Troubleshooting the Security Appliance
|
|
|
- Naomi Brooks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 43 This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the security appliance, and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 43-1 Reloading the Security Appliance, page 43-6 Performing Password Recovery, page 43-7 Other Troubleshooting Tools, page Common Problems, page Testing Your Configuration This section describes how to test connectivity for the single mode security appliance or for each security context. The following steps describe how to ping the security appliance interfaces, and how to allow hosts on one interface to ping hosts on another interface. We recommend that you only enable pinging and debug messages during troubleshooting. When you are done testing the security appliance, follow the steps in the Disabling the Test Configuration section on page This section includes the following topics: Enabling ICMP Debug Messages and System Messages, page 43-1 Pinging Security Appliance Interfaces, page 43-2 Pinging Through the Security Appliance, page 43-4 Disabling the Test Configuration, page 43-5 Enabling ICMP Debug Messages and System Messages Debug messages and system messages can help you troubleshoot why your pings are not successful. The security appliance only shows ICMP debug messages for pings to the security appliance interfaces, and not for pings through the security appliance to other hosts. To enable debugging and system messages, perform the following steps: To show ICMP packet information for pings to the security appliance interfaces, enter the following command: hostname(config)# debug icmp trace 43-1
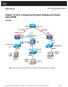
2 Testing Your Configuration Chapter 43 Step 4 To set system messages to be sent to Telnet or SSH sessions, enter the following command: hostname(config)# logging monitor debug You can alternately use logging buffer debug to send messages to a buffer, and then view them later using the show logging command. To send the system messages to your Telnet or SSH session, enter the following command: hostname(config)# terminal monitor To enable system messages, enter the following command: hostname(config)# logging on The following example shows a successful ping from an external host ( ) to the security appliance outside interface ( ): hostname(config)# debug icmp trace Inbound ICMP echo reply (len 32 id 1 seq 256) > Outbound ICMP echo request (len 32 id 1 seq 512) > Inbound ICMP echo reply (len 32 id 1 seq 512) > Outbound ICMP echo request (len 32 id 1 seq 768) > Inbound ICMP echo reply (len 32 id 1 seq 768) > Outbound ICMP echo request (len 32 id 1 seq 1024) > Inbound ICMP echo reply (len 32 id 1 seq 1024) > The preceding example shows the ICMP packet length (32 bytes), the ICMP packet identifier (1), and the ICMP sequence number (the ICMP sequence number starts at 0 and is incremented each time a request is sent). Pinging Security Appliance Interfaces To test that the security appliance interfaces are up and running and that the security appliance and connected routers are routing correctly, you can ping the security appliance interfaces. Note For security purposes the security appliance does not support far-end interface ping, that is pinging the IP address of the outside interface from the inside network. To ping the security appliance interfaces, perform the following steps: Create a sketch of your single mode security appliance or security context showing the interface names, security levels, and IP addresses. Note Although this procedure uses IP addresses, the ping command also supports DNS names and names assigned to a local IP address with the name command. The sketch should also include any directly connected routers, and a host on the other side of the router from which you will ping the security appliance. You will use this information for this procedure as well as the procedure in the Pinging Through the Security Appliance section on page For example: 43-2
3 Chapter 43 Testing Your Configuration Figure 43-1 Network Sketch with Interfaces, s, and s dmz dmz security outside security0 inside security Routed Security Appliance dmz dmz security outside security0 inside security Transp. Security Appliance Ping each security appliance interface from the directly connected routers. For transparent mode, ping the management IP address. This test ensures that the security appliance interfaces are active and that the interface configuration is correct. A ping might fail if the security appliance interface is not active, the interface configuration is incorrect, or if a switch between the security appliance and router is down (see Figure 43-2). In this case, no debug messages or system messages appear on the security appliance, because the packet never reaches it. Figure 43-2 Ping Failure at Security Appliance Interface Ping Security Appliance If the ping reaches the security appliance, and the security appliance responds, you see debug messages like the following: ICMP echo reply (len 32 id 1 seq 256) > ICMP echo request (len 32 id 1 seq 512) > If the ping reply does not return to the router, then you might have a switch loop or redundant IP addresses (see Figure 43-3). 43-3
4 Testing Your Configuration Chapter 43 Figure 43-3 Ping Ping Failure Because of IP Addressing Problems Security Appliance Ping each security appliance interface from a remote host. For transparent mode, ping the management IP address. This test checks that the directly connected router can route the packet between the host and the security appliance, and that the security appliance can correctly route the packet back to the host. A ping might fail if the security appliance does not have a route back to the host through the intermediate router (see Figure 43-4). In this case, the debug messages show that the ping was successful, but you see system message indicating a routing failure. Figure 43-4 Ping Ping Failure Because the Security Appliance has no Route? Security Appliance Pinging Through the Security Appliance After you successfully ping the security appliance interfaces, you should make sure traffic can pass successfully through the security appliance. For routed mode, this test shows that NAT is working correctly, if configured. For transparent mode, which does not use NAT, this test confirms that the security appliance is operating correctly; if the ping fails in transparent mode, contact Cisco TAC. To ping between hosts on different interfaces, perform the following steps: To add an access list allowing ICMP from any source host, enter the following command: hostname(config)# access-list ICMPACL extended permit icmp any any By default, when hosts access a lower security interface, all traffic is allowed through. However, to access a higher security interface, you need the preceding access list. To assign the access list to each source interface, enter the following command: hostname(config)# access-group ICMPACL in interface interface_name Repeat this command for each source interface. To enable the ICMP inspection engine, so ICMP responses are allowed back to the source host, enter the following commands: hostname(config)# class-map ICMP-CLASS 43-4
5 Chapter 43 Testing Your Configuration hostname(config-cmap)# match access-list ICMPACL hostname(config-cmap)# policy-map ICMP-POLICY hostname(config-pmap)# class ICMP-CLASS hostname(config-pmap-c)# inspect icmp hostname(config-pmap-c)# service-policy ICMP-POLICY global Step 4 Alternatively, you can also apply the ICMPACL access list to the destination interface to allow ICMP traffic back through the security appliance. Ping from the host or router through the source interface to another host or router on another interface. Repeat this step for as many interface pairs as you want to check. If the ping succeeds, you see a system message confirming the address translation for routed mode ( or ) and that an ICMP connection was established (302020). You can also enter the show xlate and show conns commands to view this information. If the ping fails for transparent mode, contact Cisco TAC. For routed mode, the ping might fail because NAT is not configured correctly (see Figure 43-5). This is more likely if you enable NAT control. In this case, you see a system message showing that the NAT translation failed ( or ). If the ping is from an outside host to an inside host, and you do not have a static translation (which is required with NAT control), you see message : deny inbound icmp. Note The security appliance only shows ICMP debug messages for pings to the security appliance interfaces, and not for pings through the security appliance to other hosts. Figure 43-5 Ping Failure Because the Security Appliance is not Translating Addresses Ping Security Appliance Disabling the Test Configuration After you complete your testing, disable the test configuration that allows ICMP to and through the security appliance and that prints debug messages. If you leave this configuration in place, it can pose a serious security risk. Debug messages also slow the security appliance performance. To disable the test configuration, perform the following steps: To disable ICMP debug messages, enter the following command: hostname(config)# no debug icmp trace To disable logging, if desired, enter the following command: hostname(config)# no logging on To remove the ICMPACL access list, and also delete the related access-group commands, enter the following command: 43-5
6 Reloading the Security Appliance Chapter 43 hostname(config)# no access-list ICMPACL Step 4 (Optional) To disable the ICMP inspection engine, enter the following command: hostname(config)# no service-policy ICMP-POLICY Traceroute You can trace the route of a packet using the traceroute feature, which is accessed with the traceroute command. A traceroute works by sending UDP packets to a destination on an invalid port. Because the port is not valid, the routers along the way to the destination will respond with an ICMP Time Exceeded Message, and report that error back to the security appliance. Packet Tracer In addition to capturing packets and the traceroute feature, it is possible to trace the lifespan of a packet through the security appliance to see if it is behaving as expected with the packet tracer tool. The packet tracer tool lets you do the following: Debug all packet drops in production network. Verify the configuration is working as intended. Show all rules applicable to a packet along with the CLI lines which caused the rule addition. Show a time line of packet changes in a data path. Inject tracer packets into the data path. The packet-tracer command provides detailed information about the packets and how they are processed by the security appliance. In the instance that a command from the configuration did not cause the packet to drop, the packet-tracer command will provide information about the cause in an easily readable manner. For example if a packet was dropped because of an invalid header validation, a message is displayed that says, packet dropped due to bad ip header (reason). Note The packet-tracer command can generate packets based on the 5 tuple information source IP, destination IP, source port, destination port, and protocol. The packet tracer does not populate the data part of the packet and as a result some engine checks will not be applicable. The packet tracer will show that the packet is dropped not because it did not pass the inspection checks but because there is not enough data to test against the inspection checks. For example the packet tracer will show drops incorrectly for dns traffic if the dns inspection is enabled. Reloading the Security Appliance In multiple mode, you can only reload from the system execution space. To reload the security appliance, enter the following command: hostname# reload 43-6
7 Chapter 43 Performing Password Recovery Performing Password Recovery This section describes how to recover if you forget passwords, or you create a lockout situation because of AAA settings. You can also disable password recovery for extra security. This section includes the following topics: Performing Password Recovery for the ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance, page 43-7 Password Recovery for the PIX 500 Series Security Appliance, page 43-8 Disabling Password Recovery, page 43-9 Resetting the Password on the SSM Hardware Module, page Performing Password Recovery for the ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance To recover passwords, perform the following steps: Step 4 Connect to the security appliance console port according to the Accessing the Command-Line Interface section on page 2-4. Power off the security appliance, and then power it on. During the startup messages, press the Escape key when prompted to enter ROMMON. To set the security appliance to ignore the startup configuration at reload, enter the following command: rommon #1> confreg The security appliance displays the current configuration register value, and asks if you want to change the value: Current Configuration Register: 0x Configuration Summary: boot TFTP image, boot default image from Flash on netboot failure Do you wish to change this configuration? y/n [n]: Step 5 Step 6 Step 7 Step 8 Step Record your current configuration register value, so you can restore it later. At the prompt, enter Y to change the value. The security appliance prompts you for new values. Accept the default values for all settings, except for the disable system configuration? value; at that prompt, enter Y. Reload the security appliance by entering the following command: rommon #2> boot The security appliance loads a default configuration instead of the startup configuration. Enter privileged EXEC mode by entering the following command: hostname> enable When prompted for the password, press Return. The password is blank. Load the startup configuration by entering the following command: 43-7
8 Performing Password Recovery Chapter 43 hostname# copy startup-config running-config Enter global configuration mode by entering the following command: hostname# configure terminal Change the passwords in the configuration by entering the following commands, as necessary: hostname(config)# password password hostname(config)# enable password password hostname(config)# username name password password Change the configuration register to load the startup configuration at the next reload by entering the following command: hostname(config)# config-register value Where value is the configuration register value you noted in Step 5 and 0x1 is the default configuration register. For more information about the configuration register, see the Cisco Security Appliance Command Reference. Save the new passwords to the startup configuration by entering the following command: hostname(config)# copy running-config startup-config Password Recovery for the PIX 500 Series Security Appliance Performing password recovery on the security appliance erases the login password, enable password, and aaa authentication console commands. To erase these commands so you can log in with the default passwords, perform the following steps: Step 4 Step 5 Step 6 Download the PIX password tool from Cisco.com to a TFTP server accessible from the security appliance. See the link in the Password Recovery Procedure for the PIX document at the following URL: b.shtml Connect to the security appliance console port according to the Accessing the Command-Line Interface section on page 2-4. Power off the security appliance, and then power it on. Immediately after the startup messages appear, press the Escape key to enter monitor mode. Configure the network settings for the interface that accesses the TFTP server by entering the following commands: monitor> interface interface_id monitor> address interface_ip monitor> server tftp_ip monitor> file pw_tool_name monitor> gateway gateway_ip Download the PIX password tool from the TFTP server by entering the following command: monitor> tftp If you have trouble reaching the server, you can enter the ping address command to test the connection. 43-8
9 Chapter 43 Performing Password Recovery Step 7 At the Do you wish to erase the passwords? prompt, enter Y. You can now log in with the default login password of cisco and the blank enable password. The following example shows the PIX password recovery with the TFTP server on the outside interface: monitor> interface 0 0: PCI(bus:0 dev:13 irq:10) 1: PCI(bus:0 dev:14 irq:7 ) Using 0: PCI(bus:0 dev:13 irq:10), MAC: ff.82b9 monitor> address address monitor> server server monitor> file np70.bin file np52.bin monitor> gateway gateway monitor> ping Sending 5, 100-byte 0xf8d3 ICMP Echoes to , timeout is 4 seconds:!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5) monitor> tftp tftp np52.bin@ via Received bytes Cisco PIX password tool (4.0) #0: Tue Aug 22 23:22:19 PDT x300 BIOS 0xd8000 Do you wish to erase the passwords? [yn] y Passwords have been erased. Rebooting... Disabling Password Recovery You might want to disable password recovery to ensure that unauthorized users cannot use the password recovery mechanism to compromise the security appliance. To disable password recovery, enter the following command: hostname(config)# no service password-recovery On the ASA 5500 series adaptive security appliance, the no service password-recovery command prevents a user from entering ROMMON with the configuration intact. When a user enters ROMMON, the security appliance prompts the user to erase all Flash file systems. The user cannot enter ROMMON without first performing this erasure. If a user chooses not to erase the Flash file system, the security appliance reloads. Because password recovery depends on using ROMMON and maintaining the existing configuration, this erasure prevents you from recovering a password. However, disabling password recovery prevents unauthorized users from viewing the configuration or inserting different passwords. In this case, to recover the system to an operating state, load a new image and a backup configuration file, if available. The service password-recovery command appears in the configuration file for informational purposes only; when you enter the command at the CLI prompt, the setting is saved in NVRAM. The only way to change the setting is to enter the command at the CLI prompt. Loading a new configuration with a different version of the command does not change the setting. If you disable 43-9
10 Other Troubleshooting Tools Chapter 43 password recovery when the security appliance is configured to ignore the startup configuration at startup (in preparation for password recovery), then the security appliance changes the setting to boot the startup configuration as usual. If you use failover, and the standby unit is configured to ignore the startup configuration, then the same change is made to the configuration register when the no service password recovery command replicates to the standby unit. On the PIX 500 series security appliance, the no service password-recovery command forces the PIX password tool to prompt the user to erase all Flash file systems. The user cannot use the PIX password tool without first performing this erasure. If a user chooses not to erase the Flash file system, the security appliance reloads. Because password recovery depends on maintaining the existing configuration, this erasure prevents you from recovering a password. However, disabling password recovery prevents unauthorized users from viewing the configuration or inserting different passwords. In this case, to recover the system to an operating state, load a new image and a backup configuration file, if available. Resetting the Password on the SSM Hardware Module To reset the password to the default of cisco on the SSM hardware module, perform the following steps: Make sure the SSM hardware module is in the Up state and supports password reset. Enter the following command: hostname (config)# hw-module module 1 password-reset Where 1 is the specified slot number on the SSM hardware module. Note On the AIP SSM, entering this command reboots the hardware module. The module is offline until the rebooting is finished. Enter the show module command to monitor the module status. The AIP SSM supports this command in version 6.0 and later. On the CSC SSM, entering this command resets web services on the hardware module after the password has been reset. You may lose connection to ASDM or be logged out of the hardware module. The CSC SSM supports this command in the most recent version of 6.1, dated November Reset the password on module in slot 1? [confirm] Enter y to confirm. Other Troubleshooting Tools The security appliance provides other troubleshooting tools to be used in conjunction with Cisco TAC: Viewing Debug Messages, page Capturing Packets, page Viewing the Crash Dump, page
11 Chapter 43 Common Problems Viewing Debug Messages Because debugging output is assigned high priority in the CPU process, it can render the system unusable. For this reason, use debug commands only to troubleshoot specific problems or during troubleshooting sessions with Cisco TAC. Moreover, it is best to use debug commands during periods of lower network traffic and fewer users. Debugging during these periods decreases the likelihood that increased debug command processing overhead will affect system use. To enable debug messages, see the debug commands in the Cisco Security Appliance Command Reference. Capturing Packets Capturing packets is sometimes useful when troubleshooting connectivity problems or monitoring suspicious activity. We recommend contacting Cisco TAC if you want to use the packet capture feature. See the capture command in the Cisco Security Appliance Command Reference. Viewing the Crash Dump If the security appliance crashes, you can view the crash dump information. We recommend contacting Cisco TAC if you want to interpret the crash dump. See the show crashdump command in the Cisco Security Appliance Command Reference. Common Problems This section describes common problems with the security appliance, and how you might resolve them. Symptom The context configuration was not saved, and was lost when you reloaded. Possible Cause You did not save each context within the context execution space. If you are configuring contexts at the command line, you did not save the context before you changed to the next context. Recommended Action Save each context within the context execution space using the copy run start command. You cannot save contexts from the system execution space. Symptom You cannot make a Telnet connection or SSH to the security appliance interface. Possible Cause You did not enable Telnet or SSH to the security appliance. Recommended Action Enable Telnet or SSH to the security appliance according to the Allowing Telnet Access section on page 40-1 or the Allowing SSH Access section on page
12 Common Problems Chapter 43 Symptom You cannot ping the security appliance interface. Possible Cause You disabled ICMP to the security appliance. Recommended Action command. Enable ICMP to the security appliance for your IP address using the icmp Symptom You cannot ping through the security appliance, even though the access list allows it. Possible Cause You did not enable the ICMP inspection engine or apply access lists on both the ingress and egress interfaces. Recommended Action Because ICMP is a connectionless protocol, the security appliance does not automatically allow returning traffic through. In addition to an access list on the ingress interface, you either need to apply an access list to egress interface to allow replying traffic, or enable the ICMP inspection engine, which treats ICMP connections as stateful connections. Symptom Traffic does not pass between two interfaces on the same security level. Possible Cause You did not enable the feature that allows traffic to pass between interfaces on the same security level. Recommended Action Enable this feature according to the Allowing Communication Between Interfaces on the Same Security Level section on page
Troubleshooting. Testing Your Configuration CHAPTER
 82 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the ASA and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 82-1 Reloading the ASA, page 82-8 Performing Password Recovery, page
82 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the ASA and includes the following sections: Testing Your Configuration, page 82-1 Reloading the ASA, page 82-8 Performing Password Recovery, page
Password Recovery Procedure for the PIX
 Password Recovery Procedure for the PIX Document ID: 8529 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Step by Step Procedure PIX With a Floppy Drive PIX Without a Floppy Drive Sample
Password Recovery Procedure for the PIX Document ID: 8529 Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Step by Step Procedure PIX With a Floppy Drive PIX Without a Floppy Drive Sample
Getting Started. Getting Started with Your Platform Model. Factory Default Configurations CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface, configure the firewall mode, and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: with Your Platform
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes how to access the command-line interface, configure the firewall mode, and work with the configuration. This chapter includes the following sections: with Your Platform
Configuring Management Access
 37 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to access the ASA for system management through Telnet, SSH, and HTTPS (using ASDM), how to authenticate and authorize users, how to create login banners, and how
37 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to access the ASA for system management through Telnet, SSH, and HTTPS (using ASDM), how to authenticate and authorize users, how to create login banners, and how
Managing Services Modules
 CHAPTER 58 This chapter describes how to manage the following module types: Security Services Cards (SSCs) Security Services Modules (SSMs) Security Services Processors (SSPs) Modules run advanced security
CHAPTER 58 This chapter describes how to manage the following module types: Security Services Cards (SSCs) Security Services Modules (SSMs) Security Services Processors (SSPs) Modules run advanced security
Firewall Stateful Inspection of ICMP
 The feature categorizes Internet Control Management Protocol Version 4 (ICMPv4) messages as either malicious or benign. The firewall uses stateful inspection to trust benign ICMPv4 messages that are generated
The feature categorizes Internet Control Management Protocol Version 4 (ICMPv4) messages as either malicious or benign. The firewall uses stateful inspection to trust benign ICMPv4 messages that are generated
Testing and Troubleshooting
 This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the Cisco ASA and test basic connectivity. View Debugging Messages, page 1 Packet Capture, page 1 View the Crash Dump, page 6 View the Coredump, page 6 vcpu Usage
This chapter describes how to troubleshoot the Cisco ASA and test basic connectivity. View Debugging Messages, page 1 Packet Capture, page 1 View the Crash Dump, page 6 View the Coredump, page 6 vcpu Usage
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM
 Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Chapter 10 - Configure ASA Basic Settings and Firewall using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces.
Overview of the Cisco NCS Command-Line Interface
 CHAPTER 1 Overview of the Cisco NCS -Line Interface This chapter provides an overview of how to access the Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) command-line interface (CLI), the different command modes,
CHAPTER 1 Overview of the Cisco NCS -Line Interface This chapter provides an overview of how to access the Cisco Prime Network Control System (NCS) command-line interface (CLI), the different command modes,
Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet
 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on the ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet Passwords, page 1
This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on the ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet Passwords, page 1
GSS Administration and Troubleshooting
 CHAPTER 9 GSS Administration and Troubleshooting This chapter covers the procedures necessary to properly manage and maintain your GSSM and GSS devices, including login security, software upgrades, GSSM
CHAPTER 9 GSS Administration and Troubleshooting This chapter covers the procedures necessary to properly manage and maintain your GSSM and GSS devices, including login security, software upgrades, GSSM
Getting Started. Access the Console for the Command-Line Interface. Access the Appliance Console
 This chapter describes how to get started with your Cisco ASA. Access the Console for the Command-Line Interface, on page 1 Configure ASDM Access, on page 9 Start ASDM, on page 15 Factory Default Configurations,
This chapter describes how to get started with your Cisco ASA. Access the Console for the Command-Line Interface, on page 1 Configure ASDM Access, on page 9 Start ASDM, on page 15 Factory Default Configurations,
Router Startup and Configuration
 Router Startup and Configuration Router Startup In general, the boot process follows these steps: Test hardware (POST) Load the bootstrap program Locate and load the Cisco IOS Locate and load the router
Router Startup and Configuration Router Startup In general, the boot process follows these steps: Test hardware (POST) Load the bootstrap program Locate and load the Cisco IOS Locate and load the router
VPN Connection through Zone based Firewall Router Configuration Example
 VPN Connection through Zone based Firewall Router Configuration Example Document ID: 112051 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
VPN Connection through Zone based Firewall Router Configuration Example Document ID: 112051 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information Configure
Configuring Passwords and Privileges
 Configuring Passwords and Privileges Using passwords and assigning privilege levels is a simple way of providing terminal access control in your network. This chapter describes the following topics and
Configuring Passwords and Privileges Using passwords and assigning privilege levels is a simple way of providing terminal access control in your network. This chapter describes the following topics and
IOS and Configuration Basics
 APPENDIX C This appendix contains basic information about the Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS) software and includes the following sections: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation Getting Context-Sensitive
APPENDIX C This appendix contains basic information about the Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS) software and includes the following sections: Cisco IOS Modes of Operation Getting Context-Sensitive
Configuring TCP State Bypass
 CHAPTER 51 This chapter describes how to configure TCP state bypass, which lets outbound and inbound flows go through separate ASAs. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About TCP
CHAPTER 51 This chapter describes how to configure TCP state bypass, which lets outbound and inbound flows go through separate ASAs. This chapter includes the following sections: Information About TCP
Access Rules. Controlling Network Access
 This chapter describes how to control network access through or to the ASA using access rules. You use access rules to control network access in both routed and transparent firewall modes. In transparent
This chapter describes how to control network access through or to the ASA using access rules. You use access rules to control network access in both routed and transparent firewall modes. In transparent
Configuring the Hostname, Domain Name, Passwords, and Other Basic Settings
 CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Hostname, Domain Name, Passwords, and Other Basic Settings This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASA 1000V that are typically required for a functioning
CHAPTER 5 Configuring the Hostname, Domain Name, Passwords, and Other Basic Settings This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on your ASA 1000V that are typically required for a functioning
Multiple Context Mode
 This chapter describes how to configure multiple security contexts on the Cisco ASA. About Security Contexts, page 1 Licensing for, page 12 Prerequisites for, page 13 Guidelines for, page 14 Defaults for,
This chapter describes how to configure multiple security contexts on the Cisco ASA. About Security Contexts, page 1 Licensing for, page 12 Prerequisites for, page 13 Guidelines for, page 14 Defaults for,
Chapter 4. Network Security. Part II
 Chapter 4 Network Security Part II CCNA4-1 Chapter 4-2 Introducing Network Security Securing Cisco Routers CCNA4-2 Chapter 4-2 Router Security Issues The Role of Routers in Network Security: Router security
Chapter 4 Network Security Part II CCNA4-1 Chapter 4-2 Introducing Network Security Securing Cisco Routers CCNA4-2 Chapter 4-2 Router Security Issues The Role of Routers in Network Security: Router security
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces.
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM This lab has been updated for use on NETLAB+ Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces.
Chapter 11. Configuring and Testing Your Network
 Chapter 11 Configuring and Testing Your Network CCNA1-1 Chapter 11 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Chapter 11 Configuring and Testing Your Network CCNA1-1 Chapter 11 Note for Instructors These presentations are the result of a collaboration among the instructors at St. Clair College in Windsor, Ontario.
Exam Name: Implementing Cisco Edge Network Security Solutions
 Vendor: Cisco Exam Code: 300-206 Exam Name: Implementing Cisco Edge Network Security Solutions Version: Demo QUESTION 1 The Cisco ASA must support dynamic routing and terminating VPN traffic. Which three
Vendor: Cisco Exam Code: 300-206 Exam Name: Implementing Cisco Edge Network Security Solutions Version: Demo QUESTION 1 The Cisco ASA must support dynamic routing and terminating VPN traffic. Which three
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces. 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All
Chapter 10 Configure Clientless Remote Access SSL VPNs Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet Interfaces. 2016 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All
Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet
 This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on the ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet Passwords, page 1
This chapter describes how to configure basic settings on the ASA that are typically required for a functioning configuration. Set the Hostname, Domain Name, and the Enable and Telnet Passwords, page 1
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI
 Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Lab 7 Configuring Basic Router Settings with IOS CLI Objectives Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices Cable equipment to match the network topology. Initialize and restart the router and switch.
CISCO EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 CISCO 642-618 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 642-618 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 39.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 642-618 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: Deploying Cisco
CISCO 642-618 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Number: 642-618 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 min File Version: 39.6 http://www.gratisexam.com/ CISCO 642-618 EXAM QUESTIONS & ANSWERS Exam Name: Deploying Cisco
Configuring the AIP SSM
 CHAPTER 18 The number of concurrent CLI sessions is limited based on the platform. IDS 4215 and NM CIDS are limited to three concurrent CLI sessions. All other platforms allow ten concurrent sessions.
CHAPTER 18 The number of concurrent CLI sessions is limited based on the platform. IDS 4215 and NM CIDS are limited to three concurrent CLI sessions. All other platforms allow ten concurrent sessions.
Integration Debugging Information
 APPENDIXC June 18, 2013, Debugging Information for Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance, page C-1 Debugging Access Edge and OCS Server, page C-5 Debugging Information for Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance
APPENDIXC June 18, 2013, Debugging Information for Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance, page C-1 Debugging Access Edge and OCS Server, page C-5 Debugging Information for Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance
Deploying Cisco ASA Firewall Features (FIREWALL) v1.0. Global Knowledge European Remote Labs Instructor Guide
 Deploying Cisco ASA Firewall Features (FIREWALL) v1.0 Global Knowledge European Remote Labs Instructor Guide Revision Draft 0.2 11/03/2011 1. Contents 1. Contents.2 2. Introduction.3 3. Remote Labs Topology,
Deploying Cisco ASA Firewall Features (FIREWALL) v1.0 Global Knowledge European Remote Labs Instructor Guide Revision Draft 0.2 11/03/2011 1. Contents 1. Contents.2 2. Introduction.3 3. Remote Labs Topology,
Configure the ASA for Dual Internal Networks
 Configure the ASA for Dual Internal Networks Document ID: 119195 Contributed by Dinkar Sharma, Bratin Saha, and Prashant Joshi, Cisco TAC Engineers. Aug 05, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Configure the ASA for Dual Internal Networks Document ID: 119195 Contributed by Dinkar Sharma, Bratin Saha, and Prashant Joshi, Cisco TAC Engineers. Aug 05, 2015 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping
 Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Setting Up the Sensor
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter contains procedures for the setting up the sensor, such as changing sensor initialization information, adding and deleting users, configuring time and setting up NTP, creating a
CHAPTER 4 This chapter contains procedures for the setting up the sensor, such as changing sensor initialization information, adding and deleting users, configuring time and setting up NTP, creating a
1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services?
 CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
CCNA 1 Practice Final Exam Answers v4.0 100% 1. Which OSI layers offers reliable, connection-oriented data communication services? application presentation session transport network 2. Refer to the exhibit.
through ftp-map Commands
 CHAPTER 12 12-1 email Chapter 12 email To include the indicated email address in the Subject Alternative Name extension of the certificate during enrollment, use the email command in crypto ca trustpoint
CHAPTER 12 12-1 email Chapter 12 email To include the indicated email address in the Subject Alternative Name extension of the certificate during enrollment, use the email command in crypto ca trustpoint
DoS Attacks Malicious Code Attacks Device Hardening Social Engineering The Network Security Wheel
 CCNA4 Chapter 4 * DoS Attacks DoS attacks are the most publicized form of attack and also among the most difficult to eliminate. DoS attacks prevent authorized people from using a service by consuming
CCNA4 Chapter 4 * DoS Attacks DoS attacks are the most publicized form of attack and also among the most difficult to eliminate. DoS attacks prevent authorized people from using a service by consuming
Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privilege Levels
 Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privilege Levels Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privileges, page 1 Information About Passwords
Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privilege Levels Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privileges, page 1 Information About Passwords
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers %
 CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100% 1. Which two features are characteristics of flash memory? (Choose two.) Flash provides nonvolatile storage. Flash receives a copy of the IOS from RAM when
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100% 1. Which two features are characteristics of flash memory? (Choose two.) Flash provides nonvolatile storage. Flash receives a copy of the IOS from RAM when
tcp-map through type echo Commands
 CHAPTER 31 31-1 tcp-map Chapter 31 tcp-map To define a set of TCP normalization actions, use the tcp-map command in global configuration mode. The TCP normalization feature lets you specify criteria that
CHAPTER 31 31-1 tcp-map Chapter 31 tcp-map To define a set of TCP normalization actions, use the tcp-map command in global configuration mode. The TCP normalization feature lets you specify criteria that
Configuring Logging. Information About Logging CHAPTER
 74 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure and manage logs for the ASA, and includes the following sections: Information About Logging, page 74-1 Licensing Requirements for Logging, page 74-5 Prerequisites
74 CHAPTER This chapter describes how to configure and manage logs for the ASA, and includes the following sections: Information About Logging, page 74-1 Licensing Requirements for Logging, page 74-5 Prerequisites
Command-Line Interfaces
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes the CLIs you use to configure the Catalyst 4500 series switch. This chapter includes the following major sections: Accessing the Switch CLI, page 2-1 Performing Command-Line
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes the CLIs you use to configure the Catalyst 4500 series switch. This chapter includes the following major sections: Accessing the Switch CLI, page 2-1 Performing Command-Line
Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privilege Levels
 Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privilege Levels Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privileges, page 1 Information About Passwords
Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privilege Levels Finding Feature Information, page 1 Restrictions for Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privileges, page 1 Information About Passwords
Configuring Routes on the ACE
 CHAPTER2 This chapter describes how the ACE is considered a router hop in the network when it is in routed mode. In the Admin or user contexts, the ACE supports static routes only. The ACE supports up
CHAPTER2 This chapter describes how the ACE is considered a router hop in the network when it is in routed mode. In the Admin or user contexts, the ACE supports static routes only. The ACE supports up
Using Cisco IOS XE Software
 This chapter describes the basics of using the Cisco IOS XE software and includes the following section: Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console, on page 1 Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console Before
This chapter describes the basics of using the Cisco IOS XE software and includes the following section: Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console, on page 1 Accessing the CLI Using a Router Console Before
Transparent or Routed Firewall Mode
 This chapter describes how to set the firewall mode to routed or transparent, as well as how the firewall works in each firewall mode. You can set the firewall mode independently for each context in multiple
This chapter describes how to set the firewall mode to routed or transparent, as well as how the firewall works in each firewall mode. You can set the firewall mode independently for each context in multiple
This study aid describes the purpose of security contexts and explains how to enable, configure, and manage multiple contexts.
 Configuring Security Contexts Created by Bob Eckhoff This study aid describes the purpose of security contexts and explains how to enable, configure, and manage multiple contexts. Security Context Overview
Configuring Security Contexts Created by Bob Eckhoff This study aid describes the purpose of security contexts and explains how to enable, configure, and manage multiple contexts. Security Context Overview
Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server
 4 CHAPTER Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server This chapter describes how to configure the GSS, primary GSSM, or standby GSSM as a client of a Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
4 CHAPTER Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server This chapter describes how to configure the GSS, primary GSSM, or standby GSSM as a client of a Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
Summer Webinar Series
 Summer Webinar Series Troubleshooting Traffic Flows Through Cisco ASA Firewalls Christopher Rose Sr. Client Network Engineer crose@mcnc.org Webinar Links: www.mcnc.org/cne-webinars Agenda 1. Firewall best
Summer Webinar Series Troubleshooting Traffic Flows Through Cisco ASA Firewalls Christopher Rose Sr. Client Network Engineer crose@mcnc.org Webinar Links: www.mcnc.org/cne-webinars Agenda 1. Firewall best
Configuring Switch-Based Authentication
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure switch-based authentication on the switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. This chapter consists
CHAPTER 7 This chapter describes how to configure switch-based authentication on the switch. Unless otherwise noted, the term switch refers to a standalone switch and to a switch stack. This chapter consists
Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy
 Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1
Laboration 2 Troubleshooting Switching and First-Hop Redundancy Topology All contents are Copyright 1992 2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1
No Service Password-Recovery
 No Service Password-Recovery Last Updated: January 18, 2012 The No Service Password-Recovery feature is a security enhancement that prevents anyone with console access from accessing the router configuration
No Service Password-Recovery Last Updated: January 18, 2012 The No Service Password-Recovery feature is a security enhancement that prevents anyone with console access from accessing the router configuration
Command Reference for Firepower Threat Defense 1
 t-z tail-logs, page 2 test aaa-server, page 4 traceroute, page 6 undebug, page 9 verify, page 11 vpn-sessiondb logoff, page 15 write net, page 16 write terminal, page 17 1 tail-logs t - z tail-logs To
t-z tail-logs, page 2 test aaa-server, page 4 traceroute, page 6 undebug, page 9 verify, page 11 vpn-sessiondb logoff, page 15 write net, page 16 write terminal, page 17 1 tail-logs t - z tail-logs To
Command-Line Interfaces
 CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes the CLIs you use to configure the Catalyst 4500 series switch. This chapter includes the following major sections: Accessing the Switch CLI, page 2-2 Performing Command-Line
CHAPTER 2 This chapter describes the CLIs you use to configure the Catalyst 4500 series switch. This chapter includes the following major sections: Accessing the Switch CLI, page 2-2 Performing Command-Line
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Chapter 10 Configure AnyConnect Remote Access SSL VPN Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Configuring Security with Passwords, Privileges, and Logins
 Configuring Security with Passwords, Privileges, and Logins Cisco IOS based networking devices provide several features that can be used to implement basic security for CLI sessions using only the operating
Configuring Security with Passwords, Privileges, and Logins Cisco IOS based networking devices provide several features that can be used to implement basic security for CLI sessions using only the operating
Identity Firewall. About the Identity Firewall
 This chapter describes how to configure the ASA for the. About the, on page 1 Guidelines for the, on page 7 Prerequisites for the, on page 9 Configure the, on page 10 Monitoring the, on page 16 History
This chapter describes how to configure the ASA for the. About the, on page 1 Guidelines for the, on page 7 Prerequisites for the, on page 9 Configure the, on page 10 Monitoring the, on page 16 History
Cisco CISCO Securing Networks with ASA Advanced. Practice Test. Version
 Cisco 642-515 CISCO 642-515 Securing Networks with ASA Advanced Practice Test Version 3.1 QUESTION NO: 1 Cisco 642-515: Practice Exam Which two statements correctly describe configuring active/active failover?
Cisco 642-515 CISCO 642-515 Securing Networks with ASA Advanced Practice Test Version 3.1 QUESTION NO: 1 Cisco 642-515: Practice Exam Which two statements correctly describe configuring active/active failover?
Maintaining the MGX RPM-PR
 APPENDIX A This appendix describes maintenance procedures you might need to perform as your internetworking needs change. It contains the following sections: Reading Front Panel LEDs Recovering a Lost
APPENDIX A This appendix describes maintenance procedures you might need to perform as your internetworking needs change. It contains the following sections: Reading Front Panel LEDs Recovering a Lost
Accessing the WAN Chapter 4 - PART II Modified by Tony Chen 07/20/2008
 Network Security Accessing the WAN Chapter 4 - PART II Modified by Tony Chen 07/20/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake on my
Network Security Accessing the WAN Chapter 4 - PART II Modified by Tony Chen 07/20/2008 ITE I Chapter 6 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Notes: If you see any mistake on my
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013
 CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1. Refer to the exhibit. A switch was configured as shown. A ping to the default gateway was issued, but the ping was not successful. Other switches in the same
CCNA 1 Chapter 2 v5.0 Exam Answers 2013 1. Refer to the exhibit. A switch was configured as shown. A ping to the default gateway was issued, but the ping was not successful. Other switches in the same
ASA Access Control. Section 3
 [ 39 ] CCNP Security Firewall 642-617 Quick Reference Section 3 ASA Access Control Now that you have connectivity to the ASA and have configured basic networking settings on the ASA, you can start to look
[ 39 ] CCNP Security Firewall 642-617 Quick Reference Section 3 ASA Access Control Now that you have connectivity to the ASA and have configured basic networking settings on the ASA, you can start to look
Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server
 CHAPTER 4 Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server This chapter describes how to configure the GSS, primary GSSM, or standby GSSM as a client of a Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
CHAPTER 4 Managing GSS User Accounts Through a TACACS+ Server This chapter describes how to configure the GSS, primary GSSM, or standby GSSM as a client of a Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
Assigning the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway
 CHAPTER 4 Assigning the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway This chapter describes how to create the initial switch configuration (for example, assigning the switch IP address and default gateway information)
CHAPTER 4 Assigning the Switch IP Address and Default Gateway This chapter describes how to create the initial switch configuration (for example, assigning the switch IP address and default gateway information)
Object Groups for ACLs
 The feature lets you classify users, devices, or protocols into groups and apply these groups to access control lists (ACLs) to create access control policies for these groups. This feature lets you use
The feature lets you classify users, devices, or protocols into groups and apply these groups to access control lists (ACLs) to create access control policies for these groups. This feature lets you use
502 / 504 GATEWAY_TIMEOUT errors when browsing to certain sites
 502 / 504 GATEWAY_TIMEOUT errors when browsing to certain sites Document ID: 118079 Contributed by Vladimir Sousa and Siddharth Rajpathak, Cisco TAC Engineers. Jul 25, 2014 Contents Question: Question:
502 / 504 GATEWAY_TIMEOUT errors when browsing to certain sites Document ID: 118079 Contributed by Vladimir Sousa and Siddharth Rajpathak, Cisco TAC Engineers. Jul 25, 2014 Contents Question: Question:
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 8: Firewalls ASA Firewall Device
 Lab 8: Firewalls ASA Firewall Device 8.1 Details Aim: Rich Macfarlane 2015 The aim of this lab is to investigate a Cisco ASA Firewall Device, its default traffic flows, its stateful firewalling functionality,
Lab 8: Firewalls ASA Firewall Device 8.1 Details Aim: Rich Macfarlane 2015 The aim of this lab is to investigate a Cisco ASA Firewall Device, its default traffic flows, its stateful firewalling functionality,
Configuring DHCP, DDNS, and WCCP Services
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure the DHCP server, dynamic DNS (DDNS) update methods, and WCCP on the security appliance. DHCP provides network configuration parameters, such as IP addresses,
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure the DHCP server, dynamic DNS (DDNS) update methods, and WCCP on the security appliance. DHCP provides network configuration parameters, such as IP addresses,
Cisco WAAS Software Command Summary
 2 CHAPTER This chapter summarizes the Cisco WAAS 4.0.7 software commands. lists the WAAS commands (alphabetically) and indicates the command mode for each command. The commands used to access modes are
2 CHAPTER This chapter summarizes the Cisco WAAS 4.0.7 software commands. lists the WAAS commands (alphabetically) and indicates the command mode for each command. The commands used to access modes are
Configuring TACACS+ Finding Feature Information. Prerequisites for TACACS+
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for TACACS+, page 1 Information About TACACS+, page 3 How to Configure TACACS+, page 7 Monitoring TACACS+, page 16 Finding Feature Information Your software
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for TACACS+, page 1 Information About TACACS+, page 3 How to Configure TACACS+, page 7 Monitoring TACACS+, page 16 Finding Feature Information Your software
Password Recovery in ROM Monitor Mode
 This chapter describes how to recover a password on the router. It also includes instructions to bypass ksh authentication on a node. Information About Password Recovery, on page 1 Recovering the Root
This chapter describes how to recover a password on the router. It also includes instructions to bypass ksh authentication on a node. Information About Password Recovery, on page 1 Recovering the Root
Chapter 10 Lab B: Configuring ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDM
 Chapter 10 Lab B: Configuring ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of Fast Ethernet interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992
Chapter 10 Lab B: Configuring ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using ASDM Topology Note: ISR G2 devices have Gigabit Ethernet interfaces instead of Fast Ethernet interfaces. All contents are Copyright 1992
Configuring System Message Logging
 CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to configure system message logging on the Cisco 4700 Series Application Control Engine (ACE) appliance. Each ACE contains a number of log files that retain records
CHAPTER 1 This chapter describes how to configure system message logging on the Cisco 4700 Series Application Control Engine (ACE) appliance. Each ACE contains a number of log files that retain records
Cisco ASA 5500 LAB Guide
 INGRAM MICRO Cisco ASA 5500 LAB Guide Ingram Micro 4/1/2009 The following LAB Guide will provide you with the basic steps involved in performing some fundamental configurations on a Cisco ASA 5500 series
INGRAM MICRO Cisco ASA 5500 LAB Guide Ingram Micro 4/1/2009 The following LAB Guide will provide you with the basic steps involved in performing some fundamental configurations on a Cisco ASA 5500 series
Setting Up the Sensor
 CHAPTER 4 This chapter provides information for setting up the sensor. This chapter contains the following sections: Understanding Initialization, page 4-1 Configuring Network Settings, page 4-1 Configuring
CHAPTER 4 This chapter provides information for setting up the sensor. This chapter contains the following sections: Understanding Initialization, page 4-1 Configuring Network Settings, page 4-1 Configuring
Using NAT in Overlapping Networks
 Using NAT in Overlapping Networks Document ID: 13774 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
Using NAT in Overlapping Networks Document ID: 13774 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Configurations Verify Troubleshoot Related Information
Chapter 6 Global CONFIG Commands
 Chapter 6 Global CONFIG Commands aaa accounting Configures RADIUS or TACACS+ accounting for recording information about user activity and system events. When you configure accounting on an HP device, information
Chapter 6 Global CONFIG Commands aaa accounting Configures RADIUS or TACACS+ accounting for recording information about user activity and system events. When you configure accounting on an HP device, information
Access Control List Enhancements on the Cisco Series Router
 Access Control List Enhancements on the Cisco 12000 Series Router Part Number, May 30, 2008 The Cisco 12000 series router filters IP packets using access control lists (ACLs) as a fundamental security
Access Control List Enhancements on the Cisco 12000 Series Router Part Number, May 30, 2008 The Cisco 12000 series router filters IP packets using access control lists (ACLs) as a fundamental security
ASA/PIX: Remote VPN Server with Inbound NAT for VPN Client Traffic with CLI and ASDM Configuration Example
 ASA/PIX: Remote VPN Server with Inbound NAT for VPN Client Traffic with CLI and ASDM Configuration Example Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
ASA/PIX: Remote VPN Server with Inbound NAT for VPN Client Traffic with CLI and ASDM Configuration Example Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions
Configuration Examples
 CHAPTER 4 Before using this chapter, be sure that you have planned your site s security policy, as described in Chapter 1, Introduction, and configured the PIX Firewall, as described in Chapter 2, Configuring
CHAPTER 4 Before using this chapter, be sure that you have planned your site s security policy, as described in Chapter 1, Introduction, and configured the PIX Firewall, as described in Chapter 2, Configuring
eigrp log-neighbor-warnings through functions Commands
 CHAPTER 12 eigrp log-neighbor-warnings through functions Commands 12-1 eigrp log-neighbor-changes Chapter 12 eigrp log-neighbor-changes To enable the logging of EIGRP neighbor adjacency changes, use the
CHAPTER 12 eigrp log-neighbor-warnings through functions Commands 12-1 eigrp log-neighbor-changes Chapter 12 eigrp log-neighbor-changes To enable the logging of EIGRP neighbor adjacency changes, use the
Configurations for the Layer 3 Switch Router
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes the initial configuration of the Layer 3 switch router and contains the following major sections: Starting Up the Layer 3 Switch Router, page 3-1 Using the Console and
CHAPTER 3 This chapter describes the initial configuration of the Layer 3 switch router and contains the following major sections: Starting Up the Layer 3 Switch Router, page 3-1 Using the Console and
Cisco Branch Routers Series Network Analysis Module (NME-NAM-120S) Installation and Configuration Note, 4.2
 Cisco Branch Routers Series Network Analysis Module (NME-NAM-120S) Installation and Configuration Note, 4.2 The Cisco Network Analysis Module (NAM) is an integrated module that enables network managers
Cisco Branch Routers Series Network Analysis Module (NME-NAM-120S) Installation and Configuration Note, 4.2 The Cisco Network Analysis Module (NAM) is an integrated module that enables network managers
Transparent or Routed Firewall Mode
 This chapter describes how to set the firewall mode to routed or transparent, as well as how the firewall works in each firewall mode. You can set the firewall mode independently for each context in multiple
This chapter describes how to set the firewall mode to routed or transparent, as well as how the firewall works in each firewall mode. You can set the firewall mode independently for each context in multiple
Configuring IP SLAs TCP Connect Operations
 This module describes how to configure an IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) TCP Connect operation to measure the response time taken to perform a TCP Connect operation between a Cisco router and devices
This module describes how to configure an IP Service Level Agreements (SLAs) TCP Connect operation to measure the response time taken to perform a TCP Connect operation between a Cisco router and devices
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam
 Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (2 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (18 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure
Skills Assessment Student Training Exam Topology Assessment Objectives Part 1: Initialize Devices (2 points, 5 minutes) Part 2: Configure Device Basic Settings (18 points, 20 minutes) Part 3: Configure
CCNA 1 Chapter 11 V4.0 Answers
 CCNA 1 Chapter 11 V4.0 Answers 1. Refer to the exhibit. What command will place the router into the correct mode to configure an appropriate interface to connect to a LAN? UBAMA# configure terminal UBAMA(config)#
CCNA 1 Chapter 11 V4.0 Answers 1. Refer to the exhibit. What command will place the router into the correct mode to configure an appropriate interface to connect to a LAN? UBAMA# configure terminal UBAMA(config)#
How to Create an IP Access List to Filter IP Options TCP Flags Noncontiguous Ports or TTL Values,
 Creating an IP Access List to Filter IP Options TCP Flags Noncontiguous Ports or TTL Values This module describes how to use an IP access list to filter IP packets that contain certain IP Options, TCP
Creating an IP Access List to Filter IP Options TCP Flags Noncontiguous Ports or TTL Values This module describes how to use an IP access list to filter IP packets that contain certain IP Options, TCP
RPR+ on Cisco 7500 Series Routers
 RPR+ on Cisco 7500 Series Routers Feature History 12.0(19)ST1 12.0(22)S 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(22)S. This feature was integrated
RPR+ on Cisco 7500 Series Routers Feature History 12.0(19)ST1 12.0(22)S 12.2(14)S This feature was introduced. This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.0(22)S. This feature was integrated
Troubleshooting Transparent Bridging Environments
 Troubleshooting Transparent Bridging Environments Document ID: 10543 This information from the Internetwork Troubleshooting Guide was first posted on CCO here. As a service to our customers, selected chapters
Troubleshooting Transparent Bridging Environments Document ID: 10543 This information from the Internetwork Troubleshooting Guide was first posted on CCO here. As a service to our customers, selected chapters
Prerequisites for Creating an IP Access List to Filter IP Options TCP Flags Noncontiguous Ports
 Creating an IP Access List to Filter IP Options, TCP Flags, Noncontiguous Ports This module describes how to use an IP access list to filter IP packets that contain certain IP Options, TCP flags, noncontiguous
Creating an IP Access List to Filter IP Options, TCP Flags, Noncontiguous Ports This module describes how to use an IP access list to filter IP packets that contain certain IP Options, TCP flags, noncontiguous
Password Recovery in ROM Monitor Mode
 This chapter describes how to recover a password on the router. It also includes instructions to bypass ksh authentication on a node. Information About Password Recovery, page 1 Recovering the Root Password
This chapter describes how to recover a password on the router. It also includes instructions to bypass ksh authentication on a node. Information About Password Recovery, page 1 Recovering the Root Password
Release Notes for Cisco ASDM Version 5.2(5)
 May 2010 This document contains release information for Cisco ASDM Version 5.2(5) on the Cisco ASA 5500. It includes the following sections: New Features, page 1 System Requirements, page 1 Upgrading ASDM,
May 2010 This document contains release information for Cisco ASDM Version 5.2(5) on the Cisco ASA 5500. It includes the following sections: New Features, page 1 System Requirements, page 1 Upgrading ASDM,
Prerequisites for Controlling Switch Access with Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+)
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Controlling Switch Access with Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+), page 1 Information About TACACS+, page 3 How to Configure
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for Controlling Switch Access with Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+), page 1 Information About TACACS+, page 3 How to Configure
ASACAMP - ASA Lab Camp (5316)
 ASACAMP - ASA Lab Camp (5316) Price: $4,595 Cisco Course v1.0 Cisco Security Appliance Software v8.0 Based on our enhanced FIREWALL and VPN courses, this exclusive, lab-based course is designed to provide
ASACAMP - ASA Lab Camp (5316) Price: $4,595 Cisco Course v1.0 Cisco Security Appliance Software v8.0 Based on our enhanced FIREWALL and VPN courses, this exclusive, lab-based course is designed to provide
Modular Policy Framework. Class Maps SECTION 4. Advanced Configuration
 [ 59 ] Section 4: We have now covered the basic configuration and delved into AAA services on the ASA. In this section, we cover some of the more advanced features of the ASA that break it away from a
[ 59 ] Section 4: We have now covered the basic configuration and delved into AAA services on the ASA. In this section, we cover some of the more advanced features of the ASA that break it away from a
Troubleshooting Transparent Bridging Environments
 CHAPTER Troubleshooting Transparent Bridging Environments Transparent bridges were first developed at Digital Equipment Corporation (Digital) in the early 1980s and are now very popular in Ethernet/IEEE
CHAPTER Troubleshooting Transparent Bridging Environments Transparent bridges were first developed at Digital Equipment Corporation (Digital) in the early 1980s and are now very popular in Ethernet/IEEE
Chapter 8 Lab Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS
 Chapter 8 Lab Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Chapter 8 Lab Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN Using Cisco IOS Topology Note: ISR G1 devices use FastEthernet interfaces instead of GigabitEthernet interfaces. 2017 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights
Troubleshooting Initial Startup Problems
 Your Cisco ASR 1000 Series Router went through extensive testing before leaving the factory. However, if you encounter problems starting the router, use the information in this chapter to help isolate
Your Cisco ASR 1000 Series Router went through extensive testing before leaving the factory. However, if you encounter problems starting the router, use the information in this chapter to help isolate
