IPv6 Implementation fundamentals for ISPs
|
|
|
- Curtis Ramsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IPv6 Implementation fundamentals for ISPs NANOG47 / ARIN XXIV Dearborn, MI Aaron Hughes, 6connect, Inc. Unifying Internet Infrastructure
2 AGENDA Obtain an IPv6 allocation My first IPv6 packets Dual stacking the backbone OSPFv3 implementation (IS-IS if you want) IPv6 ibgp implementation IPv6 ebgp implementation IPv6 peering Extending dual stack from the backbone IPv6 for your customers 2
3 AUDIENCE Successful IPv6 implementation requires: ARIN Supporting policies Allocations / Assignments Decision influencers NANOG Designers / Architects Implementors Operators 3
4 REMEMBER YOUR ROLE! Attending and participating is not enough. We must influence our respective companies to make good decisions about future viability. This includes the decision to implement IPv6. Typically Strategy / Revenue generation / P&L / BisDev / Marketing / Customer demand drives product. IPv6 decisions based on survivability + costs $ s Business justification -> another presentation. 4
5 IPV6 OBJECTIONS... Dispel the myths! Obtaining IPv6 space from my RIR is hard My transit providers don t support IPv6 yet No BGP multihoming Lack of general support IPv6 is hard to implement Existing infrastructure doesn t support IPv6 This one is harder to address, but better plan now! Question of _when_ not _if_ 5
6 OBTAINING AN ALLOCATION IS HARD! Lots of coverage on this topic.. Dear RIR, I am planning on assigning IPv6 space to 200 customers in the coming five years. Dear LIR, [ARIN ] IPV6 REQUEST --APPROVED 6
7 7
8 WHERE ARE WE? Obtain an IPv6 allocation My first IPv6 packets Dual stacking the backbone OSPFv3 implementation IPv6 ibgp implementation IPv6 ebgp implementation IPv6 peering Extending dual stack from the backbone IPv6 for your customers 82
9 MY PROVIDER DOESN T SUPPORT IPV6 No need to cry, let s just route around them. 9
10 IPV6 TRANSIT IS FREE! (right now...) 30 IPv6 locations as of Sept 25th,
11 Others?? 23 IPv6 locations as of Sept 25th,
12 WHERE TO START? Existing IX locations IX provider, I am an existing customer at location X, Y, and Z. My existing IPv4 addresses are X.X.X.X, X.X.X.X, etc. What are my IPv6 addresses for those respective locations? You likely have already been assigned IPv6 12
13 PEERING INFORMATION LIST Make a list of all relevant peering information: $My_Company info: AS: XXXX AS-SET: ALTDB AS-COMPANY Equinix Ashburn IPv4: X Equinix Ashburn IPv6 : 2001:504:0:X:XXXX:1 Equinix San Jose IPv4 : X Equinix San Jose IPv6 : 2001:504:0:1:0:X:XXXX:1 PAIX Palo Alto IPv4 : X PAIX Palo Alto IPv6 : 2001:504:D::XXXX Peering Contact : peering@domain.com etc.. NOC Contact : support@domain.com 13
14 UPDATE PEERINGDB Add your IPv6 records and check the v6 box. 14
15 WHAT NEXT? We ve a direct allocation We ve IPv6 addresses for each of our IX locations We ve made a list of info we will need to start We ve updated peeringdb.com 15
16 DISCLAIMER Follow your own company change process! 16
17 CONFIGURING IPV6 Locate existing IPv4 peering interfaces Enable IPv6 (Cisco) Configure the IPv6 address on the peering int Test First Cisco, then Juniper 17
18 CONFIGURING IPV6 CONT.. Enable IPv6 (Cisco) Find the v4 int Verify existing config 18
19 CONFIGURING IPV6 CONT.. Configure Test We are passing IPv6 packets! 19
20 ZOOM IT A LITTLE Enabling IPv6 unicast on the router Cisco: ipv6 unicast-routing Juniper enabled by default 20
21 INTERFACE CONFIG Cisco interface $interface_name ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:1::1/64 Juniper set interface $interface_name unit $unit family inet6 address 2001:1::1/64; 21
22 REACHING ACROSS THE INTERFACE Now that we have configured an interface and we know we can ping ourself, let s see if we can exchange some packets over IPv6 with the outside world. Finding other hosts in the subnet is no longer as simple as sending ICMP to the broadcast address. Instead IPv6 utilizes neighbor discovery. Let s take the easy way out and use peeringdb. 22
23 REACHING ACROSS THE INTERFACE 23
24 CONFIGURING IPV6 ON A JUNIPER Find the IPv4 interface Verify the config Configure the IPv6 address 24
25 CONFIGURING ON A JUNIPER CONT. IPv6 packets are passing! 25
26 WHERE ARE WE? IPv6 addresses are configured on the IX edges IX IX IX Backbone IX IX IPv6 IX 26
27 WHERE ARE WE? Obtain an IPv6 allocation My first IPv6 packets Dual stacking the backbone OSPFv3 implementation IPv6 ibgp implementation IPv6 ebgp implementation IPv6 peering Extending dual stack from the backbone IPv6 for your customers 2782
28 IPV6 INTERNAL ASSIGNMENTS Keeping track of your peering interface address is one thing, however, keeping track of your internal assignments is an entirely different thing. If you have the resources to do so, write a tool to manage IPv6 DNS and assignments. If not? Spreadsheet? Database? DNS zone files? 28
29 ALLOCATION AND ASSIGNMENT TOOLS If you have the resources, write a tool 29
30 ALLOCATION AND ASSIGNMENT TOOLS If you don t, DNS zones work well. 30
31 NUMBERING PLAN 31
32 NUMBERING PLAN Cut first /48 for infrastructure Cut a /64 off the top for loopbacks 32
33 ARCHITECTURE OF YOUR NETWORK Opportunity to change vs. keep the same as v4 33
34 ARCHITECTURE CHOICES There are a ton of opinions about how to architect a network. For the purpose of this presentation, I ve just picked one. Basic Network Architecture Loopbacks and connected infrastructure into OSPF ibgp full mesh sourced off loopbacks ibgp next-hop-self All connected except loopbacks into ibgp ebgp distribution via route-maps and communities 34
35 CONFIGURING YOUR BACKBONE Open your mail client, DNS zone editor and whatever application you use to access routers. 35
36 NUMBERING PLAN Back to the DNS zone.. Let s get started IPv4 4th octet/32 -> IPv6 ::X/128 36
37 STARTING ROUTER Pick one router connected to an IX to start with. Some versions of IOS require this. Enable IPv6 on the interface Add the IPv6 Address Enable IPv6 OSPF name-lookup Extend to edge interfaces facing backbone routers. 37
38 EXTENDING IPV6 INTO YOUR CORE Rinse. Repeat. Extend from the outside in and watch as the OSPFv3 IPv6 sessions come up 38
39 EXTENDING IN FROM THE PEERING EDGE 1 2 Router 1 Loopack Router 2 Loopack 4Connected Interface 3Connected Interface IPv6 Address configured Some Peering IX 5 Verify OSPF session 39
40 10,000 FOOT VIEW IX IX IX IX IX Pick a starting point Slowly work your way out across the connected links. 40
41 MANAGING ASSIGNMENTS WITH DNS ZONE First /48 for all internal infrastructure Alternatively you can get a direct allocation for this. First /64 of the /48 for router loopbacks Second /64 is for your first connected interface 41
42 CUT, PASTE, INCREMENT 42
43 WHAT COMES AFTER 9? 43
44 CONFIGURE THE BACKBONE Time passes.. /64s and /128s in OSPF 44
45 WHERE ARE WE? Obtain an IPv6 allocation My first IPv6 packets Dual stacking the backbone OSPFv3 implementation IPv6 ibgp implementation IPv6 ebgp implementation IPv6 peering Extending dual stack from the backbone IPv6 for your customers
46 WHERE ARE WE CONT. IPv6 configured on all exchange interfaces IPv6 configured on all loopback interfaces IPv6 configured on all connected interfaces between backbone routers. OSPFv3 configured on Loopbacks (/128s) OSPFv3 configured on connected (/64s) What s next? I want to access the rest of the IPv6 world Next we configure ibgp 46
47 IPV6 PEER PEER-GROUP Peer group for an IPv6 peer: neighbor PEERS-v6 peer-group neighbor PEERS-v6 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor PEERS-v6 prefix-list Sanity-v6 in neighbor PEERS-v6 prefix-list Sanity-v6 out neighbor PEERS-v6 route-map PEER-IN-v6 in neighbor PEERS-v6 route-map PEER-OUT-v6 out 47
48 IPV6 IBGP PEER-GROUP Peer group for an IPv6 core router: neighbor CORE-v6 peer-group neighbor CORE-v6 remote-as XXXX < your ASN neighbor CORE-v6 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor CORE-v6 update-source Loopback0 neighbor CORE-v6 send-community neighbor CORE-v6 next-hop-self 48
49 IBGP OVER OSPFV3 IX IX IX IX IX OSPFv3 49
50 IBGP SOURCES OFF LOOPBACKS IX IX Setup full ibgp mesh IX IX IX 50
51 OPEN AN EDITOR FOR COMMON CONFIGS 51
52 IBGP CONFIGURATION Remember ibgp is going to handle connected interfaces (except loopbacks) We use a route-map to do this: route-map redist-connected-v6 deny 10 match interface Loopback0 route-map redist-connected-v6 permit 20 match ipv6 address matchall set community 6:1 52
53 BASIC IPV6 BGP CONFIG router bgp XXXX <- your ASN address-family ipv6 network 2607:ffff::/32 <- Your block neighbor CORE-v6 peer-group neighbor CORE-v6 remote-as XXXX < your ASN neighbor CORE-v6 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor CORE-v6 update-source Loopback0 neighbor CORE-v6 send-community neighbor CORE-v6 next-hop-self redistribute connected route-map redist-connected-v6 no synchronization 53
54 MAKE A LIST OF ROUTER LOOPBACKS 2607:ffff: :ffff: :ffff: :ffff: :ffff: :ffff: :ffff: :ffff: :ffff:254 54
55 BUILD NEIGHBOR CONFIG Convert to internal neighbor statements neighbor 2607:ffff:66 peer-group CORE-v6 neighbor 2607:ffff:67 peer-group CORE-v6 neighbor 2607:ffff:92 peer-group CORE-v6 neighbor 2607:ffff:95 peer-group CORE-v6 neighbor 2607:ffff:251 peer-group CORE-v6 neighbor 2607:ffff:252 peer-group CORE-v6 neighbor 2607:ffff:253 peer-group CORE-v6 neighbor 2607:ffff:254 peer-group CORE-v6 55
56 CONFIG FILE TO PUSH 56
57 PUSHING THE CONFIG FILE At this point we can either push the config file as is or wait until we have the peering peergroup defined as well. For the sake of simplicity, let s push this now Push using ssh, telnet, rancid, etc. NOTE: Remove the neighbor statement to yourself for each of the routers. 57
58 IBGP SESSIONS COME UP At this point you will only see the connected exchange interfaces in the table. 58
59 WHERE ARE WE? Obtain an IPv6 allocation My first IPv6 packets Dual stacking the backbone OSPFv3 implementation IPv6 ibgp implementation IPv6 ebgp implementation IPv6 peering Extending dual stack from the backbone IPv6 for your customers
60 WHERE ARE WE CONT. IPv6 configured on all exchange interfaces IPv6 configured on all loopback interfaces IPv6 configured on all connected interfaces between backbone routers. OSPFv3 configured on Loopbacks (/128s) OSPFv3 configured on connected (/64s) All inter-as routers are exchanging IPv6 BGP routes OSPFv3 is managing ibgp routing based on next-hop (Loopback0s) 60
61 CONFIGURING PEERS We ve done all this work, and still can t reach the outside world! We need a peering peer-group and a peer! neighbor PEERS-v6 peer-group neighbor PEERS-v6 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor PEERS-v6 prefix-list Sanity-v6 in neighbor PEERS-v6 prefix-list Sanity-v6 out neighbor PEERS-v6 route-map PEER-IN-v6 in neighbor PEERS-v6 route-map PEER-OUT-v6 out 61
62 CONFIGURING PEERS BASIC SANITY Basic sanity prefix-list ipv6 prefix-list Sanity-v6 seq 5 permit ::/0 ge 16 le 48 seq 10 deny ::/0 le 128 Don t redistribute peering points connecteds ipv6 prefix-list PEERINGPOINTS seq 5 permit 2001:504:0:1::/64 seq 10 permit 2001:504:D:1::/64 seq 15 permit 2001:504:13:1::/64 seq 20 permit 2001:504:0:3::/64 seq 25 permit 2001:504:0:2::/64 seq 30 etc... 62
63 CONFIGURE PEERS CONT. Create a list of your ASNs IPv6 prefix(es) ipv6 prefix-list MINE seq 5 permit 2607:ffff::/32 Create a route-map to apply outbound route-map PEER-OUT-v6 deny 5 match ipv6 address prefix-list PEERINGPOINTS route-map PEER-OUT-v6 permit 10 match community ALL-CUSTOMERS route-map PEER-OUT-v6 permit 20 match ipv6 address prefix-list MINE 63
64 CONFIGURE PEERS CONT. Create a route-map to apply inbound route-map PEER-IN-v6 permit 10 match ip address prefix-list Sanity-v6 set local-preference 400 set community 8038:117 Use the same community for peers 64
65 TURN UP A PEER! Send to peering@he.net HE Peering, I have completed the dual-stack of my backbone and am ready to turn up IPv6 peering. I would greatly appreciate turning up sessions with you at our common locations. Also, I would appreciate the full IPv6 BGP table. Cheers, Aaron Remember to attach your peering info file 65
66 TURN UP A PEER! CONT. 66
67 TURN UP A PEER! CONT. Receive reply with sessions have been configured 67
68 TURN UP A PEER! CONT. Now we configure our side of the session: router bgp XXXX address-family ipv6 neighbor 2001:504:D::10 remote-as 6939 neighbor 2001:504:D::10 peer-group PEERS-v6 neighbor 2001:504:D::10 description HE Router log should show: %BGP-5-ADJCHANGE: neighbor 2001:504:D::10 Up 68
69 TEST THE SESSION Make sure things look good: br01-paix-pao#sh bgp ipv6 u s in 2001:504:D:: :504:D:: m 1793 Session is up and we see 1793 prefixes! br01-paix-pao#sh bgp ipv6 u ne 2001:504:D::10 ad BGP table version is , local router ID is Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP,? - incomplete Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 2607:F3A0::/32 :: i Total number of prefixes 1 I m advertising my /32! 69
70 TEST REACHABILITY Now we can finally reach the outside world! traceroute ipv6 arin.net. Translating "arin.net."...domain server ( ) [OK] Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to arin.net (2001:500:4:13::80) 1 paix.ipv6.he.net (2001:504:D::10) 4 msec 0 msec 0 msec 2 10gigabitethernet2-4.core1.ash1.he.net (2001:470:0:35::2) [AS 6939] 76 msec 76 msec 72 msec 3 equi6ix-ash.arin.net (2001:504:0:2:0:1:745:1) 76 msec 76 msec 76 msec :500:4:10::12 [AS 10745] 76 msec 76 msec 76 msec :500:4:11::2 [AS 10745] 80 msec 88 msec 80 msec 6 * * * traceroute ipv6 ripe.net. Translating "ripe.net."...domain server ( ) [OK] Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to ripe.net (2001:610:240:11::C100:1319) 1 paix.ipv6.he.net (2001:504:D::10) 0 msec 4 msec 0 msec 2 10gigabitethernet4-1.core1.sjc2.he.net (2001:470:0:32::1) [AS 6939] 0 msec 0 msec 0 msec 3 10gigabitethernet1-3.core1.nyc4.he.net (2001:470:0:33::2) [AS 6939] 80 msec 80 msec 96 msec 4 10gigabitethernet1-2.core1.lon1.he.net (2001:470:0:3E::2) [AS 6939] 156 msec 148 msec 148 mse 5 10gigabitethernet1-1.core1.ams1.he.net (2001:470:0:3F::2) [AS 6939] 156 msec 156 msec 156 ms 6 gw.ipv6.amsix.nikrtr.ripe.net (2001:7F8:1::A500:3333:1) [AS 1200] 156 msec 156 msec 160 msec 7 gw.ipv6.transit.nsrp.ripe.net (2001:610:240:101::1) [AS 3333] 156 msec 156 msec 156 msec 70 8 ripe.net (2001:610:240:11::C100:1319) [AS 3333] 156 msec 156 msec 160 msec
71 SETUP FIRST PEER CONT. Setup the others sessions and look at the table 71
72 WHERE ARE WE? Obtain an IPv6 allocation My first IPv6 packets Dual stacking the backbone OSPFv3 implementation IPv6 ibgp implementation IPv6 ebgp implementation IPv6 peering Extending dual stack from the backbone IPv6 for your customers
73 ATTACHING A HOST TO THE V6 NETWORK Now that we have a functioning IPv6 network, let s get a host on-line to play with. Something non-production? A small segment of the office? A development environment? Your desktop or laptop? Keep in mind that you are not yet monitoring or supporting your IPv6 network. 73
74 NETWORK CONFIG FOR FIRST HOST Find the interface on the network the host is connected to via IPv4. In this case we have chosen ns0 as our dev box: 74
75 NETWORK CONFIG FOR FIRST HOST Look at the existing v4 config interface Vlan705 description [UL:VLAN] Dev nameservers ip address no ip redirects no ip proxy-arp! 75
76 NETWORK CONFIG FOR FIRST HOST Grab the next /64 from your DNS zone file: In this case I just added We can worry about regional aggregation later. 76
77 NETWORK CONFIG FOR THE FIRST HOST Add the IPv6 config to the interface of the router config t int vl705 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2607:F3A0:0:1002::2/64 Wait a few seconds.. Poof! 77
78 NETWORK CONFIG FOR FIRST HOST A little testing... 78
79 NETWORK CONFIG FOR FIRST HOST From the routers perspective: This will be the first connected IPv6 prefix: 79
80 TESTING THE HOST If you have a web-browser on this machine, try Look at the top right corner. 80
81 A QUICK SLAAC NOTE It is important to note that all hosts setup for autoconfig (default on all UNIX OS s and any other current OS) will receive an IPv6 address if they are connected to the same subnet. This means if your dev box is on the same subnet as production boxes, they too will autoconfig via SLAAC and receive a pubic IPv6 address. 81
82 TIME TO ADD NAMESERVICE Add DNS Reverse: a.e e.f.f.f IN PTR ns0.ipv6 Forward: ns0 IN A ns0 IN AAAA 2607:f3a0:0:1002:230:48ff:fe42:59ea rndc reload and test! 82
83 ADDING DNS CONT. Our first host on IPv6! 83
84 SECURITY NOTE This machine is now globally accessible on the IPv6 Internet with no filters in place. It is listening on all ports daemons are running on. Everything connected to this VLAN or interface with autoconf enabled has an IPv6 address. Use show ipv6 neighbors to view configured hosts. If you have a security policy implemented for IPv4 you will need to implement the IPv6 version of that at this time. 84
85 WHAT S NEXT? MORE PEERING! 85
86 MORE PEERING! 86
87 MORE PEERING It s IPv6 peering so today: Policies are more flexible Almost all networks have an open IPv6 peering policy Others will want to peer with you everyone regardless of IPv4 peering policy Watch the IX lists for new IPv6 peers Today, every bit moved over IPv6 is FREE! 87
88 WHERE ARE WE? Obtain an IPv6 allocation My first IPv6 packets Dual stacking the backbone OSPFv3 implementation IPv6 ibgp implementation IPv6 ebgp implementation IPv6 peering Extending dual stack from the backbone IPv6 for your customers
89 TURN UP YOUR FIRST CUSTOMER I have a customer picked, what now? You guessed it, back to router configs! 89
90 V4->V6 ROUTE-MAPS 90
91 V4 -> V6 ROUTE-MAPS 91
92 V4 -> V6 ROUTE-MAPS 92
93 V4 -> V6 PEER-GROUPS 93
94 IPV6 CUSTOMER TURN UP IPv4: conf t router bgp XXXXX neighbor x.x.x.x remote-as 8038 neighbor x.x.x.x description Customer-Bind neighbor x.x.x.x peer-group CUSTOMERFULL IPv6: conf t router bgp XXXXX neighbor 2607:F3A0:0:1F remote-as 8038 neighbor 2607:F3A0:0:1F description Customer-Bind neighbor 2607:F3A0:0:1F peer-group CUSTOMERFULLv6 94
95 95
96 IPV6 CUSTOMER TURN UP CONT What are we advertising? 96
97 OTHER WAYS TO DUAL STACK CUSTOMERS Connected interface Colo customers Metro E Static routes no BGP Connected /64 + Static /64 -> /48 Add route-map for redist static 97
98 WHERE ARE WE? Obtain an IPv6 allocation My first IPv6 packets Dual stacking the backbone OSPFv3 implementation IPv6 ibgp implementation IPv6 ebgp implementation IPv6 peering Extending dual stack from the backbone IPv6 for your customers
99 NEXT STEPS Address your security policy Get your operations staff to use IPv6 Dual stack your NOC Get IPv6 objects in monitoring Dual stack your offices Start updating tools Work with all departments on education Get a test customer up and running Make a longer term plan from here.. 99
100 CONCLUSION Obtaining IPv6 space is easy IPv6 BGP multihoming works IPv6 generally well supported on routers Transit providers are not needed to implement IPv6 Lots of IPv6 peers out there to connect with Dual stacking the backbone will not impact your edges until you are ready Implementation is not hard Config mostly intuitive and same as IPv4 100
101 QUESTIONS? Get IPv6 implemented today! 101
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
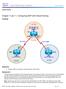 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP First Published: May 2, 2005 Last Updated: August 21, 2007 This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
All participants will work within their groups in pairs. Each group has three routers and three switches to work with.
 Layer 3 - Exercises All participants will work within their groups in pairs. Each group has three routers and three switches to work with. The lab is divided into four components: 1. Static Routing 2.
Layer 3 - Exercises All participants will work within their groups in pairs. Each group has three routers and three switches to work with. The lab is divided into four components: 1. Static Routing 2.
Border Gateway Protocol - BGP
 BGP Fundamentals Border Gateway Protocol - BGP Runs over TCP (port 179) TCP connection required before BGP session Need to be reachable! Path vector routing protocol Best path selection based on path attributes
BGP Fundamentals Border Gateway Protocol - BGP Runs over TCP (port 179) TCP connection required before BGP session Need to be reachable! Path vector routing protocol Best path selection based on path attributes
2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab
 2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab Basic BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Understand the routing implications of connecting to multiple external domains Learn to configure basic
2016/01/17 04:05 1/19 Basic BGP Lab Basic BGP Lab Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Understand the routing implications of connecting to multiple external domains Learn to configure basic
Multihoming with BGP and NAT
 Eliminating ISP as a single point of failure www.noction.com Table of Contents Introduction 1. R-NAT Configuration 1.1 NAT Configuration 5. ISPs Routers Configuration 3 15 7 7 5.1 ISP-A Configuration 5.2
Eliminating ISP as a single point of failure www.noction.com Table of Contents Introduction 1. R-NAT Configuration 1.1 NAT Configuration 5. ISPs Routers Configuration 3 15 7 7 5.1 ISP-A Configuration 5.2
Configuration and Management of Networks 2012
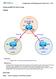 Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
Configuring BGP with default routing Topology Objectives Background Instructions Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on
DE-CIX Academy: BGP - Multihoming
 Notice of Liability Despite careful checking of content, we accept no liability for the content of external links. Content on linked sites is exclusively the responsibility of the respective website operator.
Notice of Liability Despite careful checking of content, we accept no liability for the content of external links. Content on linked sites is exclusively the responsibility of the respective website operator.
IPv6 DEPLOYMENT GLOBAL TRANSIT COMMUNICATIONS. Presented by Mark Tinka Chief Network Architect Global Transit Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
 IPv6 DEPLOYMENT GLOBAL TRANSIT COMMUNICATIONS Presented by Mark Tinka Chief Network Architect Global Transit Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia IPv6: The Interest IPv6: The Interest Main reason; readiness for effects
IPv6 DEPLOYMENT GLOBAL TRANSIT COMMUNICATIONS Presented by Mark Tinka Chief Network Architect Global Transit Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia IPv6: The Interest IPv6: The Interest Main reason; readiness for effects
Introduction to BGP. ISP Workshops. Last updated 30 October 2013
 Introduction to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 Border Gateway Protocol p A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks n Exterior gateway protocol
Introduction to BGP ISP Workshops Last updated 30 October 2013 1 Border Gateway Protocol p A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks n Exterior gateway protocol
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing. Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing Topology Objectives Background Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. The International Travel
IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp
 IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Topology : Figure 1 BGP AS Numbers
IPv6 Module 6x ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of IS-IS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Topology : Figure 1 BGP AS Numbers
BGP Attributes and Policy Control
 BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP `2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job `2005,
BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP `2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job `2005,
IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
Module 6 Implementing BGP
 Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
Module 6 Implementing BGP Lesson 1 Explaining BGP Concepts and Terminology BGP Border Gateway Protocol Using BGP to Connect to the Internet If only one ISP, do not need BGP. If multiple ISPs, use BGP,
Module 16 An Internet Exchange Point
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 16 An Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Exchange Points Presentation
ISP Workshop Lab Module 16 An Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12 and 13, and the Exchange Points Presentation
APNIC elearning: BGP Basics. 30 September :00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Revision: 2.0
 APNIC elearning: BGP Basics 30 September 2015 1:00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Issue Date: 07 July 2015 Revision: 2.0 Presenter Nurul Islam (Roman) Senior Training Specialist, APNIC Nurul maintains the APNIC
APNIC elearning: BGP Basics 30 September 2015 1:00 PM AEST Brisbane (UTC+10) Issue Date: 07 July 2015 Revision: 2.0 Presenter Nurul Islam (Roman) Senior Training Specialist, APNIC Nurul maintains the APNIC
BGP Attributes and Policy Control
 BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
DE-CIX Academy: BGP Introduction. Notice of Liability. BGP Configuration Examples. Network Diagram for all examples. Links and Examples
 Notice of Liability Despite careful checking of content, we accept no liability for the content of external links. Content on linked sites is exclusively the responsibility of the respective website operator.
Notice of Liability Despite careful checking of content, we accept no liability for the content of external links. Content on linked sites is exclusively the responsibility of the respective website operator.
BGP and the Internet
 BGP and the Internet Transit and Internet Exchange Points 1 Definitions Transit carrying traffic across a network, usually for a fee traffic and prefixes originating from one AS are carried across an intermediate
BGP and the Internet Transit and Internet Exchange Points 1 Definitions Transit carrying traffic across a network, usually for a fee traffic and prefixes originating from one AS are carried across an intermediate
BGP Protocol & Configuration. Scalable Infrastructure Workshop AfNOG2008
 BGP Protocol & Configuration Scalable Infrastructure Workshop AfNOG2008 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP4) Case Study 1, Exercise 1: Single upstream Part 6: BGP Protocol Basics Part 7: BGP Protocol - more
BGP Protocol & Configuration Scalable Infrastructure Workshop AfNOG2008 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP4) Case Study 1, Exercise 1: Single upstream Part 6: BGP Protocol Basics Part 7: BGP Protocol - more
BGP Attributes and Policy Control
 BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
BGP Attributes and Policy Control ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Agenda BGP Attributes BGP Path Selection Applying Policy 2 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 3 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop......
IPv6 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use ISIS, ibgp and ebgp appropriately to
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use ISIS, ibgp and ebgp appropriately to
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador July 06)
 South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
BGP Attributes and Path Selection
 BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Training Workshops 1 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... Part of a BGP Update Describes the characteristics
BGP Attributes and Path Selection ISP Training Workshops 1 BGP Attributes The tools available for the job 2 What Is an Attribute?... Next Hop AS Path MED...... Part of a BGP Update Describes the characteristics
LAB1: BGP IPv4. BGP: Initial Config. Disclaimer
 Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
Page1 LAB1: BGP IPv4 Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in respective technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
The feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed. BGP next-hop address tracking is event driven. BGP prefixes are automatically tracked as peering sessions are established.
BGP Techniques for ISP. Terutaka Komorizono
 BGP Techniques for ISP Terutaka Komorizono Introduction Presentation has many configuration examples Using Cisco IOS CLI Aimed at Service Providers Techniques can be used by many enterprises
BGP Techniques for ISP Terutaka Komorizono Introduction Presentation has many configuration examples Using Cisco IOS CLI Aimed at Service Providers Techniques can be used by many enterprises
BGP Tutorial AFNOG2000 Class IP Assignments
 BGP Tutorial AFNOG2000 Class IP Assignments Note: Refer to this sheet for your IP assignments throughout the BGP lab exercises. Anatomy of a BGP Configuration ip bgp-community new-format router bgp 3582
BGP Tutorial AFNOG2000 Class IP Assignments Note: Refer to this sheet for your IP assignments throughout the BGP lab exercises. Anatomy of a BGP Configuration ip bgp-community new-format router bgp 3582
Organization of Product Documentation... xi
 Contents Organization of Product Documentation... xi Chapter 1 Getting Started... 1-1 Introduction...1-1 Software Versions Covered...1-1 Audience...1-1 Conventions...1-1 Terminology...1-2 Support and Warranty
Contents Organization of Product Documentation... xi Chapter 1 Getting Started... 1-1 Introduction...1-1 Software Versions Covered...1-1 Audience...1-1 Conventions...1-1 Terminology...1-2 Support and Warranty
BGP and the Internet
 BGP and the Internet Communities, Transit, Collocation ISP/IXP Workshops 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Advanced Community usage ISP/IXP Presentation_ID Workshops 2000, 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
BGP and the Internet Communities, Transit, Collocation ISP/IXP Workshops 2000, Cisco Systems, Inc. 1 Advanced Community usage ISP/IXP Presentation_ID Workshops 2000, 1999, Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
Module 10 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 10 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 1 to 4, and the Exchange
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 10 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 1 to 4, and the Exchange
Lab 3 Multihoming to the Same ISP
 Lab 3 Multihoming to the Same ISP ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone The following will be the common topology used.
Lab 3 Multihoming to the Same ISP ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone The following will be the common topology used.
LACNIC XIII. Using BGP for Traffic Engineering in an ISP
 LACNIC XIII Using BGP for Traffic Engineering in an ISP Program Using BGP Attributes Implementing IBGP Implementing EBGP Emphasis in Stability, Scalability and Configuration Examples BGP Review Why use
LACNIC XIII Using BGP for Traffic Engineering in an ISP Program Using BGP Attributes Implementing IBGP Implementing EBGP Emphasis in Stability, Scalability and Configuration Examples BGP Review Why use
Ravi Chandra cisco Systems Cisco Systems Confidential
 BGP4 1 Ravi Chandra cisco Systems 0799_04F7_c2 Cisco Systems Confidential 2 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Introduction to BGP BGP Peer Relationship BGP Attributes Applying Policy with BGP Putting it all
BGP4 1 Ravi Chandra cisco Systems 0799_04F7_c2 Cisco Systems Confidential 2 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Introduction to BGP BGP Peer Relationship BGP Attributes Applying Policy with BGP Putting it all
Configuring IPv6 Provider Edge over MPLS (6PE)
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Configuring 6PE, page 1 Finding Feature Information Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature
Introduction to BGP. ISP/IXP Workshops
 Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks Exterior gateway protocol Described in RFC4271 RFC4276
Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol A Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between different networks Exterior gateway protocol Described in RFC4271 RFC4276
CertifyMe. CertifyMe
 CertifyMe Number: 642-661 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CertifyMe-642-661 Exam A QUESTION 1 Exhibit: Certkiller router#show ip route Codes: C - connected,
CertifyMe Number: 642-661 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 7.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CertifyMe-642-661 Exam A QUESTION 1 Exhibit: Certkiller router#show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp
 Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces,
Module 1 Basic Topology, OSPF and ibgp ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number. Ensure that all routers, interfaces,
H3C BGP Configuration Examples
 H3C BGP Configuration Examples Copyright 2017 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
H3C BGP Configuration Examples Copyright 2017 New H3C Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
BGP Routing and BGP Policy. BGP Routing. Agenda. BGP Routing Information Base. L47 - BGP Routing. L47 - BGP Routing
 BGP Routing and BGP Policy BGP Routing The BGP Routing Principles and Route Decisions based on AS-Path in a simple topology of AS s routing policy is reduced to a minimal function demonstrated in example
BGP Routing and BGP Policy BGP Routing The BGP Routing Principles and Route Decisions based on AS-Path in a simple topology of AS s routing policy is reduced to a minimal function demonstrated in example
IPv6 Module 16 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point
 IPv6 Module 16 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 14 and 15, and the Exchange Points Presentation
IPv6 Module 16 An IPv6 Internet Exchange Point Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 14 and 15, and the Exchange Points Presentation
Page1. Cisco IOS Software, Linux Software (I86BI_LINUX-ADVENTERPRISEK9-M), Version 15.2(4)M1, DEVELOPMENT TEST SOFTWARE
 BGP Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as complete
BGP Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made to ensure that all material is as complete
Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP
 Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone Prerequisites: Module 11 and Multihoming
Module 12 Multihoming to the Same ISP ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate various methods for multihoming onto the same upstream s backbone Prerequisites: Module 11 and Multihoming
BGP Multihoming ISP/IXP Workshops
 BGP Multihoming ISP/IXP 1 Why Multihome? Redundancy One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: Local router (configuration, software, hardware) WAN media (physical failure, carrier failure)
BGP Multihoming ISP/IXP 1 Why Multihome? Redundancy One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: Local router (configuration, software, hardware) WAN media (physical failure, carrier failure)
IPv4/IPv6 BGP Routing Workshop. Organized by:
 IPv4/IPv6 BGP Routing Workshop Organized by: Agenda Multihoming & BGP path control APNIC multihoming resource policy 2 ISP Hierarchy Default free zone Made of Tier-1 ISPs who have explicit routes to every
IPv4/IPv6 BGP Routing Workshop Organized by: Agenda Multihoming & BGP path control APNIC multihoming resource policy 2 ISP Hierarchy Default free zone Made of Tier-1 ISPs who have explicit routes to every
Advanced IPv6 Training Course. Lab Manual. v1.3 Page 1
 Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Module 6 IPv6 ibgp and Basic ebgp
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 6 IPv6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP.
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 6 IPv6 ibgp and Basic ebgp Objective: Using IPv6, simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of OSPF, internal BGP, and external BGP.
Internet Routing Basics
 Internet Routing Basics Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E connectivity (app-to-app) Port
Internet Routing Basics Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E connectivity (app-to-app) Port
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
Chapter 6 Lab 6-4, BGP Route Reflectors and Route Filters Topology Objectives Background Configure IBGP routers to use a route reflector and a simple route filter. The International Travel Agency maintains
Adapted from the Synchronization example in g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html
 Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
Adapted from the Synchronization example in http://www.cisco.com/en/us/docs/internetworkin g/case/studies/icsbgp4.html When an AS provides transit service to other ASs when there are non-bgp routers in
Setup. Grab a vncviewer like: Or https://www.realvnc.com/download/viewer/
 IPv6 Matt Clemons Topology 2 Setup Grab a vncviewer like: http://uvnc.com/download/1082/1082viewer.html Or https://www.realvnc.com/download/viewer/ Connect where I tell you and enter the password to see
IPv6 Matt Clemons Topology 2 Setup Grab a vncviewer like: http://uvnc.com/download/1082/1082viewer.html Or https://www.realvnc.com/download/viewer/ Connect where I tell you and enter the password to see
Introduction to Computer Networks
 Introduction to Computer Networks Tian Song ( 嵩天 ), Ph.D., Assoc. Prof. songtian@bit.edu.cn Introduction to Computer Networks ICMP, ARP, DHCP, OSPF, BGP Tian Song ( 嵩天 ), Ph.D., Assoc. Prof. songtian@bit.edu.cn
Introduction to Computer Networks Tian Song ( 嵩天 ), Ph.D., Assoc. Prof. songtian@bit.edu.cn Introduction to Computer Networks ICMP, ARP, DHCP, OSPF, BGP Tian Song ( 嵩天 ), Ph.D., Assoc. Prof. songtian@bit.edu.cn
LARGE SCALE IP ROUTING
 Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Building ISP Networks Xantaro Page 1 / 18 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. LAB ACCESS 4 1.1 Accessing the Jumphost... 4 1.2 Access to your routers... 4 1.3 Local Network Topology... 5 1.4 Global Network Topology...
Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute
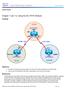 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Hands-on Routing configuration / Local laboratory
 Testbed setup Hands-on Routing configuration / Local laboratory Router7 Router10 Router1 vlan30 Router2 Router14 Router4 Router3 vlan30 vlan3 0 Router5 Router9 Router11 Router8 Router13 Router6 Router12
Testbed setup Hands-on Routing configuration / Local laboratory Router7 Router10 Router1 vlan30 Router2 Router14 Router4 Router3 vlan30 vlan3 0 Router5 Router9 Router11 Router8 Router13 Router6 Router12
IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
 IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 22, 2013 Last Modified: January 22, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
IP Routing: BGP Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) First Published: January 22, 2013 Last Modified: January 22, 2013 Americas Headquarters Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN. APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by:
 Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
Deploy MPLS L3 VPN APNIC Technical Workshop October 23 to 25, 2017. Selangor, Malaysia Hosted by: Issue Date: [201609] Revision: [01] Acknowledgement Cisco Systems Course Outline MPLS L3 VPN Models L3
Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration
 Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use OSPF, ibgp and ebgp appropriately
Module 11 Advanced Router Configuration ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection with two autonomous systems. Each AS should use OSPF, ibgp and ebgp appropriately
BGP Multihoming Techniques
 BGP Multihoming Techniques Philip Smith , Oakland 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Presentation Slides Available on NANOG Web site www.nanog.org/mtg-0110/smith.html Available
BGP Multihoming Techniques Philip Smith , Oakland 2001, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 Presentation Slides Available on NANOG Web site www.nanog.org/mtg-0110/smith.html Available
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking
 BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking Last Updated: November 26, 2012 The BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed.
BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking Last Updated: November 26, 2012 The BGP Support for Next-Hop Address Tracking feature is enabled by default when a supporting Cisco software image is installed.
An Operational Perspective on BGP Security. Geoff Huston February 2005
 An Operational Perspective on BGP Security Geoff Huston February 2005 Disclaimer This is not a description of the approach taken by any particular service provider in securing their network. It is intended
An Operational Perspective on BGP Security Geoff Huston February 2005 Disclaimer This is not a description of the approach taken by any particular service provider in securing their network. It is intended
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) What Is BGP?
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) http:// What Is BGP? Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 Standards based RFC 4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Exterior Gateway Protocol
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) http:// What Is BGP? Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 Standards based RFC 4271 A Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4) Exterior Gateway Protocol
BGP Scaling Techniques
 BGP Scaling Techniques ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last updated
BGP Scaling Techniques ISP Workshops These materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) Last updated
BGP101. Howard C. Berkowitz. (703)
 BGP101 Howard C. Berkowitz hcb@clark.net (703)998-5819 What is the Problem to be Solved? Just configuring the protocol? Participating in the Internet and/or running Virtual Private Networks A Life Cycle
BGP101 Howard C. Berkowitz hcb@clark.net (703)998-5819 What is the Problem to be Solved? Just configuring the protocol? Participating in the Internet and/or running Virtual Private Networks A Life Cycle
Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE
 MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
MPLS Layer3 VPN with OSPF Protocol between CE-PE Disclaimer This Configuration Guide is designed to assist members to enhance their skills in particular technology area. While every effort has been made
BGP Commands. Network Protocols Command Reference, Part 1 P1R-355
 BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number (optionally running on top of an existing
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number (optionally running on top of an existing
BGP Multihoming Techniques
 BGP Multihoming Techniques Philip Smith SANOG 2, Sri Lanka July 2003 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com/pfs/seminars/sanog2-multihoming.pdf 2 Preliminaries Presentation
BGP Multihoming Techniques Philip Smith SANOG 2, Sri Lanka July 2003 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com/pfs/seminars/sanog2-multihoming.pdf 2 Preliminaries Presentation
MPLS VPN C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T. BGP Advertising IPv4 Prefixes with a Label
 7 C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T This online supplement of Chapter 7 focuses on two important developments. The first one is Inter-Autonomous. Inter-Autonomous is a concept whereby two service provider
7 C H A P T E R S U P P L E M E N T This online supplement of Chapter 7 focuses on two important developments. The first one is Inter-Autonomous. Inter-Autonomous is a concept whereby two service provider
BGP Part-1.
 BGP Part-1 www.ine.com Comparison between IGPs & BGP» Similarities and differences between BGP and IGPs (OSPF and EIGRP): BGP needs to form neighborship like IGPs. BGP needs to advertise prefixes, just
BGP Part-1 www.ine.com Comparison between IGPs & BGP» Similarities and differences between BGP and IGPs (OSPF and EIGRP): BGP needs to form neighborship like IGPs. BGP needs to advertise prefixes, just
BGP Multihoming Techniques
 BGP Multihoming Techniques Philip Smith 15-22 January 2004 Bangalore, India 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com/pfs/seminars/sanog3-multihoming.pdf 2 Preliminaries
BGP Multihoming Techniques Philip Smith 15-22 January 2004 Bangalore, India 1 Presentation Slides Available on ftp://ftp-eng.cisco.com/pfs/seminars/sanog3-multihoming.pdf 2 Preliminaries
Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration
 ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
ISP Workshop Lab Module 6 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external BGP. Prerequisites:
Back to basics J. Addressing is the key! Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Transport. Transport (TCP/UDP) Internet (IPv4/IPv6)
 Routing Basics Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E connectivity (app-to-app) Port numbers
Routing Basics Back to basics J Application Presentation Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Data Application (HTTP, DNS, FTP) Session Transport Transport (TCP/UDP) E2E connectivity (app-to-app) Port numbers
BGP Configuration for a Transit ISP
 BGP Configuration for a Transit ISP ISP Workshops Last updated 24 April 2013 1 Definitions p Transit carrying traffic across a network, usually for a fee n traffic and prefixes originating from one AS
BGP Configuration for a Transit ISP ISP Workshops Last updated 24 April 2013 1 Definitions p Transit carrying traffic across a network, usually for a fee n traffic and prefixes originating from one AS
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
 Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP This module describes configuration tasks that will enable your Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) network to access peer devices in external networks such
IETF RFCs Supported by Cisco NX-OS Unicast Features Release 6.x
 IETF Supported by Cisco NX-OS Unicast Features Release 6.x BGP, page 1 First-Hop Redundancy Protocols, page 2 IP Services, page 3 IPv6, page 3 IS-IS, page 4 OSPF, page 5 RIP, page 5 BGP RFC 1997 BGP Communities
IETF Supported by Cisco NX-OS Unicast Features Release 6.x BGP, page 1 First-Hop Redundancy Protocols, page 2 IP Services, page 3 IPv6, page 3 IS-IS, page 4 OSPF, page 5 RIP, page 5 BGP RFC 1997 BGP Communities
Configuring a BGP Route Server
 BGP route server is a feature designed for internet exchange (IX) operators that provides an alternative to full ebgp mesh peering among the service providers who have a presence at the IX. The route server
BGP route server is a feature designed for internet exchange (IX) operators that provides an alternative to full ebgp mesh peering among the service providers who have a presence at the IX. The route server
Routing Concepts. IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols
 Routing Basics 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 Addresses are 32 bits long Range from 1.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 0.0.0.0
Routing Basics 1 Routing Concepts IPv4 Routing Forwarding Some definitions Policy options Routing Protocols 2 IPv4 Internet uses IPv4 Addresses are 32 bits long Range from 1.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 0.0.0.0
Module 19 Internet Exchange Points
 Module 19 Internet Exchange Points ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 13 and 18, and the Exchange
Module 19 Internet Exchange Points ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Objective: To investigate methods for connecting to an Internet Exchange Point. Prerequisites: Modules 12, 13 and 18, and the Exchange
BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing
 2016/09/08 10:01 1/6 BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Apply the concepts of BGP policy learned in class to achieve the
2016/09/08 10:01 1/6 BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing BGP Policy Lab - Partial Routing Introduction The purpose of this exercise is to: Apply the concepts of BGP policy learned in class to achieve the
Introduction. Keith Barker, CCIE #6783. YouTube - Keith6783.
 Understanding, Implementing and troubleshooting BGP 01 Introduction http:// Instructor Introduction Keith Barker, CCIE #6783 CCIE Routing and Switching 2001 CCIE Security 2003 kbarker@ine.com YouTube -
Understanding, Implementing and troubleshooting BGP 01 Introduction http:// Instructor Introduction Keith Barker, CCIE #6783 CCIE Routing and Switching 2001 CCIE Security 2003 kbarker@ine.com YouTube -
BGP Multihoming. ISP/IXP Workshops
 BGP Multihoming ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Why Multihome? Redundancy One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: Local router (configuration, software, hardware) WAN media (physical failure,
BGP Multihoming ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Why Multihome? Redundancy One connection to internet means the network is dependent on: Local router (configuration, software, hardware) WAN media (physical failure,
Configuring BGP on Cisco Routers Volume 1
 Volume 1 I. Course Introduction A. Overview/Learner Skills and Knowledge B. Course Flow C. Additional References 1. Cisco Glossary of Terms D. Your Training Curriculum II. BGP Overview III. Introducing
Volume 1 I. Course Introduction A. Overview/Learner Skills and Knowledge B. Course Flow C. Additional References 1. Cisco Glossary of Terms D. Your Training Curriculum II. BGP Overview III. Introducing
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED
 Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Configuring IBGP and EBGP Sessions, Local Preference, and MED Topology Objectives Background For IBGP peers to correctly exchange routing information, use the next-hop-self command with
Chapter 4: Network Layer
 Chapter 4: Network Layer 4. 1 Introduction 4.2 Virtual circuit and datagram networks 4.3 What s inside a router 4.4 IP: Internet Protocol Datagram format IPv4 addressing ICMP IPv6 4.5 Routing algorithms
Chapter 4: Network Layer 4. 1 Introduction 4.2 Virtual circuit and datagram networks 4.3 What s inside a router 4.4 IP: Internet Protocol Datagram format IPv4 addressing ICMP IPv6 4.5 Routing algorithms
IPv6 Bootcamp Course (5 Days)
 IPv6 Bootcamp Course (5 Days) Course Description: This intermediate - advanced, hands-on course covers pertinent topics needed for IPv6 migration and deployment strategies. IPv6 novices can expect to gain
IPv6 Bootcamp Course (5 Days) Course Description: This intermediate - advanced, hands-on course covers pertinent topics needed for IPv6 migration and deployment strategies. IPv6 novices can expect to gain
MultiVRF Deployment Example
 MultiVRF Deployment Example BGP Session Per VRF Loopback13 192.168.1.13/32 AVPN VLAN10/VE10/RED VRF/172.16.16.2/30 VLAN11/VE11/GREEN VRF/172.16.16.6/30 VLAN13/VE13/Manage VRF/172.16.16.10/30 (2) Customer
MultiVRF Deployment Example BGP Session Per VRF Loopback13 192.168.1.13/32 AVPN VLAN10/VE10/RED VRF/172.16.16.2/30 VLAN11/VE11/GREEN VRF/172.16.16.6/30 VLAN13/VE13/Manage VRF/172.16.16.10/30 (2) Customer
Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops
 Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between networks exterior gateway protocol RFC1771 work in progress to update draft-ietf-idr-bgp4-18.txt
Introduction to BGP ISP/IXP Workshops 1 Border Gateway Protocol Routing Protocol used to exchange routing information between networks exterior gateway protocol RFC1771 work in progress to update draft-ietf-idr-bgp4-18.txt
Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 2 More ibgp, and Basic ebgp Configuration Objective: Simulate four different interconnected ISP backbones using a combination of ISIS, internal BGP, and external
Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks
 Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks Document ID: 47807 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Route Leaking from a Global Routing Table into a VRF and Route
Route Leaking in MPLS/VPN Networks Document ID: 47807 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Route Leaking from a Global Routing Table into a VRF and Route
Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network
 APNIC IPv6/Routing Workshop Lab Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network Objective: All the workshop lab routers are configured with required basic & interface configuration according to the
APNIC IPv6/Routing Workshop Lab Module 2 OSPF Configuration for Training Lab Network Objective: All the workshop lab routers are configured with required basic & interface configuration according to the
Example: Conditionally Generating Static Routes
 1 of 5 9/30/2012 5:46 PM Example: Conditionally Generating Static Routes Understanding Conditionally Generated Routes Example: Configuring a Conditional Default Route Policy Understanding Conditionally
1 of 5 9/30/2012 5:46 PM Example: Conditionally Generating Static Routes Understanding Conditionally Generated Routes Example: Configuring a Conditional Default Route Policy Understanding Conditionally
IPv6 Module 1a OSPF. Prerequisites: IPv4 Lab Module 1, knowledge of Cisco router CLI, and previous hands on experience.
 ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 1a OSPF Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure. Prerequisites: IPv4 Lab Module
ISP Workshop Lab IPv6 Module 1a OSPF Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure. Prerequisites: IPv4 Lab Module
Laura McDonnell 11 th June 2008
 Laura McDonnell 11 th June 2008 Background Why? How? Problems encountered? What next? 7 PoP sites 29 Connected Sites Including Kent Schools Network 5 HE s KM Core BT wavestream circuits (DWDM) 2.5Gbps
Laura McDonnell 11 th June 2008 Background Why? How? Problems encountered? What next? 7 PoP sites 29 Connected Sites Including Kent Schools Network 5 HE s KM Core BT wavestream circuits (DWDM) 2.5Gbps
Intelligent WAN Multiple VRFs Deployment Guide
 Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Multiple VRFs Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deploying the Cisco IWAN Multiple VRFs...
Cisco Validated design Intelligent WAN Multiple VRFs Deployment Guide September 2017 Table of Contents Table of Contents Deploying the Cisco Intelligent WAN... 1 Deploying the Cisco IWAN Multiple VRFs...
BGP. BGP Overview. BGP Operation. BGP Neighbors
 BGP BGP Overview BGP Operation BGP Neighbors BGP Overview AS - Autonomous Systems Multihoming IGP vs. EGP When to use BGP? 2 BGP Overview AS - Autonomous Systems Multihoming IGP vs. EGP When to use BGP?
BGP BGP Overview BGP Operation BGP Neighbors BGP Overview AS - Autonomous Systems Multihoming IGP vs. EGP When to use BGP? 2 BGP Overview AS - Autonomous Systems Multihoming IGP vs. EGP When to use BGP?
Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp
 Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number (optionally running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure). Prerequisites:
Module 1 IPv6 OSPF and ibgp Objective: Create a basic physical lab interconnection using IPv6 with one OSPF Area and one BGP AS number (optionally running on top of an existing IPv4 infrastructure). Prerequisites:
BGP Commands. Network Protocols Command Reference, Part 1 P1R-355
 BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
BGP Commands Use the commands in this chapter to configure and monitor Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For BGP configuration information and examples, refer to the Configuring BGP chapter of the Network
Module 3 BGP route filtering and advanced features
 ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 3 BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 2, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate
ISP/IXP Networking Workshop Lab Module 3 BGP route filtering and advanced features Objective: Using the network configured in Module 2, use various configuration methods on BGP peerings to demonstrate
