicast 2. Receiver access control (i.e. data confidentiality)
Adapting GDOI for Balanced Batch LKH
 Josep Pegueroles Telematics Engineering Department. Technical University of Catalonia Barcelona, Spain Contents Introduction Benchmark Scenarios Performance of Batch Rekeying with benchmark scenarios Balanced
Josep Pegueroles Telematics Engineering Department. Technical University of Catalonia Barcelona, Spain Contents Introduction Benchmark Scenarios Performance of Batch Rekeying with benchmark scenarios Balanced
Overview. SSL Cryptography Overview CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is an application-level protocol that provides encryption technology for the Internet. SSL ensures the secure transmission of data between a client and a server through
CHAPTER 1 Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is an application-level protocol that provides encryption technology for the Internet. SSL ensures the secure transmission of data between a client and a server through
A Survey on Multicast rekeying for secure group communication
 S.Sasikala Devi,Dr.Antony Selvadoss Danamani, Int. J. Comp. Tech. Appl., Vol 2 (3), 385-391 A Survey on Multicast rekeying for secure group communication S.Sasikala Devi Assistant Professor CMS College
S.Sasikala Devi,Dr.Antony Selvadoss Danamani, Int. J. Comp. Tech. Appl., Vol 2 (3), 385-391 A Survey on Multicast rekeying for secure group communication S.Sasikala Devi Assistant Professor CMS College
Decentralized Key Management for Large Dynamic Multicast Groups using Distributed Balanced Trees
 Decentralized Key Management for Large Dynamic Multicast Groups using Distributed Balanced Trees Thesis by Junaid Haroon MSCS018 Supervised by Mr Shafiq ur Rahman Flow of Presentation Background Proposed
Decentralized Key Management for Large Dynamic Multicast Groups using Distributed Balanced Trees Thesis by Junaid Haroon MSCS018 Supervised by Mr Shafiq ur Rahman Flow of Presentation Background Proposed
SECURED KEY MANAGEMENT ALGORITHM FOR DATA TRANSMISSION IN MOBILE ADHOC NETWORKS
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering and Technology (IJECET) Volume 7, Issue 6, November-December 2016, pp. 96 100, Article ID: IJECET_07_06_014 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijecet/issues.asp?jtype=ijecet&vtype=7&itype=6
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering and Technology (IJECET) Volume 7, Issue 6, November-December 2016, pp. 96 100, Article ID: IJECET_07_06_014 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijecet/issues.asp?jtype=ijecet&vtype=7&itype=6
Source Anonymous Message Authentication and Source Privacy using ECC in Wireless Sensor Network
 Source Anonymous Message Authentication and Source Privacy using ECC in Wireless Sensor Network 1 Ms.Anisha Viswan, 2 Ms.T.Poongodi, 3 Ms.Ranjima P, 4 Ms.Minimol Mathew 1,3,4 PG Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor,
Source Anonymous Message Authentication and Source Privacy using ECC in Wireless Sensor Network 1 Ms.Anisha Viswan, 2 Ms.T.Poongodi, 3 Ms.Ranjima P, 4 Ms.Minimol Mathew 1,3,4 PG Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor,
A Centralized Key Table based Communication Efficient Group Key Management Protocol
 I. J. Computer Network and Information Security, 2015, 8, 49-55 Published Online July 2015 in MECS (http://www.mecs-press.org/) DOI: 10.5815/ijcnis.2015.08.06 A Centralized Key Table based Communication
I. J. Computer Network and Information Security, 2015, 8, 49-55 Published Online July 2015 in MECS (http://www.mecs-press.org/) DOI: 10.5815/ijcnis.2015.08.06 A Centralized Key Table based Communication
Keywords Session key, asymmetric, digital signature, cryptosystem, encryption.
 Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Review of Diffie
Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Review of Diffie
An Information Theoretic Analysis of Rooted-Tree Based Secure Multicast Key Distribution Schemes
 An Information Theoretic Analysis of Rooted-Tree Based Secure Multicast ey Distribution Schemes R. Poovendran J. S. Baras Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Institute for Systems Research University of
An Information Theoretic Analysis of Rooted-Tree Based Secure Multicast ey Distribution Schemes R. Poovendran J. S. Baras Dept. of Electrical Engineering & Institute for Systems Research University of
Group Key Agreement Protocols for Dynamic Peer Groups
 Nirav Jasapara jasapara@isi.edu Group Key Agreement Protocols for Dynamic Peer Groups ABSTRACT With the increased use of distributed services and applications, secure group communication over unsecured
Nirav Jasapara jasapara@isi.edu Group Key Agreement Protocols for Dynamic Peer Groups ABSTRACT With the increased use of distributed services and applications, secure group communication over unsecured
This document is a preview generated by EVS
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 16512-2 Third edition 2016-04-01 Information technology Relayed multicast protocol: Specification for simplex group applications Technologies de l'information Protocole de
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO/IEC 16512-2 Third edition 2016-04-01 Information technology Relayed multicast protocol: Specification for simplex group applications Technologies de l'information Protocole de
TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT
 TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT A Scalable Extension of Group Key Management Protocol by R. Poovendran, S. Ahmed, S. Corson, J. Baras CSHCN T.R. 98-5 (ISR T.R. 98-14) The Center for Satellite and Hybrid Communication
TECHNICAL RESEARCH REPORT A Scalable Extension of Group Key Management Protocol by R. Poovendran, S. Ahmed, S. Corson, J. Baras CSHCN T.R. 98-5 (ISR T.R. 98-14) The Center for Satellite and Hybrid Communication
Communication in Broadband Wireless Networks. Jaydip Sen Convergence Innovation Lab Tata Consultancy Services Ltd. Kolkata, INDIA
 Secure Multicast and Broadcast Communication in Broadband Wireless Networks Jaydip Sen Convergence Innovation Lab Tata Consultancy Services Ltd. Kolkata, INDIA Agenda Network entry procedure for a mobile
Secure Multicast and Broadcast Communication in Broadband Wireless Networks Jaydip Sen Convergence Innovation Lab Tata Consultancy Services Ltd. Kolkata, INDIA Agenda Network entry procedure for a mobile
IBM i Version 7.2. Security Digital Certificate Manager IBM
 IBM i Version 7.2 Security Digital Certificate Manager IBM IBM i Version 7.2 Security Digital Certificate Manager IBM Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information
IBM i Version 7.2 Security Digital Certificate Manager IBM IBM i Version 7.2 Security Digital Certificate Manager IBM Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information
Collusion-Resistant Group Key Management Using Attributebased
 Collusion-Resistant Group Key Management Using Attributebased Encryption Presented by: Anurodh Joshi Overview of the Paper Presents a ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption (CP-ABE) scheme to solve
Collusion-Resistant Group Key Management Using Attributebased Encryption Presented by: Anurodh Joshi Overview of the Paper Presents a ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption (CP-ABE) scheme to solve
The World Wide Web is widely used by businesses, government agencies, and many individuals. But the Internet and the Web are extremely vulnerable to
 1 The World Wide Web is widely used by businesses, government agencies, and many individuals. But the Internet and the Web are extremely vulnerable to compromises of various sorts, with a range of threats
1 The World Wide Web is widely used by businesses, government agencies, and many individuals. But the Internet and the Web are extremely vulnerable to compromises of various sorts, with a range of threats
An IBE Scheme to Exchange Authenticated Secret Keys
 An IBE Scheme to Exchange Authenticated Secret Keys Waldyr Dias Benits Júnior 1, Routo Terada (Advisor) 1 1 Instituto de Matemática e Estatística Universidade de São Paulo R. do Matão, 1010 Cidade Universitária
An IBE Scheme to Exchange Authenticated Secret Keys Waldyr Dias Benits Júnior 1, Routo Terada (Advisor) 1 1 Instituto de Matemática e Estatística Universidade de São Paulo R. do Matão, 1010 Cidade Universitária
Key Management Techniques for Dynamic Secure Multicasting: A Distributed Computing Approach
 Key Management Techniques for Dynamic Secure Multicasting: A Distributed Computing Approach Madhu Sudana Rao Koneni April 30, 2003 Blacksburg, VA Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic
Key Management Techniques for Dynamic Secure Multicasting: A Distributed Computing Approach Madhu Sudana Rao Koneni April 30, 2003 Blacksburg, VA Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic
I Metric I Explanation Robustness
 Towards Solving Multicast Key Management Problem Fan Du, Lionel M. Ni and Abdol-Hossein Esfahanian Department of Computer Science and Engineering Michigan State University East Lansing, M 48824 Abstract-
Towards Solving Multicast Key Management Problem Fan Du, Lionel M. Ni and Abdol-Hossein Esfahanian Department of Computer Science and Engineering Michigan State University East Lansing, M 48824 Abstract-
Group Key Establishment Protocols
 Group Key Establishment Protocols Ruxandra F. Olimid EBSIS Summer School on Distributed Event Based Systems and Related Topics 2016 July 14, 2016 Sinaia, Romania Outline 1. Context and Motivation 2. Classifications
Group Key Establishment Protocols Ruxandra F. Olimid EBSIS Summer School on Distributed Event Based Systems and Related Topics 2016 July 14, 2016 Sinaia, Romania Outline 1. Context and Motivation 2. Classifications
Networking interview questions
 Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
A Secure Routing Protocol for Wireless Adhoc Network Creation
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 6, June 2014, pg.88
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 6, June 2014, pg.88
IBM. Security Digital Certificate Manager. IBM i 7.1
 IBM IBM i Security Digital Certificate Manager 7.1 IBM IBM i Security Digital Certificate Manager 7.1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure to read the information in
IBM IBM i Security Digital Certificate Manager 7.1 IBM IBM i Security Digital Certificate Manager 7.1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure to read the information in
Source Authentication in Group Communication Systems
 Source Authentication in Group Communication Systems Xin Zhao University of Michigan 1301 Beal Ave, Ann Arbor, MI, 48105, USA zhaoxin@eecs.umich.edu Atul Prakash University of Michigan 1301 Beal Ave, Ann
Source Authentication in Group Communication Systems Xin Zhao University of Michigan 1301 Beal Ave, Ann Arbor, MI, 48105, USA zhaoxin@eecs.umich.edu Atul Prakash University of Michigan 1301 Beal Ave, Ann
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 10. Fourth Edition by William Stallings
 Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 10 Fourth Edition by William Stallings Chapter 10 Key Management; Other Public Key Cryptosystems No Singhalese, whether man or woman, would venture out of the
Cryptography and Network Security Chapter 10 Fourth Edition by William Stallings Chapter 10 Key Management; Other Public Key Cryptosystems No Singhalese, whether man or woman, would venture out of the
Secure Multi-Hop Infrastructure Access
 Secure Multi-Hop Infrastructure Access presented by Reza Curtmola (joint work with B. Awerbuch, D. Holmer, C. Nita-Rotaru and H. Rubens) 600.647 Advanced Topics in Wireless Networks Wireless Infrastructure
Secure Multi-Hop Infrastructure Access presented by Reza Curtmola (joint work with B. Awerbuch, D. Holmer, C. Nita-Rotaru and H. Rubens) 600.647 Advanced Topics in Wireless Networks Wireless Infrastructure
(In)security of ecient tree-based group key agreement using bilinear map
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository (In)security of ecient tree-based group key agreement using bilinear map This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by
Loughborough University Institutional Repository (In)security of ecient tree-based group key agreement using bilinear map This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by
Group Key Management Techniques
 Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Network, Web & Security Volume 13 Issue 11 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology Network, Web & Security Volume 13 Issue 11 Version 1.0 Year 2013 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Security Digital Certificate Manager
 System i Security Digital Certificate Manager Version 6 Release 1 System i Security Digital Certificate Manager Version 6 Release 1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure
System i Security Digital Certificate Manager Version 6 Release 1 System i Security Digital Certificate Manager Version 6 Release 1 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure
Cristina Nita-Rotaru. CS355: Cryptography. Lecture 17: X509. PGP. Authentication protocols. Key establishment.
 CS355: Cryptography Lecture 17: X509. PGP. Authentication protocols. Key establishment. Public Keys and Trust Public Key:P A Secret key: S A Public Key:P B Secret key: S B How are public keys stored How
CS355: Cryptography Lecture 17: X509. PGP. Authentication protocols. Key establishment. Public Keys and Trust Public Key:P A Secret key: S A Public Key:P B Secret key: S B How are public keys stored How
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, FL 33431, USA
 Int. J.Securityand Networks, Vol. An efficient group key management scheme for mobile ad hoc networks Bing Wu Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Fayetteville State University, Fayetteville,
Int. J.Securityand Networks, Vol. An efficient group key management scheme for mobile ad hoc networks Bing Wu Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Fayetteville State University, Fayetteville,
Computer Networks. Network Security and Ethics. Week 14. College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University
 Computer Networks Network Security and Ethics Week 14 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Security Intro for Admins l Network administrators can break security into two
Computer Networks Network Security and Ethics Week 14 College of Information Science and Engineering Ritsumeikan University Security Intro for Admins l Network administrators can break security into two
Key Management Schemes for Stateless Receivers Based on Time Varying Heterogeneous Logical Key Hierarchy
 Key Management Schemes for Stateless Receivers Based on Time Varying Heterogeneous Logical Key Hierarchy Miodrag J. Mihaljević Mathematical Institute Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts Kneza Mihaila
Key Management Schemes for Stateless Receivers Based on Time Varying Heterogeneous Logical Key Hierarchy Miodrag J. Mihaljević Mathematical Institute Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts Kneza Mihaila
ZigBee Security Using Attribute-Based Proxy Re-encryption
 J. lnf. Commun. Converg. Eng. 10(4): 343-348, Dec. 2012 Regular Paper ZigBee Security Using Attribute-Based Proxy Re-encryption Hwajeong Seo and Howon Kim*, Member, KIICE Department of Computer Engineering,
J. lnf. Commun. Converg. Eng. 10(4): 343-348, Dec. 2012 Regular Paper ZigBee Security Using Attribute-Based Proxy Re-encryption Hwajeong Seo and Howon Kim*, Member, KIICE Department of Computer Engineering,
VPN World. MENOG 16 Istanbul-Turkey. By Ziad Zubidah Network Security Specialist
 VPN World MENOG 16 Istanbul-Turkey By Ziad Zubidah Network Security Specialist What is this Van used for?! Armed Van It used in secure transporting for valuable goods from one place to another. It is bullet
VPN World MENOG 16 Istanbul-Turkey By Ziad Zubidah Network Security Specialist What is this Van used for?! Armed Van It used in secure transporting for valuable goods from one place to another. It is bullet
BIG-IP System: SSL Administration. Version
 BIG-IP System: SSL Administration Version 13.1.0 Table of Contents Table of Contents About SSL Administration on the BIG-IP System...7 About SSL administration on the BIG-IP system... 7 Device Certificate
BIG-IP System: SSL Administration Version 13.1.0 Table of Contents Table of Contents About SSL Administration on the BIG-IP System...7 About SSL administration on the BIG-IP system... 7 Device Certificate
A New Symmetric Key Algorithm for Modern Cryptography Rupesh Kumar 1 Sanjay Patel 2 Purushottam Patel 3 Rakesh Patel 4
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 2, Issue 08, 2014 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 A New Symmetric Key Algorithm for Modern Cryptography Rupesh Kumar 1 Sanjay Patel 2 Purushottam
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 2, Issue 08, 2014 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 A New Symmetric Key Algorithm for Modern Cryptography Rupesh Kumar 1 Sanjay Patel 2 Purushottam
Introduction. CSE 5351: Introduction to cryptography Reading assignment: Chapter 1 of Katz & Lindell
 Introduction CSE 5351: Introduction to cryptography Reading assignment: Chapter 1 of Katz & Lindell 1 Cryptography Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary: 1. secret writing 2. the enciphering and deciphering
Introduction CSE 5351: Introduction to cryptography Reading assignment: Chapter 1 of Katz & Lindell 1 Cryptography Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary: 1. secret writing 2. the enciphering and deciphering
Key Distribution and Update for Secure Inter-group Multicast Communication
 Key Distribution and Update for Secure Inter-group Multicast Communication ABSTRACT Weichao Wang Department of EECS and ITTC University of Kansas Lawrence, KS 66045 weichaow@eecs.ku.edu Group communication
Key Distribution and Update for Secure Inter-group Multicast Communication ABSTRACT Weichao Wang Department of EECS and ITTC University of Kansas Lawrence, KS 66045 weichaow@eecs.ku.edu Group communication
Enhancing Reliability and Scalability in Dynamic Group System Using Three Level Security Mechanisms
 Enhancing Reliability and Scalability in Dynamic Group System Using Three Level Security Mechanisms A.Sarika*1, Smt.J.Raghaveni*2 M.Tech Student, Dept of CSE, S.R.K.R Engineering college, Bhimavaram, AP,
Enhancing Reliability and Scalability in Dynamic Group System Using Three Level Security Mechanisms A.Sarika*1, Smt.J.Raghaveni*2 M.Tech Student, Dept of CSE, S.R.K.R Engineering college, Bhimavaram, AP,
KALASALINGAM UNIVERSITY
 KALASALINGAM UNIVERSITY (Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education) DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CLASS NOTES CRYPTOGRAPHY AND NETWOTK SECURITY (CSE 405) Prepared by M.RAJA AP/CSE
KALASALINGAM UNIVERSITY (Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education) DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CLASS NOTES CRYPTOGRAPHY AND NETWOTK SECURITY (CSE 405) Prepared by M.RAJA AP/CSE
Key Management and Distribution
 CPE 542: CRYPTOGRAPHY & NETWORK SECURITY Chapter 10 Key Management; Other Public Key Cryptosystems Dr. Lo ai Tawalbeh Computer Engineering Department Jordan University of Science and Technology Jordan
CPE 542: CRYPTOGRAPHY & NETWORK SECURITY Chapter 10 Key Management; Other Public Key Cryptosystems Dr. Lo ai Tawalbeh Computer Engineering Department Jordan University of Science and Technology Jordan
Subject: Adhoc Networks
 ISSUES IN AD HOC WIRELESS NETWORKS The major issues that affect the design, deployment, & performance of an ad hoc wireless network system are: Medium Access Scheme. Transport Layer Protocol. Routing.
ISSUES IN AD HOC WIRELESS NETWORKS The major issues that affect the design, deployment, & performance of an ad hoc wireless network system are: Medium Access Scheme. Transport Layer Protocol. Routing.
CSE 127: Computer Security Cryptography. Kirill Levchenko
 CSE 127: Computer Security Cryptography Kirill Levchenko October 24, 2017 Motivation Two parties want to communicate securely Secrecy: No one else can read messages Integrity: messages cannot be modified
CSE 127: Computer Security Cryptography Kirill Levchenko October 24, 2017 Motivation Two parties want to communicate securely Secrecy: No one else can read messages Integrity: messages cannot be modified
Security Analysis of Shim s Authenticated Key Agreement Protocols from Pairings
 Security Analysis of Shim s Authenticated Key Agreement Protocols from Pairings Hung-Min Sun and Bin-san Hsieh Department of Computer Science, National sing Hua University, Hsinchu, aiwan, R.O.C. hmsun@cs.nthu.edu.tw
Security Analysis of Shim s Authenticated Key Agreement Protocols from Pairings Hung-Min Sun and Bin-san Hsieh Department of Computer Science, National sing Hua University, Hsinchu, aiwan, R.O.C. hmsun@cs.nthu.edu.tw
Broadcast Encryption Based on Braid Groups
 12 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.12 No.2, February 2012 Broadcast Encryption Based on Braid Groups Norranut Saguansakdiyotin and Pipat Hiranvanichakorn National
12 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.12 No.2, February 2012 Broadcast Encryption Based on Braid Groups Norranut Saguansakdiyotin and Pipat Hiranvanichakorn National
SENETAS ENCRYPTION KEY MANAGEMENT STATE-OF-THE-ART KEY MANAGEMENT FOR ROBUST NETWORK SECURITY
 SENETAS ENCRYPTION KEY MANAGEMENT STATE-OF-THE-ART KEY MANAGEMENT FOR ROBUST NETWORK SECURITY WHO SHOULD READ THIS DOCUMENT System Integrators, Cloud and Data Centre Service Providers, Layer 2 Data Networks
SENETAS ENCRYPTION KEY MANAGEMENT STATE-OF-THE-ART KEY MANAGEMENT FOR ROBUST NETWORK SECURITY WHO SHOULD READ THIS DOCUMENT System Integrators, Cloud and Data Centre Service Providers, Layer 2 Data Networks
Request for Comments: 4046 Category: Informational IBM L. Dondeti Qualcomm F. Lindholm Ericsson April 2005
 Network Working Group Request for Comments: 4046 Category: Informational M. Baugher Cisco R. Canetti IBM L. Dondeti Qualcomm F. Lindholm Ericsson April 2005 Multicast Security (MSEC) Group Key Management
Network Working Group Request for Comments: 4046 Category: Informational M. Baugher Cisco R. Canetti IBM L. Dondeti Qualcomm F. Lindholm Ericsson April 2005 Multicast Security (MSEC) Group Key Management
Computer Networks. Wenzhong Li. Nanjing University
 Computer Networks Wenzhong Li Nanjing University 1 Chapter 7. Network Security Network Attacks Cryptographic Technologies Message Integrity and Authentication Key Distribution Firewalls Transport Layer
Computer Networks Wenzhong Li Nanjing University 1 Chapter 7. Network Security Network Attacks Cryptographic Technologies Message Integrity and Authentication Key Distribution Firewalls Transport Layer
Self-Healing Group Key Distribution
 International Journal of Network Security, Vol.1, No.2, PP.110 117, Sep. 2005 (http://isrc.nchu.edu.tw/ijns/) 110 Self-Healing Group Key Distribution Muhammad Junaid Bohio and Ali Miri (Corresponding author:
International Journal of Network Security, Vol.1, No.2, PP.110 117, Sep. 2005 (http://isrc.nchu.edu.tw/ijns/) 110 Self-Healing Group Key Distribution Muhammad Junaid Bohio and Ali Miri (Corresponding author:
Key Management in IP Multicast
 Key Management in IP Multicast Petri Jokela Helsinki University of Technology petri.jokela@nomadiclab.com ABSTRACT The IP networking was originally designed to operate in point topoint way. However, when
Key Management in IP Multicast Petri Jokela Helsinki University of Technology petri.jokela@nomadiclab.com ABSTRACT The IP networking was originally designed to operate in point topoint way. However, when
Internet Protocols (chapter 18)
 Internet Protocols (chapter 18) CSE 3213 Fall 2011 Internetworking Terms 1 TCP/IP Concepts Connectionless Operation Internetworking involves connectionless operation at the level of the Internet Protocol
Internet Protocols (chapter 18) CSE 3213 Fall 2011 Internetworking Terms 1 TCP/IP Concepts Connectionless Operation Internetworking involves connectionless operation at the level of the Internet Protocol
Data Security and Privacy. Topic 14: Authentication and Key Establishment
 Data Security and Privacy Topic 14: Authentication and Key Establishment 1 Announcements Mid-term Exam Tuesday March 6, during class 2 Need for Key Establishment Encrypt K (M) C = Encrypt K (M) M = Decrypt
Data Security and Privacy Topic 14: Authentication and Key Establishment 1 Announcements Mid-term Exam Tuesday March 6, during class 2 Need for Key Establishment Encrypt K (M) C = Encrypt K (M) M = Decrypt
Public-key Cryptography: Theory and Practice
 Public-key Cryptography Theory and Practice Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Chapter 1: Overview What is Cryptography? Cryptography is the study of
Public-key Cryptography Theory and Practice Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Chapter 1: Overview What is Cryptography? Cryptography is the study of
Efficient and Secure Source Authentication for Multicast
 Efficient and Secure Source Authentication for Multicast Authors: Adrian Perrig, Ran Canetti Dawn Song J. D. Tygar Presenter: Nikhil Negandhi CSC774 Network Security Outline: Background Problem Related
Efficient and Secure Source Authentication for Multicast Authors: Adrian Perrig, Ran Canetti Dawn Song J. D. Tygar Presenter: Nikhil Negandhi CSC774 Network Security Outline: Background Problem Related
BS801E-BSCS. Cryptography
 Jay-Ar Baliguat BS801E-BSCS Ms.Myrlen Maria Antoni Cryptography Cryptography can be defined as the conversion of data into a scrambled code that can be deciphered and sent across a public or private network.
Jay-Ar Baliguat BS801E-BSCS Ms.Myrlen Maria Antoni Cryptography Cryptography can be defined as the conversion of data into a scrambled code that can be deciphered and sent across a public or private network.
Research Statement. Yehuda Lindell. Dept. of Computer Science Bar-Ilan University, Israel.
 Research Statement Yehuda Lindell Dept. of Computer Science Bar-Ilan University, Israel. lindell@cs.biu.ac.il www.cs.biu.ac.il/ lindell July 11, 2005 The main focus of my research is the theoretical foundations
Research Statement Yehuda Lindell Dept. of Computer Science Bar-Ilan University, Israel. lindell@cs.biu.ac.il www.cs.biu.ac.il/ lindell July 11, 2005 The main focus of my research is the theoretical foundations
ET4254 Communications and Networking 1
 Topic 9 Internet Protocols Aims:- basic protocol functions internetworking principles connectionless internetworking IP IPv6 IPSec 1 Protocol Functions have a small set of functions that form basis of
Topic 9 Internet Protocols Aims:- basic protocol functions internetworking principles connectionless internetworking IP IPv6 IPSec 1 Protocol Functions have a small set of functions that form basis of
Junos Security. Chapter 8: IPsec VPNs Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. Worldwide Education Services
 Junos Security Chapter 8: IPsec VPNs 2012 Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. www.juniper.net Worldwide Education Services Chapter Objectives After successfully completing this chapter, you will
Junos Security Chapter 8: IPsec VPNs 2012 Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. www.juniper.net Worldwide Education Services Chapter Objectives After successfully completing this chapter, you will
Internet Group Management Protocol, Version 3 <draft-ietf-idmr-igmp-v3-07.txt> STATUS OF THIS MEMO
 INTERNET-DRAFT Brad Cain, Mirror Image Internet Steve Deering, Cisco Systems Bill Fenner, AT&T Labs - Research Isidor Kouvelas, Cisco Systems Ajit Thyagarajan, Ericsson Expires September 2001 March 2001
INTERNET-DRAFT Brad Cain, Mirror Image Internet Steve Deering, Cisco Systems Bill Fenner, AT&T Labs - Research Isidor Kouvelas, Cisco Systems Ajit Thyagarajan, Ericsson Expires September 2001 March 2001
2.1 Basic Cryptography Concepts
 ENEE739B Fall 2005 Part 2 Secure Media Communications 2.1 Basic Cryptography Concepts Min Wu Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park Outline: Basic Security/Crypto Concepts
ENEE739B Fall 2005 Part 2 Secure Media Communications 2.1 Basic Cryptography Concepts Min Wu Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland, College Park Outline: Basic Security/Crypto Concepts
Configuring Port-Based and Client-Based Access Control (802.1X)
 9 Configuring Port-Based and Client-Based Access Control (802.1X) Contents Overview..................................................... 9-3 Why Use Port-Based or Client-Based Access Control?............
9 Configuring Port-Based and Client-Based Access Control (802.1X) Contents Overview..................................................... 9-3 Why Use Port-Based or Client-Based Access Control?............
Internet Engineering Task Force Mark Baugher(Cisco) Expires: April, 2003 October, 2002
 Internet Engineering Task Force Mark Baugher(Cisco) INTERNET-DRAFT Thomas Hardjono (Verisign) Category: Standards Track Hugh Harney (Sparta) Document: draft-ietf-msec-gdoi-06.txt Brian Weis (Cisco) Expires:
Internet Engineering Task Force Mark Baugher(Cisco) INTERNET-DRAFT Thomas Hardjono (Verisign) Category: Standards Track Hugh Harney (Sparta) Document: draft-ietf-msec-gdoi-06.txt Brian Weis (Cisco) Expires:
Efficient, Authenticated, and Fault-Tolerant Key Agreement for Dynamic Peer Groups
 Efficient, Authenticated, and Fault-Tolerant Key Agreement for Dynamic Peer Groups Li Zhou and Chinya V. Ravishankar Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of California, Riverside Riverside,
Efficient, Authenticated, and Fault-Tolerant Key Agreement for Dynamic Peer Groups Li Zhou and Chinya V. Ravishankar Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of California, Riverside Riverside,
Group Key Rekeying Technique with Secure Data Encryption in MANETs
 Group Key Rekeying Technique with Secure Data Encryption in MANETs C. Shanmuganathan Research Scholar, CSE Manonmaniam Sundaranar University Tirunelveli, India Dr. P. Raviraj Professor / Department of
Group Key Rekeying Technique with Secure Data Encryption in MANETs C. Shanmuganathan Research Scholar, CSE Manonmaniam Sundaranar University Tirunelveli, India Dr. P. Raviraj Professor / Department of
Session Based Ciphertext Policy Attribute Based Encryption Method for Access Control in Cloud Storage
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 04, Issue 09 (September. 2014), V3 PP 21-25 www.iosrjen.org Session Based Ciphertext Policy Attribute Based Encryption
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 04, Issue 09 (September. 2014), V3 PP 21-25 www.iosrjen.org Session Based Ciphertext Policy Attribute Based Encryption
Computers and Security
 The contents of this Supporting Material document have been prepared from the Eight units of study texts for the course M150: Date, Computing and Information, produced by The Open University, UK. Copyright
The contents of this Supporting Material document have been prepared from the Eight units of study texts for the course M150: Date, Computing and Information, produced by The Open University, UK. Copyright
Inter-Domain Identity-based Authenticated Key Agreement Protocol from the Weil Pairing
 Inter-Domain Identity-based Authenticated Key Agreement Protocol from the Weil Pairing Tsai, Hong-Bin Chiu, Yun-Peng Lei, Chin-Laung Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University July 10,
Inter-Domain Identity-based Authenticated Key Agreement Protocol from the Weil Pairing Tsai, Hong-Bin Chiu, Yun-Peng Lei, Chin-Laung Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University July 10,
TopSec Product Family Voice encryption at the highest security level
 Secure Communications Product Brochure 01.01 TopSec Product Family Voice encryption at the highest security level TopSec Product Family At a glance The TopSec product family provides end-to-end voice encryption
Secure Communications Product Brochure 01.01 TopSec Product Family Voice encryption at the highest security level TopSec Product Family At a glance The TopSec product family provides end-to-end voice encryption
Multiway Tree-Based Group Key Management Using Chinese Remainder Theorem for Multi-Privileged Group Communications
 Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 81 92 (2014) DOI: 10.6180/jase.2014.17.1.10 Multiway Tree-Based Group Key Management Using Chinese Remainder Theorem for Multi-Privileged
Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 81 92 (2014) DOI: 10.6180/jase.2014.17.1.10 Multiway Tree-Based Group Key Management Using Chinese Remainder Theorem for Multi-Privileged
Network Security Issues and Cryptography
 Network Security Issues and Cryptography PriyaTrivedi 1, Sanya Harneja 2 1 Information Technology, Maharishi Dayanand University Farrukhnagar, Gurgaon, Haryana, India 2 Information Technology, Maharishi
Network Security Issues and Cryptography PriyaTrivedi 1, Sanya Harneja 2 1 Information Technology, Maharishi Dayanand University Farrukhnagar, Gurgaon, Haryana, India 2 Information Technology, Maharishi
Digital Certificates Demystified
 Digital Certificates Demystified Ross Cooper, CISSP IBM Corporation RACF/PKI Development Poughkeepsie, NY Email: rdc@us.ibm.com August 9 th, 2012 Session 11622 Agenda Cryptography What are Digital Certificates
Digital Certificates Demystified Ross Cooper, CISSP IBM Corporation RACF/PKI Development Poughkeepsie, NY Email: rdc@us.ibm.com August 9 th, 2012 Session 11622 Agenda Cryptography What are Digital Certificates
An Information-Theoretic Approach for Design and Analysis of Rooted-Tree-Based Multicast Key Management Schemes
 2824 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 47, NO. 7, NOVEMBER 2001 An Information-Theoretic Approach for Design and Analysis of Rooted-Tree-Based Multicast Key Management Schemes Radha Poovendran,
2824 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 47, NO. 7, NOVEMBER 2001 An Information-Theoretic Approach for Design and Analysis of Rooted-Tree-Based Multicast Key Management Schemes Radha Poovendran,
WiMAX Security: Problems & Solutions
 (JCSCR) - ISSN 2227-328X WiMAX Security: Problems & Solutions Paul Semaan LACSC Lebanese Association for Computational Sciences Registered under No. 957, 2011, Beirut, Lebanon Abstract This paper is a
(JCSCR) - ISSN 2227-328X WiMAX Security: Problems & Solutions Paul Semaan LACSC Lebanese Association for Computational Sciences Registered under No. 957, 2011, Beirut, Lebanon Abstract This paper is a
Protocols II. Computer Security Lecture 12. David Aspinall. 17th February School of Informatics University of Edinburgh
 Protocols II Computer Security Lecture 12 David Aspinall School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 17th February 2011 Outline Introduction Shared-key Authentication Asymmetric authentication protocols
Protocols II Computer Security Lecture 12 David Aspinall School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 17th February 2011 Outline Introduction Shared-key Authentication Asymmetric authentication protocols
CSC 774 Network Security
 CSC 774 Network Security Mid-Term Exam #2 4:10pm 5:00pm, March 26, 2004 Student Name: Score: You are allowed to use your textbook and notes; however, you are not allowed to exchange anything before you
CSC 774 Network Security Mid-Term Exam #2 4:10pm 5:00pm, March 26, 2004 Student Name: Score: You are allowed to use your textbook and notes; however, you are not allowed to exchange anything before you
SIDE CHANNEL ATTACKS AGAINST IOS CRYPTO LIBRARIES AND MORE DR. NAJWA AARAJ HACK IN THE BOX 13 APRIL 2017
 SIDE CHANNEL ATTACKS AGAINST IOS CRYPTO LIBRARIES AND MORE DR. NAJWA AARAJ HACK IN THE BOX 13 APRIL 2017 WHAT WE DO What we do Robust and Efficient Cryptographic Protocols Research in Cryptography and
SIDE CHANNEL ATTACKS AGAINST IOS CRYPTO LIBRARIES AND MORE DR. NAJWA AARAJ HACK IN THE BOX 13 APRIL 2017 WHAT WE DO What we do Robust and Efficient Cryptographic Protocols Research in Cryptography and
An Enhanced and Cost Effective Group Key Management Scheme for Multicast Network
 Journal of Computer Science, 9 (4): 477-487, 2013 ISSN 1549-3636 2013 doi:10.3844/jcssp.2013.477.487 Published Online 9 (4) 2013 (http://www.thescipub.com/jcs.toc) An Enhanced and Cost Effective Group
Journal of Computer Science, 9 (4): 477-487, 2013 ISSN 1549-3636 2013 doi:10.3844/jcssp.2013.477.487 Published Online 9 (4) 2013 (http://www.thescipub.com/jcs.toc) An Enhanced and Cost Effective Group
A Survey on Efficient Group Key Management Schemes in Wireless Networks
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(14), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i14/87972, April 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Survey on Efficient Group Key Management Schemes
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(14), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i14/87972, April 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Survey on Efficient Group Key Management Schemes
Service Managed Gateway TM. Configuring IPSec VPN
 Service Managed Gateway TM Configuring IPSec VPN Issue 1.2 Date 12 November 2010 1: Introduction 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 What is a VPN?... 3 1.2 The benefits of an Internet-based VPN... 3 1.3 Tunnelling
Service Managed Gateway TM Configuring IPSec VPN Issue 1.2 Date 12 November 2010 1: Introduction 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 What is a VPN?... 3 1.2 The benefits of an Internet-based VPN... 3 1.3 Tunnelling
W H I T E P A P E R : O P E N. V P N C L O U D. Implementing A Secure OpenVPN Cloud
 W H I T E P A P E R : O P E N. V P N C L O U D Implementing A Secure OpenVPN Cloud Platform White Paper: OpenVPN Cloud Platform Implementing OpenVPN Cloud Platform Content Introduction... 3 The Problems...
W H I T E P A P E R : O P E N. V P N C L O U D Implementing A Secure OpenVPN Cloud Platform White Paper: OpenVPN Cloud Platform Implementing OpenVPN Cloud Platform Content Introduction... 3 The Problems...
Create New Virtual Hub window.
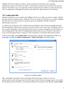 SoftEther VPN Server makes it possible to create a plurality of Virtual Hubs, and to separate administration objects and VPN session layer 2 communication between each Virtual Hub. This manual explains
SoftEther VPN Server makes it possible to create a plurality of Virtual Hubs, and to separate administration objects and VPN session layer 2 communication between each Virtual Hub. This manual explains
HIGH LEVEL SECURITY IMPLEMENTATION IN DATA SHARING ON SOCIAL WEBSITES
 HIGH LEVEL SECURITY IMPLEMENTATION IN DATA SHARING ON SOCIAL WEBSITES P.Senthil Kumar 1 Associate professor, PSNA college of engineering and technology,dindigul,tamilnadu,india Abstract: With the recent
HIGH LEVEL SECURITY IMPLEMENTATION IN DATA SHARING ON SOCIAL WEBSITES P.Senthil Kumar 1 Associate professor, PSNA college of engineering and technology,dindigul,tamilnadu,india Abstract: With the recent
A Modified Approach for Kerberos Authentication Protocol with Secret Image by using Visual Cryptography
 A Modified Approach for Kerberos Authentication Protocol with Secret Image by using Visual Cryptography Ashok Kumar J 1, and Gopinath Ganapathy 2 1,2 School of Computer Science, Engineering and Applications
A Modified Approach for Kerberos Authentication Protocol with Secret Image by using Visual Cryptography Ashok Kumar J 1, and Gopinath Ganapathy 2 1,2 School of Computer Science, Engineering and Applications
Issues. Separation of. Distributed system security. Security services. Security policies. Security mechanism
 Module 9 - Security Issues Separation of Security policies Precise definition of which entities in the system can take what actions Security mechanism Means of enforcing that policy Distributed system
Module 9 - Security Issues Separation of Security policies Precise definition of which entities in the system can take what actions Security mechanism Means of enforcing that policy Distributed system
