Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab
|
|
|
- Rosemary Potter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
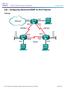
1 Lab 9.6.1: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab Topology Diagram Address Table 1
2 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup configuration and reload a router to the default state. Perform basic configuration tasks on a router. Configure and activate interfaces. Configure EIGRP routing on all routers. Verify EIGRP routing using show commands. Disable automatic summarization. Configure manual summarization. Document the EIGRP configuration. Scenario In this lab activity, you will learn how to configure the routing protocol EIGRP using the network shown in the Topology Diagram. A loopback address will be used on the R2 router to simulate a connection to an ISP, where all traffic that is not destined for the local network will be sent. Some segments of the network have been subnetted using VLSM. EIGRP is a classless routing protocol that can be used to provide subnet mask information in the routing updates. This will allow VLSM subnet information to be propagated throughout the network. Task 1: Prepare the Network. Step 1: Cable a network that is similar to the one in the Topology Diagram. This activity begins with an initial network in the logical workspace. Step 2: Clear any existing configurations on the routers. Task 2: Perform Basic Router Configurations. Perform basic configuration of the R1, R2, and R3 routers according to the following guidelines: 1. Configure the router hostname. 2. Disable DNS lookup. 3. Configure an EXEC mode password. 4. Configure a message of the day banner. 5. Configure a password for console connections. 6. Configure a password for VTY connections. Task 3: Configure and Activate Serial and Ethernet Addresses. Step 1: Configure the interfaces on the R1, R2, and R3 routers. Configure the interfaces on the R1, R2, and R3 routers with the IP addresses from the table under the Topology Diagram. Step 2: Verify IP addressing and interfaces. Use the show ip interface brief command to verify that the IP addressing is correct and that the interfaces are active. When you have finished, be sure to save the running configuration to the NVRAM of the router. Step 3: Configure Ethernet interfaces of PC1, PC2, and PC3. Configure the Ethernet interfaces of PC1, PC2, and PC3 with the IP addresses and default gateways from the table under the Topology Diagram. 2
3 Task 4: Configure EIGRP on the R1 Router. Step 1: Enable EIGRP. Use the router eigrp command in global configuration mode to enable EIGRP on the R1 router. Enter 1 for the autonomous system parameter. R1(config)#router eigrp 1 Step 2: Configure classful network Once you are in the Router EIGRP configuration sub mode, configure the classful network to be included in the EIGRP updates that are sent out of R1. R1(config router)#network The router will begin to send EIGRP update messages out each interface belonging to the network. EIGRP updates will be sent out of the FastEthernet0/0 and Serial0/0/0 interfaces because they are both on subnets of the network. Step 3: Configure the router to advertise the /30 network attached to the Serial0/0/1 interface. Use the wildcard mask option with the network command to advertise only the subnet and not the entire classful network. Note: Think of a wildcard mask as the inverse of a subnet mask. The inverse of the subnet mask is To calculate the inverse of the subnet mask, subtract the subnet mask from : Subtract the subnet mask Wildcard mask R1(config router)# network When you are finished with the EIGRP configuration for R1, return to privileged EXEC mode and save the current configuration to NVRAM. Task 5: Configure EIGRP on the R2 and R3 Routers. Step 1: Enable EIGRP routing on the R2 router using the router eigrp command. Use an autonomous system number of 1. R2(config)#router eigrp 1 Step 2: Use the classful address to include the network for the FastEthernet0/0 interface. R2(config router)#network Notice that DUAL sends a notification message to the console stating that a neighbor relationship with another EIGRP router has been established. 3
4 What is the IP address of the EIGRP neighbor router? What interface on the R2 router is the neighbor adjacent to? Step 3: Configure the R2 router to advertise the /30 network attached to the Serial0/0/1 interface. Use the wildcard mask option with the network command to advertise only the subnet and not the entire classful network. When you are finished, return to privileged EXEC mode. R2(config router)#network R2(config router)#end Step 4: Configure EIGRP on the R3 router using the router eigrp and network commands. Use an autonomous system number of 1. Use the classful network address for the network attached to the FastEthernet0/0 interface. Include the wildcard masks for the subnets attached to the Serial0/0/0 and Serial 0/0/1 interfaces. When you are finished, return to privileged EXEC mode. R3(config)#router eigrp 1 R3(config router)#network R3(config router)#network R3(config router)# Notice that when the networks for the serial links from R3 to R1 and R3 to R2 are added to the EIGRP configuration, DUAL sends a notification message to the console stating that a neighbor relationship with another EIGRP router has been established. Task 6: Verify EIGRP Operation. Step 1: View neighbors. On the R1 router, use the show ip eigrp neighbors command to view the neighbor table and verify that EIGRP has established an adjacency with the R2 and R3 routers. You should be able to see the IP address of each adjacent router and the interface that R1 uses to reach that EIGRP neighbor. R1#show ip eigrp neighbors Step 2: View routing protocol information. On the R1 router, use the show ip protocols command to view information about the routing protocol operation. Notice that the information that was configured in Task 5, such as protocol, autonomous system number, and networks, is shown in the output. The IP addresses of the adjacent neighbors are also shown. 4
5 R1#show ip protocols Notice that the output specifies the autonomous system number used by EIGRP. Remember, the autonomous system number must be the same on all routers for EIGRP to establish neighbor adjacencies and share routing information. Task7: Examine EIGRP Routes in the Routing Tables. Step1: View the routing table on the R1 router. EIGRP routes are denoted in the routing table with a D, which stands for DUAL (Diffusing Update Algorithm), which is the routing algorithm used by EIGRP. R1#show ip route Notice that the /16 parent network is variably subnetted with three child routes using either a /24 or /30 mask. Also notice that EIGRP has automatically included a summary route to Null0 for the /16 network. The /16 route does not actually represent a path to reach the parent network, /16. If a packet destined for /16 does not match one of the level 2 child routes, it is sent to the Null0 interface. The /24 Network is also variably subnetted and includes a Null0 route. Step 2: View the routing table on the R3 router. The routing table for R3 shows that both R1 and R2 are automatically summarizing the /16 network and sending it as a single routing update. Because of automatic summarization, R1 and R2 are not propagating the individual subnets. Because R3 is getting two equal cost routes for /16 from both R1 and R2, both routes are included in the routing table. Task 8: Configure EIGRP Metrics. Step 1: View the EIGRP metric information. Use the show ip interface command to view the EIGRP metric information for the Serial0/0/0 interface on the R1 router. Notice the values that are shown for the bandwidth, delay, reliability, and load. R1#show interface serial0/0/0 Step 2: Modify the bandwidth of the Serial interfaces. On most serial links, the bandwidth metric will default to 1544 Kbits. If this is not the actual bandwidth of the serial link, the bandwidth will need to be changed so that the EIGRP metric can be calculated correctly. For this lab, the link between R1 and R2 will be configured with a bandwidth of 64 kbps, and the link between R2 and R3 will be configured with a bandwidth of 1024 kbps. Use the bandwidth command to modify the bandwidth of the Serial interfaces of each router. R1 router: R1(config)#interface serial0/0/0 R1(config if)#bandwidth 64 R2 router: 5
6 R2(config)#interface serial0/0/0 R2(config if)#bandwidth 64 R2(config)#interface serial0/0/1 R2(config if)#bandwidth 1024 R3 router: R3(config)#interface serial0/0/1 R3(config if)#bandwidth 1024 Note: The bandwidth command only modifies the bandwidth metric used by routing protocols, not the physical bandwidth of the link. Step 3: Verify the bandwidth modifications. Use the show ip interface command to verify that the bandwidth value of each link has been changed. Note: Use the interface configuration command no bandwidth to return the bandwidth to its default value. Task 9: Examine Successors and Feasible Distances. Step 1: Examine the successors and feasible distances in the routing table on R2. R2#show ip route Step 2: Answer the following questions: What is the best path to PC1? A successor is a neighboring router that is currently being used for packet forwarding. A successor is the least cost route to the destination network. The IP address of a successor is shown in a routing table entry right after the word via. What is the IP address and name of the successor router in this route? Feasible distance (FD) is the lowest calculated metric to reach that destination. FD is the metric listed in the routing table entry as the second number inside the brackets. What is the feasible distance to the network that PC1 is on? Task 10: Determine if R1 is a Feasible Successor for the Route from R2 to the Network. A feasible successor is a neighbor who has a viable backup path to the same network as the successor. In order to be a feasible successor, R1 must satisfy the feasibility condition. The feasibility condition (FC) is met when a neighbor s reported distance (RD) to a network is less than the local router s feasible distance to the same destination network. Step 1: Examine the routing table on R1. 6
7 What is the reported distance to the network? Step 2: Examine the routing table on R2. What is the feasible distance to the network? Would R2 consider R1 to be a feasible successor to the network? Task 11: Examine the EIGRP Topology Table. Step 1: View the EIGRP topology table. Use the show ip eigrp topology command to view the EIGRP topology table on R2. Step 2: View detailed EIGRP topology information. Use the [network] parameter of the show ip eigrp topology command to view detailed EIGRP topology information for the network. R2#show ip eigrp topology How many successors are there for this network? What is the feasible distance to this network? What is the IP address of the feasible successor? What is the reported distance for from the feasible successor? What would be the feasible distance to if R1 became the successor? Task 12: Disable EIGRP Automatic Summarization. Step 1: Examine the routing table of the R3 router. Notice that R3 is not receiving individual routes for the /24, /24, and /24 subnets. Instead, the routing table only has a summary route to the classful network address of /16 through the R1 router. This will cause packets that are destined for the /24 network to be sent through the R1 router instead of being sent straight to the R2 router. 7
8 Why is the R1 router ( ) the only successor for the route to the /16 network? Notice that the reported distance from R2 is higher than the feasible distance from R1. R3#show ip eigrp topology Step 2: Disable automatic summarization on all three routers with the no auto summary command. R1(config)#router eigrp 1 R1(config router)#no auto summary R2(config)#router eigrp 1 R2(config router)#no auto summary R3(config)#router eigrp 1 R3(config router)#no auto summary Step 3: View the routing table on R1 again. Notice that individual routes for the /24, /24, and /24 subnets are now present and the summary Null route is no longer listed. Task 13: Configure Manual Summarization. Step 1: Add loopback addresses to R3 router. Add two loopback addresses, /24 and /24, to the R3 router. These virtual interfaces will be used to represent networks to be manually summarized along with the /24 LAN. R3(config)#interface loopback1 R3(config if)#ip address R3(config if)#interface loopback2 R3(config if)#ip address Step 2: Add the and networks to the EIGRP configuration on R3. R3(config)#router eigrp 1 R3(config router)#network R3(config router)#network Step 3: Verify new routes. View the routing table on the R1 router to verify that the new routes are being sent out in the EIGRP updates sent by R3. Step 4: Apply manual summarization to outbound interfaces. The routes to the /24, /24, and /24 networks can be summarized in the single network /22. Use the ip summary address eigrp as number network address subnet mask command to configure manual summarization on each of the outbound interfaces connected to EIGRP neighbors. R3(config)#interface serial0/0/0 8
9 R3(config if)#ip summary address eigrp R3(config if)#interface serial0/0/1 R3(config if)#ip summary address eigrp R3(config if)# Step 5: Verify the summary route. View the routing table on the R1 router to verify that the summary route is being sent out in the EIGRP updates sent by R3. At the end of this activity your completion rate should be 100%. If the completion rate is not 100%, use the Check Results button and troubleshoot as necessary. All contents are Copyright Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. 9
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP
 Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Topology Lab10- Configuring EIGRP Page 1 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup
Lab 9.6.2: Challenge EIGRP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway HQ BRANCH1 BRANCH2 PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC All
Lab : Challenge OSPF Configuration Lab. Topology Diagram. Addressing Table. Default Gateway. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 HQ S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Lo1 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 Branch1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 Branch2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 PC1
Chapter 9. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I
 Chapter 9 Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I CCNA2-1 Chapter 9-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College
Chapter 9 Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) Part I CCNA2-1 Chapter 9-2 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College
Final exam study Guide
 Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
Final exam study Guide K-1A * In relationship to the OSI layer model and encapsulation/decapsulation process, what happen to a packet that travels through multiple hops of routers? - What happen to the
EIGRP. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9. Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech
 Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 9.0.1 Introduction Enhanced Interior
Video Frank Schneemann, MS EdTech EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 ITE PC v4.0 Chapter 1 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 9.0.1 Introduction Enhanced Interior
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
CIS 83 LAB 3 - EIGRP Rich Simms September 23, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring EIGRP on three routers. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary distance-vector
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM
 Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Lab: RIP v2 with VLSM Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 Lo1 S0/0/0 Lo1 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 S/0/0/1 Learning Objectives
Lab 5.6.2: Challenge RIP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 PC3 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 Fa0/0 S0/0/1 NIC NIC NIC Learning Objectives Upon completion
EIGRP 04/01/2008. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen
 EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen 04/01/2008 1 Introduction 2 EIGRP Roots of EIGRP: IGRP -Developed in 1985 to overcome RIPv1 s limited hop count -Distance vector routing
EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 Modified by Tony Chen 04/01/2008 1 Introduction 2 EIGRP Roots of EIGRP: IGRP -Developed in 1985 to overcome RIPv1 s limited hop count -Distance vector routing
ITE PC v4.0. Chapter Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
 EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 1 Objectives Describe the background and history of Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). Examine the basic EIGRP configuration commands and
EIGRP Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 9 1 Objectives Describe the background and history of Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP). Examine the basic EIGRP configuration commands and
Lab 2.8.2: Challenge Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 Web Server Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 209.165.200.225
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP PC1 PC2 Web Server Fa0/0 S0/0/0 Fa0/0 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 209.165.201.2 255.255.255.252 Fa0/0 209.165.200.225
Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks
 Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks Lecturers Amnach Khawne Jirasak Sittigorn Chapter 1 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 8 : The Routing Table: A Closer Look Chapter 9 : EIGRP Chapter
Introduction to Local and Wide Area Networks Lecturers Amnach Khawne Jirasak Sittigorn Chapter 1 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 8 : The Routing Table: A Closer Look Chapter 9 : EIGRP Chapter
CCNP Route Questions/Answers Labs
 Refer to the exhibit. R2 is an ASBR for EIGRP AS 100 and OSPF Area 24. R3 is an ASBR for EIGRP AS 100 and OSPF Area 34. R1 is configured for EIGRP AS 100, and is router where you can ping from. R4 has
Refer to the exhibit. R2 is an ASBR for EIGRP AS 100 and OSPF Area 24. R3 is an ASBR for EIGRP AS 100 and OSPF Area 34. R1 is configured for EIGRP AS 100, and is router where you can ping from. R4 has
TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS
 QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
Lab Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems
 Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
Lab 9.4.2 Correcting RIPv2 Routing Problems e Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Device Host Name Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 BRANCH1 Fast Ethernet 0/0 172.16.0.1
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS. Cisco Lab Øvelse Af Kim Donnerborg / RTS. Side 0 af 8
 KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
Lab : OSPF Troubleshooting Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 10.10.0.1 255.255.252.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 172.16.7.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.7.5 255.255.255.252 N/A
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 10.10.0.1 255.255.252.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 172.16.7.1 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 172.16.7.5 255.255.255.252 N/A
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway BRANCH HQ ISP Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0 135 points 1.1.1 What are the common components between a router and other computers? CPU RAM ROM Operating System 1.1.1.2 What does a router connect?
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 1 Planning and Cabling a Network V 4.0 135 points 1.1.1 What are the common components between a router and other computers? CPU RAM ROM Operating System 1.1.1.2 What does a router connect?
Lab 9.6.3: EIGRP Troubleshooting Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 172.18.64.1 255.255.192.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 209.165.202.129 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.202.133 255.255.255.252
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 172.18.64.1 255.255.192.0 N/A HQ S0/0/0 209.165.202.129 255.255.255.252 N/A S0/0/1 209.165.202.133 255.255.255.252
Lab - Configuring Multi-area OSPFv2
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.252 R1 R2 R3 Lo1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 Lo2 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 S0/0/0 (DCE) 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing
 Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 9 EIGRP João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts Introduction to EIGRP EIGRP:
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 9 EIGRP João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts Introduction to EIGRP EIGRP:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing
 Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN
Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN
Lab Configuring Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features Topology
 Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 4: Routing using OSPF
 Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Network Topology:- Lab 4: Routing using OSPF Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Description Rate Fa 0/0 172.16.1.17 255.255.255.240 ----- R1 LAN R1 Se 0/0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.252
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Lab 2 - EIGRP Stub / / /24
 Lab 2 - EIGRP Stub Lo0 1.1.0.1/24 1.1.1.1/24 Lo1 200.1.1.1/24 200.2.2.2/24 F0/0.1.2 F0/0 R1 1.1.2.1/24 Lo2.1 S1/2 CE 1.1.3.1/24 Lo3 12.1.1.0 /24.2 S1/1 2.2.3.2/24 Lo3 R2 2.2.2.2/24 Lo2 Lo0 2.2.0.2/24 2.2.1.2/24
Lab 2 - EIGRP Stub Lo0 1.1.0.1/24 1.1.1.1/24 Lo1 200.1.1.1/24 200.2.2.2/24 F0/0.1.2 F0/0 R1 1.1.2.1/24 Lo2.1 S1/2 CE 1.1.3.1/24 Lo3 12.1.1.0 /24.2 S1/1 2.2.3.2/24 Lo3 R2 2.2.2.2/24 Lo2 Lo0 2.2.0.2/24 2.2.1.2/24
Routing Protocol. RIPv1
 Outline Routing Protocol RIPv1, RIPv2, EIGRP OSPF o RIPv1, RIPv2 o EIGRP o OSPF 2 3 RIPv1 RIP Characteristics A classful, Distance Vector (DV) routing protocol Metric = hop count Routes with a hop count
Outline Routing Protocol RIPv1, RIPv2, EIGRP OSPF o RIPv1, RIPv2 o EIGRP o OSPF 2 3 RIPv1 RIP Characteristics A classful, Distance Vector (DV) routing protocol Metric = hop count Routes with a hop count
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, Objective. Scenario. Topology
 CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
CIS 83 LAB 2 - Single Area OSPF Rich Simms September 12, 2006 Objective The objective of this lab is to become familiar setting up and configuring OSPF on three routers for a single area. OSPF is our first
Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7
 EIGRP Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7 Copyleft 2014 Hacklab Cosenza (http://hlcs.it) Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright
EIGRP Advanced Networking: Routing & Switching 2 Chapter 7 Copyleft 2014 Hacklab Cosenza (http://hlcs.it) Released under Creative Commons License 3.0 By-Sa Cisco name, logo and materials are Copyright
Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs Topology
 Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates. Topology. Objectives. CCNPv7 ROUTE
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
Chapter 4 Lab 4-2, Controlling Routing Updates Topology Objectives Filter routes using a distribute list and ACL. Filter routes using a distribute list and prefix list. Filter redistributed routes using
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
CCNA Questions/Answers Routing Protocols
 Refer to the exhibit and configuration shown above. Routers R1 and R2 are properly configured with eigrp 976 protocol and are able to ping interfaces fa0/1 and fa0/2, respectively. Which commands are necessary
Refer to the exhibit and configuration shown above. Routers R1 and R2 are properly configured with eigrp 976 protocol and are able to ping interfaces fa0/1 and fa0/2, respectively. Which commands are necessary
Section 6. Implementing EIGRP ICND2
 ICND2 Section 6 Implementing EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 9.21 as an enhancement to the limitations of IGRP. IGRP was developed by Cisco
ICND2 Section 6 Implementing EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) was introduced in Cisco IOS Release 9.21 as an enhancement to the limitations of IGRP. IGRP was developed by Cisco
Lab 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration Lab
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 R3 Default Gateway Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 R3 Default Gateway Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 8.4.2: Show IP Route Challenge Lab
 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Determine network topology based on the outputs from the show
Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Determine network topology based on the outputs from the show
Lab Configuring the OSPF Routing Process
 Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies Topology Objectives Background Configure EIGRP on multiple routers. Configure the bandwidth command to modify the EIGRP metric. Verify
Lab Using the CLI to Gather Network Device Information Topology
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Lo0 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 N/A S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-7-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 7 Exam Answers
Chapter 7: Routing Dynamically. Routing & Switching
 Chapter 7: Routing Dynamically Routing & Switching The Evolution of Dynamic Routing Protocols Dynamic routing protocols used in networks since the late 1980s Newer versions support the communication based
Chapter 7: Routing Dynamically Routing & Switching The Evolution of Dynamic Routing Protocols Dynamic routing protocols used in networks since the late 1980s Newer versions support the communication based
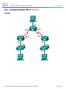
EIGRP Lab / lo1. .1 lo / /30
 EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
EIGRP Lab 172,16,1.0/24.1 lo1 192.168.20.0/30.2.1 Merida fa0 fa0 Vargas lo2.1 lo2.5.1 lo1 192.168.30.0/24 172.16.2.0/24 192.168.20.4.0/30 Scenario: Loopback0 is used for RouterID Loopback1 is a virtual
9.1. Routing Protocols
 9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
9.1. Routing Protocols Each organization that has been assigned a network address from an ISP is considered an autonomous system (AS). That organization is free to create one large network, or divide the
Lab Configuring Basic RIPv2 (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
(Solution) Topology 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
EXAM Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE)
 CISCO EXAM - 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/642-902.html Examskey CISCO 642-902 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This
CISCO EXAM - 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) TYPE: DEMO http://www.examskey.com/642-902.html Examskey CISCO 642-902 exam demo product is here for you to test the quality of the product. This
Lab Modifying OSPF Cost Metric
 Lab 2.3.3 Modifying OSPF Cost Metric Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF cost metric on an interface. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.3 Modifying OSPF Cost Metric Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF cost metric on an interface. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.4.1: Basic Inter-VLAN Routing
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
CCNA EXPLORATION V4.0 ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND CONCEPTS ACCESSIBLE INSTRUCTOR MATERIALS POWERPOINT OBJECTIVES
 CCNA EXPLORATION V4.0 ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND CONCEPTS ACCESSIBLE INSTRUCTOR MATERIALS Prepared by Cisco Learning Institute June 23, 2008 Chapter 1 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Objectives
CCNA EXPLORATION V4.0 ROUTING PROTOCOLS AND CONCEPTS ACCESSIBLE INSTRUCTOR MATERIALS Prepared by Cisco Learning Institute June 23, 2008 Chapter 1 Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding Objectives
Claim desired outcome
 Assessment Authoring - Table of Specification (TOS) The Table of Specification (TOS) is a high-level design template for a given assessment. It identifies the claims, components skills, targeted number
Assessment Authoring - Table of Specification (TOS) The Table of Specification (TOS) is a high-level design template for a given assessment. It identifies the claims, components skills, targeted number
Lab Student Lab Orientation
 Lab 1.1.1 Student Lab Orientation Objective In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Review the lab bundle equipment Understand the security pod topology Understand the pod naming and
Lab 1.1.1 Student Lab Orientation Objective In this lab, the students will complete the following tasks: Review the lab bundle equipment Understand the security pod topology Understand the pod naming and
RIP version 1. Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 5. Version Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1
 RIP version 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 5 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Describe the functions, characteristics, and operation of the RIPv1 protocol. Configure a device for using RIPv1. Verify
RIP version 1 Routing Protocols and Concepts Chapter 5 Version 4.0 1 Objectives Describe the functions, characteristics, and operation of the RIPv1 protocol. Configure a device for using RIPv1. Verify
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
outing and Switching Elective : Le
 Routing and Switching Elective : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan Chapters covered: Cabling Router Configuration
Routing and Switching Elective : Lecture Notes Nepal Engineering College Compiled by: Junior Professor: Daya Ram Budhathoki Nepal Engineering college, Changunarayan Chapters covered: Cabling Router Configuration
Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ]
![Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Cisco Exam Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ]](/thumbs/78/78661506.jpg) s@lm@n Cisco Exam 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Topic 1, Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Cisco
s@lm@n Cisco Exam 642-902 Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Version: 15.0 [ Total Questions: 375 ] Topic 1, Implement an EIGRP based solution, given a network design and a set of requirements Cisco
IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1
 IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1 Andrea Detti Electronic Engineering dept. E-mail: andrea.detti@uniroma2.it Some sources: Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND1 and ICND2 Slide
IP Routing Tecnologie e Protocolli per Internet II rev 1 Andrea Detti Electronic Engineering dept. E-mail: andrea.detti@uniroma2.it Some sources: Cisco CCNA Routing and Switching ICND1 and ICND2 Slide
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication
Smart Serial. Show interfaces. Shut down. logging synchronous
 SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
SEMESTER 2 Chapter 2 Static Networking V 4.0 2.1.1 What are the primary responsibilities of the router? 2.1.3 What is the first serial connector described called at the router end? What is the first serial
EIGRP Features and Operation
 EIGRP Features and Operation Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a classless, enhanced distance-vector protocol. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. EIGRP includes the subnet mask in its route updates. And as
EIGRP Features and Operation Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP) is a classless, enhanced distance-vector protocol. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. EIGRP includes the subnet mask in its route updates. And as
EIGRP CHAPTER 9. Configuring Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
 CHAPTER 9 EIGRP This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) EIGRP auto-summarization Load balancing: variance
CHAPTER 9 EIGRP This chapter provides information and commands concerning the following topics: Configuring Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) EIGRP auto-summarization Load balancing: variance
Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam Topology Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam Topology Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 15 Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
 Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
NAT Internetworking Standards and Technologies, Computer Engineering, KMITL 2
 EIGRP & NAT Jirasak Sittigorn Internetworking Standards & Technologies Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang EIGRP Characteristics
EIGRP & NAT Jirasak Sittigorn Internetworking Standards & Technologies Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang EIGRP Characteristics
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0
 Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Routing Information Protocol Version 2.0 RIPv2 Objective: onfigure RIPv2 between R1 and R2 to obtain connectivity between Networks Directions onfigure R1's interface F0/0 with the IP address 10.1.0.1/16
Lab 6: Access Lists. Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/ R1
 Lab 6: Access Lists Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 ----- R1 Fa 0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 ----- Se 0/0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
Lab 6: Access Lists Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 ----- R1 Fa 0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 ----- Se 0/0/0 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
CCNA 3 (v v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers % Full
 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers 2017 100% Full ccnav6.com /ccna-3-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-6-exam-answers-2017-100-full.html CCNA Exam Answers 2017 CCNA 3 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Chapter 6 Exam Answers
Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two)
 ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
ICND1 OSPF Questions Question 1 Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C.
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
 Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) http:// What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol Successor to Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
Internetwork Expert s CCNP Bootcamp Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) http:// What is EIGRP? Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol Successor to Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
Building the Routing Table. Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles
 Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
Building the Routing Table Introducing the Routing Table Directly Connected Networks Static Routing Dynamic Routing Routing Table Principles Introducing the Routing Table R1# show ip route Codes: C - connected,
CCNP ROUTE Workbook - EIGRP
 CCNP ROUTE Workbook - EIGRP EIGRP Initial Configuration Load the task1-1 initial configurations before starting. Task Configure EIGRP on Routers-1, 2, and 4 using the following guidelines: Classic-mode
CCNP ROUTE Workbook - EIGRP EIGRP Initial Configuration Load the task1-1 initial configurations before starting. Task Configure EIGRP on Routers-1, 2, and 4 using the following guidelines: Classic-mode
8. Refer to the exhibit. The ORL router is unable to form a neighbor relationship with the JAX router. What is a possible cause of this problem?
 1. Refer to the exhibit. A new PC was deployed in the Sales network. It was given the host address of 192.168.10.31 with a default gateway of 192.168.10.17. The PC is not communicating with the network
1. Refer to the exhibit. A new PC was deployed in the Sales network. It was given the host address of 192.168.10.31 with a default gateway of 192.168.10.17. The PC is not communicating with the network
Configuration and Management of Networks
 EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
EIGRP Summarization and efault Network Advertisement The lab is built on the topology: Topology Objectives Review a basic EIGRP configuration. onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization. onfigure and
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name Score Grade Question Answer Question Answer
 CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
CIS 83 Midterm Spring 2004 Answer Sheet Name: Score: Grade: Question Answer Question Answer 1 A B C D E F 51 A B C D E F 2 A B C D E F 52 A B C D E F 3 A B C D E F 53 A B C D E F 4 A B C D E F 54 A B C
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default
Release Notes CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Release
 Release Notes CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Release 4.0.5.0 Purpose Release 4.0.5.0 of Routing Protocols and Concepts is the fifth maintenance release of the second course in the CCNA
Release Notes CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts Release 4.0.5.0 Purpose Release 4.0.5.0 of Routing Protocols and Concepts is the fifth maintenance release of the second course in the CCNA
Chapter 6 Reading Organizer
 Name Date Chapter 6 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and plan a network using OSPF Design and configure a network using single-area OSPF Work with multi-protocol
Name Date Chapter 6 Reading Organizer After completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Describe and plan a network using OSPF Design and configure a network using single-area OSPF Work with multi-protocol
Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6
 Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this
Chapter 8 Lab 8-2, Using Manual IPv6 Tunnels with EIGRP for IPv6 Topology Objectives Configure EIGRP for IPv4. Create a manual IPv6 tunnel. Configure EIGRP for IPv6 across the tunnel. Background In this
Lab 2-3 Summarization and Default Network Advertisement
 Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Lab 2-3 Summarization and efault Network Advertisement Learning Objectives Review basic EIGRP configuration onfigure and verify EIGRP auto-summarization onfigure and verify EIGRP manual summarization Learn
Lab - Building a Switch and Router Network
 Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway G0/0 192.168.0.1 N/A G0/1 192.168.1.1 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 PC-B NIC 192.168.0.3 192.168.0.1 R1 Objectives
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4
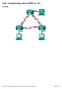 Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
Lab- Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP for 1Pv4 Topology G0/0 G0/0 PC-A PC-C 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 27 Addressing Table efault Gateway
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs
 TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
TDC 363 Introduction to LANs Routing Protocols and RIP Greg Brewster DePaul University TDC 363 1 Dynamic Routing Routing Protocols Distance Vector vs. Link State Protocols RIPv1 & RIPv2 RIP Problems Slow
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard ACLs Topology
 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
EIGRP Stub Routing. Finding Feature Information. Information About EIGRP Stub Routing. EIGRP Stub Routing
 The EIGRP stub routing feature improves network stability, reduces resource utilization, and simplifies the stub device configuration. Stub routing is commonly used in hub-and-spoke network topologies.
The EIGRP stub routing feature improves network stability, reduces resource utilization, and simplifies the stub device configuration. Stub routing is commonly used in hub-and-spoke network topologies.
Lab Configuring and Verifying Standard IPv4 ACLs Topology
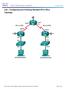 Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Topology 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 10 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.10.1
Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 16 Addressing Table Assessment Objectives Device
Skills Assessment (EIGRP) Student Training Exam Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 16 Addressing Table Assessment Objectives Device
Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
 Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP onfiguration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Lab - Examining Telnet and SSH in Wireshark
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure the Devices
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Part 1: Configure the Devices
Chapter 5 RIP version 1
 Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Cisco CCNA 2 Exploration - Routing Chapter 5 RIP version 1 João José jjose@ualg.pt http://w3.ualg.pt/~jjose/cisco/ Based on: Graziani, R. (2008) CIS 82 Routing Theory and Concepts RIPv1: A Distance Vector,
Lab Troubleshooting Basic PPP with Authentication Topology
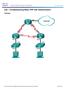 Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 8 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (2 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (18 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (2 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (18 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure
2016 Braindump2go Valid Cisco Exam Preparation Materials:
 2016 NEW Cisco CCNP Routing and Switching 300-101: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Exam Questions and Answers RELEASED in Braindump2go.com Online IT Study Website Today! 2016 Braindump2go Valid Cisco
2016 NEW Cisco CCNP Routing and Switching 300-101: Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE) Exam Questions and Answers RELEASED in Braindump2go.com Online IT Study Website Today! 2016 Braindump2go Valid Cisco
Two types of routing protocols are used in internetworks: interior gateway protocols (IGPs) and exterior gateway protocols (EGPs).
 Introduction Dynamic routing is when protocols are used to find networks and update routing tables on routers. True, this is easier than using static or default routing, but it ll cost you in terms of
Introduction Dynamic routing is when protocols are used to find networks and update routing tables on routers. True, this is easier than using static or default routing, but it ll cost you in terms of
Symbols. Numerics I N D E X
 I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
I N D E X Symbols? (question mark), CLI help system, 126 Numerics A 2-router BGP topology, configuring, 279 284 4-router BGP topology, configuring, 266, 276 279 ABRs (area border routers), 9, 87, 95, 141
