Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
|
|
|
- Whitney Allen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
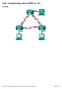
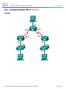
1 Lab - Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues Topology Addressing Table R1 ISP Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/ N/A S0/0/ N/A S0/0/ N/A Lo N/A S1 VLAN PC-A NIC Part 1: Identify the Problem Part 2: Implement Network Changes Part 3: Verify Full Functionality Part 4: Document Findings and Configuration Changes Background / Scenario In this lab, the company that you work for is experiencing problems with their Local Area Network (LAN). You have been asked to troubleshoot and resolve the network issues. In Part 1, you will connect to devices on the LAN and use troubleshooting tools to identify the network issues, establish a theory of probable cause, and test that theory. In Part 2, you will establish a plan of action to resolve and implement a solution. In Part 3, you will verify full functionality has been restored. Part 4 provides space for you to document your troubleshooting findings along with the configuration changes that you made to the LAN devices. Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). The switches used are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions may be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of this lab for the correct interface identifiers Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 12
2 Required Resources 2 Router (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable) 1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable) 1 PC (Windows 7 or 8 with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term) Ethernet and Serial cables as shown in the topology Troubleshooting Configurations The following settings must be configured on the devices shown in the topology. Paste the configurations onto the specified devices prior to starting the lab. S1: no ip domain-lookup hostname S1 ip domain-name ccna-lab.com username admin01 privilege 15 secret 9 $9$lJgfiLCHj.Xp/q$hA2w.oyQPTMhBGPeR.FZo3NZRJ9T1FdqvgRCFyBYnNs interface FastEthernet0/1 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/2 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/3 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/4 shutdown interface FastEthernet0/5 duplex full interface Vlan1 ip address line vty 0 4 login local transport input ssh line vty 5 15 login local transport input ssh crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus 1024 end R1: hostname R1 no ip domain-lookup ip domain-name ccna-lab.com username admin01 privilege 15 secret 9 $9$8a4jGjbPPpeeoE$WyPsIiOaYT4ATlJzrR6T9E6vIdESOGF.NYX53arPmtA interface GigabitEthernet0/0 shutdown interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ip address duplex half 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 2 of 12
3 speed auto no shutdown interface Serial0/0/0 ip address no shutdown interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown line vty 0 4 login local transport input ssh crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus 1024 end ISP: hostname ISP no ip domain-lookup interface Serial0/0/0 ip address no shut interface Lo0 ip address ip route end Part 1: Identify the Problem. The only available information about the network problem is that the users are experiencing slow response times and that they are not able to reach an external device on the Internet at IP address To determine probable cause(s) for these network issues, you will need to utilize network commands and tools on the LAN equipment shown in the topology. Note: The user name admin01 with a password of cisco12345 will be required to log into the network equipment. Step 1: Troubleshoot from the PC. a. From the PC command prompt, ping the external server IP Address b. Use the ipconfig command to determine the network settings on the PC Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 3 of 12
4 Step 2: Troubleshoot from S1 using a SSH client session. Note: Any SSH client software can be used. Tera Term is used in the examples in this lab. a. SSH to S1 using its IP Address of and log into the switch using admin01 for the user name and cisco12345 for the password. b. Issue the terminal monitor command on S1 to allow log messages to be sent to the VTY line of your SSH session. After a few seconds you notice the following error message being displayed in your SSH window. S1# terminal monitor S1# *Mar 1 02:08:11.338: %CDP-4-DUPLEX_MISMATCH: duplex mismatch discovered on FastEthernet0/5 (not half duplex), with R1.ccna-lab.com GigabitEthernet0/1 (half duplex). S1# c. On S1, issue the show interface f0/5 command to view the duplex setting of the interface. S1# show interface f0/5 FastEthernet0/5 is up, line protocol is up (connected) Hardware is Fast Ethernet, address is 0cd9.96e8.8a05 (bia 0cd9.96e8.8a05) 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 4 of 12
5 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit/sec, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Full-duplex, 100Mb/s, media type is 10/100BaseTX input flow-control is off, output flow-control is unsupported ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:35, output 00:00:01, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue: 0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 849 packets input, bytes, 0 no buffer Received 123 broadcasts (122 multicasts) 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored 0 watchdog, 122 multicast, 0 pause input 0 input packets with dribble condition detected 4489 packets output, bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 1 interface resets 0 unknown protocol drops 0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred 0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out S1# Step 3: Troubleshoot on R1 using an SSH client. a. SSH to R1 s LAN interface and log in using admin01 for the user name and cisco12345 as the password. b. Issue the terminal monitor command on R1 to allow log messages to be sent to the VTY line of your SSH session for R1. After a few seconds the duplex mismatch message appears on R1 s SSH session Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 5 of 12
6 terminal monitor *Nov 23 16:12:36.623: %CDP-4-DUPLEX_MISMATCH: duplex mismatch discovered on GigabitEthernet0/1 (not full duplex), with S1.ccna-lab.com FastEthernet0/5 (full duplex). c. Issue the show interface G0/1 command on R1 to display the duplex setting. show interfaces g0/1 GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is CN Gigabit Ethernet, address is d48c.b5ce.a0c1 (bia d48c.b5ce.a0c1) Internet address is /24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit/sec, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Half Duplex, 100Mbps, media type is RJ45 output flow-control is unsupported, input flow-control is unsupported ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:15, output 00:00:05, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue: 0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 641 packets input, bytes, 0 no buffer Received 453 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts) 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored 0 watchdog, 361 multicast, 0 pause input 1043 packets output, bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 1 interface resets 235 unknown protocol drops 0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred 0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out d. Issue the ping command on R1 to test connectivity to the external server. ping Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:... Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) e. Issue the show ip interface brief command on R1 to verify interface IP Address settings. show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 6 of 12
7 Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/ YES manual up up Serial0/0/ YES manual up up Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down f. Issue the show ip route command on R1 to verify the router s default gateway setting. show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP a - application route + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is not set C L C L /8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/ /32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/ /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks /24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/ /32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 List the probable causes for the network problems that employees are experiencing. Part 2: Implement Network Changes You have communicated the problems that you discovered in Part 1 to your supervisor. She has approved these changes and has requested that you implement them Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 7 of 12
8 Step 1: Set the Default Gateway on the PC to Step 2: Set the duplex setting for interface G0/1 on R1 to full duplex. conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)# *Nov 23 17:23:36.879: %CDP-4-DUPLEX_MISMATCH: duplex mismatch discovered on GigabitEthernet0/1 (not full duplex), with S1.ccna-lab.com FastEthernet0/5 (full duplex). R1(config)# R1(config)# interface g0/1 R1(config-if)# duplex full R1(config-if)# exit *Nov 23 17:24:08.039: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to down R1(config)# *Nov 23 17:24:10.363: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface GigabitEthernet0/1, changed state to up *Nov 23 17:24:10.459: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console R1(config)# Step 3: Reconfigure the IP address for S0/0/0 to IP Address /30 on R1. R1(config)# interface s0/0/ Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 8 of 12
9 R1(config-if)# ip address R1(config-if)# exit Step 4: Configure the Gateway of last resort on R1 with a default route. R1(config)# ip route R1(config)# end Part 3: Verify Full Functionality Verify that full functionality has been restored. Step 1: Verify that all interfaces and routes have been set correctly and that routing has been restored on R1. a. Issue the show ip route command to verify that the default gateway has been set correctly. show ip route Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP a - application route + - replicated route, % - next hop override Gateway of last resort is to network S* /0 [1/0] via /8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C /30 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 L /32 is directly connected, Serial0/0/ /24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks C /24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 L /32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 b. Issue the show ip interface s0/0/0 command to verify that the IP Address on S0/0/0 is set correctly. show ip interface s0/0/0 Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is /30 Broadcast address is Address determined by setup command MTU is 1500 bytes <output omitted> IPv4 WCCP Redirect exclude is disabled c. Issue the ping command to verify that the external server is reachable now. ping Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 9 of 12
10 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to , timeout is 2 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms d. Issue the show interface g0/1 command to verify that the duplex setting is full duplex. show interface g0/1 GigabitEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is CN Gigabit Ethernet, address is d48c.b5ce.a0c1 (bia d48c.b5ce.a0c1) Internet address is /24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW Kbit/sec, DLY 100 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set Keepalive set (10 sec) Full Duplex, 100Mbps, media type is RJ45 output flow-control is unsupported, input flow-control is unsupported ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 00:00:04, output 00:00:04, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue: 0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 559 packets input, bytes, 0 no buffer Received 279 broadcasts (0 IP multicasts) 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored 0 watchdog, 208 multicast, 0 pause input 742 packets output, bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 0 collisions, 2 interface resets 133 unknown protocol drops 0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred 1 lost carrier, 0 no carrier, 0 pause output 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 10 of 12
11 Step 2: Verify End-to-End connectivity from the LAN PC. a. Issue the ipconfig command from the command prompt on the PC. b. Issue the ping command from the CMD window on the PC Part 4: Document Findings and Configuration Changes Use the space provided below to document the issues found during your troubleshooting and the configurations changes made to resolve those issues Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 11 of 12
12 Reflection This lab had you troubleshoot all devices before making any changes. Is there another way to apply the troubleshooting methodology? Router Interface Summary Table Router Interface Summary Router Model Ethernet Interface #1 Ethernet Interface #2 Serial Interface #1 Serial Interface # Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) 1900 Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) 2801 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) 2811 Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) 2900 Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 12 of 12
Management IP Interface
 The management interface is used for the video control plane messages, such as session creation and deletion, between the Logical Edge Devices (LED) and the external Edge Resource Manager (ERM) server.
The management interface is used for the video control plane messages, such as session creation and deletion, between the Logical Edge Devices (LED) and the external Edge Resource Manager (ERM) server.
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2
 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area SPFv2 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Lab Viewing Network Device MAC Addresses
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure Devices
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure Devices
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
CCNA Semester 2 labs Part 2 of 2 Labs for chapters 8 11 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 8.3.3.6 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv3 9.2.2.7 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Standard
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example
 GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
GRE Tunnel with VRF Configuration Example Document ID: 46252 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Caveats
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers
 Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Troubleshoot Methodology Troubleshoot Examples Introduction This document describes troubleshoot
Troubleshoot interface down issues in Cisco routers Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Conventions Troubleshoot Methodology Troubleshoot Examples Introduction This document describes troubleshoot
Lab Configuring Switch Security Features Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 172.16.99.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 99 172.16.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.16.99.1 PC-A NIC 172.16.99.3
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 172.16.99.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 99 172.16.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.16.99.1 PC-A NIC 172.16.99.3
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4
 Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Lab Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control
 hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
hapter 5 Lab 5-1, onfigure and Verify Path ontrol Topology Objectives Background onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations.
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 4 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Lab - Exploring Router Physical Characteristics
 Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Router External Characteristics Part 2: Examine Router Internal Characteristics Using Show Commands Background / Scenario In this lab, you will examine the outside of
Topology Objectives Part 1: Examine Router External Characteristics Part 2: Examine Router Internal Characteristics Using Show Commands Background / Scenario In this lab, you will examine the outside of
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
CCNA Practice test. 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage? A. NTP B. WCCP C. Telnet D. SNMP Answer: D
 1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
1. Which network would support at least 30 hosts? A. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 B. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.240 C. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 D. 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.248 2. Which protocol can cause high CPU usage?
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
 This chapter explains how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the Cisco ASR 901 router. Configuring the Interface, page 1 Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode, page 2 Enabling the Interface,
This chapter explains how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the Cisco ASR 901 router. Configuring the Interface, page 1 Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode, page 2 Enabling the Interface,
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
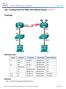 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card
 CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
CHAPTER 34 Configuring Link Aggregation on the ML-MR-10 card This chapter applies to the ML-MR-10 card and describes how to configure link aggregation for the ML-Series cards, both EtherChannel and packet-over-sonet/sdh
Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Switch configuration. By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch.
 By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
By the end of this session, you will be able to: Describe basic switch configuration methods. Configure a switch. 4 SESSION OVERVIEW... 2 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS... 3 WHY CONFIGURE SWITCHES?... 4 CONSOLE PORT...
Lab Using the CLI to Gather Network Device Information Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Lab Exploring Cisco IOS and Configuring Basic Switch Settings
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Cable
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Cable
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
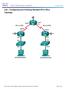 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
CCNA Semester 2 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 2 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes 2.3.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Static Routes 3.2.1.9 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 5.2.2.9 Lab - Configuring
The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol.
 CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
CIS 83 LAB 4 - Spanning Tree Protocol Rich Simms October 3, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar with Cisco switches as well as the Spanning Tree Protocol. Scenario This lab was
Peter, Please approve us apply a new ISP connection to separate with CCA for ccahalmar. The bandwidth is 100M.
 All test are done in business time. Our testing are not professional. Not like ZBRELLA using www.speedtest.net as professional test. All testing report followed after. 1 From ISP s test shows the connection
All test are done in business time. Our testing are not professional. Not like ZBRELLA using www.speedtest.net as professional test. All testing report followed after. 1 From ISP s test shows the connection
Application Guide. VLANs for improved Q-SYS performance
 Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Application Guide Rev. A, 6 June 2018 OPTIMIZE Q-SYS PERFORMANCE: CREATE DEDICATED VLANS. One way to greatly ensure the reliability and performance of a Q-SYS network is putting Q-SYS traffic on one or
Lab Securing Network Devices
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3
Lab - Examining Telnet and SSH in Wireshark
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure the Devices
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure the Devices
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLs Topology
 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device First Published: August 9, 2005 Last Updated: December 3, 2010 Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device
 Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
Using Setup Mode to Configure a Cisco Networking Device Setup mode provides an interactive menu to help you to create an initial configuration file for a new networking device, or a device that you have
Configuring Interfaces on the ML-Series Card
 5 CHAPTER This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and running. Advanced packet-over-sonet (POS) interface configuration is covered
5 CHAPTER This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and running. Advanced packet-over-sonet (POS) interface configuration is covered
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network
 IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
IPv6 Tunnel through an IPv4 Network Document ID: 25156 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations (Manual IPv6 Mode) Configurations
Configuring IRB. Integrated Routing and Bridging CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure integrated routing and bridging (IRB) for the ML-Series card. For more information about the Cisco IOS commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure integrated routing and bridging (IRB) for the ML-Series card. For more information about the Cisco IOS commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
Cisco Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam. Practice Test. Version 2.2. https://certkill.com
 Cisco 640-821 640-821 Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam Practice Test Version 2.2 QUESTION NO: 1 Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received? A. No VTY password has been set B.
Cisco 640-821 640-821 Introduction to Cisco Networking Technologies Exam Practice Test Version 2.2 QUESTION NO: 1 Refer to the exhibit. Why was this message received? A. No VTY password has been set B.
If this is your first time configuring the switch, you will notice that the Switch IOS is almost identical to Router IOS.
 Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Spanning Tree Lab Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other switch to be selected
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
The configuration of the router at the initial stage was fairly simple (quoting only significant commands, not the entire config):
 Gentlemen, As was to be expected, Joseph was correct on all accounts. My testbed consisted of a 2811 router running 12.4(24)T4 Advanced IP Services, and two PCs connected to it. One PC was used as the
Gentlemen, As was to be expected, Joseph was correct on all accounts. My testbed consisted of a 2811 router running 12.4(24)T4 Advanced IP Services, and two PCs connected to it. One PC was used as the
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology
 Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives
Lab - Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACL Configuration and Placement Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives
Lab - Troubleshooting ACL Configuration and Placement Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ G0/1 192.168.1.1
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing
 Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Configuring IEEE 802.3ad Link Bundling and Load Balancing This document describes how the IEEE 802.3ad link bundling and load balancing leverages the EtherChannel infrastructure within Cisco software to
Lab - Configuring IPv6 Addresses on Network Devices
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway Objectives R1 G0/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 64 N/A G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 64 N/A S1 VLAN 1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::B 64 N/A PC-A
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address Prefix Length Default Gateway Objectives R1 G0/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1 64 N/A G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 64 N/A S1 VLAN 1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::B 64 N/A PC-A
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router (InterVLAN Routing)
 Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
CS IT ports switch basic configuration. Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee.
 Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
Lecture (01) Introduction to 24 ports managed switches By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee CS IT Agenda 24 ports switch basic configuration Switch remote configuration peer2peer star network clients/server star network
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1, Configure and Verify Path Control Using PBR. Topology. Objectives. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 hapter 5 Topology Objectives onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations. Verify the configuration and operation by using
hapter 5 Topology Objectives onfigure and verify policy-based routing. Select the required tools and commands to configure policy-based routing operations. Verify the configuration and operation by using
configuring and connecting 24
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch
 Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lecture (01) configuring and connecting 24 ports switch Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee ١ ٢ Step 1: connecting your PC to the Console Port. Open HyperTerminal software Press RETURN to get started. Switch> (User
Lab Configuring HSRP and GLBP Topology
 Topology 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Chapter 3: Using Maintenance & Troubleshooting Tools and Applications
 Chapter 3: Using Maintenance & Troubleshooting Tools and Applications CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 3 Objectives Use Cisco IOS commands to gather information
Chapter 3: Using Maintenance & Troubleshooting Tools and Applications CCNP TSHOOT: Maintaining and Troubleshooting IP Networks Course v6 1 Chapter 3 Objectives Use Cisco IOS commands to gather information
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab - Troubleshooting DHCPv4 Topology
 Topology 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.0.1
Topology 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.0.1
Lab 19a. Router On A Stick
 Rev. 00.0 Lab a. Router On A Stick c cnac o okbook.com G O A L Configure routing on R, enabling host H to communicate with host H, then make VLAN 0 native on the trunk. Topology You'll need A router (R)
Rev. 00.0 Lab a. Router On A Stick c cnac o okbook.com G O A L Configure routing on R, enabling host H to communicate with host H, then make VLAN 0 native on the trunk. Topology You'll need A router (R)
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication Topology
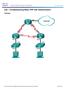 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 The chapter applies to the ML-Series (ML100T-2, ML100X-8, ML1000-2 cards. This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and
CHAPTER 6 The chapter applies to the ML-Series (ML100T-2, ML100X-8, ML1000-2 cards. This chapter describes basic interface configuration for the ML-Series card to help you get your ML-Series card up and
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
CHAPTER 6 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces for the Catalyst 4500 series switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following
Lab 15d. PPPoE Troubleshooting
 MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 Rev. 0808.88 Lab d. PPPoE Troubleshooting cc na c ookb ook.com T O P O L O G Y & G O A L Client Pool: 0.0.0. 0.0.0. Create a PPPoE connection from an edge router
MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 MAC: 0:00:00:00:00:0 Rev. 0808.88 Lab d. PPPoE Troubleshooting cc na c ookb ook.com T O P O L O G Y & G O A L Client Pool: 0.0.0. 0.0.0. Create a PPPoE connection from an edge router
Inverse MUX Application using Multilink PPP
 Inverse MUX Application using Multilink PPP Document ID: 10235 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used Related Products onventions onfigure Network Diagram onfigurations Verify Troubleshoot
Inverse MUX Application using Multilink PPP Document ID: 10235 ontents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements omponents Used Related Products onventions onfigure Network Diagram onfigurations Verify Troubleshoot
Chapter 6: Network Layer
 Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Lab Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing Topology
 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 7 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1.1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 7 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1.1 192.168.1.1
Configuring Interfaces
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. This chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Configuration, page 9-2 Using the Interface,
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure interfaces on the Catalyst 6500 series switches. This chapter consists of these sections: Understanding Interface Configuration, page 9-2 Using the Interface,
Configuring Virtual Interfaces
 Configuring Virtual Interfaces Virtual interfaces are software-based interfaces that you create in the memory of the networking device using Cisco IOS commands. Virtual interfaces do not have a hardware
Configuring Virtual Interfaces Virtual interfaces are software-based interfaces that you create in the memory of the networking device using Cisco IOS commands. Virtual interfaces do not have a hardware
Lab - Building a Switch and Router Network
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
Lab - Designing and Implementing a Subnetted IPv4 Addressing Scheme
 Lab - Designing and Implementing a Subnetted IPv4 Addressing Scheme Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G00 NA G01 NA Lo0 Lo1 NA NA S1 VLAN 1
Lab - Designing and Implementing a Subnetted IPv4 Addressing Scheme Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G00 NA G01 NA Lo0 Lo1 NA NA S1 VLAN 1
TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS
 QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE
 Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE Document ID: 4105 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Configuring PPPoE Client on the Cisco 2600 to Connect to a Non Cisco DSL CPE Document ID: 4105 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations
Configuring the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Modular Ethernet Line Card
 Configuring the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Modular Ethernet Line Card This chapter provides information about configuring the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Modular Ethernet Line Card on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.
Configuring the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Modular Ethernet Line Card This chapter provides information about configuring the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Modular Ethernet Line Card on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.
Lab Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity
 Lab 9.2.5 Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.252
Lab 9.2.5 Troubleshooting WAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Serial 0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.252
Lab Configuring IPv6 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IPv6 Address / Prefix Length Default Gateway R1 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 eui-64 N/A S0/0/1 FC00::1/64 N/A R3 G0/1 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 eui-64 N/A
Lab Troubleshooting IPv4 and IPv6 Static Routes (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
Throughput Issues on ASR1000 Series Router
 Throughput Issues on ASR1000 Series Router Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Problem Solution Scenario 1. High Bandwidth Ingress Interface(s) and Low Bandwidth
Throughput Issues on ASR1000 Series Router Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Problem Solution Scenario 1. High Bandwidth Ingress Interface(s) and Low Bandwidth
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Retake - Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key)
 Retake - Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key) Name:. Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Develop the IPv4 Address Scheme (15 points, 0 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device IPv4 and Security
Retake - Skills Assessment Student Training (Answer Key) Name:. Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Develop the IPv4 Address Scheme (15 points, 0 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device IPv4 and Security
Ethernet over GRE Tunnels
 The feature allows customers to leverage existing low end residential gateways to provide mobility services to mobile nodes using Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Tunneling
The feature allows customers to leverage existing low end residential gateways to provide mobility services to mobile nodes using Proxy Mobile IPv6 (PMIPv6), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Tunneling
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM
 Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Auto In-Service State for Ports
 This document describes the Auto In-Service State (AINS) feature on the port. Effective Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.1, the Cisco NCS 4200 Series support management of equipment and port state model in two
This document describes the Auto In-Service State (AINS) feature on the port. Effective Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.6.1, the Cisco NCS 4200 Series support management of equipment and port state model in two
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software
 Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
15d. PPPoE Troubleshooting
 Rev. 0800.0900 d. PPPoE Troubleshooting cc na c ookb ook.com PPPoE troubleshooting has been a part of the CCNA longer than certification guide authors have made any serious attempt to cover the topic.
Rev. 0800.0900 d. PPPoE Troubleshooting cc na c ookb ook.com PPPoE troubleshooting has been a part of the CCNA longer than certification guide authors have made any serious attempt to cover the topic.
Configuring Management Interfaces on Cisco IOS XR Software
 Configuring Management Interfaces on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes configuration procedures for management interfaces on the route processors (RPs). Although the management interfaces on
Configuring Management Interfaces on Cisco IOS XR Software This module describes configuration procedures for management interfaces on the route processors (RPs). Although the management interfaces on
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Chapter 8 Lab 8-3, Configuring 6to4 Tunnels Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a 6to4 tunnel. Configure static IPv6 routes. Background In this lab, you configure EIGRP for full connectivity
Address Resolution Protocol
 The (ARP) feature performs a required function in IP routing. ARP finds the hardware address, also known as Media Access Control (MAC) address, of a host from its known IP address. ARP maintains a cache
The (ARP) feature performs a required function in IP routing. ARP finds the hardware address, also known as Media Access Control (MAC) address, of a host from its known IP address. ARP maintains a cache
Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay
 Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1
Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame Relay Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1
Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable
 Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable Document ID: 12084 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Configuring GRE Tunnel Over Cable Document ID: 12084 Introduction Before You Begin Conventions Prerequisites Components Used Background Theory Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot
Lab Configuring Basic RIPv2 (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
(Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
Lab Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity
 Lab 9.2.4 Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fast Ethernet 0/2 S1 S1 VLAN
Lab 9.2.4 Troubleshooting LAN Connectivity Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Switch Port R1 R1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fast Ethernet 0/2 S1 S1 VLAN
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS. Cisco Lab Øvelse Af Kim Donnerborg / RTS. Side 0 af 8
 KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
Lab - Configuring a Switch Management Address
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 N/A Part 1: Configure a Basic Network
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 N/A Part 1: Configure a Basic Network
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Configuring the SM-1-STM1
 4 CHAPTER To continue your SM-1-STM1 service module installation, you must configure the STM-1 interface. This chapter contains the following sections: Configuring the Interface, page 4-1 Checking the
4 CHAPTER To continue your SM-1-STM1 service module installation, you must configure the STM-1 interface. This chapter contains the following sections: Configuring the Interface, page 4-1 Checking the
Lab QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping
 Lab 8.9.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC) is likely to lead
Lab 8.9.9 QoS Manually Configured Frame Relay Traffic Shaping Objective Failing to perform traffic shaping before injecting traffic into a Frame Relay permanent virtual circuit (PVC) is likely to lead
