FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
|
|
|
- Tamsin James
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FiberstoreOS V3.3 IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
2 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands area default-cost area range area stub auto-cost clear ipv6 ospf default-information originate (OSPFv3) default-metric (OSPFv3) distance (OSPFv3) distribute-list (OSPFv3) enable db-summary-opt ipv6 ospf cost ipv6 ospf dead-interval ipv6 ospf hello-interval ipv6 ospf mtu-ignore ip ospf priority Ipv6 ospf retransmit-interval ipv6 ospf transmit-delay passive-interface (OSPF) redistribute (OSPFv3) router-id (OSPF) router ipv6 ospf summary-address (OSPFv3) show ipv6 ospf show ipv6 ospf database show ipv6 ospf interface show ipv6 ospf neighbor show ipv6 ospf database database-summary show ipv6 ospf route show ipv6 ospf route summary show ipv6 protocols ospf timers spf max-concurrent-dd debug ipv6 ospf debug ipv6 ospf events...38
3 1.35 debug ipv6 ospf ifsm debug ipv6 ospf nfsm debug ipv6 ospf lsa debug ipv6 ospf packet debug ipv6 ospf route show debugging ipv6 ospf show resource ipv6 ospf RIPng Commands router ipv6 rip ipv6 router rip ipv6 rip metric-offset ipv6 rip split-horizon default-information originate (RIPng) default-metric (RIPng) distance (RIPng) neighbor (RIPng) offset-list (RIPng) passive-interface (RIPng) redistribute (RIPng) timers basic (RIPng) distribute-list(ripng) aggregate-address (RIPng) route map(ripng) maximum-prefix(ripng) show ipv6 rip database show ipv6 rip interface show ipv6 rip database database-summary show ipv6 protocol rip debug ipv6 rip show debugging ipv6 rip show resource ipv6 rip clear ipv6 rip route IPv6UC Commands ipv6 enable max-static-v6routes ipv6 route ipv6 address show ipv6 route show ipv6 interface ipv6 verify unicast reverse-path ipv6 icmp error-interval... 77
4 1 OSPFv3 Commands 1.1 area default-cost To specify a cost for the default summary route sent into a stub, use the area default-cost command in router configuration mode. To remove the assigned default route cost, use the no form of this command. area AREA-ID default-cost COST no area AREA-ID default-cost AREA-ID COST Identifier of the area for which authentication is to be enabled. The identifier can be specified as either a decimal value or an IP address Cost for the default summary route used for a stub. The acceptable value is a 24-bit number Router Configuration COST: 1 The command is used only on an Area Border Router (ABR) attached to a stub. There are two stub area router configuration commands: the stub and default-cost options of the area command. In all routers and access servers attached to the stub area, the area should be configured as a stub area using the stub option of the area command. Use the default-cost option only on an ABR attached to the stub area. The default-cost option provides the metric for the summary default route generated by the ABR into the stub area. The following example assigns a default cost of 20 to stub network : 4
5 Switch(config)#router ipv6 ospf 201 Switch(config-router)#area stub Switch(config-router)#area default-cost area range To consolidate and summarize routes at an area boundary, use the area range command in router configuration mode. To disable this function, use the no form of this command. area AREA-ID range ADDRESS/PREFIX-LENGTH (advertise not-advertise ) no area AREA-ID range ADDRESS/PREFIX-LENGTH AREA-ID ADDRESS PREFIX-LENGTH advertise not-advertise Identifier of the area for which authentication is to be enabled. The identifier can be specified as either a decimal value or an IP address IPv4 address Prefix length of the address Advertise this range (default) DoNotAdvertise this range Router Configuration This command is disabled by default. The area range command is used only with Area Border Routers (ABRs). It is used to consolidate or summarize routes for an area. The result is that a single summary route is advertised to other areas by the ABR. Routing information is condensed at area boundaries. External to the area, a single route is advertised for each address range. This behavior is called route summarization. 5
6 Multiple area router configuration commands specifying the range option can be configured. Thus, OSPF can summarize addresses for many different sets of address ranges. The following example specifies one summary route to be advertised by the ABR to other areas for all subnets on area 10: Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf 201 Switch(config-router)#area 10 range 2004::1/ area stub To define an area as a stub area, use the area stub command in router configuration mode. To disable this function, use the no form of this command. area AREA-ID stub (no-summary ) no area AREA-ID stub (no-summary ) AREA-ID no-summary Identifier of the area for which authentication is to be enabled. The identifier can be specified as either a decimal value or an IP address (Optional) Prevents an Area Border Router (ABR) from sending summary link advertisements into the stub area Router Configuration No stub area is defined. You must configure the area stub command on all routers and access servers in the stub area. Use the area router configuration command with the default-cost keyword to specify the cost of a default internal router sent into a stub area by an ABR. There are two stub area router configuration commands: the stub and default-cost options of the area router configuration command. In all routers attached to the stub area, the area should 6
7 be configured as a stub area using the stub keyword of the area command. Use the default-cost keyword only on an ABR attached to the stub area. The default-cost keyword provides the metric for the summary default route generated by the ABR into the stub area. To further reduce the number of link-state advertisements (LSAs) sent into a stub area, you can configure the no-summary keyword on the ABR to prevent it from sending summary LSAs (LSA type 3) into the stub area. The following example assigns a default cost of 20 to stub network : Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf 201 Switch(config-router)#area stub Switch(config-router)#area default-cost auto-cost To control how Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) calculates default metrics for the interface; use the auto-cost command in router configuration mode. To assign cost based only on the interface type, use the no form of this command. auto-cost reference-bandwidth RATE no auto-cost reference-bandwidth reference-bandwidth RATE Rate in Mbps (bandwidth). The range is from 1 to ; the default is 100 Router Configuration 100 Mbps 7
8 The value set by the ipv6 ospf cost command overrides the cost resulting from the auto-cost command. The following example changes the cost of the cost link to 1GBps. Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf 1 Switch(config-router)#auto-cost reference-bandwidth 1000 ipv6 ospf cost 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf To clear routing information based on the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing process ID, use the clear ipv6 ospf command in privileged EXEC mode. clear ipv6 ospf (PID ) process PID (Optional) Process ID Privileged EXEC Use the PID argument to clear only one OSPFv3 process. If the PID argument is not specified, all OSPFv3 processes are cleared. The following example clears all OSPFv3 processes: 8
9 Switch# clear ipv6 ospf process 1.6 default-information originate (OSPFv3) To generate a default external route into an Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) routing domain, use the default-information originate command in router configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command. default-information originate [route-map WORD ] [always] [metric METRIC-VALUE] [metric-type TYPE-VALUE] no default-information originate [always] [metric] [metric-type] [route-map] always (Optional) Always advertises the default route regardless of whether the system has a default route metric metric-value (Optional) Metric used for generating the default route. If you omit a value and do not specify a value using the default-metric router configuration command, the default metric value is 10. The value used is specific to the protocol metric-type route-map (Optional) External link type associated with the default route advertised into the OSPF routing domain. It can be one of the following values Route map reference Router Configuration This command is disabled by default. Whenever you use the redistribute or the default-information router configuration command to redistribute routes into an OSPFv3 routing domain, the switch automatically becomes an autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR). However, an ASBR does not, by default, generate a default route into the OSPFv3 routing domain. The system still must have a default route for itself before it generates one, except when you have specified the always keyword. 9
10 The following example specifies a metric of 100 for the default route redistributed into the OSPFv3 routing domain and an external metric type of Type 1: Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf 109 Switch(config-router)# redistribute rip metric 100 Switch(config-router)#default-information originate metric 100 metric-type 1 redistribute (OSPFv3) 1.7 default-metric (OSPFv3) To set default metric values for the Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol, use the default-metric command in router configuration mode. To return to the default state, use the no form of this command. default-metric METRIC-VALUE no default-metric (METRIC-VALUE) METRIC-VALUE metric value appropriate for the specified routing protocol. Built-in, automatic metric translations, as appropriate for each routing protocol. The metric of redistributed connected and static routes is set to 0 Router Configuration The default-metric command is used in conjunction with the redistribute router configuration command to cause the current routing protocol to use the same metric value for all redistributed routes. A default metric helps solve the problem of redistributing routes with incompatible metrics. Whenever metrics do not convert, using a default metric provides a reasonable substitute and enables the redistribution to proceed. 10
11 The following example shows a router in autonomous system using both the Routing Information Protocol (RIPng) and the OSPFv3 routing protocols. The example advertises OSPFv3-derived routes using RIPng and assigns the Internal Gateway Protocol (IGP)-derived routes a RIPng metric of 10. Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf Switch(config-router)#default-metric 10 Switch(config-router)# redistribute ripng redistribute (OSPFv3) 1.8 distance (OSPFv3) To define Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) route administrative distances based on route type, use the distance command in router configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command. distance {DISTANCE ospfv3 [external DIST1] [inter-area DIST2] [intra-area DIST3]} no distance (ospfv3 ) DISTANCE external DIST1 inter-area DIST2 intra-area DIST3 Administrative distance. An integer from 1 to 255. (Routes with a distance value of 255 are not installed in the routing table.) (Optional) Sets the distance for routes from other routing domains, learned by redistribution. Range is 1 to 255. The default value is 110 (Optional) Sets the distance for all routes from one area to another area. Range is 1 to 255. The default value is 110 (Optional) Sets the distance for all routes within an area. Range is 1 to 255. The default value is 110 Router Configuration DIST1:
12 DIST2: 110 DIST3: 110 You may specify one of the keywords or use distance only to apply to all types of routes. The distance command allows you to set a distance for an entire group of routes, rather than a specific route that passes an access list. A common reason to use the distance command is when you have multiple OSPFv3 processes with mutual redistribution, and you want to prefer internal routes from one over external routes from the other. The following example shows a router in autonomous system using both the Routing Information Protocol (RIPng) and the OSPFv3 routing protocols. The example advertises OSPFv3-derived routes using RIPng and assigns the Internal Gateway Protocol (IGP)-derived routes a RIPng distance of 90.. Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf Switch(config-router)#distance 90 Switch(config-router)# redistribute ripng 1.9 distribute-list (OSPFv3) To filter networks received in updates or suppress networks from being advertised in updates, use the distribute-list command in router configuration mode. To cancel this function, use the no form of this command. distribute-list ACCESSS-LIST-NAME (in out (bgp connected ospfv3 ripng static)) no distribute-list ACCESSS-LIST-NAME (in out (bgp connected ospfv3 ripng static)) ACCESSS-LIST-NAME in out Name of an access list to be applied Filter networks received in updates Suppress networks from being advertised in updates 12
13 Router Configuration This command is disabled by default. This command must specify an access list. In the following example, OSPFv3 process 1 is configured to accept two prefixes, prefix 2001:1:1::1/32 and prefix 3001:1:1::1/32: Switch(config)# ipv6 access-list fiter-as-router Switch(config-ip-acl)# permit any 2001:1:1::1/32 any Switch(config-ip-acl)# permit any 3001:1:1::1/32 any Switch(config-ip-acl)#deny any any any Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf 1 Switch(config-router)#distribute-list acl1 in ipv6 access-list 1.10 enable db-summary-opt Use this command to enable optimize the process when building ospfv3 neighborship. enable db-summary-opt no enable db-summary-opt Router Configuration Disable 13
14 . The following example enables this optimization: Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf 1 Switch(config-if)# enable db-summary-opt 1.11 ipv6 ospf cost To explicitly specify the cost of sending a packet on an interface, use the ipv6 ospf cost command in interface configuration mode. To reset the path cost to the default value, use the no form of this command. ipv6 ospf cost INTERFACE-COST no ipv6 ospf cost INTERFACE-COST Unsigned integer value expressed as the link-state metric. It can be a value in the range from 1 to Interface Configuration No default cost is predefined. You can set the metric manually using this command, if you need to change the default. Using the bandwidth command changes the link cost as long as this command is not used. The link-state metric is advertised as the link cost in the router link advertisement. In general, the path cost is calculated using the following formula: 14
15 Reference Bandwidth / bandwidth The following example sets the interface cost value to 65: Switch(config)# interface eth-0-1 Switch(config-if)# no switchport Switch(config-if)# ipv6 ospf cost 65 auto-cost reference bandwidth 1.12 ipv6 ospf dead-interval To set the interval during which at least one hello packet must be received from a neighbor before the router declares that neighbor down, use the ipv6 ospf dead-interval command in interface configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command. ipv6 ospf dead-interval SECONDS (instance ID ) no ipv6 ospf dead-interval (instance ID ) SECONDS ID Interval (in seconds) during which the router must receive at least one hello packet from a neighbor or else that neighbor is removed from the peer list and does not participate in routing. The range is 1 to The value must be the same for all nodes on the network Instance ID Interface Configuration SECONDS: The neighbor is considered as dead in 40s by default. The dead interval is advertised in OSPFv3 hello packets. This value must be the same for all networking devices on a specific network. 15
16 Specifying a smaller dead interval (seconds) will give faster detection of a neighbor being down and improve convergence, but might cause more routing instability. The following example sets the OSPFv3 dead interval to 20 seconds: Switch(config)# interface eth-0-1 Switch(config-if)# no switchport Switch(config-if)# ipv6 ospf dead-interval 20 ipv6 ospf hello-interval show ipv6s ospf interface 1.13 ipv6 ospf hello-interval To specify the interval between hello packets that the switch sends on the interface, use the ip ospf hello-interval command in interface configuration mode. To return to the default time, use the no form of this command. ip ospf hello-interval SECONDS (instance ID ) no ip ospf hello-interval (instance ID ) SECONDS ID Interval (in seconds) during which the router must receive at least one hello packet from a neighbor or else that neighbor is removed from the peer list and does not participate in routing. The range is 1 to The value must be the same for all nodes on the network Instance ID Interface Configuration 10 seconds (Ethernet) 30 seconds (non-broadcast) 16
17 This value is advertised in the hello packets. The smaller the hello interval, the faster topological changes will be detected, but more routing traffic will ensue. This value must be the same for all routers and access servers on a specific network. The following example sets the interval between hello packets to 15 seconds: Switch(config)# interface eth-0-1 Switch(config-if)# no switchport Switch(config-if)# ipv6 ospf hello-interval 15 ipv6 ospf dead-interval 1.14 ipv6 ospf mtu-ignore To disable Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) maximum transmission unit (MTU) mismatch detection on receiving Database Descriptor (DBD) packets, use the ipv6 ospf mtu-ignore command in interface configuration mode. To reset to default, use the no form of this command. ipv6 ospf mtu-ignore no ipv6 ospf mtu-ignore Interface Configuration OSPFv3 MTU mismatch detection is enabled. OSPFv3 checks whether neighbors are using the same MTU on a common interface. This check is performed when neighbors exchange DBD packets. If the receiving MTU in the DBD packet is higher than the IP MTU configured on the incoming interface, OSPFv3 adjacency will not be established. 17
18 The following example disables MTU mismatch detection on receiving DBD packets: Switch(config)# interface eth-0-1 Switch(config-if)# no switchport Switch(config-if)# ipv6 ospf mtu-ignore 1.15 ip ospf priority To set the router priority, which helps determine the designated router for this network, use the ip ospf priority command in interface configuration mode. To return to the default value, use the no form of this command. ipv6 ospf priority NUMBER-VALUE no ipv6 ospf priority NUMBER-VALUE A number value that specifies the priority of the router. The range is from 0 to 255 Interface Configuration Priority of 1 When two routers attached to a network both attempt to become the designated router, the one with the higher router priority takes precedence. If there is a tie, the router with the higher router ID takes precedence. A router with a router priority set to zero is ineligible to become the designated router or backup designated router. Router priority is configured only for interfaces to multi-access networks (in other words, not to point-to-point networks). This priority value is used when you configure Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) for non-broadcast networks using the neighbor router configuration command for OSPFv3. 18
19 The following example sets the router priority value to 4: Switch(config)# interface eth-0-1 Switch(config-if)# no switchport Switch(config-if)# ipv6 ospf priority Ipv6 ospf retransmit-interval To specify the time between link-state advertisement (LSA) retransmissions for adjacencies belonging to the interface, use the ipv6 ospf retransmit-interval command in interface configuration mode. To return to the default value, use the no form of this command. ipv6 ospf retransmit-interval SECONDS no ipv6 ospf retransmit-interval SECONDS Time (in seconds) between retransmissions. It must be greater than the expected round-trip delay between any two routers on the attached network. The range is from 1 to seconds. The default is 5 seconds Interface Configuration 5 seconds When a router sends an LSA to its neighbor, it keeps the LSA until it receives back the acknowledgment message. If the router receives no acknowledgment, it will resend the LSA. The setting of this parameter should be conservative, or needless retransmission will result. The value should be larger for serial lines and virtual links. 19
20 The following example sets the retransmit interval value to 8 seconds: Switch(config)# interface eth-0-1 Switch(config-if)# no switchport Switch(config-if)# ipv6 ospf retransmit-interval ipv6 ospf transmit-delay To set the estimated time required to send a link-state update packet on the interface, use the ipv6 ospf transmit-delay command in interface configuration mode. To return to the default value, use the no form of this command. ipv6 ospf transmit-delay SECONDS no ipv6 ospf transmit-delay SECONDS Time (in seconds) between retransmissions. It must be greater than the expected round-trip delay between any two routers on the attached network. The range is from 1 to seconds. The default is 5 seconds Interface Configuration 1 second Link-state advertisements (LSAs) in the update packet must have their ages incremented by the amount specified in the seconds argument before transmission. The value assigned should take into account the transmission and propagation delays for the interface. If the delay is not added before transmission over a link, the time in which the LSA propagates over the link is not considered. This setting has more significance on very low-speed links. 20
21 The following example sets the retransmit delay value to 3 seconds: Switch(config)# interface eth-0-1 Switch(config-if)# no switchport Switch(config-if)# ipv6 ospf transmit-delay passive-interface (OSPF) To disable sending routing updates for the Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) on an interface, use the passive-interface command in router configuration mode. To re-enable the sending of routing updates, use the no form of this command. passive-interface INTERFACE-ID no passive-interface INTERFACE-ID INTERFACE-ID The interface name Router Configuration Routing updates are sent on the interface. If you disable the sending of routing updates on an interface, the particular subnet will continue to be advertised to other interfaces, and updates from other switches on that interface continue to be received and processed. The following example sets the interface eth-0-1 as passive: Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf
22 Switch(config-router)# passive-interface eth-0-1 router ipv6 ospf 1.19 redistribute (OSPFv3) To redistribute routes from one routing domain into Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) routing domain, use the redistribute command in router configuration mode. To disable redistribution, use the no form of this command. redistribute PROTOCOL [route-map WORD] [tag TAG-VALUE] [metric METRIC-VALUE] [metric-type TYPE-VALUE] no redistribute PROTOCOL[route-map WORD] [tag TAG-VALUE] [metric METRIC -VALUE] [metric-type TYPE-VALUE] route-map WORD PROTOCOL Route map reference. WORD :Pointer to route-map entries tag tag-value Set tag for routes redistributed into OSPF.tag-value: < > 32-bit tag value (Optional) The name of a routing protocol, or the keyword connected, or static. If you specify a routing protocol, use one of the following keywords: bgp, and ripng tag TAG-VALUE Set tag for routes redistributed into OSPF.tag-value: < > 32-bit tag value metric METRIC-VALUE metric-type TYPE-VALUE (Optional) When redistributing other processes to an OSPF process, the default metric is 20 when no metric value is specified For OSPF, the external link type associated with the default route advertised into the OSPF routing domain. It can be one of two values Router Configuration Route redistribution is disabled. metric metric-value: 20 metric-type TYPE-VALUE: Type 2 external route 22
23 The metric value specified in the redistribute command supersedes the metric value specified using the default-metric command. The following example redistribute the static routes into OSPFv3 with metric 10: Switch(config)# router ospf 119 Switch(config-router)# redistribute static metric 10 default-metric 1.20 router-id (OSPF) To use a fixed router ID, use the router-id command in router configuration mode. To force Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) to use the previous OSPF router ID behavior, use the no form of this command. router-id IP-ADDRESS no router-id IP-ADDRESS Router ID in IP address format Router Configuration No OSPF routing process is defined. You can configure an arbitrary value in the IP address format for each router. However, each router ID must be unique. 23
24 If this command is used on an OSPFv3 router process which is already active (has neighbors), the new router-id is used at the next reload or at a manual OSPFv3 process restart. To manually restart the OSPFv3 process, use the clear ip ospf command. The following example specifies a fixed router-id: Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf 119 Switch(config-router)# router-id clear ipv6 ospf router ipv6 ospf 1.21 router ipv6 ospf To configure an Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) routing process, use the router ipv6 ospf command in global configuration mode. To terminate an OSPFv3s routing process, use the no form of this command. router ipv6 ospf [PROCESS-ID] no router ipv6 ospf [PROCESS-ID] PROCESS-ID Internally used identification parameter for an OSPF routing process. It is locally assigned and can be any positive integer. A unique value is assigned for each OSPF routing process Global Configuration No OSPF routing process is defined. You can specify multiple OSPFv3 routing processes in each router. If you do not specify the process-id, the process-id will be the default 0. 24
25 The following example configures an OSPFv3 routing process and assigns a process number of 109: Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf summary-address (OSPFv3) To create aggregate addresses for Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3), use the summary-address command in router configuration mode. To restore the default, use the no form of this command. summary-address PREFIX / PREFIX-LENGTH (not-advertise tag TAG-VALUE ) no summary-address PREFIX / PREFIX-LENGTH (not-advertise tag TAG-VALUE ) PREFIX PREFIX-LENGTH not-advertise tag TAG- VALUE IP route prefix for the destination Prefix length for the network (Optional) Suppress routes that match the specified prefix/mask pair. This keyword applies to OSPFv3 only < > Set tag. tag-value:32-bit tag value Router Configuration This command is disabled by default. Routes learned from other routing protocols can be summarized. The metric used to advertise the summary is the largest metric of all the more specific routes. This command helps reduce the size of the routing table. Using this command for OSPFv3 causes an OSPFv3 Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) to advertise one external route as an aggregate for all redistributed routes that are 25
26 covered by the address. For OSPFv3, this command summarizes only routes from other routing protocols that are being redistributed into OSPFv3. Use the area range command for route summarization between OSPF areas. OSPFv3 does not support the summary-address /0 command. In the following example, the summary address 2001:1:1::/48 includes address 2001:1:1:1::/64, 2001:1:1:2::/64, and so on. Only the address 2001:1:1::/48 is advertised in an external link-state advertisement. Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf Switch(config-router)# summary-address 2001:1:1::/48 area range 1.23 show ipv6 ospf To display general information about Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) routing processes, use the show ipv6 ospf command in user EXEC or privileged EXEC mode. show ipv6 ospf (PROCESS-ID ) PROCESS-ID Internally used identification parameter for an OSPFv3 routing process. It is locally assigned and can be any positive integer. A unique value is assigned for each OSPFv3 routing process Privileged EXEC 26
27 The following is sample output from the show ipv6 ospf command when entered without a specific OSPFv3 process ID: Switch# show ip ospf Routing Process "OSPFv3 (65535)" with ID Process uptime is 1 hour 52 minutes SPF schedule delay min secs, SPF schedule delay max 50.0 secs Minimum LSA interval 5 secs, Minimum LSA arrival 1 secs Number of incomming current DD exchange neighbors 0/5 Number of outgoing current DD exchange neighbors 0/5 Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x0000 Number of AS-Scoped Unknown LSA 0 Number of LSA originated 3 Number of LSA received 19 Number of areas in this router is 1 Area BACKBONE(0) Number of interfaces in this area is 1(1) SPF algorithm executed 6 times Number of LSA 4. Number of Unknown LSA 0 Checksum Sum 0x show ipv6 ospf database To display lists of information related to the Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) database for a specific router, use the show ip ospf database command in EXEC mode. show ipv6 ospf (PROCESS-ID ) database show ipv6 ospf (PROCESS-ID ) database adv-router ROUTER-ID show ipv6 ospf (PROCESS-ID ) database (external inter-prefix inter-router intra-prefix link network router ) [LINK-STATE-ID] [adv-router ROUTER-ID self-originate ] show ipv6 ospf (PROCESS-ID ) database max-age show ipv6 ospf (PROCESS-ID ) database self-originate PROCESS-ID adv-router Internally used identification parameter for an OSPFv3 routing process. It is locally assigned and can be any positive integer. A unique value is assigned for each OSPFv3 routing process (Optional) Displays all the LSAs of the specified router. If no IP address is included, the information is about the local router itself (in this case, the same 27
28 [IP-ADDRESS] LINK-STATE-ID as self-originate) (Optional) Portion of the Internet environment that is being described by the advertisement. The value entered depends on the advertisement s LS type. It must be entered in the form of an IP address Privileged EXEC The various forms of this command deliver information about different OSPFv3 link state advertisements. The following is sample output from the show ipv6 ospf database command when no arguments or keywords are used: Switch# show ip ospf database OSPFv3 Router with ID ( ) (Process 65535) Link-LSA (Interface vlan1000) Link State ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum Prefix x x27e x xcc94 1 Router-LSA (Area ) Link State ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum Link x x42d x x24f0 1 Network-LSA (Area ) Link State ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum x x7f99 Intra-Area-Prefix-LSA (Area ) Link State ID ADV Router Age Seq# CkSum Prefix Reference x x96fd 2 Network-LSA 28
29 1.25 show ipv6 ospf interface To display Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3)-related interface information; use the show ipv6 ospf interface command in EXEC mode. show ipv6 ospf interface [INTERFACE-NAME] INTERFACE-NAME (Optional) Interface name. If the interface-name argument is included, only information for the specified interface is included Privileged EXEC The following is sample output of the show ipv6 ospf interface command when vlan12 is specified: Switch# show ip ospf interface vlan12 vlan12 is up, line protocol is up Interface ID 4108 IPv6 Prefixes fe80::8eb5:d5ff:fed9:ff00/10 (Link-Local Address) 2004:12:0:12::1/96 OSPFv3 Process (0), Area , Instance ID 0 Router ID , Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State Backup, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) Interface Address fe80::188f:beff:fe99:9800 Backup Designated Router (ID) Interface Address fe80::8eb5:d5ff:fed9:ff00 29
30 Timer interval configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 Hello due in 00:00:06 Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is show ipv6 ospf neighbor To display Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3)-neighbor information on a per-interface basis, use the show ipv6 ospf neighbor command in privileged EXEC mode. show ipv6 ospf neighbor [INTERFACE-NAME (detail )] [NEIGHBOR-ID] INTERFACE-NAME NEIGHBOR-ID detail (Optional) Interface name. If the interface-name argument is included, only information for the specified interface is included (Optional) Neighbor ID (Optional) Displays all neighbors given in detail (lists all neighbors) Privileged EXEC The following is sample output from the show ipv6 ospf neighbor command showing a single line of summary information for each neighbor: Switch# show ip ospf neighbor OSPFv3 Process (0) Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface Instance ID Full/DR 00:00:31 vlan Full/DR 00:00:33 vlan
31 OSPFv3 Process (65535) Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface Instance ID Full/DR 00:00:31 vlan show ipv6 ospf database database-summary To display the summary of database used by OSPFv3, use the show ip ospf database database-summary command in privileged EXEC mode. show ipv6 ospf (PROCESS-ID )database database-summary PROCESS-ID (Optional) Internal identification. It is locally assigned and can be any positive integer. The number used here is the number assigned administratively when enabling the OSPF routing process Privileged EXEC The following example shows how to use show ipv6 ospf database database-summary command. Switch# show ipv6 ospf database database-summary OSPFv3 Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 65535) Area ( ) database summary LSA Type Count MaxAge Router 2 0 Network 1 0 Inter-Prefix
32 Inter-Router 0 0 Intra-Prefix 1 0 Subtotal 4 0 Process database summary LSA Type Count MaxAge Router 2 0 Network 1 0 Inter-Prefix 0 0 Inter-Router 0 0 Type-5 Ext 0 0 Link 2 0 Intra-Prefix 1 0 Total show ipv6 ospf route To display the summary of routes used by OSPFv3, use the show ipv6 ospf route summary command in privileged EXEC mode. show ipv6 ospf (PROCESS-ID ) route PROCESS-ID (Optional) Internal identification. It is locally assigned and can be any positive integer. The number used here is the number assigned administratively when enabling the OSPFv3 routing process Privileged EXEC 32
33 The following example shows how to use show ipv6 ospf route command. Switch# show ipv6 ospf route OSPFv3 Process (0) Codes: C - connected, D - Discard, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 Destination Metric Next-hop C 2004:1:0:10::/96 1 directly connected, vlan10, Area C 2004:1:0:20::/96 1 directly connected, vlan20, Area C 2004:1:0:100::/96 1 directly connected, vlan100, Area C 2004:1:0:200::/96 1 directly connected, vlan200, Area O 2004:2:0:10::/96 2 via fe80::188f:beff:fe99:9800, vlan1212, Area via fe80::188f:beff:fe99:9800, vlan12, Area IA 2004:2:0:20::/96 2 via fe80::188f:beff:fe99:9800, vlan1212, Area via fe80::188f:beff:fe99:9800, vlan12, Area show ipv6 ospf route summary To display the summary of routes used by OSPFv3, use the show ipv6 ospf route summary command in privileged EXEC mode. show ipv6 ospf (PROCESS-ID ) route summary PROCESS-ID (Optional) Internal identification. It is locally assigned and can be any positive integer. The number used here is the number assigned administratively when enabling the OSPFv3 routing process Privileged EXEC 33
34 The following example shows how to use show ipv6 ospf route summary command. Switch# show ipv6 ospf route summary OSPFv3 Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 0) Route Type Count (C)Connected 8 (D)Discard 0 (O)Intra area 2 (IA)Inter area 4 (E1)Ext type 1 0 (E2)Ext type 2 0 (N1)NSSA Ext type 1 0 (N2)NSSA Ext type 2 0 Total 14 OSPFv3 Router with ID ( ) (Process ID 65535) Route Type Count (C)Connected 1 (D)Discard 0 (O)Intra area 1 (IA)Inter area 0 (E1)Ext type 1 0 (E2)Ext type 2 0 (N1)NSSA Ext type 1 0 (N2)NSSA Ext type 2 0 Total show ipv6 protocols ospf To display IPv6 routing protocol process parameters and statistics of Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3).use the show ipv6 ospf protocols ospf command in privileged EXEC mode. 34
35 show ipv6 protocols ospf Privileged EXEC The following example shows how to use show ipv6 protocols ospf command. Switch # show ipv6 protocols ospf Routing Protocol is "OSPFv3 (0)" with ID Redistributing: Distance: (default is 110) Routing Protocol is "OSPFv3 (65535)" with ID Redistributing: Distance: (default is 110) 1.31 timers spf To turn on Open Shortest Path First Version3 (OSPFv3) shortest path first (SPF) throttling, use the timers spf command in router configuration mode. To turn off SPF throttling, use the no form of this command. timers spf exp SPF-HOLD_MIN SPF-HOLD_MAX no timers spf exp SPF-HOLD_MIN Indicates the maximum hold time between two consecutive SPF calculations. Value range is 0 to milliseconds 35
36 SPF-HOLD_MAX Indicates the minimum hold time between two consecutive SPF calculations. Value range is 0 to milliseconds Router Configuration The following example shows how to configure SPF calculation parameters. Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf 1 Switch(config-router)# router-id Switch(config-router)# timers spf exp max-concurrent-dd To specify Maximum number allowed to process DD concurrently, use the max-concurrent-dd command in router configuration mode. To restore default value, use the no form of this command max-concurrent-dd NUMBER-VALUE no max-concurrent-dd NUMBER-VALUE < >Number of DD process 36
37 Router Configuration This command used to specify Maximum number allowed to process DD concurrently. The following example shows how to use max-concurrent-dd command. Switch(config)# router ipv6 ospf 100 Switch(config-router)# router-id Switch(config-router)# max-concurrent-dd debug ipv6 ospf Use this command to specify all debugging options for OSPFv3. Use the no parameter with this command to disable this function. debug ipv6 ospf (all ) no debug ipv6 ospf (all ) all enable all debugging Privileged Exec 37
38 The debug ospf all command enables the display of all debug information. Switch# debug ipv6 ospf all 1.34 debug ipv6 ospf events Use this command to specify debugging options for OSPFv3 event troubleshooting. Use this command without parameters to turn on all the options. Use the no parameter with this command to disable this function. debug ipv6 ospf events (abr asbr nssa os router vlink) no debug ipv6 ospf events (abr asbr nssa os router vlink) abr asbr nssa os router vlink shows ABR events shows ASBR events shows NSSA events shows OS interaction events shows others router events shows virtual link events Privileged EXEC 38
39 The debug ospf event command enables the display of debug information related to OSPFv3 internal events. Switch# debug ipv6 ospf events nssa 1.35 debug ipv6 ospf ifsm Use this command to specify debugging options for OSPFv3 Interface Finite State Machine (IFSM) troubleshooting. Use the no parameter with this command to disable this function. debug ipv6 ospf ifsm (status ) (events ) (timers ) no debug ipv6 ospf ifsm (status ) (events ) (timers ) status events timers Displays IFSM status information Displays IFSM event information Displays IFSM TIMER information Privileged EXEC The debug ospf ifsm command enables the display of debug information related to the Interface Finite State Machine (IFSM). 39
40 Switch# debug ipv6 ospf ifsm timers 1.36 debug ipv6 ospf nfsm Use this command to specify debugging options for OSPFv3 Neighbor Finite State Machine (NFSM) troubleshooting. Use the no parameter with this command to disable this function. debug ipv6 ospf nfsm (status events timers ) no debug ipv6 ospf nfsm (status events timers ) status events timers Displays NFSM status information Displays NFSM event information Displays NFSM TIMER information Privileged EXEC The debug ospf nfsm command enables the display of debug information related to the Neighbor Finite State Machine (NFSM). Switch# debug ipv6 ospf nfsm timers 40
41 1.37 debug ipv6 ospf lsa Use this command to specify debugging options for OSPFv3 Link State Advertisements (LSA) troubleshooting. Use the no parameter with this command to disable this function. debug ipv6 ospf lsa (flooding generate install maxage refresh ) no debug ipv6 ospf lsa (flooding generate install maxage refresh ) flooding generate install maxage refresh Displays LSA flooding Displays LSA generate Displays LSA installation Displays the maximum age of LSA in seconds Displays LSA refresh Privileged EXEC The debug ospf lsa command enables the display of debug information related to internal operations of LSAs. Switch# debug ipv6 ospf lsa install 41
42 1.38 debug ipv6 ospf packet Use this command to specify debugging options for OSPFv3 packets. Use the no parameter with this command to disable this function.. debug ipv6 ospf packet [PARAMETERS] no debug ipv6 ospf packet [PARAMETERS] PARAMETERS = dd detail hello ls-ack ls-request ls-update recv send dd detail hello ls-ack ls-request ls-update recv send Specifies debugging for OSPF database descriptions Sets the debug option to detailed information Specifies debugging for OSPF hello packets Specifies debugging for OSPF link state acknowledgments Specifies debugging for OSPF link state requests Specifies debugging for OSPF link state updates Specifies the debug option set for received packets Specifies the debug option set for sent packets Privileged EXEC The debug ospf packet command enables the display of debug information related to the sending and receiving of packets. Switch# debug ipv6 ospf packet dd send detail 42
43 1.39 debug ipv6 ospf route Use this command to specify which route calculation to debug. Use this command without parameters to turn on all the options. Use the no parameter with this command to disable this function. debug ipv6 ospf route (ase ia install spf ) no debug ipv6 ospf route (ase ia install spf ) ase ia install spf Specifies the debugging of external route calculation Specifies the debugging of Inter-Area route calculation Specifies the debugging of route installation Specifies the debugging of SPF calculation Privileged EXEC The debug ospf route command enables the display of debug information related to route-calculation Switch# debug ipv6 ospf route install 1.40 show debugging ipv6 ospf Use this command to display the set OSPFv3 debugging option.. 43
44 show debugging ipv6 ospf Privileged EXEC This is a sample output from the show debugging ipv6 ospf command. Some lines in this output wrap around, they might not wrap around in the actual display. Switch# show debugging ipv6 ospf OSPFv3 debugging status: OSPFv3 all packet detail debugging is on OSPFv3 all IFSM debugging is on OSPFv3 all NFSM debugging is on OSPFv3 all LSA debugging is on OSPFv3 all route calculation debugging is on OSPFv3 all event debugging is on 1.41 show resource ipv6 ospf Use this command to display the route resources used by OSPFv3 protocol. show resource ipov6 ospf Privileged EXEC 44
45 . The following is sample output from the show resource ipv6 ospf command: Switch# show resource ipv6 ospf OSPFv3 Resource Used Capability ============================================================= Routes show ipv6 ospf route summary 45
46 2 RIPng Commands 2.1 router ipv6 rip To enable or configure the Routing Information Protocol next generation (RIPng) routing process, use the router ipv6 rip command in global configuration mode. To disable the RIPng routing process, use the no form of this command. router ipv6 rip no router ipv6 rip Global Configuration No RIPng routing process is defined. The following example shows how to begin the RIPng routing process: Switch(config)# router ipv6 rip 46
47 2.2 ipv6 router rip To enable RIPng routing process on specifical interface, use the command ipv6 router rip in interface configuration mode. Use the no parameter with this command to disable RIPng routing process on interface. ipv6 router rip no ipv6 router rip Interface configuration. Use this command to enable RIPng routing on the interface. In the following example, enable RIPng routing on the interface eth-0-1. Switch (config)# interface eth-0-1 Switch (config-if)# no switchport Switch (config-if)# ipv6 router rip 2.3 ipv6 rip metric-offset Use this command to set RIP metric offset in interface mode. To restore the default metric, use the no form of this command. ipv6 rip metric-offset NUMBER-VALUE no ipv6 rip metric-offset 47
48 NUMBER-VALUE metric value is 1, the number range is 1 to 16 Interface configuration Metric offset value is 1. Metric offset value is used to add the metric of the network on which the message arrived (as the RFC describes).. In the following example, RIPng specify the adding metric value 2 when the RIPng message arrives Switch(config)#interface eth-0-1 Switch (config-if)# ipv6 rip metric-offset ipv6 rip split-horizon To enable the split horizon mechanism for Routing Information Protocol next generation (RIPng), use the ipv6 rip split-horizon command in interface configuration mode. To disable the split horizon mechanism, use the no form of this command. ipv6 rip split-horizon (poisoned ) no ipv6 rip split-horizon poisoned Split horizon with poisoned reverse 48
49 Interface Configuration This command is enabled with poisoned reverse by default. In general, changing the default state for the ipv6 rip split-horizon command is not recommended, unless you are certain that your application requires a change in order to properly advertise routes. The following example enables split horizon without poisoned reverse: Switch(config)# interface eth-0-1 Switch(config-if)# ipv6 rip split- horizon 2.5 default-information originate (RIPng) To generate a default route into Routing Information Protocol next generation (RIPng), use the default-information originate command in router configuration mode. To disable this feature, use the no form of this command. default-information originate (route-map name ) no default-information originate route-map name Route map reference Router Configuration 49
50 This command is disabled by default. The default route can be learned by neighbor, but can t be stored in FIB. The following example originates a default route (0::0/0) into RIPng. Switch(config)# router ipv6 rip Switch(config-router)# default-information originate 2.6 default-metric (RIPng) To specify the metrics to be assigned to redistributed routers for Routing Information Protocol next generation (RIPng), use the default-metric command in router configuration mode. To return to the default state, use the no form of this command. default-metric NUMBER-VALUE no default-metric NUMBER-VALUE metric value is 1, the number range is 1 to 16 Router Configuration By default, the metric is set to 1. 50
51 The default-metric command is used in conjunction with the redistribute router configuration command to cause the current routing protocol to use the same metric value for all redistributed routes. A default metric helps solve the problem of redistributing routes with incompatible metrics. Whenever metrics do not convert, using a default metric provides a reasonable substitute and enables the redistribution to proceed. The following example shows a switch using both the RIPng and the Open Shortest Path First (OSPFv3) routing protocols. The example advertises OSPFv3-derived routes using RIPng and assigns the OSPFv3-derived routes a RIPng metric of 10. Switch(config)# router ipv6 rip Switch(config-router)#default-metric 10 Switch(config-router)#redistribute ospfv3 redistribute (RIPng) 2.7 distance (RIPng) To define an administrative distance for routes that are inserted into the routing table, use the distance command in router configuration mode. To return the administrative distance to its default distance definition, use the no form of this command. distance DISTANCE no distance DISTANCE Administrative distance, an integer from 1 to 255 (routes with a distance value of 255 are not installed in the routing table) Router Configuration By default, the distance is
52 Route Source Distance Connected interface 0 Static route 1 External Border Gateway Protocol (ebgp) 20 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) 110 Routing Information Protocol (RIP)/ Routing Information Protocol next generation (RIPng) 120 Internal BGP 200 Unknown 255 An administrative distance is a rating of the trustworthiness of a routing information source, such as an individual switch or a group of switches. Numerically, an administrative distance is an integer from 0 to 255. In general, the higher the value is, the lower the trust rating. An administrative distance of 255 means the routing information source cannot be trusted at all and should be ignored. The following is sample output from the distance command: Switch(config)#router ipv6 rip Switch(config-router)#distance neighbor (RIPng) To specify a neighboring router to which to notify routing updating information, use the neighbor command in router configuration mode. To remove the neighbor, use the no form of this command. neighbor IP-ADDRESS INTERFACE-NAME no neighbor IP-ADDRESS INTERFACE-NAME 52
53 IP-ADDRESS INTERFACE-NAME Link-local IP address of a peer switch with which routing information will be notified Interface name to which the neighbor is specified Router Configuration No neighboring switches are defined. Especially use the neighbor command in conjunction with the passive-interface command to send routing updates to specific neighbors. This command permits the point-to-point (non-multicast) notification of routing update information. Multiple neighbors can be configured In the following example, RIPng updates are sent to all interfaces which have been enabled RIPng routing except eth-0-1. However, in this case a neighbor switch configuration command is included. This command permits the sending of routing updates to specific neighbors. Switch(config)#router ipv6 rip Switch(config-router)# passive-interface eth-0-1 Switch(config-router)# neighbor fe80:db8::1 eth-0-1 router rip 2.9 offset-list (RIPng) To add an offset to incoming and outgoing metrics to routes exchangion via Routing Information Protocol next generation (RIPng), use the offset-list command in router configuration mode. To remove an offset list, use the no form of this command. offset-list ACCESSS-LIST-NAME (in out) METRIC-OFFSET (INTERFACE-NAME ) no offset-list (in out) (INTERFACE-NAME ) 53
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FSOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 5 1.1 area default-cost...5 1.2 area range...6 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS. IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 6 1.1 area default-cost... 6 1.2 area range...7 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 OSPFv3 Commands... 6 1.1 area default-cost... 6 1.2 area range...7 1.3 area stub... 7 1.4 auto-cost...8 1.5 clear ipv6 ospf...9 1.6 default-information
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 IP Unicast-Routing Commands...6 1.1 ip address...6 1.2 ip icmp error-interval...7 1.3 ip redirects... 8 1.4 ip unreachables...9 1.5 ip verify unicast
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 IP Unicast-Routing Commands...6 1.1 ip address...6 1.2 ip icmp error-interval...7 1.3 ip redirects... 8 1.4 ip unreachables...9 1.5 ip verify unicast
FSOS IP Routing Command Line Reference
 FSOS IP Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 IP Unicast-Routing Commands... 7 1.1 ip address...7 1.2 ip icmp error-interval... 9 1.3 ip redirects...10 1.4 ip unreachables...11 1.5 ip verify unicast
FSOS IP Routing Command Line Reference Contents 1 IP Unicast-Routing Commands... 7 1.1 ip address...7 1.2 ip icmp error-interval... 9 1.3 ip redirects...10 1.4 ip unreachables...11 1.5 ip verify unicast
FiberstoreOS. IP Routing Command Line Reference
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 IP Unicast-Routing Commands...7 1.1 ip address... 7 1.2 ip icmp error-interval...8 1.3 ip redirects... 9 1.4 ip unreachables...9 1.5 ip verify
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Command Line Reference 1 Contents 1 IP Unicast-Routing Commands...7 1.1 ip address... 7 1.2 ip icmp error-interval...8 1.3 ip redirects... 9 1.4 ip unreachables...9 1.5 ip verify
OSPF Commands. Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 3: Routing Protocols IP2R-61
 OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
OSPF Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For OSPF configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring OSPF
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Topology... 6 1.3 Configuration... 6 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP... 10 2.1 Overview...10
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview...6 1.2 Topology... 6 1.3 Configuration... 6 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP... 10 2.1 Overview...10
OSPF Commands: A through Z
 OSPF Commands: A through Z area nssa, page 3 area nssa translate, page 5 area virtual-link, page 9 capability vrf-lite, page 13 capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3), page 15 clear ip ospf, page 17 compatible rfc1587,
OSPF Commands: A through Z area nssa, page 3 area nssa translate, page 5 area virtual-link, page 9 capability vrf-lite, page 13 capability vrf-lite (OSPFv3), page 15 clear ip ospf, page 17 compatible rfc1587,
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
FiberstoreOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 1 1.1 Overview... 1 1.2 Topology...1 1.3 Configuration... 2 1.4 Validation... 3 2 Configuring RIP...5 2.1 Overview...
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide
 FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
FSOS IP Routing Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IP Unicast-Routing... 6 1.1 Overview... 6 1.2 Topology...6 1.3 Configuration... 7 1.4 Validation... 8 2 Configuring RIP...10 2.1 Overview... 10
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands
 Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
Chapter 16 OSPF Version 3 Commands NOTE: The OSPF version 3 configuration level is present only on HP devices that support IPv6. area Assigns OSPF version 3 areas. You can assign an IPv4 address or a number
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
OSPFv3 Address Families
 The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
The Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) address families feature enables both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast traffic to be supported. With this feature, users may have two processes per interface, but only
Configuring Networking Protocols
 11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
11 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure the ML-Series card for supported IP routing protocols. It is intended to provide enough information for a network administrator to get the protocols up
OSPFv3 Commands. address-family (OSPFv3), page 4. authentication (OSPFv3), page 7
 This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the IP Version 6 (IPv6) Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPFv3 concepts, configuration
This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the IP Version 6 (IPv6) Open Shortest Path First Version 3 (OSPFv3) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPFv3 concepts, configuration
OSPF Commands. adjacency stagger, page 7. authentication-key (OSPF), page 14
 OSPF Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and
OSPF Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and
IPv6 Routing: OSPFv3
 Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) is an IPv4 and IPv6 link-state routing protocol that supports IPv6 and IPv4 unicast address families (AFs). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites
Open Shortest Path First version 3 (OSPFv3) is an IPv4 and IPv6 link-state routing protocol that supports IPv6 and IPv4 unicast address families (AFs). Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites
OSPF Commands on Cisco IOS XR Software
 This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration RIP Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
Table of Contents 1 Static Routing Configuration 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Static Route 1-1 Default Route 1-1 Application Environment of Static Routing 1-1 Configuring a Static Route 1-2 Configuration Prerequisites
A Commands. Send comments to
 This chapter describes the Cisco NX-OS Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) commands that begin with A. UCR-555 area authentication (OSPF) area authentication (OSPF) To enable authentication for an Open Shortest
This chapter describes the Cisco NX-OS Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) commands that begin with A. UCR-555 area authentication (OSPF) area authentication (OSPF) To enable authentication for an Open Shortest
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands
 Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
Chapter 15 OSPF Commands NOTE: This chapter contains information about OSPF version 2 commands only. For information about OSPF version 3 commands, see OSPF Version 3 Commands on page 16-1. area Assigns
How To Configure Basic OSPFv3 Scenarios
 How To Configure Basic OSPFv3 Scenarios Contents 1. Contents...... 1 2. Introduction...... 2 3. OSPFv3 Basic Configuration...... 3 Commands for basic OSPFv3 configuration... 4 OSPFv3 basic configuration
How To Configure Basic OSPFv3 Scenarios Contents 1. Contents...... 1 2. Introduction...... 2 3. OSPFv3 Basic Configuration...... 3 Commands for basic OSPFv3 configuration... 4 OSPFv3 basic configuration
OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router
 OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF
OSPF Commands on Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. For detailed information about OSPF
OSPF. About OSPF. CLI Book 1: Cisco ASA Series General Operations CLI Configuration Guide, 9.4 1
 This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Open Shortest Path First () routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco ASA to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Open Shortest Path First () routing protocol. About, page 1 Guidelines
Sample Configuration for OSPFv3
 Sample Configuration for OSPFv3 Document ID: 112100 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configuration Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
Sample Configuration for OSPFv3 Document ID: 112100 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configuration Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Table of Contents 1 OSPF Configuration 1-1 Introduction to OSPF 1-1 Basic Concepts 1-2 OSPF Area Partition 1-4 Router Types 1-7 Classification of OSPF Networks 1-9 DR and BDR 1-9 OSPF Packet Formats 1-11
Brocade 5600 vrouter OSPFv3 Configuration Guide
 CONFIGURATION GUIDE Brocade 5600 vrouter OSPFv3 Configuration Guide Supporting Brocade 5600 vrouter 4.2R1 53-1004266-01 16 May 2016 2016, Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Brocade,
CONFIGURATION GUIDE Brocade 5600 vrouter OSPFv3 Configuration Guide Supporting Brocade 5600 vrouter 4.2R1 53-1004266-01 16 May 2016 2016, Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Brocade,
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands
 IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
IP Enhanced IGRP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor IP Enhanced IGRP. For configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring IP Enhanced IGRP chapter of the
Operation Manual IPv4 Routing H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Static Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Default Route... 1-1 1.1.3 Application Environment of Static Routing...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration... 1-1 1.1 Introduction... 1-1 1.1.1 Static Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Default Route... 1-1 1.1.3 Application Environment of Static Routing...
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
Operation Manual Routing Protocol. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 IP Routing Protocol Overview... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to IP Route and Routing Table... 1-1 1.1.1 IP Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Routing Table... 1-1 1.2 Routing Management
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 IP Routing Protocol Overview... 1-1 1.1 Introduction to IP Route and Routing Table... 1-1 1.1.1 IP Route... 1-1 1.1.2 Routing Table... 1-1 1.2 Routing Management
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF
 Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
Chapter 8 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF on HP routing switches using the CLI and Web management interface. To display OSPF configuration information and statistics, see
Brocade 5600 vrouter OSPFv3
 14 September 2015 Brocade 5600 vrouter OSPFv3 Reference Guide Supporting Brocade 5600 vrouter 3.5R6 2015, Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ADX, Brocade, Brocade Assurance, the
14 September 2015 Brocade 5600 vrouter OSPFv3 Reference Guide Supporting Brocade 5600 vrouter 3.5R6 2015, Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ADX, Brocade, Brocade Assurance, the
Configuring OSPF. Cisco s OSPF Implementation
 Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
Configuring OSPF This chapter describes how to configure OSPF. For a complete description of the OSPF commands in this chapter, refer to the OSPF s chapter of the Network Protocols Reference, Part 1. To
OSPF Protocol Overview on page 187. OSPF Standards on page 188. OSPF Area Terminology on page 188. OSPF Routing Algorithm on page 190
 Chapter 17 OSPF Protocol Overview The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF uses link-state information
Chapter 17 OSPF Protocol Overview The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) that routes packets within a single autonomous system (AS). OSPF uses link-state information
Command Manual IPv4 Routing H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1.1 delete static-routes all... 1-1 1.1.2 ip route-static...
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1 Static Routing Configuration Commands... 1-1 1.1.1 delete static-routes all... 1-1 1.1.2 ip route-static...
Routing Configuration Commands
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1.1 auto-summary...2 1.1.2 -information originate...3 1.1.3 -metric...3 1.1.4 ip rip authentication...4
Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1 RIP Configuration Commands...1 1.1.1 auto-summary...2 1.1.2 -information originate...3 1.1.3 -metric...3 1.1.4 ip rip authentication...4
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv3 Topology
 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address R1 R2 R3 S0/0/0 (DCE) Lo0 Lo1 Lo2 Lo3 S0/0/0 S0/0/1
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address R1 R2 R3 S0/0/0 (DCE) Lo0 Lo1 Lo2 Lo3 S0/0/0 S0/0/1
OSPF Stub Router Advertisement
 The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
The feature allows you to bring a new router into a network without immediately routing traffic through the new router and allows you to gracefully shut down or reload a router without dropping packets
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Link State Routing. Link State Packets. Link State Protocol. Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and pitfalls
 Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 16.3, 2017/03/09 11:25:31) Tuesday, March 7, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and
Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 16.3, 2017/03/09 11:25:31) Tuesday, March 7, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and
IPv6 Commands: sn to v
 IPv6 Commands: sn to v sntp address, page 3 spd extended-headroom, page 5 spd headroom, page 7 spf-interval (IPv6), page 9 split-horizon (IPv6 RIP), page 11 standby ipv6, page 13 summary-prefix (IPv6 IS-IS),
IPv6 Commands: sn to v sntp address, page 3 spd extended-headroom, page 5 spd headroom, page 7 spf-interval (IPv6), page 9 split-horizon (IPv6 RIP), page 11 standby ipv6, page 13 summary-prefix (IPv6 IS-IS),
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information
 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by the OSPF working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). OSPF
RIP Commands. output-delay, page 32 passive-interface (RIP), page 33 poison-reverse, page 35 receive version, page 37 redistribute (RIP), page 39
 RIP Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). For detailed information about RIP concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
RIP Commands This module describes the commands used to configure and monitor the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). For detailed information about RIP concepts, configuration tasks, and examples, see
Configuring OSPF. Finding Feature Information. Contents
 Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
Configuring OSPF First Published: May 5, 2008 Last Updated: March 18 2011 This module describes how to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) developed by
Table of Contents. 2 Static Route Configuration Commands 2-1 Static Route Configuration Commands 2-1 delete static-routes all 2-1 ip route-static 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 display ip routing-table 1-1 display ip routing-table acl 1-3 display ip routing-table ip-address 1-5 display ip routing-table
Table of Contents 1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 IP Routing Table Commands 1-1 display ip routing-table 1-1 display ip routing-table acl 1-3 display ip routing-table ip-address 1-5 display ip routing-table
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Agenda OSPF Primer OSPF in Service Provider Networks OSPF BCP - Adding Networks OSPF Command Summary 2 OSPF Primer 3
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Agenda OSPF Primer OSPF in Service Provider Networks OSPF BCP - Adding Networks OSPF Command Summary 2 OSPF Primer 3
Config. Router# show ip ospf
 Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
Config cc na c ookb ook.com R1(config)#router ospf 10 R1(config-router)#router-id 0.0.0.1 Do router-id first, before relationships are formed using it R3(config-router)#do clear ip ospf process Necessary
IP Routing Volume Organization
 IP Routing Volume Organization Manual Version 20091105-C-1.03 Product Version Release 6300 series Organization The IP Routing Volume is organized as follows: Features IP Routing Overview Static Routing
IP Routing Volume Organization Manual Version 20091105-C-1.03 Product Version Release 6300 series Organization The IP Routing Volume is organized as follows: Features IP Routing Overview Static Routing
Operation Manual OSPF. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 OSPF Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to OSPF... 1-1 1.1.2 Process of OSPF Route Calculation... 1-2 1.1.3 OSPF Packets... 1-2 1.1.4 LSA Type... 1-3 1.1.5
Table of Contents Table of Contents... 1-1 1.1 OSPF Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 Introduction to OSPF... 1-1 1.1.2 Process of OSPF Route Calculation... 1-2 1.1.3 OSPF Packets... 1-2 1.1.4 LSA Type... 1-3 1.1.5
Configuring RIP. Information About RIP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 23 This chapter describes how to configure the ASASM to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). This chapter includes
CHAPTER 23 This chapter describes how to configure the ASASM to route data, perform authentication, and redistribute routing information using the Routing Information Protocol (RIP). This chapter includes
Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP
 Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
Appendix D Memory Tables Chapter 1 Table 1-2 Routing Protocol Characteristics Routing Protocol Type Primarily IGP or EGP RIP Distance-Vector IGP EIGRP OSPF IS-IS BGP Chapter 3 Table 3-2 Hexadecimal/Binary
Basic IP Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About Basic IP Routing. Variable-Length Subnet Masks
 This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
Chapter 1 The IP Routing Protocols
 Chapter 1 The IP Routing Protocols 1 This chapter describes routing protocol options for the Internet Protocol (IP) suite. The chapter Routing IP contains all the information you need for configuring IP.
Chapter 1 The IP Routing Protocols 1 This chapter describes routing protocol options for the Internet Protocol (IP) suite. The chapter Routing IP contains all the information you need for configuring IP.
Logging neighbor state changes 38 Configuring OSPF network management 39 Enabling message logging 39 Enabling the advertisement and reception of
 Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 Area based OSPF network partition 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported features
Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 Area based OSPF network partition 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported features
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training
 REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
REDDIG II Computer Networking Training JM SANCHEZ / PH RASSAT -20/06/2012 Invierno 2011 Capacitacion en fabrica - CORPAC Dynamic Routing Dynamic Routing Function(s) of Dynamic Routing Protocols: Dynamically
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers
 OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Finding Feature Information OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers Last Updated: June 24, 2011 The OSPF Support for Multi-VRF on CE Routers feature provides the
Link State Routing. Link State Packets. Link State Protocol. Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems and pitfalls
 Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 17.4, 2017/11/30 12:33:57) Tuesday, November 28, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems
Link State Routing In particular OSPF Karst Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam (version 17.4, 2017/11/30 12:33:57) Tuesday, November 28, 2017 Link State Protocols Basic ideas Problems
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives Configure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies. Verify
IPv6 Commands: ipv6 ospf de to ipv6 sp
 ipv6 ospf dead-interval, on page 3 ipv6 ospf demand-circuit, on page 5 ipv6 ospf encryption, on page 7 ipv6 ospf flood-reduction, on page 9 ipv6 ospf hello-interval, on page 11 ipv6 ospf mtu-ignore, on
ipv6 ospf dead-interval, on page 3 ipv6 ospf demand-circuit, on page 5 ipv6 ospf encryption, on page 7 ipv6 ospf flood-reduction, on page 9 ipv6 ospf hello-interval, on page 11 ipv6 ospf mtu-ignore, on
Configuring OSPF with CLI
 OSPF Configuring OSPF with CLI This section provides information to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) using the command line interface. Topics in this section include: OSPF Configuration Guidelines
OSPF Configuring OSPF with CLI This section provides information to configure Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) using the command line interface. Topics in this section include: OSPF Configuration Guidelines
HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches
 HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Routing Command Reference Part number: 5998-3168a Software version: Release 2103 and later Document version: 6W102-20141218 Legal and notice information
HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Routing Command Reference Part number: 5998-3168a Software version: Release 2103 and later Document version: 6W102-20141218 Legal and notice information
Basic IP Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About Basic IP Routing. Variable-Length Subnet Masks
 This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
This module describes how to configure basic IP routing. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a network layer (Layer 3) protocol that contains addressing information and some control information that enables
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
Introduction to OSPF 1 OSPF Open Shortest Path First Link state or SPF technology Developed by OSPF working group of IETF (RFC 1247) OSPFv2 standard described in RFC2328 Designed for: TCP/IP environment
2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 OSPFv3 2 OSPFv2 Latest revision is RFC 2328 April 1998 OSPF uses a 2 level hierarchical model SPF calculation is performed independently for each area Typically
2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 OSPFv3 2 OSPFv2 Latest revision is RFC 2328 April 1998 OSPF uses a 2 level hierarchical model SPF calculation is performed independently for each area Typically
Juniper Exam JN0-643 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) Version: 13.0 [ Total Questions: 221 ]
![Juniper Exam JN0-643 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) Version: 13.0 [ Total Questions: 221 ] Juniper Exam JN0-643 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) Version: 13.0 [ Total Questions: 221 ]](/thumbs/85/92097848.jpg) s@lm@n Juniper Exam JN0-643 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) Version: 13.0 [ Total Questions: 221 ] Topic 1, Volume A Question No : 1 - (Topic 1) Which connection method do OSPF
s@lm@n Juniper Exam JN0-643 Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional (JNCIP-ENT) Version: 13.0 [ Total Questions: 221 ] Topic 1, Volume A Question No : 1 - (Topic 1) Which connection method do OSPF
Explanation: In order to verify proper route redistribution, use the "show ip route" command on all routers
 QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
QUESTION 401 The 192.168.0.0/16 network is not being propagated throughout the network via BGP as expected. Observe the BGP configuration commands from the advertising router shown below. Router bgp 65111
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example
 Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
Easy Virtual Network Configuration Example Document ID: 117974 Contributed by Fabrice Ducomble, Cisco TAC Engineer. Aug 04, 2014 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background
Configuration and Management of Networks
 onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
onfiguration and Management of Networks Single Area SPF Link osts and Interface Priorities The lab is built on the topology: bjectives Background! onfigure single-area SPF on a r.! Advertise loopback interfaces
Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent. Exam Code: 4A Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability.
 Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent Exam Code: 4A0-101 Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Version: Demo QUESTION 1 When a router receives an IP packet, but does not find a match
Vendor: Alcatel-Lucent Exam Code: 4A0-101 Exam Name: Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability Version: Demo QUESTION 1 When a router receives an IP packet, but does not find a match
Configuring OSPF network management 39 Enabling message logging 39 Enabling the advertisement and reception of opaque LSAs 40 Configuring OSPF to
 Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 OSPF areas 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported OSPF features 17 Protocols and
Contents Configuring OSPF 1 Introduction to OSPF 1 Basic concepts 1 OSPF areas 3 Router types 6 OSPF network classification 7 DR and BDR 8 OSPF packet formats 9 Supported OSPF features 17 Protocols and
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link Costs and Interface Priorities
 NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
NPv6 ROUTE hapter 3 Lab 3-1, Single-Area OSPF Link osts and Interface Priorities Topology Objectives onfigure single-area OSPF on a router. Advertise loopback interfaces into OSPF. Verify OSPF adjacencies.
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Unit 3: Dynamic Routing
 Unit 3: Dynamic Routing Basic Routing The term routing refers to taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network. Routers don t really care about
Unit 3: Dynamic Routing Basic Routing The term routing refers to taking a packet from one device and sending it through the network to another device on a different network. Routers don t really care about
debug ip ospf database external default-metric subnet area 0 stub distribute-list in Serial0/1
 Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Which statement about stateless autoconfiguration is true? A host can autoconfigure itself by appending its MAC address to the local link prefix (64 bits). 2 Autoconfiguration allows devices to connect
Introduction to OSPF
 Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
Introduction to OSPF ISP/IXP Workshops ISP/IXP Workshops 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 OSPF Dynamic Routing Protocol Link State technology Runs over IP, protocol 89 Designed by IETF for TCP/IP Supports VLSM
EECS 122, Lecture 16. Link Costs and Metrics. Traffic-Sensitive Metrics. Traffic-Sensitive Metrics. Static Cost Metrics.
 EECS 122, Lecture 16 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu Link Costs and Metrics Routing protocols compute shortest/cheapest paths using some optimization criteria Choice of criteria has strong effect
EECS 122, Lecture 16 Kevin Fall kfall@cs.berkeley.edu edu Link Costs and Metrics Routing protocols compute shortest/cheapest paths using some optimization criteria Choice of criteria has strong effect
OSPF Virtual Link. Contents. Prerequisites. Document ID: Requirements. Components Used
 OSPF Virtual Link Document ID: 47866 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations How the Virtual Link Operates Calculate the Shortest
OSPF Virtual Link Document ID: 47866 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations How the Virtual Link Operates Calculate the Shortest
Routing Protocols. Technology Description BGP CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes the level of support that Cisco ANA provides for routing protocols, as follows: Technology Description, page 11-1 Information Model Objects (IMOs), page 11-3 Vendor-Specific
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes the level of support that Cisco ANA provides for routing protocols, as follows: Technology Description, page 11-1 Information Model Objects (IMOs), page 11-3 Vendor-Specific
DD2490 p Link-state routing and OSPF. Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC
 DD2490 p4 200 Link-state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 232: Browse through Section. Section 2 gives a very good understanding of OSPF issues. The example is realistic (complex) and
DD2490 p4 200 Link-state routing and OSPF Olof Hagsand KTH/CSC Literature RFC 232: Browse through Section. Section 2 gives a very good understanding of OSPF issues. The example is realistic (complex) and
HP 7500 Switch Series
 HP 7500 Switch Series Layer 3 - IP Routing Command Reference Part number: 5998-1881 Software version: Release 6701 and later Document version: 6W102-20130226 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013
HP 7500 Switch Series Layer 3 - IP Routing Command Reference Part number: 5998-1881 Software version: Release 6701 and later Document version: 6W102-20130226 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
OSPFv2 deep dive. Михайловский Василий Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015
 OSPFv2 deep dive Михайловский Василий vamikhai@cisco.com Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015 Содержание TBD OSPFv2 transport Using IP-multicast 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6; Protocol number 89; Unicast for immediate
OSPFv2 deep dive Михайловский Василий vamikhai@cisco.com Cisco TAC Poland Ноябрь 17, 2015 Содержание TBD OSPFv2 transport Using IP-multicast 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6; Protocol number 89; Unicast for immediate
scope scope {global vrf vrf-name} no scope {global vrf vrf-name} Syntax Description
 Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
Multi-Toplogy Routing Commands scope scope To define the scope for a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing session and to enter router scope configuration mode, use the scope command in router configuration
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs OSPF Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 Greg Brewster, DePaul University 1 OSPF Link State Routing Algorithms Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Message Types Operations
Vanguard Managed Solutions
 Vanguard Managed Solutions Vanguard Applications Ware IP and LAN Feature Protocols Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Notice 2003 Vanguard Managed Solutions, LLC 575 West Street Mansfield, Massachusetts 02048
Vanguard Managed Solutions Vanguard Applications Ware IP and LAN Feature Protocols Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Notice 2003 Vanguard Managed Solutions, LLC 575 West Street Mansfield, Massachusetts 02048
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
HP Load Balancing Module
 HP Load Balancing Module Appendix Protocol Reference Part number: 5998-4222 Software version: Feature 3221 Document version: 6PW100-20130326 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
HP Load Balancing Module Appendix Protocol Reference Part number: 5998-4222 Software version: Feature 3221 Document version: 6PW100-20130326 Legal and notice information Copyright 2013 Hewlett-Packard
Routing in the Internet
 Routing in the Internet Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Scaling Routing for the Internet 2/29 scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes
Routing in the Internet Daniel Zappala CS 460 Computer Networking Brigham Young University Scaling Routing for the Internet 2/29 scale 200 million destinations - can t store all destinations or all prefixes
Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 5 Objectives Diagnose network layer connectivity problems using
OSPF Command Reference
 OSPF OSPF Command Reference Command Hierarchies Configuration Commands on page 329 Show Commands on page 333 Clear Commands on page 333 Debug Commands on page 333 Configuration Commands config [no] ospf
OSPF OSPF Command Reference Command Hierarchies Configuration Commands on page 329 Show Commands on page 333 Clear Commands on page 333 Debug Commands on page 333 Configuration Commands config [no] ospf
Cabrillo College. Rick Graziani, Instructor
 Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
Cabrillo College CCNP Advanced Routing Ch. 5 - Multi-areas (Part I) Rick Graziani, Instructor Mar. 4, 2002 1 Multi-Area Part I Areas LSAs show ip ospf database (summary of link state database) show ip
IP Routing: RIP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
 IP Routing: RIP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 11, 2013 Last Modified: January 11, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
IP Routing: RIP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 11, 2013 Last Modified: January 11, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Passit4Sure.4A Questions 4A Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability
 Passit4Sure.4A0-101.300Questions Number: 4A0-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability
Passit4Sure.4A0-101.300Questions Number: 4A0-101 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.5 http://www.gratisexam.com/ 4A0-101 Alcatel-Lucent Interior Routing Protocols and High Availability
Lab- Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
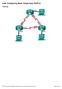 Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Lab- onfiguring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 Topology G0/0 G0/0 2013 isco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is isco Public. Page 1 of 29 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface
Internet Routing Protocols Tuba Saltürk
 Internet Routing Protocols 15505068 Tuba Saltürk Outline Internet Routers Routing Protocol Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) Distance- Vector Routing Protocol Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Interior
Internet Routing Protocols 15505068 Tuba Saltürk Outline Internet Routers Routing Protocol Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) Distance- Vector Routing Protocol Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Interior
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions. Net412- Network troubleshooting
 Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
Ch. 5 Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions Net412- Network troubleshooting Troubleshooting Routing Network Layer Connectivity EIGRP OSPF 2 Network Connectivity Just like we did when we looked
