Step 2. Manual configuration of global unicast and link-local addresses
|
|
|
- Stephen Summers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
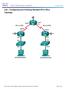
1 Lab: ICMPv6 and ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz DHCPv6 Lab. Part 1: Setup Step 1. Basics a. Log into NetLab: ccnp.bayict.cabrillo.edu b. Schedule IPv6 Pod 1: no configs loaded (clean) c. Configure each router with the following commands: Router> enable Router# conf t Router(config)# hostname <R1, R2 or R2> R1(config)# no ip domain-lookup R1(config)# line con 0 R1(config-line)# logging synchronous R1(config-line)# exec-timeout 0 0 Note: If using the interface configurations from a previous lab, make sure the router has not been configured as an IPv6 router: Router(config)# no ipv6 unicast-routing Step 2. Manual configuration of global unicast and link-local addresses Note: R2 and R3 are not used in this lab, but the configurations are provided for your enjoyment. J R1 conf t R1(config)# interface g 0/0 R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:cab:828::1/64 R1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::828:1 link-local R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# exit
2 R1(config)# interface g 0/1 R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:cab:1000::1/64 R1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# end R2 conf t R2(config)# interface g 0/1 R2(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:cab:1000::2/64 R2(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local R2(config-if)# no shutdown R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface g 0/0 R2(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:cab:2000::2/64 R2(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local R2(config-if)# no shutdown R2(config-if)# end R3 R3# conf t R3(config)# interface g 0/1 R3(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:cab:2000::1/64 R3(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::3 link-local R3(config-if)# no shutdown R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface g 0/0 R3(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:cab:828::1/64 R3(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::829:1 link-local R3(config-if)# no shutdown R3(config-if)# end Verify show ipv6 interface brief GigabitEthernet0/0 [up/up] FE80::828:1 2001:DB8:CAB:828::1 GigabitEthernet0/1 [up/up] FE80::1 2001:DB8:CAB:1000::1 show ipv6 interface brief GigabitEthernet0/0 [up/up] FE80::2 2001:DB8:CAB:2000::2 GigabitEthernet0/1 [up/up] FE80::2 2001:DB8:CAB:1000::2 R3# show ipv6 interface brief GigabitEthernet0/0 [up/up] FE80::829:1
3 2001:DB8:CAB:828::1 GigabitEthernet0/1 [up/up] FE80::3 2001:DB8:CAB:2000::1 R3# Step 3. Enabling the router as an IPv6 router Configure all three routers as IPv6 routers: R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R2(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing R3(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing Step 4. Enabling EIGRP for IPv6 Enable all three routers for EIGRP for IPv6 R1(config)# ipv6 router eigrp 1 R1(config-router)# eigrp router-id R1(config-router)# exit R1(config)# interface g 0/0 R1(config-if)# ipv6 eigrp 1 R1(config-if)# exit R1(config)# interface g 0/1 R1(config-if)# ipv6 eigrp 1 R1(config-if)# end R2(config)# ipv6 router eigrp 1 R2(config-router)# eigrp router-id R2(config-router)# exit R2(config)# interface g 0/0 R2(config-if)# ipv6 eigrp 1 R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface g 0/1 R2(config-if)# ipv6 eigrp 1 R2(config-if)# end R3(config)# ipv6 router eigrp 1 R3(config-router)# eigrp router-id R3(config-router)# exit R3(config)# interface g 0/0 R3(config-if)# ipv6 eigrp 1 R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface g 0/1 R3(config-if)# ipv6 eigrp 1 R3(config-if)# end R3#
4 Part 2: ICMPv6 Error Message Packet Too Big In this part you will examine what happens when a packet is received larger than the forwarding egress interface. Step 1. Modify the MTU Modify the MTU between R2 and R3 so it is less than the MTU of R1 s LAN. R2(config)# interface g 0/0 R2(config-if)# mtu 1350 R2(config-if)# R3(config)# interface g 0/1 R3(config-if)# mtu 1350 R3(config-if)# Step 2. Enable debug on R2 and send the extended pings from R1 Enable debug for ICMPv6 on R2 to monitor any ICMPv6 messages. debug ipv6 icmp ICMPv6 Packet debugging is on Using the extended ping command, from R1 s G0/0 interface ping the R3 s G0/0 interface. Use a datagram size of 1500 to ensure the packet size is greater than the MTU between R2 and R3. ping Protocol [ip]: ipv6 Target IPv6 address: 2001:db8:cab:829::1 Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: 1500 Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands? [no]: yes Source address or interface: gigabitethernet0/0 UDP protocol? [no]: Verbose? [no]: Precedence [0]: DSCP [0]: Include hop by hop option? [no]: Include destination option? [no]: Sweep range of sizes? [no]: Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 1500-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:DB8:CAB:829::1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 2001:DB8:CAB:828::1 B!!!! Success rate is 80 percent (4/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms Notice the first ping failed. The B which refers to a Packet to Big message that was received. The rest of the pings were adjusted to the MTU sent in the ICMPv6 Packet to Big message and succeeded in being forwarded to their destination.
5 Examine the output from debug ip icmpv6 and notice the ICMPv6 Packet Too Big message sent to R1. Also, notice the MTU of the egress interface (1350) towards R3 is included in the Packet Too Big message back to R1. Disable debug with undebug all. *Nov 19 20:33:17.363: ICMPv6: Sent Too Big about 2001:DB8:CAB:829::1, MTU=1350, Src=2001:DB8:CAB:1000::2, Dst=2001:DB8:CAB:828::1 undebug all All possible debugging has been turned off Step 3. Reset the MTUs back to their default Reset the MTU between R2 and R3 to their defaults. R2(config)# interface g 0/0 R2(config-if)# no mtu R2(config-if)# R3(config)# interface g 0/1 R3(config-if)# no mtu R3(config-if)# Part 3: ICMPv6 Error Message Time Exceeded In this part you will examine what happens when a packet is received with a Hop Limit of 1. Step 1. Enable debug on R2 Enable debug for ICMPv6 on R2 to monitor any ICMPv6 messages. debug ipv6 icmp ICMPv6 Packet debugging is on Step 1. Send a traceroute from R1 to R3 s LAN Send a traceroute from R1 to R3 s G0/0 interface. traceroute 2001:db8:cab:829::1 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 2001:DB8:CAB:829:: :DB8:CAB:1000::2 0 msec 0 msec 0 msec :DB8:CAB:2000::1 4 msec 0 msec 0 msec Examine the output from the debug ipv6 icmp command on R2. Notice the three ICMPv6 Time Exceeded messages sent to R1. This was the result of the first trace route with an initial Hop Limit of 1. *Nov 19 21:36:56.279: ICMPv6: Sent Time Exceeded, Src=2001:DB8:CAB:1000::2, Dst=2001:DB8:CAB:1000::1 *Nov 19 21:36:56.279: ICMPv6: Sent Time Exceeded, Src=2001:DB8:CAB:1000::2, Dst=2001:DB8:CAB:1000::1
6 *Nov 19 21:36:56.279: ICMPv6: Sent Time Exceeded, Src=2001:DB8:CAB:1000::2, Dst=2001:DB8:CAB:1000::1 Part 4: ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery Router Solicitation and Router Advertisement In this part you will use Wireshark to do packet analysis on both Router Solicitation Message and Router Advertisement Message. Step 1. Using Wireshark In order for Wireshark to capture packets, the Ethernet interface must be enabled. Devices send a Router Solicitation message immediately after the Ethernet interface is enabled, which makes it difficult to capture with Wireshark. To solve this problem, we will do the Wireshark capture using another device. Using Windows PC 2, start Wireshark. Be sure the Local Area Connection is enabled: Capture > Interfaces or Once you have begun the capture, use the icmpv6 filter to restrict the number of packets displayed. Type icmpv6 in the autocomplete filter and clock Apply Next, start the Windows PC 1 VM. If you have it already started, restart the VM using Start > Shutdown > Restart. Step 2. Examining the ICMPv6 Router Solicitation Message Locate and examine the Router Solicitation Message. Ethernet II Destination: 33:33:00:00:00:02 (IPv6mcast)
7 Source: 00:50:56:af:97:68 Internet Protocol Version = Version: = Traffic class: 0x = Flowlabel: 0x Payload length: 16 Next header: ICMPv6 (58) Hop limit: 255 Source: fe80::d0f8:9ff6:4201:7086 Destination: ff02::2 Internet Control Message Protocol v6 Type: 133 (Router solicitation Code: 0 Checksum: 0x3277 [correct] ICMPv6 Option (Source link-layer address) Type: Source link-layer address (1) Length: 1 (8 bytes) Link-layer address: 00:50:56:af:97:68 Question 1: The destination IPv6 address is: Question 2: The destination MAC address of the RS message is an Ethernet: Question 3: The low-order 32 bits of the destination MAC address is copied from the: Step 3. Examining the ICMPv6 Router Advertisement Message Locate and examine the Router Advertisement Message. Ethernet II Destination: 33:33:00:00:00:01 (IPv6mcast) Source: 04:62:73:5e:f9:00 Internet Protocol Version = Version: = Traffic class: 0x000000e = Flowlabel: 0x Payload length: 64 Next header: ICMPv6 (58) Hop limit: 255 Source: fe80::828:1 Destination: ff02::1 Internet Control Message Protocol v6 Type: 134 (Router advertisement) Code: 0 Checksum: 0x79aa [correct] Cur hop limit: 64 Flags: 0x = Managed address configuration: Not set
8 = Other configuration: Not set = Home Agent: Not set = Prf (Default Router Preference): Medium (0) = Proxy: Not set = Reserved: 0 Router lifetime (s): 1800 Reachable time (ms): 0 Retrans timer (ms): 0 ICMPv6 Option (Source link-layer address : 04:62:73:5e:f9:00) Type: Source link-layer address (1) Length: 1 (8 bytes) Link-layer address: 04:62:73:5e:f9:00 (04:62:73:5e:f9:00) ICMPv6 Option (MTU : 1500) Type MTU (5) Length: 1 (8 bytes) Reserved MTU: 1500 ICMPv6 Option (Prefix information : 2001:db8:cab:828::/64) Type: Prefix information (3) Length: 4 (32 bytes) Prefix Length: 64 Flag: 0xc = On-link flag(l): Set = Autonomous address-configuration flag(a): Set = Router address flag(r): Not set = Reserved: 0 Valid Lifetime: Preferred Lifetime: Reserved Prefix: 2001:db8:cafe:1:: (2001:db8:cab:828::) Question 4: The destination IPv6 address is: Question 5: The destination MAC address of the RA message is an Ethernet: Question 6: The low-order 32 bits of the destination MAC address is copied from the: Question 7: The M Flag is set to: Question 8: The O Flag is set to: Question 9: The A Flag is set to: Question 10: The L Flag is set to: Part 5: ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery Neighbor Solicitation and Neighbor Advertisement Step 1. Examining the ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation Message From router R1, ping WinPC 1 s global unicast address.
9 ping 2001:db8:cab:828:d0f8:9ff6:4201:7086 ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation and Neighbor Advertisement messages are used for Layer 3 to Layer 2 address resolution the same way as ARP Requests and ARP Replies in IPv4. The following NS and NA messages are a result of R1 pinging WinPC 1. Locate and examine the Neighbor Solicitation Message. Ethernet II Destination: 33:33:ff:01:70:86 (IPv6mcast) Source: 04:62:73:5e:f9:00 Internet Protocol Version = Version: = Traffic class: 0x = Flowlabel: 0x Payload length: 32 Next header: ICMPv6 (58) Hop limit: 255 Source: 2001:db8:cab:828::1 Destination: ff02::1:ff01:7086 Internet Control Message Protocol v6 Type: 135 (Neighbor solicitation) Code: 0 Checksum: 0x48ed [correct] Reserved: 0 (Should always be zero) Target: 2001:db8:cab:828:d0f8:9ff6:4201:7086 ICMPv6 Option (Source link-layer address) Type: Source link-layer address (1) Length: 8 (64 bytes) Link-layer address: 04:62:73:5e:f9:00 Question 11: The destination IPv6 address is: Question 12: The destination MAC address of the RA message is an Ethernet: Question 13: The low-order 32 bits of the destination MAC address is copied from the: Question 14: The target (IPv6 address) is: Step 2. Examining the ICMPv6 Neighbor Advertisement Message The following Neighbor Advertisement message is in response to the previous Neighbor Solicitation message. Locate and examine the Neighbor Solicitation Message. Ethernet II Destination: 04:62:73:5e:f9:00 Source: 00:50:56:af:97:68 Internet Protocol Version 6
10 = Version: = Traffic class: 0x = Flowlabel: 0x Payload length: 32 Next header: ICMPv6 (58) Hop limit: 255 Source: 2001:db8:cab:828:d0f8:9ff6:4201:7086 Destination: 2001:db8:cab:828::1 Internet Control Message Protocol v6 Type: 136 (Neighbor advertisement) Code: 0 Checksum: 0xf621 [correct] Flags: 0x = Router: Not set = Solicited: Set = Override: Set = Reserved: 0 Target: 2001:db8:cab:828:d0f8:9ff6:4201:7086 ICMPv6 Option (Target link-layer address) Type: Target link-layer address (2) Length: 1 (8 bytes) Link-layer address: 00:50:56:af:97:68 Question 15: The destination IPv6 address is: Question 16: The destination MAC address of the RA message is: Part 6: ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery Neighbor Cache The Neighbor cache is used to maintain the mapping of IPv6-to-MAC addresses. Devices with an IPv6 address and an Ethernet interface will maintain an Neighbor cache. Step 1. Clear Neighbor Cache on R1 clear ipv6 neighbors show ipv6 neighbors Step 2. Debug IPv6 ND debug ipv6 nd ICMP Neighbor Discovery events debugging is on Step 3. From R1, Ping WinPC 1 ping 2001:db8:cab:828:d0f8:9ff6:4201:7086 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086, timeout is 2 seconds:
11 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms *Nov 20 02:30:35.482: ICMPv6-ND: (GigabitEthernet0/0,2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086) Resolution request *Nov 20 02:30:35.482: ICMPv6-ND: (GigabitEthernet0/0,2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086) DELETE -> INCMP *Nov 20 02:30:35.482: ICMPv6-ND: (GigabitEthernet0/0,2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086) Sending NS *Nov 20 02:30:35.482: ICMPv6-ND: (GigabitEthernet0/0,2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086) Queued data for resolution *Nov 20 02:30:35.486: ICMPv6-ND: (GigabitEthernet0/0,2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086) Received NA from 2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086 *Nov 20 02:30:35.486: ICMPv6-ND: (GigabitEthernet0/0,2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086) LLA af.9768 *Nov 20 02:30:35.486: ICMPv6-ND: (GigabitEthernet0/0,2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086) INCMP -> REACH undebug all All possible debugging has been turned off Step 4. Display R1 s Neighbor Cache show ipv6 neighbors IPv6 Address 2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086 Age Link-layer Addr State Interface af.9768 REACH Gi0/0 <Wait 30 seconds> show ipv6 neighbors IPv6 Address 2001:DB8:CAB:828:D0F8:9FF6:4201:7086 Age Link-layer Addr State Interface af.9768 STALE Gi0/0 Question 17: The ARP cache in IPv4 is equivalent to the in IPv6. Question 18: During address resolution, the neighbor cache is in Incomplete state right before sending a message. Question 19: During address resolution, the neighbor cache is in Incomplete state while waiting for a message. Question 20: If after 30 seconds or if no additional packets are received, the neighbor cache state will transition from the reachable state to the state.
Step 2. Manual configuration of global unicast and link-local addresses
 Lab: DHCPv6 CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz DHCPv6 Lab. Step 1. Setup a. Log into NetLab: ccnp.bayict.cabrillo.edu b. Schedule IPv6 Pod 1: no
Lab: DHCPv6 CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz DHCPv6 Lab. Step 1. Setup a. Log into NetLab: ccnp.bayict.cabrillo.edu b. Schedule IPv6 Pod 1: no
Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz Ch.5 Global Unicast Address + Lab. Additional questions are included in the quiz.
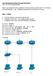 Lab: Introducing Global Unicast Addresses CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz Ch.5 Global Unicast Address + Lab. Additional questions are included
Lab: Introducing Global Unicast Addresses CIS 116 IPv6 Fundamentals Enter your answers to the questions in this lab using Canvas Quiz Ch.5 Global Unicast Address + Lab. Additional questions are included
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration
 Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Chapter 1 Lab 1-1, Basic RIPng and Default Gateway Configuration Topology Objectives Configure IPv6 addressing. Configure and verify RIPng on R1 and R2. Configure IPv6 static routes between R2 and R3.
Guide to TCP/IP Fourth Edition. Chapter 6: Neighbor Discovery in IPv6
 Guide to TCP/IP Fourth Edition Chapter 6: Neighbor Discovery in IPv6 Objectives Describe Neighbor Discovery in IPv6 and how it compares to ARP in IPv4 Explain Neighbor Discovery message interaction between
Guide to TCP/IP Fourth Edition Chapter 6: Neighbor Discovery in IPv6 Objectives Describe Neighbor Discovery in IPv6 and how it compares to ARP in IPv4 Explain Neighbor Discovery message interaction between
Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Configuration IPv6 Application Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Configuration 1-1 IPv6 Overview 1-1 IPv6 Features 1-1 Introduction to IPv6 Address 1-3 Introduction to IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol 1-5 Introduction to IPv6 DNS 1-8 Protocols
Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Configuration 1-1 IPv6 Overview 1-1 IPv6 Features 1-1 Introduction to IPv6 Address 1-3 Introduction to IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol 1-5 Introduction to IPv6 DNS 1-8 Protocols
IPv6 ND Configuration Example
 IPv6 ND Configuration Example Keywords: IPv6 ND Abstract: This document describes the application environment and typical configuration of IPv6 ND. Acronyms: Acronym Full spelling ARP FIB Address Resolution
IPv6 ND Configuration Example Keywords: IPv6 ND Abstract: This document describes the application environment and typical configuration of IPv6 ND. Acronyms: Acronym Full spelling ARP FIB Address Resolution
IPv4 and IPv6 Commands
 This module describes the Cisco IOS XR software commands used to configure the IPv4 and IPv6 commands for Broadband Network Gateway (BNG) on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. For details regarding the
This module describes the Cisco IOS XR software commands used to configure the IPv4 and IPv6 commands for Broadband Network Gateway (BNG) on the Cisco ASR 9000 Series Router. For details regarding the
Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Configuration IPv6 Application Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Configuration 1-1 IPv6 Overview 1-1 IPv6 Features 1-1 Introduction to IPv6 Address 1-3 Introduction to IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol 1-6 Introduction to IPv6 DNS 1-8 Protocols
Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Configuration 1-1 IPv6 Overview 1-1 IPv6 Features 1-1 Introduction to IPv6 Address 1-3 Introduction to IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol 1-6 Introduction to IPv6 DNS 1-8 Protocols
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
 The IPv6 neighbor discovery process uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages and solicited-node multicast addresses to determine the link-layer address of a neighbor on the same network (local
The IPv6 neighbor discovery process uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages and solicited-node multicast addresses to determine the link-layer address of a neighbor on the same network (local
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
 About, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 2 Guidelines for, page 2 Defaults for, page 4 Configure, page 5 View and Clear Dynamically Discovered Neighbors, page 10 History for, page 11 About The IPv6 neighbor
About, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 2 Guidelines for, page 2 Defaults for, page 4 Configure, page 5 View and Clear Dynamically Discovered Neighbors, page 10 History for, page 11 About The IPv6 neighbor
Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Basics Configuration 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Basics Configuration 1-1 IPv6 Overview 1-1 IPv6 Features 1-1 Introduction to IPv6 Address 1-3 Introduction to IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol 1-5 IPv6 PMTU Discovery 1-8 Introduction
Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Basics Configuration 1-1 IPv6 Overview 1-1 IPv6 Features 1-1 Introduction to IPv6 Address 1-3 Introduction to IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol 1-5 IPv6 PMTU Discovery 1-8 Introduction
Introduction to IPv6 - II
 Introduction to IPv6 - II Building your IPv6 network Alvaro Vives 27 June 2017 Workshop on Open Source Solutions for the IoT Contents IPv6 Protocols and Autoconfiguration - ICMPv6 - Path MTU Discovery
Introduction to IPv6 - II Building your IPv6 network Alvaro Vives 27 June 2017 Workshop on Open Source Solutions for the IoT Contents IPv6 Protocols and Autoconfiguration - ICMPv6 - Path MTU Discovery
Chapter 3 Lab 3-2, Multi-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 with Stub Area
 Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Chapter 3 Topology Objectives Configure multi-area OSPFv2 for IPv4. Configure multi-area OSPFv3 for IPv6 Verify multi-area behavior. Configure stub and totally stubby areas for OSPFv2. Configure stub and
Configuring IPv6 for Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
 CHAPTER 46 IP version 6 (IPv6) provides extended addressing capability beyond those provided in IP version 4 (IPv4) in Cisco MDS SAN-OS. The architecture of IPv6 has been designed to allow existing IPv4
CHAPTER 46 IP version 6 (IPv6) provides extended addressing capability beyond those provided in IP version 4 (IPv4) in Cisco MDS SAN-OS. The architecture of IPv6 has been designed to allow existing IPv4
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Configuring BGP with Default Routing
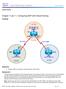 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Configure BGP to exchange routing information with two ISPs. Background The International Travel Agency (ITA) relies extensively on the Internet for sales. For this reason,
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
 About, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 2 Guidelines for, page 2 Defaults for, page 4 Configure, page 5 Monitoring, page 10 History for, page 11 About The IPv6 neighbor discovery process uses ICMPv6 messages
About, page 1 Prerequisites for, page 2 Guidelines for, page 2 Defaults for, page 4 Configure, page 5 Monitoring, page 10 History for, page 11 About The IPv6 neighbor discovery process uses ICMPv6 messages
Routing IPV6. Copyright Cisco Academy. Yannis Xydas
 Routing IPV6 Copyright Cisco Academy Yannis Xydas Quick review of IPv6 Static Routing Single Area OSPF Multi-Area OSPF Access Control Lists Quick Review of IPv6 Addresses Focus on: Global Unicast (GUA)
Routing IPV6 Copyright Cisco Academy Yannis Xydas Quick review of IPv6 Static Routing Single Area OSPF Multi-Area OSPF Access Control Lists Quick Review of IPv6 Addresses Focus on: Global Unicast (GUA)
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
 The IPv6 neighbor discovery process uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages and solicited-node multicast addresses to determine the link-layer address of a neighbor on the same network (local
The IPv6 neighbor discovery process uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages and solicited-node multicast addresses to determine the link-layer address of a neighbor on the same network (local
Operation Manual IPv6 H3C S3610&S5510 Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents. Table of Contents
 Operation Manual IPv6 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 IPv6 Basics Configuration... 1-1 1.1 IPv6 Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 IPv6 Features... 1-2 1.1.2 Introduction to IPv6 Address... 1-3 1.1.3
Operation Manual IPv6 Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 IPv6 Basics Configuration... 1-1 1.1 IPv6 Overview... 1-1 1.1.1 IPv6 Features... 1-2 1.1.2 Introduction to IPv6 Address... 1-3 1.1.3
Lab - Configuring IPv6 Addresses on Network Devices
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway Objectives R1 G0/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 64 N/A G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 64 N/A S1 VLAN 1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::B 64 N/A PC-A
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway Objectives R1 G0/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 64 N/A G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 64 N/A S1 VLAN 1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::B 64 N/A PC-A
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
 IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Last Updated: September 19, 2012 The IPv6 neighbor discovery process uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages and solicited-node multicast addresses to determine the
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Last Updated: September 19, 2012 The IPv6 neighbor discovery process uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) messages and solicited-node multicast addresses to determine the
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador July 06)
 South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
South America Workshop WALC 2006 (Quito, Ecuador 26-28 July 06) Multiprotocol BGP configuration Pedro Lorga (lorga@fccn.pt) Miguel Baptista (miguel.baptista@fccn.pt) Simon Muyal (muyal@renater.pt) Laboratory
IPv6 Protocols and Networks Hadassah College Spring 2018 Wireless Dr. Martin Land
 IPv6 1 IPv4 & IPv6 Header Comparison IPv4 Header IPv6 Header Ver IHL Type of Service Total Length Ver Traffic Class Flow Label Identification Flags Fragment Offset Payload Length Next Header Hop Limit
IPv6 1 IPv4 & IPv6 Header Comparison IPv4 Header IPv6 Header Ver IHL Type of Service Total Length Ver Traffic Class Flow Label Identification Flags Fragment Offset Payload Length Next Header Hop Limit
Rocky Mountain IPv6 Summit April 9, 2008
 Rocky Mountain IPv6 Summit April 9, 2008 Introduction to the IPv6 Protocol Scott Hogg GTRI - Director of Advanced Technology Services CCIE #5133, CISSP 1 IPv6 Header IPv4 Header 20 bytes IPv6 Header, 40
Rocky Mountain IPv6 Summit April 9, 2008 Introduction to the IPv6 Protocol Scott Hogg GTRI - Director of Advanced Technology Services CCIE #5133, CISSP 1 IPv6 Header IPv4 Header 20 bytes IPv6 Header, 40
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
IPv6 Client IP Address Learning
 Prerequisites for IPv6 Client Address Learning, on page 1 Information About IPv6 Client Address Learning, on page 1 Configuring IPv6 Unicast, on page 6 Configuring RA Guard Policy, on page 7 Applying RA
Prerequisites for IPv6 Client Address Learning, on page 1 Information About IPv6 Client Address Learning, on page 1 Configuring IPv6 Unicast, on page 6 Configuring RA Guard Policy, on page 7 Applying RA
Veryx ATTEST TM Conformance Test Suite
 Veryx ATTEST TM Conformance Test Suite IPv6 ReadyTest Host (IPv6-Host) Sample Test case List Overview Part Number: T / TCL IPv6-Host 1.0-0612/1.1 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction 1 Introduction
Veryx ATTEST TM Conformance Test Suite IPv6 ReadyTest Host (IPv6-Host) Sample Test case List Overview Part Number: T / TCL IPv6-Host 1.0-0612/1.1 This page is intentionally left blank. Introduction 1 Introduction
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
Configuring IPv6 First-Hop Security
 This chapter describes the IPv6 First-Hop Security features. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Introduction to First-Hop Security, on page 1 RA Guard,
This chapter describes the IPv6 First-Hop Security features. This chapter includes the following sections: Finding Feature Information, on page 1 Introduction to First-Hop Security, on page 1 RA Guard,
IPv6. IPv4 & IPv6 Header Comparison. Types of IPv6 Addresses. IPv6 Address Scope. IPv6 Header. IPv4 Header. Link-Local
 1 v4 & v6 Header Comparison v6 Ver Time to Live v4 Header IHL Type of Service Identification Protocol Flags Source Address Destination Address Total Length Fragment Offset Header Checksum Ver Traffic Class
1 v4 & v6 Header Comparison v6 Ver Time to Live v4 Header IHL Type of Service Identification Protocol Flags Source Address Destination Address Total Length Fragment Offset Header Checksum Ver Traffic Class
Chapter 7 Lab 7-2, Using the AS_PATH Attribute
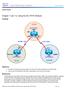 Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Chapter 7 Topology Objectives Use BGP commands to prevent private AS numbers from being advertised to the outside world. Use the AS_PATH attribute to filter BGP routes based on their source AS numbers.
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Juniper Netscreen Security Device. How to Enable IPv6 Page-51
 Juniper Netscreen Security Device Page-51 Netscreen Firewall - Interfaces Below is a screen shot for a Netscreen Firewall interface. All interfaces have an IPv6 address except ethernet0/0. We will step
Juniper Netscreen Security Device Page-51 Netscreen Firewall - Interfaces Below is a screen shot for a Netscreen Firewall interface. All interfaces have an IPv6 address except ethernet0/0. We will step
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
IPv6 Stateless Autoconfiguration
 The IPv6 stateless autoconfiguration feature can be used to manage link, subnet, and site addressing changes. Information About, page 1 How to Configure, page 2 Configuration Examples for, page 3 Additional
The IPv6 stateless autoconfiguration feature can be used to manage link, subnet, and site addressing changes. Information About, page 1 How to Configure, page 2 Configuration Examples for, page 3 Additional
Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Configuration IPv6 Application Configuration 2-1
 Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Configuration 1-1 IPv6 Overview 1-1 IPv6 Features 1-1 Introduction to IPv6 Address 1-2 Introduction to IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol 1-5 Introduction to ND Snooping 1-7 Introduction
Table of Contents 1 IPv6 Configuration 1-1 IPv6 Overview 1-1 IPv6 Features 1-1 Introduction to IPv6 Address 1-2 Introduction to IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol 1-5 Introduction to ND Snooping 1-7 Introduction
Configuring IPv6 basics
 Contents Configuring IPv6 basics 1 IPv6 overview 1 IPv6 features 1 IPv6 addresses 2 IPv6 neighbor discovery protocol 5 IPv6 PMTU discovery 8 IPv6 transition technologies 8 Protocols and standards 9 IPv6
Contents Configuring IPv6 basics 1 IPv6 overview 1 IPv6 features 1 IPv6 addresses 2 IPv6 neighbor discovery protocol 5 IPv6 PMTU discovery 8 IPv6 transition technologies 8 Protocols and standards 9 IPv6
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Table of Contents 1 System Maintenance and Debugging Commands 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 System Maintenance and Debugging Commands 1-1 System Maintenance Commands 1-1 ping 1-1 ping ipv6 1-5 tracert 1-6 tracert ipv6 1-7 System Debugging Commands 1-8 debugging 1-8 display
Table of Contents 1 System Maintenance and Debugging Commands 1-1 System Maintenance Commands 1-1 ping 1-1 ping ipv6 1-5 tracert 1-6 tracert ipv6 1-7 System Debugging Commands 1-8 debugging 1-8 display
tcp ipv6 timer fin-timeout 40 tcp ipv6 timer syn-timeout 40 tcp ipv6 window 41
 Table of Contents IPv6 Basics Configuration Commands 1 IPv6 Basics Configuration Commands 1 display ipv6 fib 1 display ipv6 fibcache 2 display ipv6 interface 2 display ipv6 neighbors 5 display ipv6 neighbors
Table of Contents IPv6 Basics Configuration Commands 1 IPv6 Basics Configuration Commands 1 display ipv6 fib 1 display ipv6 fibcache 2 display ipv6 interface 2 display ipv6 neighbors 5 display ipv6 neighbors
Lab Configuring IPv6 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
HPE FlexNetwork 5510 HI Switch Series
 HPE FlexNetwork 5510 HI Switch Series Layer 3 IP Services Command Reference Part number: 5200-0078b Software version: Release 11xx Document version: 6W102-20171020 Copyright 2015, 2017 Hewlett Packard
HPE FlexNetwork 5510 HI Switch Series Layer 3 IP Services Command Reference Part number: 5200-0078b Software version: Release 11xx Document version: 6W102-20171020 Copyright 2015, 2017 Hewlett Packard
SDN Workshop. Contact: WSDN01_v0.1
 SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Segment Routing - Lab SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Segment Routing Configuration 3 Configuration
SDN Workshop Contact: training@apnic.net WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Segment Routing - Lab SDN Workshop WSDN01_v0.1 Issue Date: [Date] Revision: [xx] Segment Routing Configuration 3 Configuration
Using the Management Ethernet Interface
 The Cisco ASR 920 Series Router has one Gigabit Ethernet Management Ethernet interface on each Route Switch Processor. The purpose of this interface is to allow users to perform management tasks on the
The Cisco ASR 920 Series Router has one Gigabit Ethernet Management Ethernet interface on each Route Switch Processor. The purpose of this interface is to allow users to perform management tasks on the
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
 Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 5: Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Troubleshooting Network Layer Connectivity 2 Routing and Routing Data Structures
Chapter 6: Network Layer
 Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Advanced IPv6 Training Course. Lab Manual. v1.3 Page 1
 Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
Advanced IPv6 Training Course Lab Manual v1.3 Page 1 Network Diagram AS66 AS99 10.X.0.1/30 2001:ffXX:0:01::a/127 E0/0 R 1 E1/0 172.X.255.1 2001:ffXX::1/128 172.16.0.X/24 2001:ff69::X/64 E0/1 10.X.0.5/30
IPv6 Configuration Commands
 IPv6 Configuration Commands Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 IPv6 Configuration Commands...1 1.1 IPv6 Configuration Commands...1 1.1.1 ipv6 address...1 1.1.2 ipv6 address anycast...2 1.1.3
IPv6 Configuration Commands Table of Contents Table of Contents Chapter 1 IPv6 Configuration Commands...1 1.1 IPv6 Configuration Commands...1 1.1.1 ipv6 address...1 1.1.2 ipv6 address anycast...2 1.1.3
(ICMP), RFC
 Internet et Control o Message Protocol (ICMP), RFC 792 http://icourse.cuc.edu.cn/networkprogramming/ linwei@cuc.edu.cn Nov. 2009 Overview The IP (Internet Protocol) relies on several other protocols to
Internet et Control o Message Protocol (ICMP), RFC 792 http://icourse.cuc.edu.cn/networkprogramming/ linwei@cuc.edu.cn Nov. 2009 Overview The IP (Internet Protocol) relies on several other protocols to
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Service Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IPv6 Service Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel...5 1.1 Overview...5 1.1.2 Manual Tunnel...6 1.1.3 6to4 Tunnel...6 1.1.4 ISATAP Tunnel...7 1.2 Configure Manual
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Service Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel...5 1.1 Overview...5 1.1.2 Manual Tunnel...6 1.1.3 6to4 Tunnel...6 1.1.4 ISATAP Tunnel...7 1.2 Configure Manual
RealCiscoLAB.com. Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 ROUTE
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 ROUTE Chapter 2 Lab 2-2, EIGRP Load Balancing Topology Objectives Background Review a basic EIGRP configuration. Explore the EIGRP topology table. Identify successors, feasible
HPE 5920 & 5900 Switch Series
 HPE 5920 & 5900 Switch Series Layer 3 IP Services Command Reference Part number: 5998-6643t Software version: Release 2422P01 Document version: 6W101-20171030 Copyright 2016, 2017 Hewlett Packard Enterprise
HPE 5920 & 5900 Switch Series Layer 3 IP Services Command Reference Part number: 5998-6643t Software version: Release 2422P01 Document version: 6W101-20171030 Copyright 2016, 2017 Hewlett Packard Enterprise
Ping, tracert and system debugging commands
 Contents Ping, tracert and system debugging commands 1 Ping and tracert commands 1 ping 1 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 9 System debugging commands 10 debugging 10 display debugging 11 i Ping, tracert
Contents Ping, tracert and system debugging commands 1 Ping and tracert commands 1 ping 1 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 9 System debugging commands 10 debugging 10 display debugging 11 i Ping, tracert
Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging Commands 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging Commands 1-1 System Maintaining Commands 1-1 ping 1-1 tracert 1-4 System Debugging Commands 1-6 debugging 1-6 display debugging 1-7 i 1 System Maintaining
Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging Commands 1-1 System Maintaining Commands 1-1 ping 1-1 tracert 1-4 System Debugging Commands 1-6 debugging 1-6 display debugging 1-7 i 1 System Maintaining
Troubleshooting Cisco Express Forwarding Routing Loops
 Troubleshooting Cisco Express Forwarding Routing Loops Document ID: 26083 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Problem Troubleshoot Solution Related
Troubleshooting Cisco Express Forwarding Routing Loops Document ID: 26083 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Network Diagram Problem Troubleshoot Solution Related
Using the Management Ethernet Interface
 This chapter covers the following topics: Gigabit Ethernet Management Interface Overview, page 1 Gigabit Ethernet Port Numbering, page 1 IP Address Handling in ROMmon and the Management Ethernet Port,
This chapter covers the following topics: Gigabit Ethernet Management Interface Overview, page 1 Gigabit Ethernet Port Numbering, page 1 IP Address Handling in ROMmon and the Management Ethernet Port,
HPE FlexNetwork 5510 HI Switch Series
 HPE FlexNetwork 5510 HI Switch Series Layer 3 IP Services Command Reference Part number: 5200-3837 Software version: Release 13xx Document version: 6W100-20170315 Copyright 2015, 2017 Hewlett Packard Enterprise
HPE FlexNetwork 5510 HI Switch Series Layer 3 IP Services Command Reference Part number: 5200-3837 Software version: Release 13xx Document version: 6W100-20170315 Copyright 2015, 2017 Hewlett Packard Enterprise
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this
Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Security Configuration Guide
 FiberstoreOS IPv6 Security Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel...4 1.1 Overview... 4 1.1.2 Manual Tunnel... 5 1.1.3 6to4 Tunnel... 6 1.1.4 ISATAP Tunnel...7 1.2 Configure Manual
FiberstoreOS IPv6 Security Configuration Guide Contents 1 Configuring IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnel...4 1.1 Overview... 4 1.1.2 Manual Tunnel... 5 1.1.3 6to4 Tunnel... 6 1.1.4 ISATAP Tunnel...7 1.2 Configure Manual
HP 6125 Blade Switch Series
 HP 6125 Blade Switch Series Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-3156 Software version: Release 2103 Document version: 6W100-20120907 Legal and notice information Copyright 2012
HP 6125 Blade Switch Series Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration Guide Part number: 5998-3156 Software version: Release 2103 Document version: 6W100-20120907 Legal and notice information Copyright 2012
CS 356: Computer Network Architectures. Lecture 10: IP Fragmentation, ARP, and ICMP. Xiaowei Yang
 CS 356: Computer Network Architectures Lecture 10: IP Fragmentation, ARP, and ICMP Xiaowei Yang xwy@cs.duke.edu Overview Homework 2-dimension parity IP fragmentation ARP ICMP Fragmentation and Reassembly
CS 356: Computer Network Architectures Lecture 10: IP Fragmentation, ARP, and ICMP Xiaowei Yang xwy@cs.duke.edu Overview Homework 2-dimension parity IP fragmentation ARP ICMP Fragmentation and Reassembly
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING
 LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
LAB THREE STATIC ROUTING In this lab you will work with four different network topologies. The topology for Parts 1-4 is shown in Figure 3.1. These parts address router configuration on Linux PCs and a
Configuring IS IS over IPv6
 Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
Configuring IS IS over IPv6 Document ID: 40262 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Troubleshooting
IPv6 Protocol & Structure. npnog Dec, 2017 Chitwan, NEPAL
 IPv6 Protocol & Structure npnog3 9-11 Dec, 2017 Chitwan, NEPAL Protocol Header Comparison IPv4 contains 10 basic header fields, while IPv6 has 6 basic header fields IPv6 header size is 40 octets compared
IPv6 Protocol & Structure npnog3 9-11 Dec, 2017 Chitwan, NEPAL Protocol Header Comparison IPv4 contains 10 basic header fields, while IPv6 has 6 basic header fields IPv6 header size is 40 octets compared
Smart Serial. Show interfaces. Shut down. logging synchronous
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
IPv6 Protocol Architecture
 IPv6 Protocol Architecture v4/v6 Header Comparison Not kept in IPv6 Renamed in IPv6 Same name and function New in IPv6 2 New Functional Improvement Address Space Increase from 32-bit to 128-bit address
IPv6 Protocol Architecture v4/v6 Header Comparison Not kept in IPv6 Renamed in IPv6 Same name and function New in IPv6 2 New Functional Improvement Address Space Increase from 32-bit to 128-bit address
Introduction to IPv6. IPv6 addresses
 Introduction to IPv6 (Chapter 4 in Huitema) IPv6,Mobility-1 IPv6 addresses 128 bits long Written as eight 16-bit integers separated with colons E.g. 1080:0000:0000:0000:0000:0008:200C:417A = 1080::8:800:200C:417A
Introduction to IPv6 (Chapter 4 in Huitema) IPv6,Mobility-1 IPv6 addresses 128 bits long Written as eight 16-bit integers separated with colons E.g. 1080:0000:0000:0000:0000:0008:200C:417A = 1080::8:800:200C:417A
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLs Topology
 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Redistribution Between EIGRP and OSPF Topology Objectives Review EIGRP and OSPF configuration. Redistribute into EIGRP. Redistribute into OSPF. Summarize routes in EIGRP. Filter routes
IPv6 Snooping. Finding Feature Information. Restrictions for IPv6 Snooping
 The feature bundles several Layer 2 IPv6 first-hop security features, including IPv6 neighbor discovery inspection, IPv6 device tracking, IPv6 address glean, and IPv6 binding table recovery, to provide
The feature bundles several Layer 2 IPv6 first-hop security features, including IPv6 neighbor discovery inspection, IPv6 device tracking, IPv6 address glean, and IPv6 binding table recovery, to provide
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM
 Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
HP FlexFabric 5930 Switch Series
 HP FlexFabric 5930 Switch Series Layer 3 IP Services Command Reference Part number: 5998-4568 Software version: Release 2406 & Release 2407P01 Document version: 6W101-20140404 Legal and notice information
HP FlexFabric 5930 Switch Series Layer 3 IP Services Command Reference Part number: 5998-4568 Software version: Release 2406 & Release 2407P01 Document version: 6W101-20140404 Legal and notice information
ECE 461 Internetworking Fall Quiz 1
 ECE 461 Internetworking Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Instructions (read carefully): The time for this quiz is 50 minutes. This is a closed book and closed notes in-class exam. Non-programmable (Type 2) calculators
ECE 461 Internetworking Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Instructions (read carefully): The time for this quiz is 50 minutes. This is a closed book and closed notes in-class exam. Non-programmable (Type 2) calculators
Contents. Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands 1 debugging 1 display debugging 2 ping 2 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 9
 Contents Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands 1 debugging 1 display debugging 2 ping 2 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 9 i Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands debugging Syntax Default
Contents Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands 1 debugging 1 display debugging 2 ping 2 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 9 i Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands debugging Syntax Default
Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS
 Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP and IS-IS Redistribute into EIGRP Redistribute into IS-IS Use a standard access list to select routes
Lab 5-3 Redistribution Between EIGRP and IS-IS Learning Objectives Review basic configuration of EIGRP and IS-IS Redistribute into EIGRP Redistribute into IS-IS Use a standard access list to select routes
Internet Control Message Protocol
 Internet Control Message Protocol The Internet Control Message Protocol is used by routers and hosts to exchange control information, and to inquire about the state and configuration of routers and hosts.
Internet Control Message Protocol The Internet Control Message Protocol is used by routers and hosts to exchange control information, and to inquire about the state and configuration of routers and hosts.
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
netkit lab IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (NDP)
 netkit lab IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (NDP) Version 1.0 Author(s) E-mail Web Description S. Doro based on work ARP by G. Di Battista, M. Patrignani, M. Pizzonia, F. Ricci, M. Rimondini sandro.doro@gmail.com
netkit lab IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (NDP) Version 1.0 Author(s) E-mail Web Description S. Doro based on work ARP by G. Di Battista, M. Patrignani, M. Pizzonia, F. Ricci, M. Rimondini sandro.doro@gmail.com
Chapter 5 Lab 5-2 DHCP INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-2 DHCP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure DHCP for IPv4 Configure Stateless DHCP for IPv6 Configure Stateful DHCP for IPv6 Background To practice the various
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-2 DHCP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure DHCP for IPv4 Configure Stateless DHCP for IPv6 Configure Stateful DHCP for IPv6 Background To practice the various
HPE FlexFabric 5940 Switch Series
 HPE FlexFabric 5940 Switch Series Layer 3 IP Services Configuration Guide Part number: 5200-1022a Software version: Release 2508 and later verison Document version: 6W101-20161101 Copyright 2016 Hewlett
HPE FlexFabric 5940 Switch Series Layer 3 IP Services Configuration Guide Part number: 5200-1022a Software version: Release 2508 and later verison Document version: 6W101-20161101 Copyright 2016 Hewlett
The Netwok Layer IPv4 and IPv6 Part 2
 ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE The Netwok Layer IPv4 and IPv6 Part 2 Jean Yves Le Boudec 2014 1 Contents 6. ARP 7. Host configuration 8. IP packet format Textbook Chapter 5: The Network Layer
ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE The Netwok Layer IPv4 and IPv6 Part 2 Jean Yves Le Boudec 2014 1 Contents 6. ARP 7. Host configuration 8. IP packet format Textbook Chapter 5: The Network Layer
Introduction to IPv6. IPv6 addresses
 Introduction to IPv6 (Chapter4inHuitema) IPv6,Mobility-1 IPv6 addresses 128 bits long Written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal integers separated with colons E.g. 1080:0000:0000:0000:0000:0008:200C:417A = 1080::8:800:200C:417A
Introduction to IPv6 (Chapter4inHuitema) IPv6,Mobility-1 IPv6 addresses 128 bits long Written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal integers separated with colons E.g. 1080:0000:0000:0000:0000:0008:200C:417A = 1080::8:800:200C:417A
Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1
 Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 Ping 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Configuring Ping 1-1 Ping Configuration Example 1-2 Tracert 1-4 Introduction 1-4
Table of Contents 1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 System Maintaining and Debugging 1-1 Ping 1-1 Introduction 1-1 Configuring Ping 1-1 Ping Configuration Example 1-2 Tracert 1-4 Introduction 1-4
ICS 451: Today's plan
 ICS 451: Today's plan ICMP ping traceroute ARP DHCP summary of IP processing ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol, 2 functions: error reporting (never sent in response to ICMP error packets) network
ICS 451: Today's plan ICMP ping traceroute ARP DHCP summary of IP processing ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol, 2 functions: error reporting (never sent in response to ICMP error packets) network
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
CCNP ROUTE 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors
ODL Summit Bangalore - Nov 2016 IPv6 Design in OpenDaylight
 ODL Summit Bangalore - Nov 2016 IPv6 Design in OpenDaylight Sridhar Gaddam (sgaddam@redhat.com) Dayavanti Gopal Kamath (dayavanti.gopal.kamat@ericsson.com) Agenda IPv6 Intro. IPv6 Neighbor Discovery. IPv6
ODL Summit Bangalore - Nov 2016 IPv6 Design in OpenDaylight Sridhar Gaddam (sgaddam@redhat.com) Dayavanti Gopal Kamath (dayavanti.gopal.kamat@ericsson.com) Agenda IPv6 Intro. IPv6 Neighbor Discovery. IPv6
Contents. Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands 1. debugging 1 display debugging 1 ping 2 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 10
 Contents Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands 1 debugging 1 display debugging 1 ping 2 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 10 i Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands debugging Syntax Default
Contents Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands 1 debugging 1 display debugging 1 ping 2 ping ipv6 5 tracert 7 tracert ipv6 10 i Ping, tracert, and system debugging commands debugging Syntax Default
HP A5830 Switch Series Layer 3 - IP Services. Configuration Guide. Abstract
 HP A5830 Switch Series Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration Guide Abstract This document describes the software features for the HP A Series products and guides you through the software configuration procedures.
HP A5830 Switch Series Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration Guide Abstract This document describes the software features for the HP A Series products and guides you through the software configuration procedures.
Introduction to IPv6. IPv6 addresses
 Introduction to IPv6 (Chapter 4 in Huitema) IPv6,Mobility-1 IPv6 addresses 128 bits long Written as eight 16-bit integers separated with colons E.g. 1080:0000:0000:0000:0000:0008:200C:417A = 1080::8:800:200C:417A
Introduction to IPv6 (Chapter 4 in Huitema) IPv6,Mobility-1 IPv6 addresses 128 bits long Written as eight 16-bit integers separated with colons E.g. 1080:0000:0000:0000:0000:0008:200C:417A = 1080::8:800:200C:417A
I Commands. iping, page 2 iping6, page 4 itraceroute, page 5 itraceroute6 vrf, page 6. itraceroute vrf encap vxlan, page 12
 iping, page 2 iping6, page 4 itraceroute, page 5 itraceroute6 vrf, page 6 itraceroute6 vrf encap vlan, page 7 itraceroute6 vrf encap vxlan dst-mac, page 8 itraceroute vrf, page 9 itraceroute vrf encap
iping, page 2 iping6, page 4 itraceroute, page 5 itraceroute6 vrf, page 6 itraceroute6 vrf encap vlan, page 7 itraceroute6 vrf encap vxlan dst-mac, page 8 itraceroute vrf, page 9 itraceroute vrf encap
Manually Configured IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnels
 This feature provides support for manually configured IPv6 over IPv4 tunnels. A manually configured tunnel is equivalent to a permanent link between two IPv6 domains over an IPv4 backbone. Finding Feature
This feature provides support for manually configured IPv6 over IPv4 tunnels. A manually configured tunnel is equivalent to a permanent link between two IPv6 domains over an IPv4 backbone. Finding Feature
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), RFC 792. Prof. Lin Weiguo Copyleft 2009~2017, School of Computing, CUC
 Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), RFC 79 Prof Lin Weiguo Copyleft 009~07, School of Computing, CUC Oct 07 Overview } The IP (Internet Protocol) relies on several other protocols to perform necessary
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), RFC 79 Prof Lin Weiguo Copyleft 009~07, School of Computing, CUC Oct 07 Overview } The IP (Internet Protocol) relies on several other protocols to perform necessary
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
TSIN02 - Internetworking
 Lecture 2: The Internet Protocol Literature: Forouzan: ch 4-9 and ch 27 2004 Image Coding Group, Linköpings Universitet Outline About the network layer Tasks Addressing Routing Protocols 2 Tasks of the
Lecture 2: The Internet Protocol Literature: Forouzan: ch 4-9 and ch 27 2004 Image Coding Group, Linköpings Universitet Outline About the network layer Tasks Addressing Routing Protocols 2 Tasks of the
IPv6 address configuration and local operation
 IPv6 address configuration and local operation Amsterdam, 16 february 2012 Iljitsch van Beijnum Today's topics IPv6 address configuration stateless autoconfig DHCPv6 DAD, NUD, timers Router solicitations/advertisements
IPv6 address configuration and local operation Amsterdam, 16 february 2012 Iljitsch van Beijnum Today's topics IPv6 address configuration stateless autoconfig DHCPv6 DAD, NUD, timers Router solicitations/advertisements
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control Using PBR. Topology. Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 hapter 5 Topology Objectives onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations. Verify the configuration and operation by using
hapter 5 Topology Objectives onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations. Verify the configuration and operation by using
IPv6 Snooping. Finding Feature Information. Restrictions for IPv6 Snooping
 The feature bundles several Layer 2 IPv6 first-hop security features, including IPv6 neighbor discovery inspection, IPv6 device tracking, IPv6 address glean, and IPv6 binding table recovery, to provide
The feature bundles several Layer 2 IPv6 first-hop security features, including IPv6 neighbor discovery inspection, IPv6 device tracking, IPv6 address glean, and IPv6 binding table recovery, to provide
